Abstract
Background
Haworthia are desert succulents belonging to the Asphodelaceae family. Haworthia species are cultivated commercially as ornamentals and some rare species are quite valuable at retail market but growth slowly and difficult to propagation. However, an efficient micropropagation protocol was remained insufficient.
Results
The organogenic cultures obtained from inflorescence explants were cultured on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with various combinations of 6-benzylaminopurine (BA) and α-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) under a light intensity of 10 μmol m−2 s−1 or 45 μmol m−2 s−1. The highest callus proliferation index (93.15%) with 1.0 mg L−1 BA + 0.1 mg L−1 NAA under a light intensity of 10 μmol m−2 s−1. The best shoot proliferation rates were on media with either 1 mg L−1 BA + 0–0.4 mg L−1 NAA (65.57–81.01%) under a light intensity of 45 μmol m−2 s−1. The highest root length (15.57 mm) and the highest rooting frequency (17 roots per shoot) were obtained when adventitious shoots were inoculated on MS medium with 0.4 mg L−1 NAA + 0.4 mg L−1 IBA. The survival rate of the transplanted plantlets was about 100%. The efficient micropropagation protocol proliferated Haworthia regenerate plants from inflorescence within 11 weeks.
Conclusions
The present study determined the best combination of light intensity and plant growth regulators (PGRs) for improved organogenesis of Haworthia during propagation by tissue culture. This optimized protocol showed light intensity is an important factor for efficient callus or shoot regeneration. These results indicate that it will be useful to optimize the light conditions for future commercial cultivation, germplasm conservation, genetic engineering and molecular biology research of this ornamental plant.
Keywords: Haworthia, Inflorescence explants, 6-Benzylaminopurine, α-Naphthalene acetic acid, Callus, Shoot, Light intensity
Background
Plants in the genus Haworthia are perennial, monocotyledonous, desert succulents belonging to the Asphodelaceae family. Species in the genus are distributed in Southeast Africa, Namibia and Madagascar. Haworthia species are cultivated commercially as ornamentals, while rare species are of interest to collectors (Bayer 1982). Some rare species are quite valuable, but growth slowly and difficult to propagation. In the retail market, the price of Haworthia specimen are determined by their population, shapes of leaf window, leaf stripe, or leaf variegation.
Traditionally, Haworthia species are propagated from seed, leaf cutting, crown division, or the propagules produced on the inflorescence (Pilbeam 1983), all of require time. In recent years, micropropagation has been shown to have a vast potential for quickening the propagation time for species in many succulent genera, including Notocactus (Seol et al. 2008), Cotyledon (Kumari et al. 2016), Pelecyphora (Badalamenti et al. 2016), Kalanchoe (Jaiswal and Sawhney 2006) and Aloe (Bairu et al. 2007). Micropropagation has also been used to aid in the reproduction of some self-incompatible Haworthia species (Mycock et al. 1997), through inducing regeneration from leaves (Beyl and Sharma 1983; Rogers 1993), inflorescences (Kaul and Sabharwal 1972; Majumdar 1970a) and ovary walls (Majumdar 1970b).
Micropropagation efficiency or success rate is affected by various factors, such as explant type, nutrients, plant growth regulators and other additives, temperature, and light intensity and duration. Haworthia callus have been induced from leaf segments, inflorescence segments, or flower buds (Kaul and Sabharwal 1972; Ogihara 1978). The in vitro growth characteristics of some Haworthia species have been examined in response to different medium supplements, such as auxins (IAA, NAA, 2,4-D) (Kaul and Sabharwal 1972; Ogihara 1978, 1979), cytokinins (BA, kinetin, zeatin) (Kaul and Sabharwal 1972; Ogihara 1979; Richwine et al. 1995; Rogers 1993), defoliants (thidiazuron) (Liu et al. 2017), casein hydrolysate (Kaul and Sabharwal 1972), coconut milk (Kaul and Sabharwal 1972) and inositol (Kaul and Sabharwal 1975). The effect of light intensity on in vitro shoot proliferation of Haworthia species has not been reported.
Light is one of the important environmental factors that controls plant growth, development, morphogenesis, metabolism and chlorophyll content in plant cell, tissue and organ cultures (Dou et al. 2017). Light intensity and light source are important parameters that influence shoot regeneration, fresh weight, and secondary metabolite biosynthesis during micropropagation in a variety of crops, including Persian shallot (Farhadi et al. 2017), cauliflower (Kumar et al. 1993), date palm (Meziani et al. 2015) and Cistanche (Ouyang et al. 2003). Light can also influence the efficacy of plant growth regulators (PGRs) as well as adjustment of endogenous hormone levels. Recent studies have resolved the light regulation of gibberellin and auxin metabolism (García-Martinez and Gil 2001; Halliday et al. 2009; Stavang et al. 2007).
To establish a highly productive and rapid in vitro plant regeneration system for Haworthia spp., the inflorescence of the Haworthia cultivar ‘Sansenjyu’ were excised for micropropagation. Besides growth regulators, light intensity was another important factor to improve the regeneration efficiency. An efficient regeneration system will be useful for future commercial cultivation and biology research of this ornamental crop, and be a foundation for regeneration system of succulent plants.
Methods
Plant material, primary culture medium and conditions
Soil-grown, adult Haworthia ‘Sansenjyu’ (H. obtusa × H. comptoniana) plants were obtained from Guoguang flower market in Taichung Taiwan. The plants were maintained at 25/30 °C night/day temperatures in a greenhouse under a 12-h/12-h photoperiod. Inflorescences were excised from healthy plants and were surface-sterilized first with 70% ethanol for 60 s and then with 0.6% sodium hypochlorite containing 1 drop of Tween 20 per 100 ml solution for 20 min. The explants were then rinsed five times with sterile, distilled water. The disinfected pedicels were then cut into 5-mm segments and inoculated on callus induction medium, which consisted of Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium (Murashige and Skoog 1962) supplemented with 30 g L−1 sucrose, 0.1 g L−1 myo-inositol, 2 mg L−1 6-benzylaminopurine (BA), 0.2 mg L−1 α-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA), and solidified with 0.8% agar. The chemicals or plant growth regulators were analytical grade (Duchefa Biochemie). All media were adjusted to pH 5.7 with 1 N NaOH or 1 N HCl before autoclaving at 121 °C and 103 kPa for 20 min. The cultures were maintained at a temperature of 26 °C and a light intensity of 45 μmol m−2 s−1 provided by cool white fluorescent light with a 16-h photoperiod. The percentage of explants producing callus tissue was recorded after 8 weeks. Calli were then used for callus propagation and plant regeneration.
Callus propagation, adventitious shoot regeneration and light conditions
The callus that developed from the inflorescence explants was separated into small pieces (≈ 50 mg) and transferred onto MS basal medium supplemented with different concentrations of BA (0, 1, 2, or 4 mg L−1) and NAA (0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1) for callus propagation and adventitious shoot initiation. Cultures were maintained in light at an intensity of 10 μmol m−2 s−1 or 45 μmol m−2 s−1 at 26 °C under a 16-h photoperiod. After 8 weeks, the weight of the callus, the number of adventitious shoots, and the browning rate of the callus were measured. Each experiment was repeated five times, each using 15 replicates (i.e., a total of 75 explants per treatment).
Root induction and plantlet acclimatization
For root induction, excised shoots (2–3 cm) were transferred to MS basal medium supplemented with different concentrations of NAA (0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1) or indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) (0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1). The cultures were maintained at a temperature of 26 °C and a light intensity of 45 μmol m−2 s−1. The root length and number of shoots were measured after 4 weeks. Each experiment was repeated five times. For plant acclimatization, rooted plantlets were carefully transferred to 9-cm pots containing a 1:1:1 mixture of perlite, vermiculite and perlite and placed in a growth chamber under a 16-h photoperiod at 90% humidity under a day/night temperature regime of 26 °C.
Statistical analysis
The experimental data were analyzed statistically by SAS 9.4 (Statistics Analysis System) software. Data on the effects of the hormone treatments at various concentrations and combinations were tested using least significant difference (LSD).
Results
Callus induction and morphogenesis in vitro
The inflorescence of H. obtusa × comptoniana ‘Sansenjyu’ were easy to collect, without harm to the mother plants, and to sterilize. On the basic callus induction medium, friable calli started to form at the cut edges of the inflorescence after 2 weeks (Fig. 1a). The green and compact embryogenic calli were observed on most of the explants within 3 weeks (Fig. 1b). Numerous globular stage and heart stage somatic embryos were visible all around the surface of the embryogenic callus after 4 weeks (Fig. 1c, d). Shoot differentiation and formation began after 5 weeks (Fig. 1e), and adventitious shoots were observed with normal green leaves after 7 weeks (Fig. 1f). Roots were formed 4 weeks after explants transferred to root induction medium (Fig. 1g), and grown in a perlite, vermiculite and soil mixture (Fig. 1h).
Fig. 1.
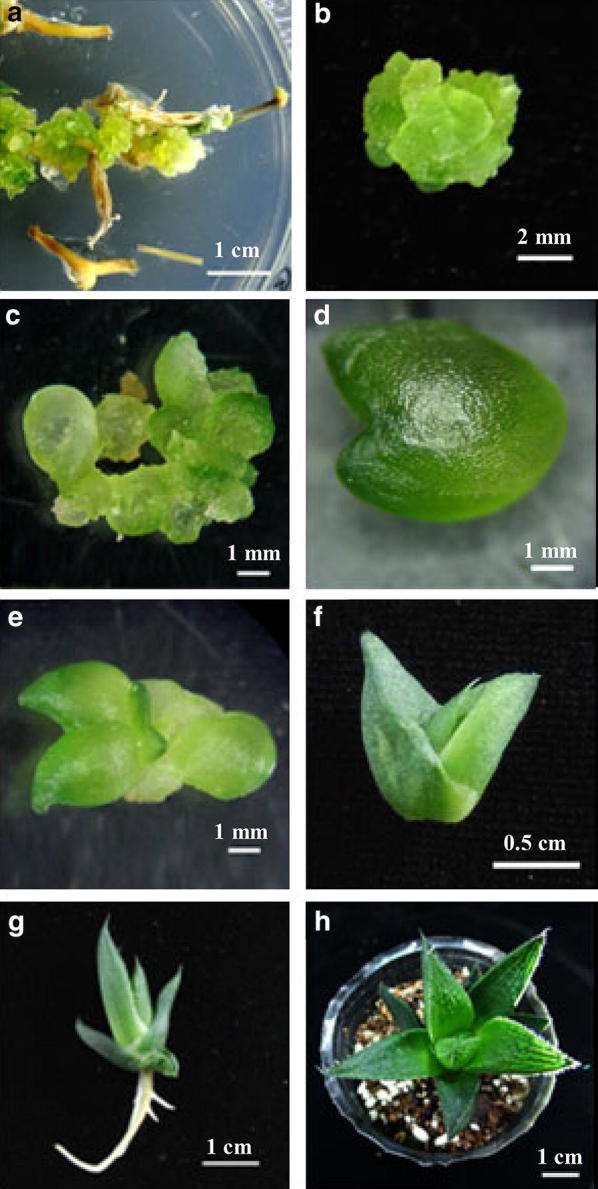

Somatic embryogenesis in Haworthia ‘Sansenjyu’ calli. a Calli initiation from inflorescences, b embryogenic calli, c globular stage somatic embryo, d heart stage somatic embryo, e shoot formation, f plantlet, g root formation, and h acclimated plant
Effect of growth regulators and light intensity on callus proliferation
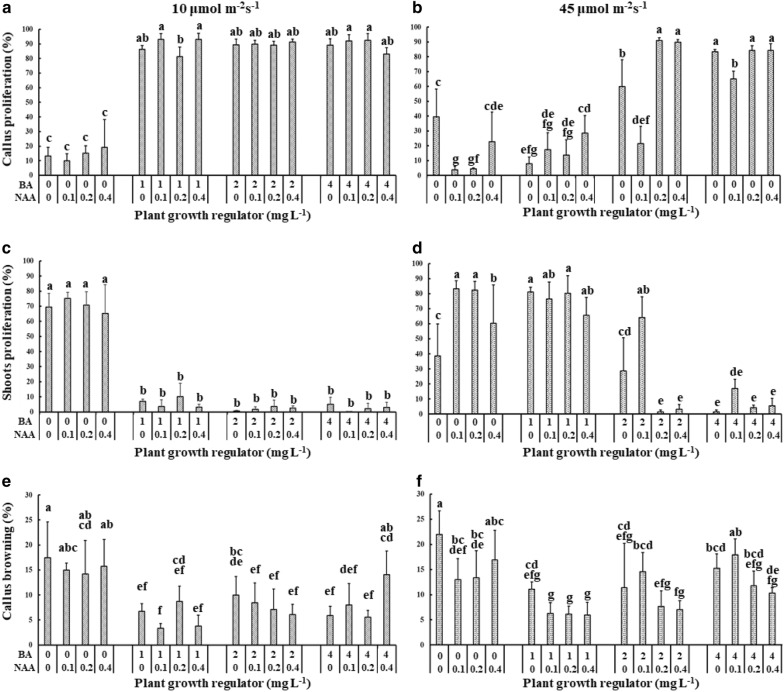
A total of 16 different medium combinations were tested under two different light intensities. The highest rates of callus proliferation were recorded when the initial callus pieces were placed on media containing 1 to 4 mg L−1 BA + 0 to 0.4 mg L−1 NAA under a light intensity of 10 μmol m−2 s−1. Under these conditions, the callus proliferation rate ranged from 81.22 to 93.15% (Fig. 2a). The lowest callus proliferation rates were observed on media containing 1 mg L−1 BA + 0 to 0.4 mg L−1 NAA media under a light intensity of 45 μmol m−2 s−1 (7.9 to 28.48%; Fig. 2b). Under the higher light intensity, callus proliferated better on medium containing 2 to 4 mg L−1 BA + 0 to 0.4 mg L−1 NAA, except on media containing 2 mg L−1 BA + 0.1 mg L−1 NAA (Fig. 2b). The results showed that a light intensity of 10 μmol m−2 s−1 was optimal for attaining proliferated callus and is more forgiving across a range of PGR combinations. The most cost-effective PGR combination with a high proliferation rate was 1 mg L−1 BA + 0.1 mg L−1 NAA.
Fig. 2.
Effect of light intensity on in vitro proliferation of Haworthia ‘Sansenjyu’. The percentage of callus proliferation (a, b), shoot proliferation (c, d) and callus browning (e, f) under 10 μmol m−2 s−1 or 45 μmol m−2 s−1 light intensities
Effect of growth regulators and light intensity on adventitious shoot initiation
Shoot proliferation ratios also varied with light intensity. Under 10 μmol m−2 s−1 light intensity, shoot proliferation was better on medium without BA, and ranged from 65.14 to 75.11%. The shoot proliferation rate was lower than 4.99% when the medium contained 1 mg L−1 or more BA (Fig. 1c). Under 45 μmol m−2 s−1 light intensity, shoot proliferation showed relatively higher rates on 0 to 1 mg L−1 BA + 0 to 0.4 mg L−1 NAA medium, reaching the highest rate of 83.15%. Shoot proliferation decreased as the BA concentration increased (Fig. 1d). Our results demonstrated that higher light intensity caused a slight increase in the shoot proliferation.
The browning rate of the callus ranged from 3 to 22%. The highest rate of browning occurred on media containing 0 mg L−1 BA + 0 to 0.4 mg L−1 NAA under both light intensities (Fig. 2e, f). This further showed that BA is essential in callus medium for reducing callus browning. The callus browning rates were higher under the stronger light intensity (Fig. 2e, f). Our experiment proved that 10 μmol m−2 s−1 is the optimal incubation light intensity for attaining fully proliferated callus.
Effect of auxins on rooting and acclimatization
Well-developed, regenerated individual Haworthia shoots (2 to 3 cm in height) from the multiplication stage were excised from the callus and transferred to root induction medium. Within 4 weeks, all shoots developed roots on MS media with or without plant growth regulators (Fig. 3). Out of the different IBA + NAA concentrations tested, the longest roots (15.57 mm) and highest rooting frequency (17 roots per shoot) were obtained after placing the shoots on MS medium supplemented with 0.4 mg L− NAA + 0.4 mg L−1 IBA (Table 1 and 2). In general, root numbers increased with increasing NAA concentration (Table 2). The well-rooted plantlets were acclimated in a 1:1:1 (v/v) vermiculite: perlite: soil growing media under greenhouse conditions, with a 100% survival rate (Fig. 4a). The ex vitro rooting and hardening process was achieved concurrently with 100% success in the greenhouse (Fig. 4b).
Fig. 3.
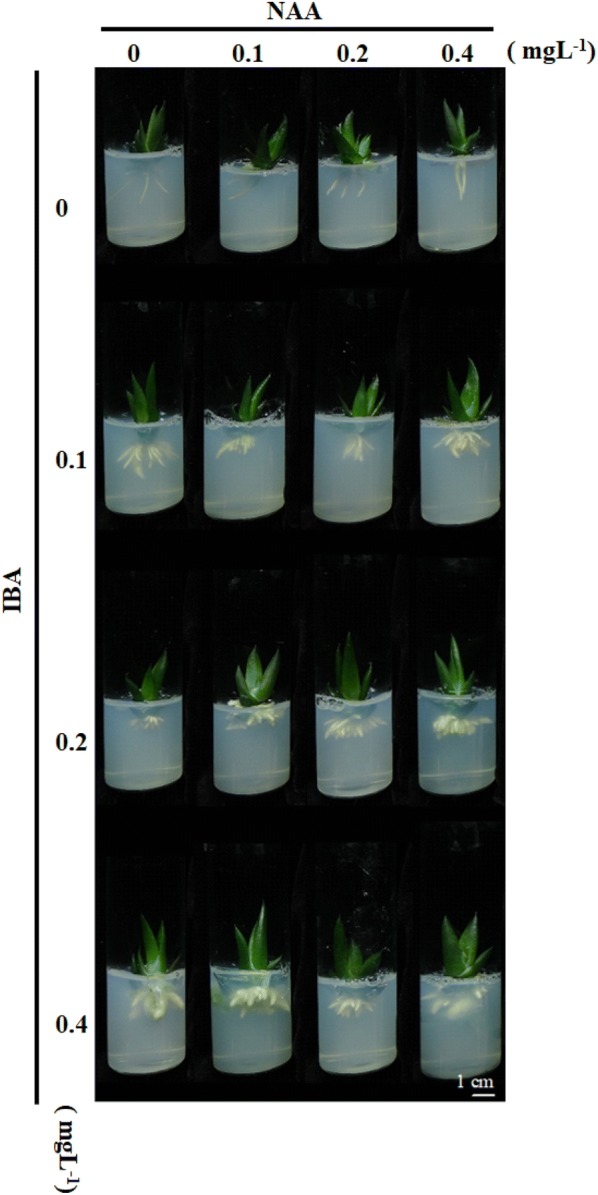
Haworthia ‘Sansenjyu’ root formation during cultivation on different concentrations of NAA and IBA for 4 weeks. MS medium contained combinations of 0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1 NAA and 0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1 IBA
Table 1.
Haworthia ‘Sansenjyu’ root length after cultivation in MS medium with different concentrations of NAA and IBA for 4 weeks
| NAA (mg L−1) | IBA (mg L−1) | Root length (mm)* |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 16.87 ± 5.65abcd |
| 0 | 0.1 | 14.37 ± 2.3abcdef |
| 0 | 0.2 | 11.32 ± 1.58bcdefghij |
| 0 | 0.4 | 10.17 ± 2.1defghij |
| 0.1 | 0 | 10.52 ± 3.85cdefghij |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 11.95 ± 2.65abcdefghij |
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 11.43 ± 2.02bcdefghij |
| 0.1 | 0.4 | 7.09 ± 0.82ghij |
| 0.2 | 0 | 5.74 ± 0.5ij |
| 0.2 | 0.1 | 12.33 ± 1.72abcdefghi |
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 9.68 ± 1.34efghij |
| 0.2 | 0.4 | 14.37 ± 1.44abcdef |
| 0.4 | 0 | 13.27 ± 5.29abcdefgh |
| 0.4 | 0.1 | 14.17 ± 1.12abcdef |
| 0.4 | 0.2 | 10.72 ± 1.31bcdefghij |
| 0.4 | 0.4 | 15.57 ± 4.36abcde |
MS medium contained combinations of 0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1 NAA and 0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1 IBA. n = 5
*Different letters in each column indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. Data were analyzed with LSD using the SAS 9.4 program
Table 2.
Haworthia ‘Sansenjyu’ root formation after cultivation on MS medium with different concentrations of NAA and IBA for 4 weeks
| NAA (mg L−1) | IBA (mg L−1) | Root number* |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3.00 ± 0.82ijk |
| 0 | 0.1 | 2.00 ± 0.82jk |
| 0 | 0.2 | 5.33 ± 0.94fghijk |
| 0 | 0.4 | 1.67 ± 0.47jk |
| 0.1 | 0 | 11.67 ± 2.05abcde |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 9.67 ± 3.09cdefg |
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 8.33 ± 2.05defghi |
| 0.1 | 0.4 | 5.67 ± 2.87fghijk |
| 0.2 | 0 | 10.00 ± 3.56cdefg |
| 0.2 | 0.1 | 14.67 ± 1.70abc |
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 13.67 ± 3.40abcd |
| 0.2 | 0.4 | 13.67 ± 4.50abcd |
| 0.4 | 0 | 9.00 ± 3.74cdefgh |
| 0.4 | 0.1 | 14.67 ± 2.87abc |
| 0.4 | 0.2 | 16.67 ± 4.78ab |
| 0.4 | 0.4 | 17.00 ± 4.32a |
MS medium contained a combination of 0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1 NAA and 0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg L−1. n = 5
*Different letters in each column indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. Data were analyzed with LSD using the SAS 9.4 program
Fig. 4.
Haworthia ‘Sansenjyu’ plantlets (a) grown in a vermiculite, perlite and soil mixture under greenhouse conditions after 4 weeks, and (b) the root regeneration
Discussion
The use of micropropagation for the improvement and propagation of Haworthia species has received little research attention. In plants, growth regulators play essential roles in controlling the growth and development. Supplementation of tissue culture media with some plant growth regulators is essential. Auxins are the main hormones responsible for stem elongation, phototropism, vascular tissue differentiation, and cell expansion in plant developmental processes and are sensitive to higher light intensity (Vanneste and Friml 2009). Cytokinins are required, in concert with auxin, for cell division in a wide variety of plant tissue cultures (D’Agostino and Kieber 1999; Dewitte et al. 1999). Cytokinins can promote stem elongation in light-grown plants (Lin and Cheng 1997; Smets et al. 2005). During tissue culture, factors including auxins, cytokinins, light and temperature influence callus induction, and at suboptimal concentrations and combinations can cause callus browning and necrosis (Afshari et al. 2011; Dou et al. 2017; Ikeuchi et al. 2013).
The present study describes the development of an efficient and reliable system for both callus and shoot proliferation from Haworthia explants derived from inflorescence. For a reliable proliferation system, both efficient and specific induction of callus amplification and shoot regeneration are essential. The combinations of 1 to 4 mg L−1 BA and 0 to 0.4 mg L−1 NAA under a light intensity of 10 μmol m−2 s−1 were found to be effective for callus proliferation (Fig. 2a). The reason for this enhanced callus proliferation may lay in the fact that natural auxin levels increase under lower light intensity or darkness (Chory et al. 1994). Higher BA concentrations were necessary for better callus proliferation under a higher light intensity (Fig. 2b).
An increased rate of callus browning was observed under the higher light intensity (Fig. 2e, f). Callus browning is caused by poly-phenolic compounds present when the explants were wounded and the enzymatic browning reaction of phenolic compounds, oxidized by polyphenol oxidase, peroxidise or exposure to air (Taranto et al. 2017). The oxidation process of phenolic compounds is enhanced by light, (Taranto et al. 2017). Therefore, the inflorescence-derived callus showed higher browning rate and darker browning color under a higher light intensity.
An efficient adventitious shoot regeneration system from direct or indirect organogenesis is an essential method for producing a large number of elite genotypes and avoiding somaclones. Multiple adventitious shoots were proliferated from calli under a higher light intensity (Fig. 2d). Light intensity or quality-dependent changes in plant physiology and morphogenesis are regulated by plant hormones (Afshari et al. 2011; Dietz 2015; Kissoudis et al. 2017). This result may be due to the interaction between light intensity, endogenous auxin and endogenous cytokinins, which directly or indirectly affect shoot proliferation.
In general, root induction can be initiated by adding auxins such as NAA, IBA,
and IAA (Sauer et al. 2013). Previous studies have reported the auxin requirements for Haworthia species such as H. turgida (Liu et al. 2017), H. retusa (Kim et al. 2018; Suzanne 1993), H. attenuata (Richwine et al. 1995) and H. turgida var. although the proliferation ability (Majumdar 1970b) for inducing adventitious root formation. A significantly higher rate of rooting (17 roots per explant; with an average root length of 15.57 mm) occurred in this study by using MS medium supplemented with 0.4 mg L−1 NAA + 0.4 mg L−1 IBA (Table 1 and Table 2). Root thickness increased with increasing IBA concentration (Fig. 3). However, in our experiments, plantlets could grow well after transfer to the greenhouse even if they had only a few roots.
A proliferation system for Haworthia planifolia var. setulifera (Albany Division) had been established from callus induced from leaf tissue and subsequent shoot and root differentiation. The calli were induced from leaf segments after 16 weeks, and the regenerated plants were obtained around 39 weeks later (Wessels et al. 1976). The inflorescence is another widely used tissue for micropropagation, and similar observations have been reported with inflorescences for several plants, e.g. Aranda orchid (Goh and Wong 1990), Elaeis (Jayanthi et al. 2015), Aloe (Rathore et al. 2011), Musa AAA (Pérez-Hernández and Rosell-García 2008), Amaranthus (Arya et al. 1993) and Spathiphyllum (Fonnesbech and Fonnesbech 1979). In this research, rapid proliferation, within 11 weeks, was achieved using inflorescence-derived calli and by optimizing plant growth regulators and light intensity for the Haworthia cultivar ‘Sansenjyu’ (H. obtusa × comptoniana). The increased multiplication rate and cost-effective, easy acclimatization process make this protocol highly advantageous. This method could be tried on different Haworthia species, although the proliferation ability and regeneration speed of different selections could be various and should be examined individually. Our data indicated that light intensity is an important factor in determining micropropagation efficiency. Furthermore, these results could promote research on the physiology, genetic engineering, and molecular biology of the Haworthia genus.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
Y-MC conceived the original idea, carried out the experiments, and supported the project. J-ZH designed experiments and wrote the manuscript. T-WH carried out the experiments and analyzed the data. I-CP managed project and all results, and contributed to the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (No. MOST 107-2313-B-005 -015 -MY3) and the Council of Agriculture, Agriculture and Food Agency (107AS-7.4.1-FD-Z1), Taiwan.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- Afshari R, Angoshtari R, Kalantari S. Effects of light and different plant growth regulators on induction of callus growth in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) genotypes. Plant Omics. 2011;4:60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Arya ID, Chakravarty TN, Sopory SK. Development of secondary inflorescences and in vitro plantlets from inflorescence cultures of Amaranthus paniculatus. Plant Cell Rep. 1993;12:286–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00237137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badalamenti O, Carra A, Oddo E, Carimi F, Sajeva M. Is in vitro micrografting a possible valid alternative to traditional micropropagation in Cactaceae? Pelecyphora aselliformis as a case study. SpringerPlus. 2016;5:201. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-1901-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairu MW, Stirk WA, Dolezal K, Van Staden J. Optimizing the micropropagation protocol for the endangered Aloe polyphylla: can meta-topolin and its derivatives serve as replacement for benzyladenine and zeatin? Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult. 2007;90:15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer MB. The new Haworthia handbook. Capetown: Cape and Transvaal Printers; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Beyl CA, Sharma GC. Picloram induced somatic embryogenesis in Gasteria and Haworthia. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult. 1983;2:123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chory J, Reinecke D, Sim S, Washburn T, Brenner M. A role for cytokinins in de-etiolation in Arabidopsis (det mutants have an altered response to cytokinins) Plant Physiol. 1994;104:339–347. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino IB, Kieber JJ. Molecular mechanisms of cytokinin action. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 1999;2:359–364. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(99)00005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewitte W, Chiappetta A, Azmi A, Witters E, Strnad M, Rembur J, Noin M, Chriqui D, Van Onckelen H. Dynamics of cytokinins in apical shoot meristems of a Day-Neutral tobacco during floral transition and flower formation. Plant Physiol. 1999;119:111–122. doi: 10.1104/pp.119.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz KJ. Efficient high light acclimation involves rapid processes at multiple mechanistic levels. J Exp Bot. 2015;66:2401–2414. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou H, Niu G, Gu M, Masabni JG. Effects of light quality on growth and phytonutrient accumulation of herbs under controlled Environments. Horticulturae. 2017;3:36. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadi N, Panahandeh J, Azar AM, Salte SA. Effects of explant type, growth regulators and light intensity on callus induction and plant regeneration in four ecotypes of Persian shallot (Allium hirtifolium) Sci Hortic. 2017;218:80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fonnesbech M, Fonnesbech A. In vitro propagation of Spathiphyllum. Sci Hortic. 1979;10:21–25. [Google Scholar]
- García-Martinez JL, Gil J. Light regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis and mode of action. J Plant Growth Regul. 2001;20:354–368. doi: 10.1007/s003440010033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh CJ, Wong PF. Micropropagation of the monopodial orchid hybrid Aranda ‘Deborah’ using inflorescence explants. Sci Hortic. 1990;44:315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Halliday KJ, Martínez-García JF, Josse EM. Integration of light and auxin signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009;1:a001586–a001586. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi M, Sugimoto K, Iwase A. Plant callus: mechanisms of induction and repression. Plant Cell. 2013;25:3159–3173. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.116053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal S, Sawhney S. Modulation of TDZ-induced morphogenetic responses by anti-auxin TIBA in bud-bearing foliar explants of Kalanchoe pinnata. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult. 2006;86:69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jayanthi M, Susanthi B, Mohan NM, Mandal PK. In vitro somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from immature male inflorescence of adult dura and tenera palms of Elaeis guineensis (Jacq.) SpringerPlus. 2015;4:256. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1025-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul K, Sabharwal PS. Morphogenetic studies on Haworthia: establishment of tissue culture and control of differentiation. Am J Bot. 1972;59:377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Kaul K, Sabharwal PS. Morphogenetic studies on Haworthia: effects of inositol on growth and differentiation. Am J Bot. 1975;62:655–659. [Google Scholar]
- Kim DH, Kang KW, Sivanesan I. Influence of auxins on somatic embryogenesis in Haworthia retusa Duval. Biologia. 2018;74:25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kissoudis C, Seifi A, Yan Z, Islam ATMT, Van der Schoot H, Van de Wiel CCM, Visser RGF, Van der Linden CG, Bai Y. Ethylene and abscisic acid signaling pathways differentially influence tomato resistance to combined powdery mildew and salt stress. Front Plant Sci. 2017;7:2009. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.02009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A, Kumar VA, Kumar J. Rapid in vitro propagation of cauliflower. Plant Sci. 1993;90:175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari A, Baskaran P, Van Staden J. In vitro propagation and antibacterial activity in Cotyledon orbiculata: a valuable medicinal plant. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2016;124:97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y, Cheng CL. A chlorate-resistant mutant defective in the regulation of nitrate reductase gene expression in Arabidopsis defines a new HY locus. Plant Cell. 1997;9:21–35. doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu BL, Fang HZ, Meng CR, Chen M, Chai QD, Zhang K, Liu SJ. Establishment of a rapid and efficient micropropagation system for succulent plant Haworthia turgida Haw. HortScience. 2017;52:1278–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar SK. Culture of Haworthia inflorescences in vitro. J South Afr Bot. 1970;36:63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar SK. Production of plantlets from the ovary wall of Haworthia turgida var. pallidifolia. Planta. 1970;90:212–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00388049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meziani R, Jaiti F, Mazri MA, Anjarne M, Chitt MA, El Fadile J, Alem C. Effects of plant growth regulators and light intensity on the micropropagation of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) cv. Mejhoul. J Crop Sci Biotechnol. 2015;18:325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Murashige T, Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant. 1962;115:493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Mycock DJ, Watt MP, Hannweg KF, Naicker K, Makwarela M, Berjak P. Somatic embryogenesis of two indigenous South African Haworthia spp. (H. limifolia and H. koelmaniorum) S Afr J Bot. 1997;63:345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara YTK. Tissue culture in Haworthia. I. Effects of auxins and kinetin on callus growth. Bot Mag Jpn. 1978;91:83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara Y. Tissue culture in Haworthia 2. effects of 3 auxins and kinetin on greening and re differentiation of calluses. Bot Mag Tokyo. 1979;92:163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang J, Wang X, Zhao B, Wang Y. Light intensity and spectral quality influencing the callus growth of Cistanche deserticola and biosynthesis of phenylethanoid glycosides. Plant Sci. 2003;165:657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Hernández JB, Rosell-García P. Inflorescence proliferation for somatic embryogenesis induction and suspension-derived plant regeneration from banana (Musa AAA, cv. ‘Dwarf Cavendish’) male flowers. Plant Cell Rep. 2008;27:965–971. doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilbeam J. Haworthia and Astroloba: a collector’s guide. London: B.T. Batsford; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Rathore MS, Chikara J, Shekhawat NS. Plantlet Regeneration from callus cultures of selected genotype of Aloe vera L.—an ancient plant for modern herbal industries. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2011;163:860–868. doi: 10.1007/s12010-010-9090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richwine AM, Tipton JL, Thompson GA. Establishment of Aloe, Gasteria, and Haworthia shoot cultures from inflorescence explants. Hortscience. 1995;30:1443–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers SMD. Optimization of plant regeneration and rooting from leaf explants of five rare Haworthia. Sci Hortic. 1993;56:157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer M, Robert S, Kleine-Vehn J. Auxin: simply complicated. J Exp Bot. 2013;64:2565–2577. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seol E, Jung Y, Lee J, Cho C, Kim T, Rhee Y, Lee S. In planta transformation of Notocactus scopa cv. Soonjung by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep. 2008;27:1197–1206. doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0540-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smets R, Le J, Prinsen E, Verbelen JP, Van Onckelen HA. Cytokinin-induced hypocotyl elongation in light-grown Arabidopsis plants with inhibited ethylene action or indole-3-acetic acid transport. Planta. 2005;221:39–47. doi: 10.1007/s00425-004-1421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavang JA, Moe R, Olsen JE, Junttila O. Differential temperature regulation of GA metabolism in light and darkness in pea. J Exp Bot. 2007;58:3061–3069. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzanne MDR. Culture phenotype affects on regeneration capacity in the monocot Haworthia comptoniana. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant. 1993;29P:9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Taranto F, Pasqualone A, Mangini G, Tripodi P, Miazzi MM, Pavan S, Montemurro C. Polyphenol oxidases in crops: biochemical, physiological and genetic aspects. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:377. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanneste S, Friml J. Auxin: a trigger for change in plant development. Cell. 2009;136:1005–1016. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels JGH, Hoeksema HL, Stemerding D. Reversion of protoplasts from dikaryotic mycelium of Schizophyllum commune. Protoplasma. 1976;89:317–321. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.