Abstract
We present a case of severe and treatment-refractory bullous pemphigoid in a 3-month-old child. After topical and systemic corticoid treatment proved inefficient, dapsone 0.75 mg/kg was added initially without success. Disease control was reached with dapsone 1.5 mg/kg in addition to both topical and systemic glucocorticoid treatment, leaving the child with several side effects of the glucocorticoid treatment.
Key Words: Bullous pemphigoid, Paediatric dermatology, Dapsone, Treatment refractory
Introduction
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an autoimmune disease characterized by tense bullae on an erythematous background, mainly affecting the elderly from the 7th decade [1], with an incidence of 13.4–66 per 1,000,000 [2]. BP has also been reported as an adverse effect of new checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab [3]. Although rare, BP occurs in infants with a mean age of 4.5 months at debut [4] and a predominant acral presentation [5].
The diagnosis is confirmed by histopathology of the skin, with dermal infiltration by eosinophils, subepidermal blisters, and linear immune globulin G (IgG) and C3 complement factor alignment at the basement membrane zone. Eosinophils may also be increased in the blood [2]. Initial BP treatment is prednisolone 0.5 mg/kg/day and potent topical steroid therapy [6]. Disease control in adults can be maintained by azathioprine or methotrexate [7], as prolonged treatment with prednisolone is associated with significant adverse events and increased mortality [8].
In a systematic review of 81 case reports of BP in infants [4], monotherapy with prednisolone was the most frequently used treatment for initial disease control. Dapsone was the second most used drug. In 19.8% of the paediatric BP cases dapsone was used in combination with prednisolone, and dapsone was given as monotherapy in 2.5% of cases.
Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment combined with prednisolone has in some cases been reported to be effective in childhood BP [4, 9, 10]. Lastly, macrolides like clarithromycin and erythromycin have also been reported as treatment options [4, 11].
Here, we present a case of infantile BP treated with prednisolone and dapsone.
Case
A 3-month-old boy, of healthy, non-related parents of Middle Eastern descent, developed an erythematous rash on the plantae of his feet. The general practitioner initiated daily topical treatment with hydrocortisone 17-butyrate.
Five days after the onset of rash, the patient was seen at Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, Aarhus University Hospital. The infant had now developed a bullous skin rash on an erythematous background located on the plantae of the feet, palms of the hands, the abdomen, and behind the ears. Furthermore, the patient was febrile with a temperature of 39.6°C.
Clinical Presentation/Histology
Initially, a bullous impetigo was suspected. Biochemistry showed a normal CRP and slight eosinophilia at 1.88 × 109/L. Staphylococcus aureus was isolated to one eroded bulla with a yellow crust and treated with amoxicillin and clavulanic acid for 14 days with good response.
The patient was readmitted to the paediatric ward 11 days after the onset of the bullous rash due to progressing skin lesions (Fig. 1). Eosinophilia was increased to 5.12 × 109/L. Topical treatment was intensified with clobetasol propionate ointment for the trunk and extremities and hydrocortisone 17-butyrate cream for inverse areas and the face.
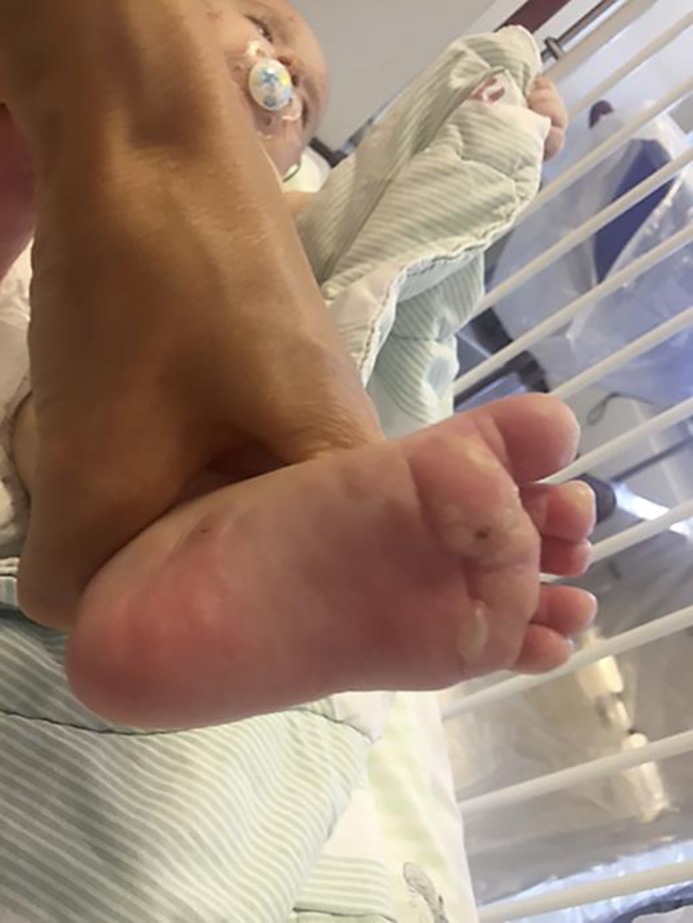
Fig. 1.
Acral presentation of bullae on the soles of the feet.
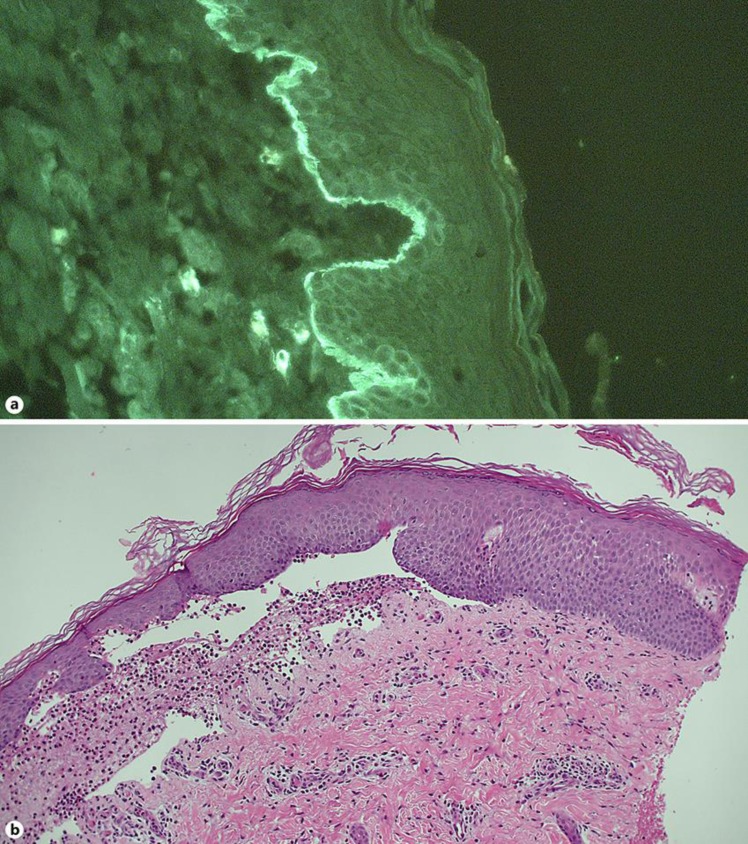
Two punch biopsies were performed – one formalin-fixed for conventional light microscopy (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded) and one unfixed for immunofluorescence microscopy. Light microscopy showed superficial perivascular and interstitial inflammation dominated by eosinophils and a bulla on the dermo-epidermal border. Direct immunofluorescence microscopy revealed both IgG and compliment C3 linear alignment at the basement membrane as well as eosinophilic inflammation (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
a Indirect immunofluorescence of a biopsy, showing IgG deposition along the dermo-epidermal border along the basement membrane. b Haematoxylin-eosin staining of a skin biopsy, demonstrating the split along the dermo-epidermal border as well as eosinophilic inflammation.
At day 15 progression of skin lesions was observed and systemic prednisolone treatment of 1 mg/kg/day was initiated. Further progression was noted after 4 days, now including the face. Systemic prednisolone treatment was increased to 2 mg/kg/day initially with good disease control.
Re-admission occurred at day 38 with new eruptions of bullae, and therefore at day 40 dapsone 0.75 mg/kg/day was initiated. At day 47 new eruptions were still occurring, and dapsone was increased to 1.5 mg/kg/day and topical treatment to twice daily. This treatment was continued until day 70, resulting in complete control of the disease and regression of symptoms. The patient was now cushingoid, with weight and length decreased from the mean to −1 ½ and −½ SD, respectively, for male infants. First, the topical treatment was steadily reduced and the prednisolone dose was tapered to zero within 3.5 months. Dapsone treatment was stopped after another 3.5 months of treatment. No new eruptions have been noticed after 1.5 years of follow-up. A treatment flowchart is presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Treatment flowchart
| Day 1 | Hydrocortisone 17-butyrate topical treatment once daily |
| Day 5 | Admission to paediatric ward |
| Day 11 | First dermatological visit; topical hydrocortisone 17-butyrate administered inversely and mometasone furoate treatment for the trunk and extremities, once daily |
| Day 15 | Systemic prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day added |
| Day 19 | Systemic prednisolone raised to 2 mg/kg/day |
| Day 21 | Topical mometasone furoate replaced with clobetasol propionate |
| Day 40 | Dapsone 0.75 mg/kg/day added |
| Day 47 | Dapsone raised to 1.5 mg/kg/day |
| Day 57 | Topical treatment increased to twice daily |
| Day 70 | Slowly decreasing topical treatment frequency and prednisolone dose |
Discussion
In a systematic review of 81 infants with BP [4], dapsone 1–1.5 mg/kg/day was a successful and safe treatment of BP. In our 3-month-old patient we used dapsone as a steroid-sparing agent. The combination of dapsone 1.5 mg/kg/day, topical corticosteroid twice daily, and systemic prednisolone up to 2 mg/kg/day was successful in controlling this severe case of treatment-refractory childhood BP.
The child became cushingoid as a consequence of systemic prednisolone treatment for 2 months. Earlier initiation of dapsone treatment could possibly have cleared the way for tapering the systemic prednisolone treatment before the child became cushingoid. As an oral treatment, dapsone is very easy to administer, whilst intravenous immunoglobulin, an often-used treatment in childhood BP, is administered intravenously. Thus, dapsone is a safer and cheaper choice of treatment, with no discomfort and pain related to obtaining an intravenous access as in immunoglobulin treatment.
We suggest that dapsone be used as a corticosteroid-sparing agent in the treatment of childhood BP. We strongly suggest that dapsone treatment should be instituted immediately after BP diagnosis has been established in order to taper corticosteroid treatment and avoid long-term corticosteroid side effects in the child.
Statement of Ethics
Written informed consent to publish this case was obtained from the parents.
Disclosure Statement
All authors have nothing to disclose, and there is no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Nishie W. Update on the pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid: an autoantibody-mediated blistering disease targeting collagen XVII. J Dermatol Sci. 2014 Mar;73((3)):179–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schmidt E, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid diseases. Lancet. 2013 Jan;381((9863)):320–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thomsen K, Diernaes J, Øllegaard TH, Spaun E, Vestergaard C. Bullous Pemphigoid as an Adverse Reaction to Pembrolizumab: Two Case Reports. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018 Jun;10((2)):154–7. doi: 10.1159/000489661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schwieger-Briel A, Moellmann C, Mattulat B, Schauer F, Kiritsi D, Schmidt E, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in infants: characteristics, diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014 Dec;9((1)):185. doi: 10.1186/s13023-014-0185-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Waisbourd-Zinman O, Ben-Amitai D, Cohen AD, Feinmesser M, Mimouni D, Adir-Shani A, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in infancy: clinical and epidemiologic characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 Jan;58((1)):41–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Khumalo N, Kirtschig G, Middleton P, Hollis S, Wojnarowska F, Murrell D. Interventions for bullous pemphigoid. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul;((3)):CD002292. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002292.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kibsgaard L, Bay B, Deleuran M, Vestergaard C. A retrospective consecutive case-series study on the effect of systemic treatment, length of admission time, and co-morbidities in 98 bullous pemphigoid patients admitted to a tertiary centre. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015 Mar;95((3)):307–11. doi: 10.2340/00015555-1925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chalmers JR, Wojnarowska F, Kirtschig G, Mason J, Childs M, Whitham D, et al. A randomised controlled trial to compare the safety, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of doxycycline (200 mg/day) with that of oral prednisolone (0.5 mg/kg/day) for initial treatment of bullous pemphigoid: the Bullous Pemphigoid Steroids and Tetracyclines (BLISTER) trial. Health Technol Assess. 2017 Mar;21((10)):1–90. doi: 10.3310/hta21100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Taquin H, Chiaverini C, Lacour JP. Spectrum of Clinical Responses to Therapies in Infantile Bullous Pemphigoid. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016 Mar-Apr;33((2)):e77–81. doi: 10.1111/pde.12779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Watanabe T, Hara S, Muto J, Watanabe D, Akiyama M. Infantile bullous pemphigoid successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017 Jul;42((5)):576–8. doi: 10.1111/ced.13104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tso S, Petrof G, Unter S, Humphreys F. Clarithromycin as a steroid sparing agent for the management of infantile bullous pemphigoid. BMJ case reports. 2018:2018. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]