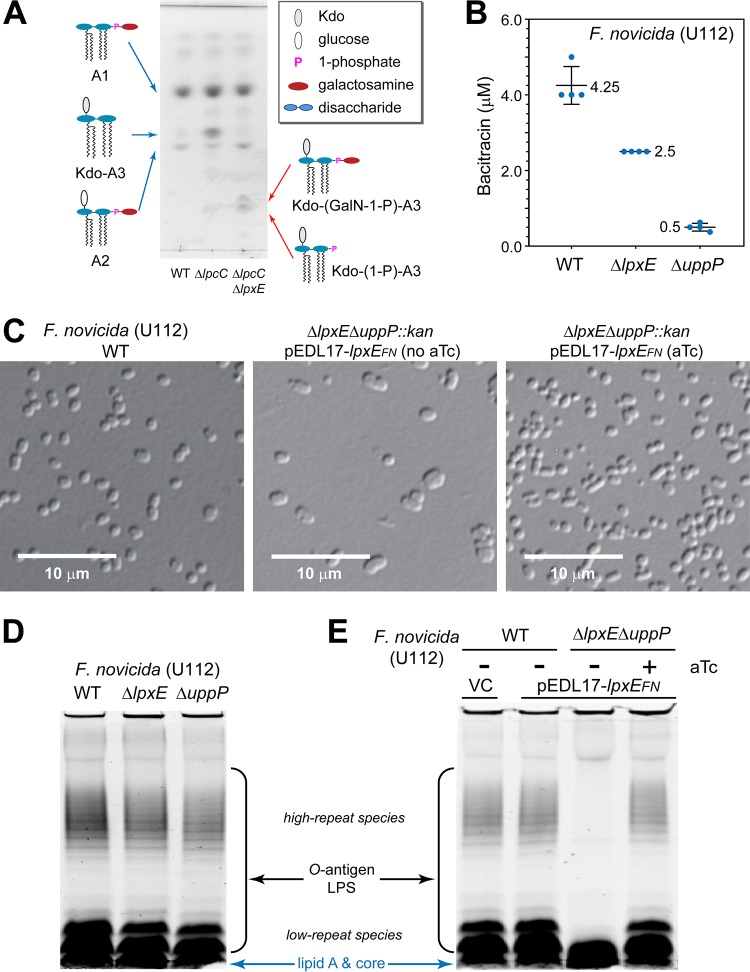
FIG 5.
LpxEFN functionally contributes to multiple layers of the F. novicida bacterial envelope biogenesis. (A) Deletion of lpxEFN results in accumulation of 1-phosphorylated Kdo-lipid A3 species. The profiles of total lipid extracts from F. novicida U112 WT, ΔlpcC, and ΔlpcC ΔlpxE strains were analyzed by TLC. Lipid A species are labeled. Abbreviations: GalN, galactosamine; A1, lipid A1; A2, lipid A2; Kdo-A3, Kdo-lipid A3; Kdo-(GalN-1-P)-A3, Kdo-(galactosamine-1-phospho)-lipid A3; Kdo-(1-P)-A3, Kdo-(1-phospho)-lipid A3. (B) Deletion of lpxEFN sensitizes F. novicida to bacitracin as reflected by reduced MIC. Error bars represent standard deviations from quadruplet measurements. (C) Suppression of the plasmid-encoded LpxEFN expression in the ΔlpxEFN ΔuppPFN::kan mutant of F. novicida causes cell deformation. Images of wild-type cells and ΔlpxEFN ΔuppPFN::kan F. novicida mutant cells without and with LpxEFN expression are shown in the left, middle, and right images, respectively. (D) Lack of LPS phenotypes in F. novicida cells containing the single deletion of lpxEFN or uppPFN. (E) Suppression of the plasmid-encoded LpxEFN expression in the ΔlpxEFN ΔuppPFN::kan mutant of F. novicida causes the loss of O-antigen repeats in LPS. LPS profiles from wild-type F. novicida cells carrying the pDEL17 vector (VC) or the C55-PP phosphatase-deficient (ΔlpxEFN ΔuppPFN::kan) cells carrying the pDEL17-lpxEFN vector without or with aTc were analyzed on SDS-PAGE gels using the Pro-Q Emerald LPS staining kit. O-antigen-containing LPS, including both high- and low-repeat species, and free lipid A/core species are labeled.