Abstract
Background
Women with breast implants may have concerns about their ability to successfully breast-feed. The Breast Implant Follow-up Study (BIFS-001) is a large, 10-year observational study evaluating the performance and safety of Natrelle round silicone gel-filled breast implants.
Objectives
This analysis compared lactation outcomes in women enrolled in BIFS-001 who gave birth after they underwent primary augmentation with Natrelle round silicone implants or saline implants.
Methods
At baseline and annually after surgery (>5-year visit window), patients completed questionnaires regarding pregnancy and lactation. Comparisons were made using summary statistics and odds ratios with 90% confidence intervals (OR [90% CI]).
Results
A total of 4679 subjects gave birth at least once after primary augmentation for a total of 5736 live births during the study (silicone, 3695 births; saline, 2041 births). Of these, 3715 (79.4%) women breast-fed at least 1 child, resulting in 80.0% (silicone) and 75.9% (saline) of babies being breast-fed. The most common complication was insufficient milk production, which was reported for 19.6% (silicone) and 19.8% (saline) of single births (OR, 0.94 [0.83, 1.06]). Complications occurred at similar rates in each group when evaluated by incision type, implant size, pocket location, and age.
Conclusions
In this large group of women who gave birth after primary breast augmentation with Natrelle round silicone implants or saline implants, most were able to breast-feed their infants without complications. Lactation complications were comparable between the silicone and saline cohorts, and the incidence was comparable to reports in the general population of women who breast-feed.
Level of Evidence: 2

Cumulative scientific evidence has shown that breast-feeding has many beneficial effects for the infant and the nursing mother.1 Advantages for the breast-fed infant include protection against infections, obesity, and diabetes, and increased intelligence.2 For the mother, breast-feeding may protect against breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and type 2 diabetes.2 Women with breast implants can successfully breast-feed,3,4 although some studies have reported high rates of insufficient milk production among women who have had breast augmentation.4-7
When silicone gel-filled breast implants were approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2006, manufacturers were required to initiate large postapproval studies to evaluate the performance and safety of these devices over a 10-year period.8 The Breast Implant Follow-up Study (BIFS-001) is a large, 10-year study designed to address this FDA requirement in women receiving Natrelle (Allergan plc, Dublin, Ireland) round silicone breast implants. Natrelle silicone implants are available worldwide for primary augmentation, revision-augmentation, primary reconstruction, and revision-reconstruction, and have demonstrated long-term safety and patient satisfaction in clinical trials.9-11
In addition to collecting long-term safety data,12 BIFS-001 evaluated lactation outcomes in women who experienced live births after undergoing primary augmentation with Natrelle round silicone implants or saline implants. The present analysis compares lactation outcomes in women who had surpassed the 5-year visit window, both overall and stratified by incision site, implant location, implant size, and subject age.
METHODS
Study Design
BIFS-001 is an ongoing, multicenter, 10-year observational study in women who received Natrelle round silicone or saline implants. Patient enrollment began in February 2007 and all patients were enrolled by March of 2010. All silicone implants were required to be Natrelle devices. The study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) at each investigational site and a central IRB (IRB Company Inc, Buena Park, CA) and is being conducted in accordance with Good Clinical Practice guidelines and World Health Organization guidelines. The study is registered at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00443274). All patients provided written informed consent before undergoing any study-related procedure.
Patients
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for BIFS-001 have been published previously.12,13 This subanalysis of BIFS-001 included only women who experienced live births after undergoing primary augmentation surgery with unilateral or bilateral silicone implants or saline implants. Eligible patients were women aged 22 years or older who were fluent in English or Spanish. Patients were excluded if they were transgender or were deemed by the investigator to be unsuitable candidates for long-term follow-up. The incision site and implant location were selected at the discretion of the investigator.
Assessments
Patients completed questionnaires at baseline and annually after surgery, which included a series of questions regarding pregnancy and lactation as well as other outcomes (eg, adverse events and satisfaction) that are reported separately.12,14 Mothers who had stopped breast-feeding a baby that was born after their primary augmentation procedure were asked if they had any of the following complications before they stopped breast-feeding: mastitis, not enough milk production, too much milk production, excess pain, nipple inversion, or another problem with their breasts.
Statistical Analyses
Lactation outcomes for women who had surpassed the 5-year visit window were compared for patients with silicone and saline implants by means of summary statistics and odds ratios (silicone/saline) with 90% confidence intervals (OR [90% CI]). Adjusted ORs were estimated from a logistic regression model and adjusted for covariates of breast-feeding difficulty history, body mass index (BMI), incision site, miscarriage history, current alcohol consumption, race, smoking status, and education level. Rates of breast-feeding and lactation complications were stratified by incision site for implant placement (inframammary, periareolar, mastopexy, and transaxillary), implant location (partial submuscular, complete submuscular, and subglandular), implant size (<400 cc vs ≥400 cc), and mother’s age at the time of implantation (22-29 years vs ≥30 years).
RESULTS
Patients
The study enrolled 29,148 eligible women who underwent primary augmentation with silicone implants and 13,725 eligible women who underwent primary augmentation with saline implants. Of 4679 women who gave birth at least once after they underwent primary augmentation, 3715 (79.4%) reported breast-feeding at least one baby during the study. Table 1 shows the baseline demographics and baseline pregnancy and breast-feeding history for women who breast-fed during the study. The median (range) age at enrollment for the women who breast-fed was 27.0 years (range, 22-44 years) in the silicone group and 26.5 years (range, 22-42 years) in the saline group. In both groups, the majority were white (silicone, 76.6%; saline, 68.0%) and had normal BMI (18.5‒24.9 kg/m2) at baseline (silicone, 80.4%; saline, 79.0%). Compared with the primary augmentation population in the overall study in both the silicone and saline groups, the women in the current study were younger (median, 27 years vs 32-34 years) and had a smaller proportion of individuals with BMI ≥25 kg/m2 (9-12% vs 14-19%).13 The median duration of follow-up after breast augmentation to the last date of data collection was 3.6 years (range, 0.85-8.3 years) for the silicone group and 3.8 years (range, 0.88-8.5 years) for the saline group.
Table 1.
Demographics and Baseline Characteristics of Women Who Had Undergone Primary Augmentation and Tried to Breast-feed During the Study
| Silicone implants (n = 2427) |
Saline implants (n = 1288) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Age, y | ||
| Mean (SD) | 27.9 (4.3) | 27.1 (3.9) |
| Median (min, max) | 27.0 (22, 44) | 26.5 (22, 42) |
| Age category, no. (%) | ||
| 22‒29 y | 1655 (68.2) | 972 (75.5) |
| 30‒39 y | 754 (31.1) | 312 (24.2) |
| 40‒49 y | 18 (0.7) | 4 (0.3) |
| Race, No. (%) | ||
| White | 1860 (76.6) | 876 (68.0) |
| Hispanic | 317 (13.1) | 259 (20.1) |
| Asian | 108 (4.5) | 62 (4.8) |
| Black | 43 (1.8) | 32 (2.5) |
| Other | 91 (3.8) | 55 (4.3) |
| Missing | 8 (0.3) | 4 (0.3) |
| BMI | n = 2393 | n = 1266 |
| Mean (SD) kg/m2 | 21.4 (2.7) | 21.9 (2.8) |
| BMI category, no. (%) | ||
| Underweight (<18.5 kg/m2) | 214 (8.8) | 94 (7.3) |
| Normal (18.5‒24.9 kg/m2) | 1950 (80.4) | 1018 (79.0) |
| Overweight (≥25 kg/m2) | 229 (9.4) | 154 (12.0) |
| Missing | 34 (1.4) | 22 (1.7) |
| Baseline pregnancy and breast-feeding history, no. (%) | ||
| Completed baseline reproductive questionnaire | n = 2400 | n = 1268 |
| Ever pregnanta | 1444 (60.2) | 774 (61.0) |
| Tried to breast-feedb | 762 (52.8) | 220 (28.4) |
| Difficulties of breast-feedingc | ||
| None | 479 (62.9) | 140 (63.6) |
| Not enough milk production | 103 (13.5) | 31 (14.1) |
| Mastitis | 101 (13.3) | 25 (11.4) |
| Excess pain | 43 (5.6) | 9 (4.1) |
| Too much milk production | 38 (5.0) | 7 (3.2) |
| Nipple inversion | 19 (2.5) | 8 (3.6) |
| Other | 22 (2.9) | 10 (4.5) |
aPercentage calculated using the number of patients who filled out the baseline reproductive questionnaire as the denominator. bPercentage calculated using the number of patients who were ever pregnant as the denominator. cPercentage calculated using the number of patients who tried to breast-feed as the denominator.
Approximately 60% of the women who breast-fed during the study had been pregnant before they underwent augmentation (Table 1). The proportion of those women who had a prestudy history of trying to breast-feed was higher in the silicone group (52.8%) than in the saline group (28.4%). Among women who breast-fed before augmentation, the most commonly (>10%) reported prestudy breast-feeding complications were insufficient milk production (silicone, 13.5%; saline, 14.1%) and mastitis (silicone, 13.3%; saline, 11.4%).
Lactation Outcomes After Primary Augmentation
Of the 5736 live births during the study (silicone, 3695 births; saline, 2041 births), 80.0% and 75.9% of babies were breast-fed by women in the silicone group and saline group, respectively (Table 2). Most women who did not breast-feed chose not to for reasons other than their implants or due to a problem with the baby that prevented breast-feeding. In approximately 4% of births, the baby had a problem that prevented breast-feeding. Breast-feeding rates were comparable among babies of mothers with different incision sites, implant sizes, and age categories (Table 2). The proportion of infants who were breast-fed was slightly lower for mothers with subglandular implant placement (silicone, 74.8%; saline, 67.7%) compared with submuscular placement (partial submuscular: silicone, 81.3%; saline: 76.1%; complete submuscular: silicone, 79.3%; saline, 76.6%). Overall, most infants (94.4%) were able to suckle (ie, able to obtain nourishment from either a bottle or the breast).
Table 2.
Number of Live Births and Rates of Breast-feeding After Primary Augmentation
| No. of live births | Silicone implants | Saline implants |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | 3695 | 2041 |
| Single birthsa | 2393 | 1331 |
| Multiple birthsb | 1302 | 710 |
| Baby was breast-fed, no. (%) | 2955 (80.0) | 1549 (75.9) |
| Reason for not breast-feeding, no. (%)c | ||
| Mother decided not to breast-feed | 514 (13.9) | 345 (16.9) |
| Baby had a problem that prevented breast-feeding | 154 (4.2) | 87 (4.3) |
| Mother decided not to due to her implants | 109 (2.9) | 75 (3.7) |
| Implant location | ||
| Submuscular-partial | 2162 | 1156 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 1758 (81.3) | 880 (76.1) |
| Submuscular-complete | 1137 | 808 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 902 (79.3) | 619 (76.6) |
| Subglandular | 373 | 65 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 279 (74.8) | 44 (67.7) |
| Incision site | ||
| Inframammary | 2322 | 989 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 1865 (80.3) | 758 (76.6) |
| Periareolar | 957 | 640 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 766 (80.0) | 470 (73.4) |
| Mastopexy | 202 | 93 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 154 (76.2) | 56 (60.2) |
| Transaxillary | 155 | 188 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 124 (80.0) | 158 (84.0) |
| Implant size | ||
| <400 cc | 2133 | 1116 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 1733 (81.2) | 869 (77.9) |
| ≥400 cc | 1540 | 921 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 1203 (78.1) | 678 (73.6) |
| Age group | ||
| 22-29 years | 2560 | 1549 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 2046 (79.9) | 1194 (77.1) |
| ≥30 years | 1135 | 492 |
| Breast-fed baby, no. (%) | 909 (80.1) | 355 (72.2) |
aSingle birth during the study. bMore than 1 birth during the study. cBased on number of births who were not breast-fed.
The percentages of mothers reporting lactation complications were similar in the silicone and saline implant groups and for both mothers who had single vs multiple births during the study (Table 3). The most common complication was insufficient milk production, which was reported for 19.6% and 19.8% of single births in the silicone and saline groups, respectively, corresponding to 25.0% and 26.3% of breast-fed single births. Mastitis was reported for 4.1% and 3.7% of single births in the silicone and the saline groups, respectively, or 5.2% and 4.9% of breast-fed single births. The complications of excess pain, excessive milk production, and nipple inversion were all reported for fewer than 5% of single births. The only complication that was significantly different between the silicone and saline groups was excessive milk production, which occurred at a lower rate in the silicone group (0.6% of single births) than in the saline group (1.3% of single births; adjusted OR [90% CI]: 0.52 [0.32, 0.84]).
Table 3.
Lactation Complications Reported by Women Who Breast-fed After Primary Breast Augmentation
| No. of live births | Silicone implants | Saline implants | Silicone/saline | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single birth (n = 2393) | Multiple birth (n = 616) | Single birth (n = 1331) | Multiple birth (n = 339) | Odds ratiob (90% CI) |
Adjusted odds ratiob (90% CI) | |
| Complication, no. (%)a | ||||||
| Not enough milk production | 470 (19.6) | 238 (18.3) | 264 (19.8) | 127 (17.9) | 1.00 (0.89, 1.12) | 0.94 (0.83, 1.06)c |
| Mastitis | 97 (4.1) | 68 (5.2) | 49 (3.7) | 33 (4.6) | 1.12 (0.89, 1.40) | 1.12 (0.89, 1.41)d |
| Excess pain | 77 (3.2) | 51 (3.9) | 59 (4.4) | 18 (2.5) | 0.92 (0.72, 1.17) | 0.96 (0.75, 1.22)e |
| Nipple inversion | 24 (1.0) | 10 (0.8) | 17 (1.3) | 3 (0.4) | 0.94 (0.59, 1.50) | 1.00 (0.63, 1.60)e |
| Too much milk production | 14 (0.6) | 9 (0.7) | 17 (1.3) | 8 (1.1) | 0.51 (0.31, 0.81) | 0.52 (0.32, 0.84)f |
| Other | 64 (2.7) | 36 (2.8) | 39 (2.9) | 15 (2.1) | 1.02 (0.77, 1.36) | 1.03 (0.78, 1.37)g |
aPercentages based on total number of live births. bEstimated from a Logistic Regression model. Saline is the reference group. cModel adjusted for the following covariates: breast-feeding difficulty history, body mass index, incision site, miscarriage history, and smoking status. dModel adjusted for miscarriage history. eModel adjusted for the following covariates: current alcohol consumption, race, and smoking status. fModel adjusted for covariate of race. gModel adjusted for education level.
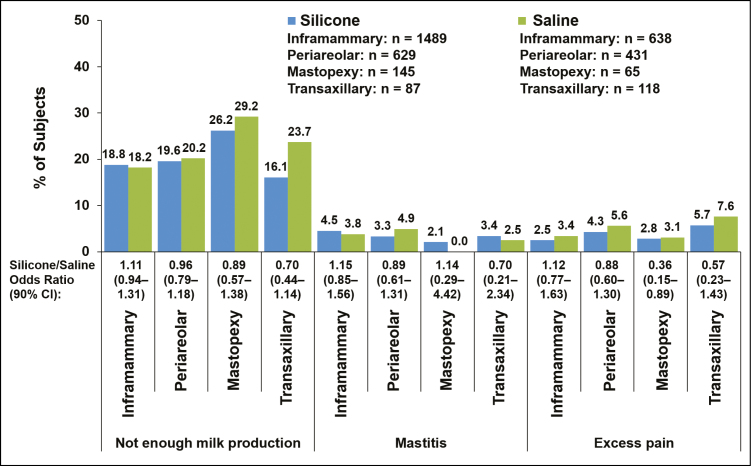
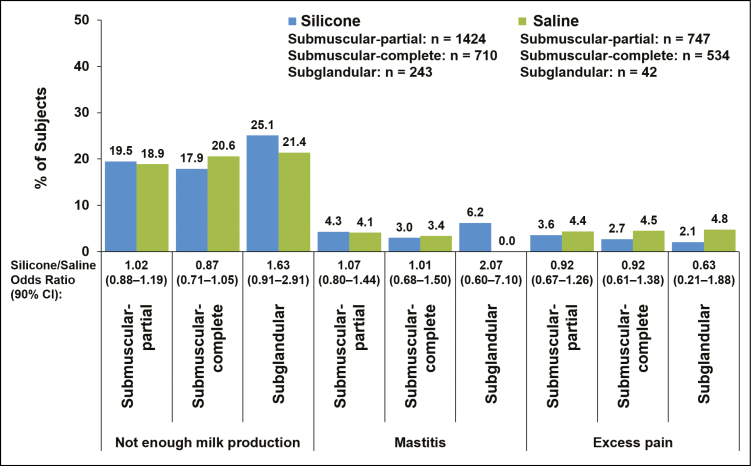
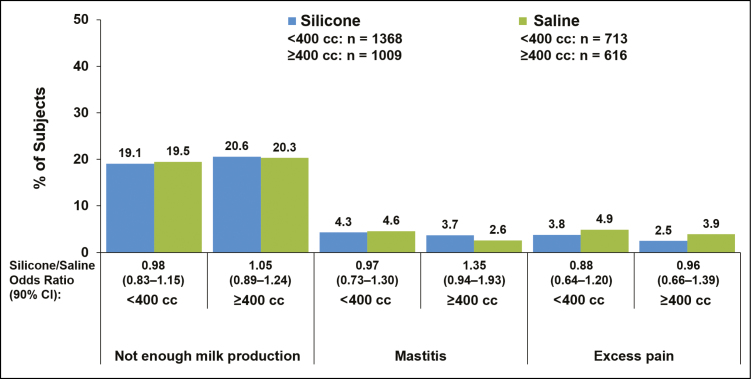
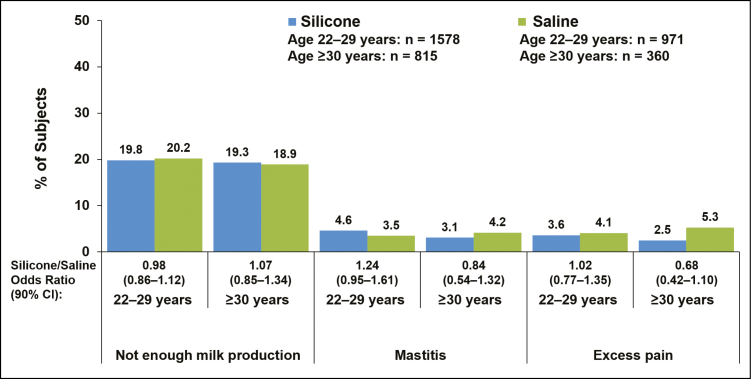
Complication rates for silicone vs saline implants were within 5 percentage points of each other for women with implants placed via inframammary, periareolar, or mastopexy incisions (Figure 1), for partial submuscular or complete submuscular pocket locations (Figure 2), and for smaller (<400 cc) or larger implants (≥400 cc) (Figure 3). Insufficient milk production was reported more frequently among women with silicone implants placed via mastopexy incision (26.2%) compared with inframammary (18.8%), periareolar (19.6%), and transaxillary incisions (16.1%); rates of insufficient milk production with saline implants were highest with mastopexy (29.2%) and transaxillary incisions (23.7%) compared with inframammary (18.2%) and periareolar incisions (20.2%; Figure 1). In general, complication rates were slightly higher among women with subglandular implant placement compared with submuscular implants (Figure 2). The rate of insufficient milk production was 25.1% with subglandular implant placement, 19.5% with partial submuscular placement, and 17.9% with complete submuscular placement for silicone implants; rates for saline implants followed a similar pattern (Figure 2). It should be noted that for the saline group the sample size for subglandular implant placement was relatively small (n = 42) compared with partial submuscular (n = 747) and complete submuscular (n = 534) implant placement. Younger (22-29 years) and older mothers (≥30 years) experienced lactation complications at similar rates (Figure 4).
Figure 1.
Percentage of patients with lactation complications shown by incision site in women who had single-births after they underwent primary augmentation with silicone or saline implants. Data for the complications of nipple inversion and excessive milk production are not shown, because they occurred in fewer than 2.5% of patients in any group.
Figure 2.
Percentage of patients with lactation complications shown by implant placement in women who had single-births after they underwent primary augmentation with silicone or saline implants. Data for the complications of nipple inversion and excessive milk production are not shown, because they occurred in fewer than 2.5% of patients in any group.
Figure 3.
Percentage of patients with lactation complications shown by implant size group (<400 cc vs ≥400 cc) in women who had single-births after undergoing primary augmentation with silicone or saline implants. Data for the complications of nipple inversion and excessive milk production are not shown, because they occurred in fewer than 2.5% of patients in any group.
Figure 4.
Percentage of patients with lactation complications shown by age group (22-29 years vs ≥30 years) in women who had single births after they underwent primary augmentation with silicone or saline implants. Data for the complications of nipple inversion and excessive milk production are not shown, because they occurred in fewer than 2.5% of patients in any group.
Representative photographs show 2 women before augmentation, with silicone implants before or during pregnancy, during lactation, and after stopping breast-feeding (Supplemental Figures 1 and 2, available online at www.aestheticsurgeryjournal.com).
DISCUSSION
BIFS-001 is the first study to report lactation outcomes in a large population of women who breast-fed after they underwent primary breast augmentation with Natrelle round silicone implants or saline implants. The study population included more than 3500 women, who gave birth to more than 5000 babies. Data from women who surpassed the 5-year visit window demonstrate that mothers with implants decided to breast-feed in approximately 80% of births, a rate that aligns well with the rate of breast-feeding initiation in the general population in the United States (79% of newborns in 2011),15 as well as previously reported rates of breast-feeding among mothers with augmented breasts (63%-93%).4,16,17 The incidences of complications in BIFS-001 were generally similar among women with silicone and saline implants, regardless of incision site, implant location, implant size, and subject age.
The most common lactation complication reported in the current study was insufficient milk production, which occurred at a rate (18%-20%) that was not unexpected based on other studies of breast-feeding mothers with and without implants. The Infant Feeding Practice Study II (IFPS II), a longitudinal survey of approximately 5000 pregnant women in the United States, evaluated breast-feeding outcomes in 2586 breast-feeding mothers of single birth infants born between 2005 and 2006.18 Although the presence of breast implants was not assessed in IFPS II, it can be assumed that most of these women were implant naïve. Nearly half (47%) of mothers stopped breast-feeding their infants before they reached the age of 3 months, and approximately half of those mothers cited insufficient milk supply as a reason for stopping breast-feeding. Inadequate milk production was reported by 36 (11%) women who breast-fed in a study that evaluated lactation outcomes in 323 women who attempted breast-feeding after primary augmentation with Natrelle 410 form-stable implants.19 The perception that a mother is not producing enough milk for adequate growth of her infant is common among women who breast-feed, but it may not be accurate.18,20 A study of 45 exclusively breast-fed infants demonstrated that despite energy intake lower than formula-fed infants, there was no difference in rate of weight gain.20 Data regarding the duration of breast-feeding, infant weight gain, or the need for formula supplementation are not available for BIFS-001; therefore, a more thorough evaluation of sufficiency of milk production after breast augmentation in this population is not possible.
Three studies published in the 1990s reported that periareolar incisions were associated with higher rates of lactation problems, such as insufficient milk production or nipple pain, compared with inframammary incisions,5-7 although this has not been confirmed in more recent studies.4,19 One author proposed that the problems in women with periareolar incisions were related to degree of disruption of glandular tissue with periareolar incision rather than the site of skin incision.21 We did not observe a higher incidence of lactation problems with periareolar incision in BIFS-001. However, mastopexy was associated with higher rates of insufficient milk production than other incision sites, presumably due to the technical aspects of this surgery.
Complication rates were slightly higher in patients with subglandular implant placement compared with submuscular placement, suggesting greater disruption of glandular tissue with this technique. Although it is not known whether subglandular placement is associated with greater pressure on glandular tissue compared with submuscular placement, it is possible that the implant itself applies pressure to the glandular tissue, which could, in turn, inhibit the ability to produce milk.5,21,22
One might expect that pressure applied to the glandular tissue by the implant could result in impaired drainage from the milk ducts,22 potentially increasing the risk of mastitis in women with implants.23 However, our data suggest that mastitis may have occurred at a higher rate before augmentation than after augmentation in BIFS-001. Approximately 11% to 13% of women in this analysis who had breast-fed before undergoing breast augmentation had a prestudy history of mastitis. In contrast, mastitis was reported for approximately 5% of breast-fed single births after augmentation. The rate was slightly higher among women who had subglandular (6.2%) vs partial or complete submuscular (3%-4%) placement of silicone implants. Although the preaugmentation incidence of mastitis aligns with reported rates in the general population, the postaugmentation rate was lower than in the general population. Approximately 20% (70/346) of implant-naïve mothers developed mastitis while breast-feeding in one prospective cohort study conducted at 2 hospitals in Australia between 2009 and 2011.24 The incidence of mastitis was 9.5% in a US study (n = 840) by physician diagnosis in the initial 12 weeks of breast-feeding.25 The reason for the low rate of mastitis in women with implants in the current study is unclear.
Breast and nipple pain are common concerns for all nursing women and have been shown to contribute to early discontinuation of breast-feeding.18,26 The IFPS II found that approximately 75% of mothers (n = 2561) reported experiencing pain at some point during the first 2 weeks of nursing.27 Of those who reported pain while breast-feeding, 5.4% rated the pain as 10 on a scale of 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain) during the first week and 3.4% rated the pain as 10 in the second week of breast-feeding. Although the threshold for “excessive pain” was not defined in the questionnaire used in BIFS-001, the reported incidence of excessive pain (~5%) is consistent with reports for the general population.
The complication of excessive milk production was reported at a significantly lower rate in the silicone group (0.6% of single births) than in the saline group (1.3% of single births). Further study is needed to determine if this difference is clinically meaningful, given the relatively low number of reported events (<1.5% or <20 events in any group).
Several limitations of the current analysis should be noted. The results of this study are limited to Allergan breast implants. While both smooth and textured round implants were included in the study, textured devices accounted for only 8.8% of silicone and 2.9% of saline implants.12 This imbalance did not allow for meaningful comparisons between textured and smooth devices. Mother-reported complications of insufficient milk production may be subjective and variable. However, standardized objective measures of milk production are not available. Furthermore, retrospective surveys are limited by the possibility that subjects’ recall of past events may not be accurate. Complications with breast-feeding prior to breast augmentation were based on recall of events that may have occurred many years in the past. Complications reported after breast augmentation were based on subject’s recall after they had completed breast-feeding. It is therefore possible that some complications may be underreported.
CONCLUSIONS
In this large group of women who underwent primary breast augmentation, most were able to successfully breast-feed their infants without complications. Lactation complications were similar between the silicone and saline groups regardless of incision type, implant placement, implant size, or age. The incidence of lactation complications was comparable to reports of such complications in the general population of women who elect to breast-feed. These findings from BIFS-001 indicate a positive outlook for the ability of women to breast-feed after primary breast augmentation.
Disclosures
Dr Jewell has served as a consultant for Allergan plc, NewBeauty magazine, Merz, and Solta; has received research funding through grants or contracts from Allergan plc, Mentor, Pfizer-Excaliard, and Solta; and holds patents or has patents pending with AorTech and Pfizer-Excaliard. Dr Edwards is a consultant for Allergan plc, Pacira, and TouchMD. Ms Murphy was an employee of Allergan plc at the time of this study and manuscript preparation and owns stock in the company. Dr Schumacher is an employee of Allergan plc and owns stock in the company.
Funding
Allergan plc, Dublin, Ireland funded editorial support for this article. Writing and editorial assistance was provided to the authors by Peloton Advantage, Parsippany, NJ. Data collection and writing of the manuscript was performed by the principal author with the assistance of his coauthors and without funding support.
Supplementary Material
REFERENCES
- 1. American Academy of Pediatrics. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Victora CG, Bahl R, Barros AJ, et al. ; Lancet Breastfeeding Series Group Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Jewell ML, Jewell JL. A comparison of outcomes involving highly cohesive, form-stable breast implants from two manufacturers in patients undergoing primary breast augmentation. Aesthet Surg J. 2010;30(1):51-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Cruz NI, Korchin L. Breastfeeding after augmentation mammaplasty with saline implants. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;64(5):530-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hurst NM. Lactation after augmentation mammoplasty. Obstet Gynecol. 1996;87(1):30-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Strom SS, Baldwin BJ, Sigurdson AJ, Schusterman MA. Cosmetic saline breast implants: a survey of satisfaction, breast-feeding experience, cancer screening, and health. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100(6):1553-1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Neifert M, DeMarzo S, Seacat J, Young D, Leff M, Orleans M. The influence of breast surgery, breast appearance, and pregnancy-induced breast changes on lactation sufficiency as measured by infant weight gain. Birth. 1990;17(1):31-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. FDA update on the safety of silicone gel-filled breast implants. 2011. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/MedicalDevices/ProductsandMedicalProcedures/ImplantsandProsthetics/BreastImplants/UCM260090.pdf. Accessed May 11, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 9. Spear SL, Murphy DK; Allergan Silicone Breast Implant U.S. Core Clinical Study Group Natrelle round silicone breast implants: core study results at 10 years. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(6):1354-1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Maxwell GP, Van Natta BW, Bengtson BP, Murphy DK. Ten-year results from the Natrelle 410 anatomical form-stable silicone breast implant core study. Aesthet Surg J. 2015;35(2):145-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Murphy DK, Beckstrand M, Sarwer DB. A prospective, multi-center study of psychosocial outcomes after augmentation with natrelle silicone-filled breast implants. Ann Plast Surg. 2009;62(2):118-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Singh N, Picha GJ, Hardas B, Schumacher A, Murphy DK. Five-year safety data for more than 55,000 subjects following breast implantation: comparison of rare adverse event rates with silicone implants versus national norms and saline implants. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(4):666-679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Singh N, Picha GJ, Murphy DK. Natrelle silicone breast implant follow-up study: demographics, lifestyle, and surgical characteristics of more than 50,000 augmentation subjects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(1):70-81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Alderman A, Pusic A, Murphy DK. Prospective analysis of primary breast augmentation on body image using the BREAST-Q: results from a nationwide study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(6):954e-960e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Breastfeeding report card United States 2014. 2014. http://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/pdf/2014breastfeedingreportcard.pdf. Accessed April 12, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 16. Roberts CL, Ampt AJ, Algert CS, Sywak MS, Chen JS. Reduced breast milk feeding subsequent to cosmetic breast augmentation surgery. Med J Aust. 2015;202(6):324-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Filiciani S, Siemienczuk GF, Nardín JM, et al. Cohort study to assess the impact of breast implants on breastfeeding. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138(6):1152-1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Li R, Fein SB, Chen J, Grummer-Strawn LM. Why mothers stop breastfeeding: mothers’ self-reported reasons for stopping during the first year. Pediatrics. 2008;122(Suppl 2):S69-S76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Lund HG, Turkle J, Jewell ML, Murphy DK. Low risk of skin and nipple sensitivity and lactation issues after primary breast augmentation with form-stable silicone implants: follow-up in 4927 subjects. Aesthet Surg J. 2016;36(6):672-680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Butte NF, Garza C, Smith EO, Nichols BL. Human milk intake and growth in exclusively breast-fed infants. J Pediatr. 1984;104(2):187-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Brody GS. Lactation after augmentation mammoplasty. Obstet Gynecol. 1996;87(6):1062-1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Michalopoulos K. The effects of breast augmentation surgery on future ability to lactate. Breast J. 2007;13(1):62-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. World Health Organization. Mastitis: Causes and Management. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 24. Cullinane M, Amir LH, Donath SM, et al. Determinants of mastitis in women in the CASTLE study: a cohort study. BMC Fam Pract. 2015;16:181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Foxman B, D’Arcy H, Gillespie B, Bobo JK, Schwartz K. Lactation mastitis: occurrence and medical management among 946 breastfeeding women in the United States. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;155(2):103-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Stuebe AM, Horton BJ, Chetwynd E, Watkins S, Grewen K, Meltzer-Brody S. Prevalence and risk factors for early, undesired weaning attributed to lactation dysfunction. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2014;23(5):404-412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Infant Feeding Practices Study II Chapter 2: Neonatal Survey. 2014. http://www.cdc.gov/ifps/pdfs/data/ifps2_tables_ch2.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.