Abstract
Bacterial α-type carbonic anhydrase (α-CA) is a zinc metalloenzyme that catalyzes the reversible and extremely rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate. In this study, we report the first crystal structure of a hyperthermostable α-CA from Persephonella marina EX-H1 (pmCA) in the absence and presence of competitive inhibitor, acetazolamide. The structure reveals a compactly folded pmCA homodimer in which each monomer consists of a 10-stranded β-sheet in the center. The catalytic zinc ion is coordinated by three highly conserved histidine residues with an exchangeable fourth ligand (a water molecule, a bicarbonate anion, or the sulfonamide group of acetazolamide). Together with an intramolecular disulfide bond, extensive interfacial networks of hydrogen bonds, ionic and hydrophobic interactions stabilize the dimeric structure and are likely responsible for the high thermal stability. We also identified novel binding sites for calcium ions at the crystallographic interface, which serve as molecular glue linking negatively charged and otherwise repulsive surfaces. Furthermore, this large negatively charged patch appears to further increase the thermostability at alkaline pH range via favorable charge-charge interactions between pmCA and solvent molecules. These findings may assist development of novel α-CAs with improved thermal and/or alkaline stability for applications such as CO2 capture and sequestration.
Keywords: carbonic anhydrase, CO2 capture and storage, CO2 mineralization, Persephonella marina EX-H1, zinc metalloenzyme
INTRODUCTION
Carbonic anhydrases (CAs; EC 4.2.1.1) are zinc-containing metalloenzymes that catalyze reversible hydration of CO2 to bicarbonate and a free proton (CO2 + H2O ↔ HCO3− + H+).They are present in all kingdoms of life and play key roles in diverse biological processes such as CO2 transport, respiration, and photosynthesis. To date, seven classes of CA genes have been identified (α, β, γ, δ, ζ, η, and θ) (Del Prete et al., 2014a; 2014b; Iverson et al., 2000; Kikutani et al., 2016; Meldrum and Roughton, 1933; Mitsuhashi et al., 2000; Xu et al., 2008). Members of the α-CA class are found in vertebrates, algae, green plants, fungi, and some eubacteria. They are among the fastest enzymes, with kcat values up to ~106 per second, which is close to the diffusion limit (Hasinoff, 1984; Pocker and Janjić, 1987). The β-CA class are predominantly present in bacteria, yeast, and plant chloroplasts (Neish, 1939; Smith et al., 1999), while γ-CAs are found in eubacteria and archaea (Alber and Ferry, 1994). Both δ- and ζ-CAs have been identified in the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissfogii (Lane et al., 2005; Roberts et al., 1997), and η- and θ-CAs were recently discovered in the pathogenic protozoan Plasmodium falciparum and a diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum, respectively (Del Prete et al., 2014a; Kikutani et al., 2016). In most cases, CAs are active as zinc enzymes, but γ- and ζ-CAs can use iron (II) (Macauley et al., 2009; Tripp et al., 2004) and cadmium (II) (Xu et al., 2008), respectively.
Among the different classes, crystal structures of α-, β-, γ-, and ζ-CA families have only been characterized to date. α- and β-CAs share common catalytic features such as CO2 hydration activity and a zinc ion as a metal cofactor, however, significant structural differences are apparent. First, most α-CAs form monomers or dimers, whereas β-CAs occur in various oligomeric states, including dimers, tetramers, hexamers, and octamers (Kimber and Pai, 2000). Second, in α-CA structures, three histidine residues and a water molecule strongly coordinate the zinc ion in the active site (Eriksson et al., 1988; Liljas et al., 1972). Crystal structures of human α-CA II (hCAII) in complex with the potent inhibitor acetazolamide revealed that the inhibitor displaces the zinc-bound water, thereby inactivating the enzyme (Nair et al., 1995). Many structures of α-CAs have enabled to propose the two-step catalytic mechanism where the first step is a deprotonation of zinc-bound water to form a hydroxide ion that actively participates in the catalytic reaction through nucleophilic attack of the CO2 molecule. The second step is the regeneration of the zinc-bound hydroxide ion to reset the enzyme for a next catalytic cycle (Silverman and Lindskog, 1988). Proton transfer from a water molecule to generate a catalytic hydroxide ion is a two-part process. The first is the proton transfer through the six ordered waters to the solvent-exposed histidine residue (H64 in hCAII). The second is the transfer of the proton between H64 to the solvent (Eriksson et al., 1988; Fisher et al., 2007; Liljas et al., 1972). By contrast, crystal structures of β-CAs revealed two distinct zinc binding environments, denoted as active (R-state) or inactive (T-state) forms (Rowlett, 2010). In the R-state conformation, one histidine, two cysteines, and a water molecule coordinate a zinc ion in the active site. In the T-state, however, a water molecule is substituted with an aspartic acid residue, indicating that this state is catalytically inactive. β-CAs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis reportedly switch between these two states in a pH-dependent manner (Covarrubias et al., 2006; Suarez Covarrubias et al., 2005). Some bacterial β-CAs also alternate between active and inactive states by binding of bicarbonate in an allosteric manner (Cronk et al., 2006), or by redox-dependent disulfide bond formation that triggers release of the zinc ion (Nienaber et al., 2015). Crystal structures of γ-CAs have all been determined from the hyperthermophilic archeon Methanosarcina thermophila and Pyrococcus horikoshii (Iverson et al., 2000; Jeyakanthan et al., 2008). γ-CAs are active as homotrimers. The catalytic metal ion binds at the trimer interface and is coordinated by three histidine residues; Two histidines are from the same monomer and the third from the other (Ferry, 2010). Crystal structures of ζ-CAs are limited to cadmium-containing enzyme, CDCA1, in Thalassiosira weissflogii (Alterio et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2008). The active site of CDCA1 resembles those of the β-CAs; the metal ion is tetrahedrally coordinated by three conserved residues, one histidine, two cysteines, and a water molecule.
In the past decade, CO2 capture and storage (CCS) technology utilizing hyperthermostable microbial α-CAs has attracted great attention for addressing global warming and climate change. Because CCS processes inevitably require harsh conditions such as high temperature (> 87°C) and strong alkaline (pH > 9) conditions, enzymes must be thermo-and alkali-stable. For this reason, much effort has been spent on finding highly thermostable CAs and/or engineering enzymes to increase thermal and pH stability. Persephonella marina EX-H1, which belongs to a new genus within the phylum Aquificales, is a marine chemolithoautotrophic thermophile isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent at 9° N and 104° W in the Pacific Ocean (Götz et al., 2002). The α-CA enzyme from this organism lacking a signal peptide was expressed at levels five-fold higher than the wild-type protein (Kanth et al., 2014). In addition, it displayed a broad pH tolerance (pH 4-10) and high thermostability up to 100°C, making it a good candidate for catalyzing a fast, economically affordable, and environmentally friendly CCS process.
Here, we present the first crystal structure of an α-CA enzyme from P. marina EX-H1 (pmCA) in the absence and presence of acetazolamide. Various characteristics of typical hyperthermostable α-CA structures are well-conserved in pmCA, which has a relatively compact dimer conformation, an intramolecular disulfide bond, and a zinc ion coordinated by three histidine residues. Unexpectedly, our structure reveals a large surface patch of negatively charged residues that provides novel calcium binding sites at the crystallographic interface and appears to increase thermostability at alkaline pH range via electrostatic interactions with solvent molecules. This structural feature is unique to pmCA and has not been observed in any other CAs thus far.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cloning, expression, and purification
Preparation of pmCA protein was performed as previously described (Kanth et al., 2014), with minor modifications. Briefly, the synthetic gene encoding α-CA from P. marina EX-H1 without a signal peptide (residues 20-243; Gene Universal, USA) was cloned between the NdeI and XhoI restriction enzyme sites in the pET21a expression vector, incorporating an N-terminal 6× His tag followed by a thrombin protease cleavage site. The protein was produced in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) cells cultured in Lysogeny Broth medium at 37°C. When the absorbance (optical density [OD]) at 600 nm (OD600) reached 0.6 to 0.8, protein expression was induced by addition of 1 mM isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside for 16 h at 20°C. After harvesting by centrifugation at 7,700g for 10 min, cells were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C.
For purification, thawed cells in lysis buffer (20 mM MES pH 5.5, 200 mM NaCl, 100 mM DNaseI, and 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) were disrupted using a microfluidizer. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 30,000g for 1 h and the supernatant was loaded onto nickel affinity resin (Incospharm, Korea) equilibrated with lysis buffer containing 20 mM imidazole. The protein was eluted using a gradient of increasing imidazole concentration. After thrombin cleavage, the protein was further purified by HiTrap SP (GE Healthcare, USA) cation exchange chromatography and Superdex 200 Increase (GE Healthcare) gel filtration chromatography. The protein was concentrated to 20 mg/ml for crystallization. All purification steps were performed either on ice or at 4°C.
CO2 hydration activity assay
The CO2 hydration activity of pmCA was measured as previously described using an electrometric method (Carter et al., 1969). Briefly, 4 ml of freshly prepared CO2-saturated water was injected rapidly into 6 ml of reaction buffer (20 mM TRIS-HCl pH 8.5) in the presence or absence of purified pmCA at varying final concentrations. The CO2 hydration activity of pmCA was measured by monitoring the time taken for the pH to change from 8.5 to 6.5. All preparations and reactions were performed on ice. The activity of pmCA was calculated in Wilbur–Anderson Units (WAU) using the following formula: WAU = (t0 − tc)/tc, where t0 and tc refer to the time taken in the absence and presence of the enzyme, respectively (Wilbur and Anderson, 1948). For acetazolamide or anion inhibition, protein samples (6.15 nM) were mixed with varying concentrations of acetazolamide, nitrate (NO3−), nitrogen dioxide (NO22−) and sulfate (SO42−) ions for 1 h on ice before measuring the decrease in pH. All measurements were repeated three times using the same preparation.
CaCO3 precipitation assay
CaCO3 precipitation assays were performed as previously described (Mirjafari et al., 2007). Briefly, 500 μl of CO2-saturated water was mixed with the same volume of reaction buffer (1 M TRIS-HCl pH 9.0 or pH 11.0, 20 mM CaCl2) containing varying final concentrations of purified pmCA. The reaction cuvette was sealed immediately to prevent CO2 leakage. CaCO3 precipitation was monitored by measuring changes in absorbance at 600 nm every 10 s to measure turbidity. For acetazolamide inhibition, protein samples (507 nM) were mixed with varying concentrations of acetazolamide for 10 min on ice before measuring the OD600. All measurements were repeated three times using the same protein preparation.
Crystallization, X-ray diffraction data collection, and structure determination
Crystals of pmCA were grown at 22°C by the sitting-drop vapor diffusion method using a reservoir solution containing 100 mM sodium HEPES pH 7.5 (or glycine pH 9.5), 28–32% (w/v) polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400, and 200–400 mM calcium chloride dehydrate. For co-crystallization, 7 mM acetazolamide was added to the concentrated protein solution and incubated on ice for 30 min. Crystals appeared after 3 days and grew to full size within 1 week. Crystals were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen after placing in reservoir solution containing ethylene glycol as a cryoprotectant. X-ray diffraction data were collected at beamlines 5C and 11C of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL). Diffraction data were processed using the HKL2000 package (HKL Research, USA). The pmCA structure was determined by molecular replacement (Phaser, CCP4) using the α-CA structure from the Logatchev hydrothermal field metagenome (LOGACA, PDB code 6EKI) as a search model (Fredslund et al., 2018). Refinement of the structure was performed using REFMAC5 and PHENIX, with non-crystallographic symmetry and secondary structure restraints (Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4, 1994). The atomic model was constructed and manipulated manually after each refinement step using the program COOT (Emsley and Cowtan, 2004). X-ray crystallographic data and refinement statistics are summarized in Supplementary Table S1. All figures in the manuscript were prepared using the program PyMOL (www.pymol.org).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
CO2 hydration and CaCO3 precipitation activities of pmCA
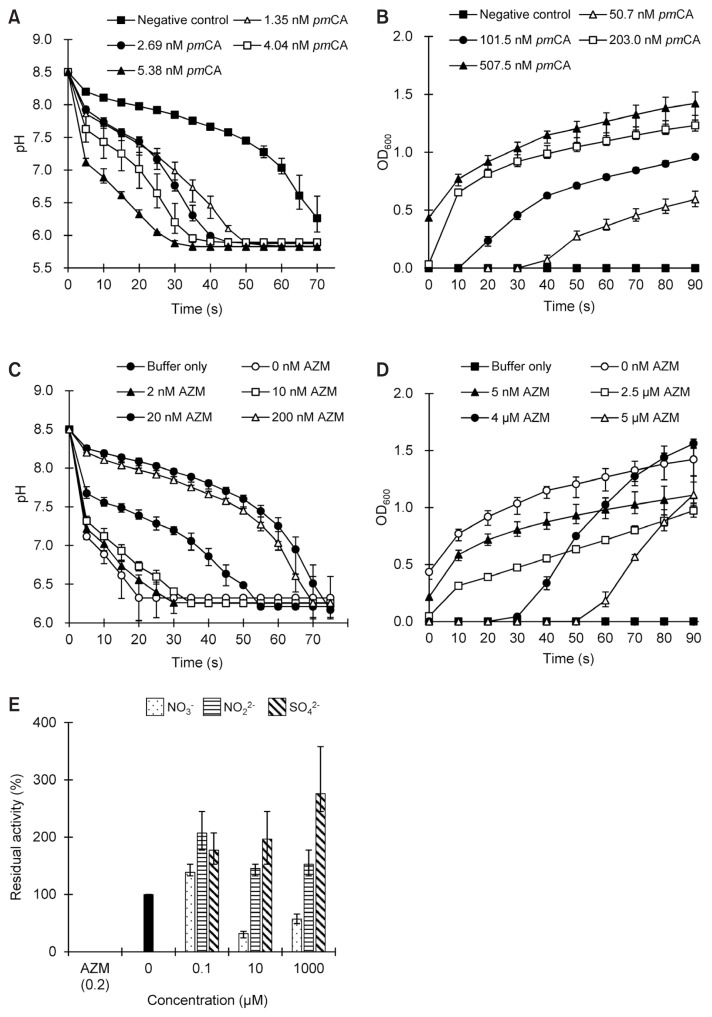
Direct CO2 hydration assays were performed to confirm whether pmCA accelerates hydration of CO2 and production of hydrogen ions. A plot of CO2 hydration activity against time showed that increasing the pmCA concentration accelerated the drop in pH (Fig. 1A). Based on the Wilbur–Anderson equation (Wilbur and Anderson, 1948), the purified protein exhibited a specific activity of ~2,500 WAU/mg, which corresponds to ~50% of the previous measurements (Kanth et al., 2014). It is likely that the different environmental conditions can alter the rate of reaction caused by the pmCA enzyme.
Fig. 1. Enzymatic activity of α-carbonic anhydrase from Persephonella marina EX-H1 (pmCA) and its inhibition by acetazolamide (AZM).
Enzymatic CO2 hydration (A) and CaCO3 precipitation (B), as measured by changes in pH and absorbance at 600 nm (OD600) over time, respectively. For AZM inhibition, protein samples were mixed with varying concentrations of AZM, and changes in pH (C) and OD600 (D) were measured as a function of time, respectively. Reactions without pmCA were prepared as negative controls. (E) Inhibition of pmCA with varying concentrations of anions. The CO2 hydration activity without any inhibitors was used as a positive control, and was set to 100% for comparison. The enzyme activity in the presence of AZM was used as a negative control. Data points indicate the means (± standard deviation [SD]) of triplicate measurements from the same preparation. Error bars indicate SD.
We further explored the biological activity of pmCA by monitoring conversion from hydrated CO2 to solid CaCO3 in the presence of calcium ions. The biomineralization of carbon dioxide using CA enzymes is one of the most efficient ways to permanently store carbon. As expected for a CA enzyme, the rate of CaCO3 precipitation was much faster with increasing pmCA concentration (Fig. 1B). As reported previously, no precipitate was observed below pH 9.0 (data not shown) because bicarbonate is converted to carbonate at pH > 8.3 (Han et al., 2006). Independent assays also showed that both CO2 hydration and CaCO3 precipitation activities were significantly inhibited in the presence of acetazolamide (Figs. 1C and 1D).
Utilization of CAs in CCS process requires the enzyme to be stable in the presence of flue gas contaminants such as NOx and SOx. To determine the effect of these anions on the pmCA activity, the major anion components in flue gas, nitrate (NO3−), nitrogen dioxide (NO22−) and sulfate (SO42−) ions, were individually added to the enzyme at various concentrations, and incubated on ice for 1 h before measuring the CO2 hydration. For comparison, enzyme activity in the absence of any inhibitor was set at 100%. As shown in Figure 1E, NO22− and SO42− anions had no inhibitory activity over the concentration ranges tested. In contrast, pmCA activity was stable in the presence of NO3− up to 0.1 μM, which corresponds to a pmCA/nitrate molar ratio of 1:16, although it retained only 30% to 57% activity beyond that. Our results suggest that pmCA are very resistant to NO22− and SO42−, but it is weakly inhibited by NO3−. Together, these functional assays demonstrate that purified pmCA under our experimental conditions has apparent in vitro enzymatic activity and a wide range of tolerance to NO22− and SO42− anions.
Overall structure of pmCA
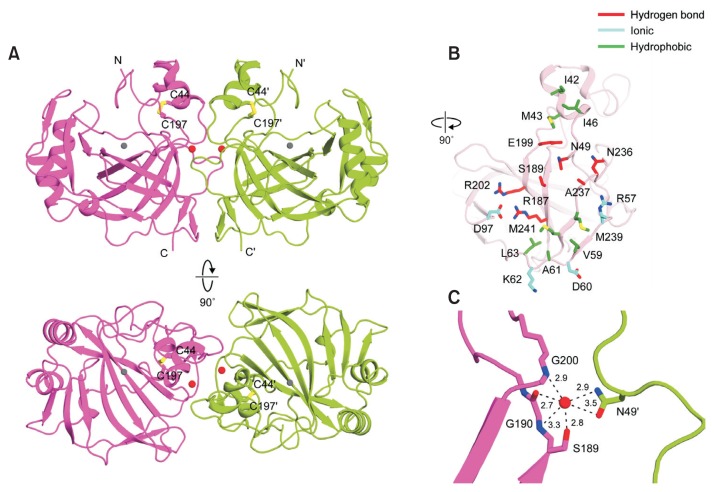
To establish the molecular basis for thermal stability and CO2 hydration of pmCA, we crystallized the purified pmCA protein with and without acetazolamide to determine its atomic structure by X-ray crystallography (Supplementary Table S1). The final models showed that two crystal forms of pmCA were obtained in the absence of acetazolamide; one crystallized in the monoclinic space group C2 (form 1) and the other in the orthorhombic space group P21212 (form 2). The acetazolamide-bound form also crystallized in the P21212 space group (form 3). Similar to other thermostable α-CAs, the crystal structure revealed that pmCA forms a homodimer, consistent with previously reported gel filtration data (Fig. 2A) (Kanth et al., 2014). All crystal forms contain three pmCA dimers within the asymmetric unit (Supplementary Fig. S1). Within each dimer, one monomer is oriented approximately 180° with respect to the other monomer, thereby resulting in overall dimensions of 41.7 × 41.4 × 78.2 Å. The pmCA structure includes typical features found in other α-CAs; namely (i) a 10-stranded β-sheet in the core, (ii) a catalytic zinc ion coordinated in the central active site, and (iii) an intramolecular disulfide bond formed between C44 and C197 (Fig. 2A). The disulfide bridge provides conformational and thermal stability by increasing structural rigidity, as supported by previous cysteine mutagenesis data showing that addition of an intramolecular disulfide bond markedly enhances the thermostability of hCAII and Neisseria gonorrhoeae NgCA (Boone et al., 2013; Jo et al., 2016; Mårtensson et al., 2002).
Fig. 2. The crystal structure and dimerization interface of pmCA.
(A) Ribbon representation of the pmCA dimer, comprising two monomers colored magenta and green, respectively. Intramolecular disulfide bonds are shown as yellow sticks, and zinc ions and water molecules are shown as gray and red spheres, respectively. Protein secondary structures were assigned using STRIDE (Heinig and Frishman, 2004). (B) Structure of residues involved in the pmCA dimeric interface. The interface is split and rotated by 90° from Figure 2A, upper panel. The pmCA residues involved in symmetrical hydrogen bonds, ionic, or hydrophobic interactions are colored red, cyan, and green, respectively. (C) The water-mediated hydrogen bond network in the pmCA dimer interface. All distances are shown in angstroms.
Structural comparison of pmCA with other thermostable α-CAs from Sulfurihydrogenibium yellowstonense YO3AOP1 (SspCA) (Di Fiore et al., 2013), Sulphurihydrogenibium azorense (SazCA) (De Simone et al., 2015), Thermovibrio ammonificans (TaCA) (James et al., 2014), Photobacterium profundum (PprCA) (Somalinga et al., 2016), NgCA, and LOGACA revealed a similar overall structure, as expected based on the high sequence identity (Supplementary Figs. S2 and S3) (Heinig and Frishman, 2004). However, superposition of pmCA and hCAII (Eriksson et al., 1988) revealed that, similar to SspCA, NgCA, and PprCA, three large surface loops (loops 1–3) are also deleted in pmCA, resulting in a more compact fold compared with the hCAII structure (Supplementary Fig. S4). In particular, loop 2 containing an α-helix formed by six residues (D130-V135) is located on the rim of the hCAII active site. Therefore, deletion of a corresponding α-helix from pmCA may enlarge the cavity entrance, resulting in a more solvent-exposed active site and easier access for the CO2 substrate to the active site. Hereafter, a single apostrophe signifies residues from a neighboring monomer within a biological dimer or symmetry-related molecule in the crystal.
The pmCA dimer interface
Analysis of the pmCA structure using the Proteins, Interfaces, Surfaces, and Assemblies (PDBePISA) server (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/pisa/) shows that the pmCA homodimer interface covers an area of ~1,024 Å2 and is semi-oval in shape (Fig. 2B). The dimer interface is highly hydrophilic, similar to the solvent-exposed surface, indicating that the pmCA dimer is held together mainly by symmetrical hydrogen bonding in the core region, surrounded by additional ionic and hydrophobic interactions at the periphery (Fig. 2B, Supplementary Fig. S5). These strong, specific interactions appear to contribute to the excellent thermal stability of pmCA. Furthermore, a number of water molecules are bound at the interface; these likely participate in additional interactions in the hydrogen bonding network, further stabilizing the dimer interface. Among them, two well-ordered symmetric water molecules are located at the center of the dimer interface that form multiple hydrogen bonds with S189, the backbone oxygen of G190, the backbone nitrogen atoms of S189 and G200, and N49′ (Fig. 2C). Such completely buried water molecules are commonly found in other bacterial α-CAs, and the coordinating residues are highly conserved, except for S189 (Supplementary Fig. S3). TaCA (James et al., 2014) and SspCA (Di Fiore et al., 2013) also have serine residues in the corresponding position, while NgCA (Huang et al., 1998) and Helicobacter pylori HpCA (Modak et al., 2015) have alanine and asparagine, respectively. Interestingly, PprCA also has an asparagine at the equivalent location, which acts as a key residue for chloride ion coordination (Somalinga et al., 2016).
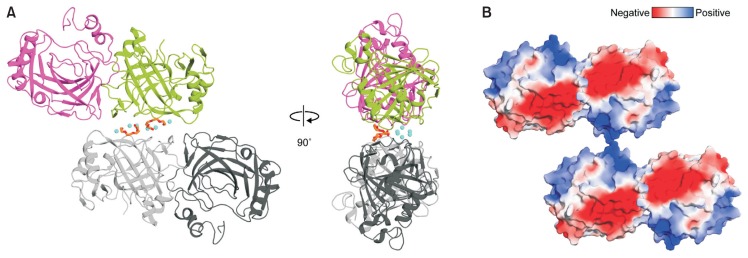
The pmCA calcium binding site
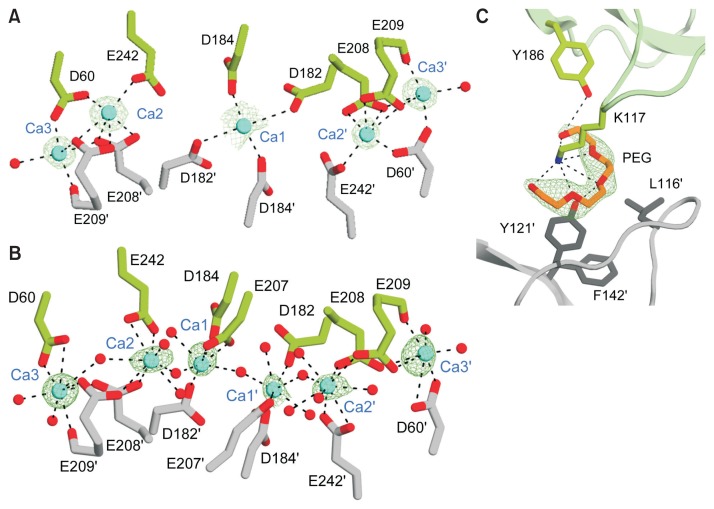
In our structures, calcium ions from the crystallization buffer were bound at the crystallographic interface of pmCA with known geometrical features (Fig. 3A). To the best of our knowledge, this feature has not been observed in previous α-CA structures. As shown in Figure 3B, there is a large patch of negative surface charge formed by a cluster of glutamic acid and aspartic acid residues. This feature facilitates direct or water-mediated binding of calcium ions in close proximity by acting as a ‘molecular glue’ to create crystal contacts by neutralizing the negatively charged and otherwise repulsive surfaces. In our structures, two different types of Ca2+ binding sites were observed. In crystal form 1, binding sites of five calcium ions starts near the center of the crystal interface, which is bracketed by a pair of two-fold symmetry-related interfaces (Fig. 4A). Ca1 interacts with four ligands, including D182 and D184 and their two-fold symmetry-related residues in the crystal. Binding site for Ca2 is coordinated by the side chains of D60, E242, E208′, and E209′. Ca3 is coordinated by the side chains of D60, E208′, and E209′, the backbone oxygen of E209′, and a water molecule. Ca2 and Ca3 are only ~4.3 Å apart, and are interlinked through the side chain oxygen atoms of D60, E208′, and E209′. In crystal forms 2 and 3, however, binding sites of six calcium ions are formed by two interfaces with two-fold symmetry (Fig. 4B). Ca1 interacts with six ligands (comprising the side chains of D184, E207, and D182′) and three water molecules in an approximately octahedral geometry. The binding site for Ca2 is coordinated by the side chains of E242, E208′, E209′, and four water molecules. Ca3 is coordinated by the side chains of D60, E208′, and E209′, the backbone oxygen of E209′, and three water molecules. In crystal forms 2 and 3, calcium ions are 5 to 6 Å apart from each other and are interlinked through bridging water molecules. Compared to hCAII, enrichment of negative charges on the solvent-accessible molecular surface of pmCA may increase the thermal and/or alkaline pH stability because acidic residues are easily deprotonated and have a high water-binding capacity under alkaline pH conditions (Supplementary Fig. S6) (Britton et al., 2006; Frolow et al., 1996; Kuntz, 1971). Therefore, negatively charged residues on the surface form the protective hydration shell that can confer high pH stability to pmCA. This structural feature is consistent with previous data showing that ~60% of pmCA activity is retained at pH 10, compared with the maximum activity at pH 7.5 (Kanth et al., 2014). Similarly, it has been reported that alkaline active phosphoserine aminotransferase and xylanase have large number of negatively charged residues on their surfaces (Dubnovitsky et al., 2005; Mamo et al., 2006; Manikandan et al., 2006).
Fig. 3. Crystallographic interface of the pmCA.
(A) Two possible dimers in crystal of pmCA. Crystal packing of pmCA in the C2 space group (crystal form 1) is almost identical with those of pmCA in the P21212 space group (crystal forms 2 and 3). Two monomers and their two-fold symmetry-related molecules are colored magenta, green, dark and light gray, respectively. Calcium ions and PEG molecules bound at the crystallographic interface are shown as cyan spheres and orange sticks, respectively. (B) Electrostatic surface potential of pmCA. The crystallographic interface is split and rotated by 90°. White, neutral; blue, positively charged; red, negatively charged. Surface electrostatic potential was calculated using the PDB2PQR and APBS server (http://www.poissonboltzmann.org).
Fig. 4. Binding sites of calcium ions and PEG molecules.
(A and B) Detailed view of calcium ion coordination at the pmCA crystallographic interface in the C2 (A) and P21212 (B) symmetry, respectively. Residues involved in calcium coordination are shown in stick representation. Green mesh represents Fo-Fc maps contoured at 3.5σ for Ca1, 8.5σ for Ca2 and Ca3 (A), and 3.5σ for Ca1, 6σ for Ca2, and 7σ for Ca3 (B), respectively. Calcium ions and water molecules are shown as cyan and red spheres, respectively. Interactions are indicated by dashed lines. (C) Close-up view of the PEG binding site in the crystallographic interface. Residues interacting with PEG are shown in stick representation. Green mesh represents Fo-Fc maps contoured at the 3σ level.
PEG molecules are bound at the pmCA crystallographic interface
Together with the calcium ions described above (Fig. 3A), two fragments of PEG molecules were also visible at the crystallographic interface, and the protein-PEG interactions also appear facilitate crystal packing (Fig. 4C). Specifically, we observed a pair of symmetrical PEG binding sites close to the calcium binding sites (Fig. 3A). The binding mode of PEG molecules are practically identical in all crystal forms. Binding of PEG molecules is stabilized predominantly through hydrophobic interactions with L116′ and Y121′ (Fig. 4C). F142′, located behind Y121′, is not directly involved in PEG coordination, but contributes to orient Y121′ via π-π interactions, enabling Y121′ to interact effectively with PEG. Moreover, five oxygen atoms of PEG engage in hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions with K117 and Y186 of one pmCA monomer, and Y121′ of a neighboring molecule in the crystal.
The pmCA active site
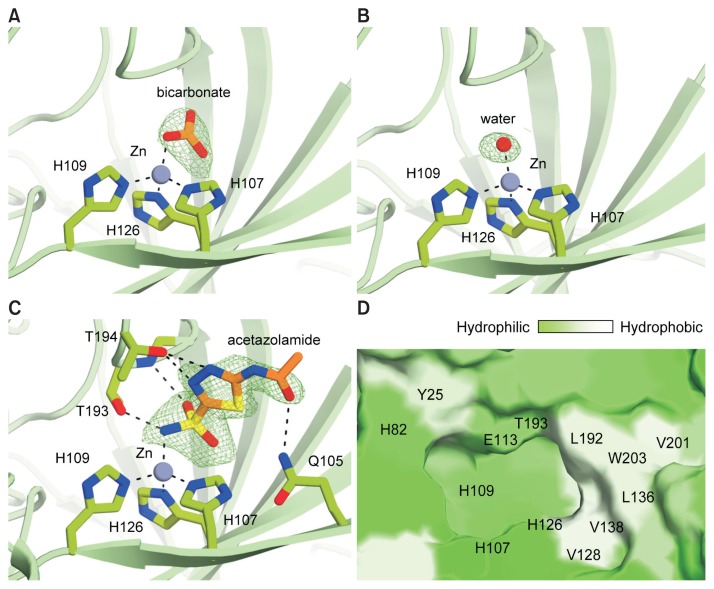
The catalytic active site of pmCA resembles those of previously studied α-CAs. The active site is located in a cone-shaped cavity in which a zinc ion is bound at the bottom (Fig. 5A). The zinc ion is tetrahedrally coordinated by three histidine residues (H107, H109, and H126), and by a replaceable fourth ligand. In crystal form 1, a strong, positive Fo-Fc peak (> 4σ), which is planar and triangular in shape, was observed in each active site. We concluded that this electron density corresponded to bicarbonate, a hydrated CO2 species (Fig. 5A). In crystal form 2, a small globular peak was observed in the corresponding position in the Fo-Fc map (> 3σ), and was modeled as a water molecule (Fig. 5B). The crystal structure of pmCA complexed with acetazolamide revealed its binding mode in the active site that is nearly identical to that observed in hCAII, NgCA, and SspCA enzyme-inhibitor structures (Di Fiore et al., 2013; Huang et al., 1998; Vidgren et al., 1990) (Fig. 5C). Specifically, (i) the nitrogen atom of the sulfonamide group of acetazolamide displaces the zinc-bound water and the deeply buried water molecule in the active site, (ii) the sulfonamide group forms hydrogen bonds with the backbone nitrogen and side chain hydroxyl group of T193, (iii) two nitrogen atoms of the thiadiazole ring interact with T194 via hydrogen bonds, and (iv) the acetylamide group is bound to Q105.
Fig. 5. Close-up view of the pmCA active site.
The zinc ion is coordinated by H107, H109, H126, and an exchangeable fourth ligand; a bicarbonate (A), a water molecule (B), or acetazolamide (C). The zinc ion is shown as a gray sphere. The Fo-Fc map superimposed on the refined bicarbonate, water, and acetazolamide is contoured at 4σ, 3σ, and 3.5σ levels, respectively. (D) Surface representation of pmCA showing the spatial distribution of hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity in the cavity. Green, hydrophilic; white, hydrophobic.
To evaluate the surface chemistry of the pmCA active site, we analyzed the spatial distribution of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity on the molecular surface. Analysis of the surface characteristics revealed polarization of surface hydrophobicity; half of the active site wall is predominantly polar and hydrophilic whereas the other half of the cavity contains a single linear hydrophobic patch (Fig. 5D). Several residues on the hydrophilic half of the cavity are catalytically important. For example, residues Y25, H82, E113, and T193, along with a zinc-bound water (or hydroxide), form a hydrogen bonding network and transfer protons from the active site to the bulk solvent (Fig. 5D) (Eriksson et al., 1988; Silverman and Lindskog, 1988; Silverman and Vincent, 1983; Tashian, 1989). By contrast, residues responsible for CO2 binding, including V128, V138, L136, L192, V201, and W203, constitute the hydrophobic half of the cavity, and mutating these residues results in a small loss of enzyme activity (Merz, 1990; 1991; Xue et al., 1993). Our structure revealed that the key elements for substrate binding and catalysis are well-conserved, suggesting that pmCA performs the same CO2 hydration mechanism carried out by other α-CAs.
In summary, we determined the first crystal structure of pmCA and provide direct evidence of dimerization, extensive intermolecular interactions, an intramolecular disulfide bond, and a large negatively charged surface patch. These characteristics explain its high pH and thermostability. These findings could be exploited to engineer α-CAs with improved pH and thermostability for use in harsh conditions such as those employed in CCS.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful for assistance from staff at beamlines 5C and 11C of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL). This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning of Korea (grant No. NRF-2017R1A2B4003278), and from the GIST Research Institute (GRI), funded by GIST in 2018 (grant No. GRI_2018).
Footnotes
Note: Supplementary information is available on the Molecules and Cells website (www.molcells.org).
Accession codes
Coordinates and structure factors for pmCA have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank under accession codes 6IM0 (bicarbonate-bound, crystal form 1), 6IM1 (water-bound, crystal form 2), and 6IM3 (acetazolamide-bound, crystal form 3).
Disclosure
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
REFERENCES
- Alber B.E., Ferry J.G. A carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alterio V., Langella E., De Simone G., Monti S.M. Cadmium-containing carbonic anhydrase CDCA1 in marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. Mar Drugs. 2015;13:1688–1697. doi: 10.3390/md13041688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C.D., Habibzadegan A., Tu C., Silverman D.N., McKenna R. Structural and catalytic characterization of a thermally stable and acid-stable variant of human carbonic anhydrase II containing an engineered disulfide bond. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013;69:1414–1422. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913008743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton K.L., Baker P.J., Fisher M., Ruzheinikov S., Gilmour D.J., Bonete M.J., Ferrer J., Pire C., Esclapez J., Rice D.W. Analysis of protein solvent interactions in glucose dehydrogenase from the extreme halophile Haloferax mediterranei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:4846–4851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508854103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J.M., Havard D.J., Parsons D.S. Electrometric assay of rate of hydration of CO2 for investigation of kinetics of carbonic anhydrase. J Physiol. 1969;204:60P–62P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collaborative Computational Project Number 4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994;50:760–763. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994003112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias A.S., Bergfors T., Jones T.A., Högbom M. Structural mechanics of the pH-dependent activity of beta-carbonic anhydrase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:4993–4999. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510756200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronk J.D., Rowlett R.S., Zhang K.Y., Tu C., Endrizzi J.A., Lee J., Gareiss P.C., Preiss J.R. Identification of a novel noncatalytic bicarbonate binding site in eubacterial beta-carbonic anhydrase. Biochemistry. 2006;45:4351–4361. doi: 10.1021/bi052272q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete S., Vullo D., Fisher G.M., Andrews K.T., Poulsen S.A., Capasso C., Supuran C.T. Discovery of a new family of carbonic anhydrases in the malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum--the eta-carbonic anhydrases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014a;24:4389–4396. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete S., Vullo D., Scozzafava A., Capasso C., Supuran C.T. Cloning, characterization and anion inhibition study of the delta-class carbonic anhydrase (TweCA) from the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014b;22:531–537. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.10.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone G., Monti S.M., Alterio V., Buonanno M., De Luca V., Rossi M., Carginale V., Supuran C.T., Capasso C., Di Fiore A. Crystal structure of the most catalytically effective carbonic anhydrase enzyme known, SazCA from the thermophilic bacterium Sulfurihydrogenibium azorense. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015;25:2002–2006. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.02.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore A., Capasso C., De Luca V., Monti S.M., Carginale V., Supuran C.T., Scozzafava A., Pedone C., Rossi M., De Simone G. X-ray structure of the first ‘extremo-alpha-carbonic anhydrase’, a dimeric enzyme from the thermophilic bacterium Sulfurihydrogenibium yellowstonense YO3AOP1. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013;69:1150–1159. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913007208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnovitsky A.P., Kapetaniou E.G., Papageorgiou A.C. Enzyme adaptation to alkaline pH: atomic resolution (1. 8 A) structure of phosphoserine aminotransferase from Bacillus alcalophilus. Protein Sci. 2005;14:97–110. doi: 10.1110/ps.041029805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emsley P., Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60:2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A.E., Jones T.A., Liljas A. Refined structure of human carbonic anhydrase II at 2.0 A resolution. Proteins. 1988;4:274–282. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J.G. The gamma class of carbonic anhydrases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1804:374–381. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.08.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S.Z., Maupin C.M., Budayova-Spano M., Govindasamy L., Tu C., Agbandje-McKenna M., Silverman D.N., Voth G.A., McKenna R. Atomic crystal and molecular dynamics simulation structures of human carbonic anhydrase II: insights into the proton transfer mechanism. Biochemistry. 2007;46:2930–2937. doi: 10.1021/bi062066y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredslund F., Borchert M.S., Poulsen J.N., Mortensen S.B., Perner M., Streit W.R., Lo Leggio L. Structure of a hyperthermostable carbonic anhydrase identified from an active hydrothermal vent chimney. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2018;114:48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2018.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolow F., Harel M., Sussman J.L., Mevarech M., Shoham M. Insights into protein adaptation to a saturated salt environment from the crystal structure of a halophilic 2Fe-2S ferredoxin. Nat Struct Biol. 1996;3:452–458. doi: 10.1038/nsb0596-452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz D., Banta A., Beveridge T.J., Rushdi A.I., Simoneit B.R., Reysenbach A.L. Persephonella marina gen. nov., sp. nov. and Persephonella guaymasensis sp. nov., two novel, thermophilic, hydrogen-oxidizing microaerophiles from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002;52:1349–1359. doi: 10.1099/00207713-52-4-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Y.S., Hadiko G., Fuji M., Takahashi M. Crystallization and transformation of vaterite at controlled pH. J Cryst Growth. 2006;289:269–274. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.11.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hasinoff B.B. Kinetics of carbonic anhydrase catalysis in solvents of increased viscosity: a partially diffusion-controlled reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984;233:676–681. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinig M., Frishman D. STRIDE: a web server for secondary structure assignment from known atomic coordinates of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:W500–W502. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Xue Y., Sauer-Eriksson E., Chirica L., Lindskog S., Jonsson B.H. Crystal structure of carbonic anhydrase from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and its complex with the inhibitor acetazolamide. J Mol Biol. 1998;283:301–310. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson T.M., Alber B.E., Kisker C., Ferry J.G., Rees D.C. A closer look at the active site of gamma-class carbonic anhydrases: high-resolution crystallographic studies of the carbonic anhydrase from Methanosarcina thermophila. Biochemistry. 2000;39:9222–9231. doi: 10.1021/bi000204s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Isupov M.N., Sayer C., Saneei V., Berg S., Lioliou M., Kotlar H.K., Littlechild J.A. The structure of a tetrameric alpha-carbonic anhydrase from Thermovibrio ammonificans reveals a core formed around intermolecular disulfides that contribute to its thermostability. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014;70:2607–2618. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714016526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeyakanthan J., Rangarajan S., Mridula P., Kanaujia S.P., Shiro Y., Kuramitsu S., Yokoyama S., Sekar K. Observation of a calcium-binding site in the gamma-class carbonic anhydrase from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2008;64:1012–1019. doi: 10.1107/S0907444908024323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo B.H., Park T.Y., Park H.J., Yeon Y.J., Yoo Y.J., Cha H.J. Engineering de novo disulfide bond in bacterial alpha-type carbonic anhydrase for thermostable carbon sequestration. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29322. doi: 10.1038/srep29322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanth B.K., Jun S.Y., Kumari S., Pack S.P. Highly thermostable carbonic anhydrase from Persephonella marina EX-H1: its expression and characterization for CO2-sequestration applications. Proc Biochem. 2014;49:2114–2121. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2014.10.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani S., Nakajima K., Nagasato C., Tsuji Y., Miyatake A., Matsuda Y. Thylakoid luminal theta-carbonic anhydrase critical for growth and photosynthesis in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:9828–9833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603112113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimber M.S., Pai E.F. The active site architecture of Pisum sativum beta-carbonic anhydrase is a mirror image of that of alpha-carbonic anhydrases. EMBO J. 2000;19:1407–1418. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.7.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I.D., Jr Hydration of macromolecules. III. Hydration of polypeptides. J Am Chem Soc. 1971;93:514–516. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane T.W., Saito M.A., George G.N., Pickering I.J., Prince R.C., Morel F.M. Biochemistry: a cadmium enzyme from a marine diatom. Nature. 2005;435:42. doi: 10.1038/435042a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A., Kannan K.K., Bergstén P.C., Waara I., Fridborg K., Strandberg B., Carlbom U., Järup L., Lövgren S., Petef M. Crystal structure of human carbonic anhydrase C. Nat New Biol. 1972;235:131–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio235131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macauley S.R., Zimmerman S.A., Apolinario E.E., Evilia C., Hou Y.M., Ferry J.G., Sowers K.R. The archetype gamma-class carbonic anhydrase (Cam) contains iron when synthesized in vivo. Biochemistry. 2009;48:817–819. doi: 10.1021/bi802246s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamo G., Hatti-Kaul R., Mattiasson B. A thermostable alkaline active endo-beta-1–4-xylanase from Bacillus halodurans S7: purification and characterization. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2006;39:1492–1498. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.03.040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Manikandan K., Bhardwaj A., Gupta N., Lokanath N.K., Ghosh A., Reddy V.S., Ramakumar S. Crystal structures of native and xylosaccharide-bound alkali thermostable xylanase from an alkalophilic Bacillus sp. NG-27: structural insights into alkalophilicity and implications for adaptation to polyextreme conditions. Protein Sci. 2006;15:1951–1960. doi: 10.1110/ps.062220206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson L.G., Karlsson M., Carlsson U. Dramatic stabilization of the native state of human carbonic anhydrase II by an engineered disulfide bond. Biochemistry. 2002;41:15867–15875. doi: 10.1021/bi020433+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum N.U., Roughton F.J. Carbonic anhydrase. Its preparation and properties. J Physiol. 1933;80:113–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp003077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz K.M., Jr Insights into the function of the zinc hydroxide-Thr199-Glu106 hydrogen bonding network in carbonic anhydrases. J Mol Biol. 1990;214:799–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90333-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz K.M., Jr Carbon dioxide binding to human carbonic anhydrase II. J Am Chem Soc. 1991;113:406–411. doi: 10.1021/ja00002a004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mirjafari P., Asghari K., Mahinpey N. Investigating the application of enzyme carbonic anhydrase for CO2 sequestration purposes. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2007;46:921–926. doi: 10.1021/ie060287u. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S., Mizushima T., Yamashita E., Yamamoto M., Kumasaka T., Moriyama H., Ueki T., Miyachi S., Tsukihara T. X-ray structure of beta-carbonic anhydrase from the red alga, Porphyridium purpureum, reveals a novel catalytic site for CO2 hydration. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5521–5526. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.8.5521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modak J.K., Liu Y.C., Machuca M.A., Supuran C.T., Roujeinikova A. Structural basis for the inhibition of Helicobacter pylori alpha-carbonic anhydrase by sulfonamides. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0127149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair S.K., Krebs J.F., Christianson D.W., Fierke C.A. Structural basis of inhibitor affinity to variants of human carbonic anhydrase II. Biochemistry. 1995;34:3981–3989. doi: 10.1021/bi00012a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neish A.C. Studies on chloroplasts: their chemical composition and the distribution of certain metabolites between the chloroplasts and the remainder of the leaf. Biochem J. 1939;33:300–308. doi: 10.1042/bj0330300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nienaber L., Cave-Freeman E., Cross M., Mason L., Bailey U.M., Amani P., Davis R.A., Taylor P., Hofmann A. Chemical probing suggests redox-regulation of the carbonic anhydrase activity of mycobacterial Rv1284. FEBS J. 2015;282:2708–2721. doi: 10.1111/febs.13313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocker Y., Janjić N. Enzyme kinetics in solvents of increased viscosity. Dynamic aspects of carbonic anhydrase catalysis. Biochemistry. 1987;26:2597–2606. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S.B., Lane T.W., Morel F.M.M. Carbonic anhydrase in the marine diatom thalassiosira weissflogii (Bacillariophyceae) J Phycol. 1997;33:845–850. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.1997.00845.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlett R.S. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the beta-carbonic anhydrases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1804:362–373. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D.N., Lindskog S. The catalytic mechanism of carbonic anhydrase: implications of a rate-limiting protolysis of water. Acc Chem Res. 1988;21:30–36. doi: 10.1021/ar00145a005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D.N., Vincent S.H. Proton transfer in the catalytic mechanism of carbonic anhydrase. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14:207–255. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K.S., Jakubzick C., Whittam T.S., Ferry J.G. Carbonic anhydrase is an ancient enzyme widespread in prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:15184–15189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.15184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somalinga V., Buhrman G., Arun A., Rose R.B., Grunden A.M. A high-resolution crystal structure of a psychrohalophilic alpha-carbonic anhydrase from Photobacterium profundum reveals a unique dimer interface. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0168022. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez Covarrubias A., Larsson A.M., Högbom M., Lindberg J., Bergfors T., Björkelid C., Mowbray S.L., Unge T., Jones T.A. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:18782–18789. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414348200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashian R.E. The carbonic anhydrases: widening perspectives on their evolution, expression and function. Bioessays. 1989;10:186–192. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp B.C., Bell C.B., 3rd, Cruz F., Krebs C., Ferry J.G. A role for iron in an ancient carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:6683–6687. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311648200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidgren J., Liljas A., Walker N.P. Refined structure of the acetazolamide complex of human carbonic anhydrase II at 1. A Int J Biol Macromol. 1990;12:342–344. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(90)90040-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur K.M., Anderson N.G. Electrometric and colorimetric determination of carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem. 1948;176:147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Feng L., Jeffrey P.D., Shi Y., Morel F.M. Structure and metal exchange in the cadmium carbonic anhydrase of marine diatoms. Nature. 2008;452:56–61. doi: 10.1038/nature06636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue Y., Liljas A., Jonsson B.H., Lindskog S. Structural analysis of the zinc hydroxide-Thr-199-Glu-106 hydrogen-bond network in human carbonic anhydrase II. Proteins. 1993;17:93–106. doi: 10.1002/prot.340170112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.