Abstract
The AAA+ GTPase McrB powers DNA cleavage by the endonuclease McrC. The GTPase itself is activated by McrC. The architecture of the GTPase and nuclease complex, and the mechanism of their activation remained unknown. Here, we report a 3.6 Å structure of a GTPase-active and DNA-binding deficient construct of McrBC. Two hexameric rings of McrB are bridged by McrC dimer. McrC interacts asymmetrically with McrB protomers and inserts a stalk into the pore of the ring, reminiscent of the γ subunit complexed to α3β3 of F1-ATPase. Activation of the GTPase involves conformational changes of residues essential for hydrolysis. Three consecutive nucleotide-binding pockets are occupied by the GTP analogue 5’-guanylyl imidodiphosphate and the next three by GDP, which is suggestive of sequential GTP hydrolysis.
Subject terms: Cryoelectron microscopy, Enzyme mechanisms
McrBC is a bacterial antiphage defense system that cleaves methylated DNA and is composed of the AAA+ GTPase motor McrB and the endonuclease McrC. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of E. coli McrBC that reveals how McrC inserts a stalk-like structure into the pore of the ring-shaped McrB hexamer and discuss mechanistic implications.
Introduction
AAA+ proteins (extended ATPases associated with various cellular activities) convert chemical energy derived from nucleotide hydrolysis to mechanical form in the cell, a process fundamental to life1,2. A feature common to many AAA+ proteins is their activation by partner proteins thus regulating energy utilization3–8. McrBC is an antiphage defense system of Escherichia coli that specifically cleaves invading DNA that are methylated9. The AAA+ GTPase motor McrB is activated by the endonuclease McrC, which in turn powers DNA cleavage by the endonuclease3. McrBC specifically cleaves DNA containing the recognition sequence 5’-G/A(5mC)-3’, where 5mC can be 5-methylcytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, or 4-methylcytosine10,11. Such systems have evolved to degrade methylated bacteriophage genomes that are modified as protection against other restriction-modification (RM) systems that cleave unmodified DNA9. They also affect horizontal gene transfer, including the spread of virulence or antibiotic resistance elements12. McrB is unique among AAA+ proteins as it hydrolyzes GTP rather than ATP1. In the presence of GTP, monomeric McrB oligomerize to hexamers13. Furthermore, upon binding of the endonuclease McrC, a higher oligomeric form—tetradecamers of 12 McrB and 2 McrC protomers—is formed13. The McrB GTPase activity is very low and is stimulated ~30-fold by McrC3,13. GTP hydrolysis by McrBC bound to a recognition sequence powers DNA translocation, and convergence of two such complexes on the DNA results in nucleolytic cleavage14. Here we present the structure of the AAA+ domain of McrB in complex with McrC at 3.6 Å resolution using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), which reveals the coupling between the endonuclease and the motor and the mechanism of activation of the GTPase. Our study provides a mechanistic framework for regulation of a AAA+ motor by its activator by remodeling of its active site.
Results
The dumbbell-shaped McrB∆NC
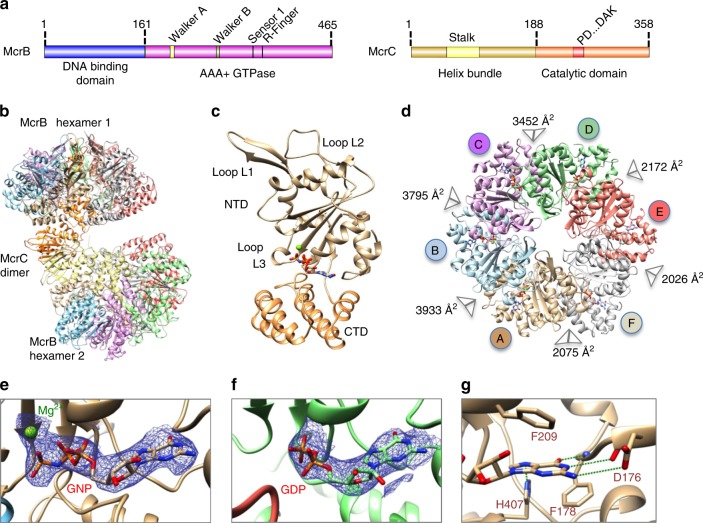
We determined the structure of the tetradecameric complex of McrC with an McrB construct lacking the first 161 residues (McrBΔN) (Fig. 1a), which is proficient as a GTPase but does not bind DNA13. The complex was formed in the presence of the GTP analog 5’-guanylyl imidodiphosphate (GNP). An atomic model of McrBΔNC was built based on a 3.6 Å resolution cryo-EM map (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Figs. 1–4, Supplementary Tables 1 and 2). McrBΔNC is dumbbell shaped with the two hexameric McrBΔN rings tilted with respect to each other and sandwiching an McrC dimer (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 3). Three-dimensional (3D) classification resulted in nine major classes with varying tilt angle, indicative of conformational plasticity (Supplementary Figs. 3–5, Supplementary Movie 1). As the structure of one McrB hexamer–McrC monomer complex is identical to the other (see “Methods”), only one of them was analyzed.
Fig. 1.
Architecture of McrB∆NC complex. a Domain organization of McrB and McrC. b Structure of McrB∆NC and c of an McrB∆N protomer. The bound nucleotide is shown in stick representation and the magnesium ion as a green sphere. d Architecture of McrB∆N hexamer. The buried surface area at the interfaces are mentioned. Cryo-electron microscopic densities shown as isosurface mesh at 1.5 σ for e GNP-Mg2+ at the AB and f GDP at the DE interface. g Interactions with the guanine base at the AB interface that establish specificity for guanine. Green dashed lines represent potential hydrogen bonds
Architecture of McrBΔN
McrBΔN has the canonical AAA+ fold comprising an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal domain (CTD) (Fig. 1c, Supplementary Fig. 6). The McrBΔN protomers form a ring-like structure, with a pseudo six-fold symmetry (Fig. 1d, Supplementary Table 3). In the hexamer, three consecutive GNP-bound interfaces have a higher buried surface than the GDP-bound interfaces (Fig. 1d–f, Supplementary Fig. 7). GDP could have been retained during McrBΔNC purification (see “Methods”). The nucleotide-binding pocket of McrBΔN comprises the conserved Walker A, Walker B, and sensor 1 residues from one protomer (cis-acting) and the arginine finger from the adjacent protomer (trans-acting). The hydrogen bonds made by the main chain carbonyl group of McrB-Asp176cis and the amino group of McrB-Phe178cis with guanine-N1 and guanine-O6, respectively, determine the specificity for guanine (Fig. 1g). McrB-Asp176cis is in the vicinity of the guanine-N2 and may also contribute to base-specificity.
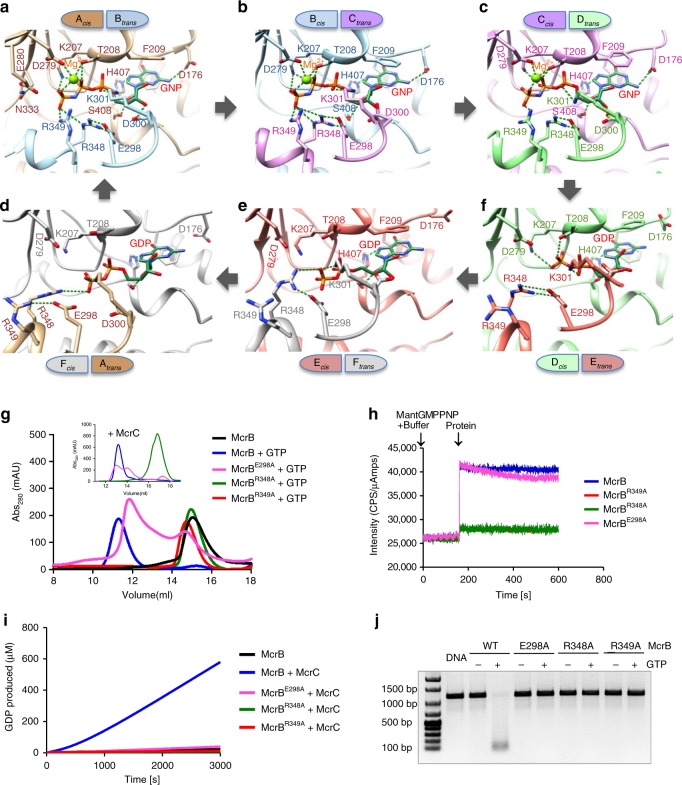
Depending on the bound nucleotide (GNP/GDP), the relative orientation of the protomers (Supplementary Fig. 8) and the interactions between McrBΔN and nucleotide at the six interfaces vary (Fig. 2a–f). At the three GNP-bound interfaces, the Walker A loop interacts with the triphosphate of GNP, while Walker B McrB-Asp279cis coordinates the magnesium ion (Fig. 2a–c). Walker B McrB-Glu280cis that activates the catalytic water and the sensor 1 McrB-Asn333cis that orients the water2 are near the γ-phosphate of GNP (Fig. 2a). The catalytically important arginine finger McrB-Arg349trans (Fig. 2g–j) interacts with the γ-phosphate.
Fig. 2.
Nucleotide binding at the McrBΔN interfaces. a–f Six panels, arranged in a clockwise cyclic manner, illustrating the interactions made with the nucleotide at the six interfaces. Green dotted lines represent potential hydrogen bonds (<3.6 Å) and ionic interactions (<4 Å). g Size exclusion chromatographic profile of McrB and its mutants in the presence of GTP using Superdex 200 column and in the presence of McrC and GTP using Superose 6 column (inset). h Comparison of GNP binding by McrB and its mutants. The binding curves of McrBR348A and McrBR349A overlapped. i Comparison of the GTPase activity of McrB and its mutants in the presence of McrC. j Nucleolytic activity of McrB and its mutants in the presence of McrC
The structure revealed that McrB does not have a canonical cis-acting sensor 2 that interacts with the β- and γ-phosphates. Instead, McrB-Arg348trans, preceding the arginine finger, is within interacting distance of the phosphates. Mutation of McrB-Arg348 to alanine (McrBR348A) affected oligomerization and GTPase activity (Fig. 2g–j). Consequently, we propose that McrB-Arg348trans is the sensor 2. McrB-Glu298trans interacts with and orients McrB-Arg348trans (Fig. 2a). The importance of the interaction was highlighted by McrBE298AC, which bound nucleotide but formed unstable oligomers and did not hydrolyze GTP or cleave DNA (Fig. 2g–j).
The two protomers at the GDP-bound interfaces move away from each other widening the nucleotide-binding pocket, with the FA interface being the widest (Supplementary Fig. 8). At the DE interface, the dinucleotide interacts extensively with the cis protomer, while the trans protomer interacts only with the α-phosphate. In contrast, at the EF and FA interfaces only the α-phosphate interacts with the cis-acting Walker A, while the β-phosphate interacts with the trans-acting sensor 2, suggestive of stepwise loss of contact between GDP and McrBΔN. The asymmetric hexamer and the consecutive arrangement of GNP- and GDP-bound interfaces (Fig. 1d) indicated that hydrolysis of GTP occurs sequentially rather than in concerted or stochastic manner. The direction of the sequential hydrolysis is such that the transition from interface CD to DE represents the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP, while the transition from FA to AB represents exchange of the loosely bound GDP by GTP. This is consistent with the direction of hydrolysis proposed for other AAA+ proteins15–17.
Architecture of McrC
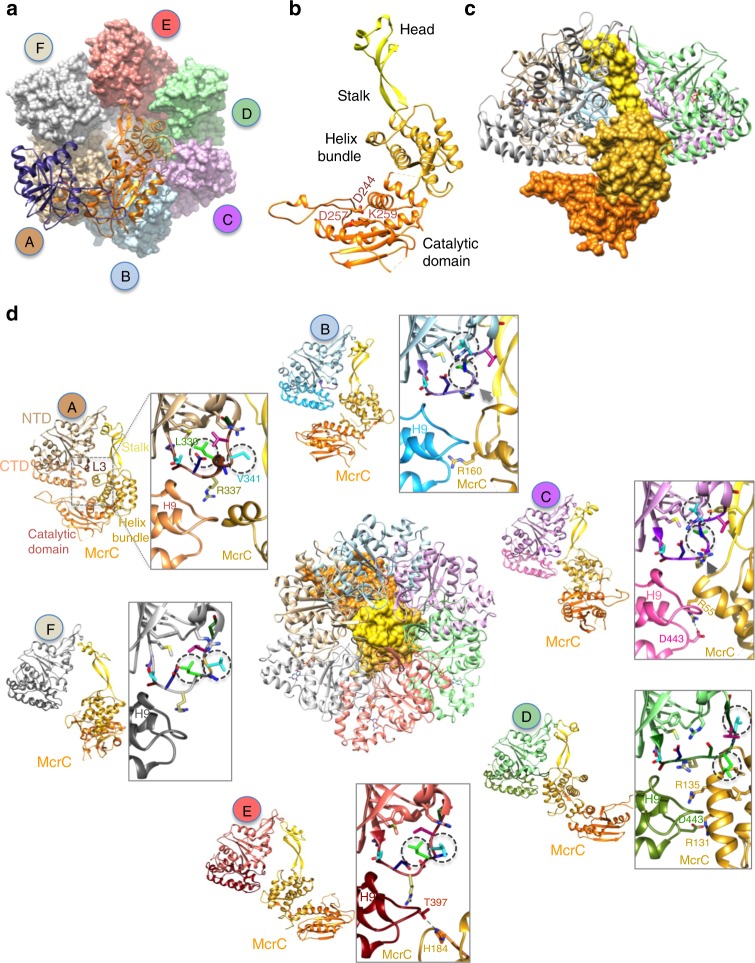
The two protomers of McrC in the McrBΔNC complex are related to each other by a two-fold symmetry (Fig. 3a). Each protomer has a domain with the canonical α/β fold of the PD…D/EXK family nucleases (Fig. 3a, b, Supplementary Fig. 9). The dimeric interface mainly constitutes helix H9 and has a total buried surface area of ~3000 Å2. The catalytic residues, Asp244, Asp257, and Lys259, are located close to the dimeric interface and aligned along the FA interface of McrB. The dimeric interface of McrC is similar to that of the catalytic domain of the mismatch restriction endonuclease EndoMS bound to DNA18 (Supplementary Fig. 10). Using run off sequencing, it has previously been shown that the cleavage results in multiple nicks about ~25–33 bp away from the target site14. Based on the similarity with the structure of EndoMS, we speculate that the cleavage by McrBC will leave behind a 3’-overhang. The stalk’s head plugs the pore of the ring through interactions with loop L1 of all the six McrBΔN protomers (Fig. 3c, d). The remaining part of the stalk interacts primarily with protomer C, mainly through van der Waals contacts. This architecture is reminiscent of the γ subunit inserting into the pore of the α3β3 ring of F1-ATP synthase and regulating ATP synthesis19.
Fig. 3.
Remodeling of McrBΔN by McrC. a The dimer of McrC (ribbon representation) in complex with McrB∆N hexamer (surface representation). Note that this view looks at the face of the ring opposite to that in Fig. 1d. b The structure of an McrC monomer with the nuclease catalytic residues highlighted. c The asymmetric interaction of a monomer of McrC with McrB∆N hexamer. For clarity, protomer E of McrB∆N has been hidden. d Structure of McrB∆NC with the pore of the ring blocked by McrC is shown in the center. Around this figure, the interactions between McrC and the six McrB∆N protomers are illustrated. The inset is a zoom of the interactions between the helix bundle of McrC and L3 and C-terminal domain of McrB∆N protomers, highlighting the McrC-mediated remodeling of L3 in subunits A, B, C and D. The side chains of L3 residues are colored differently. Note the change in position of McrB-V341 (turquoise) and McrB-L339 (green), marked in dashed circles. The steric interaction between the helix bundle of McrC and L3 of B and C subunits are indicated by arrows (gray)
Asymmetric interaction of McrC remodels McrBΔN protomers
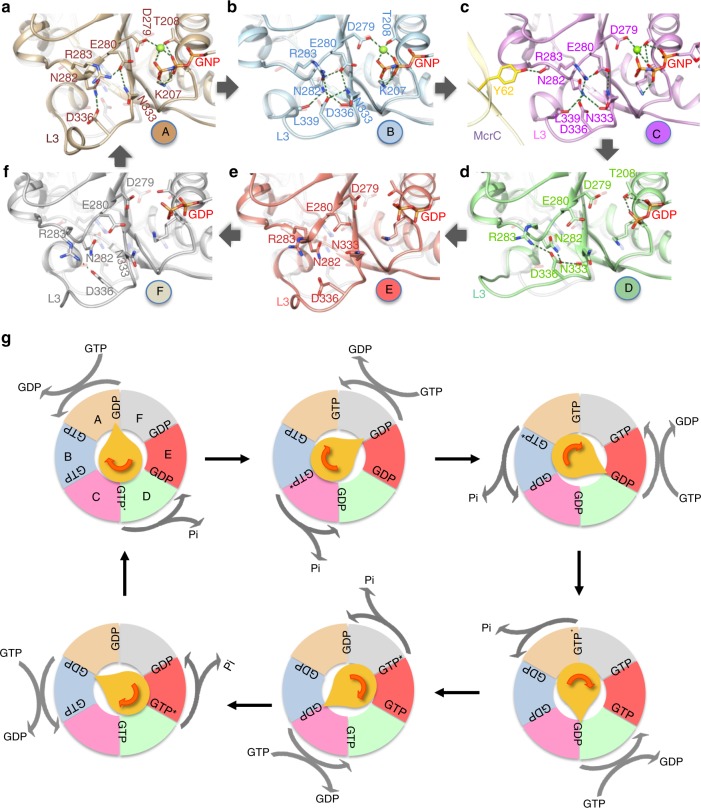
The McrC helix bundle interacts with loop L3 (residues 333–343) and the CTD helix H9 of all the McrBΔN protomers, except F, to varying extent (Fig. 3d). These interactions change the conformation of L3. Based on conformational similarities, L3 of the six interfaces can broadly be grouped into four—that of A in one, B and C in the second, D in the third, and E and F in the fourth—as highlighted by the positions of McrB-Leu339 and McrB-Val341 within a group (Fig. 3d, Supplementary Fig. 11). Conformational change in L3 affects the cis-acting active site residues (Fig. 4a–f).
Fig. 4.
Sequential GTP hydrolysis by McrBC. a–f A zoom of loop L3 of McrB∆N protomers highlighting the conformational changes in them and the interaction network with the catalytically important McrB-Glu280 and Asn333. Overlaid on each panel is the faded image of this region in protomer C. The panels are arranged to follow the clockwise cyclic arrangement of the protomers in the hexamer. g A schematic model illustrating the McrC (yellow) stimulated GTP hydrolysis by McrB. For clarity, only one hexamer and an McrC monomer are shown, and the ring is viewed from the McrC side as in Fig. 3a. GTP* represents the transition state. The pointed end of McrC is located at the interface of GDP-to-GTP exchange and the rounded end is at the interface of GTP hydrolysis
In comparison to L3 of protomer Acis at the AB interface, the conformation of L3 in the protomers Bcis and Ccis at BC and CD, respectively, positions the main-chain carbonyl of McrB-Leu339cis within hydrogen-bonding distance of McrB-Asn282cis (Fig. 4b, c). In addition, McrB-Asn333cis (sensor 1) main-chain carbonyl is hydrogen bonded to McrB-Asn282cis, while the side chain interacts with McrB-Glu280cis (Walker B). Also, the L3 residue McrB-Asp336cis interacts with McrB-Asn333cis. These interactions are absent at the AB interface.
Here McrB-Asn282cis and McrB-Asp336cis appear to function as nodes that communicate the binding of McrC to McrB-Glu280cis and McrB-Asn333cis. These structural alterations could activate the catalytic water for nucleotide hydrolysis (note that water molecules were not observed due to insufficient resolution). Consistent with this proposal, McrBN282A or McrBD336A are not stimulated by McrC20. In addition, at the CD interface, McrC-Y62 interacts with the main-chain carbonyl of McrB-Arg283cis of protomer C, and the region around McrB-Arg283cis undergoes subtle changes (Fig. 4c). The limited resolution of the map cautioned us from drawing conclusions regarding the importance of these changes to hydrolysis. Nevertheless, as the next interface, DE, is GDP-bound, we propose that at the CD interface GTP will be in a transition or hydrolyzed state.
At the DE interface, L3 of protomer Dcis has a unique conformation that changes the position of McrB-Asp336cis along with McrB-Arg283cis (Fig. 4d). At all the GNP-bound interfaces, McrB-Arg283cis, which appears functionally important as McrBR283A cannot hydrolyze GTP or cleave DNA20, electrostatically interacts with McrB-Glu280cis (Fig. 4a–c). The movement of McrB-Arg283cis upon transition to the GDP-bound state affects its interaction with and the orientation of McrB-Glu280cis (Fig. 4d–f). At EF and FA interfaces, where the conformations of the cis-acting L3 are similar, the interaction network among the cis-acting active site residues is absent (Fig. 4e, f). At the next interface, AB, the trans-acting arginine finger and sensor 2 interact with the γ-phosphate of the GNP (Fig. 4a). The conformational change in L3 of protomer Acis and the sensing of the γ-phosphate re-establishes the contacts between McrB-Arg283cis–McrB-Glu280cis and McrB-Asp336cis–McrB-Asn282cis (Fig. 4a) through a network of interactions (Supplementary Fig. 12).
Discussion
Based on the above analysis, we propose that the hydrolysis of GTP by McrB would be initiated at the interface that interacts with the McrC stalk (here the CD interface), while at the diametrically opposite interface (FA) a GTP would enter the hydrolysis cycle (Fig. 4g). For the cycle to continue, McrC will have to reorient such that the stalk positions at the neighboring GTP-bound interface to stimulate hydrolysis, while leaving behind a GDP-bound interface. GDP, which makes very few interactions with the interface residues, will be exchanged by GTP resulting in the movement of the protomers and formation of larger number of interactions with the interface residues. Consistent with this proposed mechanism, it has been shown previously that McrB on its own has a higher affinity for GTP than GDP3. The conformational changes emanating from nucleotide hydrolysis could promote the movement of McrC. A 360° rotation of McrC, akin to that of the F1-ATP synthase γ subunit, will result in hydrolysis of six GTPs (Fig. 4g). Consequently in the tetradecamer, the dimeric McrC will appear stationary, while the two hexameric rings will rotate about their respective pivots, the McrC stalk. We note that the direction of rotation of McrC in the model is opposite to that of the γ subunit, due to the difference in the direction of nucleotide hydrolysis cycle.
Our structure-based mechanism reveals that McrC activates McrB GTPase by remodeling its active site. This is distinct from mechanisms proposed for the activation of other AAA+ proteins by their regulators. In the case of NSF, SNAP binds and alters the conformation of the domain N-terminal to the AAA+ domain to stimulate the ATPase activity4. Activation of the AAA+ ATPase Torsin, which lacks the arginine finger, by LAP1/LULL1 is achieved by providing the arginine through hetero-oligomerization5,6. Thus the mechanism derived here provides a new framework for activation of AAA+ proteins, a phenomenon that remains to be discovered and understood for many other proteins of this family.
The structure also provides mechanistic insights and poses interesting questions on the mode of DNA binding by McrBC and its nucleolytic activity. A single N-terminal DNA-binding domain of McrB recognizes and binds to the 5’-G/A(5mC)-3’ target site11. As in the case of substrate-binding domains/subunits in other AAA+ proteins, the DNA-binding domain of McrB is likely to be located on the surface of the AAA+ hexamer and is not expected to interact with McrC13 (Supplementary Fig. 13). Subsequent to recognition, the DNA interacts with the AAA+ domain. A common feature among nucleic acid binding and translocating AAA+ motors is threading of the substrate through the pore. The inside of the central channel of the AAA+ McrB ring shows a circular patch of positively charged residues (Supplementary Fig. 14a), suggesting the possibility of the DNA threading through the central channel. A particularly interesting feature of McrBΔNC is that the McrC stalk blocks the pore of the McrB ring. It is possible that the DNA substrate requires sliding in through the widest interface cleft (the FA interface in the structure) or that the enzyme complex disassembles and reassembles on the substrate.
The DNA could enter the central channel of the McrB ring and fit together with the stalk of McrC. This would require rearrangement of the McrB protomers to let the DNA in. Previous studies found that DNA binding does not affect the rate of GTP hydrolysis3,14. Consequently, the rearrangement of the AAA+ protomers is not expected to disturb the GTP hydrolyzing catalytic interface. However, the rearrangement could be effected at the GDP-bound interface, which has a lower interface buried surface area. Like many other AAA+ proteins bound to their DNA substrate1, rearrangements at the GDP-bound interface could open the McrB hexamer to form a spiral/lockwasher structure and accommodate the DNA. The active site cleft of McrC with a patch of positive residues, possibly for DNA binding (Supplementary Fig. 14b), is aligned along the FA interface, suggesting a mode of engagement of the nuclease with the substrate DNA (Fig. 2a). The existing structural data does not rule out the possibility of the DNA wrapping around the external surface of the AAA+ ring, without threading into the central channel, to be fed to the active site cleft of dimeric McrC.
DNA cleavage by McrBC requires at least two recognition sequences separated by 40–3000 bp21. The convergence of two tetradecameric complexes possibly activates the dimeric McrC endonuclease. Cleavage happens close to one of the sites because at least one of the two tetradecamers is bound to its target site. As was proposed previously14, and similar to Type I RM enzymes22, the two tetradecamers could converge while remaining bound to their respective target sites via translocation-mediated DNA looping. Convergence of the two tetradecamers results in DNA cleavage by only one of them. Alternatively, one of the tetradecamers could translocate along the DNA, similar to a Type ISP RM enzyme23, while the other remains stationery (Supplementary Fig. 15). DNA translocation will be performed by the hexameric AAA+ domains of McrB. As in the case of AAA+ helicases and proteases1,15–17, the pore loop L1 of McrB protomers are likely to interact with the DNA asymmetrically. The sequential hydrolysis of GTP by the AAA+ domains will alter the interactions made by L1 in a cyclic manner resulting in the translocation of the DNA. We think that translocation of the DNA by McrBC tetradecamer would require engagement of the DNA with only one of the two McrB hexamer.
Interestingly, the hydrolysis of GTP does not change on DNA binding3,14. Hence, it is possible that the GTPase activity of McrBC is not coupled to its movement along the DNA. Instead of GTP-dependent translocation, McrBC could move along DNA by diffusion (Supplementary Fig. 14), facilitating the convergence of the two oligomers of McrBC, as in the case of Type III RM enzymes. In Type III RM enzymes, which have a Superfamily 2 helicase-like ATPase, hydrolysis of the nucleotide (ATP) makes the enzyme proficient to execute passive 1D diffusion along the DNA and cleave it24,25. In conclusion, the structure described here provides a platform for addressing the above questions on the mechanism of DNA cleavage by the AAA+-coupled endonuclease McrBC.
Methods
Mutation of McrB
All the mutations were performed using restriction-free cloning method. The sequence of the primers used to introduce the mutations are listed in Supplementary Table 4. These PCR-amplified fragments with the mutations were used as primers in a second PCR reaction and a plasmid containing McrB wild-type gene, pHISMcrB13, was used as the template to obtain full-length mutant genes. The amplified product was used for restriction-free cloning. All the genes were sequenced to ensure only the desired mutations were incorporated.
Protein purification
Proteins used for the experiment were purified using the protocol in Nirwan et al.13. McrB, McrBΔN, and their mutants were expressed with six histidine tags at C-terminus by overexpression of their respective plasmids (pHISMcrB, pHISMcrBΔN) while the untagged McrC was overexpressed using pHISMcrC. Cultures of transformed E. coli BL21(AI) cells were grown in LB broth (2 l) containing 100 μg/ml ampicillin using a shaker incubator at 37 °C to an OD600 of 0.6. The temperature was then reduced to 18 °C, and expression was induced with 0.06% w/v L-Arabinose. The cultures were grown further overnight (15–16 h) at 18 °C. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation at 4 °C and 3315 × g for 15 min and the pellet was resuspended in 50 ml lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 25 mM imidazole, 500 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 10% glycerol, 0.04% CHAPS). Then the cells were lysed by sonication at 4 °C using Vibra-CellTM system set. The cell lysate was then subjected to ultracentrifugation at 4 °C and 159,200 × g for 40 min in Beckman-OptimaTM ultracentrifuge. The supernatant was then loaded onto 5 ml HiTrap™ Ni-NTA column (GE Life Sciences) equilibrated with Buffer A (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 25 mM imidazole, 500 mM NaCl). The elution of the protein was followed by a step gradient of Buffer B (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 500 mM Imidazole, 500 mM NaCl) from 5 to 100% at intervals of 20%. The purest of the Ni-NTA fractions observed in a 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel were dialyzed against 2 l buffer B50 (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT). Dialyzed McrB or McrBΔN was loaded onto an 8 ml MonoQ 10/100 GL column (GE Life Sciences) equilibrated with Buffer B50. Protein was eluted (in 2 ml fractions) by a linear gradient of 0–50% buffer B1000 (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 1000 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 1 mM DTT) over 20 column volumes. The pure fractions based on 12% SDS denaturing gel were pooled, concentrated up to 500 μl using a 2 ml 10 kDa vivaspin2 concentrator (GE Life Sciences), and washed with 5 ml of buffer B100 (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 100 mM NaCl, and 1 mM DTT) to remove EDTA. The concentrated protein was then incubated with 2.5 mM GTP and 5 mM MgCl2 for 10 min at room temperature followed by centrifugation at 21,000 × g before loading onto 24 ml Superdex200 10/300 GL column (GE Life Sciences) and equilibrated with buffer B100+GTP (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 100 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM GTP, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT). Pure fractions were pooled, concentrated, and washed with storage buffer (100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-Cl pH 7.4 and 1 mM DTT) to remove GTP and finally stored in −80 °C.
McrC was purified with a method very similar to that of McrB and McrB∆N purification. After affinity purification with Ni-NTA column, to which the protein is bound, it was loaded on to 8 ml MonoS 10/100 GL column (GE Life Sciences) equilibrated with Buffer B50. Protein elution was followed by a linear gradient of buffer B1000 from 0 to 50% over 20 column volumes. Based on gel analysis, the pure fractions are pooled, washed with storage buffer, concentrated, and stored in −80 °C.
Reconstitution of McrB∆NC complex
After purifying the individual subunits, a complex of McrB∆N with McrC was purified using size exclusion chromatography (SEC). McrB∆N was mixed with McrC at 4-fold higher molar concentration (i.e., 4:1 ratio) and incubated with 2.5 mM GTP and 5 mM MgCl2 in buffer B100 (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT) for 10 min at room temperature. The sample was centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 15 min before loading onto 120 ml Superdex200 10/300 GL column (GE Life Sciences), equilibrated with buffer B100 + 0.1 mM GTP. Pure fractions were pooled and concentrated using a 2-ml 10 kDa Vivaspin2 concentrator (GE Life Sciences). The concentrated protein was washed to remove GTP with a buffer containing 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-Cl pH 7.4, and 1 mM DTT. The concentrated complex was stored in storage buffer at −80 °C. The bound GDP in the structure could have resulted from the hydrolysis of GTP used during purification.
Grid preparation
Final concentration of 4.0 mg/ml McrBΔNC sample was prepared at room temperature in the buffer 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 2.0 mM GNP, 0.10 M NaCl, and 5.0 mM MgCl2. Three-μl of sample was applied to a freshly glow-discharged holey carbon grid (C-flat CF-2/2-4Cu-T). The grids were then incubated for 3 s at 4 °C, 100% humidity in a Vitrobot (FEI), blotted for 3 s, and plunge cooled in liquid ethane.
Image processing
An initial cryo-EM reconstruction of McrBΔNC at 7.4 Å was obtained using 15,918 particles subsequent to two-dimensional (2D) classification from data collected on a Titan Krios microscope (FEI) operated at 300 kV and with a Falcon 3 detector at the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology (Cambridge, UK). Subsequently, a larger data set was collected at the Cryo-EM Swedish National Facility in SciLifeLab (Solna, Sweden) on a Titan Krios microscope (FEI) operated at 300 kV and equipped with a K2 Summit direct electron detector (Gatan). Micrographs were obtained from automated data collections (EPU software, FEI) at ×130,000 magnification, yielding a pixel size of 1.05 Å. Eight-s exposures yielded a total dose of 30 e−/Å2 in 20 frames, with defocus values ranging from −0.3 to −5.0 μm. A total of 3335 micrographs were recorded and kept. Movie frames were aligned and averaged by global and local motion corrections by the program MotionCor226. Contrast transfer function parameters were estimated by Gctf27.
Particles were picked by Gautomatch and 2D classified by Relion 228. In the first round, particles are picked by Gaussian-based picking, followed by reference-free 2D classification. Several representative 2D classes were used as references for the second-round picking. Finally, 771,763 particles were picked and subjected to 2D classification to discard poorly aligned particles (Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2). The remaining 761,793 particles underwent 3D classification using a 3D reference generated by Relion 3D initial model. Well-resolved classes were selected (corresponding to 225,201 particles) and subjected to 3D refinement. We tried refinement with and without C2 symmetry applied, which gave 4.1 and 3.9 Å resolution, respectively, after post processing.
To achieve higher resolution, the particles were symmetry expanded and 3D refined with local angular search applying the mask covering only one McrB hexamer and the McrC dimerizing part. The final overall resolution was 3.6 Å after post processing (Local EM map 1). To improve the local resolution of the McrB hexamer and the McrC dimerizing part, further 3D refinements with local angular search were performed applying two other local masks followed by post processing (Local EM maps 2 and 3) (Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2).
Simultaneously, 3D classification was performed to classify the movement between the McrB hexamers (Supplementary Fig. 5). Although the movement is continuous, nine distinct classes were obtained. These classes were subjected to 3D refinement and post processing. C2 symmetry was applied during refinement since it gave higher resolution than without symmetry application. Five classes gave relatively high resolution (4.2–4.8 Å, Supplementary Figs. 2–4).
Model building and refinement
Three locally masked maps (Local EM maps 1–3) were used for building and revising of the model using Coot. One McrB hexamer (chains A–F), a full-length McrC (chain M), and the dimerization part (residues 193–343) of the other McrC (chain N) were built as a high-resolution consensus structure. GNP, GDP, and Mg ions were placed at their binding sites. The model was subjected to energy minimization and B factor refinement against the local EM map 1 using phenix.real_space_refine in Phenix. Prior to refinement, hydrogen atoms were added to the model by ReadySet in Phenix to have better clash score. Ramachandran restraints were applied. Non-crystallographic symmetry (NCS) restrains were applied only for the dimerization parts of McrC. The refined structure was validated by MolProbity_ENREF_3529. The statistics are listed in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2.
The full complex models for the five relatively high-resolution 3D classes were built by superposing the refined consensus structures into the maps. The models were first rigid-body fitted in Coot30 and further subjected to energy minimization and B factor refinement by phenix.real_space_refine. Ramachandran, NCS, and reference restraints were applied. The input models were used as the references in Phenix. The statistics are listed in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2. All the structural illustrations were made using Chimera31.
SEC to study oligomerization
The oligomerization of McrB and its mutants (18 μM) in the presence and absence of McrC (4.5 μM) and GTP (2.5 mM) was studied at 4 °C using 24 ml Superdex200 10/300 GL (GE Life Sciences) SEC column in the absence of McrC and 24 ml Superose6 10/300 GL SEC column (GE Life Sciences) in the presence of McrC, as described above. The equilibration buffer contained 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, 5 mM MgCl2, and 0.1 mM GTP. The injected sample volume was 400 μl.
NADH-coupled GTPase assay
NADH-coupled GTPase assay32 was carried out in 200 μl reaction volume consisting of 0.8 μM of McrB or its mutants and 0.2 μM of McrC in hydrolysis buffer supplemented with 1 mM GTP (Jena Bioscience), 0.6 mM NADH (Sigma-Aldrich), 1 mM phosphoenolpyruvate, and 2 U each of pyruvate kinase and lactate dehydrogenase at 37 °C. The three enzymes were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The reaction was performed in 96-well flat bottom plates and absorption at 340 nm and readings were taken at an interval of 10 s for 3000 s using a Varioscan plate reader.
DNA cleavage assay
A 1127-bp substrate was amplified from pHISMcrBΔN plasmid by PCR using T7-Forward (5’-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG-3’) and T7-Reverse (5’-GCTAGTTATTGCTCAGCGG-3’) as primers. Methylation was introduced by using 5-methyldeoxycytosine instead of deoxycytosine in the dNTP mix. The amplified product was purified from PCR mix by using the Qiagen PCR Purification Kit. Nucleolytic cleavage of DNA was carried out in 10 μl reaction mix in digestion buffer (10 mM Tris-Cl pH 8, 50 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT) containing 75 ng substrate DNA incubated with 50 nM McrBC in the presence of 1 mM GTP (Jena bioscience). The reaction was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. Two-μl 6× STES buffer (40% Sucrose, 0.2 M Tris-Cl pH 7.5, 40 mM EDTA, 1% SDS) was added and sample was heated at 65 °C for 10 min to stop the reaction. The cleaved products were resolved on a 0.8% agarose gel containing 2 μg/ml ethidium bromide at 110 V for 45 min and imaged on E-GelTM Imager System (InvitrogenTM Life Technologies).
Nucleotide-binding assay
Nucleotide binding by McrB and its mutants was assessed using fluorescent analog 2’/3’-O-(N-methyl-anthraniloyl) GNP (mantGNP) (Jena Biosciences). Time-dependent change in mantGNP fluorescence was recorded on Horiba FluoroMax® 4 spectrophotometer (Jobin Yvon) at 25 °C in a 10 × 10 mm quartz cuvette. The data were collected with excitation wavelength set at 360 nm and fluorescence signal (S1/R1) was measured at 440 nm (I440) with a slit width of 2 nm. The reaction was started by measuring the fluorescence of 400 nM mantGNP in buffer containing 10 mM Tris-Cl (pH 8.0), 50 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM DTT for 160 s followed by addition of 4 μM protein (McrB or its mutants). The fluorescence signal was further recorded till 600 s. Data from three independent experiments were averaged and plotted using GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Software, Inc, San Diego, CA).
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Supplementary information
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Acknowledgements
The cryo-EM data were collected at the Swedish national cryo-EM facility funded by the Knut and Alice Wallenberg, Family Erling Persson, and Kempe Foundations. We thank M. Carroni, J. Conrad, J-M de la Rosa Trevin, and S. Fleischmann for the smooth running of the data collection and processing and Manali Lalchandani for generating the clones of McrBR348A and McrBR349A mutants. K.S. acknowledges the support of Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India (EMR/2016/000872). N.N. acknowledges Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, India for Senior Research Fellowship. A.A and Y.I. acknowledge the support of the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (FFL15:0325), Ragnar Söderberg Foundation (M44/16), Swedish Research Council (NT_2015-04107), Cancerfonden (CAN 2017/1041), and H2020-MSCA-IF-2017 (799399-Itohribo). K.R.V. acknowledges the Medical Research Council grant (number U105184322) as part of Richard Henderson’s group.
Author contributions
N.N.: Conceptualization, preparation of protein samples for cryo-EM, standardization of biochemical assays, and preparation of mutant proteins and their biochemical characterization. Y.I.: Grid preparation, data collection, 3D reconstruction of high-resolution map, model building, and refinement. P.S.: SEC and GTPase assays of wild-type and mutant proteins. S.B.: GTP binding assays. K.R.V.: Grid preparation, data collection, and 3D reconstruction of the preliminary low-resolution map. A.A.: Access to cryo-EM and supervision of cryo-EM structure determination. K.S.: Conceptualization, supervision, model building, structure and data analyses, and manuscript writing with inputs from all the co-authors.
Data availability
Cryo-EM maps and models are deposited in the Electron Microscopy and Protein Data Banks: EMD-0310 and 6HZ4. Maps and coordinates of five major classes are deposited — EMD-0311 and 6HZ5; EMD-0312 and 6HZ6; EMD-0313 and 6HZ7; EMD-0314 and 6HZ8; EMD-0315 and 6HZ9. Other data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Peer review information: Nature Communications thanks Mohinder Pal and other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Neha Nirwan, Yuzuru Itoh.
Contributor Information
Alexey Amunts, Email: amunts@scilifelab.se.
Kayarat Saikrishnan, Email: saikrishnan@iiserpune.ac.in.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41467-019-11084-1.
References
- 1.Erzberger JP, Berger JM. Evolutionary relationships and structural mechanisms of AAA+ proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2006;35:93–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.101933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wendler P, Ciniawsky S, Kock M, Kube S. Structure and function of the AAA+ nucleotide binding pocket. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012;1823:2–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pieper U, Brinkmann T, Kruger T, Noyer-Weidner M, Pingoud A. Characterization of the interaction between the restriction endonuclease McrBC from E. coli and its cofactor GTP. J. Mol. Biol. 1997;272:190–199. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhao M, et al. Mechanistic insights into the recycling machine of the SNARE complex. Nature. 2015;518:61–67. doi: 10.1038/nature14148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sosa BA, et al. How lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1) activates Torsin. eLife. 2014;3:e03239. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brown RS, Zhao C, Chase AR, Wang J, Schlieker C. The mechanism of Torsin ATPase activation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:E4822–E4831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415271111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schlothauer T, Mogk A, Dougan DA, Bukau B, Turgay K. MecA, an adaptor protein necessary for ClpC chaperone activity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0535717100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kappel L, et al. Rlp24 activates the AAA-ATPase Drg1 to initiate cytoplasmic pre-60S maturation. J. Cell Biol. 2012;199:771–782. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201205021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Loenen WA, Raleigh EA. The other face of restriction: modification-dependent enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:56–69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kruger, T., Wild, C. & Noyer-Weidner, M. McrB: a prokaryotic protein specifically recognizing DNA containing modified cytosine residues. EMBO J. 14, 2661–2669 (1995). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Sukackaite R, Grazulis S, Tamulaitis G, Siksnys V. The recognition domain of the methyl-specific endonuclease McrBC flips out 5-methylcytosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:7552–7562. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vasu K, Nagaraja V. Diverse functions of restriction-modification systems in addition to cellular defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013;77:53–72. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00044-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nirwan N, et al. Hexameric assembly of the AAA+ protein McrB is necessary for GTPase activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:868–882. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Panne D, Raleigh EA, Bickle TA. The McrBC endonuclease translocates DNA in a reaction dependent on GTP hydrolysis. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;290:49–60. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Enemark EJ, Joshua-Tor L. Mechanism of DNA translocation in a replicative hexameric helicase. Nature. 2006;442:270–275. doi: 10.1038/nature04943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gates SN, et al. Ratchet-like polypeptide translocation mechanism of the AAA+ disaggregase Hsp104. Science. 2017;357:273–279. doi: 10.1126/science.aan1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ripstein ZA, Huang R, Augustyniak R, Kay LE, Rubinstein JL. Structure of a AAA+ unfoldase in the process of unfolding substrate. eLife. 2017;6:e25754. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nakae S, et al. Structure of the EndoMS-DNA complex as mismatch restriction endonuclease. Structure. 2016;24:1960–1971. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abrahams JP, Leslie AGW, Lutter R, Walker JE. Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature. 1994;370:621–628. doi: 10.1038/370621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pieper U, Schweitzer T, Groll DH, Gast FU, Pingoud A. The GTP-binding domain of McrB: more than just a variation on a common theme? J. Mol. Biol. 1999;292:547–556. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stewart FJ, Raleigh EA. Dependence of McrBC cleavage on distance between recognition elements. Biol. Chem. 1998;379:611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Studier FW, Bandyopadhyay PK. Model for how type I restriction enzymes select cleavage sites in DNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1988;85:4677–4681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chand MK, et al. Translocation-coupled DNA cleavage by the Type ISP restriction-modification enzymes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015;11:870–877. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ramanathan SP, et al. Type III restriction enzymes communicate in 1D without looping between their target sites. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:1748–1753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807193106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ahmad I, Kulkarni M, Gopinath A, Saikrishnan K. Single-site DNA cleavage by Type III restriction endonuclease requires a site-bound enzyme and a trans-acting enzyme that are ATPase-activated. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:6229–6237. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zheng SQ, et al. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:331–332. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang K. Gctf: real-time CTF determination and correction. J. Struct. Biol. 2016;193:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kimanius D, Forsberg BO, Scheres SH, Lindahl E. Accelerated cryo-EM structure determination with parallelisation using GPUs in RELION-2. eLife. 2016;5:e18722. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen VB, et al. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010;66:12–21. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909042073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010;66:486–501. doi: 10.1107/S0907444910007493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pettersen EF, et al. UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004;13:1605–1612. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Norby JG. Coupled assay of Na+,K+-ATPase activity. Methods Enzymol. 1988;156:116–119. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)56014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Data Availability Statement
Cryo-EM maps and models are deposited in the Electron Microscopy and Protein Data Banks: EMD-0310 and 6HZ4. Maps and coordinates of five major classes are deposited — EMD-0311 and 6HZ5; EMD-0312 and 6HZ6; EMD-0313 and 6HZ7; EMD-0314 and 6HZ8; EMD-0315 and 6HZ9. Other data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.