ABSTRACT
Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome (APS) type 1 is a rare autoimmune disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern due to loss of function of the AIRE gene and defective removal of self-reactive T-lymphocytes during the process of thymic T cell maturation. Its manifestation starts early in life with the cardinal clinical disorders being one of muco-cutaneous candidiasis, Addison’s disease, and hypoparathyroidism. Recognizing the syndromic nature of one autoimmune disease will facilitate an active search for other conditions which would allow early detection, management, follow-up, and most importantly patient education and counselling to avoid potential complications. We present the case of a young immigrant with multiple endocrinopathies and mucocutaneous candidiasis who presented with features of adrenal insufficiency. Our aim was to briefly review APS type 1 as a disease entity and to highlight the importance of patient education in its management.
KEYWORDS: APS type 1, muco-cutaneous candidiasis, Addison’s disease, hypoparathyroidism
1. Introduction
Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome (APS) type 1, also known as autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy/dysplasia (APECED) [1] or Whitaker syndrome [2], is defined as the presence of two or more of the following: Addison’s disease, chronic muco-cutaneous candidiasis, and hypoparathyroidism [3]. It occurs in childhood with 1:1 male to female ratio, inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, and has an incidence of about 3/1,000,000 people. Although treatment is identical whether it occurs in isolation or as part of an APS, clinicians must be alert to syndromic associations of autoimmune diseases to prevent delayed diagnosis.
2. Case report
A 29-year-old man with past medical history of Addison’s disease and hypothyroidism who recently relocated to the USA from Puerto Rico presented to the emergency department (ED) with chief complaints of fatigue, palpitations, and light headedness.
He was previously maintained on twice daily hydrocortisone and daily levothyroxine supplementation but had been off his medications for 5 days. He denied chest pain or shortness of breath. He also denied tremors, easy fatigability, weight gain, hoarseness of voice, or changes in bowel habit. Of note, he reported a childhood history of recurrent seizures due to hypocalcemia and had since been on calcium and vitamin D supplementation. He had no family history of autoimmune disease and review of systems was otherwise unremarkable. His knowledge about his medical condition was limited.
On physical examination, he was in no acute distress. He was hypotensive with BP 89/67 and tachycardic with pulse rate of 115 bpm. Other vital signs were normal. Chvostek sign was negative and there was no thyromegaly on neck palpation. Oral examination showed multiple hyperpigmented lesions on the dorsum of his tongue (Figure 1) and multiple deformed and pitting finger nails in both hands (Figure 2). The remainder of the physical examination was unremarkable.
Figure 1.
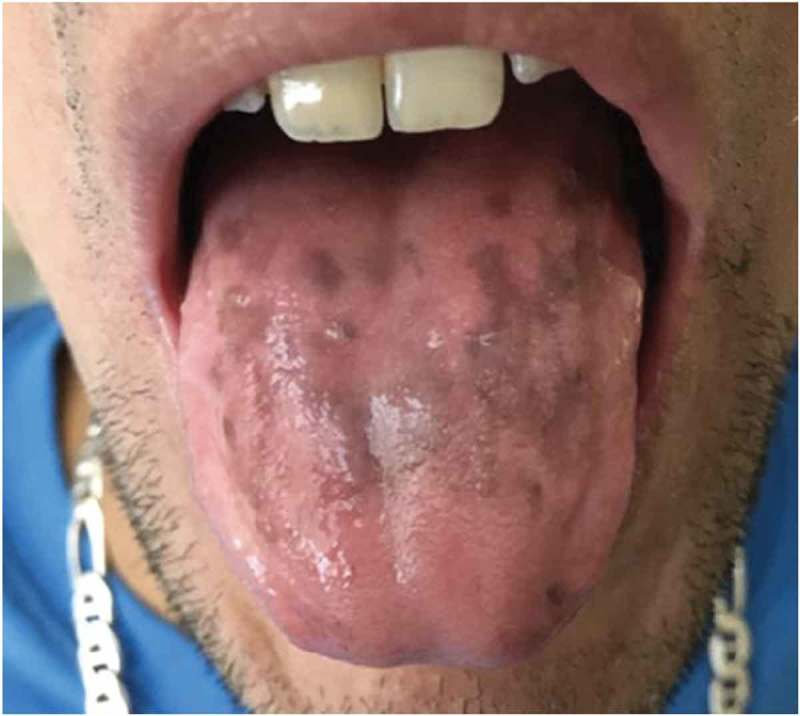
Showing oral candidiasis.
Figure 2.
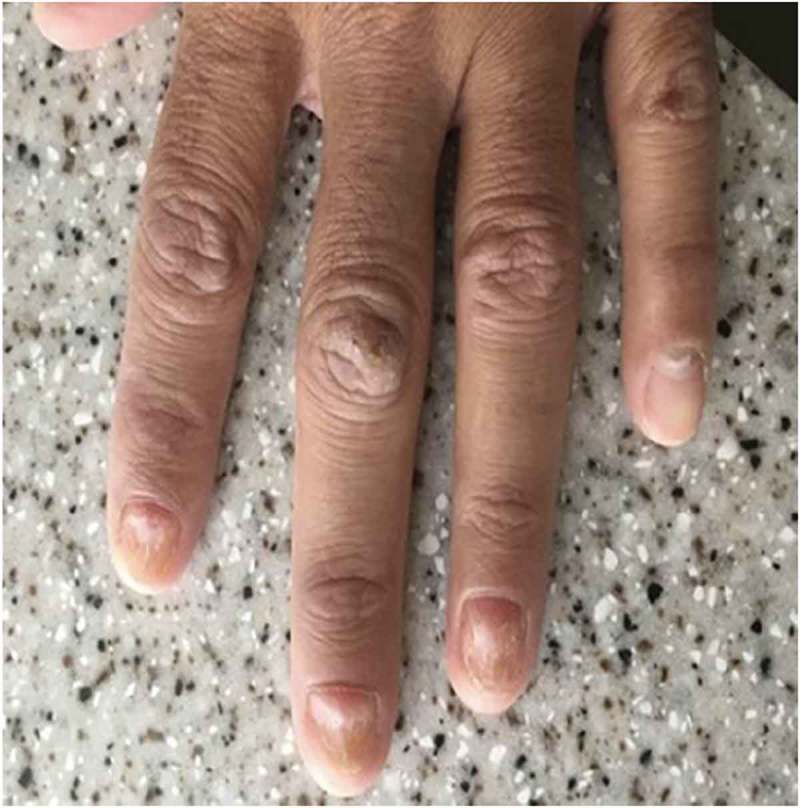
The finger nail changes.
Basic metabolic panel revealed hyponatremia with Na 129 meq/L (136–145) and potassium of 4.8 meq/L (3.5–5.1). He was also severely hypocalcemia with ionized calcium of 0.96 mmol/L (1.15–1.33). Fasting blood glucose was normal. Thyroid function test showed elevated thyrotropin level at 5.807 uIU/mL (0.450–5.330) with normal free thyroxine level at 0.94 ng/dL (0.58–1.64). AM cortisol was markedly reduced at <1 mcg/dL (6.7–22.6). ACTH was markedly elevated at 785 pg/mL (7–69) and direct renin was also very elevated at 390 pg/mL (2.5–45.7). Parathyroid hormone was markedly reduced at <6 pg/mL (12–88). Complete blood count was normal, as was coagulation profile.
ECG also showed sinus tachycardia with no ischemic changes.
The patient was given intravenous saline and double his normal dose of his steroids. His levothyroxine dose was continued at 75 mcg daily while intravenous and oral calcium were given to correct hypocalcemia. His symptoms gradually improved, and he was discharged home on hydrocortisone 20 mg in the morning and 10 mg at night with fludrocortisone 0.1 mg daily and levothyroxine 75 mcg daily.
On follow-up in clinic 2 weeks later, patient was noted to be doing well. Patient education regarding medication adherence and stress dosing to avoid potentially life-threatening adrenal crisis and the importance of medic alert bracelets was reinforced. The patient was classified as having APS type 1 because of the presence of hypoparathyroidism, Addison’s disease, and chronic muco-cutaneous candidiasis, and promptly referred to the endocrinologist for continuity of care (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
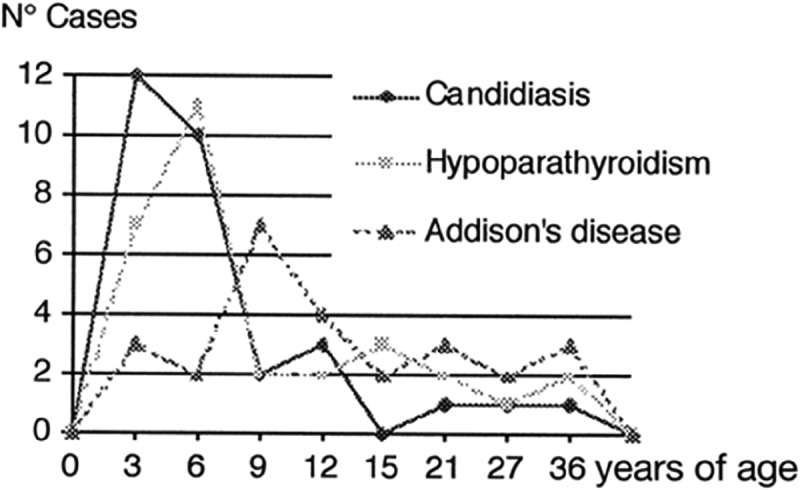
Timing of major clinical features in APS type 1.
3. Discussion
APS type 1 occurs due to loss of function of the autoimmune regulator gene – AIRE (AI – autoimmune, RE – regulator) gene, located on chromosome 21 particularly expressed in the thymus gland which plays an important role in immune regulation by distinguishing self from non-self. The result is the formation of auto-antibodies directed against specific tissue [4–6].
APS type 1 is almost always inherited as autosomal recessive with both set of AIRE genes affected, although cases of autosomal dominant mutation in AIRE have been described [5] and the disease spectrum is much more narrow than in the recessive type [6].
Other less frequent autoimmune diseases occurring in association with this condition include type 1 diabetes mellitus, vitiligo, pernicious anemia, primary hypothyroidism, hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (primary hypogonadism), pituitary failure, autoimmune hepatitis, alopecia, interstitial nephritis, malabsorption syndrome, splenic aplasia or hypoplasia, and pure red cell aplasia [5,7].
Onset typically begins in childhood with multiple autoimmune disorders manifesting throughout patient’s lifetime [8]. In most cases, the first symptom is a chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis even before the development of endocrine disorders and usually affects the oral cavity, esophagus, and the skin. It is the most common manifestation of APS type 1 and is seen in almost 100% of cases [5].
The cause of muco-cutaneous candidiasis in these patients, a hallmark of the disease, was initially unknown and not attributed to autoimmune dysfunction [4]. More recent studies found that the disruption of the T helper-17 cell (Th-17)-based adaptive immunity to fungal infection is responsible for the chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC) [9]. Patients with APS type1 produce autoantibodies against specific Th-17 cells cytokines mainly IL17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 thus disrupting the innate anti-fungal immunity [9,10].
Hypoparathyroidism is usually the first endocrine disorder to manifest during the course of the disease and has been reported in about 70–93% of cases. Addison’s disease has a prevalence of about 60–100% [5]. Timing of the major clinical features is illustrated in the table below. Other clinical presentation may include fatigue due to pernicious anemia, enamel hypoplasia, dystrophic nails, diarrhea, and cholelithiasis from malabsorption syndrome, and abnormal liver enzymes in autoimmune hepatitis [11]. Apart from the more common cutaneous associations, a rare case of acquired generalized lipodystrophy has been associated with APS type1 [12].
Diagnosis of APS type 1 is largely based on the measurement of serum endocrine and organ-specific autoantibody in patients presenting with clinical history suggestive of one or more endocrine disorder and (or) chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. A definitive diagnosis can be made through DNA analysis for AIRE gene mutation [13], and this may be of benefit in patients who do not meet the diagnostic criteria of APS type 1 at initial presentation [14]. The finding of one organ-specific autoimmune disorder should prompt further evaluation for other associations.
The mainstay of treatment remains hormone replacement and systemic antifungal therapy. Correction of deficient electrolytes such as calcium and sodium may be required. Immunosuppressive therapy has been used with variable success rates. Routine monitoring and investigation of patient for upper gastrointestinal symptoms as risk of oral/esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) increases.
4. Conclusion
In summary, this case highlights the need for high index of suspicion for APS and judicious search for other autoimmune conditions whenever one organ-specific autoimmune disorder is diagnosed. Long-term monitoring of patients with autoimmune disorders is important because the time interval before the appearance of other endocrine disorders cannot be predicted. Given how common chronic muco-cutaneous candidiasis is as well as its early manifestation, routine evaluation is advised to detect any oral or esophageal SCC. Also, the importance of patient education cannot be over-emphasized.
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
References
- [1].Ahonen P, Myllärniemi S, Sipilä I, et al. Clinical variation of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy–candidiasis–ectodermal Dystrophy (APECED) in a series of 68 patients. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1829–1836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Whitaker J, Landing BH, Esselborn VM, et al. The syndrome of familial juvenile hypoadrenocorticism, hypoparathyroidism and superficial moniliasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956;16:1374–1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Betterle C, Greggio NA, Volpato M.. Clinical review 93: autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:1049–1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Kämpe O.Introduction: autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1): a rare monogenic disorder as a model to improve understanding of tolerance and autoimmunity: symposium. J Intern Med. 2009;265:511–513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Weiler FG, Dias-da-Silva MR, Lazaretti-Castro M. Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1: case report and review of literature. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2012;56:54–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Anderson MS, Su MA. AIRE expands: new roles in immune tolerance and beyond. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:247–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Ponranjini V, Bakyalakshmi K, Jayachandran S, et al. Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2012;2:62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Michels AW, Gottlieb PA. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010;6:270–277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Koo S, Kejariwal D, Al-Shehri T, et al. Oesophageal candidiasis and squamous cell cancer in patients with gain-of-function STAT1 gene mutation. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2017;5:625–631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Hernández-Santos N, Gaffen SL. Th17 cells in immunity to Candida albicans. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;11:425–435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Białkowska J, Zygmunt A, Lewiński A, et al. Hepatitis and the polyglandular autoimmune syndrome, type 1. Arch Med Sci. 2011;7:536–539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Sorkina E, Frolova E, Rusinova D, et al. Progressive generalized lipodystrophy as a manifestation of autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:1344–1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Kahaly GJ. Genetics of polyglandular failure. Genet Diagnosis Endocr Disord. 2016;361–373. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800892-8.00025-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Guttmann-Bauman I, Shi J-D, Wang C-Y, et al. Detection of AIRE mutation in atypical Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome Type 1 (APS1). Int J Disabil Hum Dev. 2001;2:115. [Google Scholar]


