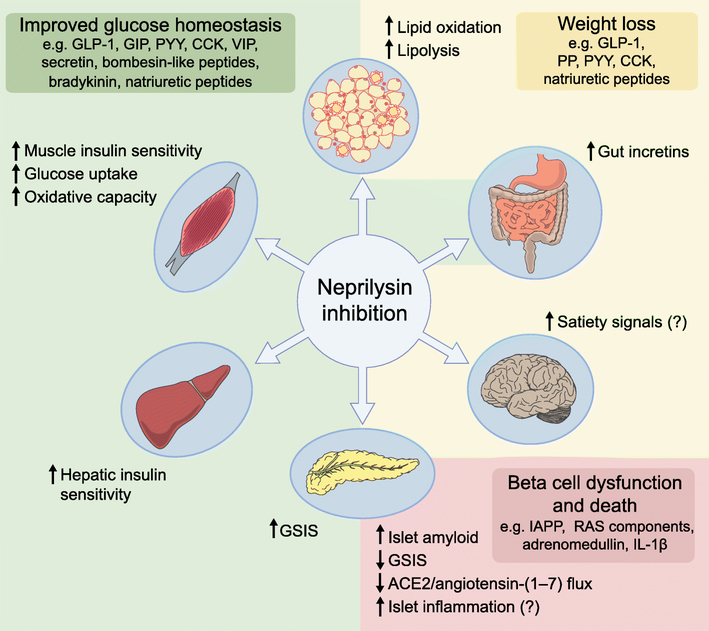
Fig. 1.
Effects of neprilysin inhibition in tissues modulating glucose homeostasis. Neprilysin inhibition improves glucose homeostasis (shaded green) and could induce weight loss (shaded yellow) by increasing levels of several peptides with direct or indirect glucoregulatory properties and anorectic effects. However, neprilysin inhibition may also have detrimental effects in pancreatic islets by increasing levels of substrates that can affect beta cell survival and function or by limiting the ability of angiotensin-(1–7) to promote insulin secretion via its cleavage to angiotensin-(1–2) (shaded pink). The image of the intestine is shaded both yellow and green to indicate that gut incretins impact both glucose homeostasis and body weight. CCK, cholecystokinin; GIP, glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide; GSIS, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion; PP, pancreatic polypeptide; PYY, peptide YY; VIP, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. This figure is available as part of a downloadable slideset