Abstract
Adaptor proteins contribute to the selection, differentiation and activation of natural killer T (NKT) cells, an innate(-like) lymphocyte population endowed with powerful immunomodulatory properties. Distinct from conventional T lymphocytes NKT cells preferentially home to the liver, undergo a thymic maturation and differentiation process and recognize glycolipid antigens presented by the MHC class I-like molecule CD1d on antigen presenting cells. NKT cells express a semi-invariant T cell receptor (TCR), which combines the Vα14-Jα18 chain with a Vβ2, Vβ7, or Vβ8 chain in mice and the Vα24 chain with the Vβ11 chain in humans. The avidity of interactions between their TCR, the presented glycolipid antigen and CD1d govern the selection and differentiation of NKT cells. Compared to TCR ligation on conventional T cells engagement of the NKT cell TCR delivers substantially stronger signals, which trigger the unique NKT cell developmental program. Furthermore, NKT cells express a panoply of primarily inhibitory NK cell receptors (NKRs) that control their self-reactivity and avoid autoimmune activation. Adaptor proteins influence NKT cell biology through the integration of TCR, NKR and/or SLAM (signaling lymphocyte-activation molecule) receptor signals or the variation of CD1d-restricted antigen presentation. TCR and NKR ligation engage the SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76kDa slp-76 whereas the SLAM associated protein SAP serves as adaptor for the SLAM receptor family. Indeed, the selection and differentiation of NKT cells selectively requires co-stimulation via SLAM receptors. Furthermore, SAP deficiency causes X-linked lymphoproliferative disease with multiple immune defects including a lack of circulating NKT cells. While a deletion of slp-76 leads to a complete loss of all peripheral T cell populations, mutations in the SH2 domain of slp-76 selectively affect NKT cell biology. Furthermore, adaptor proteins influence the expression and trafficking of CD1d in antigen presenting cells and subsequently selection and activation of NKT cells. Adaptor protein complex 3 (AP-3), for example, is required for the efficient presentation of glycolipid antigens which require internalization and processing. Thus, our review will focus on the complex contribution of adaptor proteins to the delivery of TCR, NKR and SLAM receptor signals in the unique biology of NKT cells and CD1d-restricted antigen presentation.
Keywords: NKT cells, CD1d, adaptor proteins, T cell receptor, NK cell receptor, differentiation, polarization
Introduction
Specific and appropriate intercellular interactions or the communication of cells with their environment requires the integration and coordination of multiple signaling pathways. Adaptor proteins contain a series of protein-binding sites that link respective interaction partners to each other and facilitate the generation of larger signaling complexes (1). This is, for example, pivotal for the delivery of signals from the T cell receptor (TCR) which plays a critical role in T cell biology (2).
There exist several T cell populations with distinct functions (3). Alpha beta (αβ) T cells, for example, termed conventional (αβ) T cells, are predominantly part of the adaptive immune system and display a large TCR diversity. TCR ligation by self-peptides embedded in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in the thymus determines the fate of developing conventional T cells. Weak TCR signals perpetuate positive selection whereas strong, agonist, signals support the removal of potentially self-reactive TCRs through negative selection (4). The resulting diverse TCR repertoire endows conventional T cells to respond to foreign antigens in the periphery upon exit from the thymus. NKT cells can be divided into two distinct subpopulations.
In contrast, mucosa-associated semi-invariant T (MAIT) cells, gamma delta (γδ) T cells and natural killer T (NKT) cells express semi-invariant TCRs with limited diversity and react rapidly to conserved self and/or microbial ligands. Most of these cells acquire memory cell features during thymic maturation and exhibit unique patterns of migration into peripheral, frequently non-lymphoid tissues where they become resident, regulate tissue homeostasis and/or fight infection (5). These innate(-like) T lymphocytes display also several other innate-like characteristics and are therefore considered to be mainly part of the innate immune system. Distinct from conventional T cells, innate(-like) lymphocytes recognize higher affinity and avidity antigens through their TCR, which has been suggested to deliver substantially stronger signals (4, 6). Thus, the TCR signal threshold for negative selection is higher. However, it is not completely understood how unconventional T cell precursors escape negative selection despite agonist signaling. Thus, adaptor proteins might play a pivotal role in the tight control of TCR signals as they tie multiple and complex intracellular pathways. Indeed, some adaptor proteins are specifically important for innate(-like) lymphocytes, and a lack of specific adaptor proteins impairs or even selectively inhibits the selection of these frequently autoreactive cell subsets. In detail, we will discuss here the impact of adaptor proteins on the biology of natural killer T (NKT) cells. We will focus thereby on type 1 or invariant NKT cells, which we will refer to as iNKT cells hereinafter.
Natural Killer T (NKT) Cells and CD1d-Mediated Antigen Presentation
Natural killer T (NKT) cells belong to the group of innate(-like) unconventional T cells. They explosively release various cytokines and chemokines upon TCR engagement and thus, exhibit powerful immunomodulatory properties. NKT cells can be divided into two distinct lineages, namely type 1 or invariant NKT cells and type 2 NKT cells. Type 2 NKT cells exhibit a more diverse TCR repertoire. In contrast, type 1 or invariant NKT cells—hereinafter referred to as iNKT cells—express a semi-invariant canonical T cell receptor (TCR), which combines the Vα14-Jα18 chain with the Vbeta2, Vbeta7, or Vbeta8 chain in mice and the Vα24-Jα18 chain with the Vβ11 chain in humans. Simultaneously, they carry a wide range of activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors (NKRs) on their surface (7). The inhibitory NKRs presumably control the self-reactivity of iNKT cells and avoid autoimmune activation (8, 9). Vice versa, the NKT cell TCR shapes the pattern of NKR expression, as exemplified for Ly49 receptors (10). Furthermore, balanced signaling through activating and inhibitory NKRs might influence the developmental program of iNKT cells (11). As NKR signaling engages also adaptor proteins, the propagation of signal transduction through adaptor molecules is in particular critical for diverse ranges of cellular processes in iNKT cells.
In contrast to conventional T cells, iNKT cells respond to glycolipid antigens and home predominantly to the liver (12). Unlike the development of conventional T cell, the selection of iNKT cells requires antigen presentation by double-positive thymocytes rather than thymic epithelial cells (13–17). iNKT cells are selected on high-affinity self-glycolipid ligands presented by the MHC class I-like molecule CD1d (18) which triggers their unique developmental program (19). Their selection uniquely requires co-stimulation via SLAM (signaling lymphocyte-activation molecule) family members and the tyrosine kinase Fyn (20–32) as discussed below. Once selected in stage 0, iNKT cells pass through complex activation, expansion, maturation and differentiation processes, termed stages 1–3 (Figure 1). These include the induction and regulation of promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger PLZF, the iNKT cell lineage transcription factor, multiple rounds of intrathymic cell divisions, the acquisition of a memory phenotype, the activation of cytokine gene loci, and the expression of multiple NKRs over the course of several weeks (7, 33). Although associated with their development (33, 34), PLZF is not unique to iNKT cells and also expressed in innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), mucosa-associated semi-invariant T (MAIT) cells and subsets of γδ T cells (35–37).
Figure 1.
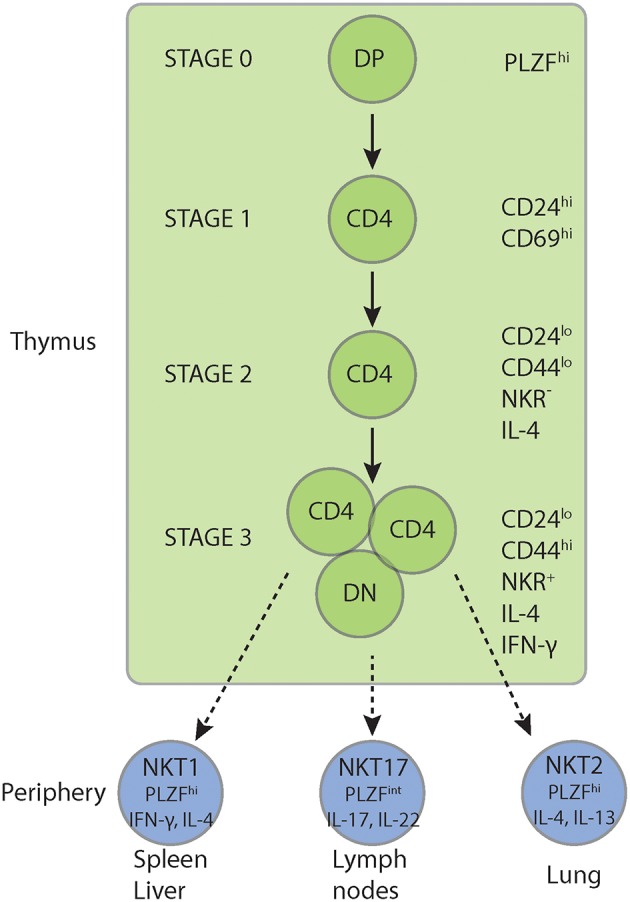
iNKT cell development. iNKT cells express PLZF upon positive selection and undergo a unique intrathymic maturation, expansion, and differentiation program. This includes multiple rounds of intrathymic cell divisions, the acquisition of a memory phenotype, the activation of Th1, Th2 and Th17 cytokine genes and the expression of a panoply of NKRs. Furthermore, iNKT cells branch into three polarized subsets, NKT1, NKT2, and NKT17 cells before egress into the periphery. In the periphery NKT1 cells home preferentially to the spleen and liver while NKT2 and NKT17 cells mainly populate the lung and peripheral lymph nodes, respectively. Although TCR signal strength has been implicated in the polarization of the three iNKT cell sublineages and the regulation of PLZF expression, the intrathymic branching traits and cellular and molecular mechanisms of sublineage diversification are still under investigation. NKR, NK lineage receptors including NK1.1, Ly49, NKG2D, CD94, DX5; PLZF, promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger.
Furthermore, iNKT cells differentiate into three polarized subsets, NKT1, NKT2, and NKT17 cells (38) before egress into the periphery (Figure 1). Although TCR signal strength has been implicated in the polarization of the three iNKT cell sublineages and the regulation of PLZF expression (39), the intrathymic branching traits and cellular and molecular mechanisms of sublineage diversification are still under investigation. TCR-specific signals contribute also to the tissue distribution and phenotypic presentation of iNKT cells (40, 41). Although the signal delivered through the iNKT cell TCR is stronger than for the conventional T cell TCR (6, 42–44), the role of the TCR signal strength in iNKT cell lineage commitment and differentiation is still under investigation.
Next to α/β-TCR+ iNKT cells CD1d-restricted γ/δ T cells also respond to (glycol-)lipid antigens (45). These γ/δ NKT cells express γ1.1 and δ6.3 chains and the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF), the lineage transcription factor of NKT cells. Further comparisons of γ/δ- with α/β-TCR expressing NKT cells revealed also converging patterns of cytokine, gene and cell surface marker expression implying similar differentiation programs in both NKT cell subsets (33, 34, 37, 46–48). Thus, several observations obtained with α/β-TCR+ iNKT cells, might be reflected in the biology of CD1d-restricted γ/δ T cells.
Another feature of iNKT cells distinct from conventional T cells is the recognition of glycolipid antigens presented by CD1d. CD1d molecules are assembled in the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER) as non-covalently linked heterodimers of an isotype-specific heavy chain and β-2-microglobulin (β2m). During its assembly in the ER, CD1d incorporates endogenous lipids and traffics to the plasma membrane. While certain lipids can load onto CD1d directly at the cell surface, CD1d with its hydrophobic binding groove of intermediate size usually has to recycle into late endosomal and lysosomal compartments for efficient antigen exchange and loading (49, 50). Upon trafficking back to the cell surface, antigens are presented by CD1d to NKT cells (51, 52).
Adaptor Proteins in iNKT Cell Biology
Adaptor molecules are multi-domain proteins lacking intrinsic catalytic activity, functioning instead by nucleating molecular complexes during signal transduction (53). Several adaptor proteins influence iNKT cell selection, differentiation and activation, either intrinsically or indirectly through interference with CD1d-mediated antigen presentation. For example, one of the pivotal molecules engaged upon TCR ligation is the intracellular adaptor protein slp-76. While the complete absence of slp-76 (54–56) or of its N-terminal region (57) leads to a lack of all peripheral T cell populations, selective mutations in the SH2 domain of slp-76 affect in particular iNKT cells (58). Most importantly and in strict contrast to conventional T cells, the selection of iNKT cells requires co-stimulation via SLAM (signaling lymphocyte-activation molecule) family members (20–24). Thus, the SLAM-associated adaptor protein (SAP) signaling pathway is selectively required for iNKT cell development. Adaptor proteins, however, can also influence CD1d expression by antigen presenting cells (APCs) and subsequently affect iNKT cell biology in an extrinsic manner. Adaptor protein complex 3 (AP-3), for example, is required for the efficient presentation of glycolipid antigens that require internalization and processing (59).
The slp-76 Family of Adaptor Proteins
The slp-76 family of adaptors includes the SH2 domain-containing leukocyte phosphoprotein of 76 kDa (slp-76), the B cell linker protein (BLNK), and the cytokine-dependent hematopoietic cell linker (Clnk) (53). All three proteins interact with similar but not identical signaling molecules and are critical for the integration of multitudinous signal cascades downstream of immunotyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-bearing receptors and integrins in various hematopoietic cell populations (60). Slp-76 is expressed in T cells, monocytes/macrophages, NK cells, mast cells and platelets (61, 62). BLNK reflects the slp-76 homolog in B cells. It shares about a 33% amino acid identity, but some of its structural domains are similar to those of slp-76 (60, 63, 64). BLNK is primarily responsible for the transmission of signals through the B cell receptor (BCR). CLNK is selectively expressed in various hematopoietic cells following cytokine stimulation (65).
The SH2 Domain-Containing Leukocyte Phosphoprotein of 76 kDa, Slp-76
Of these three family members primarily slp-76 is pivotal for T cell development and TCR signaling (61, 62). Due to impaired signals from the pre-TCR, double negative 3 (DN3) T cells cannot transform into the double negative 4 (DN4) stage (54, 55, 57). Consequently, slp-76−/− mice lack all peripheral mature T cells (57).
The divergent functions of slp-76 are mediated by its distinct signaling domains (Figure 2). The N-terminal acidic domain contains three tyrosine residues (66) which become phosphorylated by the protein tyrosine kinase ZAP-70 upon TCR ligation (67, 68) and subsequently bind the SH2 domains of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav (68–70), the adaptor protein Nck (71, 72) and the Tec-family kinase Itk (73, 74). The deletion of this N-terminal region (57) leads to a lack of all peripheral T cell populations, similar as the complete knockout of slp-76 protein (54, 55, 57). Of these three binding partners in particular Itk affects the development, maturation, cytokine production and survival of NKT cells (75–79). Itk-deficiency affected thereby not only α/β-TCR-, but also γ/δ-TCR-expressing NKT cells which in particular affect the control of Th2 responses and IgE production (80).
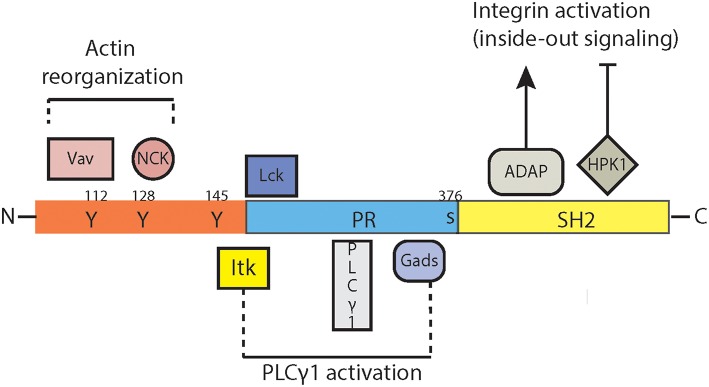
Figure 2.
Signaling domains of slp-76. SLP76 (SRC homology 2 (SH2)-domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa) contains inducibly phosphorylated tyrosines in the amino (N) terminus, a central proline-rich (PR-) domain and a carboxy (C)-terminal SH2 domain. The N-terminal acidic domain binds to the SH2 domains of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav, the adaptor protein Nck and the Tec-family kinase Itk. The subsequent signaling pathways influence predominantly the reorganization of actin. This domain of slp-76 interacts also with the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3K) which interfere with multiple cellular functions such as proliferation, differentiation and survival. The central proline-rich domain of slp-76 interacts with the phospholipase PLCγ-1 and the adaptor molecule GADS (Grb2-related adaptor downstream of Shc). The C-terminal SH2 domain of slp-76 binds to the serine-threonine kinase HPK-1 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1) and to the adhesion and degranulation-promoting adaptor protein (ADAP), two molecule associated with the formation of the immunological synapse, integrin activation/expression and inside-out and outside-in signaling cascades. ADAP, adhesion- and degranulation-promoting adaptor protein; GADS, GRB2-related adaptor protein; GRB2, growth-factor-receptor-bound protein 2; HPK1, hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1; ITK, interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase; Lck, lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; NCK, non-catalytic region of tyrosine kinase; PLCγ1, phospholipase Cgamma1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PR, proline-rich; Vav, guanine nucleotide exchange factor.
The central proline-rich domain of slp-76 interacts with the phospholipase PLCγ-1 (81) and the adaptor molecule GADS (Grb2-related adaptor downstream of Shc) (82). For none of these two molecules a role in NKT cell biology has been established so far.
The C-terminal SH2 domain of slp-76 binds to the serine-threonine kinase HPK-1 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1) (83) and to the adhesion and degranulation-promoting adaptor protein (ADAP) (84, 85). ADAP is required for thymocyte selection and TCR-mediated integrin activation (86–88). Thus, slp-76 interferes with inside-out and outside-in signaling cascades and integrin-expression (89) due to its multipoint binding with ADAP (90).
A missense mutation within the SH2-domain of slp-76 led to an accumulation of iNKT cells in the thymus and in peripheral lymph nodes. In contrast, iNKT cells were selectively reduced in the spleens and livers of mice with the same mutation, along with a reduced cytokine response, decreased levels of ADAP protein and altered integrin and NKR expression patterns (58). Although TCR signals were affected by these mutations, NKRs might contribute to the observed phenotype as this mutation affected also synapse formation and elimination of missing-self targets by natural killer (NK) cells (91). In this context, it is important to note that the tyrosine protein phosphatase SHP-1 dephosphorylates its direct substrate slp-76 (92), which reflects an important mechanism for the negative regulation of immune cell activation by inhibitory NKRs. Further studies need to delineate the mechanisms underlying the altered pattern of NKR expression in mice with this slp-76 mutation and the role of TCR signals in these processes. In addition, the specificity of this mutation for iNKT cells needs to be characterized in further detail by assessing the alterations in subsequent signaling pathways and by screening additional slp-76 mutations. Interestingly, despite exhibiting an NKR distribution that has been associated with enhanced Th1 polarization (7, 38), a simultaneous reduction of both IL-4- and IFN-γ-expression along with a reduced TCR-reactivity was observed in iNKT cells carrying this missense mutation within the SH2-domain of slp-76 (58). Thus, variations in the tissue distribution rather than the cytokine polarization are to be considered in patients with allelic mutations in TCR signaling molecules before pursuing vaccination strategies involving α-GalCer, the prototypical iNKT cell ligand as an adjuvant.
The Cytokine-Dependent Hematopoietic Cell Linker (clnk)
Next to cytokine driven expression clnk plays a role in Fc-epsilon R1-mediated mast cell degranulation, B cell receptor (BCR) and TCR signaling (60, 65). While not found in resting T cells, clnk is abundantly expressed in previously activated T cells (65). Similar to slp-76, clnk consists of a tyrosine- and proline-rich amino-terminal basic domain, an SH2 domain and a carboxy-terminal tail (60). While the SH2 domains of slp-76 and clnk exhibit the highest degree of homology within their SH2 domains the sequence variations outside this region suggest that clnk might not be phosphorylated by ZAP-70 and does not associate with Vav, Nck, or GADS. Clnk can rescue TCR signals in slp-76-deficient T cells (65), but clnk itself is dispensable for T cell function and differentiation (93). Clnk might contribute to the coordination of antigen-receptor signaling and cytokine stimulation. Interestingly, clnk might mediate diverse or even opposite signals by TCRs and NKRs as it promotes iNKT cell responses, but impairs NK cell function (94). Thus, clnk might function as a molecular switch, which controls diverse immune responses in different cell populations.
Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule (SLAM) and Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule-Associated Protein (SAP)
The signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family of cell surface receptors comprises six members named 2B4 (CD244), Ly9 (CD229), CRACCSLAM (CD150), CD84, and Ly108 (95, 96) which are exclusively expressed on hematopoietic cells. They represent homophilic receptors with the exception of 2B4, which recognizes CD48. SLAM family receptors possess an extracellular segment with two or four immunoglobulin-like domains responsible for ligand recognition, a single transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic domain. This cytoplasmic domain bears one to three inhibitory or activating immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motifs (ITSMs) (97).
Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM)-associated proteins (SAPs) are adaptor molecules which contain Src homology 2 (SH2) domains. SAPs are expressed in T cells, NK cells, and iNKT cells. The SAP family of adaptors includes three members most commonly known as SAP (also named SH2D1A), Ewing's sarcoma-associated transcript-2 (EAT-2; also named SH2D1B1) and EAT-2-related transducer (ERT; also named SH2D1B2) (98). Mutations in the SAP (SH2D1A) gene located on chromosome X are responsible for X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (XLP), characterized by higher susceptibility to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, B cell lymphomas, severe immune dysregulation, a nearly complete loss of iNKT cells and an impaired humoral immunity (22, 23, 99–102). The correlation of an augmented susceptibility to EBV infections with the lack of iNKT cells together with the observation that the SLAM family receptor 2B4 exhibits defect signaling function in SAP-deficiency (103–105) suggest a key role for iNKT cells and SLAM family receptors in the immune response to EBV.
SAP family adaptor proteins respond through their SH2 domains to the cytoplasmic domains of SLAM family receptors by recruiting and activating the downstream tyrosine kinase Fyn (Figure 3) (106). However, SLAM family receptors can also signal through other SH2 domain–containing molecules such as the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 or the SH2 domain inositol phosphatase 1 (SHIP-1), particularly in SAP deficiency (25, 97, 101, 107–111). While SAP-dependent SLAM family receptor signaling is pivotal for the selection of iNKT cells, these receptors inhibit SAP-independently follicular helper T cells and humoral immune responses (25).
Figure 3.
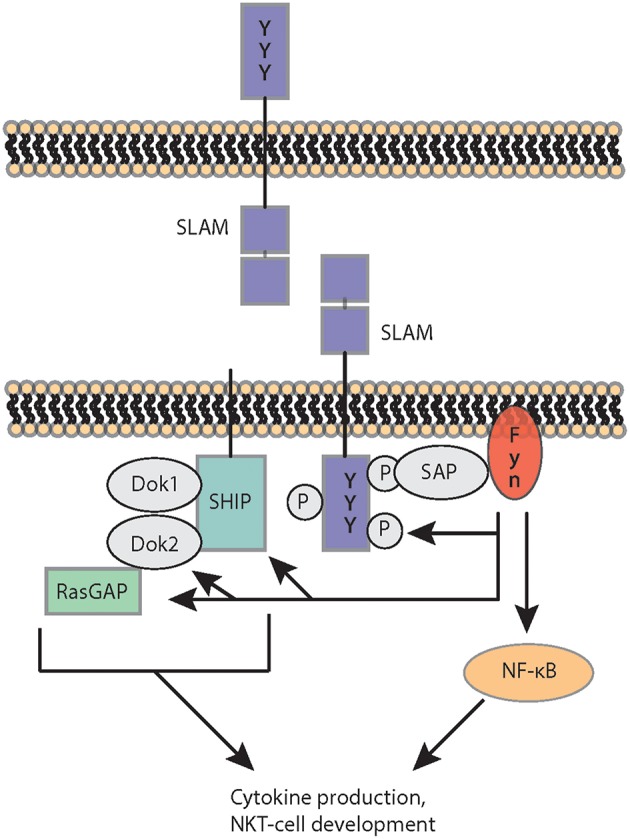
SLAM receptor signaling. SLAM receptor ligation recruits and activates via SAP the protein tyrosine kinase FYN, which phosphorylates SLAM and subsequently generates docking sites for SRC homology 2 (SH2)-domain-containing downstream adaptor proteins and enzymes. SLAM engagement also cooperates with TCR-mediated signals leading to nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, cytokine production and NKT cell development. DOK1 and 2, docking proteins 1 and 2; RasGAP, RAS–GTPase-activating protein; SAP, Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM)-associated proteins; SLAM, signaling lymphocytic activation molecule; SHIP, SH2-domain-containing inositol−5′ phosphatase.
iNKT cells are known to use unique signaling pathways (26). Fyn, for example, is required for iNKT cell development, but not for the differentiation of conventional T lymphocytes or NK cells (20, 21). The loss of SAP resulted in a complete absence of iNKT cells from both mice and humans. SAP-transmitted signaling events were uniquely required for the development of iNKT cells, as conventional T cells and NK cells developed normally in the absence of SAP (22, 23). The selection of iNKT cells also strictly requires co-stimulation via SLAM (signaling lymphocyte-activation molecule) family members (20–24). Homotypic interactions involving the SLAM family receptors 1 and 6 are required for iNKT cell differentiation (24). While SAP deficiency blocks positive selection at stage 0, the most immature stage of iNKT cell development (22, 23), mice lacking SLAM receptors exhibit less pronounced iNKT cell defects that appear to spare stage 0 iNKT cells (24, 25). Indeed, unlike SAP, SLAM family receptors promoted iNKT cell development and intrathymic maturation due to the restriction of TCR signal strength following positive selection and the limitation of activation induced cell death (27). This process involves the adaptor SAP-kinase Fyn complex and the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1. Thus, this study uncovers important differences in SAP and SLAM signaling and highlights the complex processes underlying iNKT cell maturation and survival (112) as auto-reactive iNKT cell activation during thymic selection is thought to induce a substantially stronger TCR stimulus in comparison to that during the development of conventional T cells (6, 113). As a consequence the expression of the transcription factors Egr1 and Egr2 is strongly increased (113), which in turn directly induce PLZF, the key transcription factor controlling iNKT cell differentiation, migration, and functions (113). SAP regulates also cytokine production, expression of transcription factors, the polarization of iNKT cells favoring the development of NKT2 cells and the formation of the immunologic synapse (28, 114, 115). Furthermore, SAP expression in iNKT cells promotes cognate help to B cells (116, 117). Thus, the SLAM-associated adaptor protein (SAP) signaling pathway is selectively required for iNKT cell development and the loss of iNKT cells has been suggested to contribute to the genesis of the lethal immunodeficiency syndrome. The need for SAP-mediated signals may reflect the unique requirements for the positive selection of iNKT cells in the thymus. However, several questions remain unresolved. For example, the role of individual SLAM family receptors in cytokine polarization and iNKT cell differentiation needs to be characterized in more detail as well as the impact of subsequent signaling cascades and their interference with NKRs and TCRs. In addition, it is still unknown, whether and how TCR and SLAM family receptors interfere on a cellular and molecular level and why this is specific for iNKT cells.
Adaptor Protein-3 (AP-3)
The hetero-tetrameric AP (adaptor protein) complexes are involved in the sorting of cargo proteins into transport vesicles that traffic between the different organelles of the cell. They are known to bind to the tyrosine or dileucine-containing sequence motifs in transmembrane proteins in order to direct their selective localization to subsets of endosomal and lysosomal compartments (118, 119). Five members, AP-1 to AP-5 and their isoforms have been characterized in this family of cytosolic complexes (118–120). In contrast to AP-4 and-5, AP-1,-2, and-3 are clathrin-associated complexes (121). AP-1 and AP-2 direct proteins from the trans-Golgi network to endosomes and recycling compartments, respectively (122, 123). AP-3 localizes membrane proteins to lysosomes, platelet-dense granules, and melanosomes (124). AP-3-deficient mice as well as Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2 (HPS-2) patients with mutations in the AP-3 gene exhibited hypopigmentation and platelet dysfunction (125–129). AP-4 mediates vesicle trafficking from the trans-Golgi network to endosomes or the basolateral plasma membrane. The function of AP-5 localized in late endosomes is largely unknown (121). To date, there have been no interactions between AP-1, AP4, and AP-5 with CD1d described. However, CD1d directly interacts with AP-2, which targets the endosomal compartment, and AP-3, which targets the lysosomal compartment (59, 130). Indeed, AP-2 restrains iNKT cell activation due to the regulation of CD1d internalization (131), and a connection of AP-2 with autophagy as a regulator of iNKT cell activation, development and survival is currently under investigation. In this context, a deletion of the essential autophagy gene Atg7 abrogated thymic iNKT cell development and peripheral iNKT cell functions in a cell-intrinsic manner (132, 133). Unexpectedly, however, Atg7-deficient thymocytes and bone marrow-derived DCs exhibited no defect in the presentation of glycolipid antigens, implying distinct differences in the mechanisms how AP-2 and autophagy genes affect iNKT cell development and activation that need to be dissected in the future.
In contrast, numerous studies have investigated the interaction of AP-3 and CD1d. Since CD1d recycles between the cell membrane and the lysosome back and forth, AP-3 interferes with glycolipid metabolism and CD1d-mediated (glyco-)lipid antigen presentation (134). Indeed, it was shown that AP-3 is required for the efficient presentation of glycolipid antigens that require internalization and processing (59, 135). AP-3 interacts with CD1d, but does not affect MHC II presentation (59, 135–137). Cells from AP-3-deficient mice show increased cell surface expression of CD1d but decreased expression in late endosomes. Consequently, AP-3-deficient splenocytes present glycolipids to iNKT cells less efficiently. Furthermore, AP-3–deficient mice exhibit significantly reduced iNKT cell numbers. The simultaneous analysis of CD1d mutants with alterations in the cytoplasmic tail to AP-3-knockout mice proved also that CD1d molecules in lysosomes are functional in antigen presentation (59, 130). iNKT cell numbers are reduced in patients with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2 (HPS-2) (138) and iNKT cell defects have been also associated with the susceptibility to infections and lymphoma in patients with this homozygous genomic AP-3 deletion (139). Thus, in summary these studies showed that the localization of CD1d to late endosomes or lysosomes is required for both (glycol-)lipid antigen presentation and the subsequent development of iNKT cells. These reports also demonstrated that different pathways mediate the intracellular trafficking of MHC II and CD1 molecules, which both scavenge late endosomes or lysosomes.
Conclusion
Adaptor proteins play a pivotal role in the biology of CD1d-restricted iNKT cells. SAP transfers SLAM receptor signals, propagates the thymic selection of iNKT cells and induces the iNKT cell effector program (33). The SH2 domain of slp-76 influences the tissue distribution and phenotype of iNKT cells in the periphery (58). AP-3 interferes with the presentation of glycolipid antigens by CD1d (59). Thus, these three adaptor proteins engage unique functions in iNKT cells biology distinct from conventional T lymphocytes. Particularly the expression of SAP and slp-76 in iNKT cells raises the question whether these two molecules interact (Figure 4). As SLAM receptors, NKRs and TCRs share adaptor proteins for signal transmission (140, 141), it will be interesting to define the contribution of the respective receptors to the observed phenotypes. Another interesting candidate to investigate in this context is the protein tyrosine kinase SHP-1 since it also interferes with all three receptor classes (111, 116, 142–144) and localizes with slp-76 and fyn in lipid rafts (145–147), even though evidence of physical interactions of these three molecules in iNKT cells is missing. As the strength of the TCR signals influences the polarization of iNKT cell subsets (39), the role of adaptor proteins in fine-tuning intracellular signal transduction is to characterize. In addition, as SLAM receptors are pivotal for the induction of the iNKT cell lineage transcription factor PLZF (33) and PLZF expression negatively correlates with the glycolytic potential of iNKT cells (148) potential connections between adaptor proteins and iNKT cell metabolism need to be identified.
Figure 4.
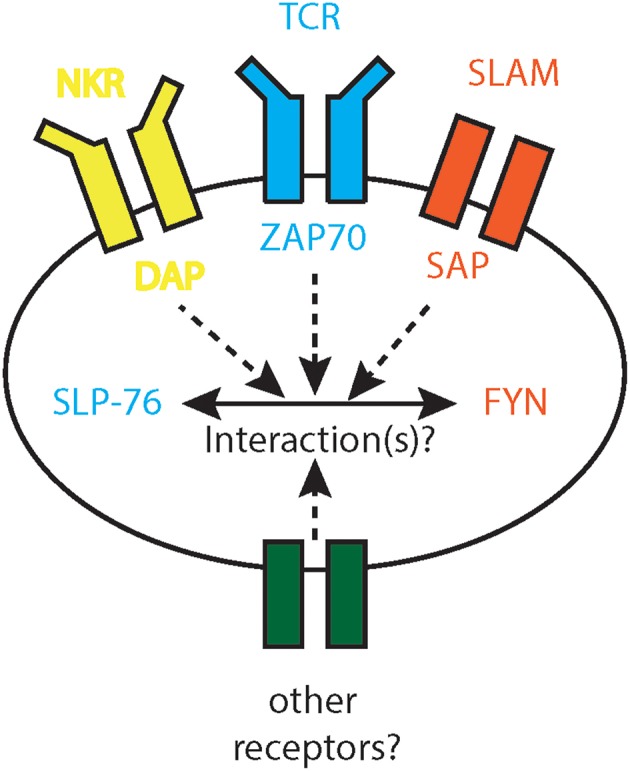
Interactions of SAP and slp-76. SLAM receptor signaling cooperates with TCR and NKR signals. While TCR and NKR signal through slp-76, SLAM receptors utilize SAP and Fyn. It is unknown to date whether slp-76 and SAP interact, whether these three receptor classes combine slp-76 and SAP signals and whether other receptors share similar signaling pathways. DAP, DNAX activation adaptor protein; Fyn, SRC family tyrosine kinase; NKR, NK cell receptor; SAP, Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM)-associated proteins; SLAM, signaling lymphocytic activation molecule; slp-76, SRC homology 2 (SH2)-domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa; TCR, T cell receptor; ZAP-70, zeta-chain associated protein kinase 70.
Author Contributions
EG prepared the figures and added comments to the manuscript. JM wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the present members of our lab for their support and their contributions.
Footnotes
Funding. This study was supported by the Staedtler Stiftung (to JM), the German Research Foundation DFG (grant MA 2621/4-1 to JM and DFG-CRC1181—project number C04 to JM).
References
- 1.Flynn DC. Adaptor proteins. Oncogene. (2001) 20:6270–2. 10.1038/sj.onc.1204769 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Peterson EJ, Clements JL, Fang N, Koretzky GA. Adaptor proteins in lymphocyte antigen-receptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol. (1998) 10:337–44. 10.1016/S0952-7915(98)80173-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Edholm ES, Banach M, Robert J. Evolution of innate-like T cells and their selection by MHC class I-like molecules. Immunogenetics. (2016) 68:525–36. 10.1007/s00251-016-0929-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moran AE, Hogquist KA. T-cell receptor affinity in thymic development. Immunology. (2012) 135:261–7. 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03547.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Legoux F, Salou M, Lantz O. Unconventional or preset alphabeta T cells: evolutionarily conserved tissue-resident T cells recognizing nonpeptidic ligands. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2017) 33:511–35. 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100616-060725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moran AE, Holzapfel KL, Xing Y, Cunningham NR, Maltzman JS, Punt J, et al. T cell receptor signal strength in Treg and iNKT cell development demonstrated by a novel fluorescent reporter mouse. J Exp Med. (2011) 208:1279–89. 10.1084/jem.20110308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2007) 25:297–336. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bendelac A, Bonneville M, Kearney JF. Autoreactivity by design: innate B and T lymphocytes. Nat Rev Immunol. (2001) 1:177–86. 10.1038/35105052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kronenberg M, Rudensky A. Regulation of immunity by self-reactive T cells. Nature. (2005) 435:598–604. 10.1038/nature03725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Skold M, Stenstrom M, Sidobre S, Hoglund P, Kronenberg M, Cardell S. MHC-dependent and -independent modulation of endogenous Ly49 receptors on NK1.1+ T lymphocytes directed by T-cell receptor type. Immunology. (2003) 110:313–21. 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01741.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Voyle RB, Beermann F, Lees RK, Schumann J, Zimmer J, Held W, et al. Ligand-dependent inhibition of CD1d-restricted NKT cell development in mice transgenic for the activating receptor Ly49D. J Exp Med. (2003) 197:919–25. 10.1084/jem.20021615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mattner J. Natural killer T (NKT) cells in autoimmune hepatitis. Curr Opin Immunol. (2013) 25:697–703. 10.1016/j.coi.2013.09.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bix M, Coles M, Raulet D. Positive selection of V beta 8+ CD4-8- thymocytes by class I molecules expressed by hematopoietic cells. J Exp Med. (1993) 178:901–8. 10.1084/jem.178.3.901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bendelac A, Killeen N, Littman DR, Schwartz RH. A subset of CD4+ thymocytes selected by MHC class I molecules. Science. (1994) 263:1774–8. 10.1126/science.7907820 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ohteki T, MacDonald HR. Major histocompatibility complex class I related molecules control the development of CD4+8- and CD4-8- subsets of natural killer 1.1+ T cell receptor-alpha/beta+ cells in the liver of mice. J Exp Med. (1994) 180:699–704. 10.1084/jem.180.2.699 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bendelac A. Positive selection of mouse NK1+ T cells by CD1-expressing cortical thymocytes. J Exp Med. (1995) 182:2091–6. 10.1084/jem.182.6.2091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Coles MC, Raulet DH. NK1.1+ T cells in the liver arise in the thymus and are selected by interactions with class I molecules on CD4+CD8+ cells. J Immunol. (2000) 164:2412–8. 10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2412 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gapin L, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J. Natural Killer T cell obsession with self-antigens. Curr Opin Immunol. (2013) 25:168–73. 10.1016/j.coi.2013.01.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Constantinides MG, Bendelac A. Transcriptional regulation of the NKT cell lineage. Curr Opin Immunol. (2013) 25:161–7. 10.1016/j.coi.2013.01.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Eberl G, Lowin-Kropf B, MacDonald HR. Cutting edge: NKT cell development is selectively impaired in Fyn- deficient mice. J Immunol. (1999) 163:4091–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gadue P, Morton N, Stein PL. The Src family tyrosine kinase Fyn regulates natural killer T cell development. J Exp Med. (1999) 190:1189–96. 10.1084/jem.190.8.1189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nichols KE, Hom J, Gong SY, Ganguly A, Ma CS, Cannons JL, et al. Regulation of NKT cell development by SAP, the protein defective in XLP. Nat Med. (2005) 11:340–5. 10.1038/nm1189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pasquier B, Yin L, Fondaneche MC, Relouzat F, Bloch-Queyrat C, Lambert N, et al. Defective NKT cell development in mice and humans lacking the adapter SAP, the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome gene product. J Exp Med. (2005) 201:695–701. 10.1084/jem.20042432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Griewank K, Borowski C, Rietdijk S, Wang N, Julien A, Wei DG, et al. Homotypic interactions mediated by Slamf1 and Slamf6 receptors control NKT cell lineage development. Immunity. (2007) 27:751–62. 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen S, Cai C, Li Z, Liu G, Wang Y, Blonska M, et al. Dissection of SAP-dependent and SAP-independent SLAM family signaling in NKT cell development and humoral immunity. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:475–89. 10.1084/jem.20161312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kronenberg M, Gapin L. The unconventional lifestyle of NKT cells. Nat Rev Immunol. (2002) 2:557–68. 10.1038/nri854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lu Y, Zhong MC, Qian J, Calderon V, Cruz Tleugabulova M, Mallevaey T, et al. SLAM receptors foster iNKT cell development by reducing TCR signal strength after positive selection. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:447–57. 10.1038/s41590-019-0334-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Michel ML, Lenoir C, Massot B, Diem S, Pasquier B, Sawa S, et al. SLAM-associated protein favors the development of iNKT2 over iNKT17 cells. Eur J Immunol. (2016) 46:2162–74. 10.1002/eji.201646313 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.De Calisto J, Wang N, Wang G, Yigit B, Engel P, Terhorst C. SAP-dependent and -independent regulation of innate T cell development involving SLAMF receptors. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:186. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huang B, Gomez-Rodriguez J, Preite S, Garrett LJ, Harper UL, Schwartzberg PL. CRISPR-mediated triple knockout of SLAMF1, SLAMF5 and SLAMF6 supports positive signaling roles in NKT cell development. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0156072. 10.1371/journal.pone.0156072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Baglaenko Y, Cruz Tleugabulova M, Gracey E, Talaei N, Manion KP, Chang NH, et al. Invariant NKT cell activation is potentiated by homotypic trans-Ly108 interactions. J Immunol. (2017) 198:3949–62. 10.4049/jimmunol.1601369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cuenca M, Punet-Ortiz J, Ruart M, Terhorst C, Engel P. Ly9 (SLAMF3) receptor differentially regulates iNKT cell development and activation in mice. Eur J Immunol. (2018) 48:99–105. 10.1002/eji.201746925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Savage AK, Constantinides MG, Han J, Picard D, Martin E, Li B, et al. The transcription factor PLZF directs the effector program of the NKT cell lineage. Immunity. (2008) 29:391–403. 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.07.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kovalovsky D, Uche OU, Eladad S, Hobbs RM, Yi W, Alonzo E, et al. The BTB-zinc finger transcriptional regulator PLZF controls the development of invariant natural killer T cell effector functions. Nat Immunol. (2008) 9:1055–64. 10.1038/ni.1641 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Constantinides MG, McDonald BD, Verhoef PA, Bendelac A. A committed precursor to innate lymphoid cells. Nature. (2014) 508:397–401. 10.1038/nature13047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Koay HF, Gherardin NA, Enders A, Loh L, Mackay LK, Almeida CF, et al. A three-stage intrathymic development pathway for the mucosal-associated invariant T cell lineage. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:1300–11. 10.1038/ni.3565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kreslavsky T, Savage AK, Hobbs R, Gounari F, Bronson R, Pereira P, et al. TCR-inducible PLZF transcription factor required for innate phenotype of a subset of gammadelta T cells with restricted TCR diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2009) 106:12453–8. 10.1073/pnas.0903895106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lee YJ, Holzapfel KL, Zhu J, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Steady-state production of IL-4 modulates immunity in mouse strains and is determined by lineage diversity of iNKT cells. Nat Immunol. (2013) 14:1146–54. 10.1038/ni.2731 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tuttle KD, Krovi SH, Zhang J, Bedel R, Harmacek L, Peterson LK, et al. TCR signal strength controls thymic differentiation of iNKT cell subsets. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:2650. 10.1038/s41467-018-05026-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Subleski JJ, Hall VL, Wolfe TB, Scarzello AJ, Weiss JM, Chan T, et al. TCR-dependent and -independent activation underlie liver-specific regulation of NKT cells. J Immunol. (2011) 186:838–47. 10.4049/jimmunol.1001735 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee YJ, Wang H, Starrett GJ, Phuong V, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Tissue-specific distribution of iNKT cells impacts their cytokine response. Immunity. (2015) 43:566–78. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Stritesky GL, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Selection of self-reactive T cells in the thymus. Annu Rev Immunol. (2012) 30:95–114. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hogquist KA, Jameson SC. The self-obsession of T cells: how TCR signaling thresholds affect fate ‘decisions’ and effector function. Nat Immunol. (2014) 15:815–23. 10.1038/ni.2938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gapin L. Development of invariant natural killer T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. (2016) 39:68–74. 10.1016/j.coi.2016.01.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Luoma AM, Castro CD, Adams EJ. gammadelta T cell surveillance via CD1 molecules. Trends Immunol. (2014) 35:613–21. 10.1016/j.it.2014.09.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Alonzo ES, Gottschalk RA, Das J, Egawa T, Hobbs RM, Pandolfi PP, et al. Development of promyelocytic zinc finger and ThPOK-expressing innate gamma delta T cells is controlled by strength of TCR signaling and Id3. J Immunol. (2010) 184:1268–79. 10.4049/jimmunol.0903218 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Verykokakis M, Boos MD, Bendelac A, Adams EJ, Pereira P, Kee BL. Inhibitor of DNA binding 3 limits development of murine slam-associated adaptor protein-dependent “innate” gammadelta T cells. PLoS ONE. (2010) 5:e9303. 10.1371/journal.pone.0009303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Narayan K, Sylvia KE, Malhotra N, Yin CC, Martens G, Vallerskog T, et al. Immunological genome project, intrathymic programming of effector fates in three molecularly distinct gammadelta T cell subtypes. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13:511–8. 10.1038/ni.2247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Koch M, Stronge VS, Shepherd D, Gadola SD, Mathew B, Ritter G, et al. The crystal structure of human CD1d with and without alpha-galactosylceramide. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:819–26. 10.1038/ni1225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zajonc DM, Cantu C, III, Mattner J, Zhou D, Savage PB, Bendelac A, et al. Structure and function of a potent agonist for the semi-invariant natural killer T cell receptor. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:810–8. 10.1038/ni1224 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hava DL, Brigl M, van den Elzen P, Zajonc DM, Wilson IA, Brenner MB. CD1 assembly and the formation of CD1-antigen complexes. Curr Opin Immunol. (2005) 17:88–94. 10.1016/j.coi.2004.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Girardi E, Zajonc DM. Molecular basis of lipid antigen presentation by CD1d and recognition by natural killer T cells. Immunol Rev. (2012) 250:167–79. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01166.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wu JN, Koretzky GA. The SLP-76 family of adapter proteins. Semin Immunol. (2004) 16:379–93. 10.1016/j.smim.2004.08.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Clements JL, Yang B, Ross-Barta SE, Eliason SL, Hrstka RF, Williamson RA, et al. Requirement for the leukocyte-specific adapter protein SLP-76 for normal T cell development. Science. (1998) 281:416–9. 10.1126/science.281.5375.416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Pivniouk V, Tsitsikov E, Swinton P, Rathbun G, Alt FW, Geha RS. Impaired viability and profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking the adaptor protein SLP-76. Cell. (1998) 94:229–38. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81422-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yablonski D, Kuhne MR, Kadlecek T, Weiss A. Uncoupling of nonreceptor tyrosine kinases from PLC-gamma1 in an SLP-76-deficient T cell. Science. (1998) 281:413–6. 10.1126/science.281.5375.413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jordan MS, Smith JE, Burns JC, Austin JE, Nichols KE, Aschenbrenner AC, et al. Complementation in trans of altered thymocyte development in mice expressing mutant forms of the adaptor molecule SLP76. Immunity. (2008) 28:359–69. 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.01.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Danzer C, Koller A, Baier J, Arnold H, Giessler C, Opoka R, et al. A mutation within the SH2 domain of slp-76 regulates the tissue distribution and cytokine production of iNKT cells in mice. Eur J Immunol. (2016) 46:2121–36. 10.1002/eji.201646331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Elewaut D, Lawton AP, Nagarajan NA, Maverakis E, Khurana A, Honing S, et al. The adaptor protein AP-3 is required for CD1d-mediated antigen presentation of glycosphingolipids and development of Valpha14i NKT cells. J Exp Med. (2003) 198:1133–46. 10.1084/jem.20030143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Myung PS, Boerthe NJ, Koretzky GA. Adapter proteins in lymphocyte antigen-receptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol. (2000) 12:256–66. 10.1016/S0952-7915(00)00085-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jackman JK, Motto DG, Sun Q, Tanemoto M, Turck CW, Peltz GA, et al. Molecular cloning of SLP-76, a 76-kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein associated with Grb2 in T cells. J Biol Chem. (1995) 270:7029–32. 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Clements JL, Ross-Barta SE, Tygrett LT, Waldschmidt TJ, Koretzky GA. SLP-76 expression is restricted to hemopoietic cells of monocyte, granulocyte, and T lymphocyte lineage and is regulated during T cell maturation and activation. J Immunol. (1998) 161:3880–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fu C, Turck CW, Kurosaki T, Chan AC. BLNK: a central linker protein in B cell activation. Immunity. (1998) 9:93–103. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80591-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Goitsuka R, Fujimura Y, Mamada H, Umeda A, Morimura T, Uetsuka K, et al. BASH, a novel signaling molecule preferentially expressed in B cells of the bursa of Fabricius. J Immunol. (1998) 161:5804–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cao MY, Davidson D, Yu J, Latour S, Veillette A. Clnk, a novel SLP-76-related adaptor molecule expressed in cytokine-stimulated hemopoietic cells. J Exp Med. (1999) 190:1527–34. 10.1084/jem.190.10.1527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Motto DG, Ross SE, Wu J, Hendricks-Taylor LR, Koretzky GA. Implication of the GRB2-associated phosphoprotein SLP-76 in T cell receptor-mediated interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med. (1996) 183:1937–43. 10.1084/jem.183.4.1937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bubeck Wardenburg J, Fu C, Jackman JK, Flotow H, Wilkinson SE, Williams DH, et al. Phosphorylation of SLP-76 by the ZAP-70 protein-tyrosine kinase is required for T-cell receptor function. J Biol Chem. (1996) 271:19641–4. 10.1074/jbc.271.33.19641 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Raab M, da Silva AJ, Findell PR, Rudd CE. Regulation of Vav-SLP-76 binding by ZAP-70 and its relevance to TCR zeta/CD3 induction of interleukin-2. Immunity. (1997) 6:155–64. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80422-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tuosto L, Michel F, Acuto O. p95vav associates with tyrosine-phosphorylated SLP-76 in antigen-stimulated T cells. J Exp Med. (1996) 184:1161–6. 10.1084/jem.184.3.1161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wu J, Motto DG, Koretzky GA, Weiss A. Vav and SLP-76 interact and functionally cooperate in IL-2 gene activation. Immunity. (1996) 4:593–602. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80485-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bubeck Wardenburg J, Pappu R, Bu JY, Mayer B, Chernoff J, Straus D, et al. Regulation of PAK activation and the T cell cytoskeleton by the linker protein SLP-76. Immunity. (1998) 9:607–16. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80658-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wunderlich L, Farago A, Downward J, Buday L. Association of Nck with tyrosine-phosphorylated SLP-76 in activated T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. (1999) 29:1068–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Su YW, Zhang Y, Schweikert J, Koretzky GA, Reth M, Wienands J. Interaction of SLP adaptors with the SH2 domain of Tec family kinases. Eur J Immunol. (1999) 29:3702–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bunnell SC, Diehn M, Yaffe MB, Findell PR, Cantley LC, Berg LJ. Biochemical interactions integrating Itk with the T cell receptor-initiated signaling cascade. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:2219–30. 10.1074/jbc.275.3.2219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Au-Yeung BB, Fowell DJ. A key role for Itk in both IFN gamma and IL-4 production by NKT cells. J Immunol. (2007) 179:111–9. 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Felices M, Berg LJ. The Tec kinases Itk and Rlk regulate NKT cell maturation, cytokine production, and survival. J Immunol. (2008) 180:3007–18. 10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.3007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Qi Q, Huang W, Bai Y, Balmus G, Weiss RS, August A. A unique role for ITK in survival of invariant NKT cells associated with the p53-dependent pathway in mice. J Immunol. (2012) 188:3611–9. 10.4049/jimmunol.1102475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Qi Q, Kannan AK, August A. Tec family kinases: Itk signaling and the development of NKT alphabeta and gammadelta T cells. FEBS J. (2011) 278:1970–9. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08074.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Yin CC, Cho OH, Sylvia KE, Narayan K, Prince AL, Evans JW, et al. The Tec kinase ITK regulates thymic expansion, emigration, and maturation of gammadelta NKT cells. J Immunol. (2013) 190:2659–69. 10.4049/jimmunol.1202531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Felices M, Yin CC, Kosaka Y, Kang J, Berg LJ. Tec kinase Itk in gammadeltaT cells is pivotal for controlling IgE production in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2009) 106:8308–13. 10.1073/pnas.0808459106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Yablonski D, Kadlecek T, Weiss A. Identification of a phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1) SH3 domain-binding site in SLP-76 required for T-cell receptor-mediated activation of PLC-gamma1 and NFAT. Mol Cell Biol. (2001) 21:4208–18. 10.1128/MCB.21.13.4208-4218.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Liu SK, Fang N, Koretzky GA, McGlade CJ. The hematopoietic-specific adaptor protein gads functions in T-cell signaling via interactions with the SLP-76 and LAT adaptors. Curr Biol. (1999) 9:67–75. 10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80017-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Sauer K, Liou J, Singh SB, Yablonski D, Weiss A, Perlmutter RM. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 associates physically and functionally with the adaptor proteins B cell linker protein and SLP-76 in lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:45207–16. 10.1074/jbc.M106811200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.da Silva AJ, Li Z, de Vera C, Canto E, Findell P, Rudd CE. Cloning of a novel T-cell protein FYB that binds FYN and SH2-domain-containing leukocyte protein 76 and modulates interleukin 2 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1997) 94:7493–8. 10.1073/pnas.94.14.7493 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Musci MA, Hendricks-Taylor LR, Motto DG, Paskind M, Kamens J, Turck CW, et al. Molecular cloning of SLAP-130, an SLP-76-associated substrate of the T cell antigen receptor-stimulated protein tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem. (1997) 272:11674–7. 10.1074/jbc.272.18.11674 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Wu JN, Gheith S, Bezman NA, Liu QH, Fostel LV, Swanson AM, et al. Adhesion- and degranulation-promoting adapter protein is required for efficient thymocyte development and selection. J Immunol. (2006) 176:6681–9. 10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.6681 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Griffiths EK, Krawczyk C, Kong YY, Raab M, Hyduk SJ, Bouchard D, et al. Positive regulation of T cell activation and integrin adhesion by the adapter Fyb/Slap. Science. (2001) 293:2260–3. 10.1126/science.1063397 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Peterson EJ, Woods ML, Dmowski SA, Derimanov G, Jordan MS, Wu JN, et al. Coupling of the TCR to integrin activation by Slap-130/Fyb. Science. (2001) 293:2263–5. 10.1126/science.1063486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Griffiths EK, Penninger JM. Communication between the TCR and integrins: role of the molecular adapter ADAP/Fyb/Slap. Curr Opin Immunol. (2002) 14:317–22. 10.1016/S0952-7915(02)00334-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Coussens NP, Hayashi R, Brown PH, Balagopalan L, Balbo A, Akpan I, et al. Multipoint binding of the SLP-76 SH2 domain to ADAP is critical for oligomerization of SLP-76 signaling complexes in stimulated T cells. Mol Cell Biol. (2013) 33:4140–51. 10.1128/MCB.00410-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Lampe K, Endale M, Cashman S, Fang H, Mattner J, Hildeman D, et al. Slp-76 is a critical determinant of NK-cell mediated recognition of missing-self targets. Eur J Immunol. (2015) 45:2072–83. 10.1002/eji.201445352 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Binstadt BA, Billadeau DD, Jevremovic D, Williams BL, Fang N, Yi T, et al. SLP-76 is a direct substrate of SHP-1 recruited to killer cell inhibitory receptors. J Biol Chem. (1998) 273:27518–23. 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Utting O, Sedgmen BJ, Watts TH, Shi X, Rottapel R, Iulianella A, et al. Immune functions in mice lacking Clnk, an SLP-76-related adaptor expressed in a subset of immune cells. Mol Cell Biol. (2004) 24:6067–75. 10.1128/MCB.24.13.6067-6075.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Sasanuma H, Tatsuno A, Hidano S, Ohshima K, Matsuzaki Y, Hayashi K, et al. Dual function for the adaptor MIST in IFN-gamma production by NK and CD4+NKT cells regulated by the Src kinase Fgr. Blood. (2006) 107:3647–55. 10.1182/blood-2005-10-4102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Cannons JL, Tangye SG, Schwartzberg PL. SLAM family receptors and SAP adaptors in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. (2011) 29:665–705. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ma CS, Nichols KE, Tangye SG. Regulation of cellular and humoral immune responses by the SLAM and SAP families of molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. (2007) 25:337–79. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141651 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Dong Z, Veillette A. How do SAP family deficiencies compromise immunity? Trends Immunol. (2010) 31:295–302. 10.1016/j.it.2010.05.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Veillette A. SLAM-family receptors: immune regulators with or without SAP-family adaptors. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2010) 2:a002469 10.1101/cshperspect.a002469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Coffey AJ, Brooksbank RA, Brandau O, Oohashi T, Howell GR, Bye JM, et al. Host response to EBV infection in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease results from mutations in an SH2-domain encoding gene. Nat Genet. (1998) 20:129–35. 10.1038/2424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Nichols KE, Harkin DP, Levitz S, Krainer M, Kolquist KA, Genovese C, et al. Inactivating mutations in an SH2 domain-encoding gene in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1998) 95:13765–70. 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13765 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Sayos J, Wu C, Morra M, Wang N, Zhang X, Allen D, et al. The X-linked lymphoproliferative-disease gene product SAP regulates signals induced through the co-receptor SLAM. Nature. (1998) 395:462–9. 10.1038/26683 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Morra M, Howie D, Grande MS, Sayos J, Wang N, Wu C, et al. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease: a progressive immunodeficiency. Annu Rev Immunol. (2001) 19:657–82. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bottino C, Falco M, Parolini S, Marcenaro E, Augugliaro R, Sivori S, et al. NTB-A [correction of GNTB-A], a novel SH2D1A-associated surface molecule contributing to the inability of natural killer cells to kill Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. J Exp Med. (2001) 194:235–46. 10.1084/jem.194.3.235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Parolini S, Bottino C, Falco M, Augugliaro R, Giliani S, Franceschini R, et al. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. 2B4 molecules displaying inhibitory rather than activating function are responsible for the inability of natural killer cells to kill Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. J Exp Med. (2000) 192:337–46. 10.1084/jem.192.3.337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Sharifi R, Sinclair JC, Gilmour KC, Arkwright PD, Kinnon C, Thrasher AJ, et al. SAP mediates specific cytotoxic T-cell functions in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. Blood. (2004) 103:3821–7. 10.1182/blood-2003-09-3359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Borowski C, Bendelac A. Signaling for NKT cell development: the SAP-FynT connection. J Exp Med. (2005) 201:833–6. 10.1084/jem.20050339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Eissmann P, Beauchamp L, Wooters J, Tilton JC, Long EO, Watzl C. Molecular basis for positive and negative signaling by the natural killer cell receptor 2B4 (CD244). Blood. (2005) 105:4722–9. 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3796 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Dong Z, Davidson D, Perez-Quintero LA, Kurosaki T, Swat W, Veillette A. The adaptor SAP controls NK cell activation by regulating the enzymes Vav-1 and SHIP-1 and by enhancing conjugates with target cells. Immunity. (2012) 36:974–85. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Le Borgne M, Shaw AS. SAP signaling: a dual mechanism of action. Immunity. (2012) 36:899–901. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Zhao F, Cannons JL, Dutta M, Griffiths GM, Schwartzberg PL. Positive and negative signaling through SLAM receptors regulate synapse organization and thresholds of cytolysis. Immunity. (2012) 36:1003–16. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.05.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Wu N, Zhong MC, Roncagalli R, Perez-Quintero LA, Guo H, Zhang Z, et al. A hematopoietic cell-driven mechanism involving SLAMF6 receptor, SAP adaptors and SHP-1 phosphatase regulates NK cell education. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:387–96. 10.1038/ni.3369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Iyer SS, Huang YH, Blumberg RS. SLAM-ing the brakes on iNKT cell selection. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:378–9. 10.1038/s41590-019-0355-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Seiler MP, Mathew R, Liszewski MK, Spooner CJ, Barr K, Meng F, et al. Elevated and sustained expression of the transcription factors Egr1 and Egr2 controls NKT lineage differentiation in response to TCR signaling. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13:264–71. 10.1038/ni.2230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Cen O, Ueda A, Guzman L, Jain J, Bassiri H, Nichols KE, et al. The adaptor molecule signaling lymphocytic activation molecule-associated protein (SAP) regulates IFN-gamma and IL-4 production in V alpha 14 transgenic NKT cells via effects on GATA-3 and T-bet expression. J Immunol. (2009) 182:1370–8. 10.4049/jimmunol.182.3.1370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Das R, Bassiri H, Guan P, Wiener S, Banerjee PP, Zhong MC, et al. The adaptor molecule SAP plays essential roles during invariant NKT cell cytotoxicity and lytic synapse formation. Blood. (2013) 121:3386–95. 10.1182/blood-2012-11-468868 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Kageyama R, Cannons JL, Zhao F, Yusuf I, Lao C, Locci M, et al. The receptor Ly108 functions as a SAP adaptor-dependent on-off switch for T cell help to B cells and NKT cell development. Immunity. (2012) 36:986–1002. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.05.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Detre C, Keszei M, Garrido-Mesa N, Kis-Toth K, Castro W, Agyemang AF, et al. SAP expression in invariant NKT cells is required for cognate help to support B-cell responses. Blood. (2012) 120:122–9. 10.1182/blood-2011-11-395913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Boehm M, Bonifacino JS. Adaptins: the final recount. Mol Biol Cell. (2001) 12:2907–20. 10.1091/mbc.12.10.2907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Robinson MS, Bonifacino JS. Adaptor-related proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2001) 13:444–53. 10.1016/S0955-0674(00)00235-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kirchhausen T. Adaptors for clathrin-mediated traffic. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (1999) 15:705–32. 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.15.1.705 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Park SY, Guo X. Adaptor protein complexes and intracellular transport. Biosci Rep. (2014) 34:e00123. 10.1042/BSR20140069 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Huang F, Nesterov A, Carter RE, Sorkin A. Trafficking of yellow-fluorescent-protein-tagged mu1 subunit of clathrin adaptor AP-1 complex in living cells. Traffic. (2001) 2:345–57. 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2001.25020506.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Rapoport I, Miyazaki M, Boll W, Duckworth B, Cantley LC, Shoelson S, et al. Regulatory interactions in the recognition of endocytic sorting signals by AP-2 complexes. EMBO J. (1997) 16:2240–50. 10.1093/emboj/16.9.2240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Daugherty BL, Straley KS, Sanders JM, Phillips JW, Disdier M, McEver RP, et al. AP-3 adaptor functions in targeting P-selectin to secretory granules in endothelial cells. Traffic. (2001) 2:406–13. 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2001.002006406.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kantheti P, Qiao X, Diaz ME, Peden AA, Meyer GE, Carskadon SL, et al. Mutation in AP-3 delta in the mocha mouse links endosomal transport to storage deficiency in platelets, melanosomes, and synaptic vesicles. Neuron. (1998) 21:111–22. 10.1016/S.0896-6273(00)80519-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Dell'Angelica EC, Shotelersuk V, Aguilar RC, Gahl WA, Bonifacino JS. Altered trafficking of lysosomal proteins in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome due to mutations in the beta 3A subunit of the AP-3 adaptor. Mol Cell. (1999) 3:11–21. 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80170-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Feng L, Seymour AB, Jiang S, To A, Peden AA, Novak EK, et al. The beta3A subunit gene (Ap3b1) of the AP-3 adaptor complex is altered in the mouse hypopigmentation mutant pearl, a model for Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome and night blindness. Hum Mol Genet. (1999) 8:323–30. 10.1093/hmg/8.2.323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Shotelersuk V, Dell'Angelica EC, Hartnell L, Bonifacino JS, Gahl WA. A new variant of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome due to mutations in a gene responsible for vesicle formation. Am J Med. (2000) 108:423–27. 10.1016/S0002-9343(99)00436-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Yang W, Li C, Ward DM, Kaplan J, Mansour SL. Defective organellar membrane protein trafficking in Ap3b1-deficient cells. J Cell Sci. (2000) 113:4077–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lawton AP, Prigozy TI, Brossay L, Pei B, Khurana A, Martin D, et al. The mouse CD1d cytoplasmic tail mediates CD1d trafficking and antigen presentation by adaptor protein 3-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Immunol. (2005) 174:3179–86. 10.4049/jimmunol.174.6.3179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Keller CW, Loi M, Ewert S, Quast I, Theiler R, Gannage M, et al. The autophagy machinery restrains iNKT cell activation through CD1D1 internalization. Autophagy. (2017) 13:1025–36. 10.1080/15548627.2017.1297907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Salio M, Puleston DJ, Mathan TS, Shepherd D, Stranks AJ, Adamopoulou E, et al. Essential role for autophagy during invariant NKT cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2014) 111:E5678–E5687. 10.1073/pnas.1413935112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Pei B, Zhao M, Miller BC, Vela JL, Bruinsma MW, Virgin HW, et al. Invariant NKT cells require autophagy to coordinate proliferation and survival signals during differentiation. J Immunol. (2015) 194:5872–84. 10.4049/jimmunol.1402154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ververs FA, Kalkhoven E, Van't Land B, Boes M, Schipper HS. Immunometabolic activation of invariant natural killer T cells. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1192. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Sugita M, Cao X, Watts GF, Rogers RA, Bonifacino JS, Brenner MB. Failure of trafficking and antigen presentation by CD1 in AP-3-deficient cells. Immunity. (2002) 16:697–706. 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00311-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Sevilla LM, Richter SS, Miller J. Intracellular transport of MHC class II and associated invariant chain in antigen presenting cells from AP-3-deficient mocha mice. Cell Immunol. (2001) 210:143–53. 10.1006/cimm.2001.1817 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Caplan S, Dell'Angelica EC, Gahl WA, Bonifacino JS. Trafficking of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules in human B-lymphoblasts deficient in the AP-3 adaptor complex. Immunol Lett. (2000) 72:113–7. 10.1016/S0165-2478(00)00176-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Jung J, Bohn G, Allroth A, Boztug K, Brandes G, Sandrock I, et al. Identification of a homozygous deletion in the AP3B1 gene causing Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 2. Blood. (2006) 108:362–9. 10.1182/blood-2005-11-4377 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Lorenzi L, Tabellini G, Vermi W, Moratto D, Porta F, Notarangelo LD, et al. Occurrence of nodular lymphocyte-predominant hodgkin lymphoma in hermansky-pudlak type 2 syndrome is associated to natural killer and natural killer T cell defects. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e80131. 10.1371/journal.pone.0080131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Yablonski D, Weiss A. Mechanisms of signaling by the hematopoietic-specific adaptor proteins, SLP-76 and LAT and their B cell counterpart, BLNK/SLP-65. Adv Immunol. (2001) 79:93–128. 10.1016/S0065-2776(01)79003-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Schwartzberg PL, Mueller KL, Qi H, Cannons JL. SLAM receptors and SAP influence lymphocyte interactions, development and function. Nat Rev Immunol. (2009) 9:39–46. 10.1038/nri2456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Plas DR, Johnson R, Pingel JT, Matthews RJ, Dalton M, Roy G, et al. Direct regulation of ZAP-70 by SHP-1 in T cell antigen receptor signaling. Science. (1996) 272:1173–6. 10.1126/science.272.5265.1173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Burshtyn DN, Scharenberg AM, Wagtmann N, Rajagopalan S, Berrada K, Yi T, et al. Recruitment of tyrosine phosphatase HCP by the killer cell inhibitor receptor. Immunity. (1996) 4:77–85. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80300-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Nakamura MC, Niemi EC, Fisher MJ, Shultz LD, Seaman WE, Ryan JC. Mouse Ly-49A interrupts early signaling events in natural killer cell cytotoxicity and functionally associates with the SHP-1 tyrosine phosphatase. J Exp Med. (1997) 185:673–84. 10.1084/jem.185.4.673 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Fawcett VC, Lorenz U. Localization of Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1 (SHP-1) to lipid rafts in T lymphocytes: functional implications and a role for the SHP-1 carboxyl terminus. J Immunol. (2005) 174:2849–59. 10.4049/jimmunol.174.5.2849 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Langlet C, Bernard AM, Drevot P, He HT. Membrane rafts and signaling by the multichain immune recognition receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. (2000) 12:250–5. 10.1016/S0952-7915(00)00084-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Boerth NJ, Sadler JJ, Bauer DE, Clements JL, Gheith SM, Koretzky GA. Recruitment of SLP-76 to the membrane and glycolipid-enriched membrane microdomains replaces the requirement for linker for activation of T cells in T cell receptor signaling. J Exp Med. (2000) 192:1047–58. 10.1084/jem.192.7.1047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Kumar A, Pyaram K, Yarosz EL, Hong H, Lyssiotis CA, Giri S, et al. Enhanced oxidative phosphorylation in NKT cells is essential for their survival and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2019) 116:7439–48. 10.1073/pnas.1901376116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]