Our study sheds mechanistic light on how multicellular biofilm units compete to successfully colonize a eukaryote host, using B. subtilis microbial communities as our lens. The microbiota and its interactions with its host play various roles in the development and prevention of diseases. Using competing beneficial biofilms that are essential microbiota members on the plant host, we found that B. subtilis biofilms activate collective migration to capture their prey, followed by nonribosomal antibiotic synthesis. Plant hosts increase the efficiency of antibiotic production by B. subtilis biofilms, as they activate the synthesis of polyketides; therefore, our study provides evidence of a mechanism by which the host can indirectly select for beneficial microbiota members.
KEYWORDS: Bacillus subtilis, biofilms, nonribosomal peptides, symbiosis
ABSTRACT
Microbial ecosystems tightly associated with a eukaryotic host are widespread in nature. The genetic and metabolic networks of the eukaryotic hosts and the associated microbes have coevolved to form a symbiotic relationship. Both the Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis and the Gram-negative Serratia plymuthica can form biofilms on plant roots and thus can serve as a model system for the study of interspecies interactions in a host-associated ecosystem. We found that B. subtilis biofilms expand collectively and asymmetrically toward S. plymuthica, while expressing a nonribosomal antibiotic bacillaene and an extracellular protease. As a result, B. subtilis biofilms outcompeted S. plymuthica for successful colonization of the host. Strikingly, the plant host was able to enhance the efficiency of this killing by inducing bacillaene synthesis. In turn, B. subtilis biofilms increased the resistance of the plant host to pathogens. These results provide an example of how plant-bacterium symbiosis promotes the immune response of the plant host and the fitness of the associated bacteria.
IMPORTANCE Our study sheds mechanistic light on how multicellular biofilm units compete to successfully colonize a eukaryote host, using B. subtilis microbial communities as our lens. The microbiota and its interactions with its host play various roles in the development and prevention of diseases. Using competing beneficial biofilms that are essential microbiota members on the plant host, we found that B. subtilis biofilms activate collective migration to capture their prey, followed by nonribosomal antibiotic synthesis. Plant hosts increase the efficiency of antibiotic production by B. subtilis biofilms, as they activate the synthesis of polyketides; therefore, our study provides evidence of a mechanism by which the host can indirectly select for beneficial microbiota members.
INTRODUCTION
In the densely populated plant root rhizosphere, soilborne microorganisms compete for resources such as nitrogen and organic material. One of the strategies evolved by rhizosphere bacteria to gain advantage over the competitors is to form complex structures referred to as biofilms. A biofilm is a differentiated community in which the residing cells are held together by an organic extracellular matrix and biogenic minerals (1–4). In a biofilm, cells use a variety of mechanisms to communicate and coordinate activity within, as well as across, species (5, 6). In many instances, biofilms formed on the surfaces of plant roots are beneficial to their hosts, for example, by preventing the growth of bacterial and fungal pathogens (7–9), and thus can be used as biocontrol agents. In addition, soil microbiota community members, such as Bacillus subtilis, belong to the group of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) which, when applied to soils, can stimulate plant growth and increase yields (10–13). In addition to beneficial interactions with plants, bacterial biofilms also have an active role in the bioremediation of contaminated soils (14) and in carbon dioxide sequestration (15) and thus are of enormous ecological importance.
B. subtilis is a Gram-positive soil bacterium used as a highly efficient biocontrol agent, protecting plants from both fungal and bacterial pathogens (16–20). This protection is proposed to be mediated by the formation of robust biofilms (7, 21) and by the production of a wide range of antibiotics (22) that shape interspecies interactions (23). B. subtilis strains can also defend plants indirectly by activating plant defenses through the classical induced systemic defense response (ISR), subsequently preventing the growth of fungal pathogens (24, 25). Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of physical and chemical interactions between B. subtilis and competing rhizosphere biofilms is of particular interest in rhizosphere ecology.
In this study, we explored the interactions between the biofilms of the Gram-positive B. subtilis and the Gram-negative beneficial soil bacterium Serratia plymuthica (26, 27). The two species simultaneously colonize plant roots, and thus, especially when studied in association with a host plant, can serve as a model for interspecies interactions in the rhizosphere. Furthermore, as both species can be beneficial to the plant, the study of three-party interactions between these colonizers and their host can provide insights into the assembly of complex beneficial communities in the soil, as well as in other host-associated microbiota communities.
RESULTS
B. subtilis biofilm actively expands toward a competing S. plymuthica colony.
When grown on a solid biofilm-inducing medium, B. sutbilis biofilms form symmetrical, circular colonies. To determine the effect of a competing S. plymuthica colony on the development of a B. subtilis biofilm, the two species were inoculated next to each other on a solid biofilm medium. After 2 days, the B. subtilis colony reached S. plymuthica, forming a thick wrinkle around its edge and penetrating toward its center. By the third day, B. subtilis biofilm completely engulfed the S. plymuthica colony, covering it with a thin, unstructured film and enclosing it within the circular wrinkle (Fig. 1A). The location and shape of the B. subtilis center of the biofilm did not change during the interaction with S. plymuthica. However, the biofilm colony advanced asymmetrically toward the S. plymuthica colony, breaking from its usual circular shape (Fig. 1A).
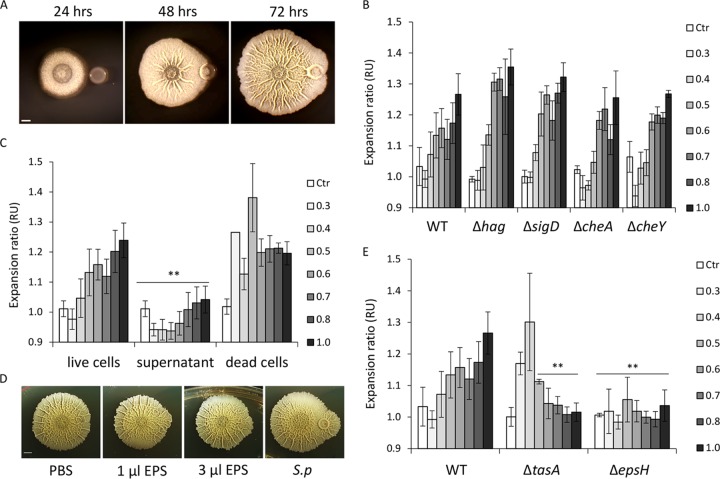
FIG 1.
B. subtilis expands asymmetrically toward S. plymuthica. (A) Time course of interaction between B. subtilis and S. plymuthica, with no contact (24 h), initial contact (48 h), and engulfment (72 h). Top-down images of biofilm colonies grown on solid biofilm-inducing medium are shown; scale bar = 0.2 cm. (B) Quantification of asymmetric expansion of B. subtilis biofilm toward S. plymuthica biofilm. Wild-type (WT) B. subtilis and the indicated mutant strains were inoculated near S. plymuthica at different distances as indicated in the key (in cm), and incubated at 30°C for 3 days. The expansion ratio was defined as the ratio between the radius from the center of the B. subtilis biofilm to the S. plymuthica colony and the radius extending to the opposite side of the biofilm. B. subtilis biofilm grown alone served as a control (Ctr). RU, relative units. (C) Quantification of asymmetric expansion of B. subtilis biofilm toward live S. plymuthica, the supernatant of S. plymuthica, or dead S. plymuthica cells. (D) Top-down images of B. subtilis biofilm expanding toward PBS (negative control), indicated amounts of isolated S. plymuthica (S.p) EPS, or S. plymuthica colony (positive control). (E) Quantification of asymmetric expansion of B. subtilis biofilm toward S. plymuthica biofilm. WT B. subtilis and the indicated mutant strains were inoculated near S. plymuthica at different distances, as indicated by the key, and incubated at 30°C for 3 days. This experimental series was done in parallel to the experiment in panel B; therefore, the same WT control is used. **, P < 0.005 based on a two-tailed Student's t test of the entire indicated measurement series. Error bars represent standard deviations. All experiments were performed at least 3 times with at least two technical repeats.
We next examined the mechanisms that could mediate this asymmetric expansion toward a competitor. Many bacterial cells are capable of directional swimming using their flagella (28). The genetic basis of flagellar swimming in B. subtilis is well known. B. subtilis has peritrichous flagella (29) that propel the cell forward (30, 31). Each flagellum is composed of a basal body, a hook, and a filament composed of many flagellin monomers (32). The flagellin is encoded by the hag gene, which is transcribed by a σD RNA polymerase encoded by sigD (33). In addition, flagellar rotation can also be controlled by chemotaxis (28). To assess whether motility and chemotaxis are responsible for the asymmetrical spreading of the B. subtilis biofilm, two motility mutants, the ΔsigD and Δhag strains, and two chemotaxis mutants, the ΔcheA and ΔcheY strains (28, 31, 34), were tested. Again, the parental B. subtilis and the mutant strains were inoculated next to S. plymuthica at various distances and allowed to grow for 3 days. The asymmetry of each colony was quantified as the ratio between the vertical radius extending toward the S. plymuthica colony and the opposite vertical radius. Wild-type B. subtilis and all four mutants exhibited similar asymmetrical growth toward the S. plymuthica colony, at inoculation distances of <1.5 cm (Fig. 1B). Those results suggest that neither flagellar motility nor chemotaxis is required for the ability of B. subtilis to expand specifically in the direction of a competitor.
We next decided to examine which component of the S. plymuthica colony could promote this behavior. We repeated the experiment, but this time, the asymmetrical expansions toward live S. plymuthica cells, heat-killed S. plymuthica, or a supernatant of S. plymuthica spotted next to the B. subtilis colony were compared. The supernatant of S. plymuthica culture had no effect on the expansion of B. subtilis, further supporting the conclusion that the movement of B. subtilis biofilm was not initiated by signaling molecules secreted by the competitor and did not involve chemotaxis (Fig. 1C). On the other hand, S. plymuthica cells killed by heat promoted asymmetrical expansion, similarly to live S. plymuthica cells (Fig. 1C). This raised the possibility that this collective movement could be aided by organic polymers associated with S. plymuthica cells. We therefore directly tested the possibility of B. subtilis movement being aided by the exopolysaccharide (EPS) of the competitor colony. EPS from an S. plymuthica colony was isolated and spotted next to B. subtilis. Indeed, B. subtilis was able to expand toward isolated EPS but not toward phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Fig. 1D). These results suggest that asymmetrical expansion might be achieved by a sliding motion and that EPS can be shared between different species to facilitate this motion.
It was previously shown that B. subtilis is capable of using its own matrix components, primarily EPS encoded by the eps operon, to slide toward new territories (35, 36). We therefore assessed the contribution of matrix components to asymmetric expansion. We tested the ability of the Δeps and ΔtasA mutants (lacking the protein component of the extracellular matrix) to asymmetrically expand toward its competitor. The Δeps mutant could not specifically expand toward S. plymuthica at any of the tested distances. The ΔtasA mutant was capable of asymmetric expansion, but only at shorter distances (Fig. 1E).
Taken together, these results demonstrate that B. subtilis biofilms are capable of directional movement toward their competitors. Interestingly, this collective migration occurs on top of 1.5% agar, which is a concentration 2-fold higher than the maximal concentration permitting sliding in B. subtilis monocultures (37), consistent with similar observations that were recently made for additional interspecies interactions between B. subtilis and Streptomyces spp. (38, 39). This movement does not require flagellar motility or chemotaxis. Instead, the cells in the expanding biofilm colony are likely sliding on the extracellular matrix produced by their own colony and, here, also by their competitor.
The ability of B. subtilis to eliminate S. plymuthica cells is mediated by bacillaene and by the extracellular protease AprE, but not by ECM.
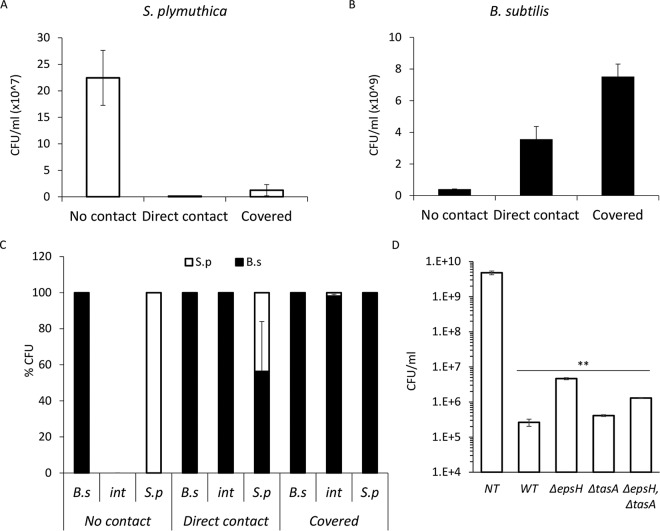
Next, we tested the outcome of the above-described interaction between the competing species regarding their viability. We determined the absolute (Fig. 2A and B) and relative (Fig. 2C) CFU of both species before contact with the competitor, at the time of the initial direct contact, and after engulfment. Contact with B. subtilis led to a dramatic reduction in the viability of S. plymuthica (Fig. 2A and C), while the number of viable B. subtilis cells actually increased during the interaction (Fig. 2B and C). Thus, upon reaching its competitor, B. subtilis was able to efficiently kill it. Unlike the ability to slide in the direction of S. plymuthica, the ability to eradicate it was not dependent on extracellular matrix (ECM) production, as all matrix mutants reduced the amount of viable S. plymuthica cells when inoculated at a short distance to compensate for their inability to expand toward it (Fig. 2D; see also Fig. S1 in the supplemental material).
FIG 2.
B. subtilis eliminates S. plymuthica cells. (A) The number of CFU of S. plymuthica isolated from the area of interaction at 24 h (no contact), 48 h (direct contact), and 72 h (covered) after inoculation. Error bars represent standard deviations of the results from 5 biological replicates. (B) CFU counts of B. subtilis isolated from the area of interaction at 24 h (no contact), 48 h (direct contact), and 72 h (covered) after inoculation. Error bars represent standard deviations of the results from 5 biological replicates. (C) Relative CFU counts at each stage of interaction. The interacting colonies were divided into three areas, as follows: B.s, the area of the B. subtilis colony most distant from the interaction area; int, the area of direct interaction; and S.p, the area of the S. plymuthica colony most distant from the interaction area. Each section was separately harvested, sonicated, and plated to determine the number of replicative cells of each species. The experiment was repeated at 24 h (no contact), 48 h (direct contact), and 72 h (covered) after inoculation. (D) Total CFU counts of S. plymuthica following the interaction with wild-type B. subtilis (WT) and the indicated strains. Colonies were inoculated 0.3 cm apart to compensate for the expansion defect. **, P < 0.005 based on a two-tailed Student's t test, compared to S. plymuthica colony grown alone (untreated control [NT]). Error bars represent standard deviations. All experiments were performed at least 3 times with at least three technical repeats.
A nonribosomal peptide that contributes to the biocontrol capacity of B. subtilis is surfactin, a surface- and membrane-acting lipopeptide (40, 41). Surfactin mediates both movement by reducing surface tension to promote collective flagellar and sliding motility (42, 43) and toxicity of B. subtilis toward biofilm competitors from related species (44). While the ΔsrfAA mutant had a defect in expansion toward S. plymuthica colonies consistent with its role in promoting sliding motility (data not shown), it was still capable of eradicating the colony cells after the formation of a direct contact (Fig. S2), further suggesting that the ability of B. subtilis to kill its competitor is independent from motility. Taken together, these results demonstrate that asymmetric expansion creates the opportunity for contact but is not essential for the eradication of S. plymuthica by B. subtilis.
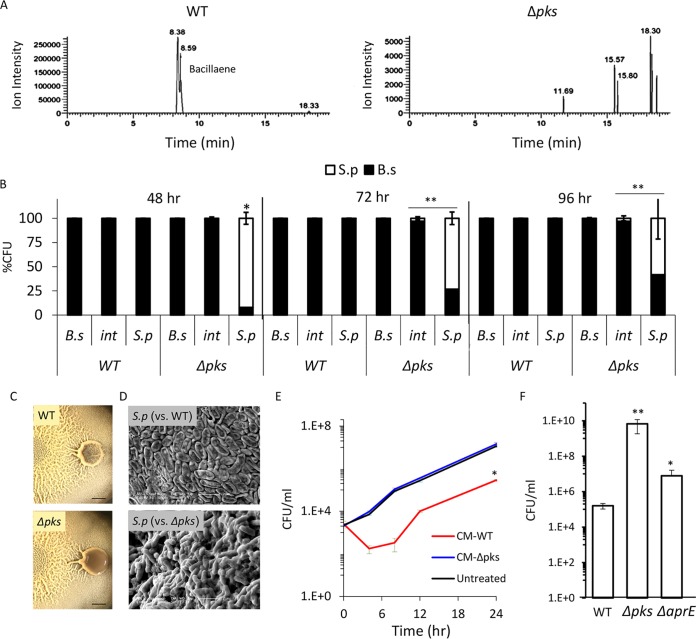
B. subtilis has a repertoire of antibacterial molecules it can produce to kill competitors. To determine which of those molecules are involved in the elimination of S. plymuthica in our system, we tested which antibiotics are secreted by B. subtilis under the conditions used in this study. We allowed B. subtilis to form biofilm colonies on solid medium and analyzed the medium to identify molecules secreted by the bacterial cells using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis (Fig. S3). We detected the presence of bacillaene (45, 46), a polyketide antibiotic synthesized by enzymatic complex encoded in a pks gene cluster and previously implicated in bacterial predator-prey interactions (47) (Fig. 3A, left). We therefore set out to test whether this is the molecule responsible for killing the competing colony.
FIG 3.
B. subtilis eliminates S. plymuthica cells in a PKS-dependent manner. (A) Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of a wild type (right) and Δpks mutant (left) biofilm colonies extracted with isopropanol. The chromatogram is focused on m/z 581.3585 and related masses. The peaks at retention times of 8.38 min and 8.59 min in the WT extract represent two isomers of bacillaene and are fully absent in the Δpks mutant extract. (B) Relative CFU counts of B. subtilis WT or Δpks mutant and S. plymuthica at each stage of the interaction. The interacting colonies were divided into three areas as follows: B.s, the area of the B. subtilis colony most distant from the interaction area; int, the area of direct interaction; S.p, the area of the S. plymuthica colony most distant from the interaction area. Each section was separately harvested, sonicated, and plated to determine the number of replicative cells of each species. The experiment was repeated at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h after inoculation. (C) Top-down images of interaction between S. plymuthica and either WT B. subtilis or Δpks mutant after 4 days of incubation. Scale bar = 0.2 cm. (D) SEM images of S. plymuthica from the interaction zone between and either WT B. subtilis or Δpks mutant. Cells were harvested and visualized after 48 h of incubation at 30°C. (E) Growth curves of S. plymuthica in liquid biofilm medium, supplemented with 50% (vol/vol) of B. subtilis WT or Δpks mutant conditioned medium (CM). Experiments were performed at 30°C. (F) The number of CFU represents S. plymuthica replicative cells, at 72 h after coinoculation with WT B. subtilis, Δpks mutant, and ΔaprE mutant strains. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.005 based on a two-tailed Student's t test of the entire indicated measurement series. Error bars represent standard deviations. All experiments were performed at least 3 times with at least three technical repeats.
To determine the role of bacillaene in competitor eradication, we tested the ability of the Δpks mutant, which is unable to produce bacillaene (Fig. 3A, right), to kill S. plymuthica. As expected, the engulfing wild-type B. subtilis colony promoted the death of S. plymuthica cells, as reflected by a drop in the number of viable cells. However, when engulfed by the Δpks mutant, S. plymuthica cells retained stable cell counts (Fig. 3B). Moreover, when the S. plymuthica cells interacting with the wild-type B. subtilis were examined by light and electron microscopy, there was a clear impact on their morphology, and an increased number of lysed cells was observed. No such effect could be detected in cells interacting with the Δpks mutant strain; the cells retained an intact morphology and a thick extracellular matrix (Fig. 3C and D). Next, we extracted the molecules secreted by a B. subtilis colony and examined their effect on planktonic growth of S. plymuthica. Molecules secreted into the solid medium by the wild-type strain, but not the Δpks mutant, inhibited the growth of S. plymuthica (Fig. S4). Moreover, deletion of the pks operon completely eliminated the toxicity of B. subtilis conditioned medium against S. plymuthica (Fig. 3E). Interestingly, the pks operon is highly conserved in bacilli residing exclusively in the rhizosphere but not in B. cereus and B. anthracis, which reside in a broader range of hosts (Fig. S5). Consistent with the hypothesis that polyketide synthesis (PKS) is relevant to the competitiveness of B. subtilis in the soil, the Δpks mutant could not eliminate an additional Gram-negative competitor from a different genus, Pseudomonas chlororaphis (Fig. S6).
In addition to antibiotics, B. subtilis biofilm cells are also capable of producing extracellular proteases that allow them to “mine” extracellular material, such as dead cells, breaking these macromolecules down into amino acids that can then be imported and used for further growth (48). As the CFU of B. subtilis increased following interaction with S. plymuthica cells (Fig. 2B), we decided to examine the contribution of the main extracellular proteases (AprE, Vpr, and Mpr) to the ability of B. subtilis to overcome its competitor during the interaction. The deletion of aprE, but not of the other proteases, inhibited the eradication of S. plymuthica (Fig. 3F and S7). However, its effect on viability of the competitor was less dramatic than that of pks (Fig. 3F), suggesting an indirect mechanism. One intriguing possibility is that consuming dead competitor cells provides B. subtilis with a growth advantage, and the increased rate of growth further enhances its ability to successfully compete and eradicate its neighbor.
Overall, our results separate two biological properties that contribute to the success of B. subtilis during the interaction with S. plymuthica, EPS-dependent sliding movement that leads to asymmetric expansion toward its competitor, and bacillaene-dependent killing once the two colonies make contact (summarized in Table S1).
Plant host promotes pks-dependent killing via Spo0A.
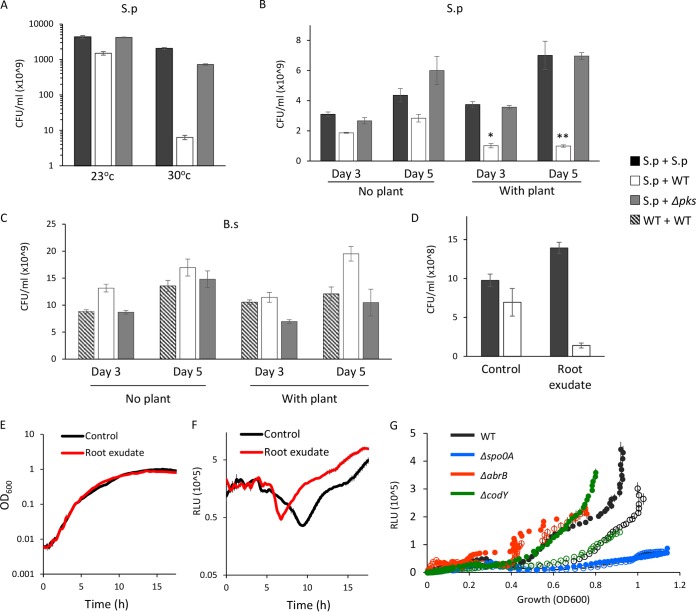
Both B. subtilis and S. plymuthica reside in the soil rhizosphere of temperate habitats, where the temperature fluctuates between 15°C and 23°C (49). We therefore decided to test whether pks-dependent killing also occurs at the environmental temperature. Surprisingly, while being highly effective in killing S. plymuthica at 30°C, we found that B. subtilis could not efficiently kill it at 23°C (Fig. 4A). However, in the natural niche, additional species are present, most importantly, the host plant. Therefore, we decided to set up a plant-host model system. Eruca sativa (salad rocket) is a winter annual undomesticated wild flowering plant that grows in nature mostly around the Mediterranean basin (50). It belongs to the Brassicaceae family, which includes various natural plant hosts for both Bacillus and Serratia species (51).
FIG 4.
pks-dependent killing of S. plymuthica by B. subtilis is induced by the plant host at an environmental temperature. (A) Relative CFU counts of S. plymuthica inoculated alone (S.p + S.p, black bars), next to WT B. subtilis (S.p + WT, white bars) or Δpks mutant (S.p + Δpks, gray bars). The interacting colonies were incubated at 30°C and 23°C for 3 and 5 days, respectively, harvested, and plated to determine the number of replicative cells. (B and C) Relative CFU counts of S. plymuthica (B) and B. subtilis (C) after interaction in proximity of 0.8 cm to E. sativa seedling (with plant) and without seedling (no plant) for 3 and 5 days at 23°C. (B) S. plymuthica CFU were obtained after interaction with either another S. plymuthica biofilm (S.p + S.p, black bars), WT B. subtilis biofilm (S.p + WT, white bars) or with Δpks mutant B. subtilis biofilm (S.p + Δpks, gray bars). (C) B. subtilis CFU were obtained after interaction with either another B. subtilis biofilm (WT + WT, striped bars) as a control, S. plymuthica biofilm (WT + S.p, white bars), or Δpks mutant with S. plymuthica (Δpks + S.p, gray bars). (D) Relative CFU counts of S. plymuthica after interaction with either another S. plymuthica biofilm (S.p + S.p, black bars) as control, or WT B. subtilis (S.p + WT, white bars) on a biofilm-inducing solid medium pretreated with root exudate or plant growth medium (control) for 5 days at 23°C. (E) Growth (OD600) PpksC-lux strain treated with root exudate (red) or plant growth medium (black). (F) Growth-normalized luminescence (relative light units [RLU]) of PpksC-lux strain treated with root exudate (red) or plant growth medium (black). (G) Luminescence (in RLU) of B. subtilis carrying the PpksC-lux construct in WT or the indicated deletion mutants. Open circles represent the untreated control, while the full circles represent the addition of root exudate to the growth medium. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.005 based on a two-tailed Student's t test. Error bars represent the standard deviations. The results are averages of the results from a representative experiment performed with at least three technical repeats out of three independent experiments.
In the presence of an E. sativa plant host at 23°C, the killing of S. plymuthica was increased from 2-fold to 26-fold in a pks-dependent manner (Fig. 4B). Again, the killing was linked to predation and resulted in an increased number of B. subtilis cells, and this result could not be attributed to growth induction of B. subtilis by the host (Fig. 4C). In contrast, while the growth of S. plymuthica was indeed improved when grown together with E. sativa (Fig. 4B), it still could not overcome the pks-dependent killing in three-party interaction experiments.
Even in the absence of the plant, the addition of root exudate was sufficient to induce the killing of S. plymuthica by B. subtilis, suggesting that this induction is mediated by a factor secreted by the plant (Fig. 4D). In order to better understand the molecular mechanism of induction of pks-dependent killing, we tested the effect of the root exudate on the expression of the pks operon. As shown, purified root exudate of E. sativa had no impact on cell growth (Fig. 4E) but had significantly (P < 10−9) induced pks expression (Fig. 4F). In contrast, we could detect no induction of pks, eps, or tasA expression by direct contact with an S. plymuthica colony during expansion and engulfment (Fig. S8) or by its conditioned medium (data not shown).
The transcription of the pksA-R operon (the operon containing pksA and pskR and the genetic material in between) initiates from a promoter located upstream of pksC and is regulated by two master regulators (52), CodY, which senses the levels of branched amino acids (53, 54), and the transition phase regulator AbrB (55). In turn, AbrB is inhibited by the master regulator of sporulation and biofilm development, Spo0A (56). Previous publications indicated that plant exudates of tomato and Arabidopsis spp. can induce Spo0A by several independent mechanisms (57, 58) and therefore may repress AbrB. We used a luciferase reporter driven by the pksC promoter to measure the induction of pks expression by root exudate in the wild type and in the Δspo0A, ΔabrB, and ΔcodY mutant strains. The activation of the pks promoter by the root exudate required Spo0A and AbrB but not CodY (Fig. 4G). Two target genes of Spo0A (sinI and sdpA) activated by low Spo0A-P were also induced by exudates of E. sativa similarly to the pks operon (Fig. S9). Altogether, these results support the hypothesis that the plant increases the pks-dependent killing of S. plymuthica by B. subtilis by inducing the transcription of the pks operon in an Spo0A-dependent manner.
pks-induced killing of S. plymuthica allows B. subtilis to enhance the systemic resistance of the plant.
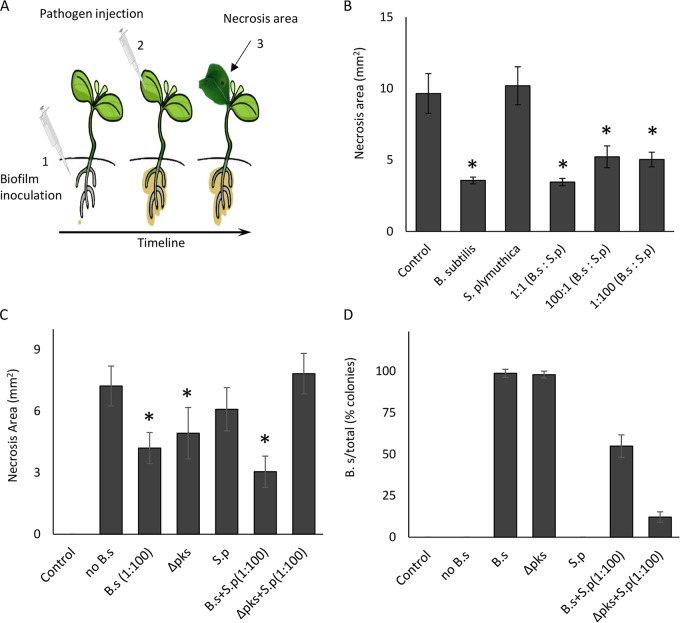
Finally, we wondered whether the plant host has an underlying preference toward B. subtilis. Both B. subtilis and S. plymuthica are considered biocontrol species (40, 59). Therefore, we explored their relative contributions to the activation of the plant’s immune system. Both bacterial species were inoculated on the root, either alone or in competition, and the bacteria were allowed to form root-associated communities. Next, the pathogen Pseudomonas syringae was injected directly into the leaves of precolonized E. sativa plants. After a week, the area of leaf necrosis was measured (Fig. 5A). As no direct contact occurred between the root-associated biofilms and P. syringae, enhanced resistance is the readout of the immune response of the plant hosts. Biofilms containing B. subtilis alone or together with S. plymuthica, but not S. plymuthica alone, provided significantly enhanced systemic resistance (Fig. 5B). When inoculated alone, the Δpks mutant could provide protection similar to that of the wild-type B. subtilis, further demonstrating that pks is not required for this aspect of interaction. However, when inoculated together with S. plymuthica, the Δpks mutant offered no protection to the plant (Fig. 5C). This was due to its inability to compete with S. plymuthica, as demonstrated by the CFU count (Fig. 5D). This result is a strong indication that the pks operon is fundamental to B. subtilis-plant interactions in competitive environments. Furthermore, these results could indicate a mechanism by which plants shape the rhizosphere communities by specifically regulating antibiotic production.
FIG 5.
The effects of B. subtilis and S. plymuthica on systemic resistance of their plant host. (A) Diagram of the experimental setting. Biofilms were established on E. sativa plant roots prior to infection of their leaves with P. syringae. (B) Quantification of necrosis area (in square millimeters) on E. sativa leaves infected by the pathogen P. syringae. The necrosis area was measured in E. sativa seedlings whose roots were inoculated with B. subtilis, S. plymuthica, and their combination in ratios of 1:1, 100:1, and 1:100. (C) Quantification of necrosis area (in square millimeters) on E. sativa leaves infected by the pathogen P. syringae. The necrosis area was measured in E. sativa seedlings whose roots were inoculated with wild type (WT) B. subtilis (diluted 1:100 in LB to an OD equivalent to that for the 1:100 ratio in panel B), Δpks mutant, S. plymuthica, or combinations of the strains as indicated in the figure. (D) CFU counts of B. subtilis isolated from the samples from panel C. After their leaves were harvested and analyzed, bacteria were harvested from the roots of the plants, and the relative CFU counts of B. subtilis were determined. *, P < 0.005. Results represent averages of the results from a representative experiment performed with at least five technical repeats out of three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations.
DISCUSSION
In a biofilm, cells use a variety of mechanisms to coordinate activity within the community, as well as across species (5, 6). In many instances, biofilms are beneficial to their hosts; e.g., biocontrol agents form biofilms on the surfaces of plant roots, thereby preventing the growth of various pathogens (7), similarly to probiotic bacteria in the gut (60).
In natural environments, such as the rhizosphere, beneficial bacterial communities are surrounded by a multitude of other organisms, including other bacteria. B. subtilis, a biocontrol agent whose genome contains numerous gene clusters that control the expression of antibiotics, generally resides within this complex environment (16, 61). It is capable of a variety of chemical interactions with its competitors, as follows: pirated siderophores promote sporulation (62), B. cereus produces thiopeptide antibiotic that promotes B. subtilis biofilm formation (63), surfactin is involved in competition between B. subtilis and B. simplex (44), and bacillaene promotes the competitiveness of B. subtilis versus the Gram-positive bacterium Streptomyces coelicolor and the Gram-negative bacterium Myxococcus xanthus (47, 64). Collectively, these findings indicate that the presence of a diverse arsenal of antibiotics assists B. subtilis in competition against various species in its natural habitats.
The mechanisms underlying activation and deployment of this arsenal of antibiotics remain largely elusive. One such possible mechanism would be sensing and responding to other species competing for the same ecological niche (61, 65). Thus, studying social interactions between B. subtilis biofilms and bacterial species invading their territory and the outcomes of such interactions on synthesis of relevant antibiotics is of particular interest.
In this work, we characterized the interactions between B. subtilis and S. plymuthica, an additional biocontrol agent that suppresses bacterial and fungal pathogens (66–71). When encountering an S. plymuthica colony, B. subtilis encircled and engulfed the colony in a flagellum- and chemotaxis-independent manner (Fig. 1). However, matrix components, such as exopolysaccharides and TasA, were necessary for B. subtilis to advance asymmetrically toward the S. plymuthica colony. Flagellum-independent surface motility has been shown to promote symmetrical expansion of B. subtilis during the growth of bacterial biofilms (43, 72–75). This behavior was suggested to improve access to nutrients while bacterial consumption equals uptake and starvation occurs (72). Our results suggest an additional layer of ecological significance to EPS-dependent collective motility, as it leads to the success of B. subtilis in competitive interspecies interactions.
When B. subtilis colonies encircled S. plymuthica, the secreted antibiotic bacillaene, produced by the pks cluster (45), eliminated the competitor colony. The secretion of the antibiotic and ability to move toward and engulf the competing colony were independent, suggesting that pks products may be diffusion limited and reach the minimal effective threshold only over short distances, as occurs when two competing colonies merge (Fig. 2 and 3). Alternatively, the pks products may remain bound to the bacterial surface and extracellular polymers, requiring direct contact. The presence of bacillaene determined the outcome of the interaction, resulting in the predation of S. plymuthica by B. subtilis (Fig. 3).
Finally, we found that the plant host played an important role in the regulation of the bacterial interactions (Fig. 4 and 5). The plant host induced pks-dependent killing of S. plymuthica by B. subtilis at an environmental temperature. In turn, B. subtilis, but not S. plymuthica, enhanced the systemic immunity of the plant host. As tomato (but not Brassicaceae) was recently found to inhibit Spo0A during overgrowth of B. subtilis biofilms (76), Spo0A induction could be highly host and temperature specific.
Since B. subtilis was first described by Ferdinand Cohn in the late 1800s, it was shown to specialize in the production of metabolites (77). Many of the biosynthetic pathways for these metabolites are conserved either across the entire Bacillus genus or within specific phylogenetic clades. Fengycin, bacillaene, iturin, and difficidin were essentially observed only within the B. subtilis group. This suggests that the different environmental niches inhabited by members of the B. subtilis clade may select for conservation of metabolites with distinct (or potentially redundant) beneficial functions (78). We here describe one such function, that of outcompeting S. plymuthica in nonfavorable growth temperature.
The complexity of these three-player interactions suggests that B. subtilis biofilms can be considered a part of the plant host microbiome, with the host actively promoting the establishment of the most beneficial bacterial community. Our findings provide a simple example of high-order interactions that shape microbiomes; the host modulates antibiotic production in the desired bacterial colonizers, providing the colonizers a clear advantage over less beneficial potential residents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and media.
All experiments were performed with the natural B. subtilis isolate NCIB 3610 and its derivatives. The strains used in this study are listed in Table 1 and were referenced previously (45, 46, 57, 79–85). A natural isolate of S. plymuthica was received from the lab of Leonid Chernin, and a natural isolate of P. chlororaphis was received from the lab of Roberto Kolter. 16S rRNA gene analysis was used to confirm the species of the S. plymuthica and P. chlororaphis strains. Assays were carried out with the biofilm-inducing medium MSgg, which contains 5 mM potassium phosphate, 100 mM morpholinepropanesulfonic acid (MOPS) (pH 7), 2 mM MgCl2, 50 μM MnCl2, 1 μM ZnCl2, 2 μM thiamine, 0.5% glycerol, 0.5% glutamate, 50 μg/ml tryptophan, 50 μg/ml phenylalanine, 50 μg/ml threonine, 700 μM CaCl2, and 50 μM (for growth assays) or 125 μM (for biofilm assays) FeCl3 (79, 86). Solid MSgg medium was obtained by adding Bacto agar (Difco) to a final concentration of 1.5%. When necessary, selective medium was prepared with LB agar or LB broth, supplemented with 100 μg/ml ampicillin (Amp; AG Scientific), 10 μg/ml kanamycin (Kan; AG Scientific), 10 μg/ml chloramphenicol (Cam; Amresco), 10 μg/ml tetracycline (Tet; Amresco), 100 μg/ml spectinomycin (Spec; Tivan Biotech), and 1 μg/ml erythromycin (Erm; Amresco) plus 25 μg/ml lincomycin (Linc; Sigma-Aldrich). To create the transcriptional luc reporter, the promoter of pksC was amplified from genomic DNA (gDNA) of B. subtilis NCIB 3610 with the following primers: primer 5′ PpksC-lux P1, GTCCTAGTAAGGTCGACAGGAGGACTCTCTGCAAATCGCCCGGCCATTCGATAAAGG, and primer 3′ PpksC-lux P2, GTATGTAAGCAAAAAGTTTCCAAATTTCATTCTCTCAAAGCCACCCTTCCGATTAGT, and further integrated into pBS3Clux by restriction-free cloning. After confirmation by sequencing, pBS3Clux was cut and integrated into the bacterial genome of B. subtilis NCIB 3610 at the neutral sacA locus.
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains used in this worka
| Strain | Genotype | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| B. subtilis | ||
| NCIB 3610 | Wild type | 79 |
| IKbs0222 | Δhag::tet | 80 |
| IKbs0210 | ΔsigD::tet amyE::Phag-gfp (Cam) | Lab collection |
| IKbs0225 | ΔcheA::tet | 81 |
| IKbs0226 | ΔcheY::tet | 81 |
| IKbs0008 | ΔepsH::tet | 82 |
| IKbs0005 | ΔtasA::kan | 83 |
| IKbs0227 | ΔsrfAA::mls | 80 |
| IKbs0042 | Δvpr::kan | Lab collection |
| IKbs0041 | Δmpr::tet | Lab collection |
| IKbs0036 | ΔaprE::mls | Lab collection |
| IKbs0224 | ΔpksA-R::spec | 46 |
| IKbs0035 | ΔpksA-E::tet | 45 |
| IKbs0085 | sacA::PsdpA-lux (Cam) | 57 |
| IKbs236 | lacA::PsinI-lux (Cam) | 84 |
| IKbs0887 | sacA::PpksC-lux (Cam) | This study |
| IKbs0888 | Δspo0A::kan sacA::PpksC-lux (Cam) | spo0A::kan (85) × IKbs0887 |
| IKbs0889 | ΔabrB::kan sacA::PpksC-lux (Cam) | abrB::kan (85) × IKbs0887 |
| IKbs0891 | ΔcodY::kan sacA::PpksC-lux (Cam) | ΔcodY::kan* × IKbs0887 |
| Serratia plymuthica IC1270 | Wild type | L. Chernin |
| Pseudomonas chlororaphis PC-449 | Wild type | R. Kolter |
All B. subtilis strains are derived from NCIB 3610 and were constructed as described in Materials and Methods. Cam, chloramphenicol resistance.
The deletion of codY was generated using the long-flanking homology (LFH) PCR mutagenesis protocol of Wach (87), replacing an endogenous locus with a kanamycin resistance gene from pIKec14. The primers used were as follows: P1, TCGATATGGATGAAGTCGGCCAGGAA; P2, CAATTCGCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTCCGCAGCTTGCAGCATGGAGTTAATA; P3, CCAGCTTTTGTTCCCTTTAGTGAGTCAGGCTTATATCAAGGCGAGAAATGTAGTT; and P4, TTCTGTAAGGCACCCACTCTCCATTC.
The product was first introduced by transformation into strain B. subtilis PY79 and the deletion further integrated into the NCIB 3610 wild type or mutant by transformation. Transformation of B. subtilis PY79 and NCIB 3610 by natural competence with linearized plasmid or genomic DNA was done as described previously (88) and as performed previously to assess natural competence in NCIB 3610 (89).
Bacillaene extraction.
Bacillaene was extracted from the biofilms of strain NCIB 3610. A single B. subtilis wild-type (WT) colony, isolated on a solid LB plate, was inoculated into 3 ml of LB broth and grown overnight at room temperature, and 2 μl of the culture was plated onto solid MSgg medium. The plate was incubated for 3 days at 30°C to allow proper biofilm development. A ∼44-mm2 MSgg agar segment was cut out of the plate (together with a piece of the biofilm) and crushed manually, and 700 μl of isopropanol was added to it. The isopropanol-containing crushed MSgg mixture was then incubated at 50°C for 1 h, with occasional vortexing, followed by centrifugation (14,000 rpm for 5 min) to precipitate MSgg agar flakes. Supernatant was extracted and evaporated using a SpeedVac. As a control, the same procedure was performed with noninoculated solid-MSgg medium. To verify that the activity of the extract was pks dependent and not due to the extraction of surfactin, the procedure was also carried out with the Δpks mutant. To analyze the activity of the extracted molecules, 6.6 μl dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 193.4 μl distilled water (dW) were added to the evaporated residues and vortexed to dissolve them (resulting in a molecule concentration of 3.5×). For S. plymuthica growth curves, liquid MSgg was supplemented with 30% of the 3.5× solution, achieving a final concentration of ∼1×. Growth assays were performed as follows: cells were grown at room temperature with agitation for 18 h in a microplate reader (Synergy 2; BioTek), and the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was measured every 15 min.
Isopropanol extracts were analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separations were carried out using a Kinetex hexyl-phenyl column (2.1 by 150 mm; particle size, 2.6 μm; Phenomenex). The mass spectrometer was operated in positive ionization mode, and the ion source parameters were as follows: spray voltage, 3.5 kV; capillary temperature, 300°C; ion-transfer optics parameters optimized using automatic tune option; sheath gas rate (arb), 35; and auxiliary gas rate (arb), 15. Mass spectra were acquired in the range of m/z 150 to 2,000 Da. The liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) system was controlled, and data were analyzed using the Chromeleon and Xcalibur software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Bacillaene was detected at m/z 581.3585. Dihydrobacillaene was not detected.
Effect of S. plymuthica supernatant, cells debris, and ECM on B. subtilis.
To acquire S. plymuthica supernatant and dead cells, an overnight LB culture of S. plymuthica grown at room temperature was inoculated into liquid MSgg medium (dilution of 1:100) and incubated at 30°C for 24 h. Cultures were then centrifuged (14,000 rpm, 10 min), and the supernatant was filtered, evaporated by SpeedVac, and rehydrated with distilled water (dW), achieving a 20× concentration. The remaining cells were washed with dW and resuspended in 2 ml dW. Cells were heat killed at 85°C for 25 min. For the interaction, 3 μl of either the 20× supernatant or the dead cells was inoculated next to a 2-μl B. subtilis LB culture (grown at room temperature overnight) and then incubated at 30°C for 3 days. For EPS extraction, S. plymuthica cells were grown at room temperature, inoculated into liquid MSgg medium (dilution of 1:100), and grown for 3 days without shaking to generate floating biofilms. Growing medium was collected and filtered, and ECM was precipitated with isopropanol as previously described (90). Solvent was evaporated overnight in a chemical hood.
Imaging of the interaction between biofilms.
Single B. subtilis or S. plymuthica colonies, isolated on solid LB plates, were inoculated into 3 ml of LB broth (Difco) and grown overnight at room temperature. For interaction analysis, 2 μl of each culture was inoculated onto solid MSgg medium at the desired distances. Plates were incubated at 23°C and 30°C for 5 and 3 days, respectively. Cells were visualized using a SteREO Discovery.V20 microscope equipped with a PlanApo S 0.5× FWD 134-mm objective or a PlanApo S 1.0× FWD 60-mm objective (Zeiss) attached to an Axiocam camera. Data were captured and analyzed using the Zen Pro AxioVision suite software (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) and ImageJ2 (91).
For quantification of a symmetric spreading of B. subtilis biofilm colony, the radius ratio was determined by dividing a vertical radius extending from the center of the biofilm toward the S. plymuthica colony by the vertical radius extending to the opposite side.
Scanning electron microscopy.
Two-day-old interactions of B. subtilis WT or the Δpks mutant with S. plymuthica were fixed overnight at 4°C with 2% glutaraldehyde, 3% paraformaldehyde, 0.1 M sodium cacodylate (pH 7.4), and 5 mM CaCl2. Samples were washed twice for 15 min with double-distilled water (ddW) and dehydrated with a series of ethanol washes at 30%, 50%, 70%, 96% and 100%. Samples were then dried overnight on filter paper (Whatman) at room temperature, mounted, and stored in a vacuum. The mounted samples were sputtered with gold-palladium before examination by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) XL30 with field emission gun (FEI).
Analysis of bacterial populations during interaction.
To analyze the cell numbers for each strain during the interaction between B. subtilis and S. plymuthica, colonies were seeded as described above and incubated for the required time period. As shown in Fig. 1 and 2A to D, the interacting colonies were divided into three sections, as follows: (i) B. subtilis, consisting of the entire B. subtilis biofilm, excluding the thick wrinkle that surrounded S. plymuthica; (ii) the manually separated wrinkle, containing cells from the contact area (also designated interaction area); and (iii) S. plymuthica, consisting of the entire S. plymuthica colony, excluding the cells that were attached to the wrinkle. For other experiments, both interacting colonies were harvested, with no further separation. Colonies of B. subtilis and S. plymuthica grown alone served as controls.
Each sample was harvested, resuspended in 500 μl phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and mildly sonicated (3× for 5 s at 15%). The samples were then diluted, plated on solid agar, and incubated at 30°C overnight to allow formation of colonies. Colonies formed by the two species are easily distinguishable on LB medium due to differences in size and colony shape. For B. subtilis biofilm mutants, confirmation of the identity of the colonies was performed by dual plating on nonselective LB and LB with the appropriate antibiotics.
Plant colonization assay.
To test bacterial interaction over roots, seeds of the annual E. sativa (Brassicaceae), originated from natural population (92), were germinated on Nitsch (93) agar plates at 25°C with an 8-h/16-h day/night photoperiod. One-week-old seedlings were transferred to solid MSgg medium plates, and bacteria were inoculated (as described above) on the next day at a distance of 0.8 cm from the root and between the inoculants. Samples were incubated in a growth chamber (MRC) with 8-h/16-h day/night photoperiods at 23°C and 30°C for 5 and 3 days, respectively. For interspecies interactions population assessment, the overall community was separated from the root, mildly sonicated, and plated to detect single colonies in triplicate.
Root exudate extraction and bioactivity assessment.
Root exudate of E. sativa seedlings was extracted from Nitsch agar growth medium 2 weeks from germination. After seedlings were removed, exudate was obtained by extracting Nitsch agar with isopropanol (3:2), followed by vigorous vortexing and incubating at room temperature (RT) for 10 min. Samples were centrifuged in 10,000 rpm for 10 min to separate the aqueous phase. Exudate samples were evaporated in a SpeedVac concentrator (Eppendorf) and rehydrated in dW. Prior to biofilm inoculation, plates were treated with either 50-μl drops of root exudate or Nitsch agar (plant growth medium) extraction used as a control.
Expression analysis.
pks expression in the presence of plant metabolites was analyzed as follows: the luminescence intensity of cells harboring a PpksC-lux transcriptional promoter fusion was analyzed. Cells were grown to a mid-logarithmic phase, diluted 1:100 in 150 μl liquid MSgg medium, either with or without root exudate. Cells were grown in a 96-well microplate (Thermo Scientific, Roskilde, Denmark) with agitation at 30°C for 16 h in a microplate reader (Synergy 2; BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA), and the luminescence intensity and the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) were measured every 15 min.
Statistical methods.
All studies were performed in duplicate or triplicate at least three separate and independent times. Data are expressed as average values ± standard deviations of the means. For triple-party interactions, data are expressed as average values ± standard errors. Parametric testing was performed when appropriate after confirming that raw data were normally distributed. A paired Student's t test was used to determine if the set of treated versus the untreated control are different from each other, and P values of less than 0.1 were considered significant.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Leonid Chernin for kindly providing us Serratia and Pseudomonas strains. We thank Oz Barazani for kindly providing us Eruca sativa seeds. We thank Yael Helman and Assaf Vardi for critical reading of our manuscript.
The Kolodkin-Gal lab is supported by ISF-icore grant 152/1 and Israel Science Foundation research grant 119/2016 and by the Skoll Center for Environment and Climate.
I.K.-G., E.H.Y., and A.O. designed the experiments; E.H.Y., A.O., R.J., T.B., and A.K.-P. performed the experiments; E.H.Y., A.O., A.K.-P., and I.K.-G. analyzed the data; O.G. provided the reagents; T.B. provided the methodologies; and I.K.-G., A.O., E.H.Y., and A.K.-P. wrote the manuscript.
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00512-19.
REFERENCES
- 1.Stoodley P, Sauer K, Davies DG, Costerton JW. 2002. Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:187–209. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keren-Paz A, Brumfeld V, Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Kolodkin-Gal I. 2018. Micro-CT X-ray imaging exposes structured diffusion barriers within biofilms. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 4:8. doi: 10.1038/s41522-018-0051-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Li X, Chopp DL, Russin WA, Brannon PT, Parsek MR, Packman AI. 2015. Spatial patterns of carbonate biomineralization in biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:7403–7410. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01585-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dragoš A, Kovacs AT. 2017. The peculiar functions of the bacterial extracellular matrix. Trends Microbiol 25:257–266. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aguilar C, Vlamakis H, Losick R, Kolter R. 2007. Thinking about Bacillus subtilis as a multicellular organism. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:638–643. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kolter R, Greenberg EP. 2006. Microbial sciences: the superficial life of microbes. Nature 441:300–302. doi: 10.1038/441300a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rudrappa T, Biedrzycki ML, Kunjeti SG, Donofrio NM, Czymmek KJ, Pare PW, Bais HP. 2010. The rhizobacterial elicitor acetoin induces systemic resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Commun Integr Biol 3:130–138. doi: 10.4161/cib.3.2.10584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schreiter S, Ding GC, Grosch R, Kropf S, Antweiler K, Smalla K. 2014. Soil type-dependent effects of a potential biocontrol inoculant on indigenous bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of field-grown lettuce. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 90:718–730. doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berg G, Koberl M, Rybakova D, Muller H, Grosch R, Smalla K. 2017. Plant microbial diversity is suggested as the key to future biocontrol and health trends. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93:fix050. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fix050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kunova A, Bonaldi M, Saracchi M, Pizzatti C, Chen X, Cortesi P. 2016. Selection of Streptomyces against soil borne fungal pathogens by a standardized dual culture assay and evaluation of their effects on seed germination and plant growth. BMC Microbiol 16:272. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0886-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen L, He LY, Wang Q, Sheng XF. 2016. Synergistic effects of plant growth-promoting Neorhizobium huautlense T1-17 and immobilizers on the growth and heavy metal accumulation of edible tissues of hot pepper. J Hazard Mater 312:123–131. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Berg G, Raaijmakers JM. 2018. Saving seed microbiomes. ISME J 12:1167–1170. doi: 10.1038/s41396-017-0028-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Müller DB, Vogel C, Bai Y, Vorholt JA. 2016. The plant microbiota: systems-level insights and perspectives. Annu Rev Genet 50:211–234. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120215-034952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jian-Zhou H, Cheng-Cheng L, Deng-Jun W, Zhou DM. 2015. Biofilms and extracellular polymeric substances mediate the transport of graphene oxide nanoparticles in saturated porous media. J Hazard Mater 300:467–474. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lidbury I, Johnson V, Hall-Spencer JM, Munn CB, Cunliffe M. 2012. Community-level response of coastal microbial biofilms to ocean acidification in a natural carbon dioxide vent ecosystem. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Emmert EA, Handelsman J. 1999. Biocontrol of plant disease: a (Gram-)positive perspective. FEMS Microbiol Lett 171:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ongena M, Jacques P. 2008. Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol 16:115–125. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Grover M, Nain L, Singh SB, Saxena AK. 2010. Molecular and biochemical approaches for characterization of antifungal trait of a potent biocontrol agent Bacillus subtilis RP24. Curr Microbiol 60:99–106. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9508-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Todorova S, Kozhuharova L. 2010. Characteristics and antimicrobial activity of Bacillus subtilis strains isolated from soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:1207–1216. doi: 10.1007/s11274-009-0290-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Janahiraman V, Anandham R, Kwon SW, Sundaram S, Karthik Pandi V, Krishnamoorthy R, Kim K, Samaddar S, Sa T. 2016. Control of wilt and rot pathogens of tomato by antagonistic pink pigmented facultative methylotrophic Delftia lacustris and Bacillus spp. Front Plant Sci 7:1626. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Raaijmakers JM, De Bruijn I, Nybroe O, Ongena M. 2010. Natural functions of lipopeptides from Bacillus and Pseudomonas: more than surfactants and antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:1037–1062. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nagórska K, Bikowski M, Obuchowski M. 2007. Multicellular behaviour and production of a wide variety of toxic substances support usage of Bacillus subtilis as a powerful biocontrol agent. Acta Biochim Pol 54:495–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shank EA, Kolter R. 2009. New developments in microbial interspecies signaling. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:205–214. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bever JD, Platt TG, Morton ER. 2012. Microbial population and community dynamics on plant roots and their feedbacks on plant communities. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:265–283. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen Y, Yan F, Chai Y, Liu H, Kolter R, Losick R, Guo JH. 2013. Biocontrol of tomato wilt disease by Bacillus subtilis isolates from natural environments depends on conserved genes mediating biofilm formation. Environ Microbiol 15:848–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fürnkranz M, Lukesch B, Muller H, Huss H, Grube M, Berg G. 2012. Microbial diversity inside pumpkins: microhabitat-specific communities display a high antagonistic potential against phytopathogens. Microb Ecol 63:418–428. doi: 10.1007/s00248-011-9942-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu X, Bimerew M, Ma Y, Müller H, Ovadis M, Eberl L, Berg G, Chernin L. 2007. Quorum-sensing signaling is required for production of the antibiotic pyrrolnitrin in a rhizospheric biocontrol strain of Serratia plymuthica. FEMS Microbiol Lett 270:299–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Porter SL, Wadhams GH, Armitage JP. 2011. Signal processing in complex chemotaxis pathways. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:153–165. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Guttenplan SB, Shaw S, Kearns DB. 2013. The cell biology of peritrichous flagella in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 87:211–229. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bischoff DS, Ordal GW. 1991. Sequence and characterization of Bacillus subtilis CheB, a homolog of Escherichia coli CheY, and its role in a different mechanism of chemotaxis. J Biol Chem 266:12301–12305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rao CV, Glekas GD, Ordal GW. 2008. The three adaptation systems of Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis. Trends Microbiol 16:480–487. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Barilla D, Caramori T, Galizzi A. 1994. Coupling of flagellin gene transcription to flagellar assembly in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 176:4558–4564. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4558-4564.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mirel DB, Chamberlin MJ. 1989. The Bacillus subtilis flagellin gene (hag) is transcribed by the sigma 28 form of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol 171:3095–3101. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3095-3101.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Garrity LF, Ordal GW. 1997. Activation of the CheA kinase by asparagine in Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis. Microbiology 143:2945–2951. doi: 10.1099/00221287-143-9-2945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.van Gestel J, Vlamakis H, Kolter R. 2015. From cell differentiation to cell collectives: Bacillus subtilis uses division of labor to migrate. PLoS Biol 13:e1002141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kovács ÁT, Grau R, Pollitt E. 2017. Surfing of bacterial droplets: Bacillus subtilis sliding revisited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E8802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710371114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fall R, Kearns DB, Nguyen T. 2006. A defined medium to investigate sliding motility in a Bacillus subtilis flagella-less mutant. BMC Microbiol 6:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-6-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liu Y, Kyle S, Straight PD. 2018. Antibiotic stimulation of a Bacillus subtilis migratory response. mSphere 3:e00586-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00586-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stubbendieck RM, Straight PD. 2015. Escape from lethal bacterial competition through coupled activation of antibiotic resistance and a mobilized subpopulation. PLoS Genet 11:e1005807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bais HP, Fall R, Vivanco JM. 2004. Biocontrol of Bacillus subtilis against infection of Arabidopsis roots by Pseudomonas syringae is facilitated by biofilm formation and surfactin production. Plant Physiol 134:307–319. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.028712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gao S, Wu H, Wang W, Yang Y, Xie S, Xie Y, Gao X. 2013. Efficient colonization and harpins mediated enhancement in growth and biocontrol of wilt disease in tomato by Bacillus subtilis. Lett Appl Microbiol 57:526–533. doi: 10.1111/lam.12144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kearns DB, Chu F, Rudner R, Losick R. 2004. Genes governing swarming in Bacillus subtilis and evidence for a phase variation mechanism controlling surface motility. Mol Microbiol 52:357–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.03996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Grau RR, de Oña P, Kunert M, Leñini C, Gallegos-Monterrosa R, Mhatre E, Vileta D, Donato V, Hölscher T, Boland W, Kuipers OP, Kovács ÁT. 2015. A duo of potassium-responsive histidine kinases govern the multicellular destiny of Bacillus subtilis. mBio 6:e00581-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00581-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rosenberg G, Steinberg N, Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Olender T, Doron S, Ben-Ari J, Sirota-Madi A, Bloom-Ackermann Z, Kolodkin-Gal I. 2016. Not so simple, not so subtle: the interspecies competition between Bacillus simplex and Bacillus subtilis and its impact on the evolution of biofilms. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2:15027. doi: 10.1038/npjbiofilms.2015.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Straight PD, Fischbach MA, Walsh CT, Rudner DZ, Kolter R. 2007. A singular enzymatic megacomplex from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:305–310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609073103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Butcher RA, Schroeder FC, Fischbach MA, Straight PD, Kolter R, Walsh CT, Clardy J. 2007. The identification of bacillaene, the product of the PksX megacomplex in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:1506–1509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610503104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Müller S, Strack SN, Hoefler BC, Straight PD, Kearns DB, Kirby JR. 2014. Bacillaene and sporulation protect Bacillus subtilis from predation by Myxococcus xanthus. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:5603–5610. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01621-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Park SS, Wong SL, Wang LF, Doi RH. 1989. Bacillus subtilis subtilisin gene (aprE) is expressed from a sigma A (sigma 43) promoter in vitro and in vivo. J Bacteriol 171:2657–2665. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2657-2665.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.U.S. Department of Agriculture. 1999. Soil taxonomy: a basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_051232.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Arias T, Beilstein MA, Tang M, McKain MR, Pires JC. 2014. Diversification times among Brassica (Brassicaceae) crops suggest hybrid formation after 20 million years of divergence. Am J Bot 101:86–91. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1300312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hanna AL, Youssef HH, Amer WM, Monib M, Fayez M, Hegazi NA. 2013. Diversity of bacteria nesting the plant cover of north Sinai deserts, Egypt. J Adv Res 4:13–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2011.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Vargas-Bautista C, Rahlwes K, Straight P. 2014. Bacterial competition reveals differential regulation of the pks genes by Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 196:717–728. doi: 10.1128/JB.01022-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Molle V, Nakaura Y, Shivers RP, Yamaguchi H, Losick R, Fujita Y, Sonenshein AL. 2003. Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis. J Bacteriol 185:1911–1922. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.6.1911-1922.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Levdikov VM, Blagova E, Young VL, Belitsky BR, Lebedev A, Sonenshein AL, Wilkinson AJ. 2017. Structure of the branched-chain amino acid and GTP-sensing global regulator, CodY, from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 292:2714–2728. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.754309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shafikhani SH, Leighton T. 2004. AbrB and Spo0E control the proper timing of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Curr Microbiol 48:262–269. doi: 10.1007/s00284-003-4186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Chu F, Kearns DB, McLoon A, Chai Y, Kolter R, Losick R. 2008. A novel regulatory protein governing biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 68:1117–1127. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chen Y, Cao S, Chai Y, Clardy J, Kolter R, Guo JH, Losick R. 2012. A Bacillus subtilis sensor kinase involved in triggering biofilm formation on the roots of tomato plants. Mol Microbiol 85:418–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Beauregard PB, Chai Y, Vlamakis H, Losick R, Kolter R. 2013. Bacillus subtilis biofilm induction by plant polysaccharides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:E1621–E1630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218984110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kalbe C, Marten P, Berg G. 1996. Strains of the genus Serratia as beneficial rhizobacteria of oilseed rape with antifungal properties. Microbiol Res 151:433–439. doi: 10.1016/S0944-5013(96)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yeom M, Sur BJ, Park J, Cho SG, Lee B, Kim ST, Kim KS, Lee H, Hahm DH. 2015. Oral administration of Lactobacillus casei variety rhamnosus partially alleviates TMA-induced atopic dermatitis in mice through improving intestinal microbiota. J Appl Microbiol 119:560–570. doi: 10.1111/jam.12844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Shank EA. 2018. Considering the lives of microbes in microbial communities. mSystems 3:e00155-17. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00155-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Grandchamp GM, Caro L, Shank EA. 2017. Pirated siderophores promote sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e03293-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03293-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bleich R, Watrous JD, Dorrestein PC, Bowers AA, Shank EA. 2015. Thiopeptide antibiotics stimulate biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:3086–3091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414272112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Straight PD, Willey JM, Kolter R. 2006. Interactions between Streptomyces coelicolor and Bacillus subtilis: role of surfactants in raising aerial structures. J Bacteriol 188:4918–4925. doi: 10.1128/JB.00162-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Steinberg N, Kolodkin-Gal I. 2013. Small molecules are natural triggers for the disassembly of biofilms. Trends Microbiol 21:594–601. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Paulsen IT, Press CM, Ravel J, Kobayashi DY, Myers GS, Mavrodi DV, DeBoy RT, Seshadri R, Ren Q, Madupu R, Dodson RJ, Durkin AS, Brinkac LM, Daugherty SC, Sullivan SA, Rosovitz MJ, Gwinn ML, Zhou L, Schneider DJ, Cartinhour SW, Nelson WC, Weidman J, Watkins K, Tran K, Khouri H, Pierson EA, Pierson LS III, Thomashow LS, Loper JE. 2005. Complete genome sequence of the plant commensal Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5. Nat Biotechnol 23:873–878. doi: 10.1038/nbt1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Corbell N, Loper JE. 1995. A global regulator of secondary metabolite production in Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5. J Bacteriol 177:6230–6236. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.21.6230-6236.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Shen X, Hu H, Peng H, Wang W, Zhang X. 2013. Comparative genomic analysis of four representative plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in Pseudomonas. BMC Genomics 14:271. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Vlamakis H, Chai Y, Beauregard P, Losick R, Kolter R. 2013. Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:157–168. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zeigler DR, Pragai Z, Rodriguez S, Chevreux B, Muffler A, Albert T, Bai R, Wyss M, Perkins JB. 2008. The origins of 168, W23, and other Bacillus subtilis legacy strains. J Bacteriol 190:6983–6995. doi: 10.1128/JB.00722-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Falardeau J, Wise C, Novitsky L, Avis TJ. 2013. Ecological and mechanistic insights into the direct and indirect antimicrobial properties of Bacillus subtilis lipopeptides on plant pathogens. J Chem Ecol 39:869–878. doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Seminara A, Angelini TE, Wilking JN, Vlamakis H, Ebrahim S, Kolter R, Weitz DA, Brenner MP. 2012. Osmotic spreading of Bacillus subtilis biofilms driven by an extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:1116–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109261108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mhatre E, Sundaram A, Holscher T, Muhlstadt M, Bossert J, Kovacs AT. 2017. Presence of calcium lowers the expansion of Bacillus subtilis colony biofilms. Microorganisms 5:7. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms5010007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kovács ÁT. 2016. Bacterial differentiation via gradual activation of global regulators. Curr Genet 62:125–128. doi: 10.1007/s00294-015-0524-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Srinivasan S, Vladescu ID, Koehler SA, Wang X, Mani M, Rubinstein SM. 2018. Matrix production and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis biofilms localize to propagating wave fronts. Biophys J 114:1490–1498. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ganin H, Kemper N, Meir S, Rogachev I, Ely S, Massalha H, Mandabi A, Keren-Paz A, Shanzer A, Meijler M, Malitsky S, Aharoni A, Kolodkin-Gal I. 2019. Indole derivatives maintain the status quo between beneficial biofilms and their plant hosts. Mol Plant Microbe Interact doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-18-0327-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.McLoon AL, Guttenplan SB, Kearns DB, Kolter R, Losick R. 2011. Tracing the domestication of a biofilm-forming bacterium. J Bacteriol 193:2027–2034. doi: 10.1128/JB.01542-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Grubbs KJ, Bleich RM, Santa Maria KC, Allen SE, Farag S, AgBiome T, Shank EA, Bowers AA. 2017. Large-scale bioinformatics analysis of Bacillus genomes uncovers conserved roles of natural products in bacterial physiology. mSystems 2:e00040-17. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00040-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Branda SS, Gonzalez-Pastor JE, Ben-Yehuda S, Losick R, Kolter R. 2001. Fruiting body formation by Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:11621–11626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191384198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Angelini TE, Roper M, Kolter R, Weitz DA, Brenner MP. 2009. Bacillus subtilis spreads by surfing on waves of surfactant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:18109–18113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905890106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kearns DB, Losick R. 2003. Swarming motility in undomesticated Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 49:581–590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kearns DB, Chu F, Branda SS, Kolter R, Losick R. 2005. A master regulator for biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 55:739–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Vlamakis H, Aguilar C, Losick R, Kolter R. 2008. Control of cell fate by the formation of an architecturally complex bacterial community. Genes Dev 22:945–953. doi: 10.1101/gad.1645008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Bucher T, Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Savidor A, Bloom-Ackermann Z, Kolodkin-Gal I. 2015. Disturbance of the bacterial cell wall specifically interferes with biofilm formation. Environ Microbiol Rep 7:990–1004. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Bloom-Ackermann Z, Steinberg N, Rosenberg G, Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Pollack D, Ely S, Storzi N, Levy A, Kolodkin-Gal I. 2016. Toxin-antitoxin systems eliminate defective cells and preserve symmetry in Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Environ Microbiol 18:5032–5047. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kolodkin-Gal I, Elsholz AK, Muth C, Girguis PR, Kolter R, Losick R. 2013. Respiration control of multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis by a complex of the cytochrome chain with a membrane-embedded histidine kinase. Genes Dev 27:887–899. doi: 10.1101/gad.215244.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wach A. 1996. PCR-synthesis of marker cassettes with long flanking homology regions for gene disruptions in S. cerevisiae. Yeast 12:259–265. doi:. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Wilson GA, Bott KF. 1968. Nutritional factors influencing the development of competence in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol 95:1439–1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Konkol MA, Blair KM, Kearns DB. 2013. Plasmid-encoded ComI inhibits competence in the ancestral 3610 strain of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 195:4085–4093. doi: 10.1128/JB.00696-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Rubinstein SM, Kolodkin-Gal I, McLoon A, Chai L, Kolter R, Losick R, Weitz DA. 2012. Osmotic pressure can regulate matrix gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 86:426–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Rueden CT, Schindelin J, Hiner MC, DeZonia BE, Walter AE, Arena ET, Eliceiri KW. 2017. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinformatics 18:529. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1934-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Westberg E, Ohali S, Shevelevich A, Fine P, Barazani O. 2013. Environmental effects on molecular and phenotypic variation in populations of Eruca sativa across a steep climatic gradient. Ecol Evol 3:2471–2484. doi: 10.1002/ece3.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Nitsch J, Nitsch C. 1969. Haploid plants from pollen grains. Science 163:85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.