This population-based cohort study of 6732 intensive care unit (ICU) patients from 9 hospitals evaluates the 30-day hospital readmission, health care utilization, and clinical outcomes of patients discharged home directly from the ICU vs from a hospital ward.
Key Points
Question
What are the health care utilization and clinical outcomes for adult patients discharged from the intensive care unit (ICU) directly home compared with those discharged home via the hospital ward?
Findings
In this population-based cohort study of 6732 ICU patients discharged home from 9 hospitals, 14% went directly home from the ICU, and 86% went first to a hospital ward from which they were subsequently discharged home; the proportions of these 2 groups with a readmission to the hospital (10% vs 11%) or with an emergency department visit (25% vs 26%) within 30 days of discharge were not significantly different. About 4% of patients in each group died within 1 year of initial discharge home.
Meaning
Discharging select patients directly home from the ICU is not associated with increased health care utilization or mortality.
Abstract
Importance
The safety of discharging adult patients recovering from critical illness directly home from the intensive care unit (ICU) is unknown.
Objective
To compare the health care utilization and clinical outcomes for ICU patients discharged directly home from the ICU with those of patients discharged home via the hospital ward.
Design, Setting, and Participants
Retrospective population-based cohort study of adult patients admitted to the ICU of 9 medical-surgical hospitals from January 1, 2014, to January 1, 2016, with 1-year follow-up after hospital discharge. All adult ICU patients were discharged home alive from hospital, and the propensity score matched cohort (1:1) was based on patient characteristics, therapies received in the ICU, and hospital characteristics.
Exposures
Patient disposition on discharge from the ICU: directly home vs home via the hospital ward.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcome was readmission to the hospital within 30 days of hospital discharge. The secondary outcomes were emergency department visit within 30 days and death within 1 year.
Results
Among the 6732 patients included in the study, 2826 (42%) were female; median age, 56 years (interquartile range, 41-67 years); 922 (14%) were discharged directly home, with significant variation found between hospitals (range, 4.4%-44.0%). Compared with patients discharged home via the hospital ward, patients discharged directly home were younger (median age 47 vs 57 years; P < .001), more likely to be admitted with a diagnosis of overdose, substance withdrawal, seizures, or metabolic coma (32% [295] vs 10% [594]; P < .001), to have a lower severity of acute illness on ICU admission (median APACHE II score 15 vs 18; P < .001), and receive less than 48 hours of invasive mechanical ventilation (42% [389] vs 34% [1984]; P < .001). In the propensity score matched cohort (n = 1632), patients discharged directly home had similar length of ICU stay (median, 3.1 days vs 3.0 days; P = .42) but significantly shorter length of hospital stay (median, 3.3 days vs 9.2 days; P < .001) compared with patients discharged home via the hospital ward. There were no significant differences between patients discharged directly home or home via the hospital ward for readmission to the hospital (10% [n = 81] vs 11% [n = 92]; hazard ratio [HR], 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.20) or emergency department visit (25% [n = 200] vs 26% [n = 212]; HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.81-1.09) within 30 days of hospital discharge. Four percent of patients in both groups died within 1 year of hospital discharge (n = 31 and n = 34 in the discharged directly home and discharged home via the hospital ward groups, respectively) (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.60-1.35).
Conclusions and Relevance
The discharge of select adult patients directly home from the ICU is common, and it is not associated with increased health care utilization or increased mortality.
Introduction
Patients recovering from critical illness have historically been transferred from the intensive care unit (ICU) to a hospital ward before being discharged home.1,2 These transitions allow patients to progressively receive lower-intensity care, physical and functional assessments, and rehabilitation before returning to the community.2,3 However, long waits for hospital ward beds in many health care systems have resulted in a new model of care where select patients recovering from critical illness are discharged directly home from the ICU.4,5
The discharge of preterm infants directly home from neonatal ICUs has been well described, shown in randomized clinical trials to be safe and efficient,6,7 and endorsed in guidelines from professional societies.8 Conversely, the discharge of adult patients directly home from the ICU has only been recently described,5,9,10,11,12,13 has not been comparatively evaluated with the historical model of patient discharge via the hospital ward, and is not mentioned in guidelines from professional societies.2 Data are lacking regarding the safety of discharging adult patients directly home from the ICU.
Methods
We used a population-based, retrospective, cohort study design to compare the characteristics, health care utilization, and outcomes of ICU patients recovering from critical illness who were discharged directly home from the ICU with those discharged home after a stay on a hospital ward. We selected this design because it was a practical approach to provide timely safety information to inform evolving clinical practice and future randomized clinical trials.14 Study methods were conducted and reported in accordance with recommendations of the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement.15 The health research ethics boards at the University of Calgary approved this study (REB16-0191), waiving patient written informed consent.
Study Cohort
We identified consecutive patients 18 years or older admitted to 9 medical-surgical ICUs in 9 hospitals in 2 cities in Alberta, Canada from January 1, 2014, to January 1, 2016; all patients were discharged alive from the hospital to their home. Patients were excluded if their home was located outside of Alberta. The first hospital admission was used if patients were admitted to the hospital more than once during the study period. The last ICU admission was used if patients were admitted to the ICU more than once during the same hospital admission. The ICUs were closed medical-surgical units (able to provide invasive monitoring, vasoactive medications, and mechanical ventilation), staffed by accredited intensive care physicians, and included vascular surgery, thoracic surgery, neurosurgery, trauma, and transplant patients.16
The exposure variable was patient disposition on ICU discharge. The exposed group comprised patients discharged directly from the ICU to home, bypassing a stay on a hospital ward (hereinafter referred to as directly home). The nonexposed group comprised patients transferred from the ICU to a hospital ward (unit not able to provide invasive monitoring, vasoactive medications, and mechanical ventilation) and subsequently discharged home (hereinafter referred to as home via the hospital ward).16 None of the hospitals had guidelines to inform the discharge of patients directly home from the ICU.
Data Sources
We used data from 3 databases that have previously been used for program evaluation and research.17,18 eCritical Alberta prospectively captures demographic, clinical, and outcome data for all patients admitted to the study ICUs using a fully integrated bedside electronic medical record (MetaVision; iMDsoft).19 The discharge abstract database captures data on all hospitalized patients, including dates of admission, discharge, and death, up to 25 Canadian Enhancement of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, diagnostic codes, and up to 20 Canadian Classification of Health Interventions procedure codes.20 The National Ambulatory Care Reporting System Metadata (NACRS) captures data on all emergency department visits.21
Patient and Hospital Factors
We identified, a priori, factors that may affect health care utilization and outcomes of patients recovering from critical illness after discharge home.1,22,23 Patient factors included demographic variables (age, sex); comorbidities; ICU admission diagnosis24; illness severity on ICU admission (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation [APACHE II] score and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment [SOFA] score in the first 24 hours in the ICU) and at ICU discharge (SOFA score on the last day in the ICU); interventions received in the ICU (mechanical ventilation, vasoactive medications, renal replacement therapy); and community support prescribed at hospital discharge (services from an external agency including attendant care, home care, food home delivery, homemaking, and supportive housing).20 The presence of comorbidities was derived using the Deyo classification of the Charlson Comorbidity Index and validated by Canadian Enhancement of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, coding algorithms.25 Hospital factors included teaching status, number of hospital and ICU beds, number of patient discharges directly home (<1 vs ≥1 patient per week), ICU occupancy (percentage), and transfer delay (time from when a patient was determined to be ready for ICU discharge to when the patient left the ICU).26,27
Health Care Utilization and Outcome Measures
The primary outcome was readmission to the hospital within 30 days.28,29,30 We examined 2 secondary outcomes: (1) emergency department visits within 30 days and (2) death at 365 days.
Statistical Analyses
We used multivariable generalized estimating equation logistic regression models with an exchangeable correlation structure accounting for clustering of patients within hospitals to determine factors associated with a patient being discharged directly home. We used Cox proportional hazards regression models accounting for clustering of patients within hospitals to determine factors associated with hospital readmission or an emergency department visit within 30 days of discharge for patients discharged directly home from the ICU. As agreed a priori, variables with P < .20 in univariable analyses were entered into each model and sequentially eliminated until all variables had P < .10. Sensitivity analyses were used to adjust for patient characteristics.
Comparisons between patients discharged directly home and home via the hospital ward were conducted both in the overall study cohort and in a propensity score matched cohort. Patients discharged directly home were matched to patients discharged home via the hospital ward using 1:1 propensity score matching. The propensity score was estimated using a logistic regression model based on patient characteristics (age, sex, comorbidities, previous ICU admission, ICU admission diagnosis, location before ICU admission, admission APACHE II score, admission SOFA score, discharge SOFA score), therapies received in the ICU (mechanical ventilation, vasoactive medications, renal replacement therapy), and hospital characteristics (hospital, ICU occupancy at discharge, individual patient transfer delays).31,32 Nearest-neighbor matching (R package software, version 3.4; MatchIt) was performed, without replacement, using the logit of the propensity score and a specified caliper width equal to 0.2 of the standard deviation of the logit of the propensity score.33 The final propensity score model had a C statistic of 0.85 and McFadden R2 value of 0.27. Model performance was similar when variables with continuous data were treated as continuous or categorized using clinically relevant thresholds. (Note that of the 899 patients discharged directly home with complete data, 83 could not be matched within the specified propensity score caliper width of 0.2 and so were excluded from the matched analyses, leaving 816 patients for propensity score matching.)
Time to first hospital readmission; first subsequent emergency department visit; and mortality at 30, 90, and 365 days after hospital discharge were compared between patients discharged directly home and home via the hospital ward using the Kaplan-Meier method to determine cumulative incidence. For the overall cohort, Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to adjust for baseline characteristics and accounted for clustering of patients within hospitals by using robust standard errors. For the propensity-matched cohort, no adjustments were made, and analyses accounted for clustering of patients within hospitals. All analyses were performed using R software, version 3.4.0 (2017-04-21).34
Results
Study Population
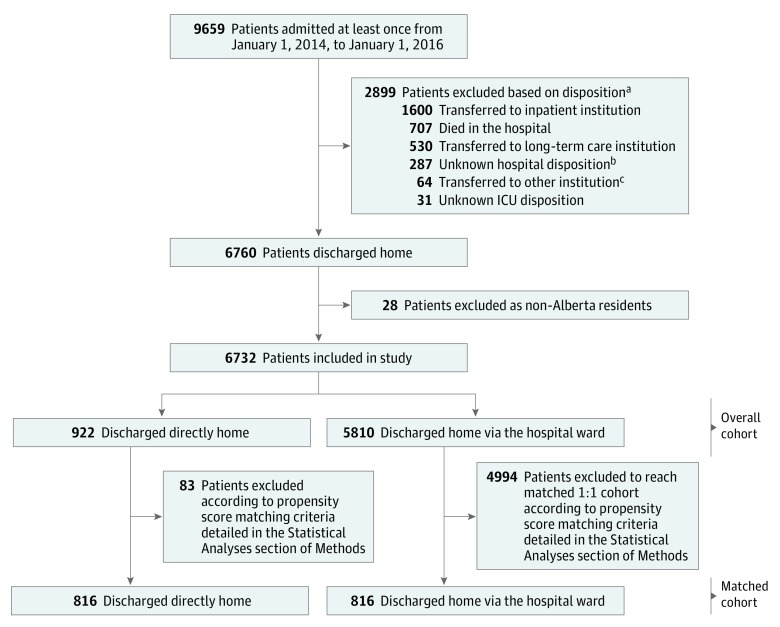
The cohort consisted of 6732 patients admitted to 9 medical-surgical ICUs and discharged alive from the hospital to their home (Figure 1). Among these, 922 were discharged directly home (14%) and 5810 were discharged home via the hospital ward (86%). The proportion of patients discharged directly home varied substantially across hospitals (range, 4.4%-44.0%) and was higher at those hospitals that were nonteaching and had fewer ICU and hospital beds (eFigure in the Supplement).
Figure 1. Selection of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Study Cohorts.
aReasons for exclusion do not sum to the total number of patients because some patients experienced more than 1 admission to ICU during the study period.
bUnable to link to discharge abstract database, data missing, or patients were not discharged from the hospital by September 30, 2016.
cIncludes emergency department and ambulatory care in another facility or within the same reporting facility, palliative care or hospice facility, addiction treatment center, and jails.
Compared with patients discharged home via the hospital ward, patients discharged directly home were younger (median age, 47 vs 57 years; P < .001), less likely to have 1 or more comorbidities (39% [n = 360] vs 65% [n = 3774]; P < .001), less likely to have been admitted to the ICU from the operating or recovery room (11% [n = 98] vs 29% [n = 1669]; P < .001), and were less acutely ill in the first 24 hours in the ICU (median APACHE II score 15 vs 18; P < .001) (Table 1). The most frequent ICU admission diagnoses among patients discharged directly home were overdose (23%; n = 208); pneumonia (11%; n = 104); and trauma or orthopedic injuries (9%; n = 79) (eTable 1 in the Supplement). During the ICU stay, patients discharged directly home were less likely to receive invasive mechanical ventilation (56% [n = 514] vs 64% [n = 3714]; P < .001) or vasoactive medications (19% [n = 176] vs 38% [n = 2204]; P < .001). In multivariable logistic regression analyses, patients were more likely to be discharged directly home from the ICU if their ICU admission diagnosis was overdose, withdrawal, seizures, or metabolic coma; if they received less than 48 hours of invasive mechanical ventilation; or if they spent more than 24 hours in ICU after being determined ready for discharge (supporting data found in eTable 2 in the Supplement). Conversely, patients were less likely to be discharged directly home if they were older; admitted to the ICU from an operating or recovery room or hospital ward; had a previous ICU admission during the hospital stay; or had higher severity of acute illness on admission or discharge (eTable 2 in the Supplement).
Table 1. Patient and Hospital Characteristicsa.
| Characteristic | Overall Cohort (n = 6732) | Matched Cohort (n = 1632)b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directly Home From ICU (n = 922) | Home via the Hospital Ward (n = 5810) | P Value | Directly Home From ICU (n = 816) | Home via the Hospital Ward (n = 816) | P Value | |
| Patient Characteristics on Admission to ICU | ||||||
| Female | 393 (43) | 2433 (42) | .67 | 353 (43) | 353 (43) | >.99 |
| Age, median (IQR), y | 47 (32-59) | 57 (43-68) | <.001 | 48 (33-61) | 49 (34-61) | .47 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Diabetes | 143 (16) | 1392 (24) | <.001 | 134 (16) | 154 (19) | .19 |
| Chronic lung disease | 151 (16) | 1077 (19) | .11 | 143 (18) | 136 (17) | .65 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 23 (2) | 315 (5) | <.001 | 21 (3) | 29 (4) | .25 |
| Liver disease | 37 (4) | 462 (8) | <.001 | 34 (4) | 37 (5) | .72 |
| Cancer | 31 (3) | 946 (16) | <.001 | 31 (4) | 26 (3) | .50 |
| Chronic heart or peripheral vascular diseasec | 72 (8) | 1009 (17) | <.001 | 71 (9) | 77 (9) | .61 |
| Neurological diseased | 17 (2) | 280 (5) | <.001 | 16 (2) | 13 (2) | .57 |
| Any comorbidity | 360 (39) | 3774 (65) | <.001 | 337 (41) | 365 (45) | .16 |
| Charlson Score, median (IQR) | 0 (0-1) | 1 (0-3) | <.001 | 0 (0-1) | 0 (0-1) | .14 |
| Admission diagnosise | <.001 | .96 | ||||
| Overdose, withdrawal, seizures, or metabolic coma | 295 (32) | 594 (10) | 241 (30) | 239 (29) | ||
| Pneumonia | 104 (11) | 800 (14) | 101 (12) | 96 (12) | ||
| Respiratory other | 133 (15) | 550 (9) | 119 (15) | 109 (13) | ||
| Medical or neurological other | 107 (12) | 360 (6) | 88 (11) | 91 (11) | ||
| Trauma or orthopedic | 79 (9) | 667 (11) | 78 (10) | 78 (10) | ||
| Cardiovascular | 67 (7) | 644 (11) | 66 (8) | 65 (8) | ||
| Sepsis (nonpulmonary) | 52 (6) | 629 (11) | 52 (6) | 55 (7) | ||
| Gastrointestinal | 45 (5) | 869 (15) | 43 (5) | 47 (6) | ||
| Pregnancy or genitourinary | 21 (2) | 281 (5) | 20 (2) | 30 (4) | ||
| Cancer | 8 (1) | 383 (7) | 8 (1) | 6 (1) | ||
| Location before ICU admissionf | <.001 | .86 | ||||
| Emergency department | 607 (66) | 2328 (40) | 529 (65) | 541 (66) | ||
| Ward | 160 (17) | 1610 (28) | 151 (19) | 151 (19) | ||
| Operating or recovery room | 98 (11) | 1669 (29) | 90 (11) | 84 (10) | ||
| Other hospital | 55 (6) | 192 (3) | 46 (6) | 40 (5) | ||
| APACHE II score, median (IQR) | 15 (10-20) | 18 (13-24) | <.001 | 15 (10-21) | 15 (11-20) | .40 |
| SOFA score, median (IQR) | 5 (3-7) | 6 (4-9) | <.001 | 5 (3-7) | 5 (3-7) | .16 |
| Previous ICU admission during hospital stay | 12 (1) | 293 (5) | <.001 | 11 (1) | 11 (1) | >.99 |
| Interventions Received in ICU | ||||||
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | <.001 | .63 | ||||
| None | 408 (44) | 2096 (36) | 357 (44) | 360 (44) | ||
| Duration <48 h | 389 (42) | 1984 (34) | 336 (41) | 321 (39) | ||
| Duration ≥48 h | 125 (14) | 1730 (30) | 123 (15) | 135 (17) | ||
| Noninvasive mechanical ventilation | 113 (12) | 730 (13) | .79 | 106 (13) | 97 (12) | .50 |
| Vasoactive medications | 176 (19) | 2204 (38) | <.001 | 171 (21) | 177 (22) | .72 |
| Renal replacement therapy | 9 (1) | 200 (3) | <.001 | 9 (1) | 12 (1) | .51 |
| Hospital characteristics | ||||||
| Teaching hospital | 692 (75) | 5355 (92) | <.001 | 627 (77) | 640 (78) | .44 |
| ≥600 Hospital beds | 398 (43) | 4097 (71) | <.001 | 373 (46) | 378 (46) | .80 |
| ≥20 ICU beds | 326 (35) | 3659 (63) | <.001 | 306 (38) | 301 (37) | .80 |
| ≥1 Patient discharged directly home per wk | 564 (61) | 2987 (51) | <.001 | 480 (59) | 464 (57) | .42 |
| ICU occupancy ≥80%g | 559 (61) | 4895 (84) | <.001 | 517 (63) | 533 (65) | .41 |
| >24 h in ICU after ready for ICU dischargeh | 353 (38) | 1909 (33) | .001 | 328 (40) | 325 (40) | .88 |
| Patient characteristics on ICU discharge, median (IQR) | ||||||
| SOFA scorei | 2 (2-5) | 2 (2-5) | <.001 | 2 (2-5) | 2 (2-5) | .07 |
| ICU length of stay, d | 2.9 (1.6-5.7) | 3.4 (1.8-6.7) | <.001 | 3.1 (1.7-5.9) | 3.0 (1.7-5.1) | .42 |
| Patient characteristics on hospital discharge | ||||||
| Hospital length of stay, median (IQR), d | 3.1 (1.7-6.1) | 13.5 (7.7-25.3) | <.001 | 3.3 (1.8-6.5) | 9.2 (5.4-17.0) | <.001 |
| Public community supports on hospital dischargej | <.001 | <.001 | ||||
| Without community support services | 805 (87) | 4225 (73) | 719 (88) | 654 (80) | ||
| With community support services | 59 (6) | 1421 (24) | 52 (6) | 131 (16) | ||
| Left against medical advice | 58 (6) | 164 (3) | 45 (6) | 31 (4) | ||
Abbreviations: APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; ICU, intensive care unit; IQR, interquartile range; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
Data presented as number (percentage) of patients unless otherwise indicated.
Propensity score 1:1 nearest-neighbor matching without replacement using the logit of the propensity score and specified caliper width equal to 0.2 of the standard deviation of the logit of the propensity score using age, sex, each listed comorbidity, admission reason, location before ICU admission, APACHE II score, admission SOFA score, previous ICU admission during hospital admission, invasive ventilation (no invasive ventilation, duration <48 h, or duration ≥48 h), noninvasive ventilation (yes or no), vasoactive medications (yes or no), renal replacement therapy (yes or no), discharge SOFA score, hospital, ICU occupancy ≥80%, transfer delay >24 h.
Congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, or peripheral vascular disease.
Cerebrovascular disease, hemiplegia or paraplegia, or dementia.
Data missing for 44 patients.
Data missing for 13 patients.
Percentage of ICU beds occupied by patients at time of patient discharge from ICU.
Defined as time from when patient was determined to be ready for ICU discharge to when patient left the ICU. Data were missing for 365 patients, and these patients were assumed to have no delay.
SOFA score calculated using data from the patient’s last day in the ICU. Mean (SD) SOFA scores for the overall cohort were 3.2 (1.8) for those discharged directly home and 3.4 (1.8) for those discharged from a hospital ward.
Defined as personal or health care services for patients living in a private residential setting that are covered by the health insurance system (eg, home care nurse visits).
Health Care Utilization and Clinical Outcomes
Due to missing patient characteristics for 105 patients (1.6%), propensity scores were calculated for 899 patients (97%) discharged directly home and 5728 patients (99%) discharged home via the hospital ward. Of the 899 patients discharged directly home with complete data, 83 could not be matched within the specified propensity score caliper width (0.2) and so were excluded from the matched analyses. The remaining 816 (91%) were matched to patients discharged home via the hospital ward, resulting in a matched cohort of 1632 patients (Table 1).
In the propensity score matched cohort, patients discharged directly home had similar length of ICU stay (median, 3.1 days vs 3.0 days; P = .42), but significantly shorter length of hospital stay (median, 3.3 days vs 9.2 days; P < .001) than patients discharged home via the hospital ward. Patients discharged directly home were more likely to leave against medical advice (6% [n = 45] vs 4% [n = 31]) and less likely to be prescribed community support services (6% [n = 52] vs 16% [n = 131]) at the time of hospital discharge (P < .001).
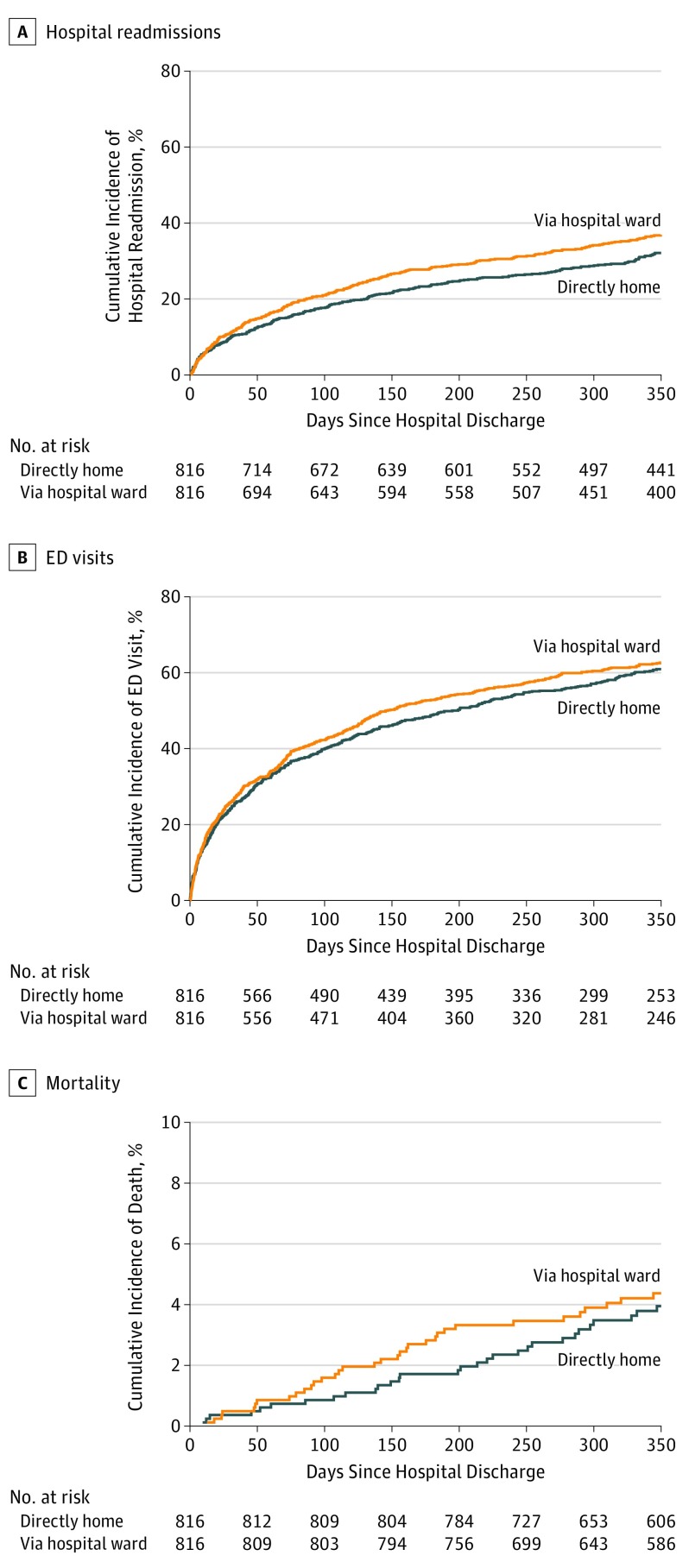
After hospital discharge, there were no significant differences in health care utilization or in outcomes between patients discharged directly home or home via the hospital ward (supporting data reported in Table 2 and Figure 2). Thirty days after hospital discharge, 10% of patients discharged directly home (n = 81) had been readmitted to the hospital compared with 11% of patients discharged home via the hospital ward (n = 92) (hazard ratio [HR], 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.20). Approximately one-quarter of patients in both groups had an emergency department visit within 30 days of hospital discharge (25% [n = 200] vs 26% [n = 212]; HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.81-1.09). A small proportion of patients, in both groups, died within 1 year of hospital discharge (4% [n = 31 directly home] vs 4% [n = 34 via hospital ward]; HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.60-1.35). Subgroup analyses of patients according to the most common ICU admission diagnoses (overdose, withdrawal, seizures, metabolic coma, pneumonia, and respiratory other) produced similar results (eTable 3 in the Supplement). Multivariable adjusted analyses of the overall study cohort produced similar findings (Table 2). Mortality is a competing risk for hospital readmission and emergency department visit, and the results from competing risk models were similar.35
Table 2. Cox Proportional Hazard Analysis of Health Care Utilization and Clinical Outcomes After Hospital Dischargea.
| Time to Event, d | Overall Cohort (n = 6732) | Matched Cohort (n = 1632) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directly Home From ICU (n = 922) | Home via the Hospital Ward (n = 5810) | Adjusted Hazard Ratio (95% CI)b,c,d | Directly Home From ICU (n = 816) | Home via the Hospital Ward (n = 816) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI)b,c | ||
| Hospital Readmission | |||||||
| 30 | 92 (10.0) | 865 (14.9) | 0.81 (0.62-1.06) | 81 (9.9) | 92 (11.3) | 0.88 (0.64-1.20) | |
| 90 | 157 (17.0) | 1388 (23.9) | 0.82 (0.70-0.95) | 138 (16.9) | 167 (20.5) | 0.81 (0.62-1.06) | |
| 365 | 291 (31.6) | 2306 (39.7) | 0.84 (0.75-0.95) | 258 (31.6) | 297 (36.4) | 0.83 (0.66-1.06) | |
| Emergency Department Visit | |||||||
| 30 | 224 (24.3) | 1696 (29.2) | 0.88 (0.77-0.99) | 200 (24.5) | 212 (26.0) | 0.94 (0.81-1.09) | |
| 90 | 360 (39.0) | 2480 (42.7) | 0.91 (0.82-1.00) | 313 (38.4) | 337 (41.3) | 0.91 (0.83-1.01) | |
| 365 | 566 (61.4) | 3701 (63.7) | 0.93 (0.87-1.01) | 493 (60.4) | 510 (62.5) | 0.94 (0.84-1.04) | |
| Death | |||||||
| 30 | 3 (0.3) | 39 (0.7) | NPe | 3 (0.4) | 4 (0.5) | NPe | |
| 90 | 9 (1.0) | 114 (2.0) | NPe | 7 (0.9) | 10 (1.2) | NPe | |
| 365 | 33 (3.6) | 368 (6.3) | 0.92 (0.65-1.31) | 31 (3.8) | 34 (4.2) | 0.90 (0.60-1.35) | |
Abbreviations: APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; ICU, intensive care unit; NP, not performed; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
Unless otherwise indicated, data are reported as number (percentage) of patients.
Models account for clustering of patients within hospitals by using a robust sandwich variance estimator.
Reference group are patients discharged home via the hospital ward.
Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for age, sex, Charlson score, patient location before ICU admission, admitting hospital, admission reason, admission SOFA score, admission APACHE II score, previous ICU admission during current hospitalization, invasive ventilation (no invasive ventilation, duration <48 h, duration ≥48 h), noninvasive ventilation (yes or no), vasoactive medications (yes or no), renal replacement therapy (yes or no), ICU occupancy ≥80%, transfer delay >24 h, number of ICU beds, volume of direct home discharges, ICU length of stay, and SOFA score on ICU discharge.
Modeling not performed (NP) owing to small number of deaths.
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Estimates of Study Outcomes for the Propensity Matched Cohort of Patients Discharged Directly Home From the ICU vs Discharged via a Hospital Ward.
ED indicates emergency department; ICU, intensive care unit.
Risk Factors for Hospital Readmission or Emergency Department Visit for Patients Discharged Directly Home
Of the 29 patient and hospital factors evaluated (eTable 4 in the Supplement), 5 were found to be associated with hospital readmission or emergency department visit within 30 days of discharge for patients discharged directly home: (1) ICU admission diagnosis of overdose, withdrawal, seizures, or metabolic coma; (2) duration of invasive mechanical ventilation of 48 hours or longer; (3) hospital with 600 or more beds; (4) ICU with 1 or more patients discharged directly home per week; and (5) leaving against medical advice (Table 3). After adjustment for patient factors, only prescription of community supports, leaving against medical advice, and ICUs with 1 or more patient discharged directly home per week remained statistically significant (Table 3).
Table 3. Multivariable Cox Proportional-Hazard Analysis of Risk Factors for Hospital Readmission or Emergency Department Visit Within 30 Days of Patient Discharge Directly Home From ICUa.
| Risk Factorb | Hospital Readmission or ED Visit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence (n = 922) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Adjusted Hazard Ratio (95% CI)c | |
| ICU admission diagnosis of overdose, withdrawal, seizures, or metabolic coma | 295 (32) | 1.40 (1.06-1.86) | 1.27 (0.90-1.79) |
| Location before ICU admissiond | |||
| ED | 607 (66) | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| Operating or recovery room | 98 (11) | 0.85 (0.67-1.09) | 0.90 (0.74-1.10) |
| Ward | 160 (17) | 1.14 (0.94-1.39) | 1.17 (0.95-1.42) |
| Other hospital | 55 (6) | 1.56 (0.95-2.58) | 1.58 (1.00-2.51) |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | |||
| None | 408 (44) | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| Duration <48 h | 389 (42) | 1.01 (0.82-1.25) | 0.87 (0.69-1.10) |
| Duration ≥48 h | 125 (14) | 1.47 (1.11-1.95) | 1.33 (0.82-2.15) |
| ≥600 Hospital beds | 398 (43) | 1.23 (1.11-1.35) | 1.12 (0.99-1.27) |
| ≥1 Patient discharged directly home per wk | 564 (61) | 1.17 (1.09-1.26) | 1.20 (1.09-1.33) |
| Public community supports at hospital dischargee | |||
| Without community support services | 805 (87) | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| With community support services | 59 (6) | 1.61 (0.94-2.73) | 1.85 (1.17-2.92) |
| Left against medical advice | 58 (6) | 1.79 (1.09-2.93) | 1.93 (1.13-3.30) |
Abbreviations: APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; ED, emergency department; ICU, intensive care unit; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
Analyses conducted only for those patients discharged directly home from the ICU.
Data presented as number (percentage) unless otherwise indicated.
Adjusted for patient age, sex, Charlson score, admission APACHE II score, admission SOFA score, discharge SOFA score, noninvasive mechanical ventilation, vasoactive medications, and length of ICU stay.
Data missing for 2 patients.
Defined as personal or health care services for patients living in a private residential setting that are covered by the health insurance system (eg, home care nurse visits).
Discussion
In this population-based, multicenter cohort study, we observed that more than 1 in 10 adult patients recovering from critical illness were discharged directly home from a medical-surgical ICU. These patients had similar lengths of ICU stay, but shorter lengths of hospital stay, compared with patients discharged home via the hospital ward. In the subsequent year, patients discharged directly home from ICU did not experience more readmissions to the hospital, emergency department visits, or deaths compared with similar patients discharged home via the hospital ward. Among those patients discharged directly home, factors associated with readmission to the hospital or an emergency department visit within 30 days included leaving against medical advice, prescription of community supports, and discharge from an ICU with 1 or more patients discharged directly home each week. Our study suggests that discharging select patients directly home from the ICU is not associated with increased health care utilization or worse outcomes.
While the transfer of patients from the ICU to a hospital ward before discharge home has been extensively studied, much less is known about the discharge of patients from the ICU directly home.1,2 Both discharge processes are likely to have common and distinct elements. What do we know about the discharge of adult patients directly home from ICU? Three articles have reported this practice in the context of palliative care, where patients were discharged home to die.9,10,11 Chawla et al12 conducted a retrospective cohort study of adult patients discharged directly home from a 20-bed medical-surgical ICU at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center between 2008 and 2010. During the study period, 5% of all patients discharged alive from the ICU were discharged directly home. Of these, 23% had an unplanned readmission to the hospital within 30 days, and two-thirds of these readmissions were for problems related to the prior ICU admission. A single study in the cardiology literature surveyed 425 patients discharged directly home and reported that within 6 weeks of discharge, 28% of patients had made an unscheduled return visit to a hospital or physician’s office.13 The quality of care was reported to be good to outstanding by 91% of patients, although 18% reported a perception that they had been discharged prematurely.13 Lau et al5 reported that the proportion of patients discharged directly home from 2 medical-surgical ICUs at a health sciences center increased from 3% of patients in 2003 to 12% of patients in 2015. In a follow-up study, the authors reported that only 5% of ICU physicians felt very comfortable with discharging patients directly home.36
Our study contributes to the literature by providing the strongest data yet reported, to our knowledge, for health care utilization and outcomes among patients discharged directly home from the ICU. The results suggest that select adult patients recovering from critical illness are being discharged directly home from the ICU and that, compared with similar patients discharged home via the hospital ward, no important differences in posthospital health care utilization or outcomes were observed. Earlier findings of our research group demonstrate that delays in patient discharge from ICU are common,16 and data from the present study show that these delays are strongly associated with discharge directly home. One in 3 patients in the present cohort spent more than 24 hours in the ICU after being determined ready for ICU discharge. This misallocation of resources may slow care progression for patients recovering from critical illness and limit ICU access for other patients. The root causes of flow failure need to be delineated and strategies developed to improve patient flow including ICU discharge.
We believe that one potential strategy to improve patient flow through the health care system is to reconceptualize the discharge of patients recovering from critical illness. First, analogous to models used by many medical and surgical hospital wards, discharge planning for ICU patients should commence as early as possible, perhaps as soon as clinical recovery is anticipated.37 Early discharge planning would extend the concept of ICU liberation of critically ill patients from life support technologies to include transitions of care to help patients, family caregivers, and clinicians prepare for patient discharge.38
Second, select patients should be eligible to be discharged directly home. The potential benefits include shortening hospital lengths of stay, reducing transitions of care, decreasing flow failure, and alleviating ICU capacity strain.39 However, strategies are needed to make the discharge of patients directly home from the ICU more effective. Our data suggest that this practice varies widely across institutions and that most ICU clinicians likely have little experience with it.
Furthermore, in the present study, all 3 factors associated with readmission to the hospital or an emergency department visit within 30 days of a patient being discharged directly home were associated with characteristics of the ICU or the discharge process, suggesting opportunities for improvement. We recommend that ICUs develop discharge procedures that include identification of candidate patients for discharge directly home, develop protocols to facilitate the process, and train ICU clinicians (including trainees) in these procedures. Processes and outcomes of care for patients discharged directly home from the ICU should be monitored to ensure that patients are not exposed to increased risk and that any burden of care is not inappropriately shifted to the community or family. Conversely, continuing to discharge all patients home via the hospital ward because that is how it has been historically done would represent a missed opportunity for improving efficiency.
Limitations
The results of our study need to be interpreted within the context of its limitations. First, even with propensity score matching using detailed patient and hospital characteristic data for risk adjustment, residual confounding is an inherent risk of observational studies. Nevertheless, our data provide a robust observational evaluation and can be used to provide clinical guidance and justify equipoise for randomized clinical trials. For example, clinicians can now ask themselves whether they are comfortable discharging a patient similar to one included in the present study directly home if their risk of readmission to the hospital within 30 days is approximately 10%. Second, despite a cohort of more than 6000 patients, we are unable to exclude small differences in mortality. Third, we are not able to provide any information about ambulatory care visits or private supports (eg, unpaid caregivers) utilized by patients after hospital discharge. Finally, our study was performed in a single publicly funded health system. This was an important strength of our methodology because it allowed us to measure health care utilization and outcomes for patients following hospital discharge. However, allocation of resources and decision-making processes may vary across health care systems, and the results may not apply to other institutions. We are unaware of any studies that have compared the incidence and experience with the discharge of patients directly home from the ICU across different health care systems. Nevertheless, common challenges to the safe and efficient transition of patients recovering from critical illness back home have been documented in diverse health care systems.1
Conclusions
In summary, we found that the discharge of select adult patients recovering from critical illness directly home from the ICU is common, associated with shorter hospital stays, but not associated with increased health care utilization or mortality in the year following hospital discharge. Three risk factors including leaving against medical advice, prescription of community supports at time of discharge, and discharge from an ICU with higher volumes of patients discharged directly home may help to identify patients at increased risk of a hospital readmission or an emergency department visit within 30 days of discharge. We recommend that ICUs develop discharge procedures that include identification of candidate patients for discharge directly home, develop protocols to facilitate the process, train ICU clinicians in these procedures, and measure outcomes.
eFigure. Proportion of Patients Discharged Directly Home from ICU by Hospital
eTable 1. Most Frequent ICU Admission Diagnoses for Patients Discharged Directly Home from ICU
eTable 2. Multivariable Logistic Regression Analysis of Patient and Hospital Characteristics Associated with Patients Discharged Directly Home
eTable 3. Cox Proportional-Hazard Analysis of Healthcare Utilization after Hospital Discharge Among Subgroups of Patients with the Most Common ICU Admission Diagnoses
eTable 4. Univariable Cox Proportional-Hazard Analysis of Risk Factors for Joint Outcome of Hospital Readmission or Emergency Department Visit within 30 days of Patient Discharge Directly Home from ICU
References
- 1.Stelfox HT, Lane D, Boyd JM, et al. . A scoping review of patient discharge from intensive care: opportunities and tools to improve care. Chest. 2015;147(2):317-327. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-2965 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nates JL, Nunnally M, Kleinpell R, et al. . ICU admission, discharge, and triage guidelines: a framework to enhance clinical operations, development of institutional policies, and further research. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(8):1553-1602. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001856 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Patient Safety Network Patient safety primers: handoffs and signouts. 2016. https://psnet.ahrq.gov/primers/primer/9. Accessed November 7, 2016.
- 4.The Economist Accident and emergency. https://www.economist.com/britain/2016/09/10/accident-and-emergency. Accessed June 29, 2018.
- 5.Lau VI, Priestap FA, Lam JNH, Ball IM. Factors associated with the increasing rates of discharges directly home from intensive care units—a Direct From ICU Sent Home Study. J Intensive Care Med. 2018;33(2):121-127. doi: 10.1177/0885066616668483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Casiro OG, McKenzie ME, McFadyen L, et al. . Earlier discharge with community-based intervention for low birth weight infants: a randomized trial. Pediatrics. 1993;92(1):128-134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brooten D, Kumar S, Brown LP, et al. . A randomized clinical trial of early hospital discharge and home follow-up of very-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 1986;315(15):934-939. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610093151505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn Hospital discharge of the high-risk neonate. Pediatrics. 2008;122(5):1119-1126. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-2174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lusardi P, Jodka P, Stambovsky M, et al. . The Going Home Initiative: getting critical care patients home with hospice. Crit Care Nurse. 2011;31(5):46-57. doi: 10.4037/ccn2011415 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Huang YC, Huang SJ, Ko WJ. Going home to die from surgical intensive care units. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35(5):810-815. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1452-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ryder-Lewis M. Going home from ICU to die: a celebration of life. Nurs Crit Care. 2005;10(3):116-121. doi: 10.1111/j.1362-1017.2005.00117.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chawla S, D’Agostino RL, Pastores SM, et al. . Homeward bound: an analysis of patients discharged home from an oncologic intensive care unit. J Crit Care. 2012;27(6):681-687. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.05.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Senaratne MP, Irwin ME, Shaben S, et al. . Feasibility of direct discharge from the coronary/intermediate care unit after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;33(4):1040-1046. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(98)00682-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.de Grood C, Leigh JP, Bagshaw SM, et al. . Patient, family and provider experiences with transfers from intensive care unit to hospital ward: a multicentre qualitative study. CMAJ. 2018;190(22):E669-E676. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.170588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP; STROBE Initiative . The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147(8):573-577. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stelfox HT, Leigh JP, Dodek PM, et al. . A multi-center prospective cohort study of patient transfers from the intensive care unit to the hospital ward. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(10):1485-1494. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4910-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chiasson TC, Manns BJ, Stelfox HT. An economic evaluation of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis strategies in critically ill trauma patients at risk of bleeding. PLoS Med. 2009;6(6):e1000098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stelfox HT, Bastos J, Niven DJ, Bagshaw SM, Turin TC, Gao S. Critical care transition programs and the risk of readmission or death after discharge from ICU. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42(3):401-410. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-4173-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Alberta Health Services Albert's Strategic Clinical Networks: eCritical. 2015. https://www.albertahealthservices.ca/assets/about/scn/ahs-scn-sb-cc-ecritical.pdf. Accessed August 3, 2017.
- 20.Canadian Institute for Health Information Discharge Abstract Database Metadata (DAD). 2017. https://www.cihi.ca/en/discharge-abstract-database-metadata. Accessed November 1, 2017.
- 21.Canadian Institute for Health Information National Ambulatory Care Reporting System Metadata. 2017. https://www.cihi.ca/en/national-ambulatory-care-reporting-system-metadata. Accessed November 1, 2017.
- 22.Lone NI, Seretny M, Wild SH, Rowan KM, Murray GD, Walsh TS. Surviving intensive care: a systematic review of healthcare resource use after hospital discharge*. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(8):1832-1843. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31828a409c [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lone NI, Gillies MA, Haddow C, et al. . Five-year mortality and hospital costs associated with surviving intensive care. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(2):198-208. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201511-2234OC [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zimmerman JE, Kramer AA, McNair DS, Malila FM. Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) IV: hospital mortality assessment for today’s critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(5):1297-1310. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000215112.84523.F0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. . Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wagner J, Gabler NB, Ratcliffe SJ, Brown SE, Strom BL, Halpern SD. Outcomes among patients discharged from busy intensive care units. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(7):447-455. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-7-201310010-00004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Iwashyna TJ, Kramer AA, Kahn JM. Intensive care unit occupancy and patient outcomes. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(5):1545-1557. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819fe8f8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zuckerman RB, Sheingold SH, Epstein AM. The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(5):494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Joynt KE, Jha AK. Characteristics of hospitals receiving penalties under the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. JAMA. 2013;309(4):342-343. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.94856 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wasfy JH, Zigler CM, Choirat C, Wang Y, Dominici F, Yeh RW. Readmission rates after passage of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program: a pre-post analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(5):324-331. doi: 10.7326/M16-0185 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rosenbaum PR, Rubin DB. Constructing a control group using multivariate matched sampling methods that incorporate the propensity score. Am Stat. 1985;39:33-38. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ho D, Imai K, King G, Stuart E. Matching as nonparametric preprocessing for reducing model dependence in parametric causal inference. Polit Anal. 2007;15:199-236. doi: 10.1093/pan/mpl013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Austin PC. Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies. Pharm Stat. 2011;10(2):150-161. doi: 10.1002/pst.433 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.R Core Team R: a language and environment for statistical computing. 2017; https://www.R-project.org/.
- 35.Fine JP, Gray RJ. A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc. 1999;94:496-509. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1999.10474144 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lam JNH, Lau VI, Priestap FA, Basmaji J, Ball IM. Patient, family, and physician satisfaction with planning for direct discharge to home from intensive care units: Direct From ICU Sent Home Study. J Intensive Care Med. 2017;885066617731263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gonçalves-Bradley DC, Lannin NA, Clemson LM, Cameron ID, Shepperd S. Discharge planning from hospital. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(1):CD000313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ely EW. The ABCDEF bundle: science and philosophy of how ICU liberation serves patients and families. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(2):321-330. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bagshaw SM, Opgenorth D, Potestio M, et al. . Healthcare provider perceptions of causes and consequences of ICU capacity strain in a large publicly funded integrated health region: a qualitative study. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(4):e347-e356. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002093 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eFigure. Proportion of Patients Discharged Directly Home from ICU by Hospital
eTable 1. Most Frequent ICU Admission Diagnoses for Patients Discharged Directly Home from ICU
eTable 2. Multivariable Logistic Regression Analysis of Patient and Hospital Characteristics Associated with Patients Discharged Directly Home
eTable 3. Cox Proportional-Hazard Analysis of Healthcare Utilization after Hospital Discharge Among Subgroups of Patients with the Most Common ICU Admission Diagnoses
eTable 4. Univariable Cox Proportional-Hazard Analysis of Risk Factors for Joint Outcome of Hospital Readmission or Emergency Department Visit within 30 days of Patient Discharge Directly Home from ICU