Abstract
Chemical synthesis typically relies on reactions that generate complexity through elaboration of simple starting materials. Less common are deconstructive strategies toward complexity—particularly those involving carbon-carbon bond scission. Here, we introduce one such transformation: the hydrodealkenylative cleavage of C(sp3)-C(sp2) bonds, conducted below room temperature, using ozone, an iron salt, and a hydrogen atom donor. These reactions are performed in nonanhydrous solvents and open to the air; reach completion within 30 minutes; and deliver their products in high yields, even on decagram scales. We have used this broadly functionality tolerant transformation to produce desirable synthetic intermediates, many of which are optically active, from abundantly available terpenes and terpenoid-derived precursors. We have also applied it in the formal total syntheses of complex molecules.
A common ideal in chemical synthesis is the assembly of complex molecules from simple precursors, often accompanied by the need to install carbon centers with precisely defined stereochemical arrangements. Despite the bevy of methods available to accomplish such goals, sometimes it can be more efficient to reorganize starting materials already containing the required complexity and/or stereo-chemistry into the desired molecular structures. Furthermore, deconstructive strategies can provide access to challenging, or otherwise inaccessible, molecular structures (1–3). The literature contains many examples of C–C bond fragmentations (Fig. 1A). Some well-established C(sp2)– C(sp2) bond scissions are oxidative cleavage (e.g., ozonolysis) and olefin metathesis (4–6). There are also reports of C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond fragmentations (1, 7–9), albeit in much smaller numbers, but these transformations typically require activation of the C–C bond through the effects of a neighboring heteroatom, ring strain, or a leaving group in the reactant. Nevertheless, general methods for the functionalization of C(sp3)–C(sp2) bonds remain elusive. Given th profuse number of organic molecules containing these linkages, activation of such bonds in a controllable manner would be extremely useful.
Fig. 1. Concept and applications of hydrodealkenylative fragmentation of C(sp3)–C(sp2) bonds.
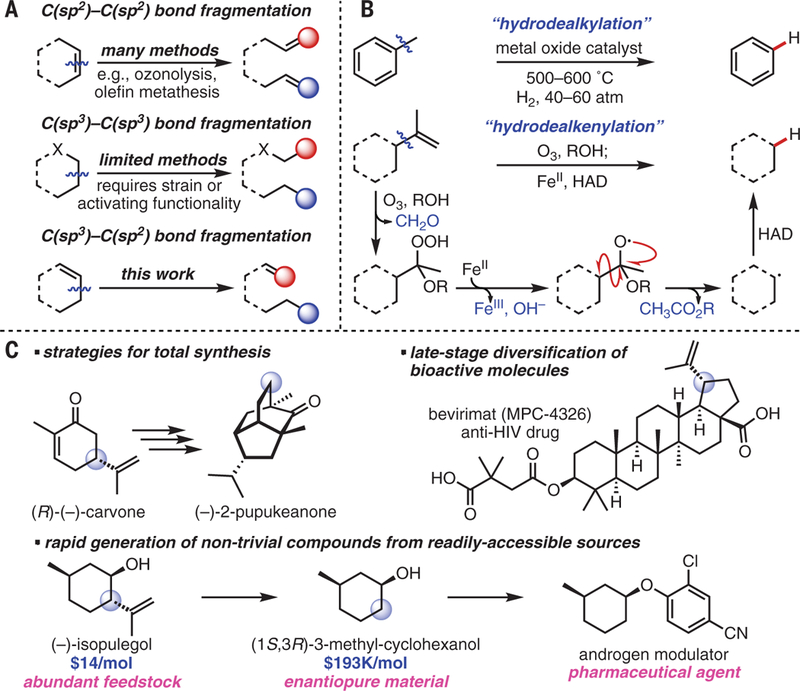
(A) Deconstructive fragmentation of C–C bonds. (B) Overview and proposed mechanism of hydrodealkenylation. (C) Applications of hydrodealkenylation. X, activating functionality; R, alkyl group.
The net reaction described here involves cleavage of a C(sp3)–C(sp2) bond, followed by formation of a new C(sp3)–H bond (Fig. 1B). We refer to this process as hydrodealkenylation, coined with a nod to the hydrodealkylation process that is most commonly exemplified in the conversion of toluene to benzene in the presence of H2 gas at high temperatures and pressures (10). Our reaction design was based on previous reports of FeII transferring an electron to the α-alkoxy hydroperoxides generated upon ozonolysis of alkenes in the presence of an alcohol. The resulting oxyradicals can subsequently engage in various forms of homolytic cleavage to produce alkenes, dimers, or halides (11–15). Nevertheless, these methods often occur with poor efficiencies and/or have limited utility. We have found that employing a readily available FeII salt with a hydrogen atom donor (HAD) under Schreiber conditions promotes C(sp3)–C(sp2) bond cleavage and subsequent construction of a new C(sp3)–H bond (16). Given the ubiquity of olefins in terpenes and other organic molecules, we envision several applications for this transformation: new retro-synthetic disconnections to aid total syntheses, the late-stage diversification of both small and large biologically active molecules, and the facile generation of useful value-added compounds from abundantly available starting materials (Fig. 1C). The huge difference in price between (–)-isopulegol and (1S,3R)-3-methylcyclohexanol, used in the synthesis of androgen modulators, highlights the contrast between the current accessibility of these two structurally similar compounds (17–19).
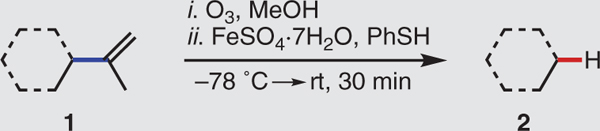
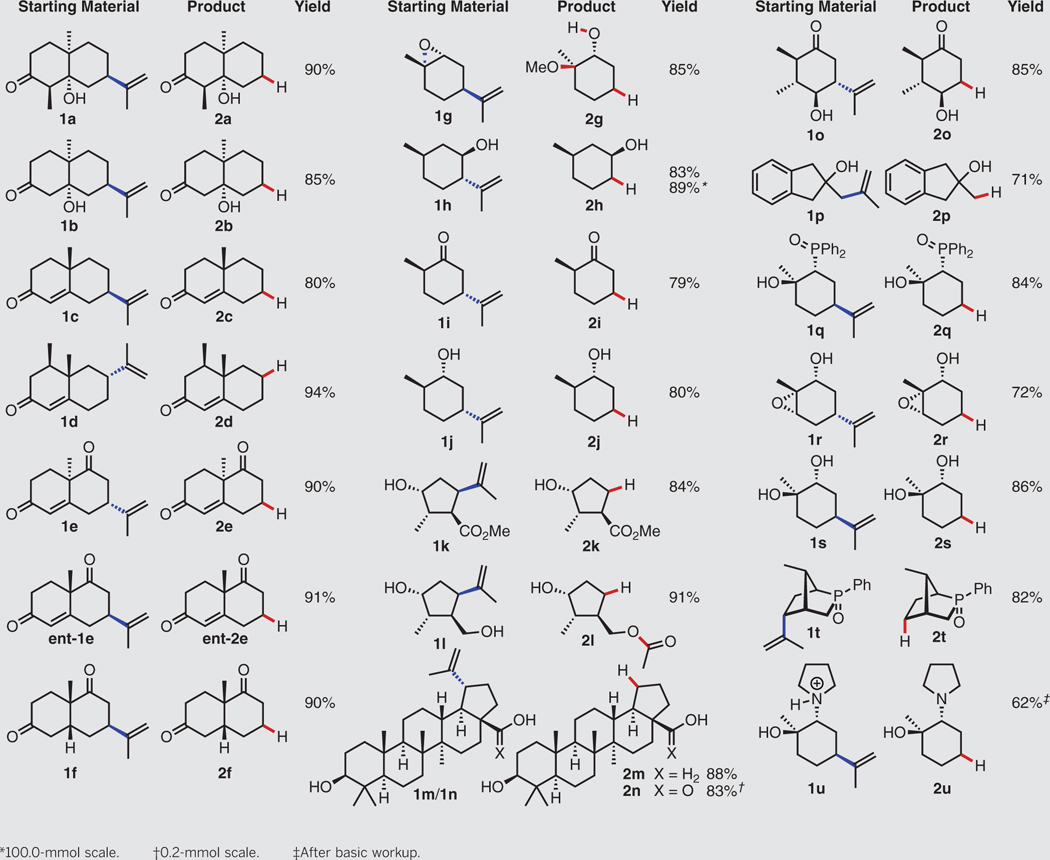
After refining the reaction parameters promoting the fragmentation of the isopropenyl group in the hydroxy ketone 1a (table S1), we obtained the desired hydrodealkenylation product 2a in 90% yield when using 1.2 equivalents of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (as the FeII salt) and 1.5 equivalents of benzenethiol (as the HAD). The reaction proceeded rapidly and produced only diphenyl disulfide, a benign by-product. Applying the optimized conditions, we investigated the substrate scope of the hydrodealkenylation. Table 1 reveals that a number of bicyclic ketones and enones (1b to 1f) underwent fragmentation cleanly to give their hydrodealkenylation products (2b to 2f) in high yields (80 to 94%). We prepared both enantiomers of the Wieland-Miescher ketone (2e and ent-2e), a prevalent synthetic intermediate used in more than 50 total syntheses (20), from the readily accessible dienediones 1e and ent-1e. Naturally occurring terpenoids were also viable substrates, providing the hydrodealkeny-lation products 2g to 2j, valuable building blocks in both total synthesis and the preparation of pharmaceutical agents (19,21–23), in good yields (79 to 89%). The epoxide in (–)-cis-limonene oxide (1g) was opened diastereoselectively under the reaction conditions to furnish the transalkoxy alcohol 2g as the sole product (presumably facilitated by a Lewis-acidic FeIII species). The carvone-derived hydroxy ester 1k and diol 1l, both of which have been used in a number of synthetic applications (24–27), smoothly delivered their products 2k and 2l, respectively. As anticipated, the primary hydroxyl group in the diol 1l underwent intramolecular trapping of the intermediate carbonyl oxide, producing the acetylated product 2l. Betulin (1m) and betulinic acid (1n), naturally occurring triterpenoids displaying wide biological activities (28), gave the hydrodealke-nylation products 2m and 2n, respectively. The hydroxy ketone 1o, containing four stereocenters, provided the fragmentation product 2o. Facile conversion of the indanol 1p to 2p illustrated the excision of the 2-propenyl substituent attached to a primary alkyl carbon. The substrates 1q to 1t delivered their fragmentation products 2q to 2t in good yields (72 to 86%), further displaying the potential of this transformation for derivatization of chiral pool-based auxiliaries. We also converted the ammonium salt 1u to the amino alcohol 2u after performing a basic workup. As validation of the robustness of this reaction, fragmentation of (–)-isopulegol (1h) on 100-mmol scale furnished the enantiomerically pure alcohol 2h in 89% yield. Both antipodes are attainable for every chiral product in Table 1 (except 2d, 2m, and 2n), owing to the ready accessibility of the enantiopure terpenoid precursors.
Table 1. Substrate scope of the hydrodealkenylation.
Experiments performed on ≥1.0-mmol scale unless otherwise noted. Yields shown refer to isolated yields after SiO2 chromatography. See the supplementary materials for experimental details. MeOH, methanol; PhSH, benzenethiol; Me, methyl; Ph, phenyl; rt, room temperature.
 |
 |
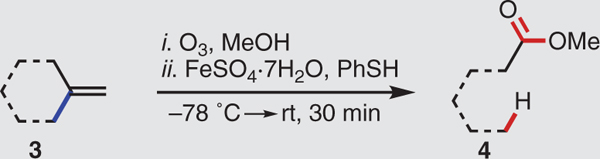
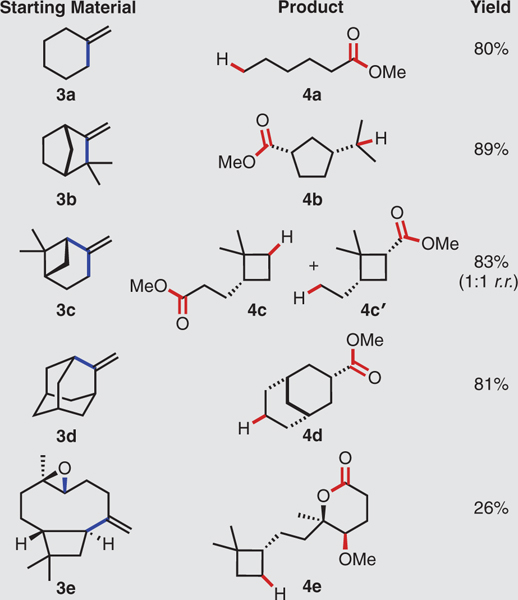
To amplify the synthetic utility of this hydro-dealkenylation, we extended it to other types of C(sp3)-C(sp2) linkages. Table 2 reveals that starting materials containing exomethylene units (3) provided carboxylic ester products (4) after the loss of a one-carbon unit as formaldehyde. Methylenecyclohexane (3a) smoothly furnished methyl hexanoate (4a). The naturally occurring terpene (±)-camphene (3b) generated a single diastereoisomer of the cyclopentanecarboxylic ester 4b. The α-alkoxy hydroperoxide intermediate fragmented to generate the tertiary carbon radical exclusively, rather than the alternative secondary carbon radical, before hydrogen atom abstraction. By contrast, (–)-β-pinene (3c) provided a 1:1 regioisomeric mixture of the products 4c and 4c’, a result of indiscriminative radical scission. Subjecting methyleneadamantane (3d) to this process furnished a single diastereoisomer of the bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane ester 4d. The reaction of (–)-caryophyllene oxide (3e) produced the lactone 4e–the result of epoxide opening (compare with 2g) and subsequent intramolecular lactonization.
Table 2. Generation of esters via C(sp3)–C(sp2) bond fragmentation.
Experiments performed on 2.0-mmol scale. Yields shown refer to isolated yields after SiO2 chromatography. See the supplementary materials for experimental details. r.r., regioisomeric ratio.
 |
 |
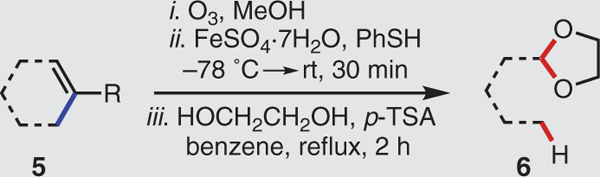
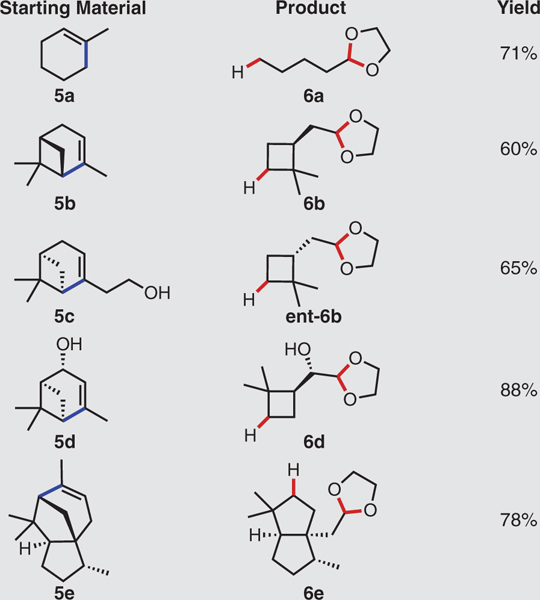
We further elaborated the substrate scope by converting various cycloalkenes (5) to ethylene glycol acetals of the aldehydes (6), involving the loss of a two-carbon (or more) unit as a methyl ester during FeII-mediated reductive fragmentation (Table 3). Because of the volatility of the aldehyde products, we protected them immediately and isolated them as 1,3-dioxolanes. Methylcyclohexene (5a) cleanly delivered the acetal of pentanal 6a. More compelling is the ability to generate optically active products from readily available and enantiomerically pure terpene and terpenoid starting materials. Although cyclobutane moieties are particularly valuable synthetic intermediates and are also present in many natural products, enantioselective preparations of these ring systems can be challenging, especially when compared with those of smaller and larger carbocycles (29–31). Cyclobutane-containing bridged terpenes are, however, prevalent; combined with hydrodealkenylation, they provide ready access to variants of this scaffold. (+)-α-Pinene (5b) and (–)-nopol (5c) produced opposite enantiomers of the cyclobutylacetaldehyde acetals 6b and ent-6b. (S)-cis-Verbenol (5d) smoothly dispensed the corresponding aldol acetal 6d, containing two stereocenters, and (–)-α-cedrene (5e) provided the cis-fused octahydropentalene 6e, with three stereocenters.
Table 3. Generation of masked aldehydes via C(sp3)–C(sp2) bond fragmentation.
Experiments performed on 2.0-mmol scale. Yields shown refer to isolated yields after SiO2 chromatography. See the supplementary materials for experimental details. p-TSA, para-toluenesulfonic acid.
 |
 |
The ease of operation, efficiency, and functional-group compatibility of the hydrodealkenylation were further confirmed through its application in the formal syntheses of several biologically active natural products (Fig. 2). In a notable example— en route to the isotwistane sesquiterpenoid (–)-2-pupukeanone—we generated the bicyclic ketoester 2v directly from 1v in 78% yield. Previously, this conversion required six steps and gave the product in only 28% overall yield (32). In another example, we obtained the ketoester 2w, an intermediate leading to (–)-seychellene, directly from its precursor 1w in 81% yield. Although our net yield was slightly lower than that reported for the five-step route (91%), the simplicity of our method obviates the five purifications required by the former (33). Other examples included one-pot conversions of the silyloxy dione 1x, an intermediate leading to the sesquiterpenoid perico-nianone A (34); the dione 1y, an intermediate in the preparation of the spirocyclic sesquiterpenoid (–)-7-epibakkenolide-A (35); and the silyloxy ketone 1z, a chiral steroid precursor (36).
Fig. 2. Applications of hydrodealkenylation in total synthesis.
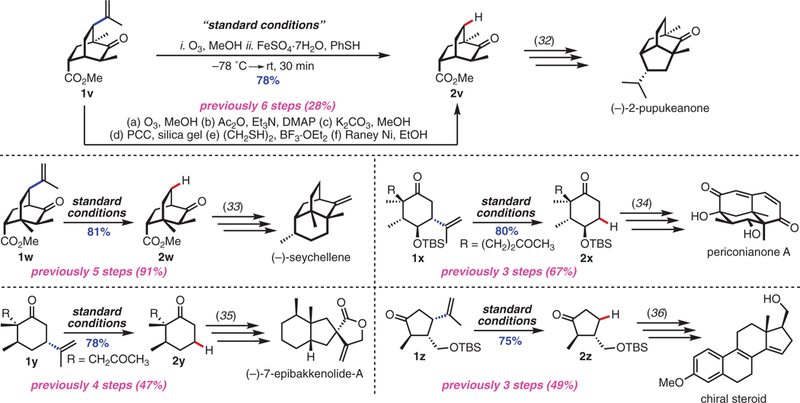
Experiments performed on 1.0-mmol scale. Yields shown refer to isolated yields after SiO2 chromatography. See the supplementary materials for experimental details. Ac2O, acetic anhydride; Et3N, triethylamine; DMAP, 4-dimethylaminopyridine; PCC, pyridinium chlorochromate; BF3.OEt2, boron trifluoride diethyl etherate; EtOH, ethanol; TBS, tert-butyldimethylsilyl.
We then performed several experiments to support the mechanistic involvement of a free carbon radical in these hydrodealkenylations and establish the possibility of engaging the radical intermediate in other useful transformations (Fig. 3). Subjecting (1S)-(+)-3-carene to the reaction conditions generated the corresponding cyclo-propylcarbinyl radical, with subsequent rearrangement, hydrogen atom abstraction, and dioxolane protection supplying a 1:0.85 mixture of the products 6f and 6f′ in 87% yield. When we substituted TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl) for the HAD, we obtained the TEMPO adducts 7a and 7a′ in a combined isolated yield of 91%. Singlecrystal x-ray diffraction of the major product 7a confirmed the equatorial stereochemistry of the aminoxyl group. Similarly, employing diphenyl disulfide as a radical trap produced the thioethers 8a and 8a’ in a combined isolated yield of 40%. For this transformation, the diastereoselectivity was higher (8:1 diastereomeric ratio), and the major product again displayed an equatorial—in this case, phenylthio—group.
Fig. 3. Observations consistent with the intermediacy of a carbon radical.
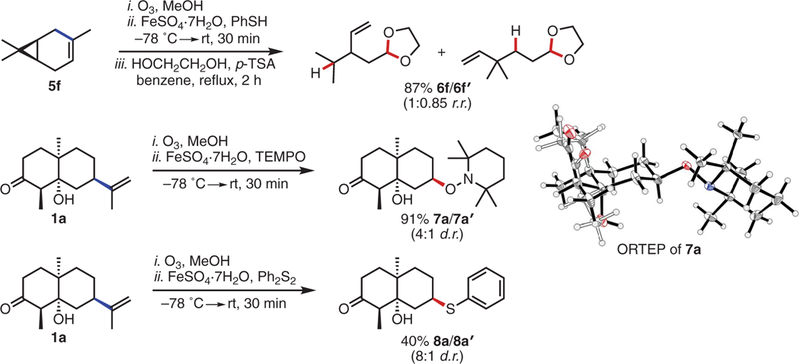
Experiments performed on ≥0.5-mmol scale. Yields shown refer to isolated yields after SiO2 chromatography. See the supplementary materials for experimental details. d.r., diastere-omeric ratio; Ph2S2, diphenyl disulfide; ORTEP, Oak Ridge thermal ellipsoid plot.
We envision that the straightforward nature of the hydrodealkenylation, performed with in-expensive and commercially available reagents and instruments, will engender innovations in synthesis and the use of chiral pool-based starting materials. Fundamentally, this unusual disconnection should prove useful in both retrosynthetic analyses and late-stage synthetic modifications. Furthermore, the ease with which these carbon-centered radicals can be trapped opens a gateway for employing common alkenes, seldom used as radical precursors, in a plethora of known radical transformations.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the UCLA Molecular Instrumentation Center for the NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and x-ray diffraction (S. I. Khaan) instrumentation.
Funding: Financial support for this study was provided by the NIH (R01GM071779).
Footnotes
Competing interests: A.J.S. and O.K. are listed as inventors on an initial patent application filed by the Regents of the University of California (U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/810,271).
Data and materials availability: Experimental procedures, optimization data, and characterization data are available in the supplementary materials. Crystallographic data are available free of charge from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre under reference number CCDC 1874958.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Roque JB, Kuroda Y, Göttemann LT, Sarpong R, Nature 564, 244–248 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Osberger TJ, Rogness DC, Kohrt JT, Stepan AF, White MC, Nature 537, 214–219 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rosen BM et al. , Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 7002–7005 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bailey PS, Chem. Rev. 58, 925–1010 (1958). [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hoveyda AH, Zhugralin AR, Nature 450, 243–251 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vougioukalakis GC, Grubbs RH, Chem. Rev. 110,1746–1787 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marek I, Masarwa A, Delaye P-O, Leibeling M, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 414–429 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nairoukh Z, Cormier M, Marek I, Nat. Rev. Chem. 1, 0035 (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fumagalli G, Stanton S, Bower JF, Chem. Rev. 117, 9404–9432 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schmidt R et al. , in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (Wiley-VCH, 2015). [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kumamoto J, De La Mare HD, Rust FF, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82, 1935–1939 (1960). [Google Scholar]
- 12.De La Mare HE, Kochi JK, Rust FF, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83, 2013 (1961). [Google Scholar]
- 13.Murai S, Sonoda N, Tsutsumi S, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 37, 1187–1190 (1964). [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schreiber S, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102, 6163–6165 (1980). [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fisher TJ, Dussault PH, Tetrahedron 73, 4233–4258 (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 16.Smaligo AJ, Vardhineedi S, Kwon O, ACS Catal. 8, 5188–5192 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Based on current list price of (–)-isopulegol, CAS 89–79-2 (Sigma-Aldrich; ). [Google Scholar]
- 18.Based on current list price of (1S,3R)-3-methylcyclohexanol, CAS 24965–92-2 (Advanced ChemBlocks and PharmaBlock; ). [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hu L-Y et al. , Androgen modulators, U.S. Patent US20060009427, January 12, 2006.
- 20.Bradshaw B, Bonjoch J, Synlett 23, 337–356 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cheng K-F, Chan K-P, Lai T-F, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1991, 2461–2465 (1991). [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhu Z et al. , Preparation of imidazolidin-2-imines and their analogs as aspartyl protease inhibitors for treating various diseases, U.S. Patent US20080200445, August 21, 2008.
- 23.Aicher TD et al. , Preparation of heterocyclic compounds as glucokinase activators, U.S. Patent US20090247526, October 1, 2009.
- 24.Oliver SF et al. , Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 5996–6000 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sun L et al. , J. Med. Chem. 53, 7864–7868 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Navickas V, Ushakov DB, Maier ME, Ströbele M, Meyer H-J, Org. Lett. 12, 3418–3421 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yang H, Gao Y, Qiao X, Xie L, Xu X, Org. Lett. 13, 3670–3673 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Alakurtti S, Mäkelä T, Koskimies S, Yli-Kauhaluoma J, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 29, 1–13 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Xu Y, Conner ML, Brown MK, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 11918–11928 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Poplata S, Tröster A, Zou Y-Q, Bach T, Chem. Rev. 116, 9748–9815 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yoon TP, Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 2307–2315 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Srikrishna A, Kumar PR, Gharpure SJ, Tetrahedron Lett. 42, 3929–3931 (2001). [Google Scholar]
- 33.Srikrishna A, Ravi G, Tetrahedron 64, 2565–2571 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liffert R, Linden A, Gademann K, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 16096–16099 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Srikrishna A, Reddy TJ, Tetrahedron 54, 11517–11524 (1998). [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pogrebnoi S, Saraber FCE, Jansen BJM, de Groot A, Tetrahedron 62, 1743–1748 (2006). [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


