Nucleophosmin (NPM1) is an abundant phosphoprotein involved in multiple cellular functions (reviewed in Falini et al, 2009) and its gene (NPM1) is the most commonly mutated gene in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) (Falini et al, 2011). NPM1 is considered essential for cellular activity and survival. The NPM1 protein contains a number of motifs, which act to mediate interactions with binding partners and influence its cellular localisation (Colombo et al, 2011). Although NPM1 contains motifs conferring cytoplasmic, nucleoplasmic and nucleolar compartmentalisation, in normal physiological conditions, the equilibrium of movement is shifted towards nuclear import. Once inside the nucleus, NPM1 is driven to the nucleolus.
NPM1 mutations are usually restricted to the terminal exon and cause a frameshift in the C‐terminus encoding region. The altered reading frame results in disruption of a nucleolar localisation signal (Falini et al, 2006, 2009; Grummitt et al, 2008) and introduction of an additional nuclear export signal (Bolli et al, 2007), resulting in aberrant cytoplasmic expression of the mutated protein (NPM1c+) (Falini et al, 2006). Mutations within NPM1 are a founder genetic alteration in AML and the presence of NPM1c+ is required for disease maintenance. Brunetti et al (2018) recently showed that NPM1c+ leukaemia cells displayed increased transcription of stem cell‐associated genes, including HOXA@, HOXB@ and MEIS1. Re‐localisation of NPM1c+ to the nucleus resulted in a downregulation of the HOX/MEIS1 gene signature and subsequent differentiation of AML cells. These results demonstrate the potential therapeutic benefit of inducing nuclear re‐localisation of NPM1.
Here we demonstrate that DNA damage induces a switch in the aberrant cytoplasmic localisation of NPM1c+ back to a predominantly nucleolar localisation. This was observed in an NPM1c+ AML cell line (OCI‐AML3) and patient‐derived AML samples. Evidence supporting the role of DNA damage in NPM1 nuclear re‐localisation was provided by the lack of effect when using a non‐DNA damaging agent and by the prevention of nucleolar re‐localisation when DNA damage response proteins were inhibited.
The cellular localisation of NPM1 in OCI‐AML3 cells was analysed in response to etoposide treatment. Etoposide was used at the 24‐h effective concentration that leads to 30% maximal response (EC30; 4 μmol/l) and was shown to induce measurable DNA damage with low levels of apoptosis (approximately 20%) (Figure S1A,B). Minimising the initiation of cell death pathways was important to prevent this process inadvertently influencing the sub‐cellular localisation of NPM1. Western blots were probed with anti‐NPM1TOTAL monoclonal antibody in order to detect both wild‐type and mutant variants (Fig 1A). Cytoplasmic NPM1 decreased by 25% following etoposide treatment relative to control cells (P < 0·05; n = 3) and nuclear NPM1 increased by 26% (P < 0·01; n = 3) (Fig 1B).
Figure 1.

(A) Western blot analysis of NPM1 in cytoplasmic and nuclear cell extracts. OCI‐AML3 cells were incubated for 4 h with or without etoposide (4 μmol/l). Cell lysates were prepared for cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions and probed for total NPM1. Controls were provided for cytoplasmic protein using β‐actin and nuclear protein by probing for lamin A/C. (B) Western blot band densitometry. Integrated densities for bands corresponding to NPM1 were normalised for the relevant controls and expressed as a ratio of NPM1 in treated cells to untreated cells for cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. The columns represent mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments (*P < 0·05; **P < 0·01). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. (C) Representative images from confocal microscope analysis of sub‐nuclear NPM1 localisation in OCI‐AML3 cells. Cells were incubated with one of three drugs at effective concentrations that lead to 30% maximal response values: etoposide (4 μmol/l/4 h), cytarabine (4 μmol/l/24 h) or SB1317 (50 nmol/l/24 h). In untreated cells, the signal corresponding to NPM1 was predominantly diffuse and localised to the cytoplasm (highlighted by arrows in the merged image). Following treatment with etoposide or cytarabine, discreet NPM1 foci were observed which co‐localised with nucleolar markers (highlighted by arrows in the merged image). (D) Intensity values for regions corresponding to NPM1 fluorescence co‐localising with nucleoli and normalised to background nuclear NPM1 fluorescence. Columns represent mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments (****P < 0·001). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. (E, F) Representative confocal microscope images are presented for untreated and etoposide treated (4 μmol/l/4 h), patient‐derived acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cells using antibodies recognising mutant NPM1 and wild‐type NPM1. Arrows in the merged images highlight the predominant cytoplasmic or nucleolar staining within a cell. (G) Intensity values for regions corresponding to NPM1 fluorescence co‐localising with nucleoli and normalised to background nuclear NPM1 fluorescence. Columns represent mean ± SD of four AML patient samples for mutant NPM1 and three for wild‐type NPM1 (*P < 0·05; **P < 0·01). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. All confocal images were recorded at 180× magnification. Final images were collated from multiple slices along the Z‐axis with a sampling depth of 2 μm and presented as maximum intensity projections. Scale bars represent 15 μm.
The western blotting demonstrated a clear decrease in cytoplasmic NPM1, and increase in nuclear NPM1, but was unable to identify the sub‐nuclear distribution of NPM1 following DNA damage. We therefore used confocal microscopy to examine whether restoration of nucleolar NPM1 occurred in OCI‐AML3 cells incubated with either etoposide or cytarabine (Fig 1C). An increase in NPM1 fluorescence at regions corresponding to nucleoli (via co‐staining with fibrillarin) was observed following treatment. This was in contrast to untreated cells, where NPM1 was predominantly diffuse and localised to the cytoplasm. Quantification of confocal images revealed that following etoposide treatment, nucleolar NPM1 increased by 118% relative to untreated cells (P < 0·0001; n = 7) (Fig 1D). A similar magnitude increase of nucleolar NPM1 fluorescence was observed in OCI‐AML3 cells treated with cytarabine [168% (P < 0·0001; n = 3)]. To assess whether the restoration of nucleolar NPM1 was a general response to chemotherapeutic drugs, OCI‐AML3 cells were incubated with the multi‐kinase inhibitor SB1317 with no observable change in nucleolar NPM1 (P = 0·561; n = 3) (Fig 1C,D).
Similar to OCI‐AML3 cells, nucleolar re‐localisation of NPM1 was also observed in 4/4 NPM1‐mutated AML patient samples following etoposide treatment. A 106% increase in nucleolar NPM1 was measured following DNA damage relative to untreated control cells (P < 0·05; n = 4) when the antibody recognising both mutant and wild‐type proteins was used (Figure S1C,D).
To investigate whether the observed nucleolar re‐localisation was due to wild‐type or mutant protein, the experiment was repeated in patient samples replacing the anti‐NPM1TOTAL antibody with a mutant (Fig 1E) or wild‐type specific antibody (Fig 1F). Surprisingly, a 100% increase in the nucleolar population of NPM1c+ relative to untreated cells was observed following DNA damage (P < 0·01; n = 4) (Fig 1G). When using a wild‐type specific antibody, NPM1 was observed within nucleoli in untreated cells as expected, however the nucleolar population of wild‐type protein increased by 40% following treatment (P < 0·05; n = 3) (Fig 1G). These results demonstrate that the increase in nucleolar NPM1 is due to both wild‐type and mutated forms of the protein.
Finally, two proteins that are activated following DNA damage – poly (ADP‐ribose) polymerase (PARP‐1) and ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM), were inhibited in OCI‐AML3 cells prior to etoposide treatment. Cells treated with either olaparib (PARP‐1 inhibitor) (Fig 2A) or KU‐55933 (ATM inhibitor) (Figure S1E,F) did not affect NPM1 localisation. Co‐treatment of cells with etoposide and olaparib prevented the nucleolar re‐localisation that was observed with etoposide alone (P = 0·642; n = 3) (Fig 2B). A similar result was observed in cells treated with etoposide and KU55933 (P = 0·181; n = 3) (Figure S1F).
Figure 2.
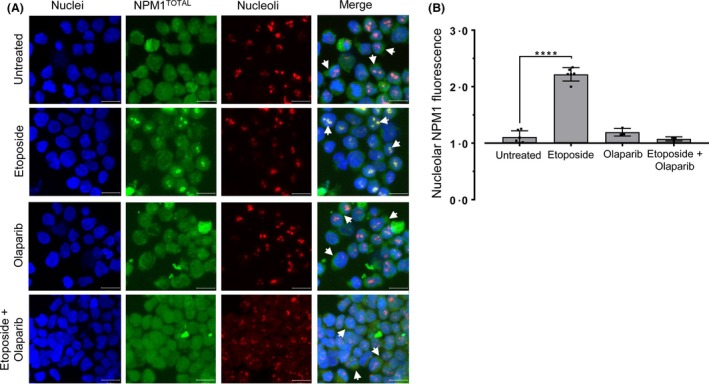
(A) Representative confocal microscope images visualising sub‐nuclear NPM1 localisation in OCI‐AML3 cells incubated with or without etoposide (4 μmol/l/4 h) and in conjunction with olaparib at 50% inhibitory concentration (1 μmol/l/24 h). (B) Intensity values for regions corresponding to NPM1 fluorescence co‐localising with nucleoli and normalised to background nuclear NPM1 fluorescence. Columns represent mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments (****P < 0·001). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. Confocal images were recorded at 180 × magnification. Final images were collated from multiple slices along the Z‐axis with a sampling depth of 2 μm and presented as maximum intensity projections. Scale bars represent 15 μm.
This study showed that DNA damage, induced by either etoposide or cytarabine treatment, alters the sub‐cellular localisation of NPM1 in NPM1‐mutated AML cells back to a predominantly nucleolar distribution akin to NPM1 wild‐type cells.
It was hypothesised by Falini et al (2015) that the depletion of nucleolar NPM1 in NPM1‐mutated AML could be exploited through the use of drugs that induce a nucleolar stress response. NPM1 acts as a hub protein, trafficking other proteins to the nucleolus and is consequently essential for the formation and maintenance of a functional nucleolus (Emmott & Hiscox, 2009). The reduction of nucleolar NPM1 could therefore leave affected cells more responsive to nucleolar stress‐inducing drugs, leading to increased levels of apoptosis (Amin et al, 2008). Our results add complexity to this hypothesis however. We show that the induction of DNA damage results in a re‐localisation of total NPM1 to the nucleolus, suggesting that the exploitation of nucleolar NPM1‐replete cells to nucleolar stress would therefore only be effective in the absence of DNA damage.
Author contributions
CS and NR conceived the study. GB and CS designed the study. GB, HS and AA performed the experiments and acquired data. GB analysed the data and carried out statistical analysis. GB wrote the manuscript. CS and NR critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supporting information
Figure S1. (A) An etoposide concentration of 4 μmol/l resulted in a 20% decrease in cell survival relative to an untreated control following a 24 h incubation in OCI‐AML3 cells. Incubating the cells for 4 h did not affect cell survivability at any etoposide concentration tested. Following incubation for the indicated times at the concentrations shown, the cells were fixed and stained with 7‐AAD before analysing using flow cytometry; n = 3. (B) OCI‐AML3 cells were incubated with 4 μmol/l etoposide for a period of 6 or 24 h. DNA damage was assessed using a neutral comet assay. An automated image analysis system (CometAssay IV software (Perceptive Instruments)) was used to measure the olive tail moment. Duplicate agarose spots were prepared for each experimental condition and 50 cells in each spot were randomly selected and analysed. An increased tail moment was measured following incubation with etoposide for 6 and 24 h. Columns indicate mean ± SD of three replicate samples (**P < 0.01). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. (C) Confocal microscope images visualising total NPM1 in patient derived samples prior to and post etoposide treatment (4 μmol/l/4 h). Arrows in the merged images highlight the predominant cytoplasmic or nucleolar staining within a cell. (D) Intensity values for regions corresponding to NPM1 fluorescence co‐localising with nucleoli and normalised to background nuclear NPM1 fluorescence. Columns represent mean ± SD of four AML patient samples (*P < 0.05). (E) Representative confocal microscope images showing total NPM1 localisation in OCI AML3 cells with or without etoposide (4 μmol/l/4 h) and in conjunction with KU55933 at IC50 (20 μmol/l/24 h). (F) Intensity values for NPM1 fluorescence in regions co‐localising with nucleoli and normalised to background nuclear NPM1 fluorescence. Columns represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments (****P < 0.001). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. Confocal images were recorded at 180× magnification. Final images were collated from multiple slices along the Z‐axis with a sampling depth of 2 μm and presented as maximum intensity projections. Scale bars represent 15 μm.
The copyright line for this article was changed on 29 April 2019 after original online publication.
References
- Amin, M.A. , Matsunaga, S. , Uchiyama, S. & Fukui, K. (2008) Depletion of nucleophosmin leads to distortion of nucleolar and nuclear structures in HeLa cells. Biochemical Journal, 415, 345–351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli, N. , Nicoletti, I. , de Marco, M.F. , Bigerna, B. , Pucciarini, A. , Mannucci, R. , Martelli, M.P. , Liso, A. , Mecucci, C. , Fabbiano, F. , Martelli, M.F. , Henderson, B.R. & Falini, B. (2007) Born to be exported: COOH‐terminal nuclear export signals of different strength ensure cytoplasmic accumulation of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants. Cancer Research, 67, 6230–6237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, L. , Gundry, M.C. , Sorcini, D. , Guzman, A.G. , Huang, Y.H. , Ramabadran, R. , Gionfriddo, I. , Mezzasoma, F. , Milano, F. , Nabet, B. , Buckley, D.L. , Kornblau, S.M. , Lin, C.Y. , Sportoletti, P. , Martelli, M.P. , Falini, B. & Goodell, M.A. (2018) Mutant NPM1 maintains the leukemic state through HOX expression. Cancer Cell, 34, e9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, E. , Alcalay, M. & Pelicci, P.G. (2011) Nucleophosmin and its complex network: a possible therapeutic target in hematological diseases. Oncogene, 30, 2595–2609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmott, E. & Hiscox, J.A. (2009) Nucleolar targeting: the hub of the matter. EMBO Reports, 10, 231–238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini, B. , Bolli, N. , Shan, J. , Martelli, M.P. , Liso, A. , Pucciarini, A. , Bigerna, B. , Pasqualucci, L. , Mannucci, R. , Rosati, R. , Gorello, P. , Diverio, D. , Roti, G. , Tiacci, E. , Cazzaniga, G. , Biondi, A. , Schnittger, S. , Haferlach, T. , Hiddemann, W. , Martelli, M.F. , Gu, W. , Mecucci, C. & Nicoletti, I. (2006) Both carboxy‐terminus NES motif and mutated tryptophan(s) are crucial for aberrant nuclear export of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants in NPMc+ AML. Blood, 107, 4514–4523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini, B. , Bolli, N. , Liso, A. , Martelli, M.P. , Mannucci, R. , Pileri, S. & Nicoletti, I. (2009) Altered nucleophosmin transport in acute myeloid leukaemia with mutated NPM1: molecular basis and clinical implications. Leukemia, 23, 1731–1743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini, B. , Martelli, M.P. , Bolli, N. , Sportoletti, P. , Liso, A. , Tiacci, E. & Haferlach, T. (2011) Acute myeloid leukemia with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1): is it a distinct entity? Blood, 117, 1109–1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini, B. , Brunetti, L. & Martelli, M.F. (2015) Dactinomycin in NPM1‐mutated acute myeloid leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine, 373, 1178–1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummitt, C.G. , Townsley, F.M. , Johnson, C.M. , Warren, A.J. & Bycroft, M. (2008) Structural consequences of nucleophosmin mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283, 23326–23332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. (A) An etoposide concentration of 4 μmol/l resulted in a 20% decrease in cell survival relative to an untreated control following a 24 h incubation in OCI‐AML3 cells. Incubating the cells for 4 h did not affect cell survivability at any etoposide concentration tested. Following incubation for the indicated times at the concentrations shown, the cells were fixed and stained with 7‐AAD before analysing using flow cytometry; n = 3. (B) OCI‐AML3 cells were incubated with 4 μmol/l etoposide for a period of 6 or 24 h. DNA damage was assessed using a neutral comet assay. An automated image analysis system (CometAssay IV software (Perceptive Instruments)) was used to measure the olive tail moment. Duplicate agarose spots were prepared for each experimental condition and 50 cells in each spot were randomly selected and analysed. An increased tail moment was measured following incubation with etoposide for 6 and 24 h. Columns indicate mean ± SD of three replicate samples (**P < 0.01). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. (C) Confocal microscope images visualising total NPM1 in patient derived samples prior to and post etoposide treatment (4 μmol/l/4 h). Arrows in the merged images highlight the predominant cytoplasmic or nucleolar staining within a cell. (D) Intensity values for regions corresponding to NPM1 fluorescence co‐localising with nucleoli and normalised to background nuclear NPM1 fluorescence. Columns represent mean ± SD of four AML patient samples (*P < 0.05). (E) Representative confocal microscope images showing total NPM1 localisation in OCI AML3 cells with or without etoposide (4 μmol/l/4 h) and in conjunction with KU55933 at IC50 (20 μmol/l/24 h). (F) Intensity values for NPM1 fluorescence in regions co‐localising with nucleoli and normalised to background nuclear NPM1 fluorescence. Columns represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments (****P < 0.001). Significance levels were indicated as P‐values calculated from unpaired parametric t‐tests. Confocal images were recorded at 180× magnification. Final images were collated from multiple slices along the Z‐axis with a sampling depth of 2 μm and presented as maximum intensity projections. Scale bars represent 15 μm.


