Abstract
BACKROUND:
Financial hardship is common among cancer survivors and is associated with both limiting care due to cost and with poor health-related quality of life (HRQOL). The present study estimates the association between limiting care due to cost and HRQOL in a diverse population of cancer survivors and tests whether limiting care mediates the association between financial hardship and HRQOL.
METHODS:
We used data from 988 participants (579 African American, 409 white) in the Detroit Research on Cancer Survivors (ROCS) pilot, a hospital-based cohort of breast, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancer survivors. We assessed associations between financial hardship, limiting care, and HRQOL (measured by the FACT-G) using linear regression and mediation analysis controlling for demographic, socioeconomic, and cancer-related variables.
RESULTS:
FACT-G scores were 4.2 (95% CI: 2.0, 6.4) points lower among survivors who reported financial hardship compared to those who did not in adjusted models. Limiting care due to cost was associated with a −7.8 point (95% CI: −5.1, −10.5) point difference in FACT-G scores. Limiting care due to cost explained 40.5% (95% CI: 25.5%, 92.7%) of the association between financial hardship and HRQOL overall, and 50.5% (95% CI: 29.1%, 188.1%) of the association for African American survivors.
CONCLUSIONS:
Financial hardship and limiting care due to cost are both associated with lower HRQOL among diverse cancer survivors and this association is partially explained by limiting care due to cost.
IMPACT:
Actions to ensure cancer patients can access appropriate care could lessen the impact of financial hardship on HRQOL.
Keywords: survivorship research, quality of life, psychosocial, financial hardship, disparities
Introduction
Financial hardship is common among cancer survivors, with close to 50% reporting adverse financial outcomes related to cancer or cancer treatment.1 Cancer survivors may experience material financial hardship such as reductions in income, utilizing assets, and incurring cancer-related debt, as well as behavioral financial hardship, including measures of limiting care (e.g. forgoing or delaying treatment, limiting medication) due to cost.1–4 (From here forward, this paper will refer to material financial hardship as “financial hardship” and behavioral financial hardship as “limiting care due to cost”.)
Cancer-related financial hardship is associated with poor health-related quality of life (HRQOL),3,5–15 including lower physical, functional, mental, and emotional wellbeing.3,6,8,15,16 Many cancer patients worry about cost when making treatment decisions,17 and experiencing financial hardship is associated with forgoing or delaying medical care.18,19 Limiting medical care because of cost concerns could be a plausible mechanism through which material financial hardship impacts HRQOL, but little is known about the association between limiting care due to cost and HRQOL. Its role as a potential mediator of the association between financial hardship and HRQOL has not been tested.
The objectives of this study are to estimate associations between financial hardship and limiting care due to cost and HRQOL among white and African American cancer survivors, and to test whether and to what extent observed associations between financial hardship and HRQOL are mediated by limiting care due to cost. We hypothesize that financial hardship and limiting care due to cost will each be associated with lower HRQOL and that limiting care due to cost will at least partially mediate the association between financial hardship and HRQOL.
Materials and Methods
Study Population
The Detroit Research On Cancer Survivors (ROCS) pilot is a hospital-based cohort study designed to investigate associations between medical history, health behaviors, financial hardship, and health-related outcomes among cancer survivors in Metropolitan Detroit.20 Participants were eligible to join the cohort if they were: white or African American; diagnosed with a first primary, invasive colorectal, lung, prostate or female breast cancer on or after January 1, 2013; ages 20–79 at diagnosis; and diagnosed and/or treated at the Karmanos Cancer Center in Detroit, MI. Participants were diagnosed a median of 17 (mean: 18.7, range: 1–54) months before completing the baseline survey. On average, lung cancer survivors were diagnosed more recently (14.9 months) than colorectal (18.8 months), prostate (18.9 months), or breast cancer survivors (20.2 months).
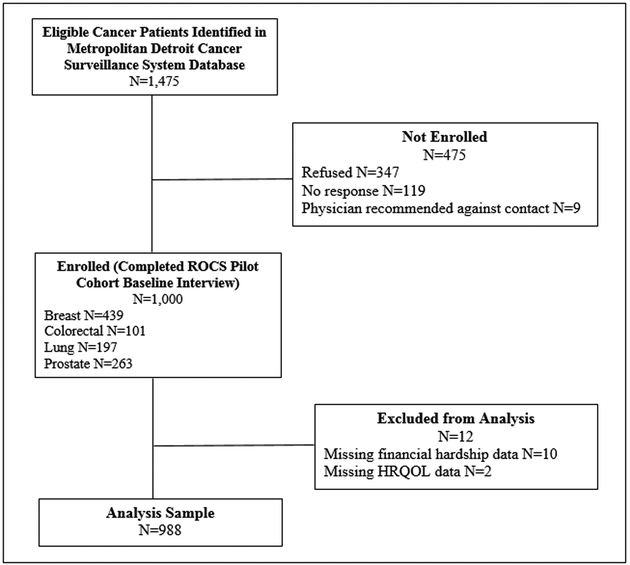
A flow diagram of participant recruitment appears in Figure 1. A total of 1,475 potentially-eligible participants were identified through a data query of the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System (MDCSS; the Detroit registry of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program). We contacted the physician of record for each potential participant asking if they objected to the patient being invited to participate. Participant invitation letters were sent if no objection was received within three weeks. Nine survivors were excluded due to physician objection, 347 refused, and 119 did not respond to repeated invitations, for a total of 1,000 survivors enrolled into the cohort (response rate=67.8%). Participants completed baseline surveys between March, 2015 and June, 2017. Analyses exclude participants missing information on financial hardship or limiting care due to cost (N=10) or HRQOL (N=2), for an analytic sample of 988 participants.
Figure 1:
Flow diagram of study sample - This figure shows the recruitment flow of participants into the Detroit ROCS pilot cohort. Abbreviations: HRQOL – health-related quality of life, ROCS – Detroit Research on Cancer Survivors
The Institutional Review Board at Wayne State University approved this research, which was conducted in concordance with the Belmont Report. Participants completing the survey online provided written informed consent. Phone participants received a written study information sheet, which was reviewed by the interviewer, and provided informed consent orally.
Data Collection
Information on individuals’ demographic and socioeconomic characteristics, HRQOL, and experiences of financial hardship and limiting care due to cost was self-reported. Participants completed surveys online via Qualtrics® or over the phone with a trained interviewer. We obtained cancer-related information including cancer site, stage, and time since diagnosis via linkage with MDCSS.
Financial Hardship and Limiting Care Due to Cost
Financial hardship information was collected using a previously-developed multidimensional instrument assessing the financial experiences of patients with cancer.4 Participants were asked whether in order to pay bills related to cancer treatment they had to do any of the following, and were instructed to select all that apply: refinance or take out a second mortgage on their home, sell their home, sell stocks or other investments, or withdraw money from retirement accounts. They were separately asked whether their income had declined since their cancer diagnosis; whether they or any member of their family had to borrow money from friends or other family members to help pay for their cancer treatment; and whether they were currently in debt due to expenses related to their cancer. We counted participants answering in the affirmative to any of the above items as experiencing financial hardship.
Participants were considered to have limited care due to cost if they answered in the affirmative to any of the following questions: Did you turn down treatments (chemotherapy, radiation, pain medications, anti-nausea medications, anti-diarrhea medications, or other recommended cancer treatments) because you were concerned about the cost? Did you ever skip doses of prescribed medication in order to save money? Was there a time in the past 12 months when you needed to see a doctor but could not because of cost?
In sensitivity analyses we separately excluded assets from the measure of financial hardship, and estimated associations between the number (0, 1, 2+) of financial hardships and care limitations reported and HRQOL, and estimated a per-hardship and per-care limitation association with HRQOL by modeling each as continuous predictors in linear regression models.
Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL)
HRQOL was measured using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy—General (FACT-G),21 including four subscales: Physical Well-Being (PWB), Social/Family Well-Being (SWB), Emotional Well-Being (EWB), and Functional Well-Being (FWB). Each subscale includes 6–7 statements (e.g. “I have a lack of energy”) and participants are asked to rate the extent to which each statement applied to them in the past seven days using a five-point scale (0=“not at all” to 4=“very much”). Responses are coded so that higher scores reflect higher quality of life. Cancer site-specific subscales assess concerns specific to survivors of individual cancers. Subscale scores are added to the FACT-G to produce total HRQOL scores for breast (FACT-B), colorectal (FACT-C), lung (FACT-L), and prostate (FACT-P) cancers.
The reliability and validity of the FACT-G and the site-specific measures have been extensively documented, with alpha coefficients for internal consistency measured at 0.60 to 0.90 and with consistent findings of sensitivity to changes in disease progression and performance status.22–25 A two-point difference on the subscale scores and a five-point difference on the total FACT-G score are associated with meaningful differences on clinical and subjective indicators.26 Differences of 2–3 points on the site-specific subscale scores, or 5–10 points for the site-specific FACT measures are associated with clinically meaningful differences in HRQOL.27–30
Statistical Analysis
We fit linear regression models with financial hardship or limiting care as the exposure and HRQOL measures as the outcomes of interest and utilizing robust standard errors. Age, sex, and race were determined a priori to be included as covariates. Additional covariates were selected using a directed acyclic graph (DAG) including relationships between financial hardship, limiting care, HRQOL, and each of the factors listed in Table 1.31 Final models controlled for continuous, mean-centered age, in addition to sex, race, marital status, income, education, employment status, health insurance, number of comorbid conditions, cancer site, stage at diagnosis, and treatments received using categories presented in Table 1. Checks of variance inflation factors did not suggest problems with multicollinearity between covariates (https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stata/webbooks/reg/chapter2/stata-webbooksregressionwith-statachapter-2-regression-diagnostics/ accessed December 10, 2018). In post hoc analyses we tested for effect modification by time since diagnosis split approximately at the median (<18 months/18+ months) by including interaction terms between since diagnosis and financial hardship or limiting care.
Table 1.
Participant characteristics and mean FACT-G scores by participant characteristics
| White | African American |
Total | FACT-G | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | Mean | 95% CI | |
| 409 | 41.4 | 579 | 58.6 | 988 | 100 | 76.0 | (74.9, 77.2) | |
| Age (mean, SD) | 59.7 | 9.5 | 59.5 | 8.8 | 59.6 | 9.1 | ||
| Age | ||||||||
| <60 | 190 | 46.5 | 292 | 50.4 | 482 | 48.8 | 73.3 | (71.8, 74.9) |
| 60-69 | 153 | 37.4 | 215 | 37.1 | 368 | 37.3 | 77.2 | (75.4, 79.0) |
| 70+ | 66 | 16.1 | 72 | 12.4 | 138 | 14.0 | 82.3 | (79.3, 85.3) |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Women | 258 | 63.1 | 352 | 60.8 | 610 | 61.7 | 74.7 | (73.3, 76.1) |
| Men | 151 | 36.9 | 227 | 39.2 | 378 | 38.3 | 78.2 | (76.3, 80.0) |
| Race | ||||||||
| White | 409 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 409 | 41.4 | 79.5 | (77.8, 81.2) |
| African American | 0 | 0 | 579 | 100.0 | 579 | 58.6 | 73.6 | (72.1, 75.0) |
| Education | ||||||||
| Less than high school | 24 | 5.9 | 88 | 15.2 | 112 | 11.3 | 67.2 | (64.0, 70.5) |
| High school/GED | 96 | 23.5 | 200 | 34.5 | 296 | 30.0 | 74.1 | (72.1, 76.1) |
| Some college/2-year degree | 133 | 32.5 | 210 | 36.3 | 343 | 34.7 | 77.3 | (75.5, 79.2) |
| College graduate/4-year degree | 156 | 38.1 | 74 | 12.8 | 230 | 23.3 | 80.8 | (78.5, 83.1) |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 7 | 1.2 | 7 | 0.7 | 80.6 | (67.6, 93.6) |
| Income | ||||||||
| <$20,000 | 58 | 14.2 | 335 | 57.9 | 393 | 39.8 | 68.1 | (66.5, 69.8) |
| $20,000-39,999 | 68 | 16.6 | 100 | 17.3 | 168 | 17.0 | 77.5 | (74.9, 80.0) |
| $40,000-59,999 | 60 | 14.7 | 53 | 9.2 | 113 | 11.4 | 80.6 | (77.5, 83.7) |
| $60,000-79,999 | 37 | 9.1 | 32 | 5.5 | 69 | 7.0 | 82.4 | (78.5, 86.4) |
| $80,000+ | 155 | 37.9 | 30 | 5.2 | 185 | 18.7 | 86.0 | (83.6, 88.4) |
| Missing | 31 | 7.6 | 29 | 5.0 | 60 | 6.1 | 77.1 | (72.9, 81.3) |
| Employment Status | ||||||||
| Employed full time | 119 | 29.1 | 77 | 13.3 | 196 | 19.8 | 85.2 | (82.9, 87.5) |
| Employed part time | 49 | 12.0 | 31 | 5.4 | 80 | 8.1 | 82.5 | (78.9, 86.0) |
| Homemaker | 17 | 4.2 | 19 | 3.3 | 36 | 3.6 | 75.2 | (69.9, 80.5) |
| Unemployed | 22 | 5.4 | 64 | 11.1 | 86 | 8.7 | 67.3 | (63.8, 70.7) |
| Retired | 151 | 36.9 | 206 | 35.6 | 357 | 36.1 | 79.2 | (77.5, 80.9) |
| On medical leave/disability | 48 | 11.7 | 172 | 29.7 | 220 | 22.3 | 64.1 | (61.9, 66.2) |
| Other/missing | 3 | 0.7 | 10 | 1.7 | 13 | 1.3 | 73.8 | (65.0, 82.6) |
| Marital Status | ||||||||
| Married or living with partner | 297 | 72.6 | 159 | 27.5 | 456 | 46.2 | 80.9 | (79.4, 82.5) |
| Widowed | 27 | 6.6 | 80 | 13.8 | 107 | 10.8 | 71.8 | (68.5, 75.1) |
| Divorced or separated | 60 | 14.7 | 164 | 28.3 | 224 | 22.7 | 74.2 | (71.9, 76.5) |
| Never married | 22 | 5.4 | 172 | 29.7 | 194 | 19.6 | 69.4 | (66.9, 71.8) |
| Missing | 3 | 0.7 | 4 | 0.7 | 7 | 0.7 | 63.1 | (50.3, 76.0) |
| Comorbid conditions (mean, SD) | 2.3 | 1.8 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 1.9 | ||
| Comorbid conditions | ||||||||
| None | 74 | 18.1 | 58 | 10.0 | 132 | 13.4 | 81.9 | (78.9, 84.9) |
| 1-2 | 167 | 40.8 | 218 | 37.7 | 385 | 39.0 | 79.0 | (77.2, 80.7) |
| 3+ | 168 | 41.1 | 303 | 52.3 | 471 | 47.7 | 72.0 | (70.4, 73.6) |
| Cancer site | ||||||||
| Breast | 172 | 42.1 | 264 | 45.6 | 436 | 44.1 | 75.3 | (73.6, 77.0) |
| Colorectal | 51 | 12.5 | 49 | 8.5 | 100 | 10.1 | 74.9 | (71.3, 78.4) |
| Lung | 100 | 24.5 | 92 | 15.9 | 192 | 19.4 | 74.7 | (72.2, 77.3) |
| Prostate | 86 | 21.0 | 174 | 30.1 | 260 | 26.3 | 78.7 | (76.5, 80.9) |
| Any chemotherapy | ||||||||
| No | 171 | 42.1 | 279 | 48.5 | 450 | 45.9 | 78.8 | (77.1, 80.4) |
| Yes | 235 | 57.9 | 296 | 51.5 | 531 | 54.1 | 73.9 | (72.4, 75.4) |
| Any surgery | ||||||||
| No | 117 | 28.6 | 175 | 30.4 | 292 | 29.7 | 75.6 | (73.5, 77.6) |
| Yes | 292 | 71.4 | 400 | 69.6 | 692 | 70.3 | 76.3 | (75.0, 77.6) |
| Any radiation | ||||||||
| No | 169 | 42.3 | 209 | 36.3 | 378 | 38.7 | 77.9 | (76.1, 79.7) |
| Yes | 231 | 57.8 | 367 | 63.7 | 598 | 61.3 | 75.0 | (73.5, 76.4) |
| Multiple treatment types | ||||||||
| No | 146 | 36.2 | 215 | 37.4 | 361 | 36.9 | 78.3 | (76.5, 80.2) |
| Yes | 257 | 63.8 | 360 | 62.6 | 617 | 63.1 | 74.8 | (73.4, 76.2) |
| Time since diagnosis | ||||||||
| <18 months | 205 | 50.1 | 304 | 52.6 | 509 | 51.6 | 76.5 | (74.9, 78.0) |
| 18+ months | 204 | 49.9 | 274 | 47.4 | 478 | 48.3 | 75.5 | (73.9, 77.2) |
| Any private insurance | ||||||||
| No | 56 | 13.8 | 244 | 42.7 | 300 | 30.7 | 68.6 | (66.7, 70.6) |
| Yes | 349 | 86.2 | 328 | 57.3 | 677 | 69.3 | 79.4 | (78.1, 80.7) |
| Any Medicare | ||||||||
| No | 238 | 58.6 | 311 | 54.3 | 549 | 56.1 | 75.7 | (74.2, 77.2) |
| Yes | 168 | 41.4 | 262 | 45.7 | 430 | 43.9 | 76.5 | (74.8, 78.2) |
| Any Medicaid | ||||||||
| No | 366 | 90.4 | 402 | 70.3 | 768 | 78.6 | 78.5 | (77.3, 79.7) |
| Yes | 39 | 9.6 | 170 | 29.7 | 209 | 21.4 | 67.1 | (64.8, 69.5) |
Abbreviations: GED – General Educational Development, FACT-G – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – General, SD – standard deviation
Column percents may not add up to 100 due to rounding.
Mediation Analysis
We used causal mediation analyses to test whether observed associations between financial hardship and HRQOL were mediated by limiting care due to cost. These models use the medeff command32 to estimate three parameters: 1) total effect of financial hardship on HRQOL; 2) average causal mediated effect (ACME), or the effect of financial hardship on HRQOL acting through limiting care due to cost; and 3) direct effect of financial hardship on HRQOL.33–35
Estimates of the proportion mediated can be unstable and can even be greater than one or negative in the presence of inconsistent mediation.36 The mediation models require the strong assumption of sequential ignorability, or that there is no uncontrolled confounding of the association between the exposure and the mediator or outcome, or between the mediator and outcome.37 To address this, we present the results of sensitivity analyses (using the medsens command32) estimating how large a departure from sequential ignorability would be required for the observed mediated effect to be zero.32–35
All analyses were conducted using Stata, version 14.2.
Results
Participant characteristics and mean FACT-G scores by participant characteristics are presented in Table 1. The mean FACT-G score was 76.0 (95% CI: 74.9, 77.2), lower than the mean of 80.1 from normative data for United States adults (not necessarily cancer survivors).38 Higher FACT-G scores were associated with being older, male, white, married or living with a partner, having higher levels of education and income, full- or part-time employment, fewer comorbid conditions, prostate cancer, not receiving chemotherapy or requiring multiple forms of cancer treatment, having private insurance and not reporting Medicaid coverage. Nearly all (99%) participants had some form of health insurance coverage at the time of study participation (data not shown).
Table 2 gives the prevalence of financial hardship and limiting care due to cost by participant characteristics. Financial hardship was more common among younger survivors, women, those with lower income and educational attainment, and unmarried survivors, as well those with breast cancer, those who received chemotherapy, and those with Medicaid coverage. Limiting care was more common among African American survivors, those with lower incomes, those on medical leave or disability, those with Medicaid and those without private insurance.
Table 2.
Financial hardship and limiting care due to cost by participant characteristics
| No Financial Hardship |
Any Financial Hardship |
No Limiting Care Due to Cost |
Any Limiting Care Due to Cost |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| 505 | 53.9 | 432 | 46.1 | 799 | 82.4 | 171 | 17.6 | |
| Age (mean, SD) | 61.2 | 8.9 | 57.3 | 8.9 | 59.9 | 9.2 | 58.6 | 8.6 |
| Age | ||||||||
| <60 | 214 | 42.4 | 253 | 58.6 | 378 | 47.3 | 93 | 54.4 |
| 60-69 | 197 | 39.0 | 151 | 34.5 | 299 | 37.4 | 63 | 36.8 |
| 70+ | 94 | 18.6 | 30 | 6.9 | 122 | 15.3 | 15 | 8.8 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Women | 286 | 56.6 | 287 | 66.4 | 495 | 62.0 | 108 | 63.2 |
| Men | 219 | 43.4 | 145 | 33.6 | 304 | 38.1 | 63 | 36.8 |
| Race | ||||||||
| White | 230 | 45.5 | 157 | 36.3 | 344 | 43.1 | 57 | 33.3 |
| African American | 275 | 54.5 | 275 | 63.7 | 455 | 57.0 | 114 | 66.7 |
| Education | ||||||||
| Less than high school | 66 | 13.1 | 39 | 9.0 | 87 | 10.9 | 23 | 13.5 |
| High school/GED | 147 | 29.1 | 137 | 31.7 | 231 | 28.9 | 57 | 33.3 |
| Some college/2-year degree | 156 | 30.9 | 168 | 38.9 | 282 | 35.3 | 56 | 32.8 |
| College graduate/4-year degree | 133 | 26.3 | 85 | 19.7 | 195 | 24.4 | 32 | 18.7 |
| Missing | 3 | 0.6 | 3 | 0.6 | 4 | 0.5 | 3 | 1.8 |
| Income | ||||||||
| <$20,000 | 174 | 34.5 | 200 | 46.3 | 283 | 35.4 | 103 | 60.2 |
| $20,000-39,999 | 82 | 16.2 | 80 | 18.5 | 135 | 16.9 | 29 | 17.0 |
| $40,000-59,999 | 64 | 12.7 | 43 | 10.0 | 97 | 12.1 | 14 | 8.2 |
| $60,000-79,999 | 34 | 6.7 | 33 | 7.6 | 59 | 7.4 | 9 | 5.3 |
| $80,000+ | 119 | 23.6 | 53 | 12.3 | 172 | 21.5 | 10 | 5.9 |
| Missing | 32 | 6.3 | 23 | 5.3 | 53 | 6.6 | 6 | 3.5 |
| Employment status | ||||||||
| Employed full time | 105 | 20.8 | 83 | 19.2 | 171 | 21.4 | 23 | 13.5 |
| Employed part time | 35 | 6.9 | 39 | 9.0 | 64 | 8.0 | 16 | 9.4 |
| Homemaker | 20 | 4.0 | 12 | 2.8 | 29 | 3.6 | 6 | 3.5 |
| Unemployed | 32 | 6.3 | 52 | 12.0 | 65 | 8.1 | 21 | 12.3 |
| Retired | 208 | 41.2 | 127 | 29.4 | 295 | 36.9 | 52 | 30.4 |
| On medical leave/disability | 99 | 19.6 | 113 | 26.2 | 164 | 20.5 | 51 | 29.8 |
| Other/missing | 6 | 1.2 | 6 | 1.4 | 11 | 1.4 | 2 | 1.2 |
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Married or living with partner | 266 | 52.7 | 170 | 39.4 | 393 | 49.2 | 54 | 31.6 |
| Widowed | 49 | 9.7 | 50 | 11.6 | 77 | 9.6 | 29 | 17.0 |
| Divorced or separated | 100 | 19.8 | 107 | 24.8 | 172 | 21.5 | 46 | 26.9 |
| Never married | 86 | 17.0 | 102 | 23.6 | 152 | 19.0 | 40 | 23.4 |
| Missing | 4 | 0.8 | 3 | 0.7 | 5 | 0.63 | 2 | 1.2 |
| Comorbid conditions (mean, SD) | 2.6 | 1.9 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 2.8 | 2.0 |
| Comorbid conditions | ||||||||
| None | 69 | 13.7 | 57 | 13.2 | 114 | 14.3 | 16 | 9.4 |
| 1-2 | 182 | 36.0 | 183 | 42.4 | 308 | 38.6 | 69 | 40.4 |
| 3+ | 254 | 50.3 | 192 | 44.4 | 377 | 47.2 | 86 | 50.3 |
| Cancer site | ||||||||
| Breast | 202 | 40.0 | 208 | 48.2 | 352 | 44.1 | 81 | 47.4 |
| Colorectal | 52 | 10.3 | 45 | 10.4 | 82 | 10.3 | 13 | 7.6 |
| Lung | 97 | 19.2 | 83 | 19.2 | 155 | 19.4 | 32 | 18.7 |
| Prostate | 154 | 30.5 | 96 | 22.2 | 210 | 26.3 | 45 | 26.3 |
| Any chemotherapy | ||||||||
| No | 269 | 53.6 | 151 | 35.2 | 375 | 47.3 | 69 | 40.6 |
| Yes | 233 | 46.4 | 281 | 64.8 | 418 | 52.7 | 101 | 59.4 |
| Any surgery | ||||||||
| No | 151 | 30.0 | 126 | 29.4 | 235 | 29.6 | 50 | 29.2 |
| Yes | 353 | 70.0 | 303 | 70.6 | 560 | 70.4 | 121 | 70.8 |
| Any radiation | ||||||||
| No | 210 | 41.9 | 151 | 35.5 | 307 | 38.8 | 63 | 37.7 |
| Yes | 291 | 58.1 | 274 | 64.5 | 485 | 61.2 | 104 | 62.3 |
| Multiple treatment types | ||||||||
| No | 207 | 41.2 | 133 | 31.2 | 300 | 37.9 | 57 | 33.7 |
| Yes | 295 | 58.8 | 293 | 68.8 | 492 | 62.1 | 112 | 66.3 |
| Time since diagnosis | ||||||||
| <18 months | 260 | 51.5 | 225 | 52.2 | 419 | 52.4 | 82 | 48.2 |
| 18+ months | 245 | 48.5 | 206 | 47.8 | 380 | 47.6 | 88 | 51.8 |
| Any private insurance | ||||||||
| No | 126 | 25.2 | 162 | 37.9 | 223 | 28.2 | 71 | 42.0 |
| Yes | 375 | 74.9 | 265 | 62.1 | 567 | 71.8 | 98 | 58.0 |
| Any Medicare | ||||||||
| No | 257 | 51.2 | 269 | 63.0 | 440 | 55.6 | 96 | 56.8 |
| Yes | 245 | 48.8 | 158 | 37.0 | 352 | 44.4 | 73 | 43.2 |
| Any Medicaid | ||||||||
| No | 413 | 82.4 | 314 | 73.5 | 635 | 80.4 | 118 | 69.8 |
| Yes | 88 | 17.6 | 113 | 26.5 | 155 | 19.6 | 51 | 30.2 |
Abbreviations: GED – General Educational Development, FACT-G – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – General, SD – standard deviation
Column percents may not add up to 100 due to rounding.
Table 3 describes the prevalence of overall and specific forms of financial hardship and limiting care due to cost for all survivors and stratified by race. Nearly half (46.1%) of participants reported experiencing some form of financial hardship associated with cancer. Financial hardship was more common in African American (50.0%) than white survivors [40.6%, risk ratio (RR) of financial hardship associated with being African American vs. white: 1.23, 95% CI: 1.06, 1.43]. Experiencing a decrease in income was the most common form of financial hardship (29.4%), followed by still being in cancer-related debt (25.5%), borrowing money from family or friends (9.7%), and utilizing assets to pay for cancer care (6.7%).
Table 3.
Prevalence of financial hardship and limiting care due to cost by race and risk ratios of reporting each form of financial hardship and care limitation associated with being African American vs. white
| Total | White | African American |
African American vs. white |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | RR | 95% CI | |
| Any financial hardship | 432 | 46.1 | 157 | 40.6 | 275 | 50.0 | 1.23 | (1.06, 1.43) |
| Borrowed money from family or friends | 95 | 9.7 | 39 | 9.7 | 56 | 9.8 | 1.01 | (0.68, 1.48) |
| Remaining debt | 249 | 25.5 | 74 | 18.3 | 175 | 30.7 | 1.68 | (1.32, 2.13) |
| Utilized assets to pay for cancer care | 66 | 6.7 | 38 | 9.3 | 28 | 4.8 | 0.68 | (0.51, 0.90) |
| Refinanced or sold home | 9 | 0.9 | 7 | 1.7 | 2 | 0.4 | 0.20 | (0.04, 0.97) |
| Sold stock or other investments | 15 | 1.5 | 8 | 2.0 | 7 | 1.2 | 0.62 | (0.23, 1.69) |
| Withdrew money from retirement | 56 | 5.7 | 31 | 7.6 | 25 | 4.3 | 0.57 | (0.34, 0.95) |
| Experienced a decrease in income | 275 | 29.4 | 109 | 28.0 | 166 | 30.5 | 1.09 | (0.89, 1.33) |
| Any care limitations | 171 | 17.6 | 57 | 14.2 | 114 | 20.0 | 1.41 | (1.05, 1.89) |
| Skipped doses of prescribed medication | 71 | 7.2 | 23 | 5.6 | 48 | 8.3 | 1.48 | (0.91, 2.39) |
| Refused recommended treatment due to cost | 49 | 5.0 | 21 | 5.2 | 28 | 4.9 | 0.94 | (0.54, 1.64) |
| Needed to see a doctor but did not go due to cost | 111 | 11.4 | 33 | 8.2 | 78 | 13.7 | 1.66 | (1.13, 2.45) |
Note: Responses are not mutually exclusive. “Any financial hardship” includes borrowing, debt, utilizing assets, and experiencing a decrease in income. “Any care limitations” includes skipping doses of prescribed medication, refusing recommended treatment, and needing to see a doctor but not going due to cost.
Abbreviations: CI – confidence interval, RR – risk ratio
Prevalence of some forms of financial hardship differed by race, with more African American than white survivors reporting still being in debt due to cancer (RR: 1.68, 95% CI: 1.32, 2.13), and fewer African American than white survivors reporting utilizing assets to pay for care (RR: 0.68, 95% CI: 0.51, 0.90). Prevalence of borrowing money from family or friends and experiencing a decrease in income did not differ by race. Limiting care due to cost was more common in African American than white survivors (RR: 1.41, 95% CI: 1.05, 1.89), driven by differences in needing to see a doctor and not going due to cost.
Associations between both financial hardship and limiting care due to cost and HRQOL are presented in Table 4. FACT-G scores were 7.5 (95% CI: 5.2, 9.8) points lower among survivors who experienced financial hardship compared to those who did not in an unadjusted model, and the difference was more than twice as great in African American compared with white survivors (Pinteraction=0.011). The association attenuated in adjusted models, particularly for white survivors, and results of the adjusted models did not differ by race.
Table 4.
Associations between financial hardship and limiting care due to cost and total and site-specific measures of health-related quality of life and physical, social, emotional, and functional wellbeing subscales
| Observed Range |
Financial Hardship | Financial Hardship | Limiting Care Due to Cost |
Limiting Care Due to Cost |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted | Unadjusted | Adjusted | ||||||||
| Mean | SD | Diff. in FACT-G score |
95% CI | Diff. in FACT-G score |
95% CI | Diff. in FACT-G score |
95% CI | Diff. in FACT-G score |
95% CI | ||
| FACT-G | 14-108 | 76.0 | 18.0 | −7.5 | (−9.8, −5.2) | −4.2 | (−6.4, −2.0) | −12.3 | (−15.2, −9.4) | −8.0 | (−10.7, −5.3) |
| White | 14-108 | 79.5 | 17.9 | −10.6 | (−14.3, −7.0) | −3.1 | (−6.8, 0.7) | −15.3 | (−20.8, −9.8) | −6.1 | (−10.8, −1.3) |
| African American | 16-108 | 73.3 | 17.6 | −4.6 | (−7.5, −1.7) | −4.4 | (−7.2, −1.6) | −9.9 | (−13.3, −6.4) | −9.0 | (−12.3, −5.6) |
| Pinteraction | 0.011 | 0.77 | 0.10 | 0.45 | |||||||
| PWB | 0-28 | 20.9 | 5.9 | −2.6 | (−3.3, −1.8) | −1.5 | (−2.3, −0.8) | −3.5 | (−4.5, −2.5) | −2.5 | (−3.5, −1.6) |
| SWB | 0-28 | 19.4 | 5.9 | −1.0 | (−1.8, −0.3) | −0.7 | (−1.5, 0.0) | −2.3 | (−3.3, −1.3) | −1.3 | (−2.2, −0.3) |
| EWB | 0-24 | 18.6 | 4.5 | −1.4 | (−2.0, −0.8) | −0.7 | (−1.3, −0.1) | −2.3 | (−3.0, −1.5) | −1.7 | (−2.5, −0.9) |
| FWB | 0-28 | 17.2 | 6.8 | −2.5 | (−3.4, −1.6) | −1.2 | (−2.0, −0.4) | −4.3 | (−5.3, −3.2) | −2.6 | (−3.5, −1.6) |
| FACT-B | 34-147 | 100.6 | 24.3 | −10.0 | (−14.6, −5.4) | −4.9 | (−9.3, −0.4) | −18.7 | (−24.2, −13.3) | −12.5 | (−17.9, −7.1) |
| FACT-C | 37-133 | 94.6 | 21.3 | −7.8 | (−16.4, 0.8) | −1.8 | (−11.4, 7.8) | −10.7 | (−24.9, 3.4) | −6.4 | (−21.7, 8.9) |
| FACT-L | 22-120 | 85.9 | 16.9 | −5.5 | (−10.5, −0.5) | −3.8 | (−8.9, 1.2) | −6.5 | (−13.3, 0.3) | −2.7 | (−8.5, 3.0) |
| FACT-P | 28-155 | 111.5 | 23.7 | −12.9 | (−19.3, −6.6) | −5.7 | (−12.1, 0.6) | −20.5 | (−28.2, −12.7) | −14.0 | (−21.4, −6.7) |
Abbreviations: CI – confidence interval, Diff. – difference, EWB – emotional wellbeing, FACT-B – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Breast, FACT-C – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Colorectal, FACT-G – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – General, FACT-L – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Lung, FACT-P – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Prostate, FWB – functional wellbeing, PWB – physical wellbeing, SD – standard deviation; SWB – social wellbeing
Adjusted models control for age, sex, race, marital status, income, education, employment status, health insurance, cancer site, and treatments received.
FACT-G scores were 12.3 (95% CI: 9.4, 15.2) points lower among all survivors, 15.3 (95% CI: 9.8, 20.8) points lower among white, and 9.9 (95% CI: 6.4, 13.3) points lower among African American survivors who limited care compared to those who did not in unadjusted models. These associations attenuated dramatically among white survivors but less so among African American survivors in adjusted models.
In sensitivity analyses we observed a dose-response association between both financial hardship and care limitations and HRQOL. FACT-G scores were 4.8 (95% CI: 2.2, 7.5) and 11.2 points (95% CI: 8.0, 14.3) lower for survivors who reported one or two or more forms of financial hardship, respectively, compared with those who reported none. Similarly, FACT-G scores were 10.4 (95% CI: 7.2, 13.6) and 17.1 (95% CI: 11.5, 22.8) points lower, respectively, for those reporting one or two or more care limitations (Supplementary Table S1). FACT-G scores were 2.4 (95% CI: 1.3, 3.6) and 5.1 (95% CI: 3.3, 6.9) points lower, respectively, for each additional financial hardship or care limitation reported (Supplementary Table S2).
Experiencing financial hardship was not associated with clinically meaningful differences in specific forms of wellbeing in adjusted models, but was associated with clinically meaningful differences in site-specific HRQOL for breast, and prostate cancer (Table 4). Limiting care due to cost was associated with clinically significant differences in physical and functional wellbeing and with lower site-specific HRQOL for breast and prostate cancer in adjusted models.
Results of the mediation models (Table 5) suggest that 40.5% (95% CI: 25.5%, 92.7%) of the difference in FACT-G scores associated with financial hardship was due to limiting care due to cost. Limiting care explained half (50.5%, 95% CI: 29.1%, 188.1%) of the association among African American survivors and 18.4% (95% CI: 9.7%, 88.7%) among white survivors.
Table 5.
Proportion of the association between financial hardship and health-related quality of life explained by limiting care due to cost
| ACME | Direct Effect | Total Effect | Proportion Mediated |
Sensitivity Analysis |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | % | 95% CI | (ρ) | |
| FACT-G | −1.6 | (−2.4, −0.9) | −2.4 | (−4.7, 0.0) | −4.0 | (−6.3, −1.7) | 40.5 | (25.5, 92.7) | −0.19 |
| White | −0.8 | (−1.8, −0.1) | −3.6 | (−7.4, 0.2) | −4.4 | (−8.1, −0.7) | 18.4 | (9.7, 88.7) | −0.12 |
| African American | −2.1 | (−3.4 −1.1) | −2.1 | (−5.2, 1.1) | −4.2 | (−7.3, −1.1) | 50.5 | (29.1, 188.1) | −0.23 |
Abbreviations: ACME – average causal mediated effect, CI – confidence interval, FACT-G – Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – General
These models control for mean-centered continuous age and for sex, race, marital status, income, education, employment status, comorbid conditions, health insurance, cancer site, stage at diagnosis, and treatments received. Because the mediation models do not allow for dummy-variable adjustment, marital status, employment status and stage at diagnosis were treated as binary variables (married/cohabitating vs. not; employed full- or part-time vs. not, stage I vs. stages II-IV, respectively) and ordinal income and education were treated as continuous variables.
In post hoc sensitivity analyses we tested whether the association between financial hardship and quality of life differed by time since diagnosis (Supplementary Table S3). These analyses revealed that among survivors diagnosed within the previous 18 months, FACT-G scores were 6.8 (95% CI: 3.7, 9.9) points lower for those who reported financial hardship, but that financial hardship was not associated with differences in FACT-G scores for longer-term survivors (−0.6, 95% CI: −3.6, 2.5; Pinteraction=0.006).
Discussion
Our results confirm previous findings of an inverse association between financial hardship and HRQOL among cancer survivors, and extend this work by including a large number of African American survivors and estimating race-specific associations. To our knowledge, this is the first work to establish an association between limiting care due to cost and HRQOL, finding clinically meaningful differences in HRQOL for survivors who limited care compared with those who did not. Mediation analyses suggest that 40% of the association between financial hardship and HRQOL is due to limiting care due to cost, and that limiting care explains half of the association between financial hardship and HRQOL for African American survivors. Post hoc analyses suggest effect modification in the association between financial hardship and HRQOL by time since diagnosis.
Previous work has examined the association between material financial hardship or financial distress and HRQOL using both the FACT-G3,5–7,14,16 and other measures.8–13,15 This work has examined associations between financial reserves,16 financial strain,8,9,13 specific types of financial burdens (e.g. debt, bankruptcy),12 living expenses,10 work impacts,10,11 and out-of-pocket medical expenses11 and HRQOL among survivors of several types of cancer, including breast,8,11 colorectal,9,13,16 lung,8,13,16 and prostate.8 In each case, adverse financial impacts of cancer were associated with worse HRQOL.
To our knowledge, this is the first work to report on associations between financial hardship and HRQOL separately by race. Previous work suggests that financial hardship is more common among African American than white survivors,39,40 but only one previous study into the association between financial hardship and HRQOL included a substantial proportion of African American participants,5 and none estimated race-specific associations.
Financial hardship was common in this population of cancer survivors even though nearly all had some form of health insurance. Even among those with health insurance, out-of-pocket costs can pose a serious threat to cancer patients’ finances. In 2018, 45% of American adults between the ages of 19 and 64 were underinsured, meaning that their out-of-pocket costs and/or deductibles were equivalent to at least 5–10% of their income.41 In one study of Medicare enrollees, out-of-pocket costs for cancer care ranged from more than $2000 per year among those with supplemental Medicaid coverage to more than $8000 per year for Medicare enrollees without supplemental coverage.42 For Medicare enrollees without supplemental coverage these out-of-pocket costs equated to 23.7% of their household income.42
These findings highlight the importance of underinsurance in the financial consequences of cancer. As Americans consider policy options to expand health insurance coverage more broadly, investigators in this area should work with policy makers to ensure that proposals to expand coverage also address underinsurance and its potential to impact cancer survivors’ finances, their ability to access appropriate care, and subsequent impacts on HRQOL.
Improving patients’ knowledge of treatment costs may also represent a promising strategy to improve financial outcomes. Although most cancer patients want to discuss treatment costs with their physicians,43,44 research suggests that cost discussions happen infrequently when patients and oncologists discuss treatment options, and may focus more on indirect costs such as missing work than on direct costs such as out-of-pocket costs and copayments.45 Improved cost discussions between cancer patients and their oncologists could help patients make more informed treatment decisions,19,46–48 connect patients with financial support,49 and potentially reduce financial hardship related to cancer.19,46,47,50
It is important to consider how some features of this study design may impact our results and their interpretations. Although the ROCS pilot includes data on several forms of financial hardship and care limitations used in previous work, this is a cross-sectional study with self-reported, retrospective information about cancer survivors’ experiences with financial hardship and care limitations. Given this design, it is possible that survivors who were negatively impacted by financial hardships and care limitations could be more likely to remember and report them than survivors for whom these problems were less severe, which could inflate our observed associations with HRQOL.
For survivors with adequate financial resources, utilizing assets to pay for cancer care may not represent a hardship. In supplemental analyses (Supplementary Table S1) we estimated the association between each individual form of financial hardship and HRQOL, finding that FACT-G scores were 5.2 (95% CI: 0.6, 9.7) points lower survivors who utilized assets to pay for care than those who did not. This is a clinically meaningful difference in HRQOL and is similar to the effect of experiencing a decrease in income, but weaker than the association observed for borrowing from friends and family or being in debt due to cancer (differences in FACT-G of 9.9–10.0). In an adjusted model, experiencing financial hardship other than utilizing assets was associated with −4.0 (95% CI: −6.2, −1.9) point difference in FACT-G scores similar to the estimate including assets (Supplementary Table S4).
A unique contribution of this work is our attempt to estimate the proportion of the association between financial hardship and HRQOL due to a particular mechanism, finding that approximately 40% of the association is explained by limiting care due to cost. Limiting care explains half of the association for African American survivors and approximately 18% among white survivors. This finding has the potential to direct resources to minimize the impact of financial hardship among African American survivors, who experience more negative financial impacts of cancer than white survivors do,39,40 and highlights the importance of ensuring cancer patients can access necessary care.
Our finding that that limiting care is strongly associated with worse HRQOL, particularly for African American survivors, suggests that future work addressing the financial consequences of cancer should focus on ensuring all cancer patients can access appropriate treatments without limitations related to cost concerns, both to improve survivors’ HRQOL and to potentially reduce disparities in outcomes related to the financial consequences of cancer.
Estimates of the proportion mediated can be unstable and can even be greater than one or negative in the presence of inconsistent mediation.36 To address this instability, we conducted sensitivity analyses32–35 and estimate that if 19% of the variation in FACT-G scores was due to unmeasured confounding, the mediation effect would no longer be observed. The mediation effect observed among African American survivors was more stable (larger absolute ρ value) than that among white survivors (Table 5).
In assessing whether differences in time since diagnosis influenced our findings, we discovered effect modification such that financial hardship was associated with HRQOL among survivors diagnosed within 18 months, but not among longer-term survivors in adjusted models (Supplementary Table S3). Previous work has examined longitudinal changes in HRQOL, finding that HRQOL improved more among patients without financial stress,6 but to our knowledge, our finding of effect modification is novel. Because late stage at diagnosis is associated with shorter expected survival, patients diagnosed with late stage disease would be less likely to be included in this cohort than longer-term survivors. However, the stage distribution in this study population does not vary substantially by time since diagnosis (stages I, II, III, and IV disease account for 31.6%, 28.9%, 19.0%, and 20.6% of recently diagnosed and 26.2%, 39.4%, 19.3%, and 15.1% of longer-term survivors, respectively). This finding warrants further examination in future research, but suggests that the impacts of financial hardship on HRQOL may not be enduring, and that survivors who face financial difficulties may regain quality of life during longer-term survival. Interestingly, we observed no effect modification in the association between limiting care and HRQOL by time since diagnosis, suggesting that care limitations may have lasting negative impacts on survivors’ HRQOL.
Important strengths of this study include its sample size sufficient to estimate associations between financial hardship and limiting care due to cost, and several measures of HRQOL; the inclusion of a large number of African American survivors, allowing for race-specific estimates; its high response rate, minimizing the potential for selection bias; and use of a detailed participant survey including validated HRQOL measures, and the ability to control for several potential confounders.
Additional limitations of this work should also be noted. Although the Detroit ROCS pilot cohort includes diversity in race, income, and cancer site, it is hospital-based, and therefore not representative of the general population of cancer survivors. The financial hardship measures included here have been used in prior research,4 but they are self-reported and have not been validated against survivors’ financial records. Additionally, information about survivors’ pre-diagnosis household income or assets is not available. Although the FACT-G and its site-specific scales have demonstrated good reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change, the available information on minimally important differences was developed in reference to changes in individuals’ scores over time rather than between groups. While the questions about financial hardship and limiting care refer to experiences since diagnosis or in the previous year and the FACT-G asks survivors about their HRQOL in the previous seven days, this study is cross sectional, and information about financial hardship, limiting care, and HRQOL were all collected at the same time, limiting our ability to establish temporal relationships.
Financial hardship is common among cancer survivors and is associated with lower HRQOL. Our results suggest that this association is at least partly explained by limiting care due to cost, making care limitations a potentially important target for interventions aimed at reducing the adverse financial consequences of cancer, particularly for African American survivors. As investigators call for interventions to minimize the impact of financial hardship on cancer survivors,51 it is critical to better understand the potential mechanisms through which financial hardship impacts survivors’ health outcomes and quality of life, and this is especially true for non-white populations where financial hardship is most common.39,40 Measures that improve access to and affordability of care represent a promising strategy as investigators, clinicians, and policymakers aim to reduce the burden of financial hardship and its impacts on health-related outcomes among cancer survivors.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Financial Support:
This research was funded by the American Cancer Society (MRSG-17–019 to TAH), the Karmanos Cancer Institute, the General Motors Foundation, and NIH grants/contracts U01CA199240 to AGS, P30CA022453 and HHSN261261201300011I.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Altice CK, Banegas MP, Tucker-Seeley RD, Yabroff KR. Financial Hardships Experienced by Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109(2):djw205. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zafar SY, Peppercorn JM, Schrag D, et al. The Financial Toxicity of Cancer Treatment: A Pilot Study Assessing Out-of-Pocket Expenses and the Insured Cancer Patient’s Experience. The Oncologist. 2013;18(4):381–390. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hamilton JG, Wu LM, Austin JE, et al. Economic survivorship stress is associated with poor health-related quality of life among distressed survivors of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Psychooncology. 2013;22(4):911–921. doi: 10.1002/pon.3091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shankaran V, Jolly S, Blough D, Ramsey SD. Risk Factors for Financial Hardship in Patients Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer: A Population-Based Exploratory Analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(14):1608–1614. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.37.9511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Delgado-Guay M, Ferrer J, Rieber AG, et al. Financial Distress and Its Associations With Physical and Emotional Symptoms and Quality of Life Among Advanced Cancer Patients. The Oncologist. 2015;20(9):1092–1098. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ell K, Xie B, Wells A, Nedjat-Haiem F, Lee P-J, Vourlekis B. Economic stress among low-income women with cancer: effects on quality of life. Cancer. 2008;112(3):616–625. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fenn KM, Evans SB, McCorkle R, et al. Impact of Financial Burden of Cancer on Survivors’ Quality of Life? J Oncol Pract. May 2014:JOP.2013.001322. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2013.001322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gupta D, Lis CG, Grutsch JF. Perceived cancer-related financial difficulty: implications for patient satisfaction with quality of life in advanced cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2007;15(9):1051–1056. doi: 10.1007/s00520-007-0214-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sharp L, O’Leary E, O’Ceilleachair A, Skally M, Hanly P. Financial Impact of Colorectal Cancer and Its Consequences: Associations Between Cancer-Related Financial Stress and Strain and Health-Related Quality of Life. Dis Colon Rectum. 2018;61(1):27–35. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000000923 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rogers SN, Harvey-Woodworth CN, Hare J, Leong P, Lowe D. Patients’ perception of the financial impact of head and neck cancer and the relationship to health related quality of life. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;50(5):410–416. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2011.07.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Meneses K, Azuero A, Hassey L, McNees P, Pisu M. Does economic burden influence quality of life in breast cancer survivors? Gynecol Oncol. 2012;124(3):437–443. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.11.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Peipert BJ, Goswami S, Helenowski I, Yount SE, Sturgeon C. Financial burden is associated with worse health-related quality of life in adults with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Surgery. 2017;162(6):1278–1285. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zafar SY, McNeil RB, Thomas CM, Lathan CS, Ayanian JZ, Provenzale D. Population-Based Assessment of Cancer Survivors’ Financial Burden and Quality of Life: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Oncol Pract. 2015;11(2):145–150. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2014.001542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.de Souza JA, Yap BJ, Wroblewski K, et al. Measuring financial toxicity as a clinically relevant patient‐reported outcome: The validation of the COmprehensive Score for financial Toxicity (COST). Cancer. 2017;123(3):476–484. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kale HP, Carroll NV. Self-reported financial burden of cancer care and its effect on physical and mental health-related quality of life among US cancer survivors. Cancer. 2016;122(8):283–289. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29808 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lathan CS, Cronin A, Tucker-Seeley R, Zafar SY, Ayanian JZ, Schrag D. Association of Financial Strain With Symptom Burden and Quality of Life for Patients With Lung or Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol. February 2016:JCO632232. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.2232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Martin MY, Fouad MN, Oster RA, et al. What do cancer patients worry about when making decisions about treatment? Variation across racial/ethnic groups. Support Care Cancer Off J Multinatl Assoc Support Care Cancer. 2014;22(1):233–244. doi: 10.1007/s00520-013-1958-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kent EE, Forsythe LP, Yabroff KR, et al. Are survivors who report cancer-related financial problems more likely to forgo or delay medical care? Cancer. 2013;119(20):3710–3717. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bestvina CM, Zullig LL, Rushing C, et al. Patient-Oncologist Cost Communication, Financial Distress, and Medication Adherence. J Oncol Pract. 2014;10(3):162–167. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2014.001406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Beebe-Dimmer JL, Albrecht TL, Baird TE, et al. The Detroit Research on Cancer Survivors (ROCS) Pilot Study: A focus on outcomes after cancer in a racially-diverse patient population. Cancer Epidemiol Prev Biomark. January 2018:cebp.0123.2018. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-0123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cella DF, Tulsky DS, Gray G, et al. The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy scale: development and validation of the general measure. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11(3):570–579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brady MJ, Cella DF, Mo F, et al. Reliability and validity of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast quality-of-life instrument. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(3):974–986. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.3.974 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ward WL, Hahn EA, Mo F, Hernandez L, Tulsky DS, Cella D. Reliability and validity of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Colorectal (FACT-C) quality of life instrument. Qual Life Res. 8(3):181–195. doi: 10.1023/A:1008821826499 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cella DF, Bonomi AE, Lloyd SR, Tulsky DS, Kaplan E, Bonomi P. Reliability and validity of the functional assessment of cancer therapy—lung (FACT-L) quality of life instrument. Lung Cancer. 1995;12(3):199–220. doi: 10.1016/0169-5002(95)00450-F [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Esper P, Mo F, Chodak G, Sinner M, Cella D, Pienta KJ. Measuring quality of life in men with prostate cancer using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-prostate instrument. Urology. 1997;50(6):920–928. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(97)00459-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brucker PS, Yost K, Cashy J, Webster K, Cella D. General Population and Cancer Patient Norms for the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (FACT-G). Eval Health Prof. 2005;28(2):192–211. doi: 10.1177/0163278705275341 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Eton DT, Cella D, Yost KJ, et al. A combination of distribution- and anchor-based approaches determined minimally important differences (MIDs) for four endpoints in a breast cancer scale. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57(9):898–910. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yost KJ, Cella D, Chawla A, et al. Minimally important differences were estimated for the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Colorectal (FACT-C) instrument using a combination of distribution- and anchor-based approaches. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(12):1241–1251. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.07.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cella D, Eton DT, Fairclough DL, et al. What is a clinically meaningful change on the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Lung (FACT-L) Questionnaire?: Results from Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Study 5592. J Clin Epidemiol. 2002;55(3):285–295. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(01)00477-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cella D, Nichol MB, Eton D, Nelson JB, Mulani P. Estimating Clinically Meaningful Changes for the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy—Prostate: Results from a Clinical Trial of Patients with Metastatic Hormone-Refractory Prostate Cancer. Value Health. 2009;12(1):124–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2008.00409.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Textor J, van der Zander B, Gilthorpe MS, Liśkiewicz M, Ellison GT. Robust causal inference using directed acyclic graphs: the R package ‘dagitty.’ Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1887–1894. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyw341 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hicks R, Tingley D. mediation: Stata package for causal mediation analysis. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Imai K, Keele L, Tingley D. A general approach to causal mediation analysis. Psychol Methods. 2010;15(4):309–334. doi: 10.1037/a0020761 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Imai K, Keele L, Tingley D, Yamamoto T. Causal Mediation Analysis Using R In: Advances in Social Science Research Using R. Lecture Notes in Statistics. Springer, New York, NY; 2010:129–154. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1764-5_8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Imai K, Keele L, Yamamoto T. Identification, Inference and Sensitivity Analysis for Causal Mediation Effects. Stat Sci. 2010;25(1):51–71. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mediation (David A. Kenny). http://davidakenny.net/cm/mediate.htm#CI. Accessed April 24, 2018.
- 37.Imai K, Keele L, Tingley D, Yamamoto T. Unpacking the Black Box of Causality: Learning about Causal Mechanisms from Experimental and Observational Studies. Am Polit Sci Rev. 2011;105(4):765–789. doi: 10.1017/S0003055411000414 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Webster K, Cella D, Yost K. The F unctional A ssessment of C hronic I llness T herapy (FACIT) Measurement System: properties, applications, and interpretation. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2003;1:79. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-1-79 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jagsi R, Pottow JAE, Griffith KA, et al. Long-Term Financial Burden of Breast Cancer: Experiences of a Diverse Cohort of Survivors Identified Through Population-Based Registries. J Clin Oncol. March 2014:JCO.2013.53.0956. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.53.0956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pisu M, Kenzik KM, Oster RA, et al. Economic hardship of minority and non-minority cancer survivors 1 year after diagnosis: Another long-term effect of cancer? Cancer. 2015;121(8):1257–1264. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Health Insurance Coverage Eight Years After the ACA — 2018 Biennial ∣ Commonwealth Fund. doi: 10.26099/penv-q932 [DOI]
- 42.Narang AK, Nicholas LH. Out-of-Pocket Spending and Financial Burden Among Medicare Beneficiaries With Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(6):757–765. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.4865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bullock AJ, Hofstatter EW, Yushak ML, Buss MK. Understanding Patients’ Attitudes Toward Communication About the Cost of Cancer Care. J Oncol Pract. 2012;8(4):e50–e58. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2011.000418 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kelly RJ, Forde PM, Elnahal SM, Forastiere AA, Rosner GL, Smith TJ. Patients and Physicians Can Discuss Costs of Cancer Treatment in the Clinic. J Oncol Pract. 2015;11(4):308–312. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2015.003780 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hamel LM, Penner LA, Eggly S, et al. Do Patients and Oncologists Discuss the Cost of Cancer Treatment? An Observational Study of Clinical Interactions Between African American Patients and Their Oncologists. J Oncol Pract. December 2016:JOP.2016.015859. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2016.015859 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ubel PA, Abernethy AP, Zafar SY. Full Disclosure — Out-of-Pocket Costs as Side Effects. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(16):1484–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1306826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schnipper LE, Davidson NE, Wollins DS, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology Statement: A Conceptual Framework to Assess the Value of Cancer Treatment Options. J Clin Oncol. June 2015:JCO.2015.61.6706. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.61.6706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Meropol NJ, Schrag D, Smith TJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology Guidance Statement: The Cost of Cancer Care. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(23):3868–3874. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.1183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Smith SK, Nicolla J, Zafar SY. Bridging the Gap Between Financial Distress and Available Resources for Patients With Cancer: A Qualitative Study. J Oncol Pract. May 2014:JOP.2013.001342. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2013.001342 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schnipper LE, Davidson NE, Wollins DS, et al. Updating the American Society of Clinical Oncology Value Framework: Revisions and Reflections in Response to Comments Received. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2925–2934. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.2518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yousuf Zafar S Financial Toxicity of Cancer Care: It’s Time to Intervene. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016;108(5). doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv370 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.