Abstract
Fusobacterium nucleatum is an important oral bacterium that has been linked to the development of chronic diseases such as periodontitis and colorectal cancer. In periodontal disease, F. nucleatum forms the backbone of the polymicrobial biofilm and in colorectal cancer is implicated in aetiology, metastasis and chemotherapy resistance. The control of this bacteria may be important in assisting treatment of these diseases. With increased rates of antibiotic resistance globally, there is need for development of alternatives such as bacteriophages, which may complement existing therapies. Here we describe the morphology, genomics and functional characteristics of FNU1, a novel bacteriophage lytic against F. nucleatum. Transmission electron microscopy revealed FNU1 to be a large Siphoviridae virus with capsid diameter of 88 nm and tail of approximately 310 nm in length. Its genome was 130914 bp, with six tRNAs, and 8% of its ORFs encoding putative defence genes. FNU1 was able to kill cells within and significantly reduce F. nucleatum biofilm mass. The identification and characterisation of this bacteriophage will enable new possibilities for the treatment and prevention of F. nucleatum associated diseases to be explored.
Subject terms: Colon cancer, Biofilms, Infection control in dentistry, Bacteriophages, Applied microbiology
Introduction
Fusobacterium nucleatum is a Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacillus that is a normal component of the oral microbiome. It has been associated with periodontal diseases1 as well as malignancies of the oral cavity, head and neck, oesophagus, cervix, stomach and colon2–4. This association with a range of malignancies has led to its referral as an “oncobacterium”4. In these diseases, F. nucleatum biofilms have been demonstrated to play a critical role.
Chronic periodontitis results from a dysbiosis in subgingival plaque biofilm communities that leads to the emergence of pathogenic species that dysregulate the host immune response leading to sustained and uncontrolled inflammation5,6. In chronic periodontitis, F. nucleatum has been shown to act as a backbone for pathogenic subgingival polymicrobial biofilms by forming a bridge between the more commensal early colonisers and the more pathogenic late colonisers1,7,8. This microbial biofilm is therefore responsible for the initiation and progression of chronic periodontitis9,10. Apart from their role in periodontitis, bacterial biofilms and microbiota organisation have also been associated with gut tumours11. In colorectal cancer, Fusobacterium has been demonstrated to be intimately involved in modulating the tumour immune microenvironment and recruiting myeloid cells that assist in tumorigenesis, tumour cell proliferation and metastasis12, modulating autophagy and resistance to chemotherapies13.
Current treatment of periodontal disease is mechanical debridement with antibiotics and antiseptics as adjuncts. However, this approach is not without controversy14, with the development of antibiotic resistance being a major caveat15, along with dysbiosis of oral microbiota contributing to inflammation and disease recurrence16,17. Current treatment of colorectal cancer includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In both cases, a targeted therapy that specifically attacks Fusobacterium in biofilms can potentially provide a new modality to combat these important diseases. Optimal treatment of biofilms in periodontitis and colorectal cancer would target specific bacteria in the biofilms, have minimal inflammatory effect, and a low risk for resistance development by bacteria.
Alternatives to antibiotics that have a narrow range in their bacterial targets, and capable of breaking down bacterial biofilms are bacteriophages18,19. Bacteriophages, which can be either lytic or temperate20, have been involved in an evolutionary arms race with bacteria, and as such are capable of overcoming or adapting to development of bacterial resistance against them21. Temperate bacteriophages are present in bacteria in a latent phase until certain conditions leading to bacterial cellular damage occurs e.g. exposure to ultra-violet radiation. Lytic bacteriophages, on the other hand, will lyse bacteria after infection and have potential for therapeutic use20. F. nucleatum is an important micro-organism in the structural composition of biofilms in periodontitis and colon cancer and as such provides a useful target for bacteriophages. To date, however, only temperate bacteriophages of F. nucleatum, ɸFunu1 and ɸFunu2, have been fully characterised22. There has been a single report of a lytic bacteriophage against F. nucleatum, Fnpɸ02 that has been isolated and phenotypically characterised23. Full genomic characterisation was not performed, and short amplicons within Fnpɸ02 showed homology ranging from 84% to 98% to Cutibacterium acnes (formally Propionibacterium acnes) bacteriophages. The genes where these amplicons were taken are highly conserved in C. acnes bacteriophages. C. acnes has been isolated frequently with F. nucleatum24 but no bacteriophages have been found that target both F. nucleatum and C. acnes.
Bacteriophages lytic against other types of bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa25, Escherichia coli26 and Streptococcus mutans27 have been shown to be able to disrupt mono-biofilms formed by their respective hosts. The potential exists for use of bacteriophages against biofilms in periodontal infection18,19 and colon cancer. We describe here the full genomic and morphological characterisation of a novel lytic bacteriophage, FNU1, which is capable of disrupting existing F. nucleatum biofilms. This bacteriophage has a novel genome (NCBI Genbank Accession Number: MK554696), with little homology to other viruses, and offers the potential for development to prevent and treat F. nucleatum-associated oral disease and cancers.
Methods
Ethics
All methods were performed in accordance with the La Trobe University Ethics, Biosafety and Integrity guidelines and regulations. Informed consent was obtained from participants for their involvement and use of samples in this study. The study protocols were approved by the La Trobe University Ethics Committee, reference number: S17-112.
Fusobacterium nucleatum bacterial growth conditions
Fusobacterium nucleatum (ATCC 10953) that had been completely characterised28 and previously studied in a polymicrobial biofilm29 was used for all experiments. The cultures were grown in brain heart infusion media (BHI; Oxoid, Australia) supplemented with 0.5% cysteine (Sigma, Australia) and 0.5% haemin (Sigma, Australia) in either broth or agar. The cultures were grown anaerobically using anaerobic generating packs (AnaeroGen) (Oxoid, Australia) at 37 °C. For this study, the identity of the strain was confirmed using 16 S rRNA gene amplification and sequencing via U27F: 5′AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG3′ and U1492R: 5′AAGGAGGTGWTCCARCC 3′ primers30. The thermocycling conditions were 95 °C for 3 minutes, 32 cycles of 95 °C for 30 seconds, 60 °C for 30 seconds, and 72 °C for 90 seconds, with a final extension at 72 °C for 10 minutes. The amplicons were cleaned using QIAquick® PCR purification kits (Qiagen, Australia) and analysed by Sanger sequencing at the Australian Genome Research Facility (AGRF) in Queensland, Australia.
Bacteriophage isolation
Mouthwash samples were collected from dental practices in Bendigo (Victoria, Australia) and screened for the presence of lytic bacteriophages against F. nucleatum using the enrichment method in BHI broth according to Gill and Hyman31. Briefly, 100 µL of F. nucleatum grown previously in broth culture for 48 hours anaerobically was added to 1 mL of sample and 20 mL of broth and incubated anaerobically at 37 °C for seven days. The enrichment was filtered using a 0.20 µm cellulose acetate filter (Microanalytix, Australia) before spotting 10 µL of the filtrate on a freshly prepared lawn of F. nucleatum on 1% agar. The plate was incubated for 48 hours anaerobically at 37 °C. Observed plaques were excised and purified as described previously32. To test the host range of the purified bacteriophage, it was also spotted onto cultures of Streptococcus mutans, Porphyromonas gingivalis and C. acnes, which are all found in the oral cavity.
Electron microscopy
The purified bacteriophage particles were visualised using a JEOL JEM-2100 Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) using 400-mesh carbon-coated copper grids (ProSciTech, Australia). The bacteriophage lysate was allowed to adsorb to the grid for 30 seconds before being washed with Milli-Q® water (Promega, Australia). The adsorbed particles were then negatively stained twice for 30 seconds with 2% [W/V] uranyl acetate (Sigma, Australia). Excess stain on the grids was removed using filter paper before being air dried for 20 minutes. The grid was visualised and images captured with a Gatan Orius SC200D 1 wide-angle camera (Gatan Microscopy Suite and Digital Micrograph Imaging software version 2.3.2.888.0) at 200 kV. Further image analysis was achieved in ImageJ software version 1.8.0_112.
DNA extraction
Bacteriophage DNA was extracted from a highly concentrated purified lysate (approximately 1011 PFU mL−1) using the phenol-chloroform method as previously described32. All compounds used in the DNA extraction process were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Australia) unless stated otherwise. The concentrated bacteriophage stock was treated with 5 mmol L−1 of MgCl2 and 1.0 µL each of RNase A (Promega, Australia) and DNase I (Promega, Australia) to a final concentration of 10 µg mL−1. The solution was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes to digest extraneous DNA or RNA. Polyethylene glycol 8000 (PEG) at 10% [W/V] and sodium chloride (NaCl at 1 g L−1) were added to the mixture and incubated overnight. The solution was centrifuged at 12000 × g for 5 minutes and pellets resuspended in 50 µL nuclease-free water (Promega, Australia). Bacteriophage proteins were digested by the addition of Proteinase K (50 µg mL−1), EDTA (20 mmol L−1) and sodium dodecyl sulphate (0.5% (v/v)) and incubating for one hour at 55 °C. An equal volume of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (29:28:1) was then added to separate viral DNA from proteins. The mixture was gently vortexed and then centrifuged at 12000 × g for 10 minutes to isolate the aqueous phase. DNA was precipitated by adding an equal volume of isopropanol and incubating overnight at −20 °C. The DNA pellet was collected by centrifugation at 12000 × g for 5 minutes. The DNA pellet was washed in 70% ethanol, air-dried and finally resuspended in 30 µL of nuclease-free water (Promega, Australia).
Whole genome sequencing and in-silico analysis
Nextera® XT DNA sample preparation kits were used to prepare DNA libraries according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Illumina, Australia). The libraries were sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq® using a MiSeq® V2 reagent kit (300 cycles) with 150 basepair (bp) paired end reads. Sequence reads were assembled de novo using Geneious software version 11.0.5. Gene prediction was achieved by predicting open reading frames (ORFs) using ATG, GTG, and TTG start codons with a minimum nucleotide length of 50 bp. The ORFs were translated using Geneious and analysed by BLASTP (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) to ascribe potential function. The genome was further examined for the presence of transfer RNA (tRNA) and transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA) using ARAGORN33 and tRNAscan-SE 2.034. Whole genome alignments and phylogenetic tree construction were performed in CLC genomics workbench version 9.5.4 by UPGMA algorithm with 1,000 replicate bootstrapping. The alignment included whole genomes of FNU1 and other bacteriophages specific for oral bacteria obtained from the NCBI Genbank.
Biofilm growth and quantification
Biofilm experiments were conducted anaerobically using BHI broth (Oxoid, Australia) supplemented with 0.5% cysteine, 0.5% haemin and 0.5% glucose in 96 well polystyrene plates (Greiner bio-one, Australia) coated with 0.5% gelatin. F. nucleatum was cultured for 48 hours and 100 µL of approximately 1 × 108 CFU mL−1 of F. nucleatum in exponential growth phase was added to each well before an equal volume of broth was added. The inoculated plates were incubated at 37 °C under anaerobic conditions and shaking at 120 rpm (Ratek Medium Orbital shaking incubator) for 4 days with sterile broth replenishment after 48 hours. To each well, 10 µL of bacteriophage FNU1 at 1011 PFU/mL was added after 4 days of biofilm formation. The biofilms were then incubated for a further 24 hours anaerobically at 37 °C before quantification assays completed as described previously35. Briefly, planktonic cells were washed off gently using MilliQ® deionised water (Merck, Australia) and the attached cells air dried. The attached biomass was then stained with 200 µL of 0.1% crystal violet for 5 minutes, washed using deionised water and air-dried for 5 minutes. An equal volume of ethanol (70%) was added to each well to decolourise the stained attached cells and the absorbance of the crystal-violet stained ethanol was evaluated at a wavelength of 600 nm (OD600) using a FlexStation 3 plate reader (Molecular Devices, United States).
Biofilm viability analysis
To test for viability, the F. nucleatum biofilm was grown on gelatin-coated microscope slides in the same manner as in the 96 well plates described above. SYBR gold® and Propidium Iodide (PI) were used to stain nucleic acids of live (membrane intact) and dead (membrane compromised) cells, respectively. Propidium Iodide (3 µL) was added to 100 µL of SYBR gold ® diluted (1:100) in dimethyl sulfoxide (Sigma, Australia). The mixture was applied to the biofilm on slides and incubated for 30 minutes. Excess PI and SYBR gold ® were rinsed off and slides air-dried before mounting with 5 µL Vectorshield® (Burlingame, USA) and coverslips. The slides were examined using an Olympus Fluoview Fv10i-confocal laser-scanning microscope (Olympus Life Science, Australia) with excitation wavelength at 485 nm. Green emission at fluorescence 535 nm and Red emission at fluorescence 635 nm were measured to indicate live versus dead cells on the slides.
Statistical analysis
The absorbance values quantifying the biofilms were analysed for normality using the Shapiro Wilk test and the medians compared by a paired T-test. The p-values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS version 25).
Results
Isolation and phenotypic characterisation of F. nucleatum bacteriophage FNU1
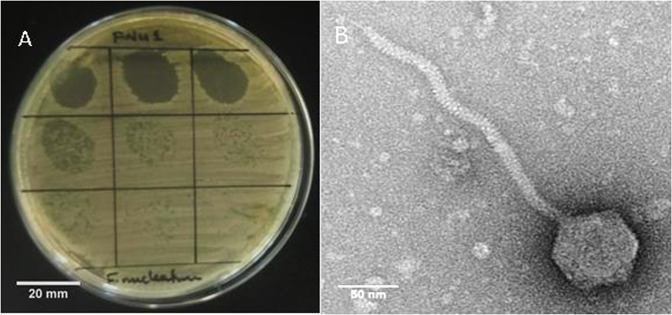
One mouthwash sample was found to produce clear plaques on 1% BHI agar. This was not observed on BHI with 1.5% agar. On the less concentrated 1% agar, clear round plaques of approximately 1 mm diameter were seen (Fig. 1A). The host range of FNU1 was restricted to F. nucleatum, and did not extend to other bacteria found in the oral cavity that we tested. TEM revealed a Siphoviridae bacteriophage with an icosahedral head of ≈88 nm in diameter and a long flexible tail terminating in a spike (Fig. 1B). The tail was approximately 310 nm long and ≈10 nm wide with a spike at the end, measuring an average of ≈20 nm long and ≈5 nm wide on the widest section.
Figure 1.
(A) Bacteriophage FNU1 spotted onto F. nucleatum culture on BHI with 1% agar. From the top left to the bottom right, each square represents a 10-fold serial dilution of FNU1. Clearing is seen at the highest concentrations with individual plaques discernible at subsequent dilutions. Each single plaque is ≈1 mm diameter. (B) TEM image of FNU1 revealing Siphoviridae bacteriophage with long ≈310 nm tail and icosahedral head diameter of ≈88 nm.
Genomic analysis
Bacteriophage DNA extraction and sequencing was performed on three separate occasions. On all occasions, a single contig of 130914 bp was obtained with coverage ranging from 121 to 2400 times. The process was repeated to ensure accuracy and because the sequence generated displayed low homology to any known bacteriophage or other genomes present in the database. The FNU1 bacteriophage genome (NCBI Genbank Accession Number: MK554696) was composed of 178 predicted ORFs of which 30.34% (54/178) had no significant homology to any sequences in the Genbank database and 38.20% (68/178) had some similarity but with E values of less than 1e-4. Of the remaining genome for bacteriophage FNU1, 31.46% (56/178 ORFs) had significant homology to other sequences, and of these, 71.43% (40/56 ORFs) had conserved domains. The overall GC content was 25.0%. The ORFs, their significant matches and E values are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Putative FNU1 proteins and their homology to published sequences.
| ORF | Coordinates | Size (aa) | Homology to known sequences in NCBI database | % Identity | % Query cover | E0 value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORF1 | 1..1659 | 553 | Gifsy-2 prophage tail fiber protein, partial [Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Newport str. SHSN010] | 55 | 9 | 1.00E − 06 |
| ORF2 | 1770..2267 | 166 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF3 | 2264..2464 | 67 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF4 | 2457..2855 | 133 | Hybrid sensor histidine kinase/response regulator [Pedobacter heparinus] | 47 | 28 | 9.40E + 00 |
| ORF5 | 2857..3399 | 181 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF6 | 3396..4223 | 276 | Nucleotidyltransferase domain-containing protein [Balneola sp.] | 35 | 92 | 2.00E − 29 |
| ORF7 | 4217..4948 | 244 | Hypothetical protein [Bacillus sp.] | 35 | 97 | 2.00E − 35 |
| ORF8 | 4950..5366 | 139 | ComF family protein [Yoonia litorea] | 31 | 38 | 8.30E − 01 |
| ORF9 | 5575..5796 | 74 | rfaE bifunctional protein [Desulfurobacterium thermolithotrophum DSM 11699] | 27 | 60 | 7.60E − 01 |
| ORF10 | 5884..6558 | 225 | Hypothetical protein [Staphylococcus xylosus] | 40 | 91 | 2.00E − 41 |
| ORF11 | 6577..7395 | 273 | Antirepressor [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 39 | 97 | 7.00E − 44 |
| ORF12 | 8220..8831 | 204 | Hypothetical protein [Olleya sp. VCSM12] | 30 | 58 | 8.40E + 00 |
| ORF13 | 8835..9557 | 241 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF14 | 9557..11392 | 612 | Hypothetical protein DRJ01_10315, partial [Bacteroidetes bacterium] | 28 | 77 | 5.00E − 41 |
| ORF15 | 11402..12949 | 516 | Hypothetical protein DRJ01_10320 [Bacteroidetes bacterium] | 29 | 96 | 1.00E − 41 |
| ORF16 | 13878..14297 | 140 | Methyl-CpG-binding domain-containing protein 9 [Cicer arietinum] | 27 | 73 | 7.40E + 00 |
| ORF17 | 14397..15473 | 359 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF18 | 15775..16071 | 99 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF19 | 16073..16444 | 124 | Myosin-IB-like [Plutella xylostella] | 31 | 50 | 8.50E + 00 |
| ORF20 | 16437..16991 | 185 | Hypothetical protein UU59_C0024G0011 [candidate division WWE3 bacterium GW2011_GWE1_41_27] | 26 | 89 | 1.00E + 00 |
| ORF21 | 16988..17623 | 212 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF22 | 17665..18798 | 378 | Type I secretion system permease/ATPase [Mesorhizobium sp. WSM4313] | 44 | 16 | 3.30E + 00 |
| ORF23 | 18866..19642 | 259 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF24 | 19639..20283 | 215 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF25 | 20293..26217 | 1975 | Phage tail tape measure protein, TP901 family, core region [Cetobacterium ceti] | 24 | 26 | 4.00E − 20 |
| ORF26 | 26279..27295 | 339 | Hypothetical protein [Brevibacillus fluminis] | 43 | 12 | 7.90E + 00 |
| ORF27 | 27390..28244 | 285 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium periodonticum] | 42 | 70 | 4.00E − 31 |
| ORF28 | 28300..28674 | 125 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF29 | 29187..32576 | 1130 | DUF1983 domain-containing protein [Rhizobium subbaraonis] | 26 | 13 | 3.00E − 05 |
| ORF30 | 33217..34371 | 385 | Transposase [Fusobacterium sp. CM1] | 84 | 97 | 0.00E + 00 |
| ORF31 | 34498..35637 | 380 | Hypothetical protein [Cetobacterium sp. ZWU0022] | 41 | 43 | 1.00E − 26 |
| ORF32 | 35640..36641 | 334 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF33 | 36653..37438 | 262 | Hypothetical protein AKJ51_02780 [candidate divison MSBL1 archaeon SCGC-AAA382A20] | 25 | 29 | 2.70E + 00 |
| ORF34 | 37551..38327 | 259 | ATP/GTP-binding protein [Streptococcus parasanguinis] | 37 | 96 | 5.00E − 26 |
| ORF35 | 38303..38713 | 137 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF36 | 39575..39889 | 105 | Anaerobic ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase [Fusobacterium perfoetens] | 44 | 90 | 3.00E − 18 |
| ORF37 | 41026..41247 | 74 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF38 | (41608..41883) | 92 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF39 | (42013..42279) | 89 | Homoserine kinase [Fusobacterium sp. CM1] | 47 | 47 | 8.60E + 00 |
| ORF40 | (42455..42775) | 107 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF41 | (43304..43540) | 79 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF42 | (44438..44680) | 81 | Serine–tRNA ligase [Candidatus Daviesbacteria bacterium RIFCSPHIGHO2_01_FULL_37_27] | 40 | 53 | 7.40E + 00 |
| ORF43 | (44816..45196) | 127 | Hypothetical protein [Lactobacillus reuteri] | 48 | 52 | 2.00E − 11 |
| ORF44 | (45315..45611) | 99 | Hypothetical protein [uncultured Mediterranean phage uvMED] | 42 | 65 | 9.00E − 03 |
| ORF45 | (46128..46544) | 139 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF46 | (46574..46885) | 104 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF47 | (46903..47127) | 75 | Hypothetical protein J132_07476 [Termitomyces sp. J132] | 37 | 65 | 6.20E + 00 |
| ORF48 | (47138..47506) | 123 | Alkaline phosphatase [Stackebrandtia nassauensis] | 23 | 75 | 9.20E + 00 |
| ORF49 | (47521..47745) | 75 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF50 | (48158..48322) | 54 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF51 | (48727..49209) | 161 | Anaerobic ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase activating protein [Fusobacterium sp.] | 51 | 91 | 2.00E − 50 |
| ORF52 | (49458..49658) | 67 | No significant similarity found. | |||
| ORF53 | (49670..49996) | 108 | Hypothetical protein DV735_g31 [Chaetothyriales sp. CBS 134920] | 36 | 71 | 7.50E − 01 |
| ORF54 | (50006..50467) | 154 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF55 | (50467..50955) | 163 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF56 | (51137..52471) | 445 | Anaerobic ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase [Fusobacterium perfoetens] | 53 | 98 | 3.00E − 167 |
| ORF57 | (52800..53834) | 345 | GIY-YIG nuclease family protein [Clostridioides difficile] | 42 | 55 | 1.00E − 35 |
| ORF58 | (53905..54813) | 303 | Anaerobic ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase [Fusobacterium varium] | 46 | 98 | 1.00E − 71 |
| ORF59 | (54800.55060) | 87 | Hypothetical protein OFPII_09960 [Osedax symbiont Rs1] | 38 | 51 | 8.30E − 01 |
| ORF60 | (55064..55387) | 108 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF61 | (55384..55851) | 156 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF62 | (56004..56456) | 151 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF63 | (56485..56724) | 80 | Mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 [Drosophila arizonae] | 40 | 53 | 8.50E + 00 |
| ORF64 | (56733..56978) | 82 | Glycosyltransferase [Algoriphagus resistens] | 36 | 59 | 8.10E − 01 |
| ORF65 | (56985..57296) | 104 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF66 | (57298..57597) | 100 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF67 | (58609..58989) | 127 | Outer membrane protein assembly factor BamA [Sutterella parvirubra] | 27 | 62 | 3.40E + 00 |
| ORF68 | (59003..59752) | 250 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium nucleatum] | 33 | 31 | 1.70E − 02 |
| ORF69 | (59754..60326) | 191 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium periodonticum] | 37 | 32 | 8.60E − 01 |
| ORF70 | (60323..60697) | 125 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF71 | (60676..60894) | 73 | ATP-dependent DNA ligase [Rhizophagus irregularis] | 37 | 67 | 5.90E + 00 |
| ORF72 | (60916..61179) | 88 | Hypothetical protein [Desulfobacula toluolica] | 26 | 70 | 5.60E − 01 |
| ORF73 | (61184..61369) | 62 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF74 | (61359..61799) | 147 | Hypothetical protein SAMN05444672_10818 [Bacillus sp. OK838] | 50 | 28 | 2.40E + 00 |
| ORF75 | (61796..62185) | 62 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF76 | (62176..62544) | 123 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF77 | (62560..63000) | 147 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF78 | (63013..63480) | 156 | Molecular chaperone DnaJ [Paenibacillus sp. Soil724D2] | 32 | 91 | 2.00E − 19 |
| ORF79 | (63778..64101) | 108 | DUF1874 domain-containing protein [Defluviitalea phaphyphila] | 57 | 97 | 2.00E − 31 |
| ORF80 | (64133..64306) | 58 | Hypothetical protein HMPREF1127_1046 [Fusobacterium necrophorum subsp. funduliforme Fnf 1007] | 49 | 82 | 1.00E − 07 |
| ORF81 | (64450..64671) | 74 | DNA segregation ATPase FtsK/SpoIIIE, S-DNA-T family [Crenotalea thermophila] | 45 | 56 | 7.10E + 00 |
| ORF82 | (64738..65517) | 260 | Radical SAM protein [Clostridium botulinum] | 49 | 94 | 5.00E − 79 |
| ORF83 | (65598..68396) | 933 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 36 | 6 | 8.80E − 01 |
| ORF84 | (68490..68984) | 165 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium hwasookii] | 41 | 88 | 6.00E − 32 |
| ORF85 | (68984..69172) | 63 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium periodonticum] | 68 | 98 | 3.00E − 22 |
| ORF86 | (69291..69605) | 105 | Hypothetical protein YYE_03786 [Plasmodium vinckei vinckei] | 36 | 62 | 5.20E − 01 |
| ORF87 | (69589..69942) | 118 | Na + /H + antiporter [Porphyromonas sp. oral taxon 279] | 26 | 73 | 3.40E + 00 |
| ORF88 | (69911..70651) | 247 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF89 | (70663..71040) | 126 | Hypothetical protein [Lactobacillus sp. CBA3605] | 33 | 41 | 5.30E + 00 |
| ORF90 | (71042..71473) | 144 | Guanylate-binding protein 6-like [Eptesicus fuscus] | 37 | 48 | 2.90E − 01 |
| ORF91 | (71466..71660) | 65 | Hypothetical protein [Rhodopirellula sp. SWK7] | 43 | 64 | 1.40E + 00 |
| ORF92 | (71647..71922) | 92 | Tyrosine recombinase XerC [Chloracidobacterium thermophilum] | 41 | 47 | 8.60E + 00 |
| ORF93 | (72047..72946) | 300 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF94 | (73058..73651) | 198 | Hypothetical protein CTER_0441 [Ruminiclostridium cellobioparum subsp. termitidis CT1112] | 33 | 43 | 5.50E + 00 |
| ORF95 | (73706..76168) | 821 | Polymerase protein [candidate division WWE3 bacterium GW2011_GWC2_44_9] | 30 | 37 | 3.00E − 28 |
| ORF96 | (76155..77018) | 288 | Guanylate kinase [Emticicia sp. MM] | 39 | 62 | 6.00E − 24 |
| ORF97 | (77327..78076) | 250 | MerR family transcriptional regulator [Bacillus sp. EB01] | 23 | 54 | 1.50E + 00 |
| ORF98 | (78095..78961) | 289 | Fic family protein [Fusobacterium nucleatum] | 38 | 66 | 8.00E − 30 |
| ORF99 | (78937..79356) | 140 | Hypothetical protein BpsS36_00041 [Bacillus phage vB_BpsS-36] | 42 | 94 | 6.00E − 18 |
| ORF100 | (79396..79920) | 175 | Siphovirus Gp157 family protein [Fusobacterium nucleatum] | 51 | 89 | 3.00E − 39 |
| ORF101 | (79933..80406) | 158 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF102 | (80372..80731) | 120 | Hypothetical protein TBLA_0I01080 [Tetrapisispora blattae CBS 6284] | 31 | 66 | 9.50E + 00 |
| ORF103 | (80744..81175) | 144 | O-acetyl-ADP-ribose deacetylase 1-like [Branchiostoma belcheri] | 44 | 98 | 3.00E − 36 |
| ORF104 | (81177..81731) | 185 | Hypothetical protein [Clostridium botulinum] | 34 | 96 | 1.00E − 20 |
| ORF105 | (81819..82436) | 206 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium nucleatum] | 32 | 83 | 2.00E − 13 |
| ORF106 | (82601..83236) | 212 | Hypothetical protein [Clostridium sp. 12(A)] | 49 | 85 | 7.00E − 53 |
| ORF107 | (83330..84430) | 367 | DNA cytosine methyltransferase [Methanobrevibacter ruminantium] | 31 | 98 | 9.00E − 57 |
| ORF108 | (84452..84640) | 63 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF109 | (84691..86247) | 519 | Hypothetical protein FUSO4_11650 [Fusobacterium necrophorum DJ-1] | 49 | 97 | 7.00E − 166 |
| ORF110 | (86400..86783) | 128 | Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase [Erythrobacter gangjinensis] | 40 | 50 | 1.30E − 01 |
| ORF111 | (86773..87030) | 86 | Hypothetical protein ABS80_03590 [Pseudonocardia sp. SCN 72–51] | 33 | 60 | 6.20E − 01 |
| ORF112 | (87053..88336) | 428 | ATP dependent DNA ligase domain protein [Clostridioides difficile] | 37 | 97 | 2.00E − 67 |
| ORF113 | (88329..88946) | 206 | VP1 protein, partial [Coxsackievirus A16] | 33 | 23 | 1.70E + 00 |
| ORF114 | (88947..89186) | 80 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF115 | (89161..89643) | 161 | DNA repair protein MmcB-related protein [Fusobacterium] | 30 | 88 | 1.00E − 15 |
| ORF116 | (89640..89858) | 73 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF117 | (89842..90486) | 215 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 45 | 80 | 1.00E − 41 |
| ORF118 | (90575..91204) | 210 | Hypothetical protein [Adhaeribacter aquaticus] | 25 | 59 | 4.30E + 00 |
| ORF119 | (91309..92733) | 475 | Hypothetical protein [Ralstonia phage RSP15] | 27 | 67 | 2.00E − 25 |
| ORF120 | (92743..93252) | 170 | dUTP diphosphatase [Clostridium bartlettii CAG:1329] | 41 | 99 | 5.00E − 28 |
| ORF121 | (93249..94526) | 426 | Hypothetical protein [Bacillus endophyticus] | 24 | 73 | 8.00E − 26 |
| ORF122 | (94529..95317) | 263 | ORF6N domain-containing protein [Fusobacterium nucleatum] | 43 | 77 | 5.00E − 44 |
| ORF123 | (95417..96418) | 334 | DNA primase (bacterial type) [Chlamydia trachomatis] | 39 | 50 | 1.00E − 18 |
| ORF124 | (96431..97912) | 494 | DNA helicase [Clostridium botulinum] | 29 | 54 | 4.00E − 25 |
| ORF125 | (97909..98334) | 142 | epsC Polysaccharide biosynthesis protein, protein-tyrosine-phosphatase [Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis] | 33 | 52 | 1.90E + 00 |
| ORF126 | (98404..99702) | 432 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF127 | (99709..100146) | 146 | Phage antirepressor [Clostridium innocuum] | 41 | 79 | 4.00E − 22 |
| ORF128 | (100272..100976) | 235 | ATP-binding protein [Peptoniphilus obesi] | 37 | 91 | 2.00E − 38 |
| ORF129 | (100986..101510) | 175 | Hypothetical protein DLH72_04485 [Candidatus Gracilibacteria bacterium] | 36 | 96 | 4.00E − 17 |
| ORF130 | (101497..101679) | 61 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF131 | (101885..102676) | 264 | DNA adenine methylase [Ruminococcus albus] | 39 | 92 | 3.00E − 41 |
| ORF132 | (102741..103346) | 202 | Ribonuclease HI [Fusobacterium russii] | 53 | 99 | 1.00E − 63 |
| ORF133 | (103346..103561) | 72 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF134 | (103545..103769) | 75 | Hypothetical protein K457DRAFT_16159 [Mortierella elongata AG-77] | 40 | 46 | 6.00E + 00 |
| ORF135 | (103871..104125) | 85 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF136 | (104118..104633) | 172 | Hypothetical protein [Selenomonas bovis] | 52 | 25 | 5.00E − 04 |
| ORF137 | (104773..104997) | 75 | Multidrug efflux RND transporter permease subunit [Motiliproteus coralliicola] | 30 | 98 | 5.50E + 00 |
| ORF138 | (104997..105212) | 72 | Peptide ABC transporter substrate-binding protein [Vibrio gangliei] | 38 | 61 | 4.80E + 00 |
| ORF139 | (105199..105858) | 220 | Transcriptional regulator, TetR family [Clostridium sp. MSTE9] | 30 | 37 | 1.60E + 00 |
| ORF140 | (105871..106029) | 53 | Hypothetical protein L915_04856, partial [Phytophthora parasitica] | 46 | 49 | 2.60E + 00 |
| ORF141 | (106133..106942) | 270 | Prohibitin family protein [Fusobacterium periodonticum] | 77 | 99 | 3.00E − 150 |
| ORF142 | (106942..107316) | 125 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 48 | 37 | 1.40E + 00 |
| ORF143 | (107317..107580) | 88 | Type II toxin-antitoxin system HipA family toxin [Prevotella sp. ICM33] | 29 | 75 | 5.20E + 00 |
| ORF144 | (107584..108336) | 251 | Hypothetical protein [Corynebacterium matruchotii] | 52 | 98 | 2.00E − 89 |
| ORF145 | (108336..108842) | 169 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium nucleatum] | 50 | 33 | 1.00E − 06 |
| ORF146 | (108939..109391) | 151 | Furin-1 precursor [Schistosoma japonicum] | 32 | 53 | 9.00E − 02 |
| ORF147 | (109396..109905) | 170 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF148 | (109906..110742) | 279 | Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase [Agrococcus casei] | 29 | 97 | 3.00E − 13 |
| ORF149 | (110730..111284) | 185 | Hypothetical protein A2Y22_00670 [Clostridiales bacterium GWD2_32_59] | 27 | 74 | 5.00E + 00 |
| ORF150 | (111332..111955) | 208 | TPA: tRNA (adenine-N(6)-)-methyltransferase [Candidatus Gastranaerophilales bacterium HUM_13] | 39 | 92 | 3.00E − 40 |
| ORF151 | (112023..114062) | 680 | AAA family ATPase [Pseudodesulfovibrio profundus] | 28 | 75 | 4.00E − 29 |
| ORF152 | (114111..115580) | 490 | Hypothetical protein [Clostridium botulinum] | 37 | 85 | 1.00E − 69 |
| ORF153 | 115966..116148 | 61 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF154 | 116254..116772 | 173 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF155 | 116783..117202 | 140 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF156 | 117202..117636 | 145 | Heparinase [Paenibacillus macerans] | 33 | 37 | 4.20E + 00 |
| ORF157 | 117630..117812 | 61 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF158 | 117915..118142 | 76 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF159 | 118123..119262 | 380 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium mortiferum] | 68 | 31 | 4.00E − 40 |
| ORF160 | 119268..119579 | 104 | Glycosyltransferase [Kingella kingae] | 35 | 62 | 7.00E + 00 |
| ORF161 | 119675..119983 | 103 | Hypothetical protein [Streptococcus sobrinus] | 35 | 86 | 5.00E − 15 |
| ORF162 | 119997..120386 | 130 | Hypothetical protein [Streptococcus oralis] | 32 | 46 | 3.20E − 02 |
| ORF163 | 120534..120965 | 144 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium periodonticum] | 33 | 84 | 3.00E − 10 |
| ORF164 | 120975..121694 | 240 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF165 | 121708..122073 | 122 | TonB-dependent receptor [Mucilaginibacter sp. OK098] | 31 | 87 | 3.70E + 00 |
| ORF166 | 122070..124286 | 739 | Metallophosphoesterase [Leptotrichia hofstadii] | 49 | 99 | 0.00E + 00 |
| ORF167 | 124339..124518 | 60 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF168 | 125623..125841 | 73 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF169 | 125880..126119 | 80 | Glutaredoxin [Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. nucleatum] | 56 | 78 | 8.00E − 17 |
| ORF170 | 126477..126656 | 60 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF171 | 126614..126901 | 96 | HU family DNA-binding protein [Neisseria weaveri] | 44 | 93 | 5.00E − 17 |
| ORF172 | 127245..128036 | 264 | ORF6N domain-containing protein [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 73 | 46 | 3.00E − 58 |
| ORF173 | 128097..128273 | 59 | No significant similarity found | |||
| ORF174 | 128354..129103 | 250 | Hypothetical protein CANCADRAFT_31211 [Tortispora caseinolytica NRRL Y-17796] | 33 | 23 | 9.00E + 00 |
| ORF175 | 129197..129547 | 117 | DUF1353 domain-containing protein [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 47 | 76 | 6.00E − 21 |
| ORF176 | 129564..129980 | 139 | Hypothetical protein [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 39 | 90 | 2.00E − 23 |
| ORF177 | 129980..130537 | 186 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase [Fusobacterium necrophorum] | 44 | 95 | 1.00E − 36 |
| ORF178 | 130553..130858 | 102 | Hypothetical protein [Aeromonas enteropelogenes] | 40 | 50 | 1.40E + 00 |
Functional genomics predictions were mapped using the Geneious software 11.0.5 (Fig. 2) with putative structural genes (pink), putative DNA manipulation genes (green), putative regulatory genes (blue), putative lytic genes (red) and hypothetical genes (yellow) marked. Although the majority of genes couldn’t be assigned functionality, a pattern of clustering of related genes was observed (Fig. 2). Putative structural genes appeared to be orientated in a clockwise direction while the rest were orientated anticlockwise. The putative structural genes were interspaced with putative lysis and regulatory genes, as well as other genes that have no known functionality or homology located between sites 1 and 40000 bp in the genome map (Fig. 2). The genes in anticlockwise orientation were comprised mostly of putative DNA manipulation genes located between sites 65000 and 130000 bp in the genome map (Fig. 2) that may be involved in the infection and packaging processes, as well as a cluster of putative lysis genes (located between 45000 and 55000 bp).
Figure 2.
FNU1 functional genome map with putative structural genes (pink), putative DNA manipulation genes (green), putative regulatory genes (blue), putative lytic genes (red) and hypothetical genes (yellow) marked. Although majority of genes couldn’t be assigned functionality, a pattern of clustering of related genes was observed. Genes in anticlockwise orientation were comprised mostly of putative DNA manipulation genes (between 65000 and 130000 bp and possibly involved in infection & packaging), as well as cluster of putative lysis genes (between 45000 and 55000 bp).
tRNAs and tmRNAs in the F. nucleatum bacteriophage FNU1 genome
There were six putative tRNAs identified using ARAGON and tRNAscan-SE 2.0. These included five that did not have any introns and one with a C-loop intron. The tRNA with a C-loop intron was a histidine-tRNA of 74 bp and GC content of 43.2%. The other five introns included an isoleucine-tRNA (91 bp, GC = 36.3%), a proline-tRNA (76 bp, GC = 47.4%), a serine-tRNA (87 bp, GC = 43.7%), a tyrosine-tRNA (89 bp, GC = 40.4%) and a cysteine-tRNA (74 bp, GC = 37.8). All introns were in a single cluster located at 44553 bp to 45210 bp in the genome (Fig. 2). No tmRNA genes were found in the FNU1 genome sequence.
Putative bacteriophage FNU1 defence against bacterial anti-phage systems
Conserved protein family (Pfam) prediction on BLASTp analysis indicated there were 13 ORFs with predicted Pfam domains that may be involved in bacteriophage FNU1 evading host immunity (Table 2). These included at least three genes each putatively encoding antirepressors, methylation genes and toxin-antitoxin systems. According to the CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) database (http://crispr.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/)36, no CRISPR regions were found in the phage FNU1 genome.
Table 2.
Putative phage defence mechanisms against bacterial anti-phage immunity.
| ORF | Coordinates | Protein family | Pfam | E- value | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORF10 | 5884..6558 | Phage regulatory protein Rha (Phage_pRha) (N-terminal) | 09669 | 2.95E-22 | Phage regulatory proteins usually found in temperate phages and bacterial prophage regions and include rha genes that interfere with bacterial infection in strains that lack integration host factor [52] |
| ORF10 | 5884..6558 | ORF6C domain (C-terminal) | 10552 | 1.14E-13 | Antirepressor protein [52] |
| ORF11 | 6577..7395 | Phage antirepressor protein KilAC domain | 03374 | 9.63E-29 | Antirepressor protein [52] |
| ORF27 | 27390..28244 | Phage antirepressor protein KilAC domain | 03374 | 8.61E-18 | Antirepressor protein [52] |
| ORF34 | 37551..38327 | AAA domain, putative AbiEii toxin | 13304 | 7.61E-05 | Type IV toxin antitoxin system that may be part of the abortive phage resistance TA system [53] |
| ORF82 | (64738..65517) | Radical SAM superfamily | 04055 | 2.25E-09 | Radical SAM proteins catalyse different reactions from unusual methylations, isomerisation, sulphur insertion, ring formation, anaerobic oxidation and protein radical formation[54] |
| ORF98 | (78095..78961) | Fic/DOC family | 02661 | 5.54E-11 | This family consists of the Fic (Filamentation Induced by cAMP) protein and DOC (death on curing) proteins. The Fic protein is involved in the regulation of cell division via folate metabolism. DOC will cure bacterial cells of prophage and also target protein synthesis machinery and inducing a reversible growth arrest. This arrest can be reversed by its antitoxin partner Phd (prevents host death) [55] |
| ORF100 | (79396..79920) | Siphovirus Gp157 | 05565 | 1.79E-33 | Bacteria that contain genes coding siphovirus GP157, a protein of Streptococcus thermophiles SFi phages are thought to have an increased resistance to phage infection[56] |
| ORF107 | (83330..84430) | C-5 cytosine-specific DNA methylase | 00145 | 4.45E-49 | These enzymes specifically methylate the C-5 carbon of cytosines in DNA to produce C5-methylcytosine [57] |
| ORF127 | (99709..100146) | Phage antirepressor protein KilAC domain | 03374 | 3.69E-07 | An antirepressor protein[52] |
| ORF131 | (101885..102676) | D12 class N6 adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase | 02086 | 5.16E-04 | These enzymes will specifically methylate the amino group at the C-6 position of adenines in DNA [58] |
| ORF132 | (102741..103346) | Caulimovirus viroplasmin (N - Terminal) | 01693 | 3.89E-04 | These form the main components of viral inclusion bodies where viral assembly, DNA synthesis and accumulation takes place [59] |
| ORF159 | 118123..119262 | Phage regulatory protein Rha (Phage_pRha) (N-terminal) | 09669 | 2.28E-04 | Phage regulatory proteins that are usually found in temperate phages and bacterial prophage regions and include rha gens that interferes with bacterial infection in strains that lack integration host factor.[52] |
| ORF159 | 118123..119262 | Phage antirepressor protein KilAC domain (C - Terminal) | 03374 | 2.68E-15 | Antirepressor protein [52]. |
| ORF172 | 127245..128036 | ORF6N domain (N-terminal) | 10543 | 1.23E-16 | Antirepressor protein [52]. |
| ORF172 | 127245..128036 | Phage antirepressor protein KilAC domain (C - Terminal) | 03374 | 1.52E-18 | Antirepressor protein [52]. |
Phylogenetic relatedness with other bacteriophage targeting oral bacteria
The genome of bacteriophage FNU1 showed little homology to any bacteriophage deposited in NCBI Genbank. To understand the relatedness of FNU1 to other bacteriophages, a phylogenetic tree was constructed. Whole genomes of bacteriophages targeting oral bacteria were downloaded from NCBI Genbank and compared with FNU1 as they are found in the same microenvironment. Bacteriophage FNU1 was found to be most closely related to Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus spp. bacteriophages (Fig. 3). The only F. nucleatum bacteriophage genome in the database is the prophage ΦFunu1, which is phylogenetically distant from FNU1, sharing very little genetic homology. ΦFunu1 branches off earlier in the phylogenetic tree and is most closely related to P1, a bacteriophage for Lactobacillus plantarum and the bacteriophage ΦEf11 for Enterococcus faecalis (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of FNU1 in relation to other bacteriophages associated with oral bacteria. FNU1 was most closely related to Streptococcus mutans and other Streptococcus spp. bacteriophages.
Effect of bacteriophage FNU1 on F. nucleatum biofilm mass
To evaluate the potential application of bacteriophage FNU1 in the treatment of gastro-intestinal biofilms, a biofilm model of F. nucleatum was generated as described above. The median [Inter-Quartile Range (IQR)] absorbance at OD600 of the biofilm without bacteriophage treatment was 2.17 (1.81–2.21). This was significantly higher (p < 0.001) than that following FNU1 bacteriophage treatment for 24 h, where median (IQR) was 0.76 (0.71–0.89), or 35% of the untreated value (Fig. 4). The bacteriophage treated biofilm had a significantly higher absorbance (p < 0.001) compared to the negative control (no bacteria control): median (IQR) absorbance at OD600 of the negative control was 0.14 (0.14–0.15) (Fig. 4). Subtracting absorbance readings for the negative control (0.14) from both the treated (0.76) and untreated (2.17) biofilms results in untreated biofilms having an OD of 2.03 and treated biofilms having an OD of 0.62. Therefore, FNU1 phage treatment results in a 70% reduction in F. nucleatum biomass.
Figure 4.
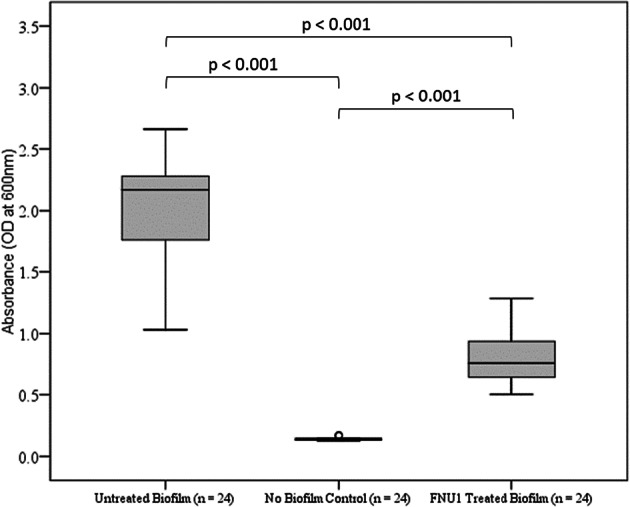
Significant reduction of Fusobacterium nucleatum biofilm treated with FNU1 bacteriophage.
Viability of the F. nucleatum biofilm after treatment with bacteriophage FNU1
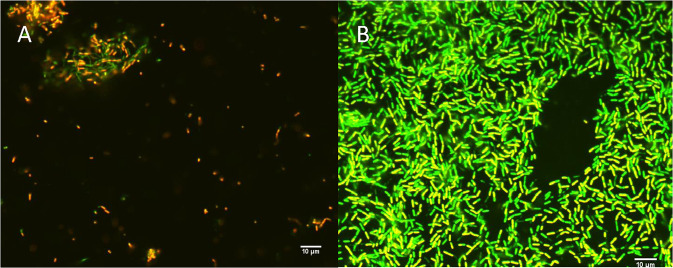
To evaluate the viability of F. nucleatum in the biofilms following treatment with bacteriophage FNU1, live/dead staining using SYBR® gold and propidium iodide was applied to biofilms formed on microscope slides and imaged using confocal microscopy. The untreated biofilm had predominantly green fluorescent cells, indicating structurally intact membranes. The bacteriophage treated biofilm showed few cells, most of which were red/yellow, indicating structurally compromised membranes, and only very few cells with intact membranes (green) in clumps (Fig. 5).
Figure 5.
Confocal images of SYBR® gold and propidium iodide staining following FNU1 bacteriophage treated (A) and untreated (B) Fusobacterium nucleatum biofilm.
Discussion
The novel bacteriophage FNU1 genome is over 130 kb in length and displays little homology to other known viral genomes. Because of this, it is difficult to describe any potential synteny between FNU1 and other bacteriophage genomes, although organisational similarity to some of the more abundant bacteriophages found in the human gut exists, where the structural and infection/packaging genes are in opposite orientation to each other37. The relatively large genome and structure of the virus, with a capsid of approximately 90 nm diameter and tail of over 300 nm in length, may have contributed to the fact that it was only able to produce clear discernible plaques when the concentration of agar it was grown on was reduced from 1.5% to 1%. The presence of several tRNAs in the FNU1 genome may indicate the requirement for additional translational mechanisms to complement those provided by the host cell. In its phylogeny, bacteriophage FNU1 clusters more closely to several bacteriophages against the oral pathogen S. mutans, and distantly from the only F. nucleatum bacteriophage in the database, the prophage ΦFunu1.
FNU1 has almost 8% of its ORFs devoted to putative defence against bacterial anti-bacteriophage systems, with several genes each coding for putative antirepressors, methylation genes to avoid restriction modification and toxin-antitoxin mechanisms that may prevent abortive infections. While some bacteriophages such as Vibrio cholerae ICP1 are known to carry CRISPR sequences which may contribute to their virulence38, the FNU1 genome had no such recognisable regions. All the F. nucleatum strains in the CRISPR database (http://crispr.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/)36 have one CRISPR with the number of spacers ranging from 3 to 52, (average approximately 25 spacers). Porphyromonas gingivalis, the major etiologic agent associated with chronic periodontitis, and for which no lytic bacteriophage has yet been isolated, has very extensive CRISPR immune mechanisms39,40. Each P. gingivalis strain in the database has more than one confirmed CRISPR locus (some with a maximum of five), with the total number of spacers in each bacterial strain ranging from 14 to 136 (http://crispr.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/). This contrasts with C. acnes strains, where none have a confirmed CRISPR locus, (although some are denoted as having possible CRISPR regions based on the database’s algorithms, filtering sequence length, matching repeats and amount of successive repeats)36, and against which there are over 80 reported bacteriophages41.
In this report, we demonstrate the capacity for FNU1 to disrupt established F. nucleatum biofilms. Our results show the capacity of FNU1 to effectively kill cells within a F. nucleatum biofilm, and although not as complex as polymicrobial biofilms shown to develop during periodontitis8,29,42, this work suggests that FNU1 has potential for application in more complex systems. F. nucleatum is one of the late colonisers in oral polymicrobial biofilms. Its capacity to co-aggregate intergenerically with representatives of all oral bacterial species8 indicates it provides the necessary scaffolding for these communities to grow, develop and flourish synergistically. We have previously shown that diverse bacteriophages are able to be formulated into dosage forms such as lozenges and pastes, and subsequently released to kill underlying bacteria in-vitro43. Both of these dosage forms would provide very useful strategies for delivery of bacteriophage such as FNU1 for testing in the treatment of periodontitis and other diseases associated with F. nucleatum, as they allow slower “release” of bacteriophage into the oral cavity, and in the case of toothpastes, can be used to gently massage the bacteriophage onto the tooth and gum surface.
Finally, F. nucleatum has recently been described as an oncobacterium, associated with a range of human cancers4. The organism has a causal role in tumorigenesis12 and also confers resistance to chemotherapy13. In their animal model, Bullman S. et al. demonstrated that treatment with metronidazole, an antibiotic that their F. nucleatum strains were sensitive to, reduced cancer cell proliferation and tumour growth. However, this approach of using antibiotics to kill Fusobacterium may be unsuitable clinically, as it has been previously demonstrated that perturbation of microbiota by antibiotics leads to reduced efficacy of chemoimmunotherapy for a range of cancers, including colorectal cancer44,45. On the other hand, the discovery of FNU1, with capacity to disrupt F. nucleatum biofilms, represents a potentially feasible means of targeted removal of this bacteria for microbiota manipulation in colorectal cancer management. In addition, while it has been suggested that bacteriophages in the gut virome may alter the microbiome such that F. nucleatum is able to overgrow and facilitate neoplasia in colon cells46, bacteriophages such as FNU1 may assist in overcoming such dysbiosis. That bacteriophages can be successfully formulated into suppositories, as we have previously shown32, may assist in delivery.
In conclusion, this work describes the first full genome sequence and functional characterisation of a novel lytic bacteriophage against F. nucleatum, a bacterium associated with periodontitis as well as cancers of the GI tract such as colon cancer. FNU1 is unique in that it shares very little homology with other known bacteriophages. Functionally, FNU1 is capable of breaking down F. nucleatum biofilms and lysing the bacterial cells composing the biofilm. This bacteriophage, then, is able to be tested in more complex oral biofilm assays and could potentially be tested in-vivo to assess capacity to treat periodontitis, as well as possibly assist in colon cancer treatment, following formulation in appropriate dosage forms.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the La Trobe University Bio-imaging facility (La Trobe Institute for Molecular Science) for the TEM images, and the contribution of Elizabeth Chewe to this research.
Author Contributions
J.T. and S.D. designed project, J.T. and M.K. Project development, J.T., S.P., S.D., T.B., and P.L. Technical advice, M.K. and H.K. Sample screening, M.K., T.B. and S.P. Genomics, M.K., L.S. and P.L. Biofilm and Imaging, M.K., J.T., H.T.C. and S.D. Manuscript writing, and M.K., J.T., H.T.C., S.D., T.B. and S.P. Manuscript editing.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
7/13/2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: 10.1038/s41598-023-38412-2
References
- 1.Bolstad AI, Jensen HB, Bakken V. Taxonomy, biology, and periodontal aspects of Fusobacterium nucleatum. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996;9:55–71. doi: 10.1128/CMR.9.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chang Chunrong, Geng Fengxue, Shi Xiaoting, Li Yuchao, Zhang Xue, Zhao Xida, Pan Yaping. The prevalence rate of periodontal pathogens and its association with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2018;103(3):1393–1404. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9475-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yamaoka Y, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum as a prognostic marker of colorectal cancer in a Japanese population. J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:517–524. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brennan Caitlin A., Garrett Wendy S. Fusobacterium nucleatum — symbiont, opportunist and oncobacterium. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2018;17(3):156–166. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0129-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hajishengallis G, Lamont RJ. Beyond the red complex and into more complexity: the polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis (PSD) model of periodontal disease etiology. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012;27:409–419. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2012.00663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hajishengallis G, et al. Low-abundance biofilm species orchestrates inflammatory periodontal disease through the commensal microbiota and complement. Cell Host Microbe. 2011;10:497–506. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bakaletz LO. Developing animal models for polymicrobial diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:552–568. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kolenbrander PE, Palmer RJ, Jr., Periasamy S, Jakubovics NS. Oral multispecies biofilm development and the key role of cell-cell distance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8:471–480. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Blehert D. S., Egland P. G., Foster J. S., Palmer R. J. Communication among Oral Bacteria. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 2002;66(3):486–505. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.66.3.486-505.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kinane DF, Stathopoulou PG, Papapanou PN. Periodontal diseases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17038. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dejea CM, et al. Microbiota organization is a distinct feature of proximal colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:18321–18326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406199111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bullman S, et al. Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic response in colorectal cancer. Science. 2017;358:1443–1448. doi: 10.1126/science.aal5240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yu T, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes Chemoresistance to Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Autophagy. Cell. 2017;170:548–563 e516. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.European Federation of Periodontology. DEBATE: Is it time for a rethink on the use of antibiotics to treat periodontitis?, https://www.efp.org/newsupdate/time-for-a-rethink-on-use-of-antibiotics (2016).
- 15.Dabija-Wolter G, Al-Zubaydi SS, Mohammed MMA, Bakken V, Bolstad AI. The effect of metronidazole plus amoxicillin or metronidazole plus penicillin V on periodontal pathogens in an in vitro biofilm model. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2018;4:6–12. doi: 10.1002/cre2.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lamont RJ, Koo H, Hajishengallis G. The oral microbiota: dynamic communities and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018;16:745–759. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0089-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shaikh HFM, Patil SH, Pangam TS, Rathod KV. Polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis: An overview. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018;22:101–106. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_385_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shlezinger M, et al. Phage Therapy: A New Horizon in the Antibacterial Treatment of Oral Pathogens. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17:1199–1211. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160930145649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Szafranski SP, Winkel A, Stiesch M. The use of bacteriophages to biocontrol oral biofilms. J Biotechnol. 2017;250:29–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Salmond GP, Fineran PC. A century of the phage: past, present and future. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015;13:777–786. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shabbir MA, et al. Bacteria vs. Bacteriophages: Parallel Evolution of Immune Arsenals. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1292. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cochrane K, et al. Complete genome sequences and analysis of the Fusobacterium nucleatum subspecies animalis 7-1 bacteriophage Funu1 and Funu2. Anaerobe. 2016;38:125–129. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2015.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Machuca P, Daille L, Vines E, Berrocal L, Bittner M. Isolation of a novel bacteriophage specific for the periodontal pathogen Fusobacterium nucleatum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:7243–7250. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01135-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Saito Y, et al. Stimulation of Fusobacterium nucleatum biofilm formation by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2008;23:1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2007.00380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sharma G, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm: potential therapeutic targets. Biologicals. 2014;42:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2013.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ribeiro KVG, et al. Bacteriophage Isolated from Sewage Eliminates and Prevents the Establishment of Escherichia Coli Biofilm. Adv Pharm Bull. 2018;8:85–95. doi: 10.15171/apb.2018.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dalmasso M, et al. Isolation of a Novel Phage with Activity against Streptococcus mutans Biofilms. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0138651. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Karpathy SE, et al. Genome sequence of Fusobacterium nucleatum subspecies polymorphum - a genetically tractable fusobacterium. PLoS One. 2007;2:e659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dashper S.G., Shen P., Sim C.P.C., Liu S.W., Butler C.A., Mitchell H.L., D’Cruze T., Yuan Y., Hoffmann B., Walker G.D., Catmull D.V., Reynolds C., Reynolds E.C. CPP-ACP Promotes SnF2 Efficacy in a Polymicrobial Caries Model. Journal of Dental Research. 2018;98(2):218–224. doi: 10.1177/0022034518809088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Turner S, Pryer KM, Miao VP, Palmer JD. Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1999;46:327–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1999.tb04612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gill JJ, Hyman P. Phage choice, isolation, and preparation for phage therapy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010;11:2–14. doi: 10.2174/138920110790725311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brown TL, et al. Characterization and formulation into solid dosage forms of a novel bacteriophage lytic against Klebsiella oxytoca. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0183510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Laslett D, Canback B. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:11–16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lowe TM, Chan PP. tRNAscan-SE On-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W54–57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Merritt, J. H., Kadouri, D. E. & O’Toole, G. A. Growing and analyzing static biofilms. Curr Protoc Microbiol Chapter 1, Unit 1B 1, 10.1002/9780471729259.mc01b01s00 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 36.Grissa I, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C. CRISPRFinder: a web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:W52–57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shkoporov AN, et al. PhiCrAss001 represents the most abundant bacteriophage family in the human gut and infects Bacteroides intestinalis. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4781. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07225-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Seed KD, Lazinski DW, Calderwood SB, Camilli A. A bacteriophage encodes its own CRISPR/Cas adaptive response to evade host innate immunity. Nature. 2013;494:489–491. doi: 10.1038/nature11927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Burmistrz M, et al. Functional Analysis of Porphyromonas gingivalis W83 CRISPR-Cas Systems. J Bacteriol. 2015;197:2631–2641. doi: 10.1128/JB.00261-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Burmistrz M, Pyrc K. CRISPR-Cas Systems in Prokaryotes. Pol J Microbiol. 2015;64:193–202. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0009.2114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Castillo David E., Nanda Sonali, Keri Jonette E. Propionibacterium (Cutibacterium) acnes Bacteriophage Therapy in Acne: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Dermatology and Therapy. 2018;9(1):19–31. doi: 10.1007/s13555-018-0275-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhu Y, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola synergistic polymicrobial biofilm development. PLoS One. 2013;8:e71727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brown Teagan, Petrovski Steve, Chan Hiu, Angove Michael, Tucci Joseph. Semi-Solid and Solid Dosage Forms for the Delivery of Phage Therapy to Epithelia. Pharmaceuticals. 2018;11(1):26. doi: 10.3390/ph11010026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Routy B, et al. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science. 2018;359:91–97. doi: 10.1126/science.aan3706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kuczma MP, et al. The impact of antibiotic usage on the efficacy of chemoimmunotherapy is contingent on the source of tumor-reactive T cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:111931–111942. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hannigan, G. D., Duhaime, M. B., Ruffin, M. T. T., Koumpouras, C. C. & Schloss, P. D. Diagnostic Potential and Interactive Dynamics of the Colorectal Cancer Virome. MBio9, 10.1128/mBio.02248-18 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]