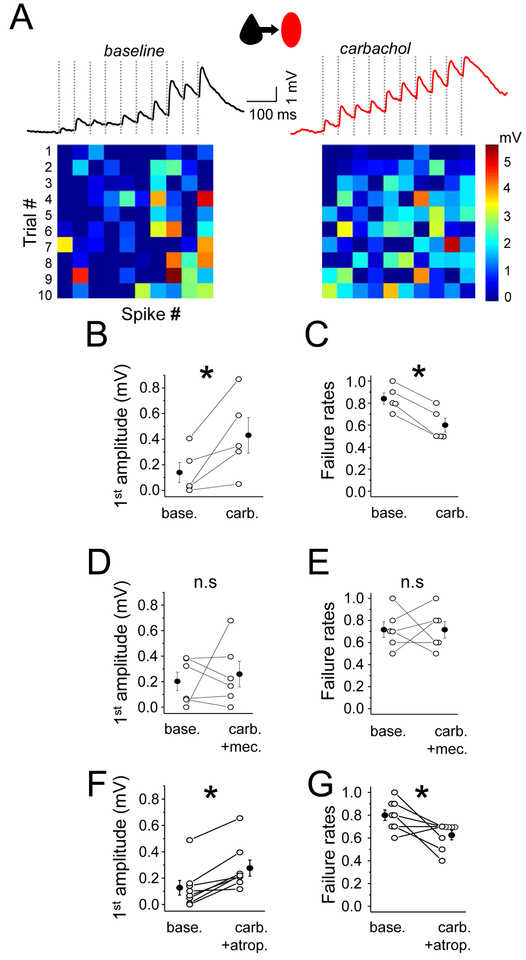
Figure 3. Nicotinic receptors enhance EPSP efficacy onto Pyr-SST connections.
(A) The averaged trace of 10 response trials for a Pyr to SST connection under baseline conditions (left) and in carbachol. Ten presynaptic spikes (dashed vertical lines) at 20 Hz were delivered. Heatmaps at bottom show response amplitude as in Figure 1. (B) Mean EPSP amplitude in response to the first spike in the train, for baseline and in carbachol conditions. (C) Mean failure rate after the first spike, for both conditions. (D) and (E) The same as in (B) and (C) but with selective nicotinic receptor activation (carbachol and atropine, a muscarinic receptor antagonist). (F) and (G) The same as in (B) and (C) but with selective muscarinic receptor activation (carbachol and mecamylamine, a nicotinic receptor antagonist). For all, open circles represent individual cell measurements and filled circles represent all-cell mean± SEM, respectively (B-G).