Abstract
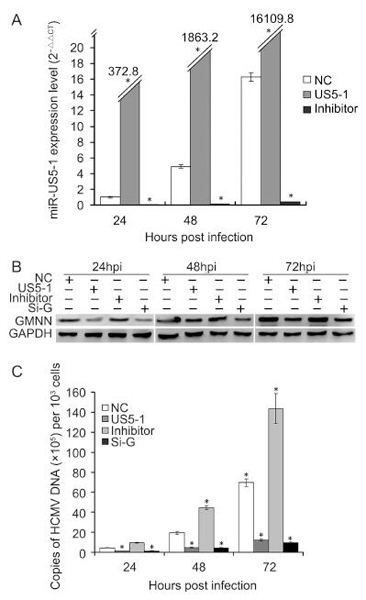
Viruses commonly create favorable cellular conditions for their survival through multiple mechanisms. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which function as post-transcriptional regulators, are utilized by human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) in its infection and pathogenesis. In the present study, the DNA replication inhibitor Geminin (GMNN) was identified to be a direct target of hcmv-miR-US5-1. Overexpression of hcmv-miR-US5-1 could block the accumulation of GMNN during HCMV infection, and the decrease of GMNN expression caused by hcmv-miR-US5-1 or GMNN specific siRNA reduced HCMV DNA copies in U373 cells. Meanwhile, ectopic expression of hcmv-miR-US5-1 and consequent lower expression of GMNN influenced host cell cycle and proliferation. These results imply that hcmv-miR-US5-1 may affect viral replication and host cellular environment by regulating expression kinetics of GMNN during HCMV infection.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material is available for this article at 10.1007/s12250-017-4064-x and is accessible for authorized users.
Keywords: Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), hcmv-miR-US5-1, Geminin (GMNN), DNA replication, cell cycle
Electronic supplementary material
Human cytomegalovirus miR-US5-1 inhibits viral replication by targeting Geminin mRNA
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371788 and 81171580) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20112104110012) and the Outstanding Scientific Fund of Shengjing Hospital.
Contributor Information
Rong He, Email: her@sj-hospital.org.
Qiang Ruan, Email: ruanq@sj-hospital.org.
References
- Babu SG, Pandeya A, Verma N, Shukla N, Kumar RV, Saxena S. Role of HCMV miR-UL70-3p and miR-UL148D in overcoming the cellular apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;393:89–98. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabeni A, Zamponi R, Moore JK, Helin K, Kirschner MW. Geminin deploys multiple mechanisms to regulate Cdt1 before cell division thus ensuring the proper execution of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:E2848–E2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310677110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry KA, Schultz KM, Payne CJ, McGarry TJ. Geminin is required for mitotic proliferation of spermatogonia. Dev Biol. 2012;371:35–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.07.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas N, Sanchez V, Spector DH. Human cytomegalovirus infection leads to accumulation of geminin and inhibition of the licensing of cellular DNA replication. J Virol. 2003;77:2369–2376. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.4.2369-2376.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffarelli N, Fehr AR, Yu D. Cyclin A degradation by primate cytomegalovirus protein pUL21a counters its innate restriction of virus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003825. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Renty C, Kaneko KJ, Depamphilis ML. The dual roles of geminin during trophoblast proliferation and differentiation. Dev Biol. 2014;387:49–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.12.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einsele H, Hebart H. Cytomegalovirus infection following stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 1999;84(EHA-4):46–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr AR, Yu D. Control the host cell cycle: viral regulation of the anaphase-promoting complex. J Virol. 2013;87:8818–8825. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00088-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu M, Gao Y, Zhou Q, Zhang Q, Peng Y, Tian K. Human cytomegalovirus latent infection alters the expression of cellular and viral microRNA. Gene. 2014;536:272–278. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottwein E, Cullen BR. Viral and cellular microRNAs as determinants of viral pathogenesis and immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2008;3:375–387. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey F, Meyers H, White EA, Spector DH, Nelson J. A human cytomegalovirus-encoded microRNA regulates expression of multiple viral genes involved in replication. PLoS Pathog. 2007;3:e163. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey F, Tirabassi R, Meyers H, Wu G, McWeeney S, Hook L. A viral microRNA down-regulates multiple cell cycle genes through mRNA 5'UTRs. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1000967. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X, Qi Y, Huang Y, Liu Z, Ma Y, Shao Y. Human cytomegalovirus miR-US33-5p inhibits viral DNA synthesis and viral replication by down-regulating expression of the host Syntaxin3. Febs Lett. 2015;589:440–446. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook LM, Grey F, Grabski R, Tirabassi R, Doyle T, Hancock M. Cytomegalovirus miRNAs target secretory pathway genes to facilitate formation of the virion assembly compartment and reduce cytokine secretion. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:363–373. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y, Qi Y, Ruan Q, Ma Y, He R, Ji Y. A rapid method to screen putative mRNA targets of any known microRNA. Virol J. 2011;8:8. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y, Chen D, He J, Cai J, Shen K, Liu X. Hcmv-miRUL112 attenuates NK cell activity by inhibition type I interferon secretion. Immunol Lett. 2014;163:151–156. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnevis M, Tyring SK. Cytomegalovirus infections. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:291–299. doi: 10.1016/S0733-8635(01)00007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S, Lee S, Shin J, Kim Y, Evnouchidou I, Kim D. Human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-US4-1 inhibits CD8(+) T cell responses by targeting the aminopeptidase ERAP1. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:984–991. doi: 10.1038/ni.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloosterman WP, Plasterk RH. The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev Cell. 2006;11:441–450. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz-Noack K, McIntosh D, Schurch N, Pratt N, Blow JJ. Re-replication induced by geminin depletion occurs from G2 and is enhanced by checkpoint activation. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:2436–2445. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmittgen TD, Lee EJ, Jiang J, Sarkar A, Yang L, Elton TS. Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA. Methods. 2008;44:31–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen ZZ, Pan X, Miao LF, Ye HQ, Chavanas S, Davrinche C. Comprehensive analysis of human cytomegalovirus microRNA expression during lytic and quiescent infection. PLoS One. 2014;9:e88531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreeram S, Sparks A, Lane DP, Blow JJ. Cell type-specific responses of human cells to inhibition of replication licensing. Oncogene. 2002;21:6624–6632. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark TJ, Amold JD, Spector DH, Yeo GW. High-resolution profiling and analysis of viral and host small RNAs during human cytomegalovirus infection. J Virol. 2012;86:226–235. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05903-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern-Ginossar N, Elefant N, Zimmermann A, Wolf DG, Saleh N, Biton M. Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA. Science. 2007;317:376–381. doi: 10.1126/science.1140956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern-Ginossar N, Saleh N, Goldberg MD, Prichard M, Wolf DG, Mandelboim O. Analysis of human cytomegalovirus-encoded microRNA activity during infection. J Virol. 2009;83:10684–10693. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01292-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada S. Cdt1 and geminin: role during cell cycle progression and DNA damage in higher eukaryotes. Front Biosci. 2007;12:1629–1641. doi: 10.2741/2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirabassi R, Hook L, Landais I, Grey F, Meyers H, Hewitt H. Human cytomegalovirus US7 is regulated synergistically by two virally encoded microRNAs and by two distinct mechanisms. J Virol. 2011;85:11938–11944. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05443-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi M, Qi Y, Ma Y, He R, Ji Y, Sun Z. Over-expression of human cytomegalovirus miR-US25-2-3p downregulates eIF4A1 and inhibits HCMV replication. Febs Lett. 2013;587:2266–2271. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.05.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlschlegel JA, Kutok JL, Weng AP, Dutta A. Expression of geminin as a marker of cell proliferation in normal tissues and malignancies. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:267–273. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64178-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M, Lu W, Santos RE, Frattini MG, Kelly TJ. Geminin inhibits a late step in the formation of human pre-replicative complexes. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:30810–30821. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.552935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K, Oyaizu N, Dutta A, Inoue I. The destruction box of human Geminin is critical for proliferation and tumor growth in human colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:58–70. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y, Srivastava D. A developmental view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32:189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2007.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Human cytomegalovirus miR-US5-1 inhibits viral replication by targeting Geminin mRNA


