Abstract
Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a strategy used worldwide for managing hypertension. In addition to converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, ACE also converts neurotoxic β-amyloid protein 42 (Aβ42) to Aβ40. Because of its neurotoxicity, Aβ42 is believed to play a causative role in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD), whereas Aβ40 has neuroprotective effects against Aβ42 aggregation and also against metal-induced oxidative damage. Whether ACE inhibition enhances Aβ42 aggregation or impairs human cognitive ability are very important issues for preventing AD onset and for optimal hypertension management. In an 8-year longitudinal study, we found here that the mean intelligence quotient of male, but not female, hypertensive patients taking ACE inhibitors declined more rapidly than that of others taking no ACE inhibitors. Moreover, the sera of all AD patients exhibited a decrease in Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity compared with sera from age-matched healthy individuals. Using human amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice, we found that a clinical dose of an ACE inhibitor was sufficient to increase brain amyloid deposition. We also generated human amyloid precursor protein/ACE+/− mice and found that a decrease in ACE levels promoted Aβ42 deposition and increased the number of apoptotic neurons. These results suggest that inhibition of ACE activity is a risk factor for impaired human cognition and for triggering AD onset.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease, amyloid-beta (AB), amyloid precursor protein (APP), neurodegeneration, amyloid, ACE inhibitor, Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), dementia, IQ decline, neurotoxicity
Introduction
Alzheimer's disease (AD)4 is the most common neurodegenerative illness that causes dementia. AD is characterized by β-amyloid protein (Aβ) deposition in the senile plaques (1). Aβ42 and Aβ40 are the major species generated by sequential proteolytic cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β- and γ-secretases. Aβ42 is essential for amyloid deposition and is considered to be the initiating molecule for AD pathogenesis (2, 3). In contrast, other studies have shown that monomeric Aβ40 has antioxidant effects against transitional metal–induced oxidative damage and inhibits Aβ42 toxicity and accumulation of Aβ42 in brain (4–7).
Familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD) is caused by point mutations in APP, presenilin 1 (PSEN1, PS1), or presenilin 2 (PSEN2, PS2) (8). PS1 and PS2 are critical components of the γ-secretase complex, and all FAD mutations in PSEN1 or PSEN2 are related to an increase in the Aβ42 level or a decrease in the Aβ40 level (9). Studies in human brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma, as well as in transgenic animals and cellular systems modeling FAD mutations, all showed that the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio is consistently elevated when PSEN is mutated (10, 11). These lines of evidence also imply that the loss of neuroprotective Aβ40 is a potential factor in the onset of AD.
To reduce the levels of toxic Aβ42 or the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio, many γ-secretase inhibitors or modulators have been designed and tested in clinical trials, but none have succeeded (3, 12). In addition to modulating the cleavage site of γ-secretase, the conversion of Aβ42 to Aβ40 after Aβ production is also considered to be an effective method for reducing the levels of Aβ42 and the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio. The Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity is found in human brain, and the converting enzyme has been identified as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (13, 14). Unlike most proteases, mammalian somatic ACE has two catalytic domains. Interestingly, the angiotensin-converting activity is predominantly mediated by the C-terminal domain, whereas the Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity is only mediated by the N-terminal domain (15, 16). ACE has two polymorphisms that lead to insertion (I) or deletion of a 287-bp sequence of DNA in intron 16. The I allele of ACE is associated with lower ACE levels in the serum and tissues and was a potent risk factor for the onset of AD in some genetic and large meta-analysis studies (17–19).
ACE inhibitors are one of the most commonly used classes of drugs for the treatment of hypertension and are also widely used in the treatment of heart failure and diabetic chronic kidney disease (20, 21). ACE is the target of antihypertensive therapy using ACE inhibitors. ACE converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent blood vessel constrictor, and degrades bradykinin, a blood vessel dilator, thus elevating blood pressure (22). Hypertension has been traditionally associated with the etiology of vascular dementia. However, vascular risk factors including hypertension are increasingly being implicated in AD (23, 24). Longitudinal studies suggest that high blood pressure in midlife is associated with a higher incidence of AD in late life, and some studies suggest that taking ACE inhibitors is risk factor for the development of AD (25, 26). However, other studies have shown that centrally acting ACE inhibitors may protect against cognitive decline in patients with AD (27, 28). ACE inhibitors vary in terms of binding affinity and ACE domain specificity with ACE (16, 29), and the role of ACE inhibitors in the pathogenesis of AD is still not fully understood.
To clarify the mechanism underlying these contradictory findings regarding the effects of ACE inhibitors on AD pathogenesis, in a longitudinal study, we assessed changes in intelligence in nondemented human subjects who were taking ACE inhibitors and other antihypertensive medicines. We also studied amyloid deposition in human APP (hAPP) transgenic mice treated with a clinical dose and a high dose of an ACE inhibitor. To mimic the effects of ACE inhibitors that partially inhibit ACE and to exclude the side effects of ACE inhibitors, we generated a mouse model of AD that lacks a single ACE locus. ACE inhibitors significantly reduced human intelligence quotient (IQ), but only in men. A clinical dose of an ACE inhibitor was sufficient to enhance brain amyloid deposition in hAPP transgenic mice. Moreover, ACE deficiency at a single locus, which leads to a partial decrease in ACE activity, significantly exacerbated brain Aβ42 deposition.
Results
Impaired intelligence in men taking ACE inhibitors and decreased Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity in AD serum
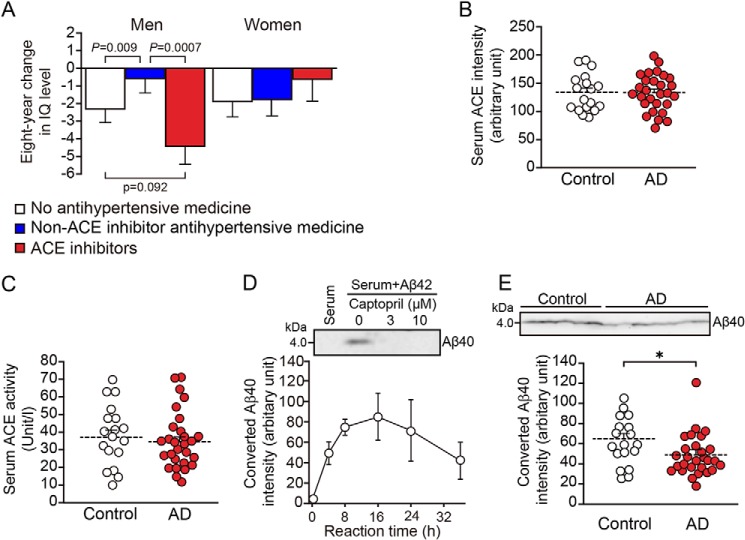
1964 participants (992 men, 972 women) completed the intelligence tests and medication interview. 339 (178 men, 161 women) were taking antihypertensive, and 81 (49 men, 32 women) were taking ACE inhibitors. The fixed effect of the antihypertensive and ACE inhibitors was highly significant in men (p = 0.0006). The estimated 8-year changes in IQ level in men aged 70–79 years old with a blood pressure of 120/80 mmHg and an IQ of 100 at baseline were −2.3 ± 0.74 (p = 0.0015) in the group taking no antihypertensive medication, −0.495 ± 0.86 (not significant) in the group taking non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medication, and −4.26 ± 1.12 (p < 0.0001) in the group taking ACE inhibitor medication. In men, the decrease in IQ level in the group taking ACE inhibitor medication was significantly greater than that in the group taking non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medication (p = 0.0007). In women, the fixed effect of the antihypertensive and ACE inhibitors was not significant, and no significant differences in IQ change among the three groups were observed (Fig. 1A). The above results suggest that taking ACE inhibitors impairs intelligence, as assessed by IQ level, in men, but not in women. By the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scales–Revised–Short Forms (WAIS-R-SF), taking ACE inhibitor medication was also associated with the decrease in similarities and picture completion in men, whereas not associated with the decrease in information or digit symbol coding in men or women (data not shown).
Figure 1.
ACE inhibition impairs human IQ in men, and serum Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity is lower in AD patients than in age-matched normal controls. A, estimated mean and standard error of the 8-year change in IQ level following use of antihypertensive medication in men and women aged 70–79 years old with blood pressure 120/80 mmHg and IQ 100 at baseline. The data are the means ± S.E., one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison. The groups were: no antihypertensive medicine (814 men and 811 women), non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medicine (129 men and 129 women), and ACE inhibitors (49 men and 32 women). B, ACE in the serum from control individuals and AD patients was examined with Western blotting, and the intensity of ACE bands was measured and quantified. C, serum ACE activity of control individuals and AD patients was analyzed. D, serum from a control individual was mixed with synthetic Aβ42, with or without captopril, and incubated for 4 h. The generation of Aβ40 was examined with Western blotting (upper panel). The generation of Aβ40 in the mixture of control serum and synthetic Aβ42 was quantified after 4–36 h of incubation (lower panel). E, serum from control individuals and AD patients was mixed with synthetic Aβ42, and the generation of Aβ40 after 4 h of incubation was examined with Western blotting. The intensity of Aβ40 bands was measured and quantified. The data are the means ± S.E. Control, n = 18; AD, n = 28. *, p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni–Dunn test.
ACE has two catalytic domains. The C-domain of ACE is the predominant site for converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, whereas the N-domain is responsible for converting Aβ42 to Aβ40 (16). We examined the ACE level and ACE activity in the serum of AD and control groups and did not find any change in the AD patients (Fig. 1, B and C). We then studied the conversion of Aβ42 to Aβ40 in the serum of both groups. The generation of Aβ40 from Aβ42 was inhibited by captopril (Fig. 1D, upper panel). Aβ40 reached a peak after 8–16 h of incubation and decreased after 36 h of incubation in the control serum, suggesting that the degradation of Aβ40 also occurred simultaneously in the serum (Fig. 1D). However, the generation of Aβ40 from Aβ42 after 4 h of incubation decreased in the serum of the AD group compared with the control group (Fig. 1E). These results demonstrate that the ACE expression level and the C domain–dependent angiotensin-converting activity in the serum of normal controls and AD patients are similar; however, the serum N domain–dependent Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity of ACE in AD patients was lower than that in normal controls. Thus, the decreased Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity in the serum may be involved in AD pathogenesis and may be useful as a diagnosis index.
A clinical dose of an ACE inhibitor enhances Aβ deposition in hAPPSw mice
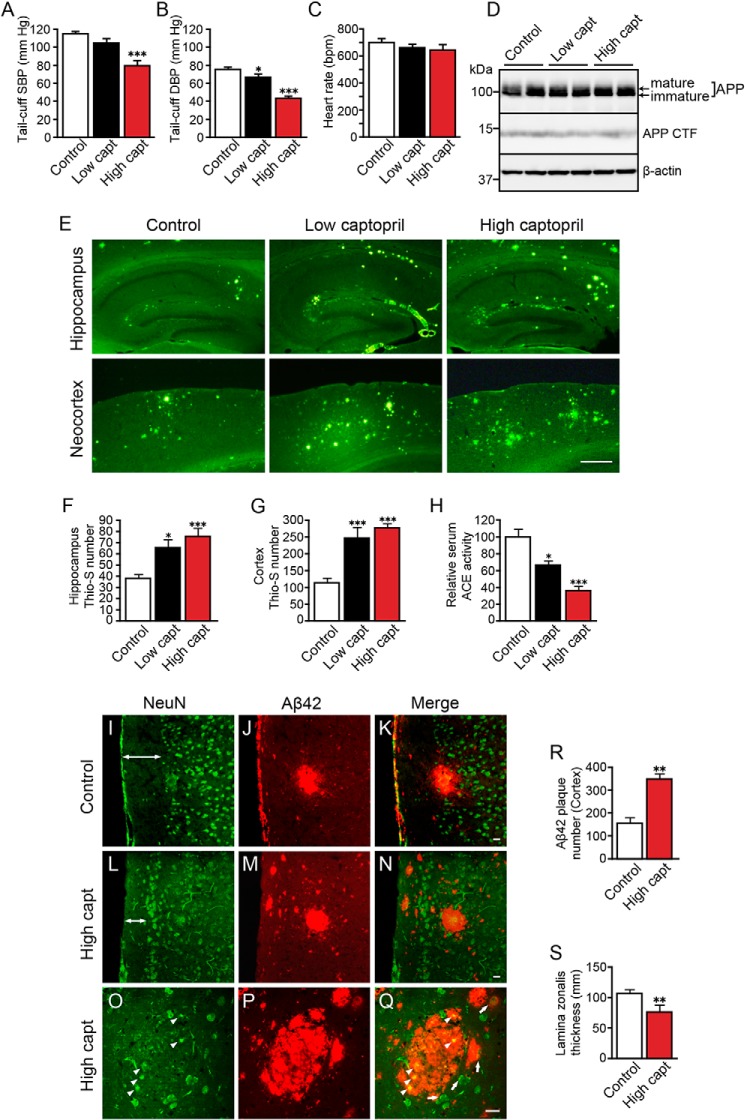
To study whether a clinical dose of an ACE inhibitor enhanced amyloid deposition, we fed 6-month-old hAPPSw mice a low or high captopril–containing diet. The average intake of captopril per animal was 1 mg/kg/day for the low captopril diet, which is similar to the level achieved with clinical treatment with captopril in humans (30), and 30 mg/kg/day for the high captopril diet. The significant blood pressure reducing effect of low captopril treatment was only observed for diastolic blood pressure, whereas high captopril treatment markedly reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure (Fig. 2, A and B). The heart rate of mice did not change in all the three groups (Fig. 2C).
Figure 2.
Captopril at a clinical dose exacerbates Aβ deposition in hAPPSw mice and induced neuronal damage at a high dose. A–C, systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and heart rate of 17-month-old mice were indirectly measured with a tail-cuff apparatus. D, APP and APP CTF expression levels in the cortex were examined with Western blotting. E, thioflavin S staining of brain sections from 17-month-old captopril (capt)–treated hAPPSw mice (Tg2576). Low captopril indicates treatment with a clinical dose of captopril. F and G, number of thioflavin S–positive plaques (per section) in the hippocampus (F) and cortex (G) of the control, low captopril-treated, and high captopril-treated mice. Three or four sections were counted and averaged for each mouse. H, relative ACE activity in the serum of control, low captopril-treated, and high captopril-treated mice. I–Q, brain sections from control (I–K) and high captopril-treated mice (L–Q) were immunolabeled with NeuN antibody (green, I, L, and O) and Aβ42 antibody (red, J, M, and P), and imaged with confocal microscopy. Apoptotic neurons are indicated with arrowheads (O and Q). Diffuse Aβ42 deposition around neurons with nuclei was indicated with arrows (Q). R, number of Aβ42-positive plaques (per section) in the cortex of the control and high captopril-treated mice. S, thickness of lamina zonalis of the control and high captopril-treated mice. The data are the means ± S.E.; n = 6–12 mice in each group; male, 3–6; female, 3–6. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni–Dunn test versus the control diet mice. Scale bars indicate 500 μm in E and 20 μm in I–Q.
We previously reported that ACE converts Aβ42 to Aβ40 and that inhibition of ACE using a high dose of captopril increases Aβ42 deposition in hAPPSw mice (13). Because we found that ACE inhibition impaired human IQ, an important issue is whether a clinical dose of ACE inhibitor enhances Alzheimer's pathology. The APP expression level and APP CTF level did not change in the cortex of low or high captopril-treated hAPPSw mice compared with control mice (Fig. 2D). ACE activity in the serum of low captopril-treated mice decreased more than 30% and decreased more than 60% in the high captopril-treated mice compared with the control mice (Fig. 2H). Thioflavin S staining of brain sections of 17-month-old hAPPSw mice showed that captopril dose-dependently enhanced amyloid deposition in both the hippocampus and cortex (Fig. 2E). High captopril–treated mice had 2–2.3 times more thioflavin S–positive plaques (per section) than control mice. Mice treated with a clinical dose of captopril had a 1.7-fold increase (per section) in hippocampal amyloid deposition and a 2-fold increase (per section) in cortical amyloid deposition (Fig. 2, F and G). These results suggest that a clinical dose of an ACE inhibitor can also increase Aβ deposition in hAPP transgenic mice.
We also examined whether potent ACE inhibition enhanced Aβ42 deposition and induced neuronal damage in the cortex of hAPPSw mice. As expected, the number Aβ42 amyloid plaques (per section) were significantly increased in the cortex of high captopril-treated hAPPSw mice compared with control mice (Fig. 2, I–N and R). Moreover, the lamina zonalis of cortex, which mainly contains neuronal fibers, became thinner in high captopril-treated mice compared with control mice (Fig. 2, I, L, double-headed arrows, and S). Notably, shrunken neuronal nuclei visualized with NeuN immunostaining were present in the center of some Aβ42 plaques (Fig. 2, O and Q, arrowheads). In addition, some Aβ42 deposition was found surrounding or on neurons with showing normal morphology as seen with NeuN immunostaining (Fig. 2Q, arrows). These results suggest that potent ACE inhibition elevates Aβ42 deposition and facilitates degeneration of neuronal fibers in hAPPSw mice and that the neuronal damage may be induced by aggregation of Aβ42 on neurons.
Aβ42 deposition and Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio increased in hAPP/ACE+/− mice
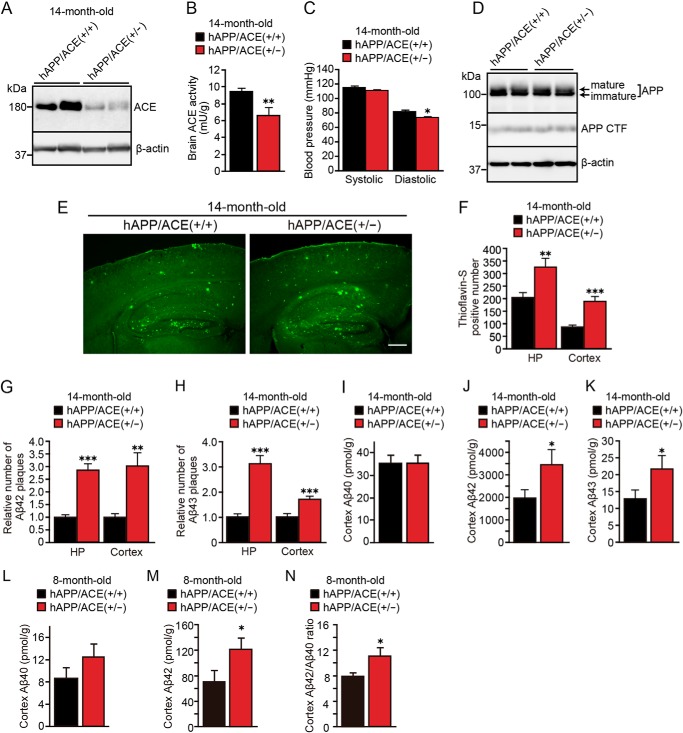
To determine the role of ACE in brain Aβ deposition in vivo and to exclude nonspecific effects of captopril, we cross-mated hAPPSwInd mice to ACE+/− mice and generated hAPP/ACE+/− mice. We found no difference in body weight, heart rate, and survival rate between 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice (data not shown). Western blotting analysis showed that the ACE protein level in the cortices of hAPP/ACE+/− mice was reduced by approximately half compared with hAPP/ACE+/+ mice (Fig. 3A). ACE activity in the cortical homogenate of hAPP/ACE+/− mice was also significantly reduced (Fig. 3B). The diastolic blood pressure of hAPP/ACE+/− mice was decreased to 73.4 ± 2.6 mmHg compared with hAPP/ACE+/+ mice (81.6 ± 2.4 mmHg), whereas the systolic blood pressure was not different between these mice (Fig. 3C). The expression levels of APP and APP CTF in the cortices of 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/− mice were similar to those of hAPP/ACE+/+ mice (Fig. 3D).
Figure 3.
Heterozygous ACE-deficient mice showed increased Aβ42 and Aβ43 deposition and increased Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio. A, Western blotting of ACE in brain homogenates from 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice. B, ACE activity in brain homogenates from 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice. C, systolic and diastolic blood pressure was measured with a tail-cuff apparatus. Only diastolic pressure showed a decrease in hAPP/ACE+/− mice. D, APP and APP CTF expression levels in the cortex of 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice were examined with Western blotting. E, thioflavin S staining of brain sections from 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice revealed that partial ACE deficiency enhanced Aβ deposition. F, number of thioflavin S–positive plaques (per section) in the hippocampus and cortex of 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice. G and H, relative numbers of Aβ42 (G) and Aβ43 (H) (per section) in the hippocampus and cortex of 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice. I–K, Aβ40, Aβ42, and Aβ43 levels in the cortex of 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice were determined with ELISA. L and M, Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in the cortex of 8-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ and hAPP/ACE+/− mice were determined with ELISA. N, Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio increased in the cortex of 8-month-old hAPP/ACE+/− mice. HP, hippocampus. The data are the means ± S.E. Three or four sections were counted and averaged for each mouse; n = 9–14 mice in each group; male, 4–7; female, 5–7. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni–Dunn test versus hAPP/ACE+/+ mice. Scale bar, 500 μm.
We next examined the effect of a partial decrease in ACE activity on brain Aβ deposition in hAPP/ACE+/− mice. Aβ42 plaques can rarely be detected in the hippocampus of 8-month-old mice, and they increase in an age-dependent manner (31). The numbers of thioflavin S–positive plaques in the hippocampus and cortex of 8-month-old hAPP/ACE+/+ mice were 39 ± 3.7 and 19 ± 2.9, respectively. In contrast, 8-month-old hAPP/ACE+/− mice showed a higher average number of thioflavin S–positive plaques in the hippocampus (63 ± 6.5, p < 0.05) but did not show significant increase of plaques in the cortex (22 ± 2.6). In 14-month-old mice, the decrease in brain ACE significantly enhanced Aβ deposition both in the cortex and hippocampus of hAPP/ACE+/− mice (Fig. 3E). Thioflavin S–positive amyloid plaques were increased 1.6-fold in the hippocampus and 2.2-fold in the cortex of hAPP/ACE+/− mice compared with hAPP/ACE+/+ mice (Fig. 3F). Analysis of hAPP/ACE+/− mice using an Aβ42-specific antibody showed 2.7- and 3.1-fold increases in the number of Aβ42-immunopositive plaques in the hippocampus and cortex, respectively, compared with the number in hAPP/ACE+/+ mice (Fig. 3G). We previously reported that ACE also converts the species that is deposited earliest, Aβ43, to Aβ41 (31). The number of Aβ43-immunopositive plaques in the hippocampus and cortex were increased 3.1- and 1.7-fold, respectively, in hAPP/ACE+/− mice than in hAPP/ACE+/+ mice (Fig. 3H). Quantitation of Aβ with ELISA also revealed significant increases in the level of Aβ42 and Aβ43 in the cortex of 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/− mice, supporting the histological findings (Fig. 3, J and K). Notably, quantitation of Aβ with ELISA revealed that Aβ42 level significantly increased in the cortex of 8-month-old hAPP/ACE+/− mice, whereas the Aβ40 level did not show significant change, thereby resulting in an increase in the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio (Fig. 3, L–N). These results suggest that reduced ACE activity in the brain leads to decreased conversion of Aβ42 and Aβ43 by ACE, increased Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio, and enhanced amyloid plaque burden consisting predominantly of Aβ43 and Aβ42 depositions in brain.
Apoptotic neurons increased in the cortex of hAPP/ACE+/− mice
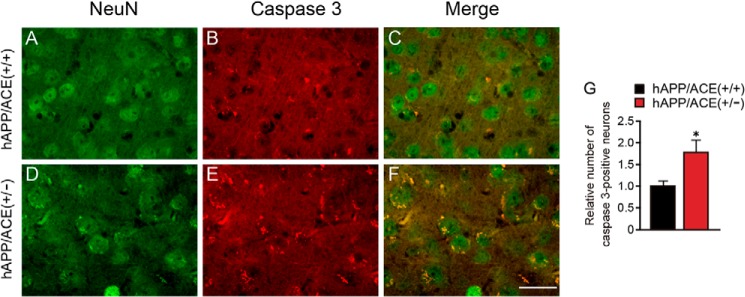
Because toxic species of Aβ (Aβ42 and Aβ43) showed high accumulation in the cortex and hippocampus, we examined whether toxic Aβ42 and Aβ43 can induce neuronal apoptosis. By using cleaved caspase-3 and NeuN antibodies, which recognize active caspase-3 and mature neurons, respectively, we found that the number of caspase-3–immunopositive neurons was 1.8-fold higher in the cortex of 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/− mice than in control mouse cortex (Fig. 4, C, F, and G). However, no shrunken neuronal nuclei or dead neurons were observed in the brain of hAPP/ACE+/− mice. These results suggest that the increase in accumulation of neurotoxic Aβ induces neuronal apoptosis.
Figure 4.
Apoptotic neurons increased in 14-month-old hAPP/ACE+/− mice. A–F, representative images of NeuN immunostaining (green, A and D), cleaved caspase-3 immunostaining (red, B and E), and their merged images (C and F) are shown. G, relative number of cleaved caspase-3–immunopositive neurons (per field) in the cortex. The data are the means ± S.E., six microscope fields were counted for each mouse; n = 12–14 mice for each group; male, 6–7; female, 6–7. *, p < 0.05, by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni–Dunn test. Scale bar, 20 μm.
Discussion
In addition to the key role played by ACE in the renin–angiotensin system, ACE also contributes to conversion of the toxic species, Aβ42 and Aβ43, to the neuroprotective species, Aβ40 (13, 31, 32). In this study, we demonstrated that hypertensive patients taking ACE inhibitors had a marked IQ decline in 8 years compared with those taking other antihypertensive drugs. Interestingly, this decline was only observed in men. We further showed that a clinical dose of captopril significantly exacerbated brain amyloid deposition in a mouse model of AD. Hypertension in midlife is a risk factor not only for cerebrovascular diseases but also for the development of AD. In contrast, hypotension in late life is consistently associated with an increased risk of AD, particularly in individuals who took antihypertensive drugs (25, 33). These findings suggest that blood pressure–regulating systems or antihypertensive drugs are associated with the pathogenesis of AD.
Meta-analyses have shown that I allele of ACE, with lower ACE activity in the serum and tissue, is related to the increased risk of AD development (18, 19). In addition, a sex difference in ACE activity was also reported in healthy individuals in which ACE activity is higher in healthy males than females (34). The basal plasma activity of ACE is significantly higher in men, and men show a greater decrease in ACE activity than women after taking ACE inhibitors (35). Taken together with our findings, these lines of evidence suggest that a greater decrease in ACE activity is associated with the IQ decline in men who took ACE inhibitors for 8 years. Notably, men taking non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medication had a lower 8-year decline in IQ than men taking ACE inhibitors or no antihypertensive medication (Fig. 1A). Thus, analyses of a larger group size are likely needed to effectively determine whether ACE inhibitor treatment has a negative effect on IQ compared with no antihypertensive medication group. Cognitive decline without dementia has commonly been considered a normal consequence of brain aging but can also indicate the onset of dementia. Less IQ level has been shown to be a risk factor for progression from mild cognitive impairment to degenerative dementia (36). A decrease of 10 points or more of IQ is considered as deteriorated IQ in schizophrenia (37), whereas the meaningful change of IQ suggesting future onset of mild cognitive impairment or AD has not yet been reported. In our study, men who had 7.5 points or more decreased IQ were 20.4% in ACE inhibitor group, 16.3% in non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medication group, and 14.9% in no antihypertensive medication group. A decrease of 7.5 points of IQ indicates that an average IQ level drops to lower one-third IQ level, which may increase the risk of further cognitive decline.
Moreover, a recent study reported that the toxic species, Aβ42, is elevated in the plasma of cognitively impaired individuals taking ACE inhibitors and that this elevation in Aβ42 may be directly caused by inhibition of ACE-mediated Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity (38). Because inhibition of ACE may elevate the Aβ42 level not only in the plasma but also in the brain, our findings suggest that IQ impairment by ACE inhibitors in men may be a consequence of the increased level of toxic Aβ42. Thus, in addition to γ-secretase, which determines the generation of Aβ42 and Aβ40, the Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity of ACE may also contribute to the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio and be involved in AD onset. Because the Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity and angiotensin-converting activity are localized in different domains of ACE, measurement of angiotensin-converting activity may not reflect the Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity. By using synthetic Aβ42 as a substrate, we found that the Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity was decreased in the serum of AD patients (Fig. 1E). This result also suggests that ACE inhibition is a risk factor for a decline in cognitive ability and AD onset. The observation that treatment of hAPP mice with a clinical dose of captopril for 11 months was sufficient to increase amyloid deposition also supports this notion. Notably, we previously reported that the treatment with a high dose of captopril for 7 months did not significantly increase amyloid deposition in 13-month-old mice (13). Similar to our results, the treatment with a high dose captopril for 28 days in two kinds of AD model mice did not result in increased Aβ levels or amyloid deposition (39). These findings suggest that a long-term, but not a short-term, ACE inhibition contributes to increased amyloid deposition.
To clarify whether neuronal damage is associated with amyloid deposition, we performed immunostaining using anti-NeuN and anti-Aβ42 antibodies. The shrunken neuronal nuclei were found in the center of condensed Aβ42-positive amyloid plaques, and diffuse Aβ42 deposition was co-localized with NeuN-positive neurons with intact nuclei (Fig. 2, O–Q). These findings suggest that the formation of diffuse Aβ42 plaques initiates from neurons and finally induces neuronal death with progression of formation of condensed Aβ42 plaques. We also observed that the lamina zonalis of the cortex became thinner in high captopril–treated mice compared with control mice, suggesting that loss of neuronal fibers occurred as a consequence of neuronal death in amyloid plaques (Fig. 2, I, L, and S). Thus, potent ACE inhibition may lead to neuronal damage by exacerbating Aβ42 deposition around neurons. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that a high concentration of captopril may induce neuronal damage independent of Aβ deposition; thus, WT mice treated with a high concentration of captopril need to be studied further.
To study the effect of ACE on Aβ deposition in vivo and to exclude side effects of ACE inhibitors, we generated hAPP/ACE+/− mice and examined Aβ deposition and neuronal apoptosis. Because hAPP/ACE−/− mice show extremely low viability and die before weaning, analysis of hAPP/ACE−/− mice was not performed. hAPP/ACE+/− mice showed lower brain ACE activity and markedly increased Aβ42 and Aβ43 deposition (Fig. 3, B and G–M), suggesting that low brain ACE activity is associated with Aβ42 and Aβ43 deposition. In the absence of captopril, reduced ACE activity significantly increased the number of apoptotic neurons in hAPP/ACE+/− mice compared with hAPP/ACE+/+ mice. A previous study showed that valsartan, an angiotensin receptor antagonist, significantly lowered amyloid deposition and improved spatial learning in a mouse model of AD (40). We also demonstrated that angiotensin type 1a receptor deficiency ameliorated brain amyloid pathology (41). These results indicate that medications lowering blood pressure by ACE inhibition and angiotensin receptor inhibition have opposite effects on amyloid deposition. In view of these findings, we conclude that a decrease in ACE activity may exacerbate Aβ42 and Aβ43 deposition and that neuronal apoptosis may be a consequence of the aggregation of Aβ42 and Aβ43 but not the lower blood pressure. A previous study demonstrated that mice lacking ACE expression in the brain, but with 100-fold cardiac ACE and normal blood pressure, showed no alterations in the endogenous Aβ concentration of brain (42), suggesting that body ACE may degrade peripheral Aβ and then affect brain Aβ levels. Because the Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity is limited to the N domain of ACE, a mouse model that selectively lacks N-domain Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity of ACE needs to be established for further investigation. The decrease in ACE protein level and ACE activity in hAPP/ACE+/− mice may also reflect the decrease in the N domain–specific Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity. A previous in vitro study demonstrated that cell-derived human Aβ40 and Aβ42 were degraded by transfected ACE and elevated by ACE inhibition (43). However, in addition to altered Aβ degradation, we cannot exclude the possibility that ACE inhibition/deletion may the enhance Aβ deposition by other functions of this enzyme. Whether soluble Aβ or Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio increases in young mice without Aβ deposition needs to be further studied.
Although women are more susceptible for developing AD than men (44), we found that ACE treatment in human subjects impaired IQ in men, which may be due to a greater decrease in ACE activity for men than for women after taking ACE inhibitors (35). We did not find any gender difference of amyloid deposition in captopril-treated hAPPSw mice or in hAPP/ACE+/− mice, suggesting that IQ decline may not be closely associated with amyloid deposition alone (45). Alternatively, soluble and toxic Aβ oligomers may be increased by ACE inhibition in men and contribute to IQ decline (46). The gender difference may be species-specific, however; whether male mice treated with captopril or with heterozygous deletion of ACE show cognitive impairment needs to be further investigated. Moreover, whether ACE inhibitors enhance amyloid deposition in human (with or without gender difference) is proving to be of importance and needs to be clarified. Taken together, our findings suggest that ACE inhibitors may impair human cognitive ability through enhancing Aβ42 and Aβ43 deposition in the brain and should be carefully used in hypertensive patients with other AD risk factors, such as APOE4 carriers. Because the Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity and angiotensin-converting activity are located in the N- and C-terminal domain of ACE, respectively, development of ACE inhibitors that specifically inhibit the C-terminal domain is desired.
Experimental procedures
Intelligence examination
The subjects in this study were participants in the National Institute for Longevity Sciences Longitudinal Study of Aging (NILS-LSA). The NILS-LSA, which started in 1997, is a population-based study of aging and age-related diseases. The participants were residents of Aichi Prefecture in central Japan who were randomly selected from the resident registration and stratified by both age and gender. Details of the NILS-LSA have been described elsewhere (47). The study protocol was approved by the Committee of Ethics of Human Research of the National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant. All studies of human subjects abide by the Declaration of Helsinki principles. The total number of participants in the first wave of examination was 2267, and they were aged 40–79 years. Of these, 1964 participants (992 men and 972 women) completed the intelligence tests and medication interview and were also determined to be eligible for follow-up. Of these, 339 (178 men and 161 women) were taking antihypertensive, and 81 (49 men and 32 women) were taking ACE inhibitors. There were no significant differences in age, gender, and smoking rate between non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medicine group and the ACE inhibitor group. In 81 patients who were taking ACE inhibitors, 32 were solely taking ACE inhibitors, 46 were also taking calcium antagonists, and 4 were also taking other antihypertensive medicine for combination therapy (with overlapping). In 258 patients who were taking antihypertensive medicine except ACE inhibitor, 178 were taking calcium antagonists, 30 were taking β-blockers, and 91 were taking other antihypertensive medicine (with overlapping). The ratios of patients taking ACE inhibitors were 68.8% after 2 years, 64.2% after 4 years, 65.5% after 6 years, and 61.8% after 8 years. ACE inhibitors taken by the patients were shown in Table 1, and the medicines taken before the investigating period were not studied. The blood pressure of ACE inhibitor group (140 ± 24/83 ± 13 mmHg) was similar with the non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medicine group (138 ± 18/82 ± 10 mmHg). The percentage of patients with ischemic heart diseases, diabetes, or cancer in ACE inhibitor group was marginally higher than the group taking antihypertensive medicine except ACE inhibitor. No exclusion criteria were used in this study. The subjects were followed up every 2 years. The cumulative number of intelligence changes from the first examination and each of the four sequential examinations was 6317 (3266 men and 3051 women).
Table 1.
ACE inhibitors used in hypertensive patients
+, brain-penetrating ACE inhibitor; −, non–braining-penetrating ACE inhibitor; NA, not applicable.
| ACE inhibitors | Number of patients | Brain-penetrating |
|---|---|---|
| Derapril | 2 | − |
| Sirazapril | 3 | − |
| Temocapril | 5 | − |
| Trandolapril | 8 | + |
| Captopril | 5 | + |
| Quinapril | 2 | − |
| Alacepril | 7 | − |
| Lisinopril | 4 | + |
| Imidapril | 15 | − |
| Benazepril | 5 | − |
| Enalapril | 18 | − |
| Fosinopril | 4 | + |
| Unknown | 3 | NA |
Intelligence was assessed in terms of the IQ level using the Japanese WAIS-R-SF (48). The difference in the changes in IQ level within 8 years with the intake of antihypertensive and ACE inhibitors was examined using a mixed-effect model that controlled for initial IQ level, age, number of follow-up years, interaction between age and number of follow-up years, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (fixed effects), adjusting with or without ischemic heart diseases, diabetes or cancer, interindividual differences (random effect), and auto regression of longitudinal data in men and women. The 8-year change in IQ level was compared among the groups with no antihypertensive medication, with non-ACE inhibitor antihypertensive medication, and with ACE inhibitor medication. The data were adjusted by interaction with age. Statistical analysis was conducted using SAS version 9.1.3 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Serum Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity
Human serum from living AD patients and normal age-matched subjects was collected using standard methods (31). In total, 28 AD patients and 18 normal subjects were enrolled from the Iwate Medical University Hospital. The samples were aliquoted and frozen at −80 °C after collection until use. The age-matched normal controls included 10 males and 8 females with no known neurological disorder whose average age was 75.1 ± 1.8 years (mean ± S.E.), and the AD patients included 11 males and 17 females with a mean age of 75.4 ± 1.2 years (mean ± S.E.). The clinical diagnosis of AD was based on National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Diseases and Stroke/Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association Alzheimer's criteria. The mean Mini-Mental State Examination score of AD patients was 18.6 ± 1.0 (mean ± S.E.). Human serum was mixed with 30 μm Aβ42 and incubated at 37 °C for 4–36 h. Aβ40 was detected by Western blotting using an anti-Aβ40 antibody (IBL catalog no. 10047, Takasaki, Japan), and the intensity of Aβ40 bands was measured using ImageJ (National Institutes of Health).
Mice and tissues
Human APP Swedish mutation transgenic mice (hAPPSw, Tg2576) were purchased from Taconic Farms (Germantown, NY), and mice expressing human APP bearing the Swedish and Indian mutations (hAPPSwInd, J20) were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. Heterozygous mice lacking both the somatic and testicular isozyme forms of the ACE gene (ACE+/−) were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. 6-month-old hAPPSw mice were fed a low or high captopril-supplemented diet for 11 months. The average intakes of captopril per animal were 1 and 30 mg/kg/day for the low and high doses of captopril, respectively. The intake of 1 mg/kg/day is similar to the clinical dose used in humans. Brain sections from 17-month-old mice were stained with thioflavin S to visualize Aβ deposition. We cross-mated hAPPSwInd mice and ACE+/− mice to generate hAPP/ACE+/− mice and control mice. The mice were housed on a 12-h light/dark schedule with ad libitum access to standard mouse chow and water. Each group in this study contained 6–14 mice, and the number of male and female mice in each group was similar. Mouse body weight, heart rate, and blood pressure were measured before sacrifice. Heart rate and blood pressure (systolic, diastolic, and mean pressure) in conscious mice were indirectly measured with a tail-cuff apparatus (BP-98A-L; Softron, Tokyo, Japan). The mice were killed by inhalation of CO2, and 0.5 ml of blood was collected from the right atrium. The mice were then perfused intracardially with cold PBS containing 5 units/ml heparin (Sigma–Aldrich). The left hemisphere of the brain was fixed in 4% buffered paraformaldehyde solution at 4 °C for immunohistochemical analysis. Brain regions (cortex and hippocampus) were dissected from the right hemisphere and used to assess expression and activity of ACE. All animal procedures were approved by the Iwate Medical University Committee for Animal Use (41).
Immunohistochemistry and thioflavin S staining
The left hemispheres of the brains of each mouse were incubated in 30% sucrose at 4 °C for more than 24 h and sagittally sectioned into 30-μm-thick slices using a freezing microtome (SM2000R; Leica, Wetzla, Germany). The sections were stained with 0.015% thioflavin S in 50% ethanol for 10 min. Fluorescence was visualized following destaining with 50% ethanol. For Aβ immunostaining, a brief formic acid pretreatment was performed for 3 min. Immunopositive signals of Aβ42 and Aβ43 were visualized using an ABC Elite kit (Vector Laboratories). The following primary antibodies were used: anti-human β-amyloid (1–42) (1:100) rabbit polyclonal IgG (IBL catalog no. 18582) and anti-human β-amyloid (1–43) (1:100) rabbit polyclonal IgG (IBL catalog no. 18583), anti-cleaved caspase-3 (1:200) rabbit polyclonal IgG (Cell Signaling catalog no. 9661), and anti-NeuN monoclonal IgG (1:50) (Chemicon catalog no. MAB377). Secondary antibodies of goat anti-mouse Alexa 488 (A11029) and goat anti-rabbit 568 (A11011; Invitrogen) were diluted at 1:200. The images were acquired using fluorescence microscopy (BZ-9000; Keyence, Osaka, Japan) and laser scanning confocal microscopy (FV1000; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Thioflavin S–positive plaques and deposits of Aβ42 and Aβ43 were counted in 3–4 sections/mouse brain by an observer blinded to the genotypes or groups of mice. Neuronal apoptosis in the cortex was quantitated by counting the number of NeuN-positive cells with or without cleaved caspase-3 signal in six random microscopic fields (500 μm × 500 μm) in the region of the lateral parietal association cortex and secondary visual cortex mediolateral area.
Aβ ELISA
Mouse cortices were homogenized in 10 volumes of lysis buffer containing 5.0 m guanidine HCl in 50 mm Tris/HCl, pH 8.0, and then stored at −80 °C until analysis, as described previously (41). The brain homogenate was diluted 1:2000 for 14-month-old Aβ42 ELISA and 1:20 for 14-month-old Aβ40 ELISA and 8-month-old Aβ40 and Aβ42 ELISA in the dilution buffer provided in the ELISA kit (Wako, Osaka, Japan). Aβ43 levels were detected with a human β-amyloid (1–43) full-length ELISA kit (IBL) after dilution at 1:10. All samples were measured in triplicate.
ACE activity assay
Mouse cortices were homogenized in 4-fold (w/v) 50 mm Tris/HCl, pH 7.5, containing 150 mm NaCl and 0.5% Nonidet P-40 and centrifuged at 4 °C at 10,000 × g for 15 min. ACE activity in the brain supernatant and in mouse serum was measured with an assay kit (LL80001; Life Laboratory, Yamagata, Japan). The fluorescence intensities were measured at an excitation wavelength of 360 nm and an emission wavelength of 480 nm using a multiplate reader (Infinite F500; TECAN, Kanagawa, Japan). The ACE activity in human serum was evaluated by with a colorimetric kit (Buhlmann Laboratories, Schonenbuch, Switzerland) as determined with the synthetic substrate N-hippuryl-l-histidyl-l-leucine following the manufacturer's protocol. The absorbance of this complex was measured at 382 nm. The reaction time was 15 min. Each sample was performed in duplicate.
Immunoblotting
Equal amounts of protein from cortex or equal volume of serum were separated by SDS-PAGE in 5–20% gel and blotted onto nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were incubated with the primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. Appropriate peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies were applied, and the membranes were visualized by SuperSignal Chemiluminesence (Thermo Scientific). The anti-ACE goat IgG was purchased from R&D (AF1513). The anti–C terminus of APP antibody (A8717) and anti–β-actin antibody (A2228) were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich. To detect Aβ42-to-Aβ40–converting activity in human serum, a mixture of serum and synthetic Aβ42 was subjected to 5–20% SDS-PAGE as described previously (13). Anti-human Aβ40 mouse IgG (IBL catalog no. 10047) was used at 1:100.
Statistical analysis
All data are shown as the means ± S.E. The 8-year change in IQ level was compared with the Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison. Statistical analysis was conducted using SAS version 9.1.3 (SAS Institute). To compare two or more groups, one-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Bonferroni–Dunn test was used. p values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Author contributions
S. L., F. A., J. L., X. S., K. K., A. M., M. Y., H. S., and K. Z. data curation; S. L., F. A., H. S., and K. Z. writing-original draft; Y. F., T. M., and C. T.-F. methodology; M. M., H. K., and K. Z. supervision; M. M., H. K., and K. Z. funding acquisition; K. Z. conceptualization; K. Z. project administration; K. Z. writing-review and editing.
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan; Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) 22700399 and 24700383; Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) 26430057 and 19K07846; Grant-in-Aid for Strategic Medical Science Research S1491001; and funds from the Daiko Foundation and the Hirose International Scholarship Foundation and from the Doctoral Startup Foundation of Liaoning Province 201601227, China. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
- AD
- Alzheimer's disease
- ACE
- angiotensin-converting enzyme
- Aβ
- β-amyloid protein
- APP
- amyloid precursor protein
- hAPP
- human APP
- Sw
- Swedish mutation
- Ind
- Indian mutation
- FAD
- familial Alzheimer's disease
- PS
- presenilin
- IQ
- intelligence quotient
- NILS-LSA
- National Institute for Longevity Sciences Longitudinal Study of Aging
- WAIS-R-SF
- Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scales–Revised–Short Forms
- ANOVA
- analysis of variance.
References
- 1. Selkoe D. J. (2011) Alzheimer's disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 3, a004457 10.1101/cshperspect.a004457 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. McGowan E., Pickford F., Kim J., Onstead L., Eriksen J., Yu C., Skipper L., Murphy M. P., Beard J., Das P., Jansen K., DeLucia M., Lin W. L., Dolios G., Wang R., et al. (2005) Aβ42 is essential for parenchymal and vascular amyloid deposition in mice. Neuron 47, 191–199 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.06.030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Selkoe D. J., and Hardy J. (2016) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 8, 595–608 10.15252/emmm.201606210 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Zou K., Gong J. S., Yanagisawa K., and Michikawa M. (2002) A novel function of monomeric amyloid β-protein serving as an antioxidant molecule against metal-induced oxidative damage. J. Neurosci. 22, 4833–4841 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-12-04833.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Zou K., Kim D., Kakio A., Byun K., Gong J. S., Kim J., Kim M., Sawamura N., Nishimoto S., Matsuzaki K., Lee B., Yanagisawa K., and Michikawa M. (2003) Amyloid β-protein (Aβ)1–40 protects neurons from damage induced by Aβ1–42 in culture and in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 87, 609–619 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02018.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Kim J., Onstead L., Randle S., Price R., Smithson L., Zwizinski C., Dickson D. W., Golde T., and McGowan E. (2007) Aβ40 inhibits amyloid deposition in vivo. J. Neurosci. 27, 627–633 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4849-06.2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kuperstein I., Broersen K., Benilova I., Rozenski J., Jonckheere W., Debulpaep M., Vandersteen A., Segers-Nolten I., Van Der Werf K., Subramaniam V., Braeken D., Callewaert G., Bartic C., D'Hooge R., Martins I. C., et al. (2010) Neurotoxicity of Alzheimer's disease Aβ peptides is induced by small changes in the Aβ42 to Aβ40 ratio. EMBO J. 29, 3408–3420 10.1038/emboj.2010.211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Scheltens P., Blennow K., Breteler M. M., de Strooper B., Frisoni G. B., Salloway S., and Van der Flier W. M. (2016) Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 388, 505–517 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01124-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Chávez-Gutiérrez L., Bammens L., Benilova I., Vandersteen A., Benurwar M., Borgers M., Lismont S., Zhou L., Van Cleynenbreugel S., Esselmann H., Wiltfang J., Serneels L., Karran E., Gijsen H., Schymkowitz J., et al. (2012) The mechanism of γ-secretase dysfunction in familial Alzheimer disease. EMBO J. 31, 2261–2274 10.1038/emboj.2012.79 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Citron M., Westaway D., Xia W., Carlson G., Diehl T., Levesque G., Johnson-Wood K., Lee M., Seubert P., Davis A., Kholodenko D., Motter R., Sherrington R., Perry B., Yao H., et al. (1997) Mutant presenilins of Alzheimer's disease increase production of 42-residue amyloid β-protein in both transfected cells and transgenic mice. Nat. Med. 3, 67–72 10.1038/nm0197-67 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Kumar-Singh S., Theuns J., Van Broeck B., Pirici D., Vennekens K., Corsmit E., Cruts M., Dermaut B., Wang R., and Van Broeckhoven C. (2006) Mean age-of-onset of familial alzheimer disease caused by presenilin mutations correlates with both increased Aβ42 and decreased Aβ40. Hum. Mutat. 27, 686–695 10.1002/humu.20336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Sacks C. A., Avorn J., and Kesselheim A. S. (2017) The failure of solanezumab: how the FDA saved taxpayers billions. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 1706–1708 10.1056/NEJMp1701047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Zou K., Yamaguchi H., Akatsu H., Sakamoto T., Ko M., Mizoguchi K., Gong J. S., Yu W., Yamamoto T., Kosaka K., Yanagisawa K., and Michikawa M. (2007) Angiotensin-converting enzyme converts amyloid β-protein 1–42 (Aβ(1–42)) to Aβ(1–40), and its inhibition enhances brain Aβ deposition. J. Neurosci. 27, 8628–8635 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1549-07.2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Zou K., and Michikawa M. (2008) Angiotensin-converting enzyme as a potential target for treatment of Alzheimer's disease: inhibition or activation? Rev. Neurosci. 19, 203–212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Fuchs S., Xiao H. D., Hubert C., Michaud A., Campbell D. J., Adams J. W., Capecchi M. R., Corvol P., and Bernstein K. E. (2008) Angiotensin-converting enzyme C-terminal catalytic domain is the main site of angiotensin I cleavage in vivo. Hypertension 51, 267–274 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.097865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Zou K., Maeda T., Watanabe A., Liu J., Liu S., Oba R., Satoh Y., Komano H., and Michikawa M. (2009) Aβ42-to-Aβ40– and angiotensin-converting activities in different domains of angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 31914–31920 10.1074/jbc.M109.011437 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kehoe P. G., Russ C., McIlory S., Williams H., Holmans P., Holmes C., Liolitsa D., Vahidassr D., Powell J., McGleenon B., Liddell M., Plomin R., Dynan K., Williams N., Neal J., et al. (1999) Variation in DCP1, encoding ACE, is associated with susceptibility to Alzheimer disease. Nat. Genet. 21, 71–72 10.1038/5009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lehmann D. J., Cortina-Borja M., Warden D. R., Smith A. D., Sleegers K., Prince J. A., van Duijn C. M., and Kehoe P. G. (2005) Large meta-analysis establishes the ACE insertion-deletion polymorphism as a marker of Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 162, 305–317 10.1093/aje/kwi202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Bertram L., McQueen M. B., Mullin K., Blacker D., and Tanzi R. E. (2007) Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nat. Genet. 39, 17–23 10.1038/ng1934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Palmer S. C., Mavridis D., Navarese E., Craig J. C., Tonelli M., Salanti G., Wiebe N., Ruospo M., Wheeler D. C., and Strippoli G. F. (2015) Comparative efficacy and safety of blood pressure-lowering agents in adults with diabetes and kidney disease: a network meta-analysis. Lancet 385, 2047–2056 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62459-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Yancy C. W., Jessup M., Bozkurt B., Butler J., Casey D. E. Jr., Colvin M. M., Drazner M. H., Filippatos G. S., Fonarow G. C., Givertz M. M., Hollenberg S. M., Lindenfeld J., Masoudi F. A., McBride P. E., Peterson P. N., et al. (2017) 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation 136, e137–e161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hooper N. M., and Turner A. J. (2003) An ACE structure. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 155–157 10.1038/nsb0303-155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kilander L., Nyman H., Boberg M., Hansson L., and Lithell H. (1998) Hypertension is related to cognitive impairment: a 20-year follow-up of 999 men. Hypertension 31, 780–786 10.1161/01.HYP.31.3.780 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Mayeux R., and Stern Y. (2012) Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2, a006239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Qiu C., Winblad B., and Fratiglioni L. (2005) The age-dependent relation of blood pressure to cognitive function and dementia. Lancet Neurol. 4, 487–499 10.1016/S1474-4422(05)70141-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Khachaturian A. S., Zandi P. P., Lyketsos C. G., Hayden K. M., Skoog I., Norton M. C., Tschanz J. T., Mayer L. S., Welsh-Bohmer K. A., and Breitner J. C. (2006) Antihypertensive medication use and incident Alzheimer disease: the Cache County study. Arch. Neurol. 63, 686–692 10.1001/archneur.63.5.noc60013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. de Oliveira F. F., Chen E. S., Smith M. C., and Bertolucci P. H. F. (2018) Pharmacogenetics of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in patients with Alzheimer's disease dementia. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 15, 386–398 10.2174/1567205014666171016101816 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Fazal K., Perera G., Khondoker M., Howard R., and Stewart R. (2017) Associations of centrally acting ACE inhibitors with cognitive decline and survival in Alzheimer's disease. BJPsych Open 3, 158–164 10.1192/bjpo.bp.116.004184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Bevilacqua M., Vago T., Rogolino A., Conci F., Santoli E., and Norbiato G. (1996) Affinity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors for N- and C-binding sites of human ACE is different in heart, lung, arteries, and veins. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 28, 494–499 10.1097/00005344-199610000-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Pitt B., Poole-Wilson P. A., Segal R., Martinez F. A., Dickstein K., Camm A. J., Konstam M. A., Riegger G., Klinger G. H., Neaton J., Sharma D., and Thiyagarajan B. (2000) Effect of losartan compared with captopril on mortality in patients with symptomatic heart failure: randomised trial: the Losartan Heart Failure Survival Study ELITE II. Lancet 355, 1582–1587 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02213-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Zou K., Liu J., Watanabe A., Hiraga S., Liu S., Tanabe C., Maeda T., Terayama Y., Takahashi S., Michikawa M., and Komano H. (2013) Aβ43 is the earliest-depositing Aβ species in APP transgenic mouse brain and is converted to Aβ41 by two active domains of ACE. Am. J. Pathol. 182, 2322–2331 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.01.053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Liu S., Liu J., Miura Y., Tanabe C., Maeda T., Terayama Y., Turner A. J., Zou K., and Komano H. (2014) Conversion of Aβ43 to Aβ40 by the successive action of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Neurosci. Res. 92, 1178–1186 10.1002/jnr.23404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Barnes D. E., and Yaffe K. (2011) The projected effect of risk factor reduction on Alzheimer's disease prevalence. Lancet Neurol. 10, 819–828 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70072-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Komukai K., Mochizuki S., and Yoshimura M. (2010) Gender and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 24, 687–698 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2010.00854.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Zapater P., Novalbos J., Gallego-Sandín S., Hernández F. T., and Abad-Santos F. (2004) Gender differences in angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity and inhibition by enalaprilat in healthy volunteers. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 43, 737–744 10.1097/00005344-200405000-00018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Allegri R. F., Taragano F. E., Krupitzki H., Serrano C. M., Dillon C., Sarasola D., Feldman M., Tufró G., Martelli M., and Sanchez V. (2010) Role of cognitive reserve in progression from mild cognitive impairment to dementia. Dement. Neuropsychol. 4, 28–34 10.1590/S1980-57642010DN40100005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Ohi K., Sumiyoshi C., Fujino H., Yasuda Y., Yamamori H., Fujimoto M., Sumiyoshi T., and Hashimoto R. (2017) A brief assessment of intelligence decline in schizophrenia as represented by the difference between current and premorbid intellectual quotient. Front. Psychiatry 8, 293 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Regenold W. T., Blumenthal J. B., Loreck D. J., Mordecai K. L., Scarinzi G., Doddi S. R., and Adler L. (2017) Elevated plasma Aβ42 in cognitively impaired individuals taking ACE inhibitor antihypertensives. Am. J. Alzheimer's Dis. Other Demen. 32, 347–352 10.1177/1533317517707288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Hemming M. L., Selkoe D. J., and Farris W. (2007) Effects of prolonged angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor treatment on amyloid β-protein metabolism in mouse models of Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 26, 273–281 10.1016/j.nbd.2007.01.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Wang J., Ho L., Chen L., Zhao Z., Zhao W., Qian X., Humala N., Seror I., Bartholomew S., Rosendorff C., and Pasinetti G. M. (2007) Valsartan lowers brain β-amyloid protein levels and improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 3393–3402 10.1172/JCI31547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Liu J., Liu S., Matsumoto Y., Murakami S., Sugakawa Y., Kami A., Tanabe C., Maeda T., Michikawa M., Komano H., and Zou K. (2015) Angiotensin type 1a receptor deficiency decreases amyloid β-protein generation and ameliorates brain amyloid pathology. Sci. Rep. 5, 12059 10.1038/srep12059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Eckman E. A., Adams S. K., Troendle F. J., Stodola B. A., Kahn M. A., Fauq A. H., Xiao H. D., Bernstein K. E., and Eckman C. B. (2006) Regulation of steady-state β-amyloid levels in the brain by neprilysin and endothelin-converting enzyme but not angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 30471–30478 10.1074/jbc.M605827200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hemming M. L., and Selkoe D. J. (2005) Amyloid β-protein is degraded by cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and elevated by an ACE inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 37644–37650 10.1074/jbc.M508460200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Mazure C. M., and Swendsen J. (2016) Sex differences in Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. Lancet Neurol. 15, 451–452 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00067-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Dubois B., Epelbaum S., Nyasse F., Bakardjian H., Gagliardi G., Uspenskaya O., Houot M., Lista S., Cacciamani F., Potier M. C., Bertrand A., Lamari F., Benali H., Mangin J. F., Colliot O., et al. (2018) Cognitive and neuroimaging features and brain β-amyloidosis in individuals at risk of Alzheimer's disease (INSIGHT-preAD): a longitudinal observational study. Lancet Neurol. 17, 335–346 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30029-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Walsh D. M., Klyubin I., Fadeeva J. V., Cullen W. K., Anwyl R., Wolfe M. S., Rowan M. J., and Selkoe D. J. (2002) Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid β protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 416, 535–539 10.1038/416535a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Shimokata H., Ando F., and Niino N. (2000) A new comprehensive study on aging: the National Institute for Longevity Sciences, Longitudinal Study of Aging (NILS-LSA). J. Epidemiol. 10, S1–S9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Matsuoka K., Uno M., Kasai K., Koyama K., and Kim Y. (2006) Estimation of premorbid IQ in individuals with Alzheimer's disease using Japanese ideographic script (Kanji) compound words: Japanese version of National Adult Reading Test. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 60, 332–339 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2006.01510.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]