Abstract
Delirium after surgery and in the intensive care unit (ICU) remains a challenge for patients, families, and caregivers. Over the years, many promising biomarkers have been investigated as potential instruments for risk stratification of delirium. This review aimed to identify and assess the clinical usefulness of candidate serum biomarkers associated with hospital delirium in patients aged 60 years and older. We performed a time-unlimited review of publications indexed in PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and MEDLINE databases until June 2019 that evaluated baseline and/or longitudinal biomarker measurements in patients suffering from delirium at some point during their hospital stay. A total of 32 studies were included in this review reporting information on 7610 patients. Of these 32 studies, twenty-four studies reported data from surgical patients including four studies in ICU cohorts, five studies reported data from medical patients (1026 patients), and three studies reported data from a mixed cohort (1086 patients), including one study in an ICU cohort. Findings confirm restricted clinical usefulness to predict or diagnose delirium due to limited evidence on which biomarkers can be used and limited availability due to non-routine use.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13613-019-0548-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Introduction
Postoperative and intensive care unit (ICU) delirium remains a challenge for patients, families, and caregivers. Identified more than half a century ago in cardiac surgery patients, delirium today is characterized by criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-V, which can be summarized as a fluctuating disturbance of consciousness evolving over a short period of time, a change in cognition, and evidence from the current history, physical examination, or laboratory findings that the disturbance is caused by the direct physiological consequences of a general medical condition.
The suffering of delirious patients is severe as they may be restless, hallucinate, and be filled with fear. Unfortunately, problems continue even after the resolution of delirium. This syndrome may be associated with prolonged ICU and hospital stay [1, 2], more hospital readmissions [3], reduced quality of life, loss of independence, and increased mortality [1, 4–7]. Furthermore, the duration of delirium is associated with worse long-term cognitive function [8, 9]. The increased socioeconomic burden should also not be underestimated [10]. However, a recently updated delirium guidance paper on prevention and management of pain, agitation/sedation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disruption in adult ICU patients summarizes that delirium in critically ill adults has not been consistently shown to be associated with ICU length of stay, discharge disposition to a place other than home, depression, functionality/dependence, or mortality [11].
Ranging from 10 to 80% [12–14] or even up to 90% depending on the type of surgery [15], the overall incidence of delirium is high during hospital stay, especially in elderly patients. Delirium usually develops within 72 h after surgery and/or ICU admission. However, its impact is likely to be underestimated due to the predominance of hypoactive delirium.
Although the pathophysiology of delirium remains poorly understood, we know that the pathogenesis of the cognitive impairments associated with delirium is multifactorial. Certain entities such as drug overdose [16] but also drug withdrawal [17] bear delirium risk. As with so many disparate etiologies, it is highly unlikely that a single mechanism is solely responsible [18]. Therefore, research focuses on the assessment of modifiable pre-, intra-, and postoperative risk factors (e.g., dehydration, fluid balance, immobilization, analgesia, and sleep deprivation) associated with delirium, [18] as well as prediction, prevention, early detection, and treatment of this common psychiatric syndrome. One promising approach is the detection of elevated or lowered biomarkers as predictors or indicators of delirium [19, 20]. Furthermore, serum biomarkers may aid in risk stratification, diagnosis, and monitoring of delirium [19] and, finally, may help to find an effective treatment. This review aims to summarize the current state of knowledge on serum biomarkers of delirium.
Methods
We performed an updated review on biomarkers of delirium based on previous publications [19]. As age is one of the most consistently reported risk factors for developing delirium, we restricted our search to publications including patients aged 60 years and older [18, 21]. Study selection and quality assessment were performed by two independent authors (AH and KT). The results were compared, and disagreements were reviewed (MS).
Literature search
An electronic search of PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and MEDLINE databases was performed. The detailed search strategy is available in “Appendix” (Additional files). Search terms used for each biomarker are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. Every biomarker term according to Additional file 1: Table S1 was searched with “delirium”, “acute brain dysfunction”, “stroke”, “hemorrhagic stroke”, “ischemic stroke”, “traumatic brain injury”, and “septic encephalopathy”. The date of the last search was June 1, 2019.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Only studies that met the following criteria were included: patients aged 60 or older, sample size of 10 or higher, use of standardized approach to diagnose delirium [e.g., Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC), Confusion Assessment Method (CAM or CAM-ICU); Nursing Delirium Screening Scale (NuDESC); Delirium Observation Screening Scale (DOS); Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-III/IV; Delirium Symptom Interview (DSI); Delirium Rating Scale Revised-98-T (DRS-R98-T); Memorial Delirium Assessment Scale (MDAS)], ICU/hospital cohort (e.g., excluding studies performed in nursing homes), and English language. Reviews from all cohorts (i.e., medical, surgical, mixed, ICU) were included. Age limitation was chosen due to significantly higher reported incidence of delirium in patients 60 to 65 and older, and to help clarify results within the flood of information on delirium biomarkers available to date for the age category at highest risk. Studies reporting data that included patients with cognitive dysfunction due to preexisting psychiatric disorders, known dementia, or alcohol-related delirium (delirium tremens) were excluded. Reviews/meta-analyses, and studies reporting animal data or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers were also excluded.
Data extraction
Study-relevant information was extracted by two independent investigators (AH and KT) for each included study. Any conflict of opinion was resolved by consensus with a third party (MS). Study location and date of study conduct, patient characteristics, past medical history including drug therapy prior to hospitalization, risk assessment scores (e.g., Charlson comorbidity index), outcome data (i.e., ICU and hospital length of stay, mortality), total number of patients, and study-specific procedures—including drug therapy during ICU and/or hospital stay—were considered relevant for data extraction. Observational and interventional study design was distinguished.
Results
Trial identification
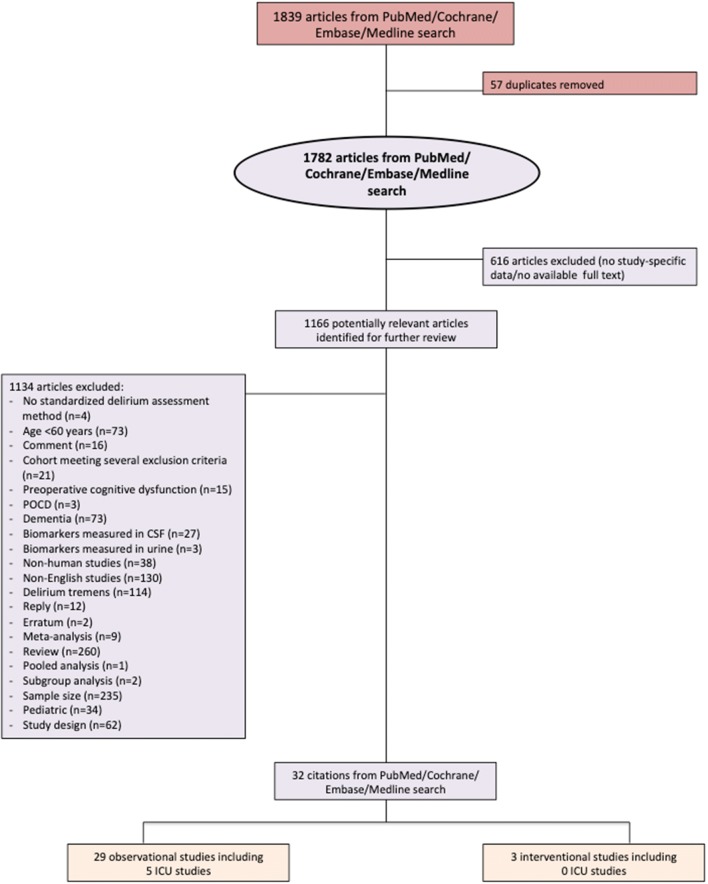
In June 2019, a search of the PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and MEDLINE databases using the search terms “delirium”, “acute brain dysfunction”, “stroke”, “hemorrhagic stroke”, “ischemic stroke”, “traumatic brain injury”, and “septic encephalopathy” [22] AND “biomarker” (term “biomarker” and each biomarker suggested by the authors, Additional file 1: Table S1) for papers published until June 1, 2019, retrieved 1839 publications (Fig. 1). After removal of 57 duplicates, a critical review of the titles and abstracts was performed, and another 616 articles without study-specific data were excluded. Thirty-two studies (29 observational and three interventional) remained after further exclusion of 1134 articles based on title, abstract, or full text as indicated in Fig. 1. The full texts of these remaining studies (Table 1) were reviewed for data extraction by two independent investigators (AH and KT). Due to age limitation a total of 73 publications on mostly mixed populations (sample size ranging from 10 to 1183) and 34 publications on the pediatric cohort have been excluded from our analysis (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram according to literature search
Table 1.
Summary of current evidence on biomarkers in elderly delirious patients determined by literature search
| Biomarker | Study | Country | Medical specialty | ICU | Sample size | Assessment tool | Event rate (%) | Biomarker value | Main findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetylcholine | Larsen (2010) | USA | S | 196a | DRS-R98 | 14.3 | L | Anticholinergic treatment (olanzapine) associated with significantly lower incidence of delirium | |
| 204 | DSM-III | 40.2 | |||||||
| Adenylate kinase | |||||||||
| Albumin | Zhang (2018) | China | S | Yes | 700 | CAM-ICU | 15.9 | L | Preoperative severe hypoalbuminemia (≤ 30 g/L) was associated with increased risk of postoperative delirium |
| Guo (2016) | China | S | 572 | CAM, DSM-IV | 21 | L | Older age, history of stroke, lower albumin, higher blood glucose, higher total bilirubin, higher CRP, longer surgery duration, and higher volume of red blood cell transfusions are independent risk factors for postoperative delirium | ||
| Capri (2014) | Italy | S | 351 | CAM | 13.4 | ND | High preoperative IL-6 level is a risk factor for postoperative delirium | ||
| Larsen (2010) | USA | S | 196a | DRS-R98 | 14.3 | L | Anticholinergic treatment (olanzapine) associated with significantly lower incidence of delirium | ||
| 204 | DSM-III | 40.2 | |||||||
| Lee (2010) | Korea | S | 81 | CAM | 13.6 | L | Albumin level before surgery significantly lower in patients developing postoperative delirium | ||
| Amyloid β1-40 | Sun (2016) | China | S | 257 | CAM | 21.8 | H | Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, cortisol, and amyloid β1-40 after surgery under general anesthesia may be involved in the onset of postoperative delirium among elderly oral cancer patients | |
| ASAT | Plaschke (2016) | Germany | M | 100 | NuDESC | 29 | L | Plasma ChEA (AChE and BChE) not associated with delirium | |
| Guo (2016) | China | S | 572 | CAM, DSM-IV | 21 | ND | Older age, history of stroke, lower albumin, higher blood glucose, higher total bilirubin, higher CRP, longer surgery duration, and higher volume of red blood cell transfusions are independent risk factors for postoperative delirium | ||
| BDNF | Brum (2015) | Brazil | M | 70 | CAM | NA | L | BDNF levels significantly lower in delirium in oncology inpatients | |
| Cholecystokinin | |||||||||
| Cholinesterase | Plaschke (2016) | Germany | M | 100 | NuDESC | 29 | ND | Plasma ChEA (AChE and BChE) not associated with delirium | |
| Cerejeira (2012) | Portugal | S | 101 | CAM, DSM-IV | 36.6 | L | Delirium associated with dysfunctional interaction between cholinergic and immune systems | ||
| Cortisol | Sun (2016) | China | S | 257 | CAM | 21.8 | H | Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, cortisol, and amyloid β1-40 after surgery under general anesthesia may be involved in the onset of postoperative delirium among elderly oral cancer patients | |
| Creatine kinase | |||||||||
| Creatine kinase BB | |||||||||
| CREB | |||||||||
| CRP | Slor (2019) | The Netherlands | S | 121 | CAM, DRS-R98 | 33.1 | NDd | CRP level trajectory after hip surgery coincides with delirium from the second day after surgery | |
| Miao (2018) | China | S | 112 | DSM-IV | 43.8 | H | Potential roles of neopterin in pathophysiology and prediction of delirium in elderly patients after open abdominal surgery | ||
| Vasunilashorn (2018) | USA | S | 560 | CAM | 24 | NA | The signature of postoperative delirium is dynamic, with some proteins important prior to surgery (risk markers: CRP and AZGP1) and others during delirium (disease markers: IL-2, IL-6, and CRP). CRP, AZGP1, and SERPINA3 were identified as top set of delirium-related proteins | ||
| Cizginer (2017) | USA | S | 556 | CAM | 24 | ND | Vocabulary knowledge, cognitive activities, and education significantly modified association of CRP and postoperative delirium | ||
| Vasunilashorn (2017) | USA | S | 560 | CAM, Chart Review | 24 | H | High preoperative and postoperative day 2 CRP are independently associated with incidence of delirium | ||
| Egberts (2017) | The Netherlands | M | 86 | DSM-IV | 15.1 | H | No significant difference of CRP level among delirious and non-delirious patients | ||
| Plaschke (2016) | Germany | M | 100 | NuDESC | 29 | H | Plasma ChEA (AChE and BChE) is not associated with delirium | ||
| Nguyen (2016) | Belgium | M + S | Yes | 101 | CAM-ICU | 78 | ND | High prolactin levels possible risk factor for delirium in septic patients | |
| Sun (2016) | China | S | 257 | CAM | 21.8 | H | Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, cortisol, and amyloid β1-40 after surgery under general anesthesia may be involved in the onset of postoperative delirium among elderly oral cancer patients | ||
| Ritchie (2014) | UK | M | 710 | CAM | 12.3 | H | Association between elevated CRP and delirium | ||
| Guo (2016) | China | S | 572 | CAM, DSM-IV | 21 | H | Older age, history of stroke, lower albumin, higher blood glucose, higher total bilirubin, higher CRP, longer surgery duration, and higher volume of red blood cell transfusions are independent risk factors for postoperative delirium | ||
| Cerejeira (2012) | Portugal | S | 101 | CAM, DSM-IV | 36.6 | H | Delirium is associated with unbalanced inflammatory response | ||
| Lee (2011) | Korea | S | 65 | K-DRS-98 | 28 | H | CRP levels within 24 and 72 h after hospitalization are significantly higher in patients with delirium | ||
| Beloosesky (2004) | Israel | S | 32 | CAM | 31.3 | H | CRP kinetics over 30 days after hip surgery is significantly associated with delirium and cardiovascular complications | ||
| Dopamine | |||||||||
| Histamine H1 | |||||||||
| Heat Shock Protein 70 | |||||||||
| IL-2 | Capri (2014) | Italy | S | 351 | CAM | 13.4 | ND | High preoperative IL-6 level is a risk factor for postoperative delirium | |
| Vasunilashorn (2018) | USA | S | 560 | CAM | 24 | NA | The signature of postoperative delirium is dynamic, with some proteins important prior to surgery (risk markers: CRP and AZGP1) and others at the time of delirium (disease markers: IL-2, IL-6, and CRP). CRP, AZGP1, and SERPINA3 were identified as top set of delirium-related proteins | ||
| IL-6 | Gao (2018) | China | S | Yes | 64 | CAM-ICU | 15.6 | NA | TEAS can alleviate POD in older patients with silent lacunar infarction and may be related to reduced neuroinflammation by lowering BBB permeability |
| Miao (2018) | China | S | 112 | DSM-IV | 43.8 | H | Potential roles of neopterin in pathophysiology and prediction of delirium in elderly patients after open abdominal surgery | ||
| Vasunilashorn (2018) | USA | S | 560 | CAM | 24 | NA | The signature of postoperative delirium is dynamic, with some proteins important prior to surgery (risk markers: CRP and AZGP1) and others at the time of delirium (disease markers: IL-2, IL-6, and CRP). CRP, AZGP1, and SERPINA3 were identified as top set of delirium-related proteins | ||
| Kuswardhani (2017) | Indonesia | M | 60 | MDAS | NA | NA | CACI score, IL-6 levels, and sepsis have a strong relationship with delirium severity | ||
| Xin (2017) | China | S | 60c | NuDESC | 11.7 | ND | TNF-α significantly associated with postoperative delirium | ||
| 60 | 38.3 | ||||||||
| Sun (2016) | China | S | 257 | CAM | 21.8 | H | Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, cortisol, and amyloid β1-40 after surgery under general anesthesia may be involved in the onset of postoperative delirium among elderly oral cancer patients | ||
| Capri (2014) | Italy | S | 351 | CAM | 13.4 | H | High preoperative IL-6 level is a risk factor for postoperative delirium | ||
| Jia (2014) | China | S | 117b | DRS-R98 | 3.4 | H | The lower incidence of delirium is at least partly attributable to the reduced systemic inflammatory response mediated by IL-6 | ||
| 116 | 12.9 | ||||||||
| Cerejeira (2012) | Portugal | S | 101 | CAM, DSM-IV | 36.6 | H | Delirium is associated with unbalanced inflammatory response | ||
| van Munster (2011) | The Netherlands | M + S | 870 | CAM | 35.7 | NA | Functional genetic variations in the IL-6, IL-6R, and IL-8 genes are not associated with delirium | ||
| van Munster (2008) | The Netherlands | S | 98 | CAM, DOS, DRS-R98 | NA | H | Patients with hyperactive or mixed subtype of delirium had significantly higher IL-6 levels than patients with hypoactive delirium. IL-6 and IL-8 may contribute to pathogenesis of postoperative delirium | ||
| IL-8 | Xin (2017) | China | S | 60c | NuDESC | 11.7 | ND | TNF-α significantly associated with postoperative delirium | |
| 60 | 38.3 | ||||||||
| Capri (2014) | Italy | S | 351 | CAM | 13.4 | ND | High preoperative IL-6 level is a risk factor for postoperative delirium | ||
| Cerejeira (2012) | Portugal | S | 101 | CAM, DSM-IV | 36.6 | H | Delirium is associated with unbalanced inflammatory response | ||
| van Munster (2011) | The Netherlands | M + S | 870 | CAM | 35.7 | NA | Functional genetic variations in the IL-6, IL-6R, and IL-8 genes are not associated with delirium | ||
| van Munster (2008) | The Netherlands | S | 98 | CAM, DOS, DRS-R98 | NA | H | IL-6 and IL-8 may contribute to pathogenesis of postoperative delirium | ||
| IL-18 | |||||||||
| Lactate dehydrogenase | |||||||||
| Leptin | Chen (2014) | China | S | 186 | CAM | 37.6 | L | Preoperative plasma leptin level may be a useful, complementary tool to predict delirium in general and prolonged delirium in elderly patients after hip surgery | |
| Sanchez (2013) | Colombia | M + S | 115 | CAM, DSM-IV | 23.5 | L | Leptin levels could be a useful clinical biomarker to establish risk in elderly patients | ||
| Neopterin | Egberts (2019) | The Netherlands | S | Yes | 211 | CAM-ICU, DSM-IV | 38.4 | H | Acutely ill medical patients with delirium had higher levels of neopterin and higher phenylalanine/tyrosine ratios after elective cardiac surgery |
| Miao (2018) | China | S | 112 | DSM-IV | 43.8 | H | Potential roles of neopterin in pathophysiology and prediction of delirium in elderly patients after open abdominal surgery | ||
| NSE | |||||||||
| PI3K | |||||||||
| Procalcitonin | Sun (2016) | China | S | 257 | CAM | 21.8 | H | Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, cortisol, and amyloid β1-40 after surgery under general anesthesia may be involved in the onset of postoperative delirium among elderly oral cancer patients | |
| Protein C | |||||||||
| S-100β | Gao (2018) | China | S | Yes | 64 | CAM-ICU | 15.6 | NA | TEAS can alleviate POD in older patients with silent lacunar infarction and may be related to reduced neuroinflammation by lowering BBB permeability |
| Xin (2017) | China | S | 60c | NuDESC | 11.7 | ND | TNF-α is significantly associated with postoperative delirium | ||
| 60 | 38.3 | ||||||||
| SDNF | |||||||||
| Thioredoxin | Wu (2017) | China | S | 192 | CAM | 36.5 | H | Thioredoxin in postoperative serum may be a potential biomarker to predict postoperative delirium and POCD in elderly patients | |
| TNF-α | Gao (2018) | China | S | Yes | 64 | CAM-ICU | 15.6 | NA | TEAS can alleviate POD in older patients with silent lacunar infarction and may be related to reduced neuroinflammation by lowering BBB permeability |
| Xin (2017) | China | S | 60c | NuDESC | 11.7 | H | TNF-α is significantly associated with postoperative delirium | ||
| 60 | 38.3 | ||||||||
| Brum (2015) | Brazil | M | 70 | CAM | NA | ND | No cross-sectional relationship of BDNF and TNF-α blood levels with delirium in oncology inpatients has been demonstrated | ||
| Capri (2014) | Italy | S | 351 | CAM | 13.4 | ND | High preoperative IL-6 level is a risk factor for postoperative delirium | ||
| Cerejeira (2012) | Portugal | S | 101 | CAM, DSM-IV | 36.6 | ND | Delirium is associated with unbalanced inflammatory response (see CRP, IL-6, and IL-8) | ||
| 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α | Zheng (2016) | China | S | 182 | CAM | 37.4 | H | Postoperative plasma 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α levels may have the potential to predict postoperative delirium and POCD in elderly patients | |
| Additional reported biomarkers resulting from literature search | |||||||||
| AZGP1 | Vasunilashorn (2018) | USA | S | 560 | CAM | 24 | L | The signature of postoperative delirium is dynamic, with some proteins important prior to surgery (risk markers: CRP and AZGP1) and others at the time of delirium (disease markers: IL-2, IL-6, and CRP). CRP, AZGP1, and SERPINA3 were identified as top set of delirium-related proteins | |
| BUN | Miao (2018) | China | S | 112 | DSM-IV | 43.8 | ND | Potential roles of neopterin in pathophysiology and prediction of delirium in elderly patients after open abdominal surgery | |
| Kuswardhani (2017) | Indonesia | M | 60 | MDAS | NA | NA | BUN only has a weak role in delirium severity in elderly patients with infection | ||
| Creatinine | Miao (2018) | China | S | 112 | DSM-IV | 43.8 | ND | Potential roles of neopterin in pathophysiology and prediction of delirium in elderly patients after open abdominal surgery | |
| Bakker (2012) | The Netherlands | S | Yes | 201 | CAM-ICU | 31.3 | H | Creatinine level is one of the three independent risk factors for delirium after cardiac surgery | |
| ILGF-1 | Miao (2018) | China | S | 112 | DSM-IV | 43.8 | L | Potential roles of neopterin in pathophysiology and prediction of delirium in elderly patients after open abdominal surgery | |
| IL-1β | Xin (2017) | China | S | 60c | NuDESC | 11.7 | ND | TNF-α significantly associated with postoperative delirium | |
| 60 | NuDESC | 38.3 | ND | ||||||
| Capri (2014) | Italy | S | 351 | CAM | 13.4 | ND | High preoperative IL-6 level is a risk factor for postoperative delirium | ||
| Cerejeira (2012) | Portugal | S | 101 | CAM, DSM-IV | 36.6 | ND | Delirium is associated with unbalanced inflammatory response (see CRP, IL-6, and IL-8) | ||
| IL-12 | van Munster (2008) | The Netherlands | S | 98 | CAM, DOS, DRS-R98 | NA | ND | IL-6 and IL-8 may contribute to the pathogenesis of postoperative delirium | |
| ILGF-1 | Chu (2016) | China | S | 103 | CAM, DSM-IV | 22.3 | ND | No association found between preoperative ILGF-1 levels and postoperative delirium | |
| MMP-9 | Gao (2018) | China | S | Yes | 64 | CAM-ICU | 15.6 | NA | TEAS can alleviate POD in older patients with silent lacunar infarction and may be related to reduced neuroinflammation by lowering BBB permeability |
| NLR | Egberts (2017) | The Netherlands | M | 86 | DSM-IV | 15.1 | H | NLR levels are significantly increased in patients with delirium | |
| Prolactin | Nguyen (2016) | Belgium | M + S | Yes | 101 | CAM-ICU | 78 | H | High prolactin levels are a possible risk factor for delirium in septic patients |
| Phenylalanine–tyrosine ratio | Egberts (2019) | The Netherlands | S | Yes | 211 | CAM-ICU, DSM-IV | 38.4 | H | Acutely ill medical patients with delirium had higher levels of neopterin and higher phenylalanine–tyrosine ratios after elective cardiac surgery |
| SERPINA3 | Vasunilashorn (2018) | USA | S | 560 | CAM | 24 | H | The signature of postoperative delirium is dynamic, with some proteins important prior to surgery (risk markers: CRP and AZGP1) and others at the time of delirium (disease markers: IL-2, IL-6, and CRP). CRP, AZGP1, and SERPINA3 were identified as top set of delirium-related proteins | |
Data are presented as event rate of delirium. Biomarker value refers to comparison of biomarker level in delirious patients to non-delirious patients. Authors bold, main biomarker investigated in the indicated study; biomarkers italic = no data available with the search terms used; authors underlined, interventional studies
M medical, S surgical, H biomarker level higher in delirious patients, L biomarker level lower in delirious patients, NA not applicable, ND no difference of biomarker level among groups, AChE acetylcholinesterase, ASAT aspartate aminotransferase, AZGP1 alpha-2 glycoprotein, BBB blood–brain barrier, BChE butyrylcholinesterase, BDNF brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BUN blood urea nitrogen, CAM Confusion Assessment Method, ChEA cholinergic enzyme activity, CREB cyclic AMP response element-binding protein, CRP C-reactive protein, DOS Delirium Observation Scale, DRS-R98 Delirium Rating Scale Revised-98, DSM Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, ICU intensive care unit, IL interleukin, ILGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1, IQR interquartile range, K-DRS-98 Korean version of DRS, MDAS Memorial Delirium Assessment Scale, MMP-9 metalloproteinase-9, NLR neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio, NSE neuron-specific enolase, NuDESC Nursing Delirium Screening Scale, PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases, POCD postoperative cognitive dysfunction, SDNF striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor, SERPINA3 alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, TEAS transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation, TNF tumor necrosis factor
aExperimental arm (olanzapine)
bExperimental arm (fast-track surgery)
cExperimental arm (hypertonic saline)
dOn postoperative day 1; significant difference thereafter
Study characteristics
All 32 studies were published before May 2019 and included information on 7610 patients. Twenty-four studies reported data from surgical patients [23–46], of which two studies analyzed the same patient cohort [29, 30]. Of these 24 studies, 12 reported data collected from delirium high-risk surgical cohorts: Two studies reported data from cardiac surgery [39, 42], and ten reported data from hip surgery patients [23, 24, 28, 32, 33, 35–37, 41, 45]. Five studies reported data from medical patients (1026 patients) [47–51], and three studies reported data from a mixed cohort (i.e., surgical and medical patients or not defined; 1086 patients) [52–54]. Twenty-nine were observational studies, and three were interventional studies (outlined in more detail below).
Biomarkers
The authors initially screened for biomarkers already known as possible markers of delirium (Additional file 2: Table S2). A second comprehensive screening of the literature was for biomarkers mentioned particularly in the context of other neurological diseases, but bearing a possible association with delirium, including dementia, delirium tremens, hypoxic brain injury, and Parkinson’s disease (Additional file 2: Table S2). These searches resulted in 11 additional biomarkers that were also investigated in the context of delirium in the elderly (Additional file 2: Table S2).
Biomarkers were grouped according to their biochemical function (i.e., cytokine, enzyme, growth factor, hormone, metabolic product, neuronotrophic factor, neurotransmitter, transcription factor, transport protein, or other; Table 2). Overall, 20 biomarkers were reported to detect or to be associated with delirium (Table 3). Of these, higher levels of 14 biomarkers [i.e., IL-6, cortisol, prolactin, amyloid, creatinine, C-reactive protein (CRP), neopterin, metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio (NLR), phenylalanine–tyrosine ratio, procalcitonin, thioredoxin, serpin family A member 3 (SERPINA3 (alpha 1-antichymotrypsin)), and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α] and lower levels of 6 biomarkers [i.e., brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), leptin, acetylcholine, albumin, insulin-like growth factor-1 (ILGF-1), and alpha-2 glycoprotein (AZGP1)] were reported in delirious patients. However, apart from CRP clinical relevance of the presented biomarkers was either questioned or denied by the authors (Table 3). With the exception of IL-1β and IL-12 all inflammatory biomarkers could be linked to delirium (Additional file 3: Table S3; Additional file 4: Table S4). Moreover, a connection to delirium was found for all four biomarkers of metabolism (Additional file 3: Table S3; Additional file 4: Table S4).
Table 2.
Grouping of suggested biomarkers of delirium according to their main function
| Function | Assigned biomarker | Established clinical use |
|---|---|---|
| Cytokine | IL-1β | Inflammatory marker |
| IL-2 | ||
| IL-6 | ||
| IL-8 | ||
| IL-12 | ||
| IL-18 | ||
| TNF-α | ||
| Enzyme | Adenylate kinase | Marker of liver cell damage |
| ASAT | Marker of cell damage | |
| Cholinesterase | Marker of liver synthetic function | |
| CK | Marker of muscle damage | |
| CK-BB | Tumor marker | |
| LDH | Marker of tissue breakdown | |
| NSE | Tumor marker; brain damage marker | |
| PI3K | ||
| Growth factor | BDNF | Diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency; marker of pituitary function |
| IGF-1 | ||
| Hormone | Cholecystokinin | |
| Cortisol | Marker of adrenal function | |
| Leptin | ||
| Prolactin | Marker of pituitary gland/hypothalamus function; fertility assessment; tumor marker | |
| Metabolic product | Amyloid | |
| Phenylalanine–tyrosine ratio | ||
| Neuronotrophic factor | S-100β | Tumor marker; brain damage marker |
| SDNF | ||
| Neurotransmitter | Acetylcholine | |
| Dopamine | ||
| Histamine | ||
| Transcription factor | CREB | |
| Transport protein | Albumin | Nutritional marker, negative acute phase protein |
| Other | AZGP1 | |
| BUN | Marker of kidney function | |
| Creatinine | Marker of kidney function | |
| CRP | Inflammatory marker, positive acute phase protein | |
| HSP70 | ||
| Metalloproteinase-9 | Proinflammatory marker | |
| Neopterin | Marker of infection | |
| NLR | ||
| Procalcitonin | Proinflammatory marker | |
| Protein C | ||
| Thioredoxin | ||
| 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α |
ASAT aspartate aminotransferase, AZGP1 alpha-2 glycoprotein, BDNF brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BUN blood urea nitrogen, CK creatine kinase, CK-BB creatine kinase BB, CREB cyclic AMP response element-binding protein, CRP C-reactive protein, HSP70 heat shock protein 70, IL interleukin, IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, NLR neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio, NSE neuron-specific enolase, PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases, PCT procalcitonin, SDNF striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor, TNF tumor necrosis factor
Table 3.
Role of suggested biomarkers of delirium according to literature reports
| Function | Assigned biomarker | Biomarker of delirium | Clinically useful |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine | IL-1β | – | – |
| IL-2 | ? | – | |
| IL-6 | + | – | |
| IL-8 | ? | – | |
| IL-12 | – | ||
| IL-18 | NR | – | |
| TNF-α | ? | – | |
| Enzyme | Adenylate kinase | NR | – |
| ASAT | ? | – | |
| Cholinesterase | ? | – | |
| CK | NR | – | |
| CK-BB | NR | – | |
| LDH | NR | – | |
| NSE | NR | – | |
| PI3K | NR | – | |
| Growth factor | BDNF | + | – |
| ILGF-1 | + | – | |
| Hormone | Cholecystokinin | NR | – |
| Cortisol | + | – | |
| Leptin | + | – | |
| Prolactin | + | – | |
| Metabolic product | Amyloid | + | ? |
| Phenylalanine–tyrosine ratio | + | ? | |
| Neuronotrophic factor | S-100β | – | – |
| SDNF | NR | – | |
| Neurotransmitter | Acetylcholine | + | – |
| Dopamine | NR | – | |
| Histamine | NR | – | |
| Transcription factor | CREB | NR | – |
| Transport protein | Albumin | + | ? |
| Other | AZGP1 | + | – |
| BUN | ? | – | |
| Creatinine | + | ? | |
| CRP | + | + | |
| HSP70 | NR | – | |
| Metalloproteinase-9 | + | ? | |
| Neopterin | + | ? | |
| NLR | + | ? | |
| Procalcitonin | + | ? | |
| Protein C | NR | – | |
| Thioredoxin | + | – | |
| SERPINA3 | + | – | |
| 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α | + | – |
NR nothing reported in the literature, + correlation with delirium, – no correlation with delirium, ASAT aspartate aminotransferase, AZGP1 alpha-2 glycoprotein, BDNF brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BUN blood urea nitrogen, CREB cyclic AMP response element-binding protein, CRP C-reactive protein, IL interleukin, ILGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1, NLR neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio, NSE neuron-specific enolase, PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases, SDNF striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor, SERPINA3 alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, TNF tumor necrosis factor
Surgical cohort
Overall, 19 studies reported on the incidence of delirium. Event rate of postoperative delirium ranged from 13.4 to 43.8% (Table 1). Four studies reported data from ICU patients (delirium incidence range 15.8 to 43.8%; Table 1) [39]. Within the studies reporting data from surgical patients, three were interventional and as such did not group patients into delirious and non-delirious prior to investigation. Each of these three studies showed a lower incidence of delirium in the experimental arm (Table 1): One compared olanzapine to placebo (delirium incidence 14.3% vs. 40.2%) [23], one compared fast-track surgery to the standard procedure (delirium incidence 3.4% vs. 12.9%) [34], and one compared hypertonic to normal saline (delirium incidence 11.7% vs. 38.3%) [33].
Biomarker assessment of postoperative delirium
Biomarkers reported from investigations of surgical cohorts are shown in Table 1. Two studies from the surgical population and one from the medical population evaluated the role of the acetylcholine pathway in delirium. Whereas anticholinergic treatment was suggested as a promising strategy to reduce the incidence of delirium [23], reports on cholinesterase were not as clear [28]. Albumin was the main focus of one study [43], but also evaluated in four other studies resulting from our literature search [23–26]. It was almost consistently reported to be lower in delirious patients. Amyloid β1-40, a protein associated with dementia, was the main focus of Sun and colleagues [27] who reported a possible role in the detection of delirium. No difference in ASAT was found among postoperatively delirious and non-delirious patients. Like albumin, ASAT was not the focus of the study cited here [24]. Among inflammatory markers, increased procalcitonin [27], CRP [24, 27, 28, 30–32, 41, 45, 46], and IL-6 [25, 27, 28, 34, 35, 44, 46] were consistently reported to be associated with delirium with the exception of one study that found no increase in IL-6 levels [33]. Of note, in this study, IL-6 was collected early (i.e., venous blood was drawn at 06:00 on the first day after surgery). Cortisol [27] and leptin were the two reported hormones with a possible link to postoperative delirium. Leptin levels were significantly lower in patients with delirium compared to those without [36]. Finally, AZGP1 [29], MMP-9 [44], neopterin [42], phenylalanine–tyrosine ratio [42], SERPINA3 [29], thioredoxin [37], and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α [38] were linked to postoperative delirium.
Medical cohort
Within the studies reporting data from medical patients, three studies reported an incidence of delirium ranging from 12.3 to 29% (Table 1).
Biomarker assessment of delirium in elderly patients admitted for medical reasons
Biomarkers reported from investigations on patients admitted for medical reasons are outlined in Table 1. The study reporting results on the assessment of cholinesterases (i.e., acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase) in medical patients found no association with delirium [47]. As opposed to the surgical cohort, ASAT was found to be lower in delirious patients admitted for medical reasons [47]. Lower BDNF levels were clearly linked to delirium in oncology patients [48]. Findings on CRP [47, 49, 50] and IL-6 [51] concurred with those reported from the surgical cohorts. NLR was additionally linked to delirium [49].
Mixed cohort
The three studies to report data from both, medical and surgical patients, reported a combined incidence of delirium of 23.5% (Sanchez [54]) and 35.7% (Van Munster [53]) in non-ICU patients, and of 78% (Nguyen [52]) in ICU patients with sepsis (Table 1).
Biomarker assessment of delirium in mixed cohorts of elderly patients
Biomarkers reported from investigations of mixed cohorts are also outlined in Table 1. The two markers reported to have a possible association with delirium in mixed patient cohorts were leptin [54] and prolactin (ICU cohort; [52]).
Discussion
Our updated findings are consistent with a review published 7 years ago, in 2011, by Khan and colleagues [19] who had reported a lack of evidence for the clinical use of biomarkers to aid in earlier detection, prevention, or treatment of delirium. As long as there are no adequate means of intervention, altered levels of biomarkers are unlikely to initiate any change in clinical practice. So far, no biomarker has been identified that would enable development of treatment strategies to lower the incidence, severity, or duration of delirium. A useful biomarker needs to be easily identifiable and reliable to enable targeted therapy while being cost-effective. These criteria were not applicable for any biomarker found in this literature review. Of note, we only reported data from patients aged 60 and older, as opposed to the review by Khan and colleagues [19].
Our main conclusion that none of the biomarkers described help to lower the incidence of delirium is based on several considerations. Pathophysiological explanations such as those addressed by the neurotransmitter hypothesis have already been described nearly 40 years ago [55]. Despite the knowledge of the role of neurotransmitters in the pathophysiology of delirium, with central cholinergic deficiency remaining the leading hypothesis [56], we have not yet been able to find a way to decrease the incidence of delirium. Dopamine excess and inflammation are important assumptions competing with or contributing to the hypothesis of cholinergic deficiency [57], but the focus should lie on modifiable factors causing delirium [18]. This includes stress reduction due to minimization of light and noise disturbances at night and adequate pain management among other things, but also preventive drug therapy in high-risk cohorts [58, 59]. Most importantly, the pathophysiology of delirium remains poorly understood [60] despite being first described by Hippocrates more than 2500 years ago [61]. So on the one hand, our findings are consistent with established theories such as the role of neurotransmitters, inflammation, and stress response in delirium (i.e., reported association of acetylcholine, IL-6, CRP, procalcitonin, and cortisol). On the other hand, there are new approaches that, however, lack sufficient evidence or validation for implementation into everyday clinical practice (i.e., BDNF, leptin, MMP-9, neopterin, phenylalanine–tyrosine ratio, prolactin, NLR, thioredoxin, 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α, AZGP1, and SERPINA3). As such, the latter are not readily available. Delirium biomarkers that are included in standard blood examinations (i.e., albumin and creatinine) may be useful to attribute higher delirium risk but are not targets specific to delirium prevention since they are routinely addressed with respect to other clinical questions. It is nevertheless interesting that an elevated creatinine level was reported to be an independent risk factor for delirium in a cardiac surgery cohort; clinicians should keep this in mind [39].
An almost exclusive association of the numerous investigated inflammatory biomarkers with delirium offers room for and discussion on a novel approach: The implementation of a widely used inflammatory marker (i.e., CRP or procalcitonin) as a diagnostic tool might help facilitate diagnosis of hypoactive delirium. The same can be said for biomarkers of metabolism. Moreover, these biomarkers could be implemented into a tool to assess delirium risk. Finally, the accepted role of amyloid β1-40 for delirium risk has also been confirmed. But clinical relevance here can be reduced to knowledge of its existence, since patients suffering from dementia are known to bear higher risk of delirium [62].
We acknowledge the following limitations of the presented review. First, we did not include any reports on biomarkers with a sample size lower than 10. Important biomarkers to be further explored in larger cohorts may thus have escaped our attention. Second, we focused on patients aged 60 and older, which led to the exclusion of numerous publications reporting other potentially important biomarkers for the elderly population including key articles on delirium biomarkers [63–68]. Interestingly, putative delirium biomarkers such as NSE and S-100β were reported/found to be irrelevant [59]. Third, there is an imbalance between medical and surgical patients investigated. In addition, high-risk surgical groups (i.e., hip and cardiac surgery) are overrepresented, whereas another important high-risk group (i.e., ICU patients) is underrepresented in the reported literature. Last, all observational studies have outlined biomarker levels comparing delirious to non-delirious patients. Overall, delirium is diagnosed clinically by established delirium assessment methods and biomarker groups and could be helpful to diagnose patients where a delirium is not so obvious (i.e., hypoactive delirium). In addition, it is not easy to influence levels of the biomarkers reported here other than by following guidelines (e.g., hygiene directives, pain control, prevention and management of infections, avoidance of unnecessary surgery, and adequate nutrition).
Conclusion
The concluding observations offer no ground-breaking recommendation for the implementation of a specific biomarker of delirium. Inflammatory biomarkers and biomarkers of metabolism could assist in diagnosing delirium and in assessing delirium risk. Expert opinions state that especially the hypoactive form is frequently undiagnosed even when using established tools to diagnose delirium. The implementation of these biomarkers in delirium assessment tools could represent a new approach. However, authors found inflammatory biomarkers not consistently reported as delirium risk factors. Their level of evidence should first be investigated in a meta-analysis.
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1. Terms used for biomarker search in alphabetical order.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Overview of biomarkers investigated in this review including references.
Additional file 3: Table S3 Role of inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers in delirium according to literature reports.
Additional file 4: Table S4 Sensitivity and specificity analysis of inflammatory biomarkers and biomarkers of metabolism that could assist in diagnosing delirium and in assessing delirium risk.
Acknowledgements
We thank Allison Dwileski for editing the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- ASAT
aspartate aminotransferase
- AZGP1
alpha-2 glycoprotein
- BDNF
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- BUN
blood urea nitrogen
- CK
creatine kinase
- CK-BB
creatine kinase BB
- CAM
Confusion Assessment Method
- DRS-R98-T
Delirium Rating Scale Revised-98-T
- CREB
cyclic AMP response element-binding protein
- CRP
C-reactive protein
- DOS
Delirium Observation Screening Scale
- DRS
delirium rating scale
- DSI
Delirium Symptom Interview
- DSM
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
- H1
histamine type 1
- HSP
heat shock protein
- ICB
intracerebral bleeding
- ICDSC
Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist
- ICU
intensive care unit
- LDH
lactate dehydrogenase
- MDAS
Memorial Delirium Assessment Scale
- MoCA
Montreal Cognitive Assessment
- NLR
neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio
- NSE
neuron-specific enolase
- NuDESC
Nursing Delirium Screening Scale
- PI3K
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases
- POD
postoperative delirium
- SDNF
striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor
- SERPINA3
serpin family A member 3 (alpha 1-antichymotrypsin)
- TNF
tumor necrosis factor
Appendix: Detailed search strategy
PubMed
“Delirium” AND “biomarkers”, “delirium” AND “Acetylcholine”, “Delirium” AND “Adenylate kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Myokinase”, “Delirium” AND “Albumin”, “Delirium” AND “Amyloid”, “Delirium” AND “ASAT”, “Delirium” AND “Aspartate transaminase”, “Delirium” AND “Aspartate aminotransferase“, “Delirium” AND “AST”, “Delirium” AND “BDNF”, “Delirium” AND “Brain-derived neurotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Cholezystokinine”, “Delirium” AND “Cholinesterase”, “Delirium” AND “Cortisol”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine phosphokinase”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine kinase BB”, “Delirium” AND “CK-BB”, “Delirium” AND “CREB”, “Delirium” AND “Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein”, “Delirium” AND “CRP”, “Delirium” AND “Dopamine”, “Delirium” AND “Histamine H1”, “Delirium” AND “Heat Shock Protein 70”, “Delirium” AND “IL-2”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-2”, “Delirium” AND “IL-6”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-6”, “Delirium” AND “IL-8”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-8”, “Delirium” AND “IL-18”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-18”, “Delirium” AND “Lactate dehydrogenase”, “Delirium” AND “Leptin”, “Delirium” AND “Neopterin”, “Delirium” AND “NSE”, “Delirium” AND “Neuron specific enolase”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases”, “Delirium” AND “PI3K”, “Delirium” AND “PCT”, “Delirium” AND “Procalcitonin”, “Delirium” AND “Protein C”, “Delirium” AND “S-100”, “Delirium” AND “S-100beta”, “Delirium” AND “S-100β”, “Delirium” AND “Calcium-binding protein B”, “Delirium” AND “S100 protein”, “Delirium” AND “SDNF”, “Delirium” AND “Mammalian striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Thioredoxin”, “Delirium” AND “TNF-α”, “Delirium” AND “TNF-alpha”, “Delirium” AND “8-iso Prostaglandin F2α”.
no limit [all fields].
Cochrane
“Delirium” AND “Biomarker”, “Delirium” AND “Acetylcholine”, “Delirium” AND “Adenylate kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Myokinase”, “Delirium” AND “Albumin”, “Delirium” AND “Amyloid”, “Delirium” AND “ASAT”, “Delirium” AND “Aspartate transaminase”, “Delirium” AND “Aspartate aminotransferase”, “Delirium” AND “AST”, “Delirium” AND “BDNF”, “Delirium” AND “Brain-derived neurotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Cholezystokinine”, “Delirium” AND “Cholinesterase”, “Delirium” AND “Cortisol”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine phosphokinase”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine kinase BB”, “Delirium” AND “CK-BB”, “Delirium” AND “CREB”, “Delirium” AND “Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein”, “Delirium” AND “CRP”, “Delirium” AND “Dopamine”, “Delirium” AND “Histamine H1”, “Delirium” AND “Heat Shock Protein 70”, “Delirium” AND “IL-2”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-2”, “Delirium” AND “IL-6”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-6”, “Delirium” AND “IL-8”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-8”, “Delirium” AND “IL-18”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-18”, “Delirium” AND “Lactate dehydrogenase”, “Delirium” AND “Leptin”, “Delirium” AND “Neopterin”, “Delirium” AND “NSE”, “Delirium” AND “Neuron specific enolase”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases”, “Delirium” AND “PI3K”, “Delirium” AND “PCT”, “Delirium” AND “Procalcitonin”, “Delirium” AND “Protein C”, “Delirium” AND “S-100”, “Delirium” AND “S-100beta”, “Delirium” AND “S-100β”, “Delirium” AND “Calcium-binding protein B”, “Delirium” AND “S100 protein”, “Delirium” AND “SDNF”, “Delirium” AND “Mammalian striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Thioredoxin”, “Delirium” AND “TNF-α”, “Delirium” AND “TNF-alpha”, “Delirium” AND “8-iso Prostaglandin F2α”.
[full text], [human].
Identical search for: “Acute Brain Dysfunction” AND “XXX”; “Stroke” AND “XXX” AND “Delirium”; “Hemorrhagic Stroke” AND “XXX” AND “Delirium”; “Ischemic Stroke” AND “XXX” AND “Delirium”; “Traumatic Brain Injury” AND “XXX” AND “Delirium”; “Septic Encephalopathy” AND “XXX” AND “Delirium”.
EMBASE/MEDLINE
“Delirium” AND “Biomarker”, “Delirium” AND “Acetylcholine”, “Delirium” AND “Adenylate kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Myokinase”, “Delirium” AND “Albumin”, “Delirium” AND “Amyloid”, “Delirium” AND “ASAT”, “Delirium” AND “Aspartate transaminase”, “Delirium” AND “Aspartate aminotransferase“, “Delirium” AND “AST”, “Delirium” AND “BDNF”, “Delirium” AND “Brain-derived neurotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Cholezystokinine”, “Delirium” AND “Cholinesterase”, “Delirium” AND “Cortisol”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine phosphokinase”, “Delirium” AND “Creatine kinase BB”, “Delirium” AND “CK-BB”, “Delirium” AND “CREB”, “Delirium” AND “Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein”, “Delirium” AND “CRP”, “Delirium” AND “Dopamine”, “Delirium” AND “Histamine H1”, “Delirium” AND “Heat Shock Protein 70”, “Delirium” AND “IL-2”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-2”, “Delirium” AND “IL-6”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-6”, “Delirium” AND “IL-8”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-8”, “Delirium” AND “IL-18”, “Delirium” AND “Interleukin-18”, “Delirium” AND “LDH”, “Delirium” AND “Lactate dehydrogenase”, “Delirium” AND “Leptin”, “Delirium” AND “Neopterin”, “Delirium” AND “NSE”, “Delirium” AND “Neuron specific enolase”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase”, “Delirium” AND “Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases”, “Delirium” AND “PI3K”, “Delirium” AND “PCT”, “Delirium” AND “Procalcitonin”, “Delirium” AND “Protein C”, “Delirium” AND “S-100”, “Delirium” AND “S-100beta”, “Delirium” AND “S-100β”, “Delirium” AND “Calcium-binding protein B”, “Delirium” AND “S100 protein”, “Delirium” AND “SDNF”, “Delirium” AND “Mammalian striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Striatal-derived neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Neuronotrophic factor”, “Delirium” AND “Thioredoxin”, “Delirium” AND “TNF-α”, “Delirium” AND “TNF-alpha”, “Delirium” AND “8-iso Prostaglandin F2α”.
Disease search, “search also as free text in all fields”, “human”, “English”, source “EMBASE” and “Medline”, for publication types “Article”, “Article in press” and “Letter”.
Example: Delirium AND biomarker AND ([article]/lim OR [article in press]/lim OR [letter]/lim) AND [humans]/lim AND [english]/lim AND ([embase]/lim OR [medline]/lim).
Authors’ contributions
AH and MS conceived or designed the work. AH, JT, KT, and SA performed the literature study; AH and KT conducted the literature search; AH and KT collected the data; AH, KT, and MS analyzed and interpreted the data; AH, KT, and MS drafted the manuscript; all authors critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was not funded by any funding agency.
Availability of supporting data
Not applicable.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Martin Siegemund and Alexa Hollinger have contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Katharina Toft, Email: katharina.toft@gmail.com.
Janna Tontsch, Email: janna.tontsch@stud.unibas.ch.
Salim Abdelhamid, Email: salim.abdelhamid@usb.ch.
Luzius Steiner, Email: luzius.steiner@usb.ch.
Martin Siegemund, Email: martin.siegemund@usb.ch.
Alexa Hollinger, Phone: +41-61-265-7254, Email: alexa.hollinger@usb.ch.
References
- 1.Aitken SJ, Blyth FM, Naganathan V. Incidence, prognostic factors and impact of postoperative delirium after major vascular surgery: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Vasc Med. 2017;22(5):387–397. doi: 10.1177/1358863X17721639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McCusker J, Cole MG, Dendukuri N, Belzile E. Does delirium increase hospital stay? J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(11):1539–1546. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bokeriia LA, Golukhova EZ, Polunina AG. Postoperative delirium in cardiac operations: microembolic load is an important factor. The Annals of thoracic surgery. 2009;88(1):349–350. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Holmes J, House A. Psychiatric illness predicts poor outcome after surgery for hip fracture: a prospective cohort study. Psychol Med. 2000;30(4):921–929. doi: 10.1017/s0033291799002548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nightingale S, Holmes J, Mason J, House A. Psychiatric illness and mortality after hip fracture. Lancet. 2001;357(9264):1264–1265. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gonzalez M, Martinez G, Calderon J, Villarroel L, Yuri F, Rojas C, et al. Impact of delirium on short-term mortality in elderly inpatients: a prospective cohort study. Psychosomatics. 2009;50(3):234–238. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.50.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Koster S, Hensens AG, Schuurmans MJ, van der Palen J. Consequences of delirium after cardiac operations. The Annals of thoracic surgery. 2012;93(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marcantonio ER, Flacker JM, Michaels M, Resnick NM. Delirium is independently associated with poor functional recovery after hip fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2000;48(6):618–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2000.tb04718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sessler CN, Gosnell MS, Grap MJ, Brophy GM, O’Neal PV, Keane KA, et al. The Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(10):1338–1344. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2107138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Leslie DL, Marcantonio ER, Zhang Y, Leo-Summers L, Inouye SK. One-year health care costs associated with delirium in the elderly population. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(1):27–32. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2007.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Gelinas C, Needham DM, Slooter AJC, Pandharipande PP, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of pain, agitation/sedation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disruption in adult patients in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(9):e825–e873. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sockalingam S, Parekh N, Bogoch II, Sun J, Mahtani R, Beach C, et al. Delirium in the postoperative cardiac patient: a review. J Card Surg. 2005;20(6):560–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8191.2005.00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hudetz JA, Patterson KM, Iqbal Z, Gandhi SD, Byrne AJ, Hudetz AG, et al. Ketamine attenuates delirium after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2009;23(5):651–657. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2008.12.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chanques G, Ely EW, Garnier O, Perrigault F, Eloi A, Carr J, et al. The 2014 updated version of the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit compared to the 5th version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders and other current methods used by intensivists. Ann Intensive Care. 2018;8(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0377-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Maldonado JR. Delirium in the acute care setting: characteristics, diagnosis and treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4):657–722. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2008.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Neuville M, El-Helali N, Magalhaes E, Radjou A, Smonig R, Soubirou JF, et al. Systematic overdosing of oxa- and cloxacillin in severe infections treated in ICU: risk factors and side effects. Ann Intensive Care. 2017;7(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0255-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang PP, Huang E, Feng X, Bray CA, Perreault MM, Rico P, et al. Opioid-associated iatrogenic withdrawal in critically ill adult patients: a multicenter prospective observational study. Ann Intensive Care. 2017;7(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0310-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hollinger A, Siegemund M, Goettel N, Steiner LA. Postoperative delirium in cardiac surgery: an unavoidable menace? J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2015;29(6):1677–1687. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2014.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Khan BA, Zawahiri M, Campbell NL, Boustani MA. Biomarkers for delirium—a review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(Suppl 2):S256–S261. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Androsova G, Krause R, Winterer G, Schneider R. Biomarkers of postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015;7:112. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Elie M, Cole MG, Primeau FJ, Bellavance F. Delirium risk factors in elderly hospitalized patients. J Gen Intern Med. 1998;13(3):204–212. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1998.00047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stocchetti N, Taccone FS, Citerio G, Pepe PE, Le Roux PD, Oddo M, et al. Neuroprotection in acute brain injury: an up-to-date review. Crit Care. 2015;19:186. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0887-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Larsen KA, Kelly SE, Stern TA, Bode RH, Jr, Price LL, Hunter DJ, et al. Administration of olanzapine to prevent postoperative delirium in elderly joint-replacement patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Psychosomatics. 2010;51(5):409–418. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.51.5.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guo Y, Jia P, Zhang J, Wang X, Jiang H, Jiang W. Prevalence and risk factors of postoperative delirium in elderly hip fracture patients. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(2):317–327. doi: 10.1177/0300060515624936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Capri M, Yani SL, Chattat R, Fortuna D, Bucci L, Lanzarini C, et al. Pre-operative, high-IL-6 blood level is a risk factor of post-operative delirium onset in old patients. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5:173. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee JK, Park YS. Delirium after spinal surgery in Korean population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35(18):1729–1732. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181c423fc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sun L, Jia P, Zhang J, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Jiang H, et al. Production of inflammatory cytokines, cortisol, and Abeta1-40 in elderly oral cancer patients with postoperative delirium. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016;12:2789–2795. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S113077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cerejeira J, Nogueira V, Luis P, Vaz-Serra A, Mukaetova-Ladinska EB. The cholinergic system and inflammation: common pathways in delirium pathophysiology. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(4):669–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Vasunilashorn SM, Ngo LH, Chan NY, Zhou W, Dillon ST, Otu HH, et al. Development of a dynamic multi-protein signature of postoperative delirium. The Journals of Gerontology Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2018;74:261–268. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gly036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Vasunilashorn SM, Dillon ST, Inouye SK, Ngo LH, Fong TG, Jones RN, et al. High C-reactive protein predicts delirium incidence, duration, and feature severity after major noncardiac surgery. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(8):e109–e116. doi: 10.1111/jgs.14913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cizginer S, Marcantonio E, Vasunilashorn S, Pascual-Leone A, Shafi M, Schmitt EM, et al. The cognitive reserve model in the development of delirium: the successful aging after elective surgery study. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2017;30(6):337–345. doi: 10.1177/0891988717732152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Beloosesky Y, Grinblat J, Pirotsky A, Weiss A, Hendel D. Different C-reactive protein kinetics in post-operative hip-fractured geriatric patients with and without complications. Gerontology. 2004;50(4):216–222. doi: 10.1159/000078350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xin X, Xin F, Chen X, Zhang Q, Li Y, Huo S, et al. Hypertonic saline for prevention of delirium in geriatric patients who underwent hip surgery. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0999-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jia Y, Jin G, Guo S, Gu B, Jin Z, Gao X, et al. Fast-track surgery decreases the incidence of postoperative delirium and other complications in elderly patients with colorectal carcinoma. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2014;399(1):77–84. doi: 10.1007/s00423-013-1151-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.van Munster BC, Korevaar JC, Zwinderman AH, Levi M, Wiersinga WJ, De Rooij SE. Time-course of cytokines during delirium in elderly patients with hip fractures. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(9):1704–1709. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.01851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chen XW, Shi JW, Yang PS, Wu ZQ. Preoperative plasma leptin levels predict delirium in elderly patients after hip fracture surgery. Peptides. 2014;57:31–35. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wu XM, Xu WC, Yu YJ, Han L, Zhang J, Yang LJ. Postoperative serum thioredoxin concentrations correlate with delirium and cognitive dysfunction after hip fracture surgery in elderly patients. Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 2017;466:93–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zheng YB, Ruan GM, Fu JX, Su ZL, Cheng P, Lu JZ. Postoperative plasma 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha levels are associated with delirium and cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients after hip fracture surgery. Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry. 2016;455:149–153. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2016.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bakker RC, Osse RJ, Tulen JH, Kappetein AP, Bogers AJ. Preoperative and operative predictors of delirium after cardiac surgery in elderly patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;41(3):544–549. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezr031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chu CS, Liang CK, Chou MY, Lin YT, Hsu CJ, Chu CL, et al. Lack of association between pre-operative insulin-like growth factor-1 and the risk of post-operative delirium in elderly chinese patients. Psychiatry Investig. 2016;13(3):327–332. doi: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee HJ, Hwang DS, Wang SK, Chee IS, Baeg S, Kim JL. Early assessment of delirium in elderly patients after hip surgery. Psychiatry Investig. 2011;8(4):340–347. doi: 10.4306/pi.2011.8.4.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Egberts A, Osse RJ, Fekkes D, Tulen JHM, van der Cammen TJM, Mattace-Raso FUS. Differences in potential biomarkers of delirium between acutely ill medical and elective cardiac surgery patients. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:271–281. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S193605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang DF, Su X, Meng ZT, Cui F, Li HL, Wang DX, et al. Preoperative severe hypoalbuminemia is associated with an increased risk of postoperative delirium in elderly patients: results of a secondary analysis. J Crit Care. 2018;44:45–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.09.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gao F, Zhang Q, Li Y, Tai Y, Xin X, Wang X, et al. Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation for prevention of postoperative delirium in geriatric patients with silent lacunar infarction: a preliminary study. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:2127–2134. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S183698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Slor CJ, Witlox J, Adamis D, Jansen R, Houdijk APJ, van Gool WA, et al. The trajectory of C-reactive protein serum levels in older hip fracture patients with postoperative delirium. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019 doi: 10.1002/gps.5139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Miao S, Shen P, Zhang Q, Wang H, Shen J, Wang G, et al. Neopterin and mini-mental state examination scores, two independent risk factors for postoperative delirium in elderly patients with open abdominal surgery. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(6):1234–1238. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.192764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Plaschke K, Petersen KA, Frankenhauser S, Weigand MA, Kopitz J, Bardenheuer HJ. The impact of plasma cholinergic enzyme activity and other risk factors for the development of delirium in patients receiving palliative care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2016;52(4):525–532. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2016.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Brum C, Stertz L, Borba E, Rumi D, Kapczinski F, Camozzato A. Association of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) with diagnosis of delirium in oncology inpatients. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2015;37(3):197–202. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2014-1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Egberts A, Mattace-Raso FU. Increased neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in delirium: a pilot study. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:1115–1121. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S137182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ritchie CW, Newman TH, Leurent B, Sampson EL. The association between C-reactive protein and delirium in 710 acute elderly hospital admissions. Int Psychogeriatr. 2014;26(5):717–724. doi: 10.1017/S1041610213002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kuswardhani RAT, Sugi YS. Factors related to the severity of delirium in the elderly patients with infection. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2017;3:2333721417739188. doi: 10.1177/2333721417739188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nguyen DN, Huyghens L, Schiettecatte J, Smitz J, Vincent JL. High prolactin levels are associated with more delirium in septic patients. J Crit Care. 2016;33:56–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.12.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.van Munster BC, Zwinderman AH, de Rooij SE. Genetic variations in the interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 genes and the interleukin-6 receptor gene in delirium. Rejuvenation Res. 2011;14(4):425–428. doi: 10.1089/rej.2011.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sanchez JC, Ospina JP, Gonzalez MI. Association between leptin and delirium in elderly inpatients. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013;9:659–666. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S44573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tune LE, Damlouji NF, Holland A, Gardner TJ, Folstein MF, Coyle JT. Association of postoperative delirium with raised serum levels of anticholinergic drugs. Lancet. 1981;2(8248):651–653. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90994-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Inouye SK. Delirium in older persons. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(11):1157–1165. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra052321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Inouye SK, Ferrucci L. Elucidating the pathophysiology of delirium and the interrelationship of delirium and dementia. The journals of gerontology Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences. 2006;61(12):1277–1280. doi: 10.1093/gerona/61.12.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Flukiger J, Hollinger A, Speich B, Meier V, Tontsch J, Zehnder T, et al. Dexmedetomidine in prevention and treatment of postoperative and intensive care unit delirium: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intensive Care. 2018;8(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0437-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Riegger H, Hollinger A, Seifert B, Toft K, Blum A, Zehnder T, et al. Baden Prevention and Reduction of Incidence of Postoperative Delirium Trial (PRIDe): a phase IV multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of ketamine versus haloperidol for prevention of postoperative delirium. Trials. 2018;19(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2498-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hshieh TT, Fong TG, Marcantonio ER, Inouye SK. Cholinergic deficiency hypothesis in delirium: a synthesis of current evidence. The journals of gerontology Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences. 2008;63:764–772. doi: 10.1093/gerona/63.7.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Adamis D, Treloar A, Martin FC, Macdonald AJ. A brief review of the history of delirium as a mental disorder. Hist Psychiatry. 2007;18(72 Pt 4):459–469. doi: 10.1177/0957154X07076467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fong TG, Davis D, Growdon ME, Albuquerque A, Inouye SK. The interface between delirium and dementia in elderly adults. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(8):823–832. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00101-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hughes CG, Pandharipande PP, Thompson JL, Chandrasekhar R, Ware LB, Ely EW, et al. Endothelial activation and blood-brain barrier injury as risk factors for delirium in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(9):e809–e817. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hughes CG, Patel MB, Brummel NE, Thompson JL, McNeil JB, Pandharipande PP, et al. Relationships between markers of neurologic and endothelial injury during critical illness and long-term cognitive impairment and disability. Intensive Care Med. 2018;44(3):345–355. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5120-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ritter C, Tomasi CD, Dal-Pizzol F, Pinto BB, Dyson A, de Miranda AS, et al. Inflammation biomarkers and delirium in critically ill patients. Crit Care. 2014;18(3):R106. doi: 10.1186/cc13887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dittrich T, Tschudin-Sutter S, Widmer AF, Ruegg S, Marsch S, Sutter R. Risk factors for new-onset delirium in patients with bloodstream infections: independent and quantitative effect of catheters and drainages-a four-year cohort study. Ann Intensive Care. 2016;6(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13613-016-0205-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Girard TD, Ware LB, Bernard GR, Pandharipande PP, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Associations of markers of inflammation and coagulation with delirium during critical illness. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(12):1965–1973. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2678-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.van den Boogaard M, Kox M, Quinn KL, van Achterberg T, van der Hoeven JG, Schoonhoven L, et al. Biomarkers associated with delirium in critically ill patients and their relation with long-term subjective cognitive dysfunction; indications for different pathways governing delirium in inflamed and noninflamed patients. Crit Care. 2011;15(6):R297. doi: 10.1186/cc10598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Terms used for biomarker search in alphabetical order.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Overview of biomarkers investigated in this review including references.
Additional file 3: Table S3 Role of inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers in delirium according to literature reports.
Additional file 4: Table S4 Sensitivity and specificity analysis of inflammatory biomarkers and biomarkers of metabolism that could assist in diagnosing delirium and in assessing delirium risk.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.