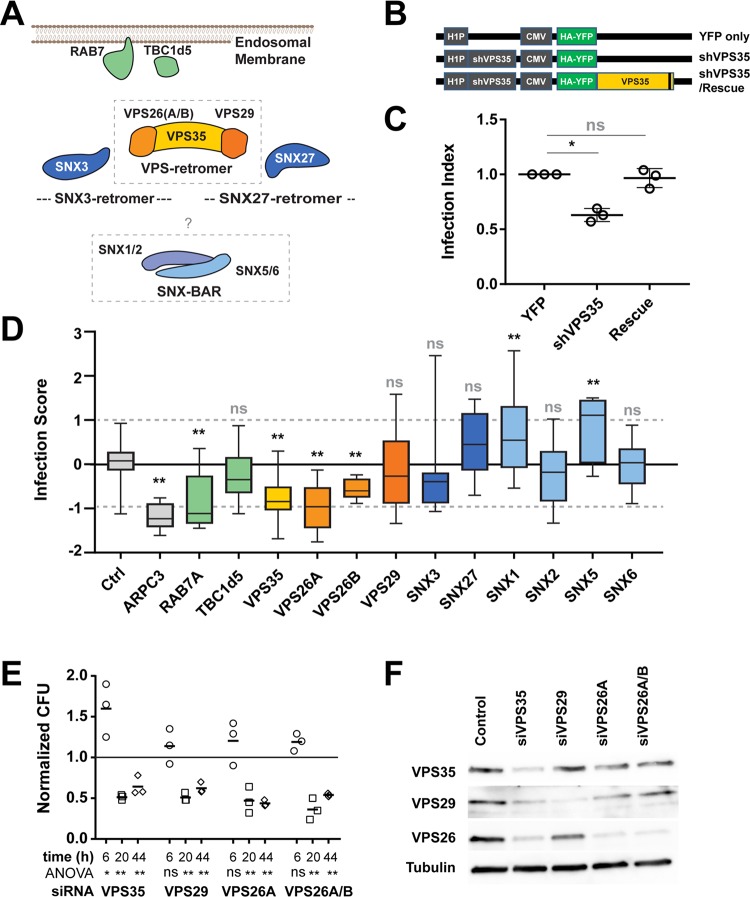
FIG 4.
The VPS retromer is a key component of Brucella intracellular trafficking. (A) Schematic representation of the retromer components and their prominent interactors. (B) Schematic representation of the shRNA constructs used in panel C. The gray box on the shVPS35/rescue construct indicates the silent mutations that prevent base-pairing with the coexpressed shRNA (41). (C) Infection index from transfected cells. Displayed are the averaged infection index and associated standard deviation after 48 h of Brucella infection. Data were normalized to the YFP-only condition (n = 3). Values that are statistically significantly different from the value for the scrambled YPF-only condition as determined by paired t test are indicated by an asterisk (*, P value of ≤0.01; ns, not significant). (D) Dot box representation of the z-scored infection score for components of the retromer and interactors, including the positive-control ARPC3. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences from the values for the scrambled siRNA-treated bacteria (control [Ctrl]) as determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (**, P value of ≤0.001; ns, not significant). (E) Normalized CFU recovered from siRNA-treated cells at 6, 20, or 44 hpi. The presented data correspond to CFU count normalized to control, siRNA-treated cells (n = 3). Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (*, P ≤ 0.01; **, P ≤ 0.001; ns, not significant). (F) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins in total lysate of HeLa cells treated with siRNA targeting the designated genes, 72 h posttransfection. Displayed is a representative example of an experiment performed in biological triplicate (n = 3). See Table S4 for the matching averaged intensity quantification.