Abstract
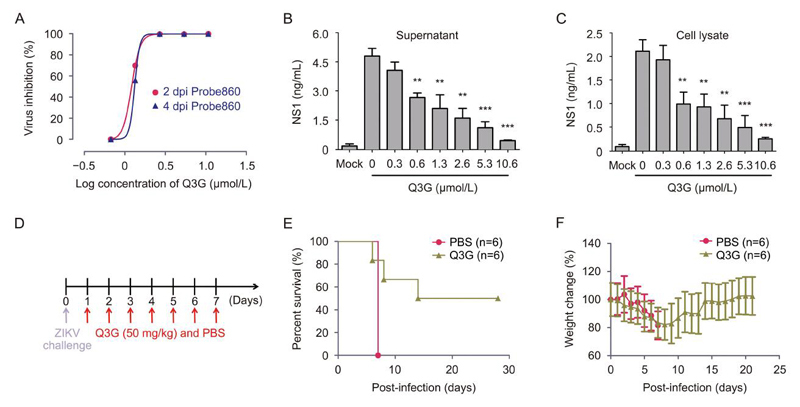
Q3G is a natural derivative of quercetin and is already widely used in various foods and drinks. Our results clearly demonstrated that Q3G exerts antiviral activity against ZIKV in both tissue culture and knockout mice, and that post-exposure in vivo treatment with Q3G could have a beneficial effect. In the future, Q3G should be tested in human cell lines (such as Huh-7, HeLa, or K048, a fetal brain neural stem cell line) to provide further data supporting its potential efficacy in humans; in addition, live viral loads or viremia should be tested in treated animals to supplement the survival results observed in this study. Although the treatment regimens will need to be further optimized (i.e., dosage, frequency of treatment, and administration routes), our results support the results of Q3G efficacy studies in nonhuman primates against ZIKV infection. Further studies will also be needed to investigate the mechanism of Q3G antiviral action, in order to obtain valuable insights into the design of novel targets for antiviral therapeutics in the future.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material is available for this article at 10.1007/s12250-017-4057-9 and is accessible for authorized users.
Electronic supplementary material
Antiviral activity of quercetin-3-β-O-D-glucoside against Zika virus infection
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally to this work.
References
- Cheng Z, Sun G, Guo W, et al. Virol Sin. 2015;30:261–268. doi: 10.1007/s12250-015-3584-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D’Andrea G. Fitoterapia. 2015;106:256–271. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2015.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govero J, Esakky P, Scheaffer SM, et al. Nature. 2016;540:438–442. doi: 10.1038/nature20556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood M, Danielewska-Nikiel B, Borzelleca JF, et al. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;45:2179–2205. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollman PC, Katan MB. Biomed Pharmacother. 1997;51:305–310. doi: 10.1016/S0753-3322(97)88045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawiecki AB, Christofferson RC. J Infect Dis. 2016;214:1357–1360. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanciotti RS, Kosoy OL, Laven JJ, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1232–1239. doi: 10.3201/eid1408.080287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazear HM, Govero J, Smith AM, et al. Cell Host Microbe. 2016;19:720–730. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma W, Li S, Ma S, et al. Cell. 2016;167:1511–1524. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu X, Kroeker A, He S, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60:5182–5188. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00307-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi M, Sharma N, Singh SK. Virol J. 2016;13:131. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0590-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richner JM, Himansu S, Dowd KA, et al. Cell. 2017;168:1114–1125. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchide N, Toyoda H. Molecules. 2011;16:2032–2052. doi: 10.3390/molecules16032032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G, Kobinger GP. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28:593–601. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00014-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanluca C, Melo VC, Mosimann AL, et al. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2015;110:569–572. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760150192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Antiviral activity of quercetin-3-β-O-D-glucoside against Zika virus infection


