Abstract
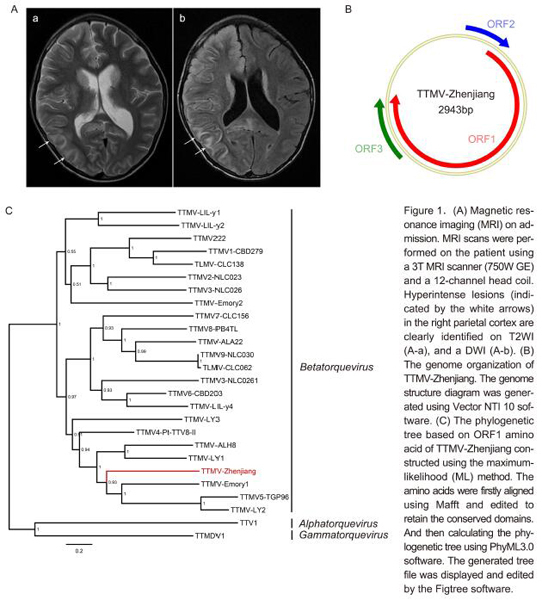
Anelloviruses are single-strand circular DNA viruses and ubiquitous within the human population. Although there is no direct evidence, many studies have suggested the anelloviruses may be associated with a variety of diseases. In this study, a novel torque teno mini virus (TTMV) was detected in a child with unexplained encephalitis. The detected virus had a circular genome of 2943 nt in length and 3 open reading frames. It shared 45.4% – 35.9% nucleotide identities with known TTMV species and < 35% with the other species of anellovirus, which suggested it might belong to a new species within the genus Betatorquevirus. Phylogenetic analysis based on the amino acid sequences of ORF1 showed that this virus represented a distinct branch within the diversity of anellovirus. Whether this novel anellovirus strain is associated with encephalitis requires further study.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material is available for this article at 10.1007/s12250-017-4042-3 and is accessible for authorized users.
Electronic supplementary material
Identification of a novel torque teno mini virus in cerebrospinal fluid from a child with encephalitis
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Gen Yan, Email: gyan@stu.edu.cn.
Zhong-Hua Lu, Email: Lu_z_h@126.com.
References
- Chan BK, Wilson T, Fischer KF, et al. PloS one. 2014;9:e93993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X, Naccache SN, Ng T, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:e46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira KB. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2015;37:357–358. doi: 10.1016/j.bjhh.2015.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinakaran V, Rathinavel A, Pushpanathan M, et al. PLoS One. 2014;9:e105221. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focosi D, Antonelli G, Pistello M, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22:589–593. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Álvarez M, Berenguer J, Alvarez E, et al. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;32:289–297. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1744-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75:i10–i15. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2003.034280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi F, Bendinelli M. Rev Med Virol. 2010;20:392–407. doi: 10.1002/rmv.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mi Z, Yuan X, Pei G, et al. Virol Sin. 2014;29:112–118. doi: 10.1007/s12250-014-3424-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa A, Xie C, Kirkness E, et al. PLoS pathogens. 2017;13:e1006292. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario K, Duffy S, Breitbart M. Arch Virol. 2012;157:1851–1871. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1391-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Li F, Shan TL. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26739. doi: 10.1038/srep26739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Identification of a novel torque teno mini virus in cerebrospinal fluid from a child with encephalitis


