Abstract
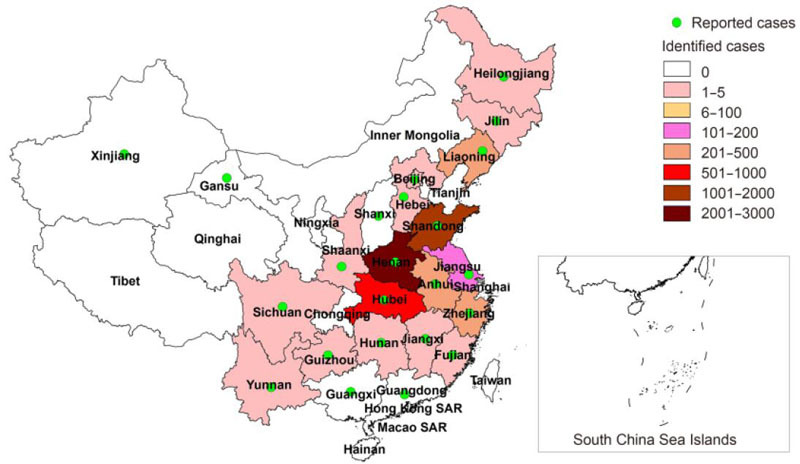
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging infectious disease caused by SFTS virus (SFTSV). SFTSV is associated with a high mortality rate and has been reported in China, South Korea and Japan. SFTSV undergoes rapid changes owing to evolution, gene mutations, and reassortment between different strains of SFTSV. In this review, we summarize the recent cases and general properties of SFTS, focusing on the epidemiology, genetic diversity, clinical features, and diagnostics of SFTSV in China. From 2010 to October 2016, SFTS cases were reported in 23 provinces of China, with increased numbers yearly. Infection and death cases are mainly found in central China, where the Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks are spread. The national average mortality rate of SFTS infection was 5.3%, with higher risk to elder people. The main epidemic period was from May to July, with a peak in May. Thus, SFTS reminds a significant public health problem, and development of prophylactic vaccines and effective antiviral drugs will be highly needed.
Keywords: severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV), Bunyaviridae
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases (2012ZX10004-207), the China-US Collaborative Program on Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases (S2012Y03), the key project of the Health Ministry of Hubei Province (JX5A06), and the Hubei Provincial Outstanding Medical Academic Leader program.
Footnotes
ORCID: 0000-0002-9657-621X
ORCID: 0000-0003-3004-0452
ORCID: 0000-0002-8297-0814
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The study was approved by the Ethics Committees of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention of Hubei Province. Written consents were obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Contributor Information
Faxian Zhan, Email: zhanfx@163.com.
Yi Song, Email: hbcdc_songyi@163.com.
Deyin Guo, Email: dguo@whu.edu.cn.
References
- Bao CJ, Guo XL, Qi X, Hu JL, Zhou MH, Varma JK, Cui LB, Yang HT, Jiao YJ, Klena JD, et al. A family cluster of infections by a newly recognized bunyavirus in eastern China, 2007: further evidence of person-to-person transmission. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:1208–1214. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang MS, Woo JH. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: Tick-Mediated Viral Disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:795–796. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.6.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi YY, Zhai SY, Wen HL, Wang L. SFTSV RNA detection in seropositive patients. J Shandong Univ (Health Sci) 2012;50:118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Cui L, Ge Y, Qi X, Xu G, Li H, Zhao K, Wu B, Shi Z, Guo X, Hu L, et al. Detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus by reverse transcription-cross-priming amplification coupled with vertical flow visualization. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:3881–3885. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01931-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui N, Liu R, Lu QB, Wang LY, Qin SL, Yang ZD, Zhuang L, Liu K, Li H, Zhang XA, Hu JG, Wang JY, Liu W, Cao WC. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus-related human encephalitis. J Infect. 2015;70:52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C, Wang H, Zhang W, Zheng X, Tong Q, Jie S, Yang D, Zhou Y. Decreased monocyte subsets and TLR4-mediated functions in patients with acute fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) Int J Infect Dis. 2016;43:37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding NZ, Luo ZF, Niu DD, Ji W, Kang XH, Cai SS, Xu DS, Wang QW, He CQ. Identification of two severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus strains originating from reassortment. Virus Res. 2013;178:543–546. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gai ZT, Zhang Y, Liang MF, Jin C, Zhang S, Zhu CB, Li C, Li XY, Zhang QF, Bian PF, et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:1095–1102. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge HM, Wang QK, Li ZF, et al. Survey of SFTSV carrying situation in rodents in SFTS epidemic area of Donghai County. Jiangsu Prevent Med. 2012;23:16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gong Z, Gu S, Zhang Y, Sun J, Wu X, Ling F, Shi W, Zhang P, Li D, Mao H, et al. Probable aerosol transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in southeastern China. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21:1115–1120. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X, Zhang L, Zhang W, Chi Y, Zeng X, Li X, Qi X, Jin Q, Zhang X, Huang M, et al. Human antibody neutralizes severe Fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, an emerging hemorrhagic Fever virus. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013;20:1426–1432. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00222-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Y, Drosten C. Editorial overview: Emerging viruses: Interspecies transmission. Curr Opin Virol. 2016;16:v–vi. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He CQ, Ding NZ. Discovery of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus strains originating from intragenic recombination. J Virol. 2012;86:12426–12430. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01317-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang YT, Zhao L, Wen HL, Yang Y, Yu H, Yu XJ. Neutralizing antibodies to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus 4 years after hospitalization, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:1985–1987. doi: 10.3201/eid2211.160414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang XL, Zhang S, Jiang M, Bi ZQ, Liang MF, Ding SJ, Wang SW, Liu JY, Zhou SQ, Zhang XM, Li DX, Xu AQ. Acluster of person-to-person transmission cases caused by SFTS virus in Penglai, China. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21:274–279. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2014.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiao Y, Zeng X, Guo X, Qi X, Zhang X, Shi Z, Zhou M, Bao C, Zhang W, Xu Y, Wang H. Preparation and evaluation of recombinant severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) nucleocapsid protein for detection of total anti-bodies in human and animal sera by double antigen sandwich ELISA. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;50:372–377. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01319-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin C, Song J, Han Y, Li C, Qiu P, Liang M. Inclusion Bodies are formed in SFTSV-infected human macrophages. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2016;32:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T, Matsuda M, Takajo I, Kawano A, Kariya Y, Kubo K, Miyauchi S, Umekita K, Nagatomo Y, Yano T, Yano K, Okayama A. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with myocardial dysfunction and encephalopathy: A case report. J Infect Chemotherapy. 2016;22:633–637. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim KH, Yi J, Kim G, Choi SJ, Jun KI, Kim NH, Choe PG, Kim NJ, Lee JK, Oh MD. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;219:1892–1894. doi: 10.3201/eid1911.130792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam TT, Liu W, Bowden TA, Cui N, Zhuang L, Liu K, Zhang YY, Cao WC, Pybus OG. Evolutionary and molecular analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndromevirus. Epidemics. 2013;5:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2012.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li DX. Summary of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Bunyavirus. Chinese J Exp Clin Virol. 2011;25:81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Han Y, Xing Y, Li S, Kong L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Liu N, Wang Q, Wang S, Lu S, Huang Z. Concurrent Measurement of Dynamic Changes in Viral Load, Serum Enzymes, T Cell Subsets, and Cytokines in Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. PLoS One. 2014;9:e91679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li ZF, Hu J, Bao CJ, et al. Rapid detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus by AllGlo probe-based real-time RT-PCR. Jiangsu Prev Med. 2016;27:516–519. [Google Scholar]
- Li Z, Cui L, Zhou M, Qi X, Bao C, Hu J, Shan J, Wu B, Wang S, Guo X, Jiao Y, Tang F, Wang H. Development and application of a one-step real-time RT-PCR using a minor-groovebinding probe for the detection of a novel bunyavirus in clinical specimens. J Med Virol. 2013;85:370–377. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z, Qi X, Zhou M, Bao C, Hu J, Wu B, Wang S, Tan Z, Fu J, Shan J, Zhu Y, Tang F. A two-tube multiplex real-time RT-PCR assay for the detection of four hemorrhagic fever viruses: severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, Hantaan virus, Seoul virus, and dengue virus. Arch Virol. 2013;158:1857–1863. doi: 10.1007/s00705-013-1677-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu JW, Wen HL, Fang LZ, Zhang ZT, He ST, Xue ZF, Ma DQ, Zhang XS, Wang T, Yu H, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Yu XJ. Prevalence of SFTSV among Asian House Shrews and Rodents, China, January-August 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;20:2126–2128. doi: 10.3201/eid2012.141013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu JW, Zhao L, Luo LM, Liu MM, Sun Y, Su X, Yu XJ. Molecular Evolution and Spatial Transmission of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Based on Complete Genome Sequences. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K, Cui N, Fang LQ, Wang BJ, Lu QB, Peng W, Li H, Wang LY, Liang S, Wang HY, Zhang YY, Zhuang L, Yang H, Gray GC, de Vlas SJ, Liu W, Cao WC. Epidemiologic features and environmental risk factors of severs fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome Xinyang, China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L, Chen W, Yang Y, Jiang Y. Molecular evolution of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukocytopenia virus (FTLSV) based on whole-genome sequences. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;39:55–63. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:763–772. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70718-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W, Lu QB, Cui N, Li H, Wang LY, Liu K, Yang ZD, Wang BJ, Wang HY, Zhang YY, et al. Case-Fatality Ratio and Effectiveness of Ribavirin Therapy Among Hospitalized Patients in China Who Had Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1292–1299. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Li Q, Hu W, Wu J, Wang Y, Mei L, Walker DH, Ren J, Wang Y, Yu XJ. Person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012;12:156–160. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2011.0758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu QB, Cui N, Hu JG, Chen WW, Xu W, Li H, Zhang XA, Ly H, Liu W, Cao WC. Characterization of immunological responses in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: a cohort study in China. Vaccine. 2015;33:1250–1255. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo LM, Zhao L, Wen HL, Zhang ZT, Liu JW, Fang LZ, Xue ZF, Ma DQ, Zhang XS, Ding SJ, Lei XY, Yu XJ. Haemaphysalis longicornis Tick as Reservoir and Vector of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus in China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:1770–1776. doi: 10.3201/eid2110.150126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei XY, Liu MM, Yu XJ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and its pathgen SFTSV. Microbes Infect. 2015;17:149–154. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2014.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma T, Sun JM, Chen LF, Shi XG, Liu K, Gong ZY, Chen J, Zhang R, Ren JP, Jiang JM. A pediatric case of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Zhejiang Province, China. J Clin Virol. 2015;72:85–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2015.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullan LK, Folk SM, Kelly AJ, MacNeil A, Goldsmith CS, Metcalfe MG, Batten BC, Albariño CG, Zaki SR, Rollin PE, Nicholson WL, Nichol ST. A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:834–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1203378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra AC, Mehta M, Mourya DT, Gandhi S. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in India. Lancet. 2011;378:372. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60680-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu G, Li J, Liang M, Jiang X, Jiang M, Yin H, Wang Z, Li C, Zhang Q, Jin C, Wang X, Ding S, Xing Z, Wang S, Bi Z, Li D. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus among domesticated animals, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:756–763. doi: 10.3201/eid1905.120245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni H, Yang F, Li Y, Liu W, Jiao S, Li Z, Yi B, Chen Y, Hou X, Hu F, Ding Y, Bian G, Du Y, Xu G, Cao G. Apodemus agrarius is a potential natural host of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS)-causing novel bunyavirus. J Clin Virol. 2015;71:82–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2015.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park SW, Song BG, Shin EH, Yun SM, Han MG, Park MY, Park C, Ryou J. Prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:975–977. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2014.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C, Wang H, Zhang W, Zheng X, Tong Q, Jie S, Yang D, Zhou Y. Decreased monocyte subsets and TLR4-mediated functions in patients with acute severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Int J Infect Dis. 2016;43:37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plegge T, Hofmann-Winkler H, Spiegel M, Pöhlmann S. Evidence that processing of the Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Gn/Gc Polyprotein Is Critical for Viral Infectivity and Requires an Internal Gc Signal Peptide. PloS One. 2016;11:e0166013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park SW, Han MG, Yun SM, Park C, Lee WJ, Ryou J. Severe Fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, South Korea, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1880–1882. doi: 10.3201/eid2011.140888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park SW, Song BG, Shin EH, Yun SM, Han MG, Park MY, Park C, Ryou J. Prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:975–977. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2014.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu B, Qi X, Wu X, Liang M, Li C, Cardona CJ, Xu W, Tang F, Li Z, Wu B, Powell K, Wegner M, Li D, Xing Z. Suppression of the interferon and NF-κB responses by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. J Virol. 2012;86:8388–8401. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00612-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard ME, Benjamin B. Emerging phleboviruses. Curr Opin Virol. 2014;5:50–57. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.01.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone R. Rival teams identify a virus behind deaths in central China. Science. 2010;330:20–21. doi: 10.1126/science.330.6000.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y, Liang M, Qu J, Jin C, Zhang Q, Li J, Jiang X, Wang Q, Lu J, Gu W, Zhang S, Li C, Wang X, Zhan F, Yao W, Bi Z, Wang S, Li D. Early diagnosis of novel SFTS bunyavirus infection by quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay. J Clin Virol. 2012;53:48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2011.09.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q, Qi X, Zhang Y, Wu X, Liang M, Li C, Li D, Cardona CJ, Xing Z. Synaptogyrin-2 Promotes Replication of a Novel Tick-borne Bunyavirus through Interacting with Viral Nonstructural Protein NSs. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:16138–16149. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.715599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y, Guo Y, Lou Z. A versatile building block: the structures and functions of negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus nucleocapsid proteins. Protein Cell. 2012;3:893–902. doi: 10.1007/s13238-012-2087-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshi K, Motohiro M, Ichiro T, Kawano A, Kariya Y, Kubo K, Miyauchi S, Umekita K, Nagatomo Y, Yano T, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with myocardial dysfunction and encephalopathy: A case report. J Infect and Chem. 2016;22:633–637. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T, Maeda K, Suzuki T, Ishido A, Shigeoka T, Tominaga T, Kamei T, Honda M, Ninomiya D, Sakai T, et al. The first identification and retrospective study of severe Fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan. J Infect Dis. 2014;209:816–827. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang X, Wu W, Wang H, Du Y, Liu L, Kang K, Huang X, Ma H, Mu F, Zhang S, Zhao G, Cui N, Zhu BP, You A, Chen H, Liu G, Chen W, Xu B. Human-to-human transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus through contact with infectious blood. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:736–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T, Matsuda M, Takajo I, Kawano A, Kariya Y, Kubo K, Miyauchi S, Umekita K, Nagatomo Y, Yano T, Yano K, Okayama A. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with myocardial dysfunction and encephalopathy: A case report. J Infect Chemother. 2016;22:633–637. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M, Pennock DG, Spik KW, Schmaljohn CS. Epitope mapping studies with neutralizing and non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the G1 and G2 envelope glycoproteins of Hantaan virus. Virology. 2012;197:757–766. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Zhang Q, Hao F, Gao X, Wu W, Liang M, Liao Z, Luo S, Xu W, Li D, Wang S. Development of a Colloidal Gold Kit for the Diagnosis of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:530621. doi: 10.1155/2014/530621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster CG, Reitz SR, Perry KL, Adkins S. A natural M RNA reassortant arising from two species of plant and insect infecting bunyaviruses and comparison of its sequence and biological properties to parental species. Virology. 2011;413:216–225. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen HL, Zhao L, Zhai S, Chi Y, Cui F, Wang D, Wang L, Wang Z, Wang Q, Zhang S, Liu Y, Yu H, Yu XJ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Shandong Province, China, 2011. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1–5. doi: 10.3201/eid2001.120532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X, Qi X, Liang M, Li C, Cardona CJ, Li D, Xing Z. Roles of viroplasm-like structures formed by nonstructural protein NSs in infection with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. FASEB Journal. 2014;28:2504–2516. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-243857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W, Zhang S, Qu J, Zhang Q, Li C, Li J, Jin C, Liang M, Li D. Simultaneous detection of IgG antibodies associated with viral hemorrhagic fever by a multiplexed Luminex-based immunoassay. Virus Res. 2014;187:84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.12.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu B, Liu L, Huang X, Ma H, Zhang Y, Du Y, Wang P, Tang X, Wang H, Kang K, et al. Metagenomic analysis of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia syndrome (FTLS) in Henan Province, China: discovery of a new bunyavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:1453–60. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang G, Li B, Liu L, Huang W, Zhang W, Liu Y. Development and evaluation of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of a new SFTS bunyavirus. Arch Virol. 2012;157:1779–1783. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1348-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa T, Fukushi S, Tani H, Fukuma A, Taniguchi S, Toda S, Shimazu Y, Yano K, Morimitsu T, Ando K, et al. Sensitive and specific PCR systems for detection of both Chinese and Japanese severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus strains and prediction of patient survival based on viral load. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:3325–3333. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00742-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu FX, Du YH, Huang XY, Ma H, Xu B, Ferdinard A, Daisuke H, Corazon C, Kouichi M. Application of recombinant severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein for the detection of SFTSV-specific human IgG and IgM antibodies by indirect ELISA. Virology J. 2015;8:12–117. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0350-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, Zhang L, Zhang QF, Popov VL, Li C, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl Med. 2011;364:1523–1532. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1010095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun SM, Lee YJ, Choi W, Kim HC, Chong ST, Chang KS, Coburn JM, Klein TA, Lee WJ. Molecular detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and tick-borne encephalitis viruses in ixodid ticks collected from vegetation, Republic of Korea, 2014. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;7:970–978. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2016.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun Y, Heo ST, Kim G, Hewson R, Kim H, Park D, Cho NH, Oh WS, Ryu SY, Kwon KT, Medlock JM, Lee KH. Phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in South Korea and migratory bird routes between China, South Korea, and Japan. Am J Trop Med Hyq. 2015;93:468–474. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L, Liu Y, Ni D, Li Q, Yu Y, Yu XJ, Wan K, Li D, Liang G, Jiang X, et al. Nosocomial transmission of human granulocytic anaplasmosis in China. JAMA. 2008;300:2263–2270. doi: 10.1001/jama.2008.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang LP, Wang YC, Zhao Y, et al. Research Progress of Epidemiology and Detection Method of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Bunyavirus. J of Inspec Quarantine. 2014;24:67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhao L, Li B, Yu H, Wen H, Yu XJ. An emerging hemorrhagic fever in China caused by a novel bunyavirus SFTSV. Sci China Life Sci. 2013;56:697–700. doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4518-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang YX, Xie QX, Sun Y, et al. Isolation of novel bunyavirus using vero cell. Anhui J Prev Med. 2011;18:249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang YZ, Xu JG. The emergence and cross species transmission of newly discovered tick-borne Bunyavirus in China. Curr Opin Virol. 2016;16:126–131. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang YZ, Zhou DJ, Qin XC, Tian JH, Xiong Y, Wang JB, Chen XP, Gao DY, He YW, Jin D, et al. The ecology, genetic diversity, and phylogeny of Huaiyangshan virus in China. J Virol. 2012;86:2864–2868. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06192-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


