Abstract
Aims
Diabetic patients have multiple risk factors for colonisation with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a nosocomial pathogen associated with significant morbidity and mortality. This meta-analysis was conducted to estimate the prevalence of MRSA among diabetic patients.
Methods
The MEDLINE, Embase, BIOSIS, and Web of Science databases were searched for studies published up to May 2018 that reported primary data on the prevalence of MRSA in 10 or more diabetic patients. Two authors independently assessed study eligibility and extracted the data. The main outcomes were the pooled prevalence rates of MRSA colonisation and infection among diabetic populations.
Results
Eligible data sets were divided into three groups containing data about the prevalence of MRSA colonisation or in diabetic foot or other infections. From 23 data sets, the prevalence of MRSA colonisation among 11577 diabetics was 9.20% (95% CI, 6.26–12.63%). Comparison of data from 14 studies that examined diabetic and non-diabetic patients found that diabetics had a 4.75% greater colonisation rate (P < 0.0001). From 41 data sets, the prevalence of MRSA in 10994 diabetic foot infection patients was 16.78% (95% CI, 13.21–20.68%). Among 2147 non-foot skin and soft-tissue infections, the MRSA prevalence rate was 18.03% (95% CI, 6.64–33.41).
Conclusions
The prevalence of MRSA colonisation among diabetic patients is often higher than among non-diabetics; this may make targeted screening attractive. In the UK, many diabetic patients may already be covered by the current screening policies. The prevalence and impact of MRSA among diabetic healthcare workers requires further research. The high prevalence of MRSA among diabetic foot infections may have implications for antimicrobial resistance, and should encourage strategies aimed at infection prevention or alternative therapies.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s00592-019-01301-0) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Diabetes, Diabetic patients, Meta-analysis, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, Prevalence, Resistance
Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus infections can be classified as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA). Individuals colonised with MRSA are typically asymptomatic; however, if the bacterium breaches the patient’s physical defences, infection can occur. The economic and clinical burden of MRSA is significant, with high rates of morbidity and mortality and increased hospital costs associated with MRSA compared to MSSA [1, 2]. Risk factors which increase susceptibility to MRSA colonisation include recent exposure to antimicrobial agents, sustained hyperglycaemia associated with diabetes mellitus (diabetes), hospitalisation within the past year, skin or soft-tissue infection (SSTI) on admission, and human immunodeficiency virus type one (HIV) infection [3]. Independently, MRSA colonisation has been associated with an increased risk of MRSA infection [4]. Certain patient groups, therefore, have multiple risk factors and a significantly increased susceptibility to MRSA colonisation and infection. These include, but are not limited to, patients with diabetes mellitus (diabetics), HIV-positive individuals, and haemodialysis patients [5, 6].
Diabetes is the most common metabolic disease in the world, and the global number of diabetics is predicted to rise from 382 million in 2013 to 592 million in 2035 [7]. Diabetes may be complicated by foot disease. In Scotland, 4.7% of diabetics are recorded as having had a foot ulcer and 0.7% as having had a lower limb amputation [8]. It has been estimated that, in England, approximately £1 of every £140 spent by the NHS goes towards the cost of caring for ulceration or amputation, and that the cost of treating diabetic foot is greater than that for any of the four most common cancers in the UK [9]. Gram-positive organisms are commonly identified from diabetic foot infections (DFIs), with S. aureus among those most commonly isolated. A 2010 systematic review of the prevalence of MRSA in diabetic foot infections estimated the prevalence to be 15–30% [10].
The rising prevalence of diabetes, predominantly in low- and middle-income countries, is occurring against the backdrop of globally increasing rates of antimicrobial resistance. Knowledge of the prevalence of colonisation or infection of diabetic patients by resistant pathogens, including MRSA, will therefore be important in assessing the extent to which interventions targeted towards diabetic patients may mitigate the spread of resistant pathogens.
Several meta-analyses have examined the prevalence of MRSA in high-risk populations, such as haemodialysis patients, HIV-positive patients and general, neonatal or paediatric intensive-care patients [5, 6, 11, 12]. However, to date, no meta-analysis has examined the prevalence of MRSA in diabetic patients. Therefore, the aim of this meta-analysis was to use studies of any design which reported data for 10 or more patients to estimate the prevalence of MRSA in diabetic patients.
Methods
Search strategy
Four electronic databases were searched for articles published up to 16 May 2018: EMBASE (1980–2018), Ovid MEDLINE® Epub Ahead of Print, In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE® Daily, Ovid MEDLINE and Versions® (1946–2018), Web of Science and the BIOSIS Citation Index (1926–2018). The Web of Science Core Collection Citation Indexes searched were: Science Citation Index Expanded (1900–2018), Conference Proceedings Citation Index- Science (1990–2018), Book Citation Index– Science (2005–2018) and the Emerging Sources Citation Index (2015–2018). The search was performed using the following terms: (“me??icillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus” OR “MRSA” OR “?A-MRSA”) AND (“diabetes” OR “DFI” OR “diabetic foot” OR “diabetes mellitus type” OR “non?insulin dependent diabetes” OR “insulin?dependent diabetes” OR “?IDDM”) AND (“prevalence” OR “incidence” OR “epidemiology” OR “frequency” OR “occurrence” OR “rate” OR “predict*”). In Ovid, these terms were followed by the suffix ‘.mp.’ and they were searched as topics in Web of Science. Further articles were obtained using reference lists from a review article [10] and manual searching [13, 14]. A study protocol was not published prior to this study.
Study selection criteria
All studies underwent title and abstract screening, eligible studies met the following criteria: (1) the patients had been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and were colonised or infected with MRSA; (2) the study reported primary patient data on the prevalence of MRSA in 10 or more patients; (3) the study was published in the English language. There were no limitations on study date or type. Eligible studies were accessed in full-text to ensure that they fulfilled the inclusion criteria and provided sufficient data for the meta-analysis. Studies which could not be accessed in full-text, including presentation abstracts, were excluded; their authors were not contacted. MRSA prevalence data can be reported in terms of positive isolates or ulcers (potentially multiple per patient) and/or patients. For clarity, only studies which reported the prevalence of MRSA in terms of patient numbers were included. Title and abstract and full-text screening were performed independently by two authors (HJS and JDJ), with discrepancies resolved by consensus. Deduplication was performed using Endnote (version X8.0.1) and Zotero (version 5.0.47). This review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines [15], and a PRISMA checklist completed (see additional file one).
Data extraction and critical appraisal
The following information was extracted from each study: author(s), year of publication, country, study design, study setting, study population size, and number of MRSA-positive patients, whether the study reported on MRSA colonisation or infection and the type of infection.
All eligible studies were critically assessed using a modified Joanna Briggs Institute checklist for prevalence studies [16]. Publication bias was assessed using funnel plots. Funnel plots of sub-group analyses were not used to assess for publication bias, as funnel plot reliability decreases with fewer studies, particularly below ten [17].
Statistical analysis
Random-effects meta-analyses were used throughout to calculate the pooled prevalence of MRSA in a given population with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). Study heterogeneity was assessed by the I2 statistic, reported with 95% CIs, and interpreted as low (≤ 25%), moderate (25–75%), or high (≥ 75%) [18]. All meta-analyses were carried out using MedCalc statistical software, version 18.0 (MedCalc Software, Ostend, Belgium). The significance of proportions was compared using the MedCalc N-1 Chi-squared calculator [19].
Results
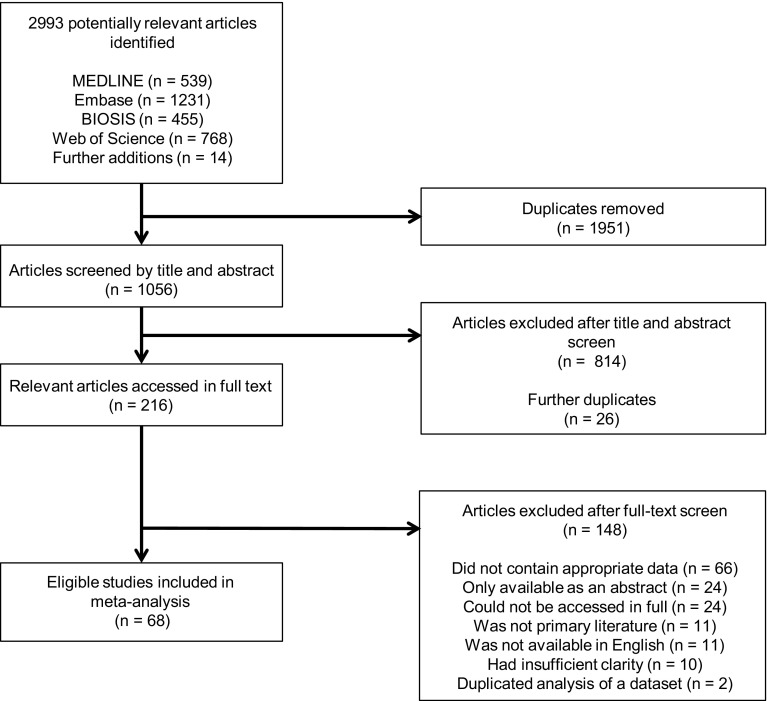
After deduplication, systematic searching yielded 1056 articles published between March 1985 and May 2018. An additional 14 manuscripts were identified from a review article (n = 12) and manual searching [10, 13, 14]. Title and abstract screening identified 216 eligible articles, 148 of which were subsequently excluded after full-text screening. Articles were excluded, because they did not contain appropriate data (n = 66), were only available as an abstract (e.g. poster, presentation; n = 24), could not be accessed in full (n = 24), were not primary literature (n = 11), were not available in English (n = 11), had insufficient clarity for data extraction (n = 10), or duplicated analysis of another data set (n = 2). The study selection process is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of study selection
A total of 68 studies were eligible for inclusion. Six studies contained two prevalence data sets; four contained data regarding the prevalence of MRSA in the nares and ulcers of diabetic foot infection (DFI) patients, another contained MRSA prevalence data for DFI and other SSTI patients, and another data regarding nasal colonisation or unspecified infection with MRSA among diabetic patients. There was, therefore, a total of 74 eligible data sets (Table 1). The data sets were categorised for subsequent meta-analysis: those with data about the prevalence of MRSA among DFIs (41/74), necrotizing fasciitis (NF) and other skin and soft-tissue infections (7/74), infections of unspecified source (3/74), and those with colonisation prevalence data (23/74). While critical appraisal of eligible studies highlighted shortcomings in reporting, it did not reveal further grounds to exclude any studies (see additional file two).
Table 1.
Eligible data sets
| Study | Study design | Study date(s) | Country | Setting | Mean age | % Male | Study population | MRSA + | % | 95% CIs | Col/Inf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldstein et al. 1996 [55] | P cohort | 1993–1994 | USA | Ipat | NR | 68 | 25 | 5 | 20.0 | 6.83–40.70 | DFI |
| Tentolouris et al. 1999 [57] | Retro | NR | UK | Opat | 61.5 | NR | 75 | 12 | 16.0 | 8.55–26.28 | DFI |
| El-Tahawy 2000 [51] | Retro | 1997–1999 | Saudi Arabia | Ipat | NR | 57 | 111 | 9 | 8.12 | 3.78–14.83 | DFI |
| Saxena et al. 2002 [32] | P cohort | 1996–1999 | Saudi Arabia | Ipat (HD) | 47.5* | 45.7* | 58 | 12 | 20.69 | 11.17–33.35 | Col (N) |
| Ge et al. 2002 [54] | RCT | NR | USA | Opat | NR | NR | 812 | 37 | 4.56 | 3.23–6.23 | DFI |
| Von Baum et al. 2002 [36] | P cohort | 1999–2002 | Germany | Com (NH) | 81.2* | 29.5* | 328 | 5 | 1.52 | 0.50–3.52 | Col (N) |
| Dang et al. 2003 [49] | Retro | 2000–2001 | UK | Opat | NR | NR | 63 | 19 | 30.16 | 19.23–43.03 | DFI |
| Hartemann-Heurtier et al. 2004 [56] | P cohort | NR | France | Ipat | 65 | 75 | 180 | 29 | 16.11 | 11.06–22.31 | DFI |
| Lipsky et al. 2005 [59] | P cohort | 1999–2001 | Int | Ipat | 61.5 | 54 | 103 | 5 | 4.85 | 1.60–10.97 | DFI |
| Shankar et al. 2005 [66] | P cohort | 2003–2004 | India | Ipat | 63 | 59.7 | 77 | 8 | 10.39 | 4.59–19.45 | DFI |
| Daeschlein et al. 2006 [22] | P cohort | 2003 | Germany | Com (NH) | 77.6* | 16.2* | 175 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–2.09 | Col (N) |
| Gadepalli et al. 2006 [52] | P cohort | NR | India | Ipat | 53.9 | 85 | 80 | 14 | 17.50 | 9.91–27.62 | DFI |
| Sharma et al. 2006 [67] | Retro | 2004–2005 | Nepal | Ipat | 61 | 55.8 | 43 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.00–8.22 | DFI |
| Citron et al. 2007 [47] | Retro | 2001–2004 | USA | Ipat | NR | NR | 433 | 48 | 11.09 | 8.29–14.43 | DFI |
| Stanaway et al. 2007 [41] | P cohort | NR | UK | Opat | 61 | 61 | 65 | 12 | 18.46 | 9.92–30.03 | DFI |
| Stanaway et al. 2007 continued | 11 | 16.92 | 8.76–28.27 | Col (N) | |||||||
| Gorwitz et al. 2008 [21] | P cohort | 2003–2004 | USA | Com | NR | 49 | 1125 | 18 | 1.60 | 0.95–2.52 | Col (N) |
| Nather et al. 2008 [62] | P cohort | 2005–2006 | Singapore | Ipat | 60 | 50 | 122 | 7 | 5.74 | 2.34–11.47 | DFI |
| Richard et al. 2008 [78] | P cohort | 2003–2004 | France | Ipat | 68 | 69.7 | 188 | 37 | 19.68 | 14.25–26.09 | DFI |
| Aragon-Sanchez et al. 2008 [44] | Retro | 2002–2007 | Spain | I, O | 64.7 | 62.7 | 185 | 35 | 19.89 | 14.26–26.56 | DFI |
| Maghsoudi et al. 2008 [84] | P cohort | 2000–2006 | Iran | Ipat | 53.4 | 40.4 | 94 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–3.85 | Inf (Burns) |
| Sotto et al. 2008 [76] | P cohort | 2004–2007 | France | Ipat | 68 | 61 | 513 | 48 | 9.36 | 6.98–12.21 | DFI |
| Garazi et al. 2009 [38] | Cross-sectional | NR | USA | Com (NH) | 83.4* | 26.7* | 51 | 18 | 35.29 | 22.43–49.93 | Col (N) |
| Galkowska et al. 2009 [53] | P cohort | 2006–2007 | Poland | I, O | 58 | 75.75 | 50 | 13 | 26.00 | 14.63–40.35 | DFI |
| Lipsky et al. 2010 [60] | Retro | 2003–2007 | USA | Ipat | 60 (med) | 64 | 2220 | 165 | 7.43 | 6.38–8.60 | DFI |
| Lipsky et al. 2010 continued | 61 (med) | 54.6 | 810 | 78 | 9.63 | 7.69–11.87 | nfSSTI | ||||
| Raju et al. 2010 [83] | P cohort | 2004 | India | I, O | NR | NR | 110 | 14 | 12.73 | 7.14–20.43 | Inf (NS) |
| Wang et al. 2010 [72] | Retro | 2004–2006 | China | Ipat | 60.8 | 57.6 | 118 | 21 | 17.80 | 11.37–25.91 | DFI |
| Changchien et al. 2011 [79] | Retro | 2004–2008 | Taiwan | Ipat | 57.9 | 64 | 155 | 35 | 22.58 | 16.26–29.98 | NF |
| Lipsky et al. 2011 [81] | Retro | Mixed | Int | Ipat | NR | NR | 868 | 349$ | 40.21 | 36.93–43.56 | nfSSTI |
| Lu et al. 2011 [3] | P cohort | 2009 | Taiwan | ED | NR | 53.4* | 124 | 9 | 7.26 | 3.37–13.33 | Col (N) |
| Schechter-Perkins et al. 2011 [33] | P cohort | 2009–2010 | USA | ED | 41* | 47* | 51 | 6 | 11.77 | 4.44–23.87 | Col (N, Ph, H, G, P, W, C) |
| Tascini et al. 2011 [69] | P cohort | 2006–2008 | Italy | Opat | NR | NR | 1295 | 76 | 5.87 | 4.65–7.29 | DFI |
| Kutlu et al. 2012 [29] | P cohort | 2006–2009 | Turkey | Opat | 56.28 | 46.4 | 304 | 30 | 9.87 | 6.76–13.79 | Col (N) |
| Mendes et al. 2012 [61] | P cohort | 2010 | Portugal | I, O | 62.7 | 42.9 | 49 | 25 | 51.02 | 36.34–65.58 | DFI |
| Acharya et al. 2013 [42] | Retro | 2003–2008 | UK | Opat | 66.2 | 66.9 | 130 | 20 | 15.39 | 9.66–22.76 | DFI |
| Djahmi et al. 2013 [50] | P cohort | 2011–2012 | Algeria | Ipat | 64* | 62.3* | 128 | 73 | 57.03 | 47.99–65.74 | DFI |
| Fowler and Ilyas 2013 [80] | Retro | 2005–2010 | USA | Ipat | NR | NR | 82 | 32 | 39.02 | 28.44–50.43 | nfSSTI |
| Gupta et al. 2013 [24] | Retro | 2008–2010 | USA | Ipat | NR | 95.7* | 5019 | 554* | 11.04 | 10.18–11.94 | Col (N) |
| Haleem et al. 2013 [25] | Cross-sectional | NR | USA | I, O | 55 | 64 | 79 | 7 | 8.86 | 3.64–17.41 | Col (N) |
| Haleem et al. 2013 continued | 7 | 8.86 | 3.64–17.41 | DFI | |||||||
| Parriott and Arah 2013 [82] | Retro | NR | USA | Ipat | NR | 0 | 28,949 | 17 | 0.06 | 0.03–0.09 | Inf (NS) |
| Torres and Sampathkumar 2013 [34] | Mixed | 2008 | USA | Ipat | Nr | NR | 336 | 33 | 9.82 | 6.86–13.52 | Col (N) |
| Ahmed et al. 2014 [43] | P cohort | 2007–2010 | Egypt | Ipat | 44.4* | N/A | 52 | 9 | 17.31 | 8.23–30.33 | DFI |
| Hennessey et al. 2014 [85] | P cohort | 2000–2011 | USA | Ipat | 55* (med) | 50.5* | 54 | 15 | 27.78 | 16.46–41.64 | Inf (Abdo) |
| Lavery et al. 2014 [58] | Retro | NR | USA | Ipat | 59.55 | NR | 57 | 17 | 29.83 | 18.43–43.40 | DFI |
| Yeoh et al. 2014 [35] | Retro | 2010–2011 | Singapore | Ipat (HD) | 59.1* | 54.5 | 139 | 25 | 17.99 | 11.99–25.40 | Col (N, A, G) |
| Cervantes-Garcia et al. 2015 [46] | P cohort | 2012–2013 | Mexico | I, O | 52.5 | 55 | 100 | 34 | 34.00 | 24.82–44.15 | DFI |
| Cheng et al. 2015 [14] | Retro | 1997–2013 | Taiwan | Ipat | 58.8* | 67* | 84 | 6 | 7.14 | 2.67–14.90 | NF |
| Commons et al. 2015 [48] | P cohort | 2012–2013 | Australia | Ipat | 54.4 | 60 | 177 | 77 | 43.50 | 36.08–51.15 | DFI |
| Daeschlein et al. 2015 [23] | Retro | 2006–2010 | Germany | Ipat | 59* | NR | 1138 | 30 | 2.64 | 1.79–3.74 | Col (N) |
| Hart et al. 2015 [26] | P cohort | 2008–2011 | Australia | Com | 65.1 | 53.1 | 660 | 8 | 1.21 | 0.53–2.37 | Col (N, A) |
| Jayarani and Sundarji 2015 [27] | Retro | 2014–2015 | Sri Lanka | Ipat | NR | 70 | 100 | 40 | 40.00 | 30.33–50.28 | Col (N) |
| Kao et al. 2015 [37] | P cohort | 2008–2010 | Taiwan | Ipat | 69.4* | 62.7* | 376 | 78 | 20.75 | 16.76–25.20 | Inf (NS) |
| Kao et al. 2015 continued | 66 | 17.55 | 13.84–21.78 | Col (N) | |||||||
| Karadag-Oncel et al. 2015 [28] | P cohort | 2005 and 2013 | Turkey | Opat | 12.1 | 61.5 | 235 | 2 | 0.85 | 0.10–3.04 | Col (N) |
| Lipsky et al. 2015 [77] | Retro | 2011–2013 | Int | I, O | 61.7 | 57.2 | 201 | 83 | 41.29 | 34.41–48.44 | DFI |
| Saltoglu et al. 2015 [64] | Retro | 2011–2013 | Turkey | I, O | 61 (med) | 68 | 455 | 7 | 1.54 | 0.62–3.14 | DFI |
| Bravo-Molina et al. 2016 [45] | P cohort | 2009–2013 | Spain | Ipat | 66 | 80 | 131 | 20 | 15.27 | 9.58–22.59 | DFI |
| Gleeson et al. 2016 [13] | P cohort | NR | Ireland | Ipat | 69* | 55* | 45 | 10 | 22.22 | 11.21–37.09 | Col (N, P, W, C) |
| Reveles et al. 2016 [63] | Retro | 2010–2014 | USA | Ipat | 52 (med) | 69 | 318 | 47 | 14.78 | 11.07–19.17 | DFI |
| Shettigar et al. 2016 [68] | P cohort | 2011–2012 | India | Ipat | 60.5 | 72.5 | 200 | 52 | 26.00 | 20.07–32.66 | DFI |
| Ashong et al. 2017 [74] | Retro | 2011–2015 | USA | Ipat | 65 (med) | NR | 158 | 31 | 19.62 | 13.74–26.68 | DFI |
| Dunyach-Remy et al. 2017 [40] | P cohort | 2010–2012 | France | Ipat | 68.5 | 72.5 | 276 | 17 | 6.16 | 3.63–9.68 | DFI |
| Dunyach-Remy et al. 2017 continued | 18 | 6.52 | 3.91–10.11 | Col (N) | |||||||
| Lin et al. 2017 [39] | Cross-sectional | 2014–15 | China | Com | 66.13 | 30.43 | 529 | 22 | 4.16 | 2.62–6.23 | Col (N) |
| Shah et al. 2017 [65] | Cross-sectional | 2014–15 | Pakistan | Ipat | 42.2 | 51.4 | 140 | 33 | 23.57 | 16.82–31.48 | DFI |
| Wu et al. 2017 [73] | P cohort | 2009–14 | China | Ipat | NR | NR | 312 | 21 | 6.73 | 4.21–10.11 | DFI |
| Legese et al. 2018 [20] | P cohort | 2016 | Ethiopia | HCW | 31.78* | 41.3* | 10 | 3 | 30.00 | 6.67–65.25 | Col (N) |
| Henig et al. 2018 [75] | Retro | 2012–15 | USA | Ipat | 58.4 | 64.3 | 648 | 224 | 34.57 | 30.91–38.37 | DFI |
| Lin et al. 2018 [39] | P cohort | 2015 | Taiwan | I, O | NR | NR | 354 | 10 | 2.83 | 1.36–5.13 | Col (N) |
| Lin et al. 2018 continued | Ipat | NR | NR | 112 | 27 | 24.11 | 16.53–33.10 | DFI | |||
| van Asten et al. 2018 [70] | Retro | 2010–14 | USA | Ipat | 53.8 | 76.9 | 143 | 11 | 7.69 | 3.90-13.35 | DFI |
| Viquez-Molina et al. 2018 [71] | P cohort | 2014–16 | Costa Rica | Ipat | NR | NR | 379 | 35 | 9.24 | 6.52–10.81 | DFI |
med median value, Abdo abdominal, CIs 95% confidence intervals, Col (N, A, G, W, C, Ph, H) colonisation (nasal, axilla, groin, surface wound, catheter, pharynx, hand), Col colonisation. Com (NH) community (nursing home), DFI diabetic foot infection, I, O, mixed in- and out- patient population, Inf infection, Int international, Ipat (HD) inpatient (haemodialysis), NF necrotizing fasciitis, nfSSTI non-foot skin and soft tissue infection, NR not reported, NS not specified. Opat outpatient, P cohort prospective cohort, RCT randomized controlled trial, Retro retrospective analysis
*Age or gender data were not available for the diabetic portion of the study population and are instead representative of a larger portion of or the whole study population
$combined data from three clinical trials. CIs, 95% confidence intervals
The prevalence of MRSA colonisation among diabetic patients
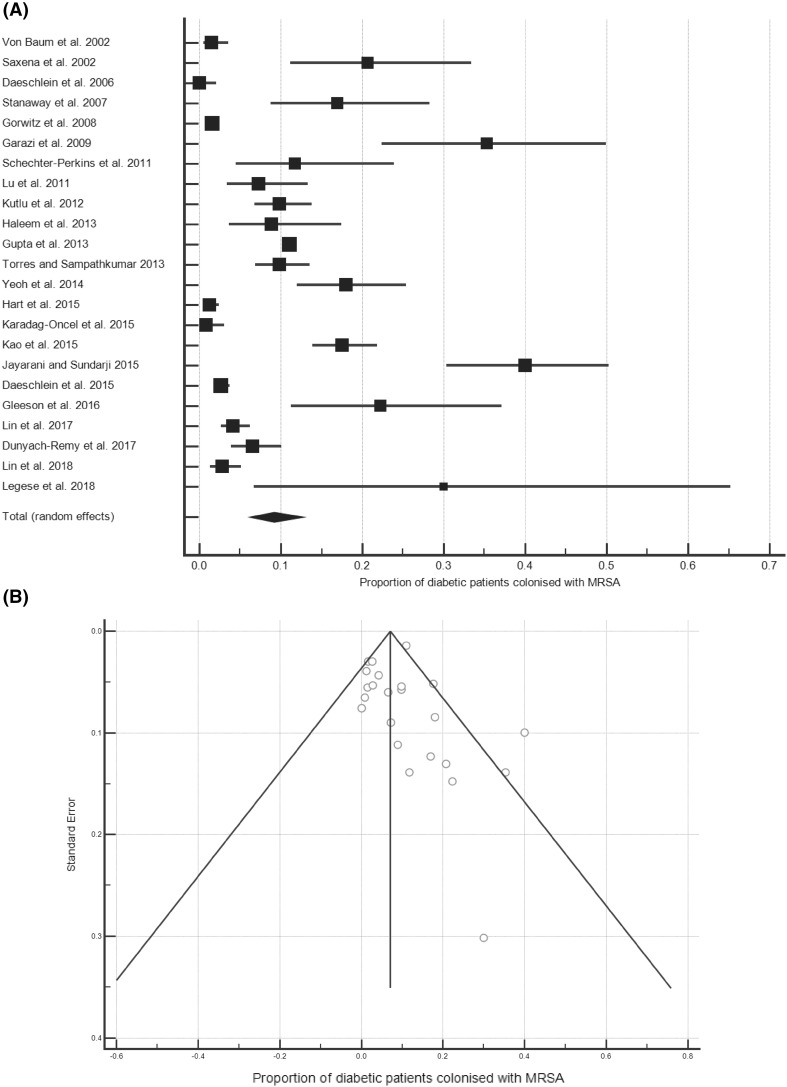
Twenty-three data sets investigated the prevalence of MRSA colonisation among diabetic patients, published from 2002 to 2018 [13, 20–41]. The majority (19/23) examined MRSA carriage in the nares, one study examined the nares and axilla, another supplemented this with groin swabs, another with perineum and sites of wounds or catheters and another used multiple sites. Together, the 23 data sets represented a pooled population of 11577 diabetic patients with an MRSA colonisation rate of 9.20% (95% CI, 6.26–12.63%; Fig. 2a); heterogeneity among the studies was high (I2 = 96.38% [95% CI, 95.45–97.12%]). All forest plots are presented in the same way, the boxes show effect estimates for each study, weighted according to a random-effects model; the horizontal lines indicate 95% CIs; the centre of the diamond shows the pooled proportion and the horizontal tips represent 95% CIs. A funnel plot—on which the vertical line represents the summary estimate derived by meta-analysis and the diagonals represent 95% CIs around the summary effect—did not indicate publication bias (Fig. 2b). Inspection of the colonisation rates across the available 16 years did not reveal any correlation (R2 = 0.0052).
Fig. 2.
The prevalence of MRSA colonisation amongst diabetic patients. a Forest plot of the proportion of diabetic patients colonised with MRSA (n = 11577). b Funnel plot
Sub-analyses of the data were conducted by patient setting and region or, where possible, nation (Table 2). Among the patient settings for which meta-analysis was possible, haemodialysis (HD) patients were found to have the highest colonisation rate (19.08%), followed by in-patients (13.46%), out- or emergency patients (8.33%), diabetics in nursing homes (6.61%), and diabetics in the community (2.19%). Only one study of 10 patients examined the prevalence of MRSA among diabetic healthcare workers (HCWs), of which 3/10 were MRSA-positive [20]. There were enough data to conduct regional and national analyses, including all patient settings, for East Asia, the Middle East, Germany, Taiwan, and the USA. The greatest colonisation prevalence was found in East Asia (12.85%) and the lowest in Germany (1.38%).
Table 2.
Sub-group analyses of the prevalence of MRSA colonisation among diabetic patients
| Nation (s) | No. of data sets | No. of patients | Pooled prevalence of MRSA % | 95% CI | I2 (%) | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetic patients | – | 23 | 11577 | 9.20 | 6.26–12.63 | 96.38 | 95.45–97.12 |
| Healthcare workers | – | 1 | 10 | 30b | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Haemodialysis patients | – | 2 | 197 | 19.08 | 13.93–24.81 | 0.00 | 0.00–0.00 |
| In-patientsa | – | 7 | 7290 | 13.46 | 7.94–20.16 | 97.01 | 95.48–98.02 |
| Out- or emergency patients | – | 5 | 779 | 8.33 | 3.10–15.77 | 89.48 | 78.25–94.91 |
| Nursing homes only | – | 3 | 554 | 6.61 | 0.01–23.99 | 96.62 | 98.36 |
| Community (excl. nursing homes) | – | 3 | 2314 | 2.19 | 0.94–3.95 | 83.40 | 49.74–94.52 |
| East Asia | China, Taiwan, Singapore, Sri Lanka | 6 | 1622 | 12.85 | 5.34–23.00 | 96.40 | 94.21–97.77 |
| Middle East | Saudi Arabia, Turkey | 3 | 597 | 8.43 | 1.05–21.86 | 94.88 | 88.39–97.75 |
| USA | – | 6 | 6661 | 11.08 | 5.14–18.92 | 97.33 | 95.88–98.27 |
| Taiwan | – | 3 | 854 | 8.48 | 1.44–20.56 | 96.00 | 91.42–98.14 |
| Germany | – | 3 | 1641 | 1.38 | 0.27–3.33 | 80.23 | 37.66–93.73 |
aIn-patients exclude haemodialysis patients, which were analysed separately
bOnly one data set available
CI confidence interval
Many of the studies which contained colonisation data did so for diabetic patients as a sub-group of a wider cohort. Next, we, therefore, selected the 14 studies that contained colonisation data for diabetic and non-diabetic patients for comparison. Meta-analyses revealed that, among a pooled population of diabetic patients (n = 8975), there was an MRSA colonisation rate of 10.27% (95% CI, 6.27–15.12%; I2 = 96.80% [95.74–97.60%]). Among the comparative non-diabetic population (n = 38976), the colonisation rate was 5.52% (95% CI, 2.93–8.88%; I2 = 99.18% [99.01–99.32%]). The 4.75% difference between these colonisation rates was significant (P < 0.0001).
There were sufficient data among the 14 studies to perform sub-analyses for American (5/14), German (3/14), and East Asian (3/14) diabetics, as well as for nursing home residents (3/14) and in-patients (5/14). Across five studies, American diabetics (n = 6582) had a pooled MRSA carriage rate of 11.46% (95% CI, 4.84–20.42%; I2 = 97.87% [95% CI, 96.65–98.64%]) compared to 8.08% (95% CI, 2.82–15.72%; I2 = 99.66% [95% CI, 99.56–99.73%]) among 31005 non-diabetic Americans (P < 0.0001). Analysis of the three German studies revealed that 1641 diabetics had an MRSA carriage rate of 1.38% (95% CI, 0.27–3.33%; I2 = 80.23% [95% CI, 37.66–93.73%]), this was greater than the comparative rate of 0.84% (95% CI, 0.40–1.45%; I2 = 73.57% [95% CI, 11.49–92.11%]) for 5883 non-diabetics in these studies (P = 0.047). Comparison across the three East Asian studies revealed that 639 diabetics had a carriage rate of 14.34% (95% CI, 8.46–21.46%; I2 = 79.70% [95% CI, 35.60–93.60%]), compared to 7.65% (95% CI, 0.84–20.40%; I2 = 96.74% [95% CI, 93.33–98.41%]) in the comparative population of 1296 non-diabetics (P < 0.0001). Among the five studies that contained data on 6914 in-patient diabetics (excluding HD patients), there was a colonisation rate of 11.17% (95% CI, 5.78–18.04%; I2 = 97.18% [95% CI, 95.39–98.28%]), compared to 7.43% (95% CI, 3.02–13.59%; I2 = 99.08% [95% CI, 98.70-99.34%]) among 17072 non-diabetic in-patients (P < 0.0001). Three studies contained data regarding 554 nursing home residents, with a pooled MRSA prevalence rate of 6.61% (95% CI, 0.01–23.99%; I2 = 96.62% [95% CI, 93.01–98.36%]). This was similar to the 6.62% (95% CI, 0.23–20.71%; I2 = 97.93% [95% CI, 96.15–98.89%]) carriage rate among the comparative population of 3298 non-diabetic residents examined by these studies (P = 0.993).
The prevalence of MRSA among patients with DFI
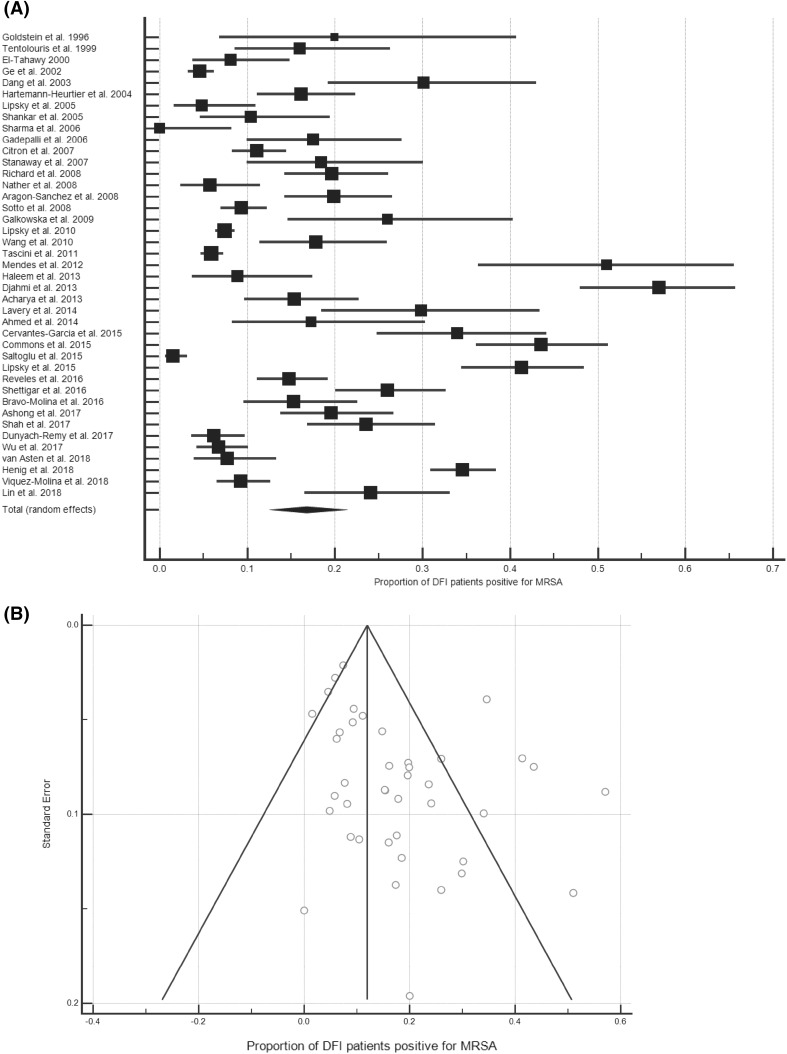
Data about the prevalence of MRSA among DFI patients were contained in 41 data sets [42–50,40,51–68,41,69–75,39,76,77,25,78], representing 10994 patients, with an MRSA prevalence rate of 16.78% (95% CI, 13.21–20.68%; Fig. 3a). Inter-study variability was high (I2 = 96.16% [95% CI, 95.43–96.77%]). A funnel plot of these studies was weakly asymmetrical (Fig. 3b). Analysis of the prevalence by publication year did not reveal any trend (R2 = 0.0487).
Fig. 3.
The prevalence of MRSA amongst DFI patients. a Forest plot of the proportion of MRSA-positive DFI patients (n = 10994). b Funnel plot
Sub-analyses by patient setting, region or nation were conducted (Table 3). These revealed that the 2.82% difference in the proportion of DFI out- and in-patients that were MRSA-positive was significant (P = 0.0008). There were sufficient data to perform sub-analyses of all patient settings for five broad regions, of which Central America had the highest (20.07%) and East Asia the lowest (12.73%) prevalence of MRSA. Among the five nations for which there were sufficient data to perform national sub-analyses, the UK had the highest prevalence (19.59%), while China had the lowest (11.65%).
Table 3.
Sub-group analyses of the prevalence of MRSA amongst DFI patients
| Nation(s) | No. of data sets | No. of patients | Pooled prevalence % | 95% CI | I2 (%) | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFI patients | – | 41 | 10994 | 16.78 | 13.21–20.68 | 96.16 | 95.43–96.77 |
| Out-patients | – | 6 | 2440 | 13.16 | 7.88–19.55 | 91.99 | 85.34–95.63 |
| In-patients | – | 28 | 7444 | 15.98 | 11.99–20.42 | 95.59 | 94.51–96.47 |
| Central America | Costa Rica, Mexico | 2 | 479 | 20.07 | 2.45–48.64 | 96.81 | 91.55–98.80 |
| North Africa & The Middle East | Algeria, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Turkey | 4 | 746 | 17.25 | 0.63–49.16 | 98.62 | 97.83–99.12 |
| Western Europe | France, Italy, Portugal, Spain | 7 | 2295 | 16.96 | 9.77–25.63 | 94.96 | 91.83–96.89 |
| Indian Subcontinent | India, Nepal, Pakistan | 5 | 540 | 14.40 | 6.43–24.87 | 89.11 | 77.32–94.77 |
| East Asia | China, Singapore, Taiwan | 4 | 664 | 12.73 | 5.64–22.15 | 89.88 | 76.99–95.55 |
| UK | – | 4 | 333 | 19.59 | 13.88–26.01 | 49.56 | 0.00-83.31 |
| India | – | 3 | 357 | 18.34 | 10.06–28.44 | 78.91 | 32.51–93.41 |
| USA | – | 10 | 4893 | 14.70 | 8.54–22.18 | 97.29 | 96.25–98.05 |
| France | – | 4 | 1157 | 12.28 | 7.18–18.51 | 88.04 | 71.78–94.93 |
| China | – | 2 | 430 | 11.65 | 3.14–24.56 | 90.40 | 65.19–97.35 |
CI confidence interval
The prevalence of MRSA among patients with NF or SSTIs and unspecified infections
Seven data sets examined the prevalence of MRSA in NF (n = 2), burns (n = 1), and non-foot SSTI (n = 4), and three further studies did not specify the type of infection in question [14, 37, 60, 79–85]. The NF and non-foot SSTI studies were grouped together for analysis and represented a population of 2147 patients with an MRSA prevalence rate of 18.03% (95% CI, 6.64–33.41%; I2 = 98.20% [95% CI, 97.44–98.73%]). The three studies that did not specify the nature of the MRSA infection studied represented 29435 patients with a prevalence rate of 8.08% (95% CI, 0.30–34.80%; I2 = 99.43% [95% CI, 99.14–99.62%]).
Discussion
Diabetes mellitus is the most prevalent metabolic disease worldwide and has been reported to be a risk factor for MRSA colonisation at the time of admission to hospital [86]. The MRSA colonisation rates of diabetic in- and out-patients in this study were 13.46% and 8.33%, respectively. These are higher than many national estimations; for example, the nasal MRSA colonisation rate has been estimated to be 2.6% in Japan [87], 3.9% among healthy Chinese children [88] and up to 2.1% across nine European countries [89]. In Scotland, a colonisation rate of 3.8% on admission has been observed, rising to 20% among patients admitted to nephrology, care of the elderly, dermatology, and vascular surgery—specialties likely to see high numbers of diabetic patients [90]. The MRSA colonisation rate among diabetics in the community identified by this study was therefore generally comparable with values for broader populations (2.19%). National sub-analyses showed that, in America, diabetics had a carriage rate 7.4 times higher than the previously estimated national prevalence rate of 1.5% [21]. While, in Germany, diabetics had an MRSA colonisation rate 1.5 times higher than has recently been estimated for the wider German population [91], although more studies of MRSA carriage among German diabetics are needed to confirm this as only three were available.
The levels of MRSA colonisation among diabetics in nursing homes or the wider community, in-patients and out-patients suggest MRSA carriage reflects the extent of interaction with the healthcare system. It is difficult to compare the values obtained here for in- and out-patients to data regarding the prevalence of MRSA colonisation among general hospital populations as such studies offer a variety of results that typically reflect different patient populations and contexts [92–95]. However, this study compared the MRSA colonisation rates for diabetic and non-diabetic patients across the 14 studies that contained data for both. This showed that diabetics had a significantly higher colonisation rate than non-diabetics, a finding which held for sub-analysis of in-patient, American, German, or East Asian populations. Notably, the rates of MRSA carriage among diabetic and non-diabetic nursing home residents were very similar, supporting the above suggestion that MRSA carriage rates reflect the extent of interaction with a healthcare environment.
Further sub-analyses showed that diabetic HD patients had the greatest colonisation rate (19.08%; n = 197). The colonisation rate of non-diabetic HD patients has been previously estimated by meta-analysis to be 6.2% (n = 5596; [11]). The higher finding here likely reflects the synergy of two high-risk states and differences in study population size. However, the MRSA colonisation rate among diabetic patients in this study (9.20%) exceeded the previous meta-analytic estimates of the colonisation rate among the other high-risk groups, e.g. 6.9% among 6,558 HIV-1 patients and 7% and 1.9% among 63740 general and 19722 neonatal or paediatric intensive-care patients, respectively [6, 11, 12].
Only one study investigated the MRSA colonisation rate among diabetic HCWs, showing that it exceeded that of non-diabetic HCWs (30% [n = 10] vs. 5.8% [n = 242]; [20]. A previous meta-analysis of MRSA colonisation among HCW in Europe and the USA has estimated carriage at 1.8–4.4%, with nurses reported have a carriage rate of 6.9% with an odds ratio of 2.58 compared to other HCWs [96]. The increased carriage risk for nurses has been recorded elsewhere, and intensive patient contact is thought to be a risk factor [97, 98]. The significance of potentially greater rates of MRSA colonisation of diabetic HCWs requires further investigation, especially given the high prevalence of obesity among some sectors of the healthcare workforce [99].
Diabetic foot infections can be mono- or poly-microbial, and may be caused by a wide range of pathogens, including MRSA. This study found that the prevalence of MRSA among 10994 DFI patients was 16.78%. This is comparable to the prevalence estimated by a 2010 systematic review [10]. A higher prevalence was identified for in-patients compared to out-patients, likely reflecting the difference in extent of interaction with the healthcare system. From the UK, one eligible study reported MRSA colonisation data among diabetics at a value lower than the proportion of MRSA-positive UK DFI patients (16.9% vs. 19.59%). Further work is therefore needed in the UK to clarify the extent to which diabetic patients are colonised with MRSA.
This study was limited by the small number of eligible studies, such that only sub-analyses based on patient setting or geographic region could be conducted. Much of the often high level of heterogeneity observed in individual sub-analyses therefore likely reflects variation in other factors not simultaneously subject to sub-analysis. Sub-analyses by geographic region, although useful for appraising broad trends, are low resolution given the complexity of factors that underlie MRSA prevalence. While there were enough studies to conduct some national sub-analyses, many included low numbers of studies and were also subject to influence by local inter-study variation. More studies, in particular of the prevalence of MRSA colonisation among diabetic patients, are needed to provide a greater evidence base and permit finer stratification of data in future analyses. The variety of detection techniques used by eligible studies may have led to a slight underestimation, with PCR and chromogenic culture media being more sensitive than nonchromogenic media [100].
Meta-analyses are designed to be reproducible and identify as many eligible manuscripts as possible. However, this may be limited by the omission of some relevant manuscripts, because they do not contain the appropriate terms in the fields searched or were incorrectly indexed [101]. During this study, we became aware of two manuscripts that contained pertinent data, but were not detected by our systematic search as they lacked terms related to diabetes [13] or MRSA [14] in the searched fields. Given the topic of this study, it was not feasible to amend the search strategy to omit either terms related to diabetes or MRSA. Therefore, although we were unable to identify these two studies systematically or through review articles, we recognised that they contained relevant data and included them as ‘manual’ search results. This transparent approach enhances the reproducibility of this study, while acknowledging some of the inherent limitations of systematic approaches.
This study may also be limited by not being pre-registered. Registration of reviews is a non-essential recommendation designed to encourage transparency, improve quality and reduce duplication. Pre-registration of reviews that are never completed is not recommended [102]. This study was conceived as a student project, many of which are not published, and the authors therefore decided it was inappropriate to register retrospectively. However, the authors are not aware of any similar studies underway and complied with the PRISMA statement throughout.
Taken together, the results of this study suggest that diabetics interacting with the healthcare system are likely to have a higher rate of MRSA colonisation than non-diabetics, raising the question of whether diabetic staff and patients should be subject to targeted screening. Targeted screening of high-risk patients has been shown to offer a cost-effective, efficacious, alternative to universal screening [103–105]. In the UK, patients admitted to high-risk specialties or with previous MRSA colonisation or infection are targeted for screening [106]. Given the rates of colonisation and infection recorded in this analysis, many diabetic patients may, therefore, be eligible for screening under the current policy. However, research is warranted to evaluate the potential benefits of amending current guidelines to specifically and proactively target colonisation among high-risk patient groups, such as diabetics. While screening of staff is not current policy, more work is required to evaluate the potential benefits of screening diabetic HCWs in reducing the spread of MSRA. However, any screening of specific patient or staff groups must avoid stigmatisation. Finally, the high prevalence of MRSA among DFI patients and consequent long-term antibiotic administration has wider implications for antimicrobial resistance. While the prevention of such infections should remain the goal, with increasing levels of antimicrobial resistance, it is also important that alternative therapies are investigated [107].
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr Medhat Khattar (School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Edinburgh) for useful discussions. We would also like to thank the three anonymous reviewers for their invaluable constructive criticism.
Abbreviations
- CIs
95% confidence intervals
- HIV-1
Human immunodeficiency virus type one
- MRSA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- NF
Necrotizing fasciitis
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- PRISMA
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- SSTI
Skin and soft-tissue infection
Author contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: JDJ and SCW. Performed the experiments: HJS, CSC, and JDJ. Analysed the data: HJS, CSC, and JDJ. Wrote the manuscript: JDJ. Reviewed the manuscript: HJS, CSC, SCW, and JDJ.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. Access to MedCalc was obtained through a license provided by the Biomedical Teaching Organisation, University of Edinburgh.
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Helen J. Stacey and Caitlin S. Clements have contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Cosgrove SE, Sakoulas G, Perencevich EN, Schwaber MJ, Karchmer AW, Carmeli Y. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36(1):53–59. doi: 10.1086/345476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Filice GA, Nyman JA, Lexau C, Lees CH, Bockstedt LA, Como-Sabetti K, et al. excess costs and utilization associated with methicillin resistance for patients with Staphylococcus aureus infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010;31(04):365–373. doi: 10.1086/651094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hidron AI, Kourbatova EV, Halvosa JS, Terrell BJ, McDougal LK, Tenover FC et al (2005) Risk factors for colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in patients admitted to an urban hospital: emergence of community-associated MRSA Nasal Carriage. Clin Infect Dis 41(2):159–166 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Davis KA, Stewart JJ, Crouch HK, Florez CE, Hospenthal DR. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Nares Colonization at Hospital Admission and Its Effect on Subsequent MRSA Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(6):776–782. doi: 10.1086/422997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zacharioudakis IM, Zervou FN, Ziakas PD, Mylonakis E. Meta-analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization and risk of infection in dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN. 2014;25(9):2131–2141. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013091028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zervou FN, Zacharioudakis IM, Ziakas PD, Rich JD, Mylonakis E. Prevalence of and risk factors for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in HIV infection: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2014;59(9):1302–1311. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103(1):137–149. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Scottish Diabetes Survey Monitoring Group. Scottish Diabetes Survey 2016 [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2018 Nov 9]. http://www.diabetesinscotland.org.uk/Publications/Scottish%20Diabetes%20Survey%202016.pdf
- 9.Insight Health Economics. Foot Care in Diabetes: The Human and Financial Cost [Internet] (2017) http://www.londonscn.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/dia-foot-care-mtg-kerr-27042017.pdf
- 10.Eleftheriadou I, Tentolouris N, Argiana V, Jude E, Boulton AJ. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diabetic foot infections. Drugs. 2010;70(14):1785–1797. doi: 10.2165/11538070-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zervou FN, Zacharioudakis IM, Ziakas PD, Mylonakis E. MRSA colonization and risk of infection in the neonatal and pediatric ICU: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2014;133(4):e1015–e1023. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-3413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ziakas PD, Anagnostou T, Mylonakis E. The prevalence and significance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization at admission in the general ICU Setting: a meta-analysis of published studies. Crit Care Med. 2014;42(2):433–444. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182a66bb8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gleeson A, Larkin P, Walsh C, O’Sullivan N. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and effects on survival of patients in a specialist palliative care unit: A prospective observational study. Palliat Med. 2016;30(4):374–381. doi: 10.1177/0269216315595158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cheng N-C, Tai H-C, Chang S-C, Chang C-H, Lai H-S. Necrotizing fasciitis in patients with diabetes mellitus: clinical characteristics and risk factors for mortality. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15(417) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. JAMA. 2000;19(15):2008–2012. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.The Joanna Briggs Institute. Critical appraisal tools - JBI [Internet]. [cited 2018 Aug 17]. http://joannabriggs.org/research/critical-appraisal-tools.html
- 17.Sedgwick P. Meta-analyses: how to read a funnel plot. BMJ. 2013;346:f1342. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h4718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.MedCalc. Comparison of proportions calculator [Internet]. [cited 2018 Jul 8]. https://www.medcalc.org/calc/comparison_of_proportions.php
- 20.Legese H, Kahsay AG, Kahsay A, Araya T, Adhanom G, Muthupandian S, et al. Nasal carriage, risk factors and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus among healthcare workers in Adigrat and Wukro hospitals, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2018;11(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3353-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gorwitz RJ, Kruszon-Moran D, McAllister SK, McQuillan G, McDougal LK, Fosheim GE, et al. Changes in the Prevalence of Nasal Colonization with Staphylococcus aureus in the United States, 2001–2004. J Infect Dis. 2008;197(9):1226–1234. doi: 10.1086/533494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Daeschlein G, Assadian O, Rangous I, Kramer A. Risk factors for Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage in residents of three nursing homes in Germany. J Hosp Infect. 2006;63(2):216–220. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2005.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Daeschlein G, von Podewils S, Bloom T, Assadian O, Napp M, Haase H, et al. Risk factors for MRSA colonization in dermatologic patients in Germany. JDDG J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13(10):1015–1022. doi: 10.1111/ddg.12705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gupta K, Martinello RA, Young M, Strymish J, Cho K, Lawler E. MRSA nasal carriage patterns and the subsequent risk of conversion between patterns, infection, and death. PLOS One. 2013;10(1):e53674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Haleem A, Schultz JS, Heilmann KP, Dohrn CL, Diekema DJ, Gardner SE. Concordance of nasal and diabetic foot ulcer staphylococcal colonization. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;79(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.01.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hart J, Hamilton EJ, Makepeace A, Davis WA, Latkovic E, Lim EM, et al. Prevalence, risk factors and sequelae of Staphylococcus aureus carriage in diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study Phase II. J Diabetes Complications. 2015;29(8):1092–1097. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jayarani K, Sundarji SS. Detection of MRSA from nasal carrier among diabetic foot ulcer patients in Tertiary Care Hospital Puducherry. Int J Pharma Bio Sci. 2015;6(3):B618–B623. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Karadag-Oncel E, Gonc N, Altay O, Cengiz AB, Ozon A, Pinar A, et al. Prevalence of nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children with diabetes mellitus: Trends between 2005 and 2013. Am J Infect Control. 2015;43(9):1015–1017. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2015.04.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kutlu SS, Cevahir N, Akalin S, Akin F, Dirgen Caylak S, Bastemir M, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in a diabetic outpatient population: a prospective cohort study. Am J Infect Control. 2012;40(4):365–368. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2011.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lin J, Xu P, Peng Y, Lin D, Ou Q, Zhang T, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization among a community-based diabetes population in Foshan, China. J Diabetes Investig. 2017;8(3):383–391. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lu S-Y, Chang F-Y, Cheng C-C, Lee K-D, Huang Y-C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization among adult patients visiting emergency department in a medical center in Taiwan. PloS One. 2011;6(6):e18620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Saxena AK, Panhotra BR, Venkateshappa CK, Sundaram DS, Naguib M, Uzzaman W, et al. The impact of nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus a ureus (MRSA & MSSA) on vascular access-related septicemia among patients with type-II diabetes on dialysis. Ren Fail. 2002;24(6):763–777. doi: 10.1081/jdi-120015679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schechter-Perkins EM, Mitchell PM, Murray KA, Rubin-Smith JE, Weir S, Gupta K. Prevalence and predictors of nasal and extranasal staphylococcal colonization in patients presenting to the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(5):492–499. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2010.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Torres K, Sampathkumar P. Predictors of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization at hospital admission. Am J Infect Control. 2013;41(11):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2013.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yeoh LY, Tan FLG, Willis GC, Ooi ST. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage in hospitalized chronic hemodialysis patients and its predisposing factors. Hemodial Int Int Symp Home Hemodial. 2014;18(1):142–147. doi: 10.1111/hdi.12061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.von Baum H, Schmidt C, Svoboda D, Bock-Hensley O, Wendt C. Risk factors for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage in residents of german nursing homes. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2002;23(9):511–515. doi: 10.1086/502098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kao K-C, Chen C-B, Hu H-C, Chang H-C, Huang C-C, Huang Y-C. Risk factors of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection and correlation with nasal colonization based on molecular genotyping in medical intensive care units: a prospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94(28):e1100. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Garazi M, Edwards B, Caccavale D, Auerbach C, Wolf-Klein G. Nursing homes as reservoirs of MRSA: myth or reality? J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2009;10(6):414–418. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2009.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lin S-Y, Lin N-Y, Huang Y-Y, Hsieh C-C, Huang Y-C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage and infection among patients with diabetic foot ulcer. J Microbiol Immunol Infect [Internet]. 2018; 10.1016/j.jmii.2018.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 40.Dunyach-Remy C, Courtais-Coulon C, DeMattei C, Jourdan N, Schuldiner S, Sultan A. Link between nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus and infected diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Metab. 2017;43(2):167–71. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2016.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stanaway S, Johnson D, Moulik P, Gill G. Methicillin-resistant Staphyloccocus aureus (MRSA) isolation from diabetic foot ulcers correlates with nasal MRSA carriage. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;75(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2006.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Acharya S, Soliman M, Egun A, Rajbhandari SM. Conservative management of diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013;101(3):e18–e20. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ahmed EF, Gad GFM, Abdalla AM, Hasaneen AM, Abdelwahab SF. Prevalence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus among Egyptian patients after surgical interventions. Surg Infect. 2014;9(4):404–411. doi: 10.1089/sur.2013.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Aragón-Sánchez FJ, Cabrera-Galván JJ, Quintana-Marrero Y, Hernández-Herrero MJ, Lázaro-Martínez JL, García-Morales E, et al. Outcomes of surgical treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: a series of 185 patients with histopathological confirmation of bone involvement. Diabetologia. 2008;51(11):1962. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bravo-Molina A, Linares-Palomino JP, Lozano-Alonso S, Asensio-García R, Ros-Díe E, Hernández-Quero J. Influence of wound scores and microbiology on the outcome of the diabetic foot syndrome. J Diabetes Complicat. 2016;30(2):329–334. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cervantes-García E, García-González R, Reséndiz-Albor A, Salazar-Schettino PM. Infections of diabetic foot ulcers with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015;14(1):44–49. doi: 10.1177/1534734614564053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Citron DM, Goldstein EJC, Merriam CV, Lipsky BA, Abramson MA. Bacteriology of moderate-to-severe diabetic foot infections and in vitro activity of antimicrobial agents. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45(9):2819–2828. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00551-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Commons RJ, Robinson CH, Gawler D, Davis JS, Price RN. High burden of diabetic foot infections in the top end of Australia: an emerging health crisis (DEFINE study) Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;110(2):147–157. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.09.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dang CN, Prasad YDM, Boulton AJM, Jude EB. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the diabetic foot clinic: a worsening problem. Diabet Med. 2003;20(2):159–161. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Djahmi N, Messad N, Nedjai S, Moussaoui A, Mazouz D, Richard J-L, et al. Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from inpatients with infected diabetic foot ulcers in an Algerian University Hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013;19(9):E398–E404. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.El-Tahawy AT. Bacteriology of diabetic foot infections. Saudi Med J. 2000;21(4):344–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gadepalli R, Dhawan B, Sreenivas V, Kapil A, Ammini AC, Chaudhry R. A clinico-microbiological study of diabetic foot ulcers in an indian tertiary care hospital. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(8):1727–1732. doi: 10.2337/dc06-0116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Galkowska H, Podbielska A, Olszewski WL, Stelmach E, Luczak M, Rosinski G, et al. Epidemiology and prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: focus on the differences between species isolated from individuals with ischemic vs. neuropathic foot ulcers. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009;84(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2009.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ge Y, MacDonald H, Hait H, Lipsky B, Zasloff M, Holroyd K. Microbiological profile of infected diabetic foot ulcers. Diabet Med. 2002;19(12):1032–1034. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00696_1.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Goldstein EJC, Citron DM, Nesbit CA. Diabetic Foot Infections: Bacteriology and activity of 10 oral antimicrobial agents against bacteria isolated from consecutive cases. Diabetes Care. 1996;19(6):638–641. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.6.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hartemann-Heurtier A, Robert J, Jacqueminet S, Van GH, Golmard JL, Jarlier V, et al. Diabetic foot ulcer and multidrug-resistant organisms: risk factors and impact. Diabet Med. 2004;21(7):710–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tentolouris N, Jude EB, Smirnof I, Knowles EA, Boulton AJM. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an increasing problem in a diabetic foot clinic. Diabet Med. 1999;16(1):767–771. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lavery LA, Fontaine JL, Bhavan K, Kim PJ, Williams JR, Hunt NA. Risk factors for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diabetic foot infections. Diabet Foot Ankle. 2014;5:3402. doi: 10.3402/dfa.v5.23575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lipsky BA, Stoutenburgh U. Daptomycin for treating infected diabetic foot ulcers: evidence from a randomized, controlled trial comparing daptomycin with vancomycin or semi-synthetic penicillins for complicated skin and skin-structure infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;55(2):240–245. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkh531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lipsky BA, Tabak YP, Johannes RS, Vo L, Hyde L, Weigelt JA. Skin and soft tissue infections in hospitalised patients with diabetes: culture isolates and risk factors associated with mortality, length of stay and cost. Diabetologia. 2010;53(5):914–923. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1672-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mendes JJ, Marques-Costa A, Vilela C, Neves J, Candeias N, Cavaco-Silva P, et al. Clinical and bacteriological survey of diabetic foot infections in Lisbon. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;95(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nather A, Bee CS, Huak CY, Chew JLL, Lin CB, Neo S, et al. Epidemiology of diabetic foot problems and predictive factors for limb loss. J Diabetes Complicat. 2008;22(2):77–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2007.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Reveles KR, Duhon BM, Moore RJ, Hand EO, Howell CK. Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus diabetic foot infections in a large academic hospital: implications for antimicrobial stewardship. PLOS One. 2016;24(8):e0161658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Saltoglu N, Yemisen M, Ergonul O, Kadanali A, Karagoz G, Batirel A, et al. Predictors for limb loss among patient with diabetic foot infections: an observational retrospective multicentric study in Turkey. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21(7):659–664. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Shah M, Shoaib M, Razaq A, Ashraf M, Ahmad W. Frequency of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diabetic foot infections. Med Forum Mon. 2017;28(9):17–21. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shankar EM, Mohan V, Premalatha G, Srinivasan RS, Usha AR. Bacterial etiology of diabetic foot infections in South India. Eur J Intern Med. 2005;16(1):567–570. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2005.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sharma VK, Khadka PB, Joshi A, Sharma R. Common pathogens isolated in diabetic foot infection in Bir Hospital. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2006;4(15):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Shettigar K, Jain S, Bhat DV, Acharya R, Ramachandra L, Satyamoorthy K, et al. Virulence determinants in clinical Staphylococcus aureus from monomicrobial and polymicrobial infections of diabetic foot ulcers. J Med Microbiol. 2016;65(12):1392–1404. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tascini C, Piaggesi A, Tagliaferri E, Iacopi E, Fondelli S, Tedeschi A, et al. Microbiology at first visit of moderate-to-severe diabetic foot infection with antimicrobial activity and a survey of quinolone monotherapy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;94(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.van Asten SAV, Mithani M, Peters EJG, La Fontaine J, Kim PJ, Lavery LA. Complications during the treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;1:58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Víquez-Molina G, Aragón-Sánchez J, Pérez-Corrales C, Murillo-Vargas C, López-Valverde ME, Lipsky BA. Virulence factor genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from diabetic foot soft tissue and bone infections. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2018;17(1):36–41. doi: 10.1177/1534734618764237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wang S-H, Sun Z-L, Guo Y-J, Yang B-Q, Yuan Y, Wei Q, et al. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from foot ulcers in diabetic patients in a Chinese care hospital: risk factors for infection and prevalence. J Med Microbiol. 2010;59(10):1219–1224. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.020537-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wu W, Liu D, Wang Y, Wang C, Yang C, Liu X, et al. Empirical antibiotic treatment in diabetic foot infection: a study focusing on the culture and antibiotic sensitivity in a population from Southern China. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2017;16(3):173–182. doi: 10.1177/1534734617725410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ashong CN, Raheem SA, Hunter AS, Mindru C, Barshes NR. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in foot osteomyelitis. Surg Infect. 2016;29(2):143–148. doi: 10.1089/sur.2016.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Henig O, Pogue JM, Cha R, Kilgore PE, Hayat U, Ja’ara M, et al. epidemiology of diabetic foot infection in the metro-detroit area with a focus on independent predictors for pathogens resistant to recommended empiric antimicrobial therapy. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018;27:11. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sotto A, Lina G, Richard J-L, Combescure C, Bourg G, Vidal L, et al. Virulence potential of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(12):2318–2324. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lipsky BA, Cannon CM, Ramani A, Jandourek A, Calmaggi A, Friedland HD, et al. Ceftaroline fosamil for treatment of diabetic foot infections: the CAPTURE study experience. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015;31(4):395–401. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Richard J-L, Sotto A, Jourdan N, Combescure C, Vannereau D, Rodier M, et al. Risk factors and healing impact of multidrug-resistant bacteria in diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34:363–369. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2008.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Changchien C-H, Chen Y-Y, Chen S-W, Chen W-L, Tsay J-G, Chu C. Retrospective study of necrotizing fasciitis and characterization of its associated Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Taiwan. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;31:297. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-11-297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Fowler JR, Ilyas AM. Epidemiology of adult acute hand infections at an urban medical center. J Hand Surg. 2013;1(6):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lipsky BA, Itani KMF, Weigelt JA, Joseph W, Paap CM, Reisman A, et al. The role of diabetes mellitus in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: results from three randomized controlled trials. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis. 2011;15(2):e140–e146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2010.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Parriott AM, Arah OA. Diabetes and early postpartum methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in US hospitals. Am J Infect Control. 2013;41(7):576–580. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2012.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Raju S, Oli AK, Patil SA, Chandrakanth RK. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diabetics clinical samples. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;1(1):171. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Maghsoudi H, Aghamohammadzadeh N, Khalili N. Burns in diabetic patients. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2008;28(1):19–25. doi: 10.4103/0973-3930.41982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Hennessy SA, Shah PM, Guidry CA, Davies SW, Hranjec T, Sawyer RG (2015) Can Nasal Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Screening Be Used to Avoid Empiric Vancomycin Use in Intra-Abdominal Infection? Surg Infect 16(4):396–400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 86.McKinnell JA, Miller LG, Eells SJ, Cui E, Huang SS. A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of factors associated with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization at time of hospital or intensive care unit admission. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2013;34(10):1077–1086. doi: 10.1086/673157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Yamasaki F, Takeuchi S, Uehara Y, Matsushita M, Arise K, Morimoto N, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in community residents of Japan. J Gen Fam Med. 2018;9(3):77–81. doi: 10.1002/jgf2.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lin J, Peng Y, Xu P, Zhang T, Bai C, Lin D, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization in chinese children: a prevalence meta-analysis and review of influencing factors. PloS One. 2016;11(7):e0159728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.den Heijer CD, van Bijnen EM, Paget WJ, Pringle M, Goossens H, Bruggeman CA, et al. Prevalence and resistance of commensal Staphylococcus aureus, including meticillin-resistant S aureus, in nine European countries: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(5):409–415. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Health Protection Scotland. MRSA Screening Programme National Targeted Rollout: MRSA Screening [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2018 Jul 8]. https://www.nes.scot.nhs.uk/media/345435/nes_0117_mrsa_screenprog_v05.pdf
- 91.Holtfreter S, Grumann D, Balau V, Barwich A, Kolata J, Goehler A, et al. Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in the general population in northeast germany: results of the study of health in pomerania (SHIP-TREND-0) J Clin Microbiol. 2016;54(11):2774–2785. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00312-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Karas JA, Enoch DA, Eagle HJ, Emery MM. Random meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrier surveillance at a district hospital and the impact of interventions to reduce endemic carriage. J Hosp Infect. 2009 Apr 1;71(4):327–32 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 93.Reilly JS, Stewart S, Christie P, Allardice G, Smith A, Masterton R et al (2010) Universal screening for meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: interim results from the NHS Scotland pathfinder project. J Hosp Infect. 74(1):35–41 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 94.Barkatali M, Heywood N, White R, Paton R. MRSA screening in orthopaedic surgery: Clinically valuable and cost effective? Acta Orthop Belg. 2013;79(4):463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Dave J, Jenkins PJ, Hardie A, Smith M, Gaston P, Gibb AP, et al. A selected screening programme was less effective in the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonisation in an orthopaedic unit. Int Orthop. 2014;38(1):163–167. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-2079-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Dulon M, Peters C, Schablon A, Nienhaus A. MRSA carriage among healthcare workers in non-outbreak settings in Europe and the United States: a systematic review. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;3:363. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Sassmannshausen R, Deurenberg RH, Köck R, Hendrix R, Jurke A, Rossen JWA et al (2016) MRSA Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors among Health-Care Workers in Non-outbreak Situations in the Dutch-German EUREGIO. Front Microbiol [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 98.Peters C, Kleinmüller O, Nienhaus A, Schablon A. Prevalence and risk factors of MRSA colonisations: a cross-sectional study among personnel in outpatient care settings in Hamburg, Germany. BMJ Open. 2018;16(7):e021204. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-021204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Kyle RG, Wills J, Mahoney C, Hoyle L, Kelly M, Atherton IM. Obesity prevalence among healthcare professionals in England: a cross-sectional study using the Health Survey for England. BMJ Open. 2017;7(12):e018498. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Luteijn JM, Hubben GAA, Pechlivanoglou P, Bonten MJ, Postma MJ. Diagnostic accuracy of culture-based and PCR-based detection tests for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17(2):146–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Weatherall M. Systematic review and meta-analysis: tools for the information age. Postgrad Med J. 2017;93(1105):696–703. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2017-135034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.University of York, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. PROSPERO [Internet]. [cited 2019 Sep 1]. https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/
- 103.Roth VR, Longpre T, Coyle D, Suh KN, Taljaard M, Muldoon KA, et al. Cost Analysis of Universal Screening vs. Risk Factor-Based Screening for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) PLOS ONE. 2016;27(7):e0159667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Roth VR, Longpre T, Taljaard M, Coyle D, Suh KN, Muldoon KA, et al. Universal vs risk factor screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a large multicenter tertiary care facility in Canada. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2016;37(1):41–48. doi: 10.1017/ice.2015.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Deeny SR, Cooper BS, Cookson B, Hopkins S, Robotham JV (2013) Targeted versus universal screening and decolonization to reduce healthcare-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Hosp Infect (1):33–44 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 106.UK Department of Health. Implementation of modified admission MRSA screening guidance for NHS (2014) [Internet]. 2014. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/345144/Implementation_of_modified_admission_MRSA_screening_guidance_for_NHS.pdf
- 107.Fish R, Kutter E, Wheat G, Blasdel B, Kutateladze M, Kuhl S. Bacteriophage treatment of intransigent Diabetic toe ulcers: a case series. J Wound Care. 2016;25(1):S27–S33. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analysed during the current study.