Highlights
-
•
Self-collected nasal swabs are sensitive for detecting respiratory virus infections.
-
•
Self-collected throat swabs add little to respiratory virus infection diagnosis.
-
•
Nasal swabs detect higher respiratory virus concentration than throat swabs.
Keywords: Nasal swabs, Throat swabs, Self-collection, Respiratory virus, Respiratory viral infection
Abstract
Background
Early and accurate detection of respiratory viruses (RV) is important for patient management. We have previously shown that self-collected nasal swabs (NS) are feasible and as sensitive as clinician-collected nasal washes for detection of RV, but the additive benefit of self-collected throat swabs is unknown.
Objectives
To evaluate the added yield of self-collected nasal to throat swabs for detection of RV by PCR in patients with upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) symptoms.
Study design
Patients with URTI symptoms self-collected paired polyurethane foam NS and nylon flocked throat swabs and completed a symptom survey. Swabs were tested for 12 RV by real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. Descriptive, McNemar's, and Wilcoxon signed rank statistical tests were used.
Results
115 paired nasal and throat swabs were collected from 63 individuals, with 71/115 (62%) positive for a RV by at least one specimen, including 51 positive by both, 17 positive by NS only, and 3 positive by throat swab only. The sensitivity of NS was 96% (95%CI: 88-99) versus 76% (95% CI: 65-85) in throat swabs, p<0.001. The median PCR cycle threshold (Ct) in 51 concordant samples was lower (indicating higher viral concentration) in NS (25.1) versus throat swabs (32.0). The three samples positive only by throat swab had high Ct values (33.8, 36.2, and 38.8, all rhinovirus).
Conclusion
Self-collection of NS was significantly more sensitive than self collection of throat swabs for detection of RV by RT-PCR. The addition of throat sampling does not appear to increase the diagnostic load in the self-testing setting.
1. Background
A non-invasive, patient-accepted, and sensitive method for diagnosis of respiratory virus infection (RVI) can have important implications for patient care, epidemiologic studies, and clinical research. Diagnosis of RVI is often limited by the need to get a clinician-collected respiratory sample. However, it may be difficult for ill patients to go to a healthcare facility, and if they do, time to diagnosis may be delayed [1] and they may expose other patients or staff to infection. Identification of sensitive methods for self-collection would address these issues, as well as provide options for community-based assessments of RVI epidemiology and longitudinal monitoring.
Previous studies have demonstrated that self-collected nasal swabs (NS) are feasible, highly accepted by patients, and/or as sensitive as nasal washes collected by clinicians [[2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]]. The role of other self-collected respiratory specimens, either alone or in combination with NS, is unclear. Our prior study comparing self-collected oral gargles to NS in lung transplant recipients with symptomatic RVI demonstrated lower sensitivity of oral gargles [9]. While Ip et al. included both self-collected NS and throat swabs in a community-based influenza study, they did not compare the two specimen types [10]. To our knowledge, the additive benefit of self-collected throat swabs have not been evaluated.
2. Objectives
We hypothesized that throat swabs would not significantly add to the diagnosis of RVI by evaluating self-collected NS and throat swabs in immunocompetent patients with upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) symptoms using reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
3. Study Design
3.1. Patients
Immunocompetent employees or affiliates of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center with three days or less of URTI symptoms were prospectively enrolled between September 2012 and April 2015. Participants were allowed to participate more than once if their symptoms were >4 weeks apart. The Fred Hutchinson Institutional Review Board approved this study.
3.2. Materials and methods
After informed consent, participants were provided with written instructions and materials for the self-collection of NS and throat swabs. Participants collected nasal specimens using a polyurethane foam nasal swab (Puritan Medical Products Co., LLC; no. 25-1805-1PF-SC2 Arrow) after instillation of 0.5 mL of normal saline into one nostril and rotating the swab five seconds in the anterior naris as previously described [8]. Throat swabs were collected by swabbing the back of the throat and each tonsil area 2–3 times using a nylon flocked swab (Copan Diagnostics, no.502CS01) and placed in universal transport media. The swabs were transferred to the laboratory by study personnel per manufacturer recommendations, and we have previously shown both specimen types to be stable for 7 days at room temperature [8]. Participants also filled out a comprehensive symptom survey as previously described [3].
3.3. Respiratory virus detection
Samples were processed in the laboratory as previously described [3]. Twelve RV were tested for using the laboratory-developed real-time RT-PCR assays: Respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza 1–4, influenza A and B, adenovirus, coronavirus, rhinovirus (HRV), metapneumovirus, and bocavirus [[11], [12], [13], [14], [15]]. Samples were considered positive if the PCR cycle threshold (Ct) value was less than 40 based on established cut-offs for laboratory-developed tests.
3.4. Statistical analysis
Identification of a RV from either specimen type was considered a true positive. Descriptive and summary statistics were used for demographics, symptoms, and RV details. McNemar’s (categorical) and Wilcoxon signed rank test (paired Ct values) were used to calculate significance.
4. Results
One-hundred fifteen paired NS and throat swabs were prospectively collected from 63 individuals (68.2% female). The median time between swab collection and processing was 1 day (IQR 0–1). Twenty-one (33.3%) participants provided specimens for more than one episode of URTI symptoms. A total of 86 symptom surveys were completed (74.8% of 115 episodes).
4.1. Symptoms
The median number of symptomatic days at time of specimen collection was 2 days (IQR 1–3). Table 1 shows the number of respondents with different symptoms and the percentage with each symptom who had RV detected versus not detected. The presence of rhinorrhea, nasal/sinus congestion, and sneezing were all significantly associated with RV detection.
Table 1.
Reported symptoms and assosciation with respiratory virus detection.
| Symptom | Total, N(%)a |
RV+, N(%)b | RV-, N(%)b | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory | ||||
| Rhinorrhea | 71 (82.6) | 51 (94.4) | 20 (62.5) | <0.001c |
| Nasal/Sinus congestion |
67 (77.9) | 46 (85.2) | 21 (65.6) | 0.035 |
| Sore Throat | 65 (75.6) | 42 (77.8) | 23 (71.9) | 0.54 |
| Cough | 60 (69.8) | 41 (75.9) | 19 (59.4) | 0.11 |
| Sneezing | 57 (66.3) | 44 (81.5) | 13 (40.6) | <0.001 |
| Sputum | 55 (64.0) | 35 (64.8) | 20 (62.5) | 0.83 |
| Any Systemic | 77 (89.5) | 48 (88.9) | 29 (90.6) | 1.0c |
| Headache | 55 (64.0) | 38 (70.4) | 17 (53.1) | 0.11 |
| Fatigue | 54 (62.8) | 35 (64.8) | 19 (59.4) | 0.61 |
| Myalgias | 38 (44.2) | 26 (48.1) | 12 (37.5) | 0.34 |
| Fever | 30 (34.9) | 19 (35.2) | 11 (34.4) | 0.94 |
| Diarrhea | 8 (9.3) | 3 (5.6) | 5 (15.6) | 0.14c |
p-values calculated using chi-square unless otherwise noted.
RV: Respiratory virus.
% of 86 surveys.
% of total number of participants with RV detected (RV+, n = 54) or no RV detected (RV-, n = 32) with specific symptoms.
Fisher’s exact.
4.2. Respiratory virus detection
Seventy-one (61.7%) of the 115 paired specimens were positive for any RV in one or both specimens. Only one RV was detected in all cases. Table 2 shows the distribution of individual RV and the breakdown of RV detection and sensitivities by specimen type and specific virus. NS were positive in 68 (59.1%) and throat swabs were positive in 44 (38.3%) of the pairs (p < 0.001). Although the numbers of individual RVs were low making statistical analysis difficult, NS had the same (adenovirus) or higher sensitivity (all other RV) compared to throat swabs. There were no significant differences between patients with specific symptoms, such as sore throat or rhinorrhea, and the sensitivity of the specimen type (data not shown).
Table 2.
Sensitivity of nasal swab and throat swab specimens by virus type.
| Respiratory Virus | Number of viruses detected by method |
Sensitivity, % (95% CI)* |
P value* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, N(%) | Both positive | NS+, TS - | TS+, NS- | NS | TS | ||
| Any | 71(100) | 51 | 17 | 3 | 95.8 (88.1-99.1) | 76.1 (64.5-85.4) | 0.002 |
| HRV | 39(54.9) | 29 | 7 | 3 | 92.3 | 82.1 | |
| CoV | 14(19.7) | 10 | 4 | 0 | 100 | 71.4 | |
| Flu | 7(9.9) | 6 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 85.7 | |
| PIV | 4(5.6) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 100 | 50.0 | |
| MPV | 2(2.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 50.0 | |
| BoV | 2(2.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 50.0 | |
| RSV | 2(2.8) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 50.0 | |
| ADV | 1(1.4) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | |
p-values and 95% CI only calculated for all viruses together given small numbers of other individual respiratory viruses. NS: nasal swab; TS: throat swab; CI: confidence interval; HRV: human rhinovirus; CoV: coronavirus; Flu: influenza A or B; MPV: metapneumovirus; BoV: bocavirus; RSV: respiratory syncytial virus; PIV: parainfluenza virus 1–4; ADV: adenovirus.
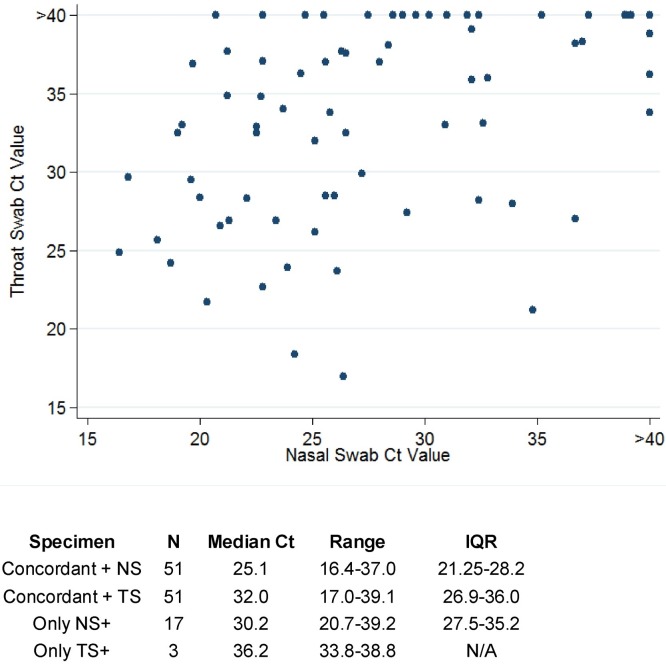
Within the RV positive samples, the median Ct value for NS was 25.9 (IQR 22.5–31.3) versus 32.5 (IQR 26.9–36.2) for throat swabs (p < 0.0001). Seventeen pairs were only positive by NS versus three only positive by throat swabs. In the latter case, the viruses detected were all HRV and had high Ct values (33.8, 36.2, and 38.8) and all had both nasal and throat symptoms. The median Ct values varied based on whether the specimens were concordant: The median Ct for NS was lower (higher viral concentration) within concordant pairs compared to when NS was the only sample positive, and findings were similar for throat swabs (Fig. 1 ). The median Ct in NS versus throat swabs did not differ in patients with sore throats versus patients with rhinorrhea (NS: 26 [IQR 22.8–32.7] and 27 [IQR 23.6–32.2]; throat swabs: 32.8 [IQR 27.8–36] and 33.1 [IQR 27–36.6] for sore throat and rhinorrhea, respectively). There was no correlation between Ct values in NS versus throat swabs (correlation coefficient: 0.214, p = 0.13).
Fig. 1.
Comparison of nasal vs. throat swab cycle threshold values in 71 pairs positive by at least one specimen type.
5. Discussion
In this prospective study of 115 paired self-collected polyurethane foam nasal and nylon flocked throat specimens in patients with respiratory symptoms, we found that throat swabs did not substantially add to the detection of RV by RT-PCR. We also determined that the Ct values in NS were significantly lower, indicating higher viral concentrations. Specific symptoms (nasal congestion, sore throat, etc.) were not associated with increased likelihood of detection by one method versus the other, although nasal symptoms and sneezing were more common in those with RV detected versus not. There were limitations to this study. There were only small numbers of episodes for several specific viruses, making it difficult to generalize results to all viruses. In a study of H5N1, De Jong, et al reported that provider-collected pharyngeal specimens were positive more frequently, and had higher viral loads, than nasal swabs [16]. We only had 7, non-typed, influenza cases, and so could not assess this finding. Second, while prior data shows our self-collected NS are equivalent to provider-collected samples, we have not evaluated this for throat swabs. However, this study focuses on the real-world application of self-collected samples, and our findings provide insight regarding viral load and detection in two separate respiratory sites. Third, we used different swabs for nasal (polyurethane foam) and throat (nylon flocked). The nasal swabs were chosen based on increased comfort and patient acceptability and our prior studies demonstrating comparability to provider-collected nasal washes [8], and flocked throat swabs were the standard at the time; however, different swab types may yield different results.
Overall, we found that collection of throat swabs in addition to NS provided minimal added RVI detection. Our findings, along with the added burden of collecting a second sample and the additional costs associated with testing, support the use of self-collected NS only for outpatient and community-based RV testing.
Funding
This work was supported by the NIH (K23HL143050 to CEF; K24HL093294 and HL081595 to MB).
Competing interests
M.B. received research support from Ansun Biopharma, Ablynx and Gilead Sciences (unrelated to this research) and is a consultant for Ansun Biopharma, Ablynx, Gilead Sciences, Vir Bio, Moderna, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was given by the Institutional Review Board of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center (FH1587 IR#5149).
Author contribution
All authors made significant contributions to the conception, design, execution, interpretation, and/or writing of the study. CEF: Formal analysis, methodology, writing-original draft, writing-review & editing, visualization. JK: Conceptualization, methodology, writing-review & editing, supervision. MB, KRJ, JE: Conceptualization, methodology, writing-review & editing.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the participants of this study. We would like to acknowledge Elsa Garnace, Cheryl Callais, Victor Chow, Noelle Gichohi, and Gynevill Jolly for study coordination and assistance, and Terry Stevens-Ayers, Tera Matson, Sam Chatterton-Kirchmeier, Abe Guerrero, Nancy Wright, Reggie Sampoleo, Rohit Shankar, and Anne Cent for laboratory expertise
References
- 1.Emerson J., Cochrane E., McNamara S., Kuypers J., Gibson R.L., Campbell A.P. Home self-collection of nasal swabs for diagnosis of acute respiratory virus infections in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2013;2(4):345–351. doi: 10.1093/jpids/pit039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dhiman N., Miller R.M., Finley J.L. Effectiveness of patient-collected swabs for influenza testing. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012;87(6):548–554. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Preiksaitis C.M., Kuypers J.M., Fisher C.E. A patient self-collection method for longitudinal monitoring of respiratory virus infection in solid organ transplant recipients. J. Clin. Virol. 2015;62:98–102. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2014.10.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Akmatov M.K., Gatzemeier A., Schughart K., Pessler F. Equivalence of self- and staff-collected nasal swabs for the detection of viral respiratory pathogens. PLoS One. 2012;7(11) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lambert S.B., Whiley D.M., O’Neill N.T. Comparing nose-throat swabs and nasopharyngeal aspirates collected from children with symptoms for respiratory virus identification using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Pediatrics. 2008;122(3):e615–620. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-0691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Akmatov M.K., Krebs S., Preusse M. E-mail-based symptomatic surveillance combined with self-collection of nasal swabs: a new tool for acute respiratory infection epidemiology. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011;15(11):e799–803. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2011.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Larios O.E., Coleman B.L., Drews S.J. Self-collected mid-turbinate swabs for the detection of respiratory viruses in adults with acute respiratory illnesses. PLoS One. 2011;6(6) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Campbell A.P., Kuypers J., Englund J.A., Guthrie K.A., Corey L., Boeckh M. Self-collection of foam nasal swabs for respiratory virus detection by PCR among immunocompetent subjects and hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013;51(1):324–327. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02871-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fisher C.E., Bornstein R., Kuypers J., Jerome K.R., Boeckh M., Limaye A.P. Comparison of self-collected nasal swabs with oral washes for sequential viral load monitoring in lung transplant recipients with respiratory virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2017;91:49–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ip D.K., Schutten M., Fang V.J. Validation of self-swab for virologic confirmation of influenza virus infections in a community setting. J. Infect. Dis. 2012;205(4):631–634. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kuypers J., Wright N., Morrow R. Evaluation of quantitative and type-specific real-time RT-PCR assays for detection of respiratory syncytial virus in respiratory specimens from children. J. Clin. Virol. 2004;31(2):123–129. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kuypers J., Wright N., Corey L., Morrow R. Detection and quantification of human metapneumovirus in pediatric specimens by real-time RT-PCR. J. Clin. Virol. 2005;33(4):299–305. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.11.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kuypers J., Wright N., Ferrenberg J. Comparison of real-time PCR assays with fluorescent-antibody assays for diagnosis of respiratory virus infections in children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006;44(7):2382–2388. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00216-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kuypers J., Martin E.T., Heugel J., Wright N., Morrow R., Englund J.A. Clinical disease in children associated with newly described coronavirus subtypes. Pediatrics. 2007;119(1):e70–76. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-1406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lu X., Holloway B., Dare R.K. Real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay for comprehensive detection of human rhinoviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008;46(2):533–539. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01739-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.de Jong M.D., Simmons C.P., Thanh T.T. Fatal outcome of human influenza A (H5N1) is associated with high viral load and hypercytokinemia. Nat. Med. 2006;12(10):1203–1207. doi: 10.1038/nm1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]