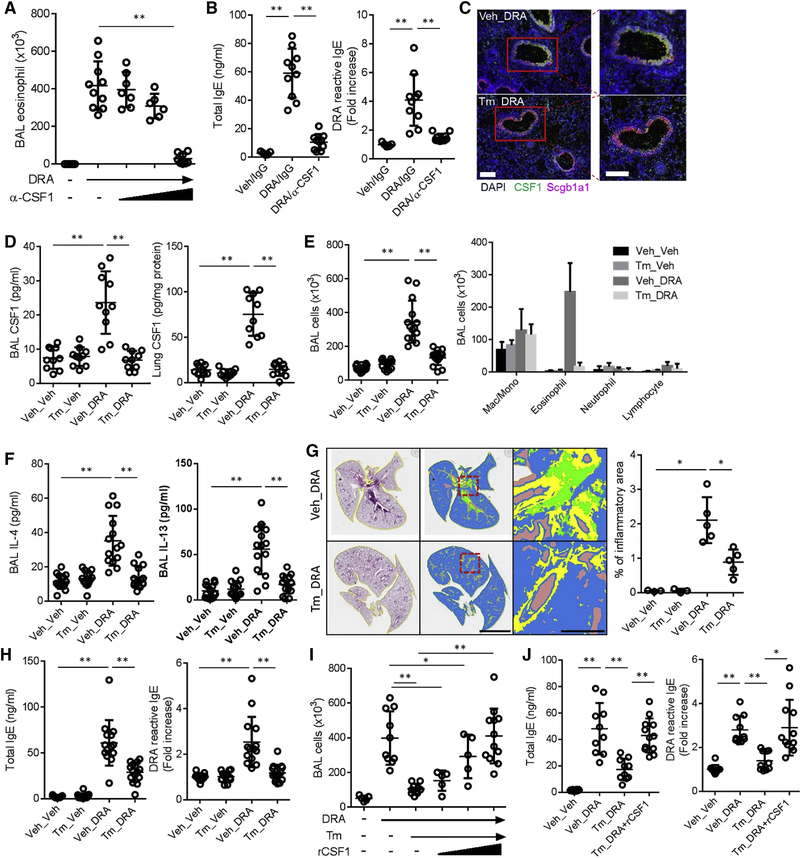
Figure 2. Deletion of CSF1 in airway epithelial cells blocks allergen sensitization and subsequent allergic lung inflammation.
(A & B) Anti-CSF1 neutralizing antibody (α-CSF1 – 1, 10, 100 ng/mouse, i.n) was administered with DRA allergen during the challenge period (n=6–10). The number of eosinophil in BAL and the total and DRA-reactive serum IgE were measured at the end of the DRA protocol. (C-D) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of lung from the Scgb1a1-creERT;Csf1fl/fl mice subjected to the DRA model with tamoxifen (Tm) or vehicle (Veh). Expression of CSF1 (green) was colocalized with Scgb1a1 (magenta) as shown by yellow cells in the merged image (the scale bar = 100μm). CSF1 was measured in BAL fluids and lung lysates. (E-H) Scgb1a1-creERT;Csf1fl/fl mice were injected with either Tm or vehicle for 5 consecutive days (day 0-day4) and subject to the DRA model (n=9–15). Total and differential cell counts and the concentrations of IL-4 and IL-13 were measured in the BAL fluids. The colors in quantification of lung pathology indicate the following, green; inflammatory cells, yellow; area of the airway, brown; void space. Scale bars are 5mm in middle and 500μm in right panels. Total and DRA reactive serum IgE were measured by ELISA. (I & J) Rescue experiment of Tm-injected Scgb1a1-creERT;Csf1fl/fl with recombinant CSF1 (rCSF1 – 0.1, 1 & 10 ng/mouse, i.n) which was co-administered with DRA during challenge period. Data in A & B are pooled data from two independent experiments and data in C-J are representative four independent experiments. *p<.05, **p<.01. Please also see figure S1E–G.