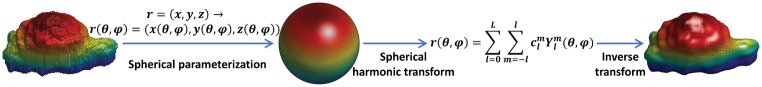
Fig. 1.
Illustration of Shape modeling using Spherical Harmonic transform. In the first step, the 3D surface mesh is mapped to a unit sphere. This results in spherical coordinates for each vertex in the original mesh. The spherical harmonic transform is then performed to get coefficients to represent the surface. A reconstruction of the original 3D surface mesh can be obtained by inverse transform followed by reversing the mapping