Abstract
Background:
Emerging evidence suggests a potential association between ambient air pollution and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), but results have been inconsistent. Accordingly, we assessed the associations between ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels with risk of GDM.
Methods:
Using linked data from birth certificates, hospital discharge diagnoses, and air pollution estimates informed by the New York City Community Air Survey, we fit conditional logistic regression models to evaluate the association between residential levels of PM2.5 and NO2 with risk of GDM among 256,372 singleton live births of non-smoking mothers in New York City born 2008 – 2010, adjusting for sociodemographic factors and stratified on zip code of maternal address.
Results:
GDM was identified in 17,065 women, yielding a risk of GDM in the study sample of 67 per 1,000 deliveries. In single pollutant models, 1st and 2nd trimester PM2.5 was associated with a lower and higher risk of GDM, respectively. In models mutually adjusting for PM2.5 levels in both trimesters, GDM was associated with PM2.5 levels in the 2nd trimester (OR: 1.06, 95% CI: 1.02, 1.10 per interquartile range increase in PM2.5), but not the 1st trimester (OR: 0.99, 95% CI: 0.96, 1.02). Conversely, GDM was associated with NO2 during the 1st trimester (OR: 1.05, 95% CI: 1.01, 1.09), but not the 2nd trimester (OR: 1.02, 95% CI: 0.98, 1.06). The positive associations between pollutants and GDM were robust to different model specifications. PM2.5 in the 2nd trimester was more strongly associated with GDM among mothers who were aged < 35 years and not Medicaid recipients. NO2 in the 1st trimester was more strongly associated with GDM among overweight and parous women.
Conclusions:
In this large cohort of singleton births in New York City, NO2 in the 1st trimester and PM2.5 in the 2nd trimester were associated with higher odds of GDM, while 1st trimester PM2.5 was weakly and inconsistently associated with lower odds of GDM.
Keywords: Air pollution, Fine particulate matter, Nitrogen dioxide, Gestational diabetes
1. Introduction
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as diabetes that develops in women for the first time during pregnancy (ACOG, 2018). The prevalence of GDM in the US population is approximately 6–7% (or 240,000 of 4 million US births), but varies from 1 to 25% depending on race, ethnicity, and other patient demographics (Moyer, 2014). The prevalence of GDM has increased substantially between the late 1980s and early 2000s, reflecting or contributing to the current patterns of increasing diabetes and obesity (Ferrara, 2007)
GDM is associated with higher risk of adverse health outcomes in both the mother and child. Specifically, GDM is associated with higher risk of perinatal complications such as preeclampsia, macrosomia, organomegaly (abnormal enlargement of fetal organs), dystocia (obstructed labor with prolonged head-to-body delivery time), Cesarean delivery, and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (Fung et al., 2014; Naylor et al., 1996; Wendland et al., 2012); higher risk of the mother subsequently developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Mirghani Dirar and Doupis, 2017); and higher risk of the child developing obesity, autism, and metabolic syndrome later in life (Hammoud et al., 2018; Xiang et al., 2015). Although treatment may be effective in partially mitigating some of these adverse effects, prevention of GDM through the modification of risk factors remains the central strategy for avoiding the potential short- and long-term adverse health effects associated with GDM (O’Reilly, 2014).
Some environmental exposures have been associated with impaired glucose homeostasis and/or higher risk of GDM, including endocrine disrupting chemicals and heavy metals (Ehrlich et al., 2016; Rahman et al., 2016). Epidemiological studies suggest that ambient air pollution may be associated with impaired glucose tolerance (Fleisch et al., 2014; Lu et al., 2017) or higher risk of GDM (Malmqvist et al., 2013; Robledo et al., 2015). Although the pathophysiologic mechanisms by which ambient air pollution might increase the risk of GDM remain unknown, there is some evidence that air pollution-induced changes in endothelial function, oxidative stress, and inflammation could lead to insulin resistance (Finch and Conklin, 2016). However, results from epidemiologic studies have been heterogeneous (Fleisch et al., 2016; Pedersen et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2017; van den Hooven et al., 2009) suggesting a need for additional studies with large sample sizes and across a variety of populations.
Accordingly, we evaluated the associations between ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels with risk of GDM, leveraging data from a unique urban air monitoring program designed to assess intra-urban variation in air pollution exposures, and to draw on a combination of birth certificate and hospital discharge diagnoses for a large, diverse population of pregnant women across New York City. Previous analysis of data from this study found that residential ambient levels of these two pollutants were associated with a small decrement in birth weight (Savitz et al., 2014), but not with risk of spontaneous preterm delivery or risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (Johnson et al., 2016; Savitz et al., 2015).
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study population
Birth records of 348,585 live births to residents of New York City occurring in New York City hospitals between 2008 and 2010 were available for analysis, excluding the estimated 4% of live births to New York residents that occurred at hospitals outside New York City, as previously described (Savitz et al., 2014; Savitz et al., 2015). Briefly, we linked birth certificate files to hospital discharge data provided by the New York State Department of Health Statewide Planning and Research Cooperative System to verify medical conditions before and during pregnancy. We excluded non-singleton births (n = 10,804, 3.6%), mothers reporting smoking during pregnancy (n = 7,615, 2.6%; to minimize the potential for residual confounding by smoking), and mothers with pre-existing diabetes (n = 3,541, 1.0%). To obtain unbiased estimates of seasonal health effects (Strand et al., 2011), we excluded 43,736 (12.5%) births with an estimated date of conception before July 31, 2007 (> 22 weeks before January 1, 2008) or after March 12, 2010 (< 42 weeks before December 31, 2010). We additionally excluded deliveries missing data on residential address needed for estimating exposure (n = 7, < 0.1%), deliveries with implausible birth weights (<500 or >5,000 g) (n = 399, 0.1%), and those missing outcome (n = 6,183, 2.2%) or covariate information (n = 5,660, 2.0%). The study population was further restricted to exclude 5,220 (1.9%) of deliveries at hospitals with <10 GDM diagnoses per hospital to protect patient privacy. The final analytic sample included 256,372 births delivered at 41 hospitals. These analyses are based on a de-identified dataset and thus did not require review or approval from the Institutional Review Board of Brown University.
2.2. Exposure assessment
We estimated PM2.5 and NO2 at the maternal home address as noted on the birth certificate at the time of delivery, as previously described (Savitz et al., 2014; Savitz et al., 2015). Briefly, as part of the New York City Community Air Survey (NYCCAS), integrated air pollution samples were collected at 150 monitoring sites in each of the four seasons for one 2-week session and in every 2-week period at five reference locations to track city-wide temporal variation (Matte et al., 2013). The 2-week average concentrations at street level (~3–4 m off the ground) of several pollutants, including PM2.5 and NO2, were measured for the period December 2008 to December 2010 (Clougherty et al., 2013; Matte et al., 2013). The annual average estimates for Year 1 (December 2008 to November 2009) were used to fit spatial models for each pollutant, and annual average estimates from Year 2 of the sampling campaign (December 2009 to November 2010) were used for validation of the spatiotemporal model (Ross et al., 2013). We used these models to estimate average pollutant concentrations within 300 m of each maternal address. Exposure estimates were computed for three distinct trimesters of each birth. Women may have moved during the course of pregnancy and/or spent substantial time at locations other than their residence (Bell et al., 2018; Bell and Belanger, 2012). In a validation, the R2 values for predictions of 2-week average concentrations of PM2.5 and NO2 against actual concentrations measured during Year 2 at the 150 NYCCAS distributed sites were 0.83 and 0.79, respectively.
2.3. Assessment of Outcome and Covariates
We assessed GDM based on the presence of discharge diagnoses indicating GDM (ICD-9-CM: 648.8), excluding deliveries where discharge diagnoses indicated preexisting diabetes (250.xx) or background diabetic retinopathy (362.01). Although there is no available information regarding if, when, or how GDM was screened for, the use of diagnostic codes to identify women with GDM has been previously shown to be both sensitive and specific (Lydon-Rochelle et al., 2005).
We assessed the following covariates potentially associated with either air pollution exposures or GDM based on previous evidence (Landon and Gabbe, 2011; Solomon et al., 1997; Zhang et al., 2016): maternal age (<20, 20–24, 25–29, 30–34, 35–39, ≥40), race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic white, black, Hispanic, Asian, or other/unknown), education (<9, 9–11, 12, 13–15, 16, or >16 years), reported pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), parity (0, 1, or ≥2), working during pregnancy (yes, no), conception year, and Medicaid beneficiary (the publicly-funded health insurance system for the poor, classified as yes or no). We did not consider gestational weight in our analyses because considerable weight gain typically occurs during the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy and potentially after the diagnosis of GDM (ACOG, 2013). To address potential confounding by neighborhood socioeconomic status (NSES), we applied a previously developed social deprivation index to the study sample, as described elsewhere (Shmool et al., 2015). Briefly, the index was developed to summarize the following seven contextual variables: proportion of residents with a college degree, proportion unemployed, proportion in a management or professional occupation, proportion residential crowding, proportion living below 200% of the federal poverty line, proportion receiving public assistance, and proportion non-white race.
2.4. Statistical analysis
We used directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to encode our assumptions regarding the relationships among study variables and identify potential confounders (Supplemental Fig. 1). We adjusted all models for potential confounding by maternal age, race/ethnicity, education, BMI, parity, working during pregnancy, NSES, conception year, and Medicaid recipient. We quantified the Pearson correlation between each pair of air pollutants across trimesters. We used conditional logistic regression stratified on zip code to assess the univariable (unadjusted) association between key covariates and the log odds of GDM and subsequently fit multivariable conditional logistic regression models to estimate the associations of PM2.5 and NO2 with GDM, adjusting for these covariates. All models were stratified on zip code (184 strata) of maternal address to minimize potential residual confounding by geographically clustered characteristics such as income level and features of the built environment. This approach to minimizing confounding by unmeasured neighborhood factors has been previously developed (Brumback et al., 2012; Neuhaus and McCulloch, 2006) and applied across a variety of settings (Filleul et al., 2005; Yi et al., 2017). Given the very large sample size of this study, we still had an average of 1,393 births per strata. Because stratification on zip code may represent over-adjustment via reduced variation in exposure within each zip code and/or reduce the precision of our estimates (Kuo et al., 2018) we repeated our main analyses using generalized mixed models with a random zip code intercept rather than conditional logistic regression stratified on zip code. Because the results from the two approaches were very similar with only minor differences in the width of the confidence intervals, we present only the results from the conditional logistic regression models.
In our main analyses, we considered pollutant levels in the 1st trimester (weeks 1–12) and 2nd trimester (weeks 13–26) in separate models. Gestational age was estimated based on the birth attendant’s final estimate of gestation using all perinatal factors and assessments including ultrasound taken early in pregnancy (preferred), the infant’s date of birth, and the date of the mother’s last menstrual period which is considered week 0 (Health, 2009; Hygiene, 2010). We did not consider 3rd trimester exposures since GDM is typically screened for and, when present, diagnosed at the end of the 2nd trimester. We initially modeled each pollutant as quartiles and subsequently considered each pollutant as a linear continuous function with results expressed as an odds ratio (OR) per interquartile range (IQR)-increase in PM2.5 (3.23 μg/m3) or in NO2 (7.96 ppb). We used generalized additive models with non-parametric smoothing splines to further assess the shape of the exposure-response curve between each air pollutant and GDM.
We conducted sensitivity analyses to assess the robustness of our findings. First, because the pollutants’ association with GDM may come from either temporal or spatial components of exposure, we separately considered exposure derived from the city-wide temporal variation alone (the average pollutant concentrations from regulatory monitors during each trimester) and exposure derived from spatial variation only (the estimated annual average pollutant concentrations from the NYCCAS spatial model based on the 300-m buffer from maternal address). Second, we used two-pollutant models to estimate the independent association of each pollutant adjusted for the other, recognizing that the degree of measurement error and temporal versus spatial contributions may differ for PM2.5 and NO2. Third, we repeated analyses for a given pollutant adjusting for the same pollutant in the other trimester. Finally, we performed analyses additionally adjusted for season of conception to account for seasonality. We evaluated whether the associations between air pollution and odds of GDM varied across strata of BMI, maternal age, ethnicity, parity, NSES, and season of conception. We conducted all the analyses in R (R Version 3.2.1). Due to the large sample size, we used the bife (Version 0.5) package to fit the conditional logistic regression models.
3. Results
There were 17,065 women identified as having GDM among 256,372 births, yielding a risk of GDM in the study sample of 67 per 1,000 deliveries. The odds of GDM were higher in women who were older, overweight or obese, multiparous, non-white, Medicaid recipients, who had <9 years of education, or who lived in neighborhoods with higher levels of the deprivation index (Table 1). Average levels of PM2.5 were 12.0±2.5 (mean ± standard deviation) μg/m3 in the 1st trimester and 11.9±2.4 μg/m3 in the 2nd trimester. For NO2, mean levels were 27.9±6.3 ppb and 27.9±6.3 ppb in the 1st and 2nd trimesters, respectively. The correlation coefficients for pairs of air pollutants ranged between 0.27 and 0.69 (Supplemental Fig. 2).
Table 1.
Characteristics of 256,372 deliveries and their univariate associations with odds of gestational diabetes, New York City, 2008–2010.
| Characteristics | All Pregnancies (n=256,372) | Gestational Diabetes (n=17,065) |
|---|---|---|
| n (%) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Maternal Age (years) | ||
| <20 | 16,994 (6.6) | 0.26 (0.23, 0.29) |
| 20–24 | 52,988 (20.7) | 0.53 (0.50, 0.56) |
| 25–29 | 67,667 (26.4) | 1.00 |
| 30–34 | 67,849 (26.5) | 1.44 (1.38, 1.50) |
| 35–39 | 39,476 (15.4) | 1.87 (1.78, 1.95) |
| ≥40 | 11,398 (4.4) | 2.56 (2.40, 2.72) |
| Maternal Ethnicity | ||
| Non-Hispanic white | 70,884 (27.6) | 1.00 |
| Black | 55,635 (21.7) | 1.67 (1.59, 1.76) |
| Hispanic | 86435 (33.7) | 1.68 (1.60, 1.76) |
| Asian | 37,948 (14.8) | 3.48 (3.31, 3.65) |
| Unknown/Other | 5,470 (2.1) | 2.19 (1.98, 2.43) |
| Maternal Education (years) | ||
| <9 | 20,494 (8.0) | 1.51 (1.43, 1.60) |
| 9–11 | 45,130 (17.6) | 0.97 (0.92, 1.02) |
| 12 | 61,256 (23.9) | 1.00 |
| 13–15 | 56,501 (22.0) | 1.05 (1.00, 1.10) |
| 16 | 41,639 (16.2) | 0.97 (0.92, 1.02) |
| >16 | 31,352 (12.2) | 0.83 (0.78, 0.88) |
| Medicaid beneficiary | 156,318 (61.0) | 1.23 (1.19, 1.27) |
| Parity | ||
| 0 | 119,645 (46.7) | 1.00 |
| 1 | 75,445 (29.4) | 1.32 (1.28, 1.37) |
| ≥2 | 195,090 (23.9) | 1.57 (1.51, 1.63) |
| Working during pregnancy | 103,913 (46.7) | 0.84 (0.81, 0.86) |
| Conception Year | ||
| 2007 | 42,554 (16.6) | 1.00 |
| 2008 | 98,977 (38.6) | 0.94 (0.90, 0.99) |
| 2009 | 95,542 (37.3) | 0.99 (0.95, 1.04) |
| 2010 | 19,299 (7.5) | 1.07 (1.00, 1.15) |
| Deprivation index | 0.36 (−0.46, 1.04)b | 1.16 (1.13, 1. 19)c |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 14,225 (2.5) | 0.73 (0.66, 0.80) |
| Normal (18.5 to <25) | 138,867 (54.2) | 1.00 |
| Overweight (25 to <30) | 60,922 (23.8) | 1.76 (1.69, 1.82) |
| Obese (≥30) | 42,358 (16.5) | 2.68 (2.57, 2.78) |
OR, odds ratio; CI, Confidence Interval; BMI, body mass index.
n (%),
Median (Q1, Q3),
OR per interquartile-range increase in deprivation index
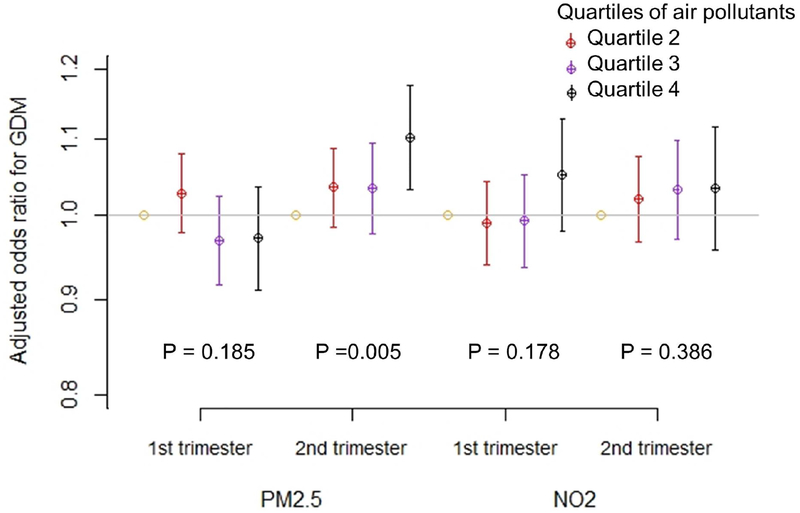
In unadjusted models, odds of GDM were negatively associated with PM2.5 in the 1st trimester and positively associated with PM2.5 in the 2nd trimester (Supplemental Table 1). Results were similar in models adjusted for a range of demographic and clinical covariates, and individual and neighborhood level markers of socioeconomic status (Figure 1). Specifically, in fully adjusted models 2nd trimester PM2.5 was associated with higher odds of GDM, with an OR of 1.10 (95% confidence intervals (CI): 1.03, 1.18) comparing the highest versus lowest quartiles of exposures, and an OR of 1.06 (95% CI: 1.03, 1.10) per IQR-increase in PM2.5 (3.23 μg/m3). The association between 1st trimester PM2.5 and GDM was close to null. PM2.5 in the 1st trimester was associated with lower odds of GDM, with an OR of 0.97 (95% CI: 0.94, 1.00) per IQR-increase.
Figure 1.
Association of quartiles of PM2.5 and NO2 with odds ratio (95% confidence interval) of gestational diabetes among 256,372 deliveries to non-smoking women in New York City, 2008 – 2010. All models are adjusted for maternal age, ethnicity, education, Medicaid status, parity, working status during pregnancy, conception year, deprivation index, and BMI, conditional on zip code of residence. P values are calculated for linear trend of quartile-specific odds ratios.
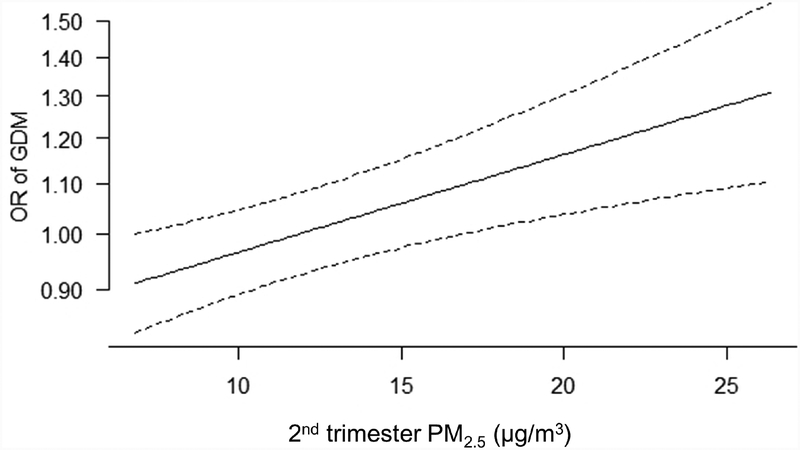
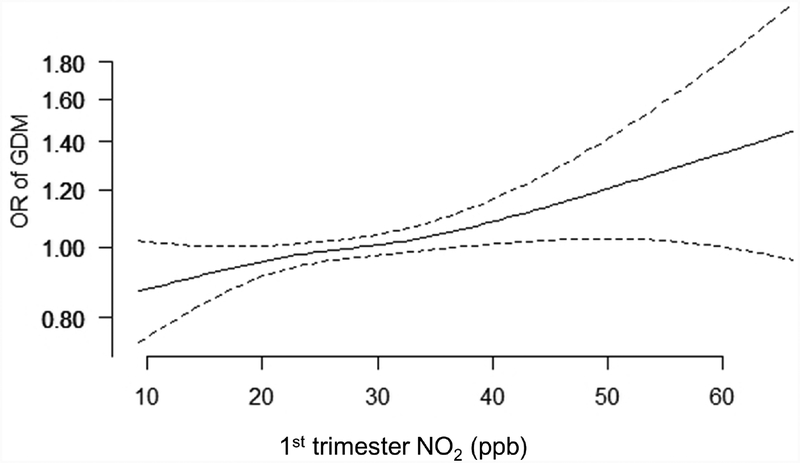
For NO2, in both unadjusted (Supplemental Table 1) and adjusted (Figure 1) models, GDM was associated with 1st trimester NO2 levels only, with an OR of 1.05 (95% CI: 0.98, 1.13) comparing the highest versus lowest quartile of NO2, and an OR of 1.05 (95% CI: 1.01, 1.09) per IQR-increase (7.96 ppb) in NO2. NO2 nd in the 2nd trimester was not associated with the odds of GDM. For the positive associations of 2nd trimester PM2.5 and 1st trimester NO2 with GDM, we found no evidence of important deviations from linearity (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Association between 2nd trimester PM2.5 (A.) and 1st trimester NO2 (B.) with odds of gestational diabetes. Models were fit using generalized additive models with the same covariates as in Figure 1.
We performed sensitivity analyses to assess the robustness of these findings (Table 2). For 2nd trimester PM2.5, results were qualitatively similar (although the magnitude of the point estimate and width of the confidence intervals varied) when we considered: 1) only the temporal component of exposure variation, 2) two-pollutant models (additional adjustment for NO2 in the same trimester), 3) two-trimester models (additional adjustment for PM2.5 in the opposite trimester), and 4) adjustment for season of conception. PM2.5 in 1st trimester showed consistently lower relative odds of GDM except when adjusted for PM2.5 in the 2nd trimester. The time-invariant spatial component of PM2.5 was associated with an OR of GDM of 1.06 (95% CI: 0.94, 1.19) per IQR-increase in PM2.5, comparable to the spatial-temporal (primary analysis) and temporal-only estimates for the 2nd trimester. In contrast, the results for NO2 were generally consistent with only modest differences in the magnitude and precision of effect estimates depending on the analytic approach.
Table 2.
Results of sensitivity analyses of the associations of PM2.5 and NO2 with odds of gestational diabetes among 256,372 births in New York City, 2008–2010.
| Model | PM2.5a | NO2a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% Cl) | P | OR (95% Cl) | P | |
| 1st trimester | ||||
| Primary analysesb | 0.97 (0.94, 1.00) | 0.030 | 1.05 (1.01,1.09) | 0.012 |
| Temporal component of exposure estimate only | 0.95 (0.92, 0.99) | 0.010 | 1.05 (1.00, 1.11) | 0.053 |
| Two-pollutant modelc | 0.95 (0.92, 0.98) | 0.001 | 1.07 (1.03, 1.12) | <0.001 |
| Adjusted for same pollutant in 2nd trimesterd | 0.99 (0.96, 1.02) | 0.510 | 1.05 (1.01,1.09) | 0.014 |
| Adjusted for seasone | 0.96 (0.93, 0.99) | 0.007 | 1.04 (0.99, 1.10) | 0.142 |
| 2nd trimester | ||||
| Primary analysesb | 1.06 (1.03, 1.10) | <0.001 | 1.02 (0.98, 1.06) | 0.28 |
| Temporal component of exposure estimate only | 1.07 (1.03, 1.11) | <0.001 | 1.01 (0.96, 1.07) | 0.63 |
| Two-pollutant modelc | 1.06 (1.03, 1.10) | <0.001 | 1.01 (0.97, 1.05) | 0.738 |
| Adjusted for same pollutant in 1st trimesterd | 1.06 (1.02, 1.10) | 0.002 | 1.02 (0.98, 1.06) | 0.365 |
| Adjusted for seasone | 1.06 (1.03, 1.10) | 0.001 | 1.06 (1.00, 1.12) | 0.049 |
| Spatial component of exposure estimate only | 1.06 (0.94, 1.19) | 0.345 | 1.06 (0.97, 1.16) | 0.169 |
OR, odds ratio; CI, Confidence Interval; BMI, body mass index. Bolded OR’s have P values < 0.05.
Estimates expressed per IQR -increase in PM2.5 (3.23 μg/m3) or NO2.(7.96 ppb).
Adjusted for maternal age, maternal ethnicity, maternal education, Medicaid status, parity, working during pregnancy, deprivation index, BMI, and conception year, conditional on zip code.
Additional adjustment for the other pollutant in the same trimester.
Additional adjustment for the same pollutant in the other trimester
Additional adjustment for season of conception.
We evaluated whether the associations between 2nd trimester PM2.5 or 1st trimester NO2 and odds of GDM varied across strata of sociodemographic variables and season of conception, adjusted for all other covariates (Table 3). PM2.5 in the 2nd trimester was more strongly associated with the relative odds of GDM among women who were younger and not Medicaid recipients while the association between 1st trimester NO2 and GDM was more pronounced in overweight and parous women.
Table 3.
Association between PM2.5, NO2 and gestational diabetes stratified by BMI, age, ethnicity, parity, socioeconomic status, and season of conception, New York City, 2008 – 2010.
| Characteristicsc | 2nd Trimester PM2.5 | 1st Trimester NO2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI)a | P | Phb | OR (95% CI)a | P | Phb | |
| BMI | ||||||
| Underweight/Normal | 1.05 (1.00, 1.10) | 0.078 | 0.062 | 1.04 (0.98, 1.09) | 0.178 | 0.027 |
| Overweight | 1.09 (1.03, 1.16) | 0.006 | 1.08 (1.01, 1.16) | 0.021 | ||
| Obese | 1.06 (1.00, 1.13) | 0.071 | 1.02 (0.95,1.09) | 0.616 | ||
| Age | ||||||
| <35 | 1.08 (1.04, 1.13) | <0.001 | 0.019 | 1.04 (0.99, 1.08) | 0.116 | 0.352 |
| ≥35 | 1.02 (0.97, 1.09) | 0.404 | 1.09 (1.02, 1.16) | 0.011 | ||
| Race/Ethnicity | ||||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 1.10 (1.02, 1.19) | 0.018 | 0.412 | 1.07 (0.99, 1.17) | 0.099 | 0.57 |
| Other | 1.06 (1.03, 1.10) | <0.001 | 1.06 (1.01, 1.10) | 0.007 | ||
| Parity | ||||||
| 0 | 1.08 (1.03, 1.14) | 0.002 | 0.532 | 1.04 (0.98, 1.10) | 0.161 | 0.007 |
| ≥ 1 | 1.05 (1.01, 1.09) | 0.027 | 1.06 (1.01,1.11) | 0.026 | ||
| Medicaid Status | ||||||
| No | 1.10 (1.04, 1.15) | <0.001 | 0.041 | 1.01 (0.95, 1.07) | 0.716 | 0.293 |
| Yes | 1.05 (1.00,1.09) | 0.031 | 1.07 (1.02, 1.12) | 0.005 | ||
| Deprivation Index | ||||||
| > Median | 1.08 (1.03, 1.13) | 0.002 | 0.703 | 1.01 (0.96, 1.06) | 0.791 | 0.128 |
| ≤ Median | 1.05 (1.00, 1.10) | 0.033 | 1.08 (1.03, 1.14) | 0.003 | ||
| Season of conception | ||||||
| Spring | 1.07 (1.00, 1.13) | 0.051 | 0.845 | 1.02 (0.90, 1.16) | 0.754 | 0.728 |
| Summer | 1.04 (0.94, 1.15) | 0.485 | 0.99 (0.83, 1.17) | 0.882 | ||
| Fall | 1.00 (0.90, 1.10) | 0.956 | 1.06 (0.97, 1.16) | 0.228 | ||
| Winter | 1.06 (1.00, 1.13) | 0.065 | 1.03 (0.94, 1.14) | 0.499 | ||
Estimates expressed per IQR increase of increase in PM2.5 (3.23 μg/m3) or NO2.(7.96 ppb). Bolded OR’s have Ph values < 0.05.
p-value for the test of homogeneity.
All models adjusted for same covariates as main analyses except effect modifier, and stratified on zip code of residence.
4. Discussion
In this large, urban population, we evaluated the association between PM2.5 and NO2 in the first two trimesters of pregnancy and the odds of GDM. We found that higher levels of PM2.5 in the 2nd trimester and higher levels of NO2 in the 1st trimester were associated with higher odds of GDM, with or without adjusting for a broad suite of potential confounders and across a number of sensitivity analyses. We also found a negative association between 1st trimester PM2.5 and GDM, but this association was weak and sensitive to the modeling approach.
Despite some evidence that air pollutants can impact glucose homeostasis during pregnancy (Lu et al., 2017; Madhloum et al., 2017), prior studies evaluating the association between air pollution or air pollution sources and risk of GDM have had mixed results. For example, positive associations between PM2.5 and GDM have been reported in Florida (Hu et al., 2015), Rhode Island (Choe et al., 2018), and Taiwan (Shen et al., 2017). On the other hand, null or negative associations between PM2.5 and GDM were reported in California (Wu et al., 2016) and Massachusetts (Fleisch et al., 2016), as well as among births in the US Consortium on Safe Labor (Robledo et al., 2015). Results have been similarly inconsistent for nitrogen oxides (NOx), with positive associations reported in Los Angeles County (Wu et al., 2016), southern Sweden (Malmqvist et al., 2013) and Taiwan (Pan et al., 2017), but not across California (Wu et al., 2016) or in a different study in Taiwan (Shen et al., 2017). In the Danish National Birth Cohort, NO2 was not associated with GDM in the primary analyses, but was positively associated in secondary analyses using a different definition of GDM that could be applied only to a subset of patients (Pedersen et al., 2017). Residential proximity to major roads, often used as an imperfect marker of long-term exposure to traffic pollution, was not associated with risk of GDM in Japan (Yorifuji et al., 2015). The current study adds to this emerging literature by leveraging a large dataset from a large, dense, and diverse metropolitan area including more than 256,000 deliveries (of which more than 17,000 were identified as having GDM), a spatial-temporal model for PM2.5 and NO2 based on an intensive air pollution monitoring campaign, and diagnostic and covariate information derived from both clinical and birth certificate data.
We note that our results are comparable in magnitude to those from some previous studies reporting a positive association. For example, our estimate of the association between 2nd trimester PM2.5 and GDM (OR: 1.10, 95% CI: 1.05, 1.16 per 5 μg/m3 increase in PM2.5) was similar to the results of a study of 410,267 births in Florida (OR: 1.15, 95% CI: 1.10, 1.20 per 5 μg/m3 increase in PM2.5) (Hu et al., 2015). Similarly, our estimated association between 1st trimester NO2 and GDM (OR: 1.07, 95% CI: 1.01, 1.12 per 10.8 ppb increase in NO2) was similar to that from an analysis of births in Los Angeles County (OR: 1.05, 95% CI: 1.02, 1.09 per 10.8 ppb increase in NO2 (Wu et al., 2016). Differences in approaches to exposure assessment or analyses, or differences in population characteristics, medical care, or pollution mixtures likely contribute to some heterogeneity across studies.
We performed a number of sensitivity analyses to assess the robustness of the findings from our main analyses and to gain further insights into the impacts of spatial versus temporal variation in pollutant levels. Based on the results of the sensitivity analyses, we noted that only 2nd trimester PM2.5 is associated with GDM in models simultaneously considering PM2.5 in both trimesters. This suggests that the negative association we observed between 1st trimester PM2.5 and GDM in the main analysis may be due to the correlation structure between PM2.5 across trimesters, a pattern previously documented by others (Gryparis et al., 2007; Wilson et al., 2017).
Our observation that PM2.5 and NO2 were each positively associated with GDM in different trimesters was unexpected. Some prior studies in the Northeastern United States similarly reported finding a positive association only with 2nd trimester PM2.5 (Choe et al., 2018; Fleisch et al., 2016). However, in Taiwan, GDM was positively associated with PM2.5 in both the 1st and 2nd trimesters (Shen et al., 2017). A Danish study found that NO2 in both the 1st and 2nd trimesters were associated with GDM (Pedersen et al., 2017). It remains unclear whether these differences in timing reflect true differences in the etiology of disease versus random variation between studies, lack of information on the timing of GDM screening or diagnosis, differences in medical practice across locations or other differences between studies.
We found that the association between air pollution and GDM varied somewhat across subgroups of the population, with modestly stronger associations among women who were younger, not receiving Medicaid (2nd trimester PM2.5), overweight, or multiparous (1st trimester NO2). These results are consistent with the limited previous studies available which have reported stronger associations between air pollution and GDM in younger women (Fleisch et al., 2016) and those with higher pre-pregnancy BMI (Pedersen et al., 2017). In some areas, younger mothers may be more likely to live in neighborhoods with higher levels of air pollution or less green space, or have less access to high quality prenatal care (Fleisch et al., 2016). However, in our study population average pollutant levels tended to be lower rather than higher in younger mothers. Since there is yet limited evidence regarding possible effect modification by other environmental and biological factors, whether the observed differences actually reflect meaningful, consistent differences in individual susceptibilities remains an open question.
The potential mechanisms by which air pollution could increase the risk of GDM remains unknown. Experimental studies have suggested that suppression of vascular insulin signaling by PM2.5 may lead to systemic insulin resistance (Haberzettl et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2009). Clearly additional research is needed to better understand the potential mechanisms underlying these associations.
We have previously shown in this same population that residential ambient levels of PM2.5 and NO2 were not associated with risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (Savitz et al., 2015). Given the very different etiologies, established risk factors, and clinical management between GDM and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, it is not particularly surprising that we would find air pollution associated with one condition but not the other.
Of note, we used conditional logistic regression stratified on zip code of residence in order to minimize residual confounding by neighborhood factors (Brumback et al., 2012; Neuhaus and McCulloch, 2006). We acknowledge that stratification on zip code may represent over-adjustment via reduced variation in exposure within each zip code and/or reduce the precision of our estimates (Kuo et al., 2018). To evaluate this possibility, we repeated the analyses using generalized mixed models with a random zip code intercept rather than conditional logistic regression stratified on zip code and the results from the two approaches were very similar, revealing only minor differences in the width of the confidence intervals.
Our study has several potential limitations. First, some degree of exposure misclassification is likely since we estimated pollutant levels based on the residential address provided at the time of delivery, which may differ from the residential address during pregnancy (Bell et al., 2018; Bell and Belanger, 2012). Unfortunately, data on residential address during the course of pregnancy are not available. Additional potential sources of exposure misclassification include varying amounts of time spent at home, use of air conditioning and other factors affecting penetration of ambient air pollution to indoor spaces, and failure to account for building height in exposure models. We expect this exposure measurement error to be non-differential with respect to the outcome and thus, on average, bias our results towards the null. Second, although hospital discharge diagnoses have been found to be reasonably sensitive and specific for assessment of GDM (a sensitivity of 0.8 to 0.9 and a specificity of > 0.9 (Lydon-Rochelle et al., 2005)), some residual misclassification of the outcome is inevitable given variation in clinical practice across study hospitals and access to prenatal care across study participants. However, we expect that universal screening of pregnant women for GDM would have been widely practiced during the study period (2008–2010) (Janevic et al., 2018; Thorpe et al., 2005). Third, we could not evaluate the independent or joint effects of other ambient pollutants of interest such as NO, CO, black carbon, ozone, or SO2 as spatial-temporal estimates of residential ambient levels of these pollutants are not currently available to us. Similarly, estimates of pre-pregnancy air pollution levels or air pollution levels in shorter averaging periods were not available, precluding us from more fully characterizing the temporal pattern of the association between exposures and GDM. Fourth, we cannot exclude the possibility of residual confounding by unmeasured factors, particularly other features of the physical and built environment such as traffic-related noise or access to green space. Finally, these results may not be generalizable to populations with different characteristics or locations characterized by different pollution mixtures, lifestyle patterns, access to prenatal care or other potentially modifying factors.
On the other hand, this study has several notable strengths, including a large sample size, spatial-temporal pollutant estimates derived from an extensive urban air monitoring program designed to assess intra-urban variation in population exposures, an usually rich dataset combining birth certificate and hospital discharge data, and a diverse population of pregnant women.
5. Conclusions
In this large, urban, diverse population, we found that 2nd trimester PM2.5 and 1st trimester NO2 were associated with higher risk of GDM. These results were robust to a number of sensitivity analyses. Although we also found that 1st trimester PM2.5 was negatively associated with GDM in some analyses, these results were weaker and sensitive to modeling choices. This study adds to the emerging evidence suggesting the presence of a positive association between air pollution and risk of GDM. Further resolving whether maternal exposure to ambient air pollution increases the risk of GDM would inform future cost-benefit analyses of air pollution mitigation efforts and provide valuable information for clinicians and patients alike. Given that there are still relatively few large studies published on this topic, additional studies leveraging routinely available markers of air pollution and indicators of GDM would continue to add meaningfully to the evidence base. Furthermore, studies that can examine air pollution in relation to more refined indicators of glucose homeostasis during pregnancy would bring new insights to the topic, regardless of the findings.
Supplementary Material
We investigated the associations between ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels with odds of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) using a large, diverse population of pregnant women across New York City.
PM2.5 in the 2nd trimester and NO2 in the 1st trimester were associated with higher odds of GDM. These positive associations were robust to different model specifications.
The association between 2nd trimester PM2.5 and GDM was more pronounced in women who were overweight or obese, younger, and not on Medicaid assistance.
Funding:
This research was supported by grants R01-ES019955 and R21-ES023073 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS, NIH). The contents of this report are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsoring organizations.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
References
- ACOG, A. C. o. O. a. G., Weight Gain During Pregnancy Committee opinion American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ACOG, A. C. o. O. a. G., 2018. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet Gynecol. 131, e49–e64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell ML, et al. , 2018. Residential mobility of pregnant women and implications for assessment of spatially-varying environmental exposures. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 28, 470–480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell ML, Belanger K, 2012. Review of research on residential mobility during pregnancy: consequences for assessment of prenatal environmental exposures. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 22, 429–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumback BA, et al. , 2012. Adjusting for confounding by neighborhood using a proportional odds model and complex survey data. Am J Epidemiol. 175, 1133–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe S-A, et al. , 2018. Air pollution, land use, and complications of pregnancy. Science of The Total Environment. 645, 1057–1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clougherty JE, et al. , 2013. Intra-urban spatial variability in wintertime street-level concentrations of multiple combustion-related air pollutants: the New York City Community Air Survey (NYCCAS). J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 23, 232–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich S, et al. , 2016. Endocrine Disruptors: A Potential Risk Factor for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Am J Perinatol. 33, 1313–1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara A, 2007. Increasing Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. A public health perspective. 30, S141–S146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filleul L, et al. , 2005. Twenty five year mortality and air pollution: results from the French PAARC survey. Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 62, 453–460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J, Conklin DJ, 2016. Air Pollution-Induced Vascular Dysfunction: Potential Role of Endothelin-1 (ET-1) System. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 16, 260–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisch AF, et al. , 2014. Air pollution exposure and abnormal glucose tolerance during pregnancy: the project Viva cohort. Environ Health Perspect. 122, 378–83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisch AF, et al. , 2016. Air pollution exposure and gestational diabetes mellitus among pregnant women in Massachusetts: a cohort study. Environ Health. 15, 40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung GP, et al. , 2014. Does gestational diabetes mellitus affect respiratory outcome in late-preterm infants? Early Hum Dev. 90, 527–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryparis A, et al. , 2007. Controlling for confounding in the presence of measurement error in hierarchical models: a Bayesian approach. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 17 Suppl 2, S20–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberzettl P, et al. , 2016. Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution Causes Vascular Insulin Resistance by Inducing Pulmonary Oxidative Stress. Environ Health Perspect. 124, 1830–1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammoud NM, et al. , 2018. Long-term BMI and growth profiles in offspring of women with gestational diabetes. Diabetologia. 61, 1037–1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Health, N. Y. S. D. o., Technical Notes. Vital Statistics of New York State 2009, Vol. 2019. New York State Department of Health, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hu H, et al. , 2015. Association of Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Ozone with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Environ Health Perspect. 123, 853–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hygiene, N. D. o. H. a. M., Guidelines for the New York City Electronic Birth Registration System (EBRS) Vol. 2018. New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Bureau of Vital Statistics New York City, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Janevic T, et al. , 2018. The role of obesity in the risk of gestational diabetes among immigrant and U.S.-born women in New York City. Ann Epidemiol. 28, 242–248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S, et al. , 2016. Ambient Fine Particulate Matter, Nitrogen Dioxide, and Preterm Birth in New York City. Environ Health Perspect. 124, 1283–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C-L, et al. , 2018. Unconditional or Conditional Logistic Regression Model for Age-Matched Case-Control Data? Frontiers in public health. 6, 57–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon MB, Gabbe SG, 2011. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Obstet Gynecol. 118, 1379–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu MC, et al. , 2017. Association of temporal distribution of fine particulate matter with glucose homeostasis during pregnancy in women of Chiayi City, Taiwan. Environ Res. 152, 81–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydon-Rochelle MT, et al. , 2005. The reporting of pre-existing maternal medical conditions and complications of pregnancy on birth certificates and in hospital discharge data. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 193, 125–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhloum N, et al. , 2017. Cord plasma insulin and in utero exposure to ambient air pollution. Environ Int. 105, 126–132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmqvist E, et al. , 2013. Gestational Diabetes and Preeclampsia in Association with Air Pollution at Levels below Current Air Quality Guidelines. Environmental Health Perspectives. 121, 488–493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matte TD, et al. , 2013. Monitoring intraurban spatial patterns of multiple combustion air pollutants in New York City: design and implementation. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 23, 223–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirghani Dirar A, Doupis J, 2017. Gestational diabetes from A to Z. World J Diabetes. 8, 489–511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer VA, 2014. Screening for gestational diabetes mellitus: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 160, 414–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor CD, et al. , 1996. Cesarean delivery in relation to birth weight and gestational glucose tolerance: pathophysiology or practice style? Toronto Trihospital Gestational Diabetes Investigators. Jama. 275, 1165–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus JM, McCulloch CE, 2006. Separating between- and within-Cluster Covariate Effects by Using Conditional and Partitioning Methods. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Statistical Methodology). 68, 859–872. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly SL, 2014. Prevention of Diabetes after Gestational Diabetes: Better Translation of Nutrition and Lifestyle Messages Needed. Healthcare. 2, 468–491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan SC, et al. , 2017. Gestational diabetes mellitus was related to ambient air pollutant nitric oxide during early gestation. Environ Res. 158, 318–323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen M, et al. , 2017. Gestational diabetes mellitus and exposure to ambient air pollution and road traffic noise: A cohort study. Environ Int. 108, 253–260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman A, et al. , 2016. Infant and mother related outcomes from exposure to metals with endocrine disrupting properties during pregnancy. Sci Total Environ. 569–570, 1022–1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robledo CA, et al. , 2015. Preconception and early pregnancy air pollution exposures and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Environ Res. 137, 316–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross Z, et al. , 2013. Spatial and temporal estimation of air pollutants in New York City: exposure assignment for use in a birth outcomes study. Environ Health. 12, 51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitz DA, et al. , 2014. Ambient fine particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and term birth weight in New York, New York. Am J Epidemiol. 179, 457–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitz DA, et al. , 2015. Ambient Fine Particulate Matter, Nitrogen Dioxide, and Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy in New York City. Epidemiology. 26, 748–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen HN, et al. , 2017. Maternal Exposure to Air Pollutants and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmool JL, et al. , 2015. Area-level socioeconomic deprivation, nitrogen dioxide exposure, and term birth weight in New York City. Environ Res. 142, 624–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon CG, et al. , 1997. A prospective study of pregravid determinants of gestational diabetes mellitus. Jama. 278, 1078–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand LB, et al. , 2011. Methodological challenges when estimating the effects of season and seasonal exposures on birth outcomes. BMC Med Res Methodol. 11, 49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q, et al. , 2009. Ambient air pollution exaggerates adipose inflammation and insulin resistance in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Circulation. 119, 538–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe LE, et al. , 2005. Trends and racial/ethnic disparities in gestational diabetes among pregnant women in New York City, 1990–2001. American journal of public health. 95, 1536–1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hooven EH, et al. , 2009. Residential traffic exposure and pregnancy-related outcomes: a prospective birth cohort study. Environmental Health. 8, 59–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendland EM, et al. , 2012. Gestational diabetes and pregnancy outcomes--a systematic review of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) diagnostic criteria. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 12, 23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A, et al. , 2017. Potential for Bias When Estimating Critical Windows for Air Pollution in Children’s Health. Am J Epidemiol. 186, 1281–1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J, et al. , 2016. Adverse Reproductive Health Outcomes and Exposure to Gaseous and Particulate-Matter Air Pollution in Pregnant Women. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 1–58. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang AH, et al. , 2015. Association of maternal diabetes with autism in offspring. Jama. 313, 1425–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi S-J, et al. , 2017. Association between Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Prevalence of Allergic Diseases in Children, Seoul, Korea. BioMed Research International. 2017, 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yorifuji T, et al. , 2015. Residential proximity to major roads and obstetrical complications. Sci Total Environ. 508, 188–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C, et al. , 2016. Risk factors for gestational diabetes: is prevention possible? Diabetologia. 59, 1385–1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.