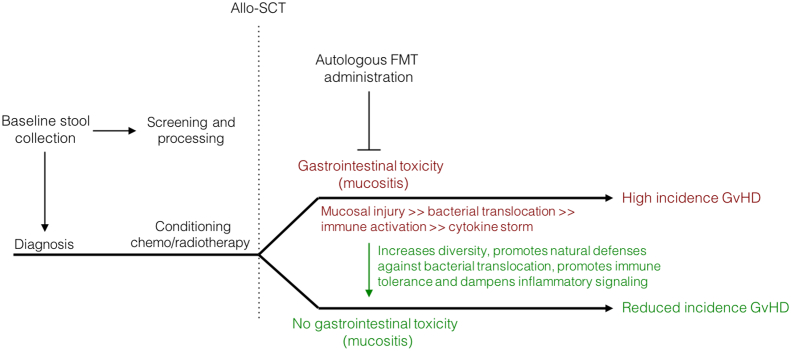
Fig. 2.
Proposed mechanistic framework for autologous FMT in the therapeutic management of acute gastrointestinal toxicity and paralleled prophylaxis of GvHD. FMT delivered therapeutically following allo-SCT may enhance microbial diversity, thus serving to enhance natural defenses to bacterial translocation and mucosal injury. Restoring an injured microbiome may also promote immune tolerance and dampen inflammatory signaling, thus mitigating GvHD development. Whilst autologous FMT is preferential due to the lower risk of transmissible diseases, implementation of appropriate criteria may be warranted to ensure suitable response. Alternatively, donor FMT prepared from a healthy relative or a superdonor may be warranted.