Abstract
Background
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a major depressive disorder that occurs after childbirth. Objective diagnostic and predictive methods for PPD are important for early detection and appropriate intervention. DNA methylation has been recognized as a potential biomarker for major depressive disorder. In this study, we used methylation analysis and peripheral blood to search for biomarkers that could to lead to the development a predictive method for PPD.
Methods
Study participants included 36 pregnant women (18 cases and 18 controls determined after childbirth). Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles were obtained by analysis with an Infinium Human Methylation 450BeadChip. The association of DNA methylation status at each DNA methylation site with PPD was assessed using linear regression analysis. We also conducted functional enrichment analysis of PPD using The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery 6.8 to explore enriched functional-related gene groups for PPD.
Results
In the analysis with postpartum depressed state as an independent variable, the difference in methylation frequency between the postpartum non-depressed group and the postpartum depressed group was small, and sites with genome-wide significant differences were not confirmed. After analysis by The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery 6.8, we revealed four gene ontology terms, including axon guidance, related to postpartum depression.
Conclusions
These findings may help with the development of an objective predictive method for PPD.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12888-019-2172-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: DNA methylation, Postpartum depression, Epigenome-wide association study, Edinburgh postnatal depression scale (EPDS)
Background
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a type of major depressive disorder that occurs after childbirth; the prevalence of PPD is estimated at approximately 13% [1]. Our study showed that 10.4% of postpartum women in Japan experienced depressive symptomatology based on the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) [2]. PPD is related to maternal suicide [3] and affects children’s development [4]. One study reported that among women who had no history of psychological disorder but who were diagnosed with PPD, 54% had bipolar disorder [5]. Therefore, objective diagnostic and predictive methods for PPD are important for early detection of patients and appropriate intervention. The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) is the most widely used screening questionnaire for PPD [6]. However, the EPDS is only a screening instrument and cannot be used to make a clinical diagnosis [7]. A diagnostic method for depression using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy was created [8], but sufficient sensitivity and specificity were not shown. Therefore, a new index is required. It is important to search for biomarkers that are predictive indicators of PPD for early detection and intervention.
Major depressive disorder is associated with both genetic and environmental factors and is considered to be associated with an epigenetic mechanism [9]. DNA methylation is the most widely studied epigenetic mechanism; it reveals changes in gene expression that are not due to alterations in the DNA sequence [10]. DNA methylation within gene promoters generally exerts a repressive effect on gene transcription, and use of this technique has been considered a potential way to identify possible biomarkers for depressive disorder [9].
Recent advances in epigenome-wide analyses have extended the field beyond a gene candidate approach toward a more comprehensive epigenome approach [11]. In terms of epigenome-wide analyses of PPD, Kaminsky et al. reported estrogen receptor- and oxytocin receptor-mediated epigenetic changes associated with PPD [12–14]. An association between PPD and the oxytocin receptor gene has also been reported with methylation analysis using the candidate gene approach [15].
In a methylation study, it is necessary to consider variations in methylation patterns due to racial and ethnic differences [16]. Therefore, a methylation analysis that examines Japanese women is indispensable for the development of PPD predictive methods in Japan. The results of this study from a methylation analysis may clarify the characteristics of the methylation frequency of women who exhibit PPD and lead to the development of an effective predictive method for PPD in Japanese women.
The pathogenic processes for psychiatric disorders likely involve the histologic pathology of the brain. However, brain tissue is not readily accessible in living patients, so biomarker studies typically use blood [17]. An association between methylation frequencies of the brain and peripheral blood has been reported [18, 19]. Similarly, a relatively high correlation has been observed between gene expression in the brain and that in peripheral blood [20]. Furthermore, a methylome-wide association study reported that peripheral blood can be a biomarker for schizophrenia [17]. Therefore, it is suggested that the methylation frequency of peripheral blood may be a useful biomarker for PPD diagnosis. Based on the above, we used methylation analysis and peripheral blood to search for biomarkers that could lead to the development of a predictive method for PPD.
Methods
Participants
Women were recruited from Nagoya University Hospital and its associated institutes. Inclusion criteria were participation in perinatal classes for pregnant Japanese women before week 25 of pregnancy, age ≥ 20 years, and the ability to understand and speak Japanese. The study was explained both orally and in writing to all participants during the perinatal classes, and all participants provided written informed consent.
Procedure
Participants were provided with a consent form and a self-reporting questionnaire during a perinatal class. The questionnaire included the EPDS and demographic questions, such as age, parity and current and previous mental illness (Additional file 1). Women were asked to complete the questionnaire in early pregnancy (before week 25) and return their responses, along with the agreement document, via mail using the provided self-addressed envelope. We provided self-addressed envelopes and postage on these envelopes. Questionnaires were mailed to women again around week 36 of pregnancy and 1 month after delivery, and returned in the same manner.
EPDS
The EPDS is a 10-item self-reporting questionnaire that assesses PPD. Each item is scored on a 4-point Likert scale, with higher scores indicating worse depression [21]. The EPDS was translated into Japanese and then reverse translated back into English, and was determined to be the same as the English version [22]. The Japanese version of the EPDS showed good internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.78) and test-retest reliability (Spearman’s correlation coefficient = 0.92) [22]. In the original version, the cut-off point is 12/13 [21], and the EPDS cut-off point 12/13 is recommended for English-speaking women [23]. In the non-English version, a cut-off point lower than 12/13 has been reported to be appropriate [24–28], as cut-off point requires validation for specific populations [29]. Although one report regarding the EPDS recommended the cut-off point 12/13 in the Japanese version [30], the cut-off point in that study was calculated by subjects who excluded pregnant women with an EPDS ≦8 during pregnancy. Participant in this study is different from that study [30]. For example, we included women with an EPDS ≦ 8 during pregnancy. As a result, we used a cut-off point 8/9 in Japanese version of the EPDS by Okano et al. [22]. A score ≥ 9 on the Japanese version of the EPDS has been used as an indication of major depressive episodes. The test has a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 93% [22]. We used the 8/9 cut-off point and defined a score ≥ 9 as depressive episodes.
Definition of PPD
We evaluated depressive symptoms using the EPDS during early pregnancy (before week 25), late pregnancy (around week 36), and 1 month after birth. We measured EPDS scores twice in pregnancy, to confirm that participants were not depressed in pregnancy both cases and controls. The incidence of peak depression in the postnatal period has been debated [31],and one report found a peak 6 weeks after birth [32]. On the other hand, “maternity blues” frequently occur during the period immediately after childbirth to 10 days after childbirth [33]. Prevalence rates of maternity blues vary from 40 to 80% [34]. We considered that the time period immediately after childbirth, when many pregnant women experience maternity blues, was not a suitable time to search for PPD biomarkers. Therefore, we chose 1 month after birth as time point for postpartum EPDS and blood collection. We defined cases and controls based on the results of the EPDS scores. The controls scored under the cut-off point before week 25, around week 36, and 1 month after birth. The cases scored under the cut-off point before week 25 and around week 36, but scored over the cut-off point at 1 month postpartum. The control group excluded participants with current or previous mental illness. In addition, we matched cases and controls in terms of age, parity, gestational weeks, and the day of blood collection after birth. A total of 18 cases and 18 controls were identified.
DNA methylation analysis
We collected peripheral blood from all participants about 1 month after birth for extraction of genomic DNA. Venous blood was collected into tubes containing EDTA, and genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood using the Qiagen QIAamp DNA bloods Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The extracted DNA was stored at − 30 °C until the start of the experiment. We performed DNA extraction from October 2006 to March 2013, and conducted experiments from March 2013 to November 2015.
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood. Bisulfite conversion of genomic DNA from peripheral blood was done using the EpiTect Plus Bisulfite Kits (Qiagen Ltd., Hilden, Germany). Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles were obtained using the Infinium Human Methylation 450BeadChip according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). To minimize potential batch effects, cases and controls were processed together and run on the same BeadChip. Samples were randomly positioned on each BeadChip to reduce any possible position effects within chips. We used a correction method applied in a previous study to reduce technical bias in the DNA methylation array data [35]. Briefly, DNA methylation values were corrected for background and normalized with the Subset-quantile Within Array Normalization function [36] of minfi in R to adjust for color bias [37]. The minfi is a flexible and comprehensive R package for the analysis of Infinium DNA methylation microarrays, and R is an open-source, free software program for statistical analysis.
DNA methylation level was quantified as an M value, which can be converted to a β value according to the equation: β = 2M/(2M + 1) [38]. The M value for all DNA methylation sites was corrected for batch effects with the ComBat function of sva in R. sva is an R package that contains functions for removing batch effects [39] and the ComBat function adjusts for known batches using an empirical Bayesian framework [40].
We estimated the cell type composition for each sample with the estimate Cell Counts function [41] of minfi in R. For each sample, probes with a detection p value ≥0.05 were assigned a status of “not detected”; this led to the exclusion of 1316 probes (5% of samples). We also excluded 30,819 probes previously found to be cross-reactive (≥47 bases) [42] and probes on the Y chromosome. Probes containing single nucleotide polymorphisms have been found to influence the assessment of DNA methylation status when using the Infinium Human Methylation 450BeadChip [43]. We therefore filtered out probes that contained single nucleotide polymorphisms with a minor allele frequency > 0.01 based on 1000 Genomes project samples of ASN (ASN: Han Chinese individuals in Beijing, Southern Han Chinese, and Japanese in Tokyo) [42] to reduce the frequency of false positives. Finally, a total of 379,277 DNA methylation sites remained.
Statistical analysis
The association of PPD with DNA methylation status at each DNA methylation site was assessed using a linear regression analysis, with DNA methylation status at each site as a dependent variable, and PPD label (case = 1, control = 0) and covariates as independent variables. The covariates comprised age and the cell type composition of samples. All p values were corrected for genomic control. The significance level α for the epigenome-wide association study analysis was determined by dividing 0.05 by the number of DNA methylation sites for Bonferroni correction (α = 0.05/379,277 = 1.32 × 10− 7). A p value < 0.05 was considered nominally significant.
Gene ontology (GO) terms are used to describe 3 categories of gene products: biological process, molecular function, and cellular component [44]. These terms are widely used in gene function studies. Identifying GO terms that are overpresented within a given list of genes can increase the understanding of the functional relevance of these genes [45].
For genes that showed differential DNA methylation between cases and controls, gene set enrichment analysis was used to identify enriched GO terms. Analyses were done using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) 6.8 [46, 47]. DAVID is a free, online bioinformatics resource that lists a comprehensive set of functional annotations that can be used to identify the biological significance of a list of genes. We selected 1000 sites with the lowest p values. A total of 711 genes that were annotated within these 1000 sites were analyzed using DAVID. GO terms with a false discovery rate < 0.05, as calculated by the Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment method, were considered significant.
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Results
Characteristics of study subjects
Table 1 shows characteristics of the study subjects. The mean ages of cases and controls were 33.3 ± 4.4 and 34.6 ± 4.6 years, respectively. There were no significant differences in age, parity, gestational weeks,baby’s weight (g), and blood collection day after birth (days) between cases and controls. EPDS score at 1 month after birth was significantly higher among cases compared with controls. The range of EPDS scores at early pregnancy and late pregnancy was 0–8 for cases and controls. The range of EPDS scores at 1 month after birth was 9–25 for cases and 0–8 for controls.
Table 1.
Characteristics of study subjects
| Controls (n = 18) Mean (SD) |
Cases (n = 18) Mean (SD) |
p value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 34.6 | (4.6) | 33.3 | (4.4) | 0.386 |
| Parity | 1.2 | (0.4) | 1.1 | (0.3) | 0.594 |
| Gestational weeks | 39.1 | (1.3) | 38.9 | (1.0) | 0.480 |
| Baby’s weight (g) | 3035 | (304.7) | 2993 | (237.9) | 0.684 |
| Blood collection day after birth (days) | 30.1 | (7.6) | 26.0 | (10.7) | 0.195 |
| EPDS score 1 month after birth | 2.3 | (2.4) | 13.6 | (4.2) | 1.9 × 10− 11 |
EPDS Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
Association analysis for DNA methylation status
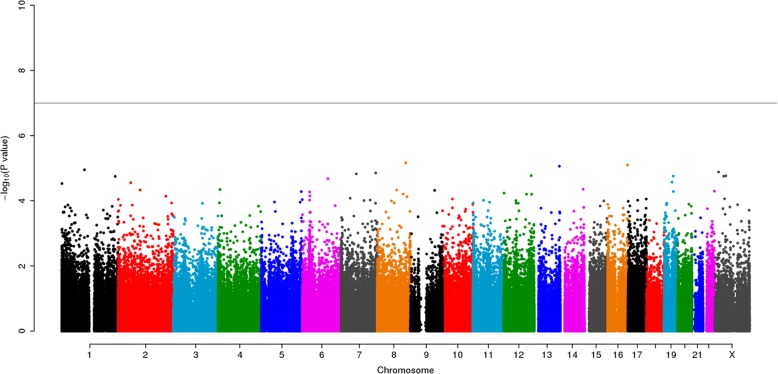
After initial processing, 18 cases and 18 controls as well as 379,277 DNA methylation sites remained for subsequent analysis. We performed an association analysis for DNA methylation level and PPD and found no genome-wide significant association (Fig. 1). In addition, no outliers were detected in the quantile-quantile plot of −log10(p) for the 379,277 tests of association between DNA methylation status and cases-controls (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
A Manhattan plot for the epigenome-wide association study analysis of PPD and DNA methylation. The genome-wide significance level (α = 1.32 × 10− 7) is denoted by the horizontal line. The p values were corrected for genomic control
Fig. 2.
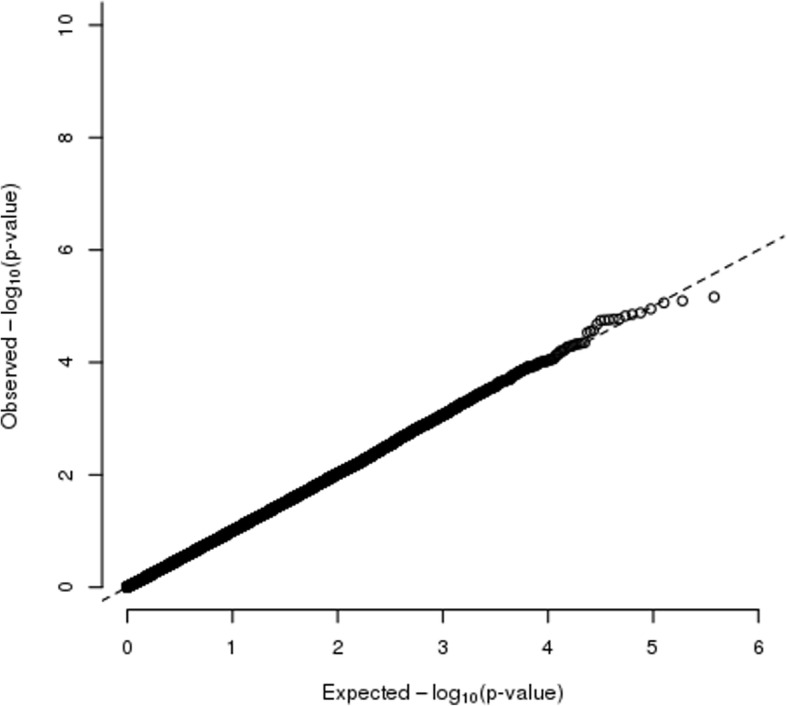
A quantile-quantile plot of the expected versus the observed –log10(p value) for tests of association between PPD and DNA methylation sites. The p values were corrected for genomic control
As a result of DAVID 6.8 analysis of the 711 genes associated with the 1000 sites with the lowest p values (Additional file 2: Table S1), we found four GOTERM DIRECT terms and 16 GOTERM FAT terms with a false discovery rate < 0.05 (Table 2). GOTERM DIRECT provides GO mappings directly annotated by the source database and GOTERM FAT filters out very broad GO terms based on a measured specificity of each term. We showed 22 genes of the axon guidance in which the Fold Enrichment was largest among the four GOTERM DIRECT terms (Table 3).
Table 2.
Gene ontology term enrichment analysis with DAVID
| Category | Term | Count | Fold Enrichment | FDRa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0007411~axon guidance | 22 | 3.27 | 0.0088 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0097485~neuron projection guidance | 27 | 2.86 | 0.0074 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0007411~axon guidance | 27 | 2.88 | 0.0136 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0030182~neuron differentiation | 83 | 1.61 | 0.0235 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0032990~cell part morphogenesis | 59 | 1.73 | 0.0257 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0007409~axonogenesis | 37 | 2.13 | 0.0259 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0048699~generation of neurons | 89 | 1.56 | 0.0271 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0048667~cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation | 42 | 2.02 | 0.0274 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0061564~axon development | 38 | 2.04 | 0.0278 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0048666~neuron development | 67 | 1.66 | 0.0284 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0021953~central nervous system neuron differentiation | 21 | 2.89 | 0.0305 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0048858~cell projection morphogenesis | 58 | 1.74 | 0.0305 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0048812~neuron projection morphogenesis | 43 | 1.89 | 0.0389 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0031175~neuron projection development | 58 | 1.70 | 0.0409 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0022008~neurogenesis | 90 | 1.48 | 0.0461 |
| GOTERM_BP_FAT | GO:0035556~intracellular signal transduction | 147 | 1.33 | 0.0486 |
| GOTERM_CC_DIRECT | GO:0005654~nucleoplasm | 157 | 1.38 | 0.0040 |
| GOTERM_MF_DIRECT | GO:0005515~protein binding | 421 | 1.15 | 0.0032 |
| GOTERM_MF_DIRECT | GO:0003714~transcription corepressor activity | 24 | 2.91 | 0.0033 |
| GOTERM_MF_FAT | GO:0003714~transcription corepressor activity | 24 | 2.63 | 0.0495 |
DAVID The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery 6.8, BP biological process, CC cellular component, MF molecular function, FDR false discovery rate
a Calculated by the Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment method
Table 3.
Gene list of axon guidance using DAVID
| Category | Term | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| GOTERM_BP_DIRECT | GO:0007411 ~axon guidance | kinesin family member 26A(KIF26A), ephrin A2 (EFNA2), neurexin 1 (NRXN1), glypican 1 (GPC1), dorsal inhibitory axon guidance protein (DRAXIN), growth factor receptor bound protein 2 (GRB2), isoprenoid synthase domain containing (ISPD), FYN proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase (FYN), ribosomal protein S6 kinase A5 (RPS6KA5), mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 3 (MAPK8IP3), nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR), laminin subunit alpha 2 (LAMA2), EPH receptor A8 (EPHA8), colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), sodium voltage-gated channel beta subunit 1 (SCN1B), EPH receptor B1 (EPHB1), contactin 2 (CNTN2), ubiquitin specific peptidase 33 (USP33), cadherin 4 (CDH4), unc-5 netrin receptor A (UNC5A), growth differentiation factor 7 (GDF7), Wnt family member 5A (WNT5A) |
DAVID The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery 6.8
Discussion
In this study, we used methylation analysis and peripheral blood to search for biomarkers that could lead to development of an objective predictive method for PPD.
In the analysis with postpartum depressed state as an independent variable, the difference in methylation frequency between the non-depressed group and the postpartum depressed group was small, and sites with a genome-wide significant difference were not confirmed. For that reason, our results could not confirm the relationship between estrogen and oxytocin receptors and PPD as reported by Kaminsky and colleagues [12–14]. It is not clear whether the reason is due to racial differences or other factors. This study had a small sample size (18 controls and 18 cases), and our results are preliminary in nature. Future examination is necessary.
We found 4 GOTERM DIRECT terms: protein binding, nucleoplasm, transcription corepressor activity, and axon guidance. Among them, axon guidance, which had the largest fold enrichment, is an important process to form a neural circuit at the stage of nervous system development, and a relationship with stress [48] and depression [49, 50] has been noted. As a result of epigenome-wide studies of depression, axon guidance was reported as a common disrupted pathway in depression [51]. Among the genes associated with axon guidance, Src family tyrosine kinase (FYN), shown in Table 3, has been reported to be associated with anxiety-related behaviors [52]. In addition, axon guidance pathway has been shown to be associated with neuroticism [53], and neuroticism is a well-known predictive factor for depression [54]. It has been reported that psychological stress may affect brain structure and brain function [55, 56], and may contribute to depression [57]. Our results suggest a relationship between axon guidance and PPD.
Strengths and limitations
In this study we started recruiting participants before week 25 of pregnancy, so we could collect detailed information from participants and match cases and controls in terms of age, parity, gestational weeks, and the day of blood collection after birth. The association between PPD and age [58, 59], parity [60, 61], and past mental illness [62, 63] has been reported. However, in this study, there were no significant differences in age and parity between the two groups. We excluded participants with current or previous mental illness and who had an EPDS score≧9 during pregnancy. Therefore, it was possible to exclude the influence of age, parity and history with mental illness to depression. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in the blood collection date of peripheral blood used for methylation analysis, and it was possible to compare the methylation status of cases and controls around 30 days postpartum. Additionally, we placed cases and controls on the same chip but in a random position to mitigate a batch effect and minimize technical bias.
This study has several limitations. First, the sample size was small. In this study, we evaluated depressive symptoms between pregnancy and the postpartum period using the EPDS, and performed blood collection after childbirth. When the number of cases is small, a large number of controls is needed to avoid bias. However, it was difficult for us to obtain a large sample. We attempted to overcome the limitation of sample size by appropriate analysis. However, it is possible that the negative findings in this study could be due to the small sample size. It is difficult to make a conclusion based on the analysis of small objects, so results of this study can only be considered preliminary data. Future studies with larger samples are needed. Second, to clarify the difference in postpartum depression, the conditions during pregnancy cases and controls were matched. That is, we excluded participants with current or previous mental illness and who had EPDS score ≥ 9 during pregnancy. Therefore, our study is subject to selection bias and the results do not reflect a general pregnant population. Depression during pregnancy and medical history are considered to be related to PPD, and it is necessary to consider these subjects in the future. Third, we defined cases and controls based on the results of the EPDS scores in this study. However, EPDS is a screening tool as opposed to diagnostic tool, and cases of PPD cannot be determined from EPDS score alone. It was a limitation of this study that diagnostic interviews could not be conducted for all the subjects. Finally, we used peripheral blood as opposed to brain tissue in this study. However, the methylation status of peripheral blood and brain may be different, and although using peripheral blood as a biomarker has a clinical advantage, it is also a study limitation.
Conclusions
Four GO terms that include sites with differences in methylation intensities between cases and controls were identified. Although epigenetic research in psychiatry is still in its early stages, it may ultimately be useful in the understanding of how temporary or chronic life events, alone or in combination with susceptible genes, may impact neuropsychiatric systems [11]. Although we did not identify any significant genome-wide associations based on DNA methylation sites and PPD, future studies that either confirm or contradict our findings may help with the development of an objective predictive method for PPD.
Additional files
Questionnaire. It shows items of the self-reporting questionnaire we used in this study. (PDF 83 kb)
Table S1 Result of DAVID 6.8 analysis of the 711 genes associated with the 1000 sites. It shows a result of DAVID 6.8 analysis of the 711 genes associated with the 1000 sites with the lowest p values of association analysis. (XLSX 99 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff of Nagoya University Hospital, Nagoya Teishin Hospital, Kaseki Hospital, and Royal Bell Clinic for their cooperation. We also thank Kazuya Iwamoto, Tadafumi Kato, and Junko Ueda for technical assistance regarding data analysis, supported by KAKENHI 18H05428.
Abbreviations
- BP
Biological process
- CC
Cellular component
- DAVID
Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery
- EPDS
Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
- FDR
False discovery rate
- GO
Gene ontology
- MF
molecular function
- PPD
Postpartum depression
Authors’ contributions
YN, SK, BA, and NO conceived and designed this study. TO, TS, MN, MO, AY, and CK performed the study. YN, MN, BA, MT, TS, MM, AY, AY, YF-H, TN, MO, CK, KY, and MA contributed reagents, materials, and analysis tools. YN, MN, BA, MT, MA, and NO conducted the statistical analysis. YN, MN, SK, BA, and NO wrote the paper. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by research grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan; the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan; the Academic Frontier Project for Private Universities, Comparative Cognitive Science Institutes, Meijo University; the Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology; Intramural Research Grant (21B-2) for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders from the National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry and the Specific Research Fund 2012 for East Japan Great Earthquake Revival by The New Technology Development Foundation; the Research and Development Grants for Comprehensive Research for Persons with Disabilities from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED under Grant Number JP18dk0307077 and JP18dk0307060; JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP26461717 and JP15K19242; and GSK Japan Research Grant. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All the data supporting our findings are contained within the manuscript. Therefore, data sets are not shown.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was explained to all participants both verbally and in writing, and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. The Ethics Committee of the Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine approved the study protocol. All experiments were performed in accordance with the Committee’s guidelines and regulations. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Yukako Nakamura, Email: y-nakamu@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Masahiro Nakatochi, Email: mnakatochi@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Shohko Kunimoto, Email: kunimot@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Takashi Okada, Phone: +81-52-744-2282, Email: okada@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Branko Aleksic, Email: branko@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Miho Toyama, Email: toyama.miho@g.mbox.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Tomoko Shiino, Email: t-shiino@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Mako Morikawa, Email: mmorikawa@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Aya Yamauchi, Email: a-yamauchi@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Akira Yoshimi, Email: akira-yoshimi@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Yoko Furukawa-Hibi, Email: yokoh@med.nagoya-cu.ac.jp.
Taku Nagai, Email: t-nagai@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Masako Ohara, Email: mskohara@tl-wam.or.jp.
Chika Kubota, Email: chikarinko2001@yahoo.co.jp.
Kiyofumi Yamada, Email: kyamada@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
Masahiko Ando, Email: mando.tsuru@gmail.com.
Norio Ozaki, Email: ozaki-n@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp.
References
- 1.O'Hara MW, Swain AM. Rates and risk of postpartum depression--a meta-analysis. Int Rev Psychiatr. 1996;8(1):37. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ishikawa N, Goto S, Murase S, Kanai A, Masuda T, Aleksic B, et al. Prospective study of maternal depressive symptomatology among Japanese women. J Psychosom Res. 2011;71(4):264–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2011.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takeda S, Takeda J, Murakami K, Kubo T, Hamada H, Murakami M, et al. Annual report of the perinatology committee, Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2015: proposal of urgent measures to reduce maternal deaths. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2017;43(1):5–7. doi: 10.1111/jog.13184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.O'Hara MW. Postpartum depression: what we know. J Clin Psychol. 2009;65(12):1258–1269. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sharma V, Khan M, Corpse C, Sharma P. Missed bipolarity and psychiatric comorbidity in women with postpartum depression. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(6):742–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2008.00606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ukatu N, Clare CA, Brulja M. Postpartum depression screening tools: a review. Psychosomatics. 2018;59(3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/j.psym.2017.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gibson J, McKenzie-McHarg K, Shakespeare J, Price J, Gray R. A systematic review of studies validating the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale in antepartum and postpartum women. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2009;119(5):350–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2009.01363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kinoshita S, Kanazawa T, Kikuyama H, Yoneda H. Clinical application of DEX/CRH test and multi-channel NIRS in patients with depression. Behav Brain Funct. 2016;12(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12993-016-0108-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saavedra Kathleen, Molina-Márquez Ana, Saavedra Nicolás, Zambrano Tomás, Salazar Luis. Epigenetic Modifications of Major Depressive Disorder. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016;17(8):1279. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Urdinguio RG, Sanchez-Mut JV, Esteller M. Epigenetic mechanisms in neurological diseases: genes, syndromes, and therapies. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(11):1056–1072. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kular L, Kular S. Epigenetics applied to psychiatry: clinical opportunities and future challenges. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018;72(4):195–211. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guintivano J, Arad M, Gould TD, Payne JL, Kaminsky ZA. Antenatal prediction of postpartum depression with blood DNA methylation biomarkers. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19(5):560–567. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Osborne L, Clive M, Kimmel M, Gispen F, Guintivano J, Brown T, et al. Replication of epigenetic postpartum depression biomarkers and variation with hormone levels. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016;41(6):1648–1658. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kimmel M, Clive M, Gispen F, Guintivano J, Brown T, Cox O, et al. Oxytocin receptor DNA methylation in postpartum depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016;69:150–160. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.King L, Robins S, Chen G, Yerko V, Zhou Y, Nagy C, et al. Perinatal depression and DNA methylation of oxytocin-related genes: a study of mothers and their children. Horm Behav. 2017;96:84–94. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2017.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kader F, Ghai M. DNA methylation-based variation between human populations. Mol Gen Genomics. 2017;292(1):5–35. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Aberg KA, McClay JL, Nerella S, Clark S, Kumar G, Chen W, et al. Methylome-wide association study of schizophrenia: identifying blood biomarker signatures of environmental insults. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014;71(3):255–264. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.3730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Davies MN, Volta M, Pidsley R, Lunnon K, Dixit A, Lovestone S, et al. Functional annotation of the human brain methylome identifies tissue-specific epigenetic variation across brain and blood. Genome Biol. 2012;13(6):R43. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-6-r43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Masliah E, Dumaop W, Galasko D, Desplats P. Distinctive patterns of DNA methylation associated with Parkinson disease: identification of concordant epigenetic changes in brain and peripheral blood leukocytes. Epigenetics. 2013;8(10):1030–1038. doi: 10.4161/epi.25865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sullivan PF, Fan C, Perou CM. Evaluating the comparability of gene expression in blood and brain. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2006;141B(3):261–268. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cox JL, Holden JM, Sagovsky R. Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the 10-item Edinburgh postnatal depression scale. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:782–786. doi: 10.1192/bjp.150.6.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Okano T, Murata M, Masuji F, Tamaki R, Nomura J, Miyaoka H, et al. Validation and reliability of Japanese version of the EPDS (in Japanese) Arch Psychiatr Diag Clin Eval. 1996;7(4):523–533. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Matthey S, Henshaw C, Elliott S, Barnett B. Variability in use of cut-off scores and formats on the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale: implications for clinical and research practice. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2006;9(6):309–315. doi: 10.1007/s00737-006-0152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lee DT, Yip SK, Chiu HF, Leung TY, Chan KP, Chau IO, et al. Detecting postnatal depression in Chinese women. Validation of the Chinese version of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale. Br J Psychiatry. 1998;172:433–437. doi: 10.1192/bjp.172.5.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jadresic E, Araya R, Jara C. Validation of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale (EPDS) in Chilean postpartum women. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 1995;16(4):187–191. doi: 10.3109/01674829509024468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vazquez MB, Miguez MC. Validation of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale as a screening tool for depression in Spanish pregnant women. J Affect Disord. 2019;246:515–521. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.12.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tesfaye M, Hanlon C, Wondimagegn D, Alem A. Detecting postnatal common mental disorders in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: validation of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale and Kessler scales. J Affect Disord. 2010;122(1–2):102–108. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tran TD, Tran T, La B, Lee D, Rosenthal D, Fisher J. Screening for perinatal common mental disorders in women in the north of Vietnam: a comparison of three psychometric instruments. J Affect Disord. 2011;133(1–2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.03.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kozinszky Z, Dudas RB. Validation studies of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale for the antenatal period. J Affect Disord. 2015;176:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.01.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Usuda K, Nishi D, Okazaki E, Makino M, Sano Y. Optimal cut-off score of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale for major depressive episode during pregnancy in Japan. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017;71(12):836–842. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Howard LM, Molyneaux E, Dennis CL, Rochat T, Stein A, Milgrom J. Non-psychotic mental disorders in the perinatal period. Lancet. 2014;384(9956):1775–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61276-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Earls MF, Yogman MW, Mattson G, Rafferty J, Committee On Psychosocial Aspects Of C, Family H. Incorporating Recognition and Management of Perinatal Depression Into Pediatric Practice. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1):e20183259. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.Henshaw C. Mood disturbance in the early puerperium: a review. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2003;6(Suppl 2):S33–S42. doi: 10.1007/s00737-003-0004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.O'Hara MW, McCabe JE. Postpartum depression: current status and future directions. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2013;9:379–407. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nakatochi M, Ichihara S, Yamamoto K, Ohnaka K, Kato Y, Yokota S, et al. Epigenome-wide association study suggests that SNPs in the promoter region of RETN influence plasma resistin level via effects on DNA methylation at neighbouring sites. Diabetologia. 2015;58(12):2781–2790. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3763-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Maksimovic J, Gordon L, Oshlack A. SWAN: subset-quantile within array normalization for illumina infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChips. Genome Biol. 2012;13(6):R44. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-6-r44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Aryee MJ, Jaffe AE, Corrada-Bravo H, Ladd-Acosta C, Feinberg AP, Hansen KD, et al. Minfi: a flexible and comprehensive Bioconductor package for the analysis of Infinium DNA methylation microarrays. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(10):1363–1369. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Du P, Zhang X, Huang CC, Jafari N, Kibbe WA, Hou L, et al. Comparison of Beta-value and M-value methods for quantifying methylation levels by microarray analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:587. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE, Storey JD. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(6):882–883. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 2007;8(1):118–127. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxj037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jaffe AE, Irizarry RA. Accounting for cellular heterogeneity is critical in epigenome-wide association studies. Genome Biol. 2014;15(2):R31. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chen YA, Lemire M, Choufani S, Butcher DT, Grafodatskaya D, Zanke BW, et al. Discovery of cross-reactive probes and polymorphic CpGs in the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 microarray. Epigenetics. 2013;8(2):203–209. doi: 10.4161/epi.23470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Price ME, Cotton AM, Lam LL, Farre P, Emberly E, Brown CJ, et al. Additional annotation enhances potential for biologically-relevant analysis of the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip array. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2013;6(1):4. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-6-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Gene Ontology Consortium Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zheng Q, Wang XJ. GOEAST: a web-based software toolkit for gene ontology enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W358–W363. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Huang d W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Huang d W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Liu Y, Nakamura S. Stress-induced plasticity of monoamine axons. Front Biosci. 2006;11:1794–1801. doi: 10.2741/1923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bocchio-Chiavetto L, Maffioletti E, Bettinsoli P, Giovannini C, Bignotti S, Tardito D, et al. Blood microRNA changes in depressed patients during antidepressant treatment. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013;23(7):602–611. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Breen Michael S., Wingo Aliza P., Koen Nastassja, Donald Kirsten A., Nicol Mark, Zar Heather J., Ressler Kerry J., Buxbaum Joseph D., Stein Dan J. Gene expression in cord blood links genetic risk for neurodevelopmental disorders with maternal psychological distress and adverse childhood outcomes. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2018;73:320–330. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Story Jovanova O, Nedeljkovic I, Spieler D, Walker RM, Liu C, Luciano M, et al. DNA methylation signatures of depressive symptoms in middle-aged and elderly persons: meta-analysis of multiethnic epigenome-wide studies. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75(9):949–959. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Miyakawa T, Yagi T, Takao K, Niki H. Differential effect of Fyn tyrosine kinase deletion on offensive and defensive aggression. Behav Brain Res. 2001;122(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(01)00171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kim SE, Kim HN, Yun YJ, Heo SG, Cho J, Kwon MJ, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide SNP- and pathway-based associations for facets of neuroticism. J Hum Genet. 2017;62(10):903–909. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2017.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Brown TA, Rosellini AJ. The direct and interactive effects of neuroticism and life stress on the severity and longitudinal course of depressive symptoms. J Abnorm Psychol. 2011;120(4):844–856. doi: 10.1037/a0023035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Christoffel DJ, Golden SA, Russo SJ. Structural and synaptic plasticity in stress-related disorders. Rev Neurosci. 2011;22(5):535–549. doi: 10.1515/RNS.2011.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wager-Smith K, Markou A. Depression: a repair response to stress-induced neuronal microdamage that can grade into a chronic neuroinflammatory condition? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011;35(3):742–764. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Csabai D, Wiborg O, Czeh B. Reduced synapse and axon numbers in the prefrontal cortex of rats subjected to a chronic stress model for depression. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:24. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zaidi F, Nigam A, Anjum R, Agarwalla R. Postpartum depression in women: a risk factor analysis. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(8):QC13–QQC6. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/25480.10479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bottino MN, Nadanovsky P, Moraes CL, Reichenheim ME, Lobato G. Reappraising the relationship between maternal age and postpartum depression according to the evolutionary theory: empirical evidence from a survey in primary health services. J Affect Disord. 2012;142(1–3):219–224. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2012.04.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Takehara K, Tachibana Y, Yoshida K, Mori R, Kakee N, Kubo T. Prevalence trends of pre- and postnatal depression in Japanese women: a population-based longitudinal study. J Affect Disord. 2018;225:389–394. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Iwata H, Mori E, Sakajo A, Aoki K, Maehara K, Tamakoshi K. Prevalence of postpartum depressive symptoms during the first 6 months postpartum: association with maternal age and parity. J Affect Disord. 2016;203:227–232. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Robertson E, Grace S, Wallington T, Stewart DE. Antenatal risk factors for postpartum depression: a synthesis of recent literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2004;26(4):289–295. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2004.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Norhayati MN, Hazlina NH, Asrenee AR, Emilin WM. Magnitude and risk factors for postpartum symptoms: a literature review. J Affect Disord. 2015;175:34–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.12.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Questionnaire. It shows items of the self-reporting questionnaire we used in this study. (PDF 83 kb)
Table S1 Result of DAVID 6.8 analysis of the 711 genes associated with the 1000 sites. It shows a result of DAVID 6.8 analysis of the 711 genes associated with the 1000 sites with the lowest p values of association analysis. (XLSX 99 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
All the data supporting our findings are contained within the manuscript. Therefore, data sets are not shown.