Abstract
Background
Current drug regimens for cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) include toxic systemic therapies such as amphotericin B (AB) and pentavalent antimonials. Fluconazole (FZ) is a well-tolerated potential oral alternative for the management CL. To date, few objective data exist to guide clinical decision-making when selecting a therapeutic agent a priori, and standardized, clinically-approved drug susceptibility testing platforms for Leishmania spp. have yet to be established. The Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 plate is a commercialized drug susceptibility plate including AB and FZ used for routine testing of non-fastidious yeast. Our objective was to adapt the readily available Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 plate, to determine drug susceptibility profiles of AB and FZ in cultured isolates of Old World and New World Leishmania spp. for the treatment of CL.
Methods
Promastigotes were cultured in Tobie’s medium with Locke’s overlay until log phase growth was achieved, inoculated into the Sensititre™ system, and incubated over 96 H. minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined colorimetrically, and promastigote death was assessed by conventional microscopy out to 96- h. Colour change correlated to MIC values.
Results
All strains tested exhibited MIC values for FZ that were ≥ 256 μg/mL. New World strains demonstrated reduced susceptibility to AB (0.25 μg/mL – 0.50 μg/mL AB) compared to Old World strains at 0.12 μg/mL AB (p = 0.02). Seventeen (61%) of 28 Viannia isolates versus 82% (27/33) of non-Viannia isolates were resistant at 0.12 μg/mL AB (p = 0.09). For L. V. braziliensis isolates, mean MIC for AB was 0.375 ± 0.14 μg/mL (range 0.25–0.50 μg/mL), while for isolates of L. V. panamensis it was 0.314 ± 0.26 μg/mL (range 0.12–1.0 μg/mL).
Conclusions
We adapted the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 plate for testing of Leishmania spp. susceptibility profiles for commonly used antifungals in the treatment of CL, including AB and FZ. Given its current utility in mycology, optimization of the system for potential clinical implementation in parasitology should be pursued. However evaluation of clinically relevant amastigote-stage stages, and higher concentrations of FZ beyond the upper limit concentration of the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ Y09 plate would be required.
Keywords: Leishmania, Drug susceptibility, Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9, Amphotericin B, Fluconazole, Azole antifungals
Background
Leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Leishmania, affects millions of the world’s poorest, and is ranked among the top three most common travel acquired dermatoses [1, 2]. Parenteral drugs available in North America include formulations of Amphotericin B (AB), pentavalent antimonials and pentamidine, while oral drugs, including miltefosine and azole antifungal compounds, are options for oral treatment of CL [3]. Pentavalent antimonials, including sodium stibogluconate and meglumine antimoniate, are regarded as first-line treatment against New World CL [2–4]. This class of drugs is highly toxic, often difficult to access, and requires enhanced clinical monitoring or hospitalization to prevent irreversible toxicities to the heart, liver, kidney, and pancreas [2–4]. Clinically significant adverse events, including but not limited to, severe thrombocytopenia and pancreatitis, are common reasons for treatment interruption with antimonials. Miltefosine is a highly effective oral alternative to antimonials for the treatment of CL [3], though its use is limited by prohibitively high cost. Amphotericin B (AB) is a polyene antifungal that targets the sterol rich membranes of Leishmania spp. by producing ion-channel pores spanning the lipid bilayer, and increasing cell membrane permeability to small ions and solute molecules, resulting in cell death [5, 6]. Four formulations of AB, including amphotericin B deoxycholate, liposomal amphotericin, cholesterol dispersion amphotericin, and lipid complex amphotericin are used as second-line treatment of CL, and vary in treatment efficacy [3, 5–8]. Severe side effects of AB, especially renal toxicity are mostly associated with amphotericin B deoxycolate compared to other amphotericin formulations [3, 5–8].
Antifungal azoles such as itraconozole, ketonazole, and fluconazole (FZ), have been evaluated in clinical trials of CL treatment, and species-specific results suggest that these comparatively well-tolerated oral regimens also demonstrate efficacy, particularly for Old World CL [3, 4, 9–11]. FZ inhibits C14α-demethylase of the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway [7]. The oral formulation, long half-life, and high skin-to-plasma concentrations make it a popular alternative in the treatment of CL [9]. Widespread use of FZ for CL treatment is limited by a lack of large randomized controlled trials demonstrating efficacy, and the need for high-dose administration in order to achieve cure [3, 9–11]. Current clinical management guidelines indicate that “no ideal or universally applicable therapy for CL has been identified”, and that selection of therapy should be individualized [3]. Given the absence of a first-line agent and considering the many factors such as patient preference, lesion localization, cost, ease of administration, probable efficacy, likelihood of subsequent mucosal disease, age, existing co-morbidities, and drug accessibility, treatment should be individualized, and this process would be enhanced by drug susceptibility platforms to inform clinical decision-making [3]. Geographic and anticipated species-specific response to therapy should also be considered when selecting a therapeutic agent, particularly given high rates of failure of antimonials in pockets of endemicity [3, 12, 13]. However, few objective parasitologic data exist to guide the clinical decision-making process when selecting a therapeutic agent a priori. Estimating the likelihood of drug failure is largely informed by physician experience and clinical and epidemiological data, rather than objective parasitologic metrics, as one would achieve through standardized in-vitro drug susceptibility testing (as is done for countless other microbial infections).
At present, in-vitro systems for assessing predominantly Old World strains of Leishmania spp. susceptibility include: agar dilution, broth microdilution, flow cytometry, reporter gene assays, enzymatic determination, H3-thymidine incorporation, and colorimetric assays including the use of resazurin based Alamar Blue [14–18]. These techniques are primarily used in research laboratories, and have yet to be validated for routine clinical use due to their time-consuming nature, and requirement of substantial technical expertise and laboratory infrastructure. Another challenge to routine drug susceptibility testing is the biphasic life cycle of Leishmania, where the larger, motile (and therefore more visible by light microscopy) promastigote stage inhabits the sandfly midgut, while the 2-μm amotile amastigote resides inside the mammalian host macrophages, where it evades immune detection. Intracellular amastigotes harvested from macrophages remain the gold standard for testing drug susceptibility in-vitro [14]. However, given that log-phase promastigotes are generally more resistant to anti-Leishmania drugs than amastigotes [14–17], and detectable in a cell-free culture system incubated at room temperature, promastigotes are surrogates of an isolate’s susceptibility pattern, independent of cell-mediated parasiticidal mechanisms [14].
The Sensititre™ YeastONE™ YO9 Susceptibility Plate (Thermo Scientific), used for routine quantitative antifungal susceptibilities (MIC) in non-fastidious yeast, such Candida spp. and Cryptococcus spp., contains the following antifungals: anidulafungin, amphotericin B, micafungin, caspofungin, 5-flucytosine, posaconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole and fluconazole [19]. The alamarBlue® technology is a colorimetric growth indicator based on detectable metabolic activity, and remains constant with extended incubation times (as are required for culture of Leishmania), and across inoculation media [19, 20]. Thus, it could be adapted for use in Leishmania susceptibility testing within an antifungal-based panel, such as the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 Susceptibility Plate.
Given the scarcity of well tolerated, easily accessible, and inexpensive therapies coupled with the necessity to treat active lesions of Latin American Viannia strains to potentially minimize the risk of downstream mucosal disease, as well as the propensity of strains to fail all available therapies with sufficient frequency, a user-friendly drug susceptibility testing platform with potential for clinical implementation should be developed. In order to address several aspects of this existing knowledge and care gap, we adapted the Sensititre™ YeastONE™ YO9 Susceptibility Plate to examine AB and FZ susceptibility profiles in log-phase Leishmania spp. promastigotes. We herein report the use of this commercialized antifungal drug susceptibility platform as proof-of-concept to assess drug susceptibility profiles of Leishmania strains imported to Canada and available via the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC®).
Materials and methods
Parasite cultures
ATCC® and clinical cultures submitted to the Public Health Ontario Laboratory for Leishmania spp. diagnostic testing were routinely sub-cultured in Tobie’s medium with Locke’s overlay (in-house) at ambient temperature every week. The following ATCC© strains were used: Leishmania Viannia braziliensis ATCC® 50135™ (MHOM/BR/75/M2903), L. V. guyanensis ATCC®50126™ (MHOM/BR/75/M4147), L. V. panamensis ATCC®50158™ (MHOM/PA/71/LS94), L. amazonensis ATCC®50159™ (IFLA/BR/67/PH8), L. chagasi Cunha and Chagas ATCC®50133™ (MHOM/BR/74/PP75), L. donovani (Laveran and Mesnil) Ross ATCC®50212™ (MHOM/IN/80/DD8), L. infantum Nicolle ATCC®50134™ (MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1), L. major ATCC®50122™ (MHOM/IL/67/JERICHO II), L. mexicana (Biagi) Garnham ATCC®50157™ (MHOM/BZ/82/BEL21), and L. tropica (Wright) Luhe ATCC®50129™ (MHOM/SU/74/K27) (Table 1). The following clinical strains were tested: L. V. braziliensis (n = 1), L. V. panamensis (n = 5), L. infantum (n = 1), and L. tropica (n = 2) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Clinical, demographic, parasitological and drug susceptibility data for all strains
| Strain | Amphotericin B (μg/mL) | Fluconazole (μg/mL) | Isolate Origin | New or Old World Origin | Clinical Manifestation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. amazonensis ATCC®50159™ | 0.58 ± 0.22 | ≥256 | Brazil | New World | CL |
| L. chagasi ATCC®50133™ | 0.33 ± 0.08 | ≥256 | Brazil | New World | VL |
| L. donovani ATCC®50212™ | 0.25 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | India | Old World | VL |
| L. infantum ATCC®50134™ | 0.22 ± 0.07 | ≥256 | Tunisia | Old World | VL |
| L. major ATCC®50122™ | 0.44 ± 0.06 | ≥256 | Israel | Old World | CL |
| L. mexicana ATCC®50157™ | 0.33 ± 0.08 | ≥256 | Belize | New World | CL |
| L. tropica ATCC®50129™ | 0.25 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Former USSR (Azerbaidjanskaya) | Old World | CL |
| L. V. braziliensis ATCC® 50135™ | 0.25 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Brazil | New World | CL or ML |
| L. V. guyanensis ATCC®50126™ | 0.39 ± 0.09 | ≥256 | Brazil | New World | CL or ML |
| L. V. panamensis ATCC®50158™ | 0.5 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Panama | New World | CL or ML |
| Clinical L. infantum 1 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Italy | Old World | VL |
| Clinical L. tropica 1 | 0.25 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Afghanistan | Old World | CL |
| Clinical L. tropica 2 | 0.25 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Afghanistan | Old World | CL |
| Clinical L. V. braziliensis 1 | 0.5 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Peru | New World | CL |
| Clinical L. V. panamensis 1 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Costa Rica | New World | CL |
| Clinical L. V. panamensis 2 | 0.16 ± 0.04 | ≥256 | Costa Rica | New World | CL |
| Clinical L. V. panamensis 3 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | ≥256 | Costa Rica | New World | CL |
| Clinical L. V. panamensis 4 | 0.67 ± 0.17 | ≥256 | Ecuador | New World | CL |
| Clinical L. V. panamensis 5 | 0.49 ± 0.08 | ≥256 | Costa Rica | New World | CL |
Species identification
Leishmania genus 18S real time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed as previously described [21]. Species identification included analysis of the internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1), ITS2, cysteine proteinase B (CPB), heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), and mannose phosphate isomerase (MPI) targets by PCR, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, and Sanger sequencing [22, 23]. As PCR-RFLP analysis of the ITS1 region can only differentiate L. V. braziliensis from the other species within the Viannia subgenus (L. V. guyanensis, L. V. peruviana, L. V. panamensis, L. V. lainsoni), both PCR-RFLP and sequencing analysis of the CPB, HSP70, MPI and ITS2 regions were used to differentiate species within the Leishmania Viannia sub-genus. Purified PCR product was used for Sanger sequencing as per Big Dye protocol (Life Technologies). Sequence products were purified and analyzed using the Applied Biosystems 3130xl Genetic Analyzer. Data were standardized using the Sequencing Analyzer program and the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) engine was used to analyze sequences.
Drug susceptibility plate
Sensititre™ YeastOne™YO9 susceptibility plates (TREK Diagnostics Systems, West Sussex, UK) were stored at room temperature away from sunlight [19]. Concentrations of impregnated AB ranged from 0.12 μg/mL to 8 μg/mL, whereas FZ ranged from 0.12 μg/mL to 256 μg/mL, as per manufacturer’s documentation (TREK Diagnostics Systems, West Sussex, UK) [19].
Promastigote assay
Clinical and ATCC® cultures of Leishmania spp. promastigotes were maintained in Tobie’s medium with Locke’s overlay at room temperature until log phase growth was achieved. Given that the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 susceptibility plates are validated for non-fastidious yeasts, Leishmania promastigote-specific alterations were made to the inoculum broth, inoculation procedure, incubation, and test reading procedures in the TREK Diagnostic Systems guidelines [19], to ensure successful growth and interpretation of Leishmania spp. promastigotes. A solution containing 100 μL of 2.5 × 105 promastigotes/mL in our in-house promastigote broth including Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) Medium 1640 (1X) (Gibco) with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (HI-FBS) (Gibco) and 20 mM HEPES (Fisher Scientific) (10% RPMI) was inoculated into each well, sealed with transparent adhesive film, and placed into an incubator at 27 °C (rather than yeast incubation of 37 °C) in 5% CO2. The plates were incubated for up to 96 h. Colour change was assessed by visual acuity (as described in the TREK Diagnostic Systems guidelines [19]) and metrics of promastigote viability were assessed using conventional inverted light microscopy every 24-h to determine an appropriate MIC up until 96 h. Viability metrics included frank motility with propulsion across the microscopic field, as well as stationary flagellar movement and retention of the structural shape of the promastigote. Resistance at a given drug concentration was defined as > 50% promastigote growth, which was determined by individual or group promastigote motility, as well as maintenance of the structural shape in > 50% of promastigotes in each low power field examined.
Replicates
Each strain was run in biological triplicates, except in the case of L. major ATCC®50122™ (MHOM/IL/67/JERICHO II) and L. V. guyanensis ATCC®50126™ (MHOM/BR/75/M4147), which included 4 biological replicates, while L. infantum Nicolle ATCC®50134™ (MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1) was performed in 5 biological replicates. Two different clinical strains of L. tropica were performed in triplicate, yielding 6 data points, whereas 5 different clinical strains of L. V. panamensis were performed in triplicate, resulting in 15 data points.
Controls
Candida parapsilosis (ATCC®22019™) with known antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) profiles was used as a positive control, and triplicate incubation was performed using the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 inoculation broth according to TREK Diagnostic Systems guidelines in order to ensure quality of plates [19]. Similarly, ATCC®22019™ was incubated on the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 platform using the Leishmania-adapted 10% RPMI promastigote inoculation broth, as previously mentioned, to assess and control for any MIC changes that may have arisen from a change in inoculation broth. Negative control plates were incubated in the same conditions described above without culture inoculation.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism 6 version 6.07 software (GraphPad Software Inc). Mean MICs at 96 h were calculated for each strain. Strains were subsequently grouped according to species, probable phenotype, and isolate source and compared using Fisher’s exact test with an alpha or 0.05 and power of 80. Species originating from Latin America were categorized as “New World”, while those originating from Africa, Asia, or the Middle East were categorized as “Old World”. Species known to localize to viscera were classified as “visceralizing” (e.g., L. donovani, L. infantum, L. chagasi), while strains causing predominantly tegumentary disease were classified as “non-visceralizing” (Viannia strains, L. major, L. tropica, L. amazonensis, L. mexicana). MICs of Viannia strains, which are known to cause disfiguring mucosal disease, were compared to both non-Viannia Latin American strains (e.g., L. mexicana, L. amazonensis), and to all non-Viannia strains including those originating from the Old World.
Results
Promastigote assay
We evaluated AB and FZ susceptibility in 19 strains of clinical and ATCC® isolates from 10 different species of Leishmania using the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 plate. The lowest concentration showing inhibition of growth (i.e., the absence of colorimetric change), correlated to promastigote death, which was assessed by inverted light microscopy at 96 h.
ATCC®22019™ C. parapsilosis
MIC interpretative criteria for Candida spp., as per Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) M27 guidelines, revealed within range susceptibilities for AB (0.83 μg/mL, n = 3) and FZ (1 μg/mL, n = 3) for ATCC®22019 C. parapsilosis following the TREK Diagnostic Systems protocol as per manufacturer’s guidelines [19]. The average MIC value observed for AB and FZ was 1 μg/mL (n = 3) after inoculation with the Leishmania-adapted 10% RPMI promastigote inoculation broth, falling within range of expected susceptibilities according to the CLSI M27 guidelines, and not differing from the MICs obtained using the standard validated inoculation broth designed for non-fastidious yeasts.
Fluconazole
MIC values of FZ for all strains of Leishmania tested were determined to be ≥256 μg/mL (Table 1). Visible promastigote motility was evident in all FZ-impregnated wells out to 96-h with no colorimetric change in the incubation broth.
Amphotericin B
Average AB MIC values were observed for the following ATCC® strains: L. amazonensis (0.58 μg/mL, n = 3), L. chagasi (0.33 μg/mL, n = 3), L. donovani (0.25 μg/mL, n = 3), L. infantum (0.22 μg/mL, n = 5), L. major (0.43 μg/mL, n = 4), L. mexicana (0.33 μg/mL, n = 3), L. tropica (0.25 μg/mL, n = 3), L. V. braziliensis (0.25 μg/mL, n = 4), L. V. guyanensis (0.25 μg/mL, n = 4), and L. V. panamensis (0.50 μg/mL, n = 3) (Table 1). Average AB MIC values were observed for the following clinical strains: L. infantum (0.12 μg/mL, n = 3), L. tropica (0.25 μg/mL, [2 strains, n = 3 replicates each for a total of 6 data points), L. V. braziliensis (0.5 μg/mL, n = 3), L. V. panamensis (0.24 μg/mL, [5 strains, n = 3 replicates each for a total of 15 data points]) (Table 1).
The following Old World strains were resistant, as defined by > 50% promastigote growth, to AB at 0.12 μg/mL: ATCC® L. donovani (n = 3, 100%), ATCC® L. infantum (n = 2, 40%), ATCC® L. tropica (n = 3, 100%), clinical L. tropica (n = 6, 100%), and ATCC® L. major (n = 4, 100%) (Table 2). The following New World strains were resistant to AB at 0.12 μg/mL: ATCC® L. amazonensis (n = 3, 100%), ATCC® L. chagasi (n = 3, 100%), ATCC® L. mexicana (n = 3, 100%), ATCC® L. V. braziliensis (n = 3, 100%), clinical L. V. braziliensis (n = 3, 100%), ATCC® L. V. guyanensis (n = 2, 50%), ATCC® L. V. panamensis (n = 3, 100%), and clinical L. V. panamensis (n = 4, 27%) (Table 2). The following strains were resistant to AB at 0.25 μg/mL: ATCC® L. V. amazonensis (n = 2, 67%), ATCC® L. chagasi (n = 1, 33%), ATCC® L. infantum (n = 1, 20%), ATCC® L. major (n = 3, 75%), ATCC® L. mexicana (n = 1, 33%), ATCC® L. V. guyanensis (n = 1, 25%), ATCC® L. V. panamensis (n = 3, 100%), clinical L. V. braziliensis (n = 3, 100%), and clinical L. V. panamensis (n = 3, 25%) (Table 2). The remaining strains were susceptible to AB at 0.50 μg/mL except 1 replicate of ATCC® L. amazonensis and clinical L. V. panamensis, respectively (Table 2).
Table 2.
Leishmania spp. Antibiogram of ATCC© and Clinical Isolates Resistant at Varying Concentrations of Amphotericin B and Fluconazole
| Species | Total Number of Isolates | Amphotericin B (μg/mL) | Fluconazole (μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | ≥256 | ||
| Old World | ||||||
| L. donovani ATCC®50212™ | 3 | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. infantum ATCC®50134™ | 5 | 2 (40%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) |
| Clinical L. infantum | 3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. tropica ATCC®50129™ | 3 | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| Clinical L. tropica | 6 | 6 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (100%) |
| L. major ATCC®50122™ | 4 | 4 (100%) | 3 (75%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (100%) |
| New World | ||||||
| L. amazonensis ATCC®50159™ | 3 | 3 (100%) | 2 (66.6%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. chagasi ATCC®50133™ | 3 | 3 (100%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. mexicana ATCC®50157™ | 3 | 3 (100%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. V. braziliensis ATCC® 50135™ | 3 | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| Clinical L. V. braziliensis | 3 | 3 (100%) | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. V. guyanensis ATCC®50126™ | 4 | 2 (50%) | 1 (25%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (100%) |
| L. V. panamensis ATCC®50158™ | 3 | 3 (100%) | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| Clinical L. V. panamensis | 15 | 4 (27%) | 3 (25%) | 1 (8.3%) | 0 (0%) | 15 (100%) |
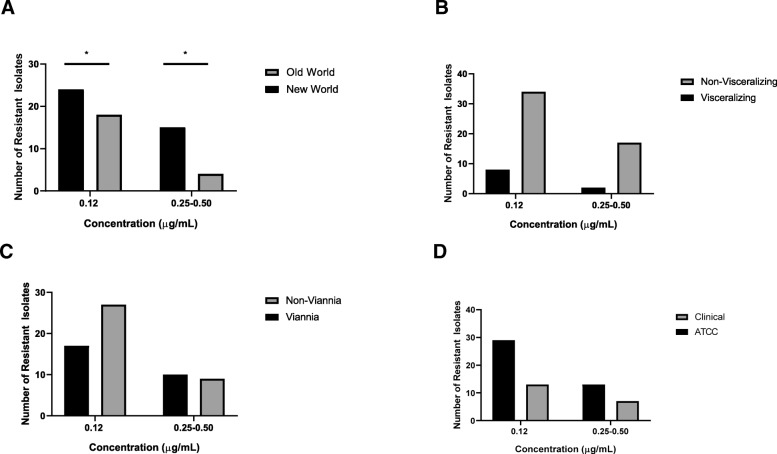
The following isolates demonstrated resistance at 0.12 μg/mL AB: 57% (21/37) of New World isolates versus 88% (21/24) of Old World isolates (p = 0.02) (Table 3, Fig. 1a). Eight (57%) of 14 visceralizing isolates were resistant at 0.12 μg/mL AB compared to 72% (34/47) of non-visceralizing isolates (p = 0.33) (Table 3, Fig. 1b). Seventeen (61%) of 28 Viannia isolates versus 82% (27/33) of non-Viannia isolates (p = 0.09) were resistant at 0.12 μg/mL AB (Table 3, Fig. 1c). Lastly, twenty-nine (85%) of 34 ATCC® isolates versus 48% (13/27) of clinical isolates (p = 0.78) were resistant at 0.12 μg/mL AB (Table 2, Fig. 1d).
Table 3.
Antibiogram of Leishmania spp. Resistance at Varying Concentrations of Amphotericin B and Fluconazole
| Species | Total Number of Isolates | Amphotericin B (μg/mL) | Fluconazole (μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | ≥256 | ||
| Old World | ||||||
| L. donovani | 3 | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. infantum | 8 | 2 (25%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 8 (100%) |
| L. major | 4 | 4 (100%) | 3 (75%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (100%) |
| L. tropica | 9 | 9 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 9 (100%) |
| New World | ||||||
| L. amazonensis | 3 | 3 (100%) | 2 (66.6%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. chagasi | 3 | 3 (100%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. mexicana | 3 | 3 (100%) | 1 (33.35%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) |
| L. V. braziliensis | 6 | 6 (100%) | 3 (50%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (100%) |
| L. V. guyanensis | 4 | 2 (50%) | 1 (25%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (100%) |
| L. V. panamensis | 18 | 7 (39%) | 6 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 18 (100%) |
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the following groups of resistant isolates at 0.12 μg/mL and 0.25 μ/mL-0.50 μg/mL AB by Fisher’s exact test: New World vs. Old World (* p < 0.05) (a); Visceralizing vs. Non-Visceralizing, (b); Viannia vs. Non-Viannia, (c); and, ATCC® vs. Clinical (d)
The following isolates demonstrated resistance at ≥0.25 μg/mL AB (0.25 μg/mL – 0.50 μg/mL): 62% (21/34) of New World isolates versus 78% (21/27) of Old World isolates (p = 0.01) (Table 3, Fig. 1a). Two (25%) of 8 visceralizing isolates versus 50% (17/34) of non-visceralizing isolates (p = 0.259) were resistant (Table 3, Fig. 1b). Ten (59%) of 17 Viannia isolates versus 33% (9/27) of non-Viannia isolates were resistant at ≥0.25 μg/mL AB (p = 0.12) (Table 3, Fig. 1c). Lastly, thirteen (45%) of 29 ATCC isolates versus 54% (7/13) of clinical isolates (p = 0.74) were resistant at ≥0.25 μg/mL AB (Table 2, Fig. 1d).
Discussion
Treatment of CL is hindered by many factors including, but not limited to: variability in clinical response to treatment with partial correlation to infecting species and region of acquisition; toxicity, expense, and inaccessibility of therapeutics with little pharmacologic innovation over decades; the absence of large-scale therapeutic clinical trials; and the lack of objective laboratory criteria by which to inform likelihood of clinical response and decision-making at the bedside. Clinicians treating patients with CL are provided with little objective parasitologic data to compel selection of one drug over another, and must present patients with clinical guidelines that incorporate a number of contingencies into the decision-making process. Azole antifungals are easily accessible, inexpensive, well tolerated, and supported by several reported trials of efficacy [3, 9], but clinical response to this class of medication can be highly variable compared to other systemic options such as amphotericin and miltefosine, which are more toxic. Development and validation of an objective drug susceptibility system to approximate probable clinical response to therapy should be encouraged, and we have herein demonstrated, as proof-of-concept, that the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 system is potentially adaptable for routine clinical laboratory testing of AB susceptibility in clinical strains of Leishmania. Adaptation of an existing commercialized system guarantees a standard of quality assurance associated with GCP/GLP manufacturing processes, while reducing errors of reproducibility and accuracy compared to systems developed on a smaller, ad hoc, non-commercial scale, as in many research laboratories [14–19]. As per TREK Diagnostic Systems, the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 system provides results within 96 h from inoculation to final reading of MICs [19]. The clinical utility of this plate is highlighted by its cost-effectiveness, time efficiency, and low burden of technical expertise required. The cost per plate including 9 dehydrated drugs with varying concentrations and media is $30 USD with a maximum of 2 h of technical support to set-up and read the plate. In comparison, other in-vitro platforms require individual drug procurement, which translates to well over $300 USD excluding reagents [14–19]. Moreover, such ad hoc investigational systems lack a standard of quality assurance inherent to commercialization and licensure, and are subject to cross contamination [14–19]. Additionally, time for technical support including experimental set-up, monitoring and reading of plates exceeds 2 h, and requires additional training for outcomes measured by flow cytometry, fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), electron microscopy, zone of inhibition (ZI) analysis, and motile cell counts for disk diffusion and broth dilution methods, respectively [14–18]. Lastly, final MIC readings in such ad hoc systems often exceed 96 h, and, in some cases, require up to 20 days [14–18]. Overall, the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 system provides a more efficient and objective measure of analysis, which can be compared between laboratories. Other advantages include the less labor intensive technologies such as the plate-impregnated alamarBlue® technology, which eliminates the need for microscopy.
Clinical case reports and studies have demonstrated the efficacy of high-dose FZ in the treatment of CL in both New and Old World strains of Leishmania [3, 9–11]. A study conducted in Saudi Arabia demonstrated a 79% cure rate of CL due to L. major at 12-weeks following initiation of 6-weeks of 200-mg daily FZ [10]. In another trial, treatment of localized CL due to L. major with FZ at 400 mg/day for 42 days led to an 81% cure rate at 6-weeks [11]. In a study of CL due to L. V. braziliensis, clinical cure was observed more rapidly and to a greater extent (mean duration of treatment 4-weeks; 100% cure) when FZ was prescribed at 8-mg/kg per day compared to a lower dose 5-mg/kg/day regimen (mean duration of treatment 7.5-weeks; 75% cure) [9]. Recent data surrounding the treatment of L. V. braziliensis and L. V. guyanensis from the Brazilian Amazon demonstrate sub-optimal cure rates with FZ 6.5–8 mg/kg/day for 28 days and 450 mg/day for 30 days, respectively [24–26], thus reinforcing the need for a standardized objective marker of expected clinical response, one component of which could be a drug susceptibility testing system that would be functional across species and geographic origins. The isolates tested in our study exhibited FZ MICs ≥256 μg/mL in every case, corroborating the observed clinical requirement of high concentrations of FZ for leishmanicidal effect. Further testing of clinical and ATCC® strains of Leishmania against higher concentrations of FZ will be important to determine the adaptability of an in vitro system for FZ susceptibility testing.
Liposomal amphotericin B is a less toxic alternative to antimonial treatment of CL and mucosal leishmaniasis (ML), however, further studies on the optimal dosage are required given species-specific cure rates and variation in reports of total treatment dosages [26–28]. Currently, treatment of CL or ML caused by L. V. brazilienisis with AB requires a minimum 3 mg/kg dosage over many days [26, 29, 30]. MIC values obtained in this study support average parasiticidal concentrations of 0.5 μg/mL for AB, which equates to a total dose below the recommended dosing schedule, suggesting that a lower, less toxic dose of AB might be effective clinically. Further testing to determine serum blood concentrations to correlate in-vitro drug susceptibility to clinical dosing of AB in cases of CL is necessary and warranted [26, 30].
AB has been proven effective in low dosages against the promastigote form of the parasite in visceralizing species, such as L. donovani [26, 29–31], and this clinical phenomenon is reflected in our data as well, given that a greater proportion of non-visceralizing strains demonstrated growth at higher concentrations of AB compared to visceralizing strains. Although we did not observe any differences in actual MIC values to AB, the proportionate growth of visceralizing compared to non-visceralizing isolates highlights a potential trend that is supported clinically, and will be further validated using amastigotes in the next phase of this work.
Limitations
We graded promastigote viability subjectively by colorimetry and assessment of motility. However, the potential influence of this subjectivity would be mitigated by the use of an objective tool such as the Sensititre™ Vizion™ Digital MIC Viewing System, which would enable easy detection of color changes. Assessment of parasite viability by motility would not exclude the possibility of immotile, metabolically active parasites that could theoretically break-through or rebound in growth following drug cessation. However, given the absence of any clinically-validated susceptibility system for Leishmania, this preliminary proof-of-concept work adds new knowledge to the field and this work should be extended by evaluating both morphologic and metabolic markers of viability. The alamarBlue® technology uses metabolism as a proxy for parasite death along with absence of motility, thereby reducing the risk of overcalling parasite death and underestimating the MIC. Additional markers of viability should be explored further. Finally, given the bipartite life cycle of the parasite, we must acknowledge that drug susceptibility testing profiles of cultured promastigotes may not approximate those exhibited by the amastigote form in mammalian hosts.
Conclusion
We have demonstrated as proof-of-concept that the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 plate could be potentially adapted for routine Leishmania spp. promastigote susceptibility testing in a clinical microbiology laboratory. Our observation of metabolic and microscopic markers of parasite death along a standardized scale of drug concentrations may be a useful and objective complement to conventional epidemiological and clinical predictors of therapeutic response. Moreover, if validated, would likely inform clinical decision-making by risk stratifying patients according to the susceptibility profile of their infecting strain of Leishmania. Future testing of both promastigotes and amastigotes is warranted as well as susceptibility to FZ at higher concentrations of drug beyond the scope of the Sensititre™ YeastOne™ YO9 plate. Customization of the plate may provide the opportunity to evaluate higher concentrations of FZ that might have efficacy against Leishmania spp., given that all isolates in this study were resistant to FZ at ≥256 μg/mL.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Mycology Lab of the Public Health Ontario Laboratory for consultation and guidance around Candida control material.
Abbreviations
- AB
Amphotericin B
- AST
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
- ATCC®
American Type Culture Collection
- BLAST
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
- CL
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
- CLSI
Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute
- CPB
Cysteine proteainse B
- FZ
Fluconazole
- GCP
Good clinical practice
- GLP
Good laboratory practice
- HI-FBS
Heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum
- HSP70
Heat shock protein 70
- ITS1
Internal transcribed spacer 1
- ITS2
Internal transcribed spacer 2
- MIC
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- ML
Mucosal leishmaniasis
- N
Number of replicates
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- RFLP
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
- RPMI
Roswell Park Memorial Institute
Authors’ contributions
RK contributed to study design; data collection, analysis, and interpretation; and was primarily responsible for writing the manuscript. PC contributed to data collection, analysis, and interpretation, and to writing the manuscript. RL contributed to data collection, analysis, and interpretation, and to revision of the manuscript. AKB conceived the study and contributed to study design, oversaw all experimental work, data analysis and interpretation, and writing of the manuscript. All authors critically appraised and revised the manuscript for content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by Public Health Ontario via the Project Initiation Fund.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Ruwandi Kariyawasam, Email: ruwandi.kariyawasam@mail.utoronto.ca.
Priyanka Challa, Email: priyanka.challa@mail.utoronto.ca.
Rachel Lau, Email: rachel.lau@oahpp.ca.
Andrea K. Boggild, Phone: 416-340-3675, Email: andrea.boggild@utoronto.ca
References
- 1.Reithinger R, Dujardin JC, Louzir H, Pirmez C, Alexander B, Brooker S. Cutaneous leishmaniasis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:581–596. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Oragnization Control of the leishmaniases. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2010;949:22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aronson N, Herwaldt BL, Libman M, Pearson R, Lopez-Velez R, Weina P, Carvalho E, Ephros M, Jeronimo S, Magill A. Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA) and the American society of tropical medicine and hygiene (ASTMH) Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63(12):e202–e264. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ponte-Sucre A, Diaz E, Padron Nieves M (Eds). Drug resistance in Leishmania parasites: consequences, molecular mechanisms and possible treatments. Vienna: Springer-Verlag Wien; 2013. p. 1–459.
- 5.Chattopadhyay A, Jafurulla M. A novel mechanism for an old drug: amphotericin B in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;416(1–2):7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Adler-Moore JP, Gangneux JP, Pappas PG. Comparison between liposomal formulations of amphotericin B. Med Mycol. 2016;54(3):223–231. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myv111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Croft SL, Sundar S, Fairlamb AH. Drug resistance in Leishmaniasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19(1):111–126. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.111-126.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sundar S, Chakravarty J. Liposomal amphotericin B and Leishmaniasis: dose and response. J Glob Infect Dis. 2010;2(2):159–166. doi: 10.4103/0974-777X.62886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sousa AS, Frutuoso MS, Moraes EA, Pearson RD, Popeu MM. High- dose Oral fluconazole therapy effective for cutaneous Leishmaniasis due to Leishmania (Vianna) braziliensis. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53(7):693–695. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Alrajhi AA, Ibrahum EA, De Vol EB, Khairat M, Faris RM, Maguire JH. Fluconazole for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania major. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(12):891–895. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Emad M, Hayati F, Fallahzadeh MJ, Namazi MR. Superior efficacy of oral fluconazole 400 mg versus daily oral fluconazole 200 mg daily in the treatment of cutaneous Leishmania major infection: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64(3):606–608. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Llanos-Cuentas A, Echevarria J, Cruz M, La Rosa A, Campos P, Campos M, Franke E, Berman J, Modabber F, Marr J. Efficacy of sodium Stibogluconate alone and in combination with allopurinol for treatment of Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis. CID. 1997;25(3):677–684. doi: 10.1086/513776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Arevalo J, Ramirez L, Adaui V, Zimic M, Tulliano G, Miranda-Verastegui C, Lazo M, Loayza-Muro R, De Doncker S, Maurer A, Chappuis F, Dujardin JC, Llanos-Cuentas A. Influence of Leishmania (Viannia) species on the response to antimonial treatment in patients with American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis. 2007;195(12):1846–1851. doi: 10.1086/518041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vermeersh M, Luz RI, Tote K, Timmermans JP, Cos P, Maes L. In vitro susceptibilities of Leishmania donovani promastigote and amastigote stages to Antileishmanial reference drugs: practical relevance to stage-specific differences. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(9):3855–3859. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00548-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Muniaraj M, Sinha PK, Das P. Antileishmanial activity of drug infused mini-agar plates on Leishmaina donovani promastigotes. Trop Biomed. 2010;27(3):657–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mohammadzadeh T, Sadjjadi SM, Habibi P, Sarkari B. Comparison of agar dilution, broth dilution, cylinder plate and disk diffusion methods for evaluation of anti-leishmanial drugs on Leishmania promastigotes. Iran J Parasitol. 2012;7(3):43–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Singh N, Dube A. Short report: fluorescent Leishmania: application to anti-leishmanial drug testing. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;71(4):400–402. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2004.71.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Maia C, Nunes M, Marques M, Henriques S, Rolao N, Campino L. In vitro drug susceptibility of Leishmania infantum isolated from humans and dogs. Exp Parasitol. 2013;135(1):36–41. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2013.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.TREK Diagnostic Systems. Instructions for Use: Thermo Scientific Sensititre YeastOne Susceptibiltity Plates, manual, Thermo fisher scientific Inc. 2015. TREK Diagnostic Systems: West Sussex, UK. Available at: http://www.mcsdiagnostics.com/site/upload/file/pdf/yo_8_yo10_v1.4_e.pdf. Accessed 5 July 2019.
- 20.Invitrogen Corp., alamarBlue® Assay, manual, Invitrogen Corporation: Carlsbad, CA, USA. Available at: http://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/manuals/PI-DAL1025-1100_TI%20alamarBlue%20Rev%201.1.pdf. Accessed 5 July 2019.
- 21.Wortmann G, Sweeney C, Houng HS, Aronson N, Stiteler J, Jackson J, Ockenhouse C. Rapid diagnosis of leishmaniasis by fluorogenic polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;65(5):583–587. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2001.65.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schonian G, Nasereddin A, Dinse N, Schweynoch C, Schallig HD, Presber W, Jaffe CL. PCR diagnosis and characterization of Leishmania in local and imported clinical samples. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003;47:349–358. doi: 10.1016/S0732-8893(03)00093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.de Almeida ME, Steurer FJ, Koru O, Herwaldt BL, Pieniazek NJ, da Silva AJ. Identification of Leishmania spp. by molecular amplification and DNA sequencing analysis of a fragment of rRNA internal transcribed spacer 2. J Clin Micro. 2011;49(9):3143–3149. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01177-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Francesconi VA, Francesconi F, Ramasawmy R, Romero GAS, Alecrim MDGC. Failure of fluconazole in treating cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania guyanensis in the Brazilian Amazon: an open, nonrandomized phase 2 trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018;12(2):e0006225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Prates FV, Dourado ME, Silva SC, Schriefer A, Guimaraes LH, Brito MD, Almeida J, Carvalho EM, Machado PR. Fluconazole in the treatment of cutaneous Leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania braziliensis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(1):67–71. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lindoso JAL, Costa JML, Goto ITQ. Review of the current treatments for leishmaniases. Res Rep Trop Med. 2012;3:69–77. doi: 10.2147/RRTM.S24764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guery R, Henry B, Martin-Blondel G, Rouzaud C, Cordoliani F, Harms G, Gangneux JP, Foulet F, Bourrat E, Baccard M, Morizot G, Consigny PH, Berry A, Blum J, Lortholary O, Buffet P. French cutaneous Leishmaniasis study group & the LeishMan network. Liposomal amphotericin B in travelers with cutaneous and muco-cutaneous leishmaniasis: not a panacea. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(11):e0006094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mosimann V, Neumayr A, Paris DH, Blum J. Liposomal amphotericin B treatment of Old World cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis: a literature review. Acta Trop. 2018;182:246–250. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Solomon M, Pavlotzky F, Barzilai A, Schwartz E. Liposomal amphotericin B in comparison to sodium stibogluconate for Leishmania braziliensis cutaneous leishmaniasis in travelers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(2):284–249. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2012.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cunha MA, Leao ACQ, Soler RC, Lindoso JAL. Efficacy and safety of liposomal amphotericin B for the treatment of mucosal Leishmaniasis from the New World: a Restrospective study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93(6):1214–1218. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Romero GAS, Costa DL, Costa CHN, de Almeida RP, de Melo EV, de Carvalho SFG, Rabello A, de Carvalho AL, Sousa AQ, Leite RD, Amaral TA, Alves FP, Rode J, Collaborative LVBrasil Group Efficacy and safety of available treatment for visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil: a multicenter, randomized, open label trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(6):e0005706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.