Summary
In the rice blast fungus M agnaporthe oryzae, the high‐affinity cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase MoPdeH is important not only for cAMP signalling and pathogenicity, but also for cell wall integrity (CWI) maintenance through an unknown mechanism. By utilizing affinity purification, we found that MoPdeH interacts with MoMck1, one of the components of the mitogen‐activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade that regulates CWI. Overexpression of MoMCK 1 suppressed defects in autolysis and pathogenicity of the ΔMopdeH mutant, although partially, suggesting that MoPdeH plays a critical role in CWI maintenance mediated by the MAP kinase pathway. We found that MoMck1 and two other MAP kinase cascade components, MoMkk1 and MoMps1, modulate intracellular cAMP levels by regulating the expression of MoPDEH through a feedback loop. In addition, disruption of MoMKK 1 resulted in less aerial hyphal formation, defective asexual development and attenuated pathogenicity. Moreover, MoMkk1 plays a role in the response to osmotic stress via regulation of MoOsm1 phosphorylation levels, whereas endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress enhances MoMps1 phosphorylation and loss of the MAP kinase cascade component affects the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that MoPdeH functions upstream of the MoMck1–MoMkk1–MoMps1 MAP kinase pathway to regulate CWI, and that MoPdeH also mediates crosstalk between the cAMP signalling pathway, the osmotic sensing high osmolarity glycerol (HOG) pathway and the dithiothreitol (DTT)‐induced UPR pathway in M. oryzae.
Keywords: cell wall integrity, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), infection‐related morphogenesis, Magnaporthe oryzae, MAP kinase signalling pathway, phosphodiesterase
Introduction
Fungal signal transduction pathways sense and transduce extracellular signals to regulate cellular growth, differentiation and/or pathogenicity (Daniel et al., 1998; Malbon, 2005). In the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, the G‐protein α subunit MoMagB, adenylyl cyclase MoMac1 and the regulator of the G‐protein signalling protein MoRgs1 are the major regulators of the signalling pathway that depends on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) (Choi and Dean, 1997; Li et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2007; Liu and Dean, 1997). cAMP is a ubiquitous second messenger that activates downstream targets, such as protein kinases or transcription factors (Daniel et al., 1998). Many elegant studies have demonstrated that, in M. oryzae, the cAMP signalling pathway plays a major role in the regulation of vegetative growth, conidiation, development of infection‐related morphogenesis and pathogenicity (Adachi and Hamer, 1998; Choi and Dean, 1997; Lee and Dean, 1993; Mitchell and Dean, 1995; Zhang et al., 2011a). In previous studies, we have found that the high‐affinity phosphodiesterase MoPdeH constitutes another major regulator of cAMP signalling through modulation of intracellular cAMP levels, and that it too regulates cellular development and fungal pathogenicity (Ramanujam and Naqvi, 2010; Zhang et al., 2011a). MoPdeH also plays a role in cell wall integrity (CWI) maintenance as the ΔMopdeH mutant strain exhibits hyphal autolysis (Zhang et al., 2011a).
In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the CWI pathway remains as one of the key pathways controlling the cellular remodelling process in response to internal cues and environmental challenges (Lesage and Bussey, 2006; Levin, 2005, 2011). CWI is activated by five cell surface sensors named Wsc1, Wsc2, Wsc3, Mid2 and Mtl1. During cell wall stress, these sensors interact with the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Rom2, which, in turn, activates the Rho family GTPase Rho1 and recruits it to the membrane. Rho1 activates the protein kinase C (Pkc1), which then phosphorylates the upstream kinase of the conserved mitogen‐activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade Bck1. Bck1, in turn, transmits the signal to MAP kinase kinases (Mkk1 and Mkk2) which activate MAP kinase (Mpk1/Slt2) through protein phosphorylation. Consequently, Mpk1/Slt2 phosphorylates the transcription factors Rlm1 and the SBF complex, including Swi4 and Swi6, to regulate the nuclear expression of genes involved in either cell wall biosynthesis and remodelling, or cell cycle progression (Jendretzki et al., 2011).
In other fungi, the CWI pathway remains largely conserved, although the biological functions of each component may differ among distinct species (Fujioka et al., 2007; Hou et al., 2002; Kojima et al., 2002; Kraus et al., 2003; Mehrabi et al., 2006; Valiante et al., 2008). In M. oryzae, MoMck1 and MoMps1, which are homologues of Bck1 and Mpk1 (or Slt2), respectively, have been found to be important for CWI and pathogenicity (Jeon et al., 2008; Xu et al., 1998). The ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 mutants also undergo significant autolysis (Jeon et al., 2008; Xu et al., 1998). A homologue of S. cerevisiae Swi6, MoSwi6, was also found to have a role in the regulation of morphogenesis and virulence, in addition to CWI (Qi et al., 2012). Surprisingly, despite the evidence implicating the role of the MAP kinase cascade in CWI of M. oryzae, the specific function of the MAP kinase kinase MoMkk1 is not known.
In M. oryzae, MoPdeH regulates cAMP levels and the ΔMopdeH mutant also exhibits hyphal autolysis, which is similar to the autolysis exhibited by the ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 mutant strains (Jeon et al., 2008; Xu et al., 1998; Zhang et al., 2011a). This observation suggests a link between MoPdeH‐mediated cAMP signalling and the MAP kinase cascade that regulates CWI. Characterization of the links between MoPdeH and MoMck1, MoMkk1 or MoMps1 constitutes an important step in our illustration of the molecular basis of rice blast pathogenesis. Here, we characterize MoMkk1 as an integral component of the CWI MAP kinase cascade. We also demonstrate that MoPdeH functions upstream of the MAP kinase pathway to regulate CWI. In addition, we provide evidence to show that MoPdeH–cAMP signalling crosstalks with multiple pathways important in the regulation of CWI affecting the growth, morphogenesis and pathogenicity of M. oryzae.
Results
MoPdeH physically interacts with MoMck1
We have shown previously that phosphodiesterase MoPdeH is important not only for cellular development and pathogenicity, but also for CWI (Zhang et al., 2011a). To investigate the mechanism by which MoPdeH regulates CWI, we used the protein affinity purification approach to identify MoMck1 as one of the proteins with which MoPdeH interacts. This interaction was verified by an in vitro glutathione transferase (GST) pull‐down assay using GST‐MoPdeH and His‐MoMck1B (342–842 amino acids) fusion proteins (Fig. 1A). We followed GST pull‐down with yeast two‐hybrid (Y2H) assays that again verified the interaction between MoPdeH and MoMck1 (Fig. 1B). Meanwhile, an interaction between MoPdeH and each of the two other components of the CWI MAP kinase cascade (MoMkk1 and MoMps1) could not be established (Fig. 1B). To demonstrate the in vivo interaction between MoPdeH and MoMck1, we employed the bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay by introducing the MoMCK1‐CYFP and MoPDEH‐NYFP fusion constructs into the protoplasts of the wild‐type strain Guy11. The occurrence of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) signal in conidia indicated that these two proteins interact in vivo (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1.
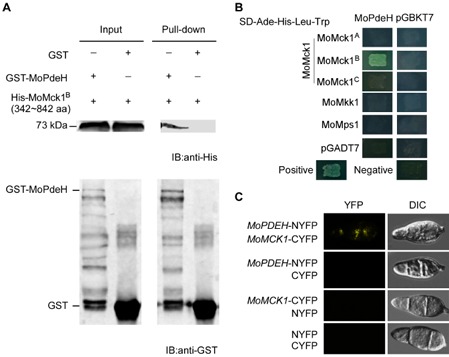
MoPdeH interacts with MoMck1. (A) In vitro pull‐down assay of His‐MoMck1 [342–842 amino acids (aa)] and GST‐MoPdeH. MoMck1A represents the protein of 1–341 aa of the whole‐length protein of MoMck1 (1529 aa for full length), MoMck1B represents 342–842 aa and MoMck1C represents 842–1489 aa of the protein. Recombinant GST‐MoPdeH or GST bound to glutathione Sepharose beads was incubated with E scherichia coli cell lysate containing His‐MoMck1B (342–842 aa). Eluted protein was analysed by immunoblot (IB) with monoclonal anti‐His and monoclonal anti‐GST antibodies. GST, glutathione transferase; His, histidine. (B) Yeast two‐hybrid analysis of the interaction between MoMck1 and MoPdeH. MoPdeH was inserted into vector pGBKT7 and three truncated parts of MoMck1 (MoMck1A, MoMck1B, MoMck1C) were inserted into pGADT7. Yeast cells were grown on synthetic dextrose (SD) medium lacking leucine (Leu), tryptophan (Trp), His and adenine (Ade), and β‐galactosidase (LacZ) activities were investigated with positive and negative controls. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3 days before being photographed. (C) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for the interaction between MoMck1 and MoPdeH. Conidia of transformants expressing the MoPDEH‐NYFP and MoMCK 1‐CYFP constructs were tested by both differential interference contrast (DIC) and epifluorescence microscopy. YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.
Moreover, we found that the expression level of MoMCK1 in the ΔMopdeH mutant was significantly reduced. We thus overexpressed MoMCK1 in ΔMopdeH to determine whether it could suppress its defects (Fig. S1, see Supporting Information). Indeed, two independent transformant strains overexpressing MoMCK1 exhibited delayed hyphal autolysis, partially suppressed defects in conidiation and virulence, and partially suppressed intracellular cAMP levels (Figs 2A–C and S2, see Supporting Information). These results indicate that MoPdeH functions in the CWI pathway mediated by MoMck1.
Figure 2.
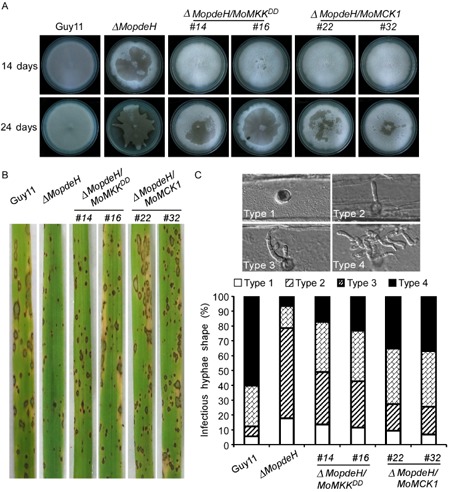
Overexpression of MoMCK 1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 (import of a MKK 1 T369D,T375D construct) in the ΔMopdeH mutant suppress the defects of hyphal autolysis and pathogenicity. (A) Autolysis observation. ΔMopdeH mutant showed apparent autolysis of mycelia on complete medium (CM) after culture for 2 weeks (top). Overexpression of MoMCK 1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 strains delayed the process of autolysis (bottom). (B) Rice spraying assay. Four millilitres of conidial suspension (5 × 104 spores/mL) of each strain were sprayed onto 2‐week‐old rice seedlings. Diseased leaves were photographed after 7 days. (C) Observation of infectious capacity on barley. Excised barley leaves from 7‐day‐old barley seedlings were inoculated with conidial suspension (5 × 104 spores/mL) of each strain. Infectious growth was observed at 24 h after inoculation. Overexpression of MoMCK 1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 in ΔMopdeH strains partially restored the infection defect of the ΔMopdeH mutant.
MAP kinase cascade components MoMck1, MoMkk1 and MoMps1 are involved in the regulation of intracellular cAMP levels
As MoPdeH plays an important role in the regulation of intracellular cAMP levels (Ramanujam and Naqvi, 2010; Zhang et al., 2011a), its interaction with MoMck1 could indicate that MAP kinase cascade components may affect intracellular cAMP levels. To test this hypothesis, we measured intracellular cAMP levels of the hyphal stage in the ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1 mutants, and found that the cAMP levels were significantly increased in comparison with those in the wild‐type strain (Fig. S3A, see Supporting Information). Accordingly, we found that the expression levels of MoPDEH in all three mutants were significantly reduced (Fig. S3B), resulting in increased cAMP levels. This type of regulation suggests the presence of a feedback regulatory mechanism.
MoMkk1 is a conserved component of the MAP kinase cascade
In S. cerevisiae, the MAP kinase cascade regulating CWI is a linear pathway composed of Pkc1, a MEKK (Bck1), a pair of redundant MEKs (Mkk1/2) and a MAP kinase (Mpk1/Slt2) (Irie et al., 1993; Lee and Levin, 1992; Lee et al., 1993; Lee and Dean, 1993; Levin, 2011; Levin et al., 1990; Martin et al., 1993). Magnaporthe oryzae MoMck1 and MoMps1 are Bck1 and Slt2 homologues, respectively, whose functions have been described previously (Jeon et al., 2008; Xu et al., 1998). However, the function of the Mkk1/Mkk2 homologue, MoMkk1, has not been described. We identified the locus MGG_06482 from the M. oryzae genome (http://www.broadinstitute.org/annotation/genome/magnaporthe_comparative/MultiHome.html) as an Mkk1/Mkk2 homologue using the S. cerevisiae Mkk1/Mkk2 sequence as query. MGG_06482 shares high amino acid sequence homology with Mkk1/Mkk2 and was named MoMkk1. To examine the genetic relationship between MoMkk1 and other components of the MAP kinase cascade, we used Y2H and BiFC assays to show that MoMkk1 indeed interacts with both MoMck1 and MoMps1 (Fig. S4A,B, see Supporting Information).
To characterize the function of MoMkk1, ΔMomkk1 mutants were obtained. Two ΔMomkk1 mutants were identified and confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Southern blot hybridization (Fig. S5, see Supporting Information). As the two mutants showed the same phenotype, we chose one mutant for detailed analysis. Interestingly, we found that ΔMomkk1 mutants exhibited apparent hyphal autolysis on complete medium (CM) plates, similar to ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 (Fig. 3A). The autolysis could be partially reversed by amending the medium with 1 m sorbitol (Fig. 3A). We also tested the activation of MoMps1 in ΔMomkk1 with the ΔMomck1 mutant strain as a control. In vegetative hyphae, phosphorylation of MoMps1 was completely abolished in both mutants (Fig. 3B), indicating that MoMkk1 is required for MoMps1 phosphorylation, similar to MoMck1.
Figure 3.
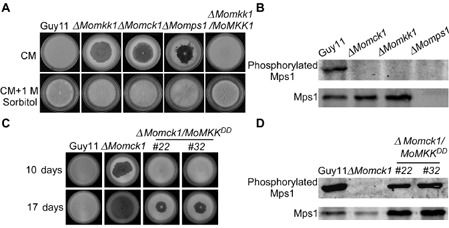
MoMkk1 functions upstream of MoMps1 and downstream of MoMck1. (A) Growth of wild‐type and mutant strains on complete medium (CM) without 1 m sorbitol (top). Growth of strains on CM with 1 m sorbitol (bottom). Consistent with ΔM omck1 and ΔM omps1, the ΔM omkk1 mutant also undergoes progressive autolysis on CM in the absence of osmotic stabilization. (B) Phosphorylation of MoMps1 in ΔM omkk1 and the other two cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway mutants. Immunoblots were performed with total proteins from hyphae of Guy11, ΔM omkk1, ΔM omck1 and ΔM omps1 mutants. The signal corresponding to phosphorylated MoMps1 was detected by binding of the antiphospho‐p44/42 antibody, with the Mpk1 antibody used as a control. MoMps1 phosphorylation in the ΔM omkk1 mutant was completely lost. (C) Autolysis observation. Wild‐type strain Guy11, the Δ M omck1 mutant and two transformants whose endogenous MKK 1 was replaced with MKK 1 T369D,T375D to obtain a constitutive activation of MoMps1 were allowed to grow on CM for 10 days. The strain with constitutively activated MoMps1 partially suppressed the autolysis of the Δ M omck1 mutant prior to 17 days of growth. (D) Phosphorylation of MoMps1 in two strains with constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔM omck1 background. Proteins were prepared from mycelia cultured in liquid CM and the phosphorylated MoMps1 was detected by binding of the antiphospho‐p44/42 antibody, with the Mpk1 antibody as a control. The phosphorylation level of MoMps1 in the two transformants with constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔM omck1 background indicated the activation of MoMps1.
To establish and confirm the relationship between MoMck1 and MoMkk1, we generated a mutant (ΔMomck1/MKK1DD) by replacing the endogenous MoMKK1 allele in ΔMomck1 with MKK1 T369D,T375D to generate a strain with constitutive activation of MoMps1 (Fujikawa et al., 2009). As shown in Fig. 3D, the intensity of MoMps1 phosphorylation, detected by binding of an antiphospho‐p44/42 antibody, was slightly increased in the ΔMomck1/MKK1DD strain, in comparison with the ΔMomck1 mutant. In addition, mycelial autolysis in the ΔMomck1 mutant was delayed (Fig. 3C), and the pathogenicity defect on barley leaves was partially rescued in the ΔMomck1/MKK1DD strain (Fig. S6, see Supporting Information). These results indicate that MoMkk1 retains the conserved position in the CWI MAP kinase cascade, i.e. downstream of MoMck1 and upstream of MoMps1.
MoMkk1 is important for aerial hyphal growth, asexual development and pathogenicity
Given that MoMkk1 functions as the middle component of the conserved MAP kinase cascade, we consequently characterized its cellular function. After incubation at 28 °C for 7 days, the ΔMomkk1 mutant strain showed no significant difference in growth rates, but a lack of aerial hyphae, on CM, minimal medium (MM), straw decoction and corn agar (SDC) and oatmeal medium (OM) plates compared with the wild‐type and complemented strains (Fig. S7A, see Supporting Information). The ΔMomkk1 mutant also did not produce any conidia on SDC medium (Fig. S7B).
To test pathogenicity, ΔMomkk1 mycelium was used to inoculate detached rice and barley seedling leaves, as the mutant has a defect in conidiation. The ΔMomkk1 mutant caused almost no disease symptoms on unwounded rice leaves, in comparison with Guy11 and the complemented strain which produced typical lesions (Fig. 4A). On wounded rice leaves, the ΔMomkk1 mutant caused limited lesions (Fig. 4B). A similar result was observed on infected barley leaves (Fig. 4C,D). These results, as well as those described above, were all similar to those shown by the ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 mutants, indicating that MoMkk1 also plays a role in aerial hyphal growth, asexual development and pathogenicity.
Figure 4.
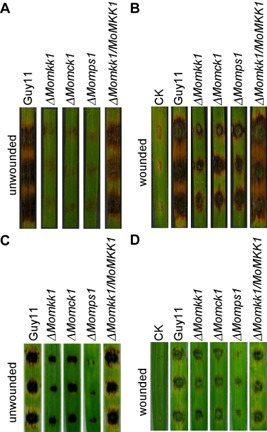
MoMkk1 is required for pathogenicity. (A, B) Pathogenicity test on rice. Detached rice leaves, unwounded and wounded by abrasion, were inoculated with Guy11, ΔM omkk1, ΔM omck1, ΔM omps1 and complemented strains. Photographs were taken 5 days after inoculation. (C, D) Pathogenicity test on barley. Detached barley leaves, unwounded and wounded by abrasion, were inoculated with Guy11, ΔM omkk1, ΔM omck1, ΔM omps1 and complemented strains. Diseased leaves were photographed 5 days after inoculation. These experiments were performed three times with similar results.
To further explore why the ΔMomkk1 mutant exhibits reduced virulence, we examined its invasive hyphal growth in infected barley leaf epidermis. We observed invasive hyphal growth at 100 appressorium penetration sites by rating the hyphal growth from level I to level IV (Fig. S8, see Supporting Information). The wild‐type strain showed at least a rate of 90% successful appressorium penetration events, with 49% of level IV invasive growth by 36 h. In contrast, only 57% of ΔMomkk1 appressoria showed successful penetration, and only 17% of penetration sites showed level III and IV invasive growth (Fig. S8). These results were similar to those of ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 strains.
MoMkk1 is required for the maintenance of CWI
As the ΔMomkk1 mutant undergoes progressive hyphal autolysis beginning at the centre of the colony and radiating outwards (Fig. 3A), which is similar to the ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 strains, we investigated whether MoMkk1 plays a role in CWI. We compared the effects of cell wall‐degrading enzymes on mycelia of ΔMomkk1 and the Guy11 strain. Hyphae of the ΔMomkk1 mutant were well digested and released more protoplasts than did Guy11 and the complemented strain (Fig. 5A,B). The ΔMomkk1 mutant also showed increased sensitivity to a variety of cell wall‐perturbing agents, including Calcofluor white (CFW), Congo red (CR), sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS), lysing enzymes and caffeine (Table 1). These results collectively indicate that MoMkk1 is required for the maintenance of CWI, similar to MoMck1 and MoMps1.
Figure 5.
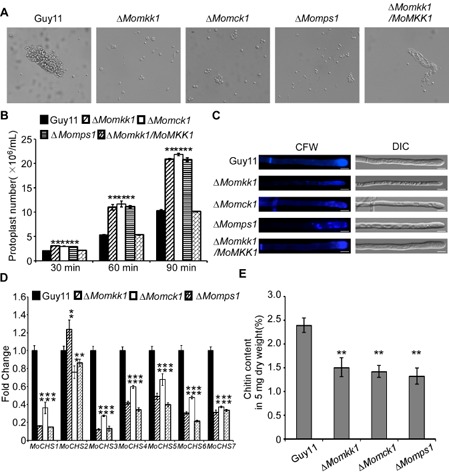
ΔM omkk1 mutant shows defects in cell wall integrity. (A) Light microscopic examination of protoplast release after treatment with cell wall‐degrading enzymes for 45 min at 30 °C. (B) Protoplast release assay. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the ΔM omkk1 mutant and the wild‐type strain at P < 0.01. (C) Deletion of MoMKK 1 altered the distribution of chitin in the cell wall. Wild‐type and mutant hyphae were stained with 10 μg/mL Calcofluor white (CFW) for 5 min without light before being photographed. The experiment was repeated several times with triple replications that yielded similar results. Scale bar equals 5 μm. DIC, differential interference contrast. (D) Transcription analysis of seven chitin synthases in M agnaporthe oryzae using quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). (E) N‐Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) determination by the fluorimetric Morgan–Elson method showed significantly decreased chitin content in the ΔM omkk1 mutant. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the mutant and wild‐type strains at P = 0.01 according to Duncan's range test. Data represent three independent experiments, each performed three times.
Table 1.
Sensitivity of three cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway mutants to several cell wall stressors
| Strain | Inhibition rate (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CFW 200 μg/mL |
CFW 400 μg/mL |
CFW 600 μg/mL |
CR 200 μg/mL |
CR 400 μg/mL |
CR 600 μg/mL |
SDS 0.005% |
SDS 0.008% |
SDS 0.01% |
Lysing enzyme | Caffeine | |
| Guy11 | 15 ± 2.4B | 25 ± 0.0C | 50 ± 0.0B | 14 ± 1.2B | 16 ± 1.2D | 21 ± 2.1D | 32 ± 2.4A | 47 ± 1.2C | 56 ± 1.2B | 3 ± 0.0B | 57 ± 1.2B |
| ΔMokk1 | 26 ± 1.9A | 31 ± 2.3B | 56 ± 2.3A | 25 ± 1.1A | 43 ± 2.1A | 56 ± 2.3A | 26 ± 3.4A | 55 ± 2.0A | 65 ± 2.0A | 12 ± 1.1A | 66 ± 1.9A |
| ΔMomck1 | 27 ± 1.1A | 36 ± 2.2A | 54 ± 1.1A | 23 ± 1.1A | 38 ± 1.1B | 52 ± 1.6B | 29 ± 2.9A | 53 ± 1.9AB | 62 ± 2.2A | 13 ± 1.8A | 67 ± 1.0A |
| ΔMomps1 | 24 ± 2.0A | 34 ± 1.7AB | 53 ± 1.0A | 24 ± 1.0A | 28 ± 0.0C | 41 ± 1.0C | 27 ± 3.9A | 51 ± 0.0B | 61 ± 1.0A | 17 ± 6.6A | 65 ± 1.0A |
| ΔMomkk1/MoMKK1 | 17 ± 1.1B | 26 ± 1.1C | 50 ± 1.2B | 15 ± 1.9B | 18 ± 1.3D | 22 ± 1.1D | 33 ± 2.2A | 47 ± 1.1C | 56 ± 1.1B | 3 ± 1.1B | 58 ± 1.1B |
Hyphal diameter of strains examined 7 days after incubation on complete medium (CM) agar plates with cell wall‐perturbing agents; the final concentrations were 0.005%, 0.008% and 0.01% for sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS), 200, 400 and 600 μg/mL for Congo red (CR), 200, 400 and 600 μg/mL for Calcofluor white (CFW), 30 mg/mL for caffeine and 15 mg/mL for lysing enzymes. The growth inhibition rate is relative to the growth rate of each untreated control [Inhibition rate = (diameter of untreated strain − diameter of treated strain)/(diameter of untreated strain × 100%)]. The experiments were repeated three times.
The superscript A, B, C and D showed the significant changes compared to the wild type. The same letters in a column showed no significant difference.
As CFW and CR bind to nascent chitin chains and inhibit the assembly enzymes that connect chitin to β‐1,3‐glucan and β‐1,6‐glucan (Ram and Klis, 2006), we hypothesized that MoMkk1 is involved in the regulation of chitin biosynthesis. To test this hypothesis, we examined the expression level of chitin synthase (CHS) genes. As shown in Fig. 5D, the expression level of seven CHS genes was significantly reduced, with the exception of CHS2. After further measurement of the chitin contents, we found that the chitin content of the ΔMomkk1 mutant was reduced to 63% compared with that of the wild‐type strain, with the ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 mutants decreased to 58% and 54% of the control strain, respectively (Fig. 5E). We further used the chitinous fluorochrome CFW to test the cell wall properties of the ΔMomkk1 mutant. Compared with Guy11 and the complemented strains, the chitin distribution in the ΔMomkk1 mutant was apparently uneven, not restricted to growing apices. In addition, we found that the hyphae of the mutant had a narrower width (Fig. 5C). These observations indicate that MoMkk1 plays a role in CWI regulation by affecting CHS gene expression.
MoMkk1 plays a role in the osmotic stress response
As MoMkk1 is required for CWI, we tested the ΔMomkk1 mutant for its response to osmotic stress inducers. The ΔMomkk1 mutant, as well as the ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 mutants, showed increased sensitivity to 0.7 m NaCl, 0.6 m KCl and 1 m sorbitol (Fig. S9, see Supporting Information). In addition, the phosphorylation level of MoOsm1, a key kinase of the high osmolarity glycerol (HOG) pathway, was tested in the ΔMomkk1, ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 mutants. The intensity of the signal corresponding to phosphorylation was detected by binding of the phosphorylated p38 (Thr180/Tyr182) antibody, with anti‐Hog1 antibody binding as control. The phosphorylation level of MoOsm1 was decreased in the ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomck1 mutants (Fig. 6A–C), indicating that both MoMck1 and MoMkk1 are involved in osmotic stress regulation mediated by MoOsm1. In order to further analyse the relationship between the CWI and HOG pathways, we used CFW to examine the phosphorylation levels of MoOsm1 in the CWI mutants (ΔMomkk1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomkk1) compared with the wild‐type strain Guy11. CFW increased the activation of MoOsm1 in the CWI mutants, as shown in Fig. 6D–F, suggesting a link between the two MAP kinase pathways.
Figure 6.
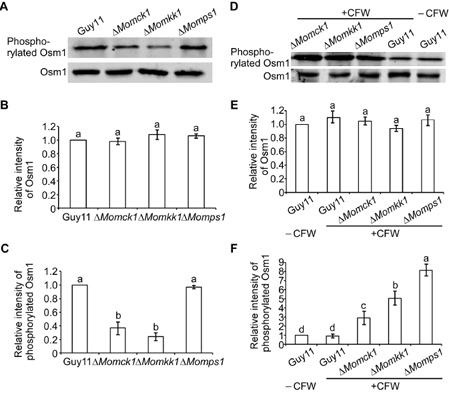
MoMkk1 is involved in the regulation of MoOsm1 phosphorylation in M agnaporthe oryzae. (A) Phosphorylation of MoOsm1 in Δ M omkk1, ΔM omck1 and ΔM omps1 mutants. Immunoblots of total hyphal proteins were obtained from Guy11, ΔM omkk1, ΔM omck1 and ΔM omps1 mutants. The intensity of the signal corresponding to phosphorylated MoOsm1 was detected by binding of the phosphorylated p38 (Thr180/Tyr182) antibody, with anti‐Hog1 antibody binding as control. (B, C) The intensities of the Western blotting bands were quantified with the ODYSSEY infrared imaging system (application software Version 2.1). The intensity of the MoOsm1 band in each mutant is relative to the amount of MoOsm1 in the wild‐type strain Guy11. Bars denote standard errors from three independent experiments. Values on the bars followed by the same letter were not significantly different at P = 0.05. (D) Phosphorylation of Osm1 in Guy11 and the three cell wall integrity (CWI) mutants with CFW treatment. The intensity of the signal corresponding to phosphorylated Osm1 was detected by binding of a phosphorylated p38 (Thr180/Tyr182) antibody, with an anti‐Hog1 antibody used as a control. (E, F) The intensity of the MoOsm1 band in each mutant is relative to the amount of MoOsm1 in the wild‐type strain Guy11. Bars denote standard errors from three independent experiments. Values on the bars followed by the same letter are not significantly different at P = 0.05.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress activates the CWI pathway
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is an intracellular signalling pathway that regulates the eukaryotic cellular response to the accumulation of misfolded proteins (Spear and Ng, 2001). In S. cerevisiae, ER and cell wall stress responses are coordinated by UPR and CWI signalling pathways to protect cells against these related stressors (Krysan, 2009). A recent study has shown the importance of the connection between these two pathways in filamentous fungi (Malavazi et al., 2014). We thereby examined whether such a connection also occurs in M. oryzae. Interestingly, although the ΔMomkk1 mutant did not show any sensitivity changes to the ER stress compared with the wild‐type strain, we found that 1 mm dithiothreitol (DTT) could completely rescue the autolysis defect of the Momck1 and Momkk1 mutants, but not the ΔMomps1 mutant (Fig. 7A). To further examine how the CWI pathway is activated, we tested the MoMps1 phosphorylation level in the wild‐type strain, ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMoMps1 mutants treated with 10 mm DTT for 4 h. We also used CFW, which activates MoMps1 phosphorylation, as a control. We found that CFW and DTT treatments can both enhance the phosphorylation level of MoMps1 (Fig. 7B). Moreover, we established an ER stress condition by deletion of the transcription factor MoHac1 protein (Tang et al., 2015), and found that it also enhanced the phosphorylation level of MoMps1 (Fig. 7C). Interestingly, DTT treatment activated the phosphorylation of MoMps1 in the ΔMomck1 mutant, but not in the ΔMomkk1 or ΔMomps1 mutant (Fig. 7B). These results indicate that ER stress (DTT) can activate the CWI pathway by enhancing the phosphorylation level of MoMps1.
Figure 7.
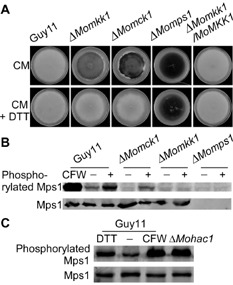
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress activates the phosphorylation of MoMps1. (A) Growth of the wild‐type and mutant strains on complete medium (CM) with and without 1 mm dithiothreitol (DTT). (B) Proteins were prepared from mycelia of Guy11 and three cell wall integrity (CWI) mutants cultured in liquid CM with 10 mm DTT for 4 h. Calcofluor white (CFW) was used as a positive control. ‘+’ represents treatment with DTT and ‘–’ represents no treatment as control. The signal intensity of phosphorylated MoMps1 increased with DTT treatment. (C) Proteins were prepared from mycelia of Guy11 with DTT and CFW treatment, and untreated Guy11 (‘–’ represents untreated Guy11) and ΔM ohac1 protein were used as controls.
Loss of CWI pathway components affects the UPR pathway
We have shown previously that the transcription factor MoHac1 protein regulates the ER stress response through a conserved UPR pathway, and the loss of MoHac1 contributes to acute ER stress (Tang et al., 2015). As both exogenous and endogenous ER stresses could activate the CWI pathway (Fig. 7C), we explored whether a defect in the CWI pathway has an effect on the UPR pathway by examining the expression of a series of putative UPR target genes, as well as MoHAC1, using quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). Treatment with DTT markedly increased the expression of these genes in wild‐type Guy11, but not to the same level in ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1 mutants (Fig. S10A–C, see Supporting Information). These results indicate that an intact CWI regulatory pathway is essential for correct function of the UPR pathway in M. oryzae.
Discussion
CWI in response to both internal cues and external challenges is imperative for growth, development and/or pathogenicity in fungi. The regulatory pathway for CWI has been most well studied in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae (Levin, 2011) and characterized in a number of pathogenic fungi. In Fusarium graminearum, the mutant strains missing Mkk1 and Slt2 homologues exhibit increased sensitivity to cell wall‐degrading enzymes and cell wall‐damaging compounds (Hou et al., 2002; Yun et al., 2014). In Ustilago maydis, the mutants of the Slt2 homologue pathway are also sensitive to cell wall stress agents (Carbo and Perez‐Martin, 2010). In the human pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans, deletion of Bck1, Mkk2 and Mpk1 homologues results in marked increases in sensitivity to SDS and CR (Donlin et al., 2014; Gerik et al., 2005; Kraus et al., 2003). In M. oryzae, previous studies have shown that the ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1 mutants are more sensitive to cell wall stressors (Jeon et al., 2008; Xu et al., 1998). Here again, the ΔMomkk1 mutant also showed increased sensitivity to these agents (Table 1), which is consistent with the model that the MAP kinase cascade functions in a conserved fashion to regulate CWI in both yeast and filamentous fungi.
In the fungus Ashbya gossypii, deletion of the components of the Slt2 MAP kinase cascade results in apparent hyphal autolysis (Lengeler et al., 2013). In M. oryzae, the ΔMomkk1 mutant also exhibited autolysis, similar to ΔMomck1 and ΔMomps1, and this type of autolysis could be partially suppressed by the presence of 1 m sorbitol as an osmotic stabilizer (Fig. 5A). Also, similarly, defects of the three Slt2 cascade mutants on the cell wall could partially be suppressed by sorbitol in U. maydis and C. neoformans (Carbo and Perez‐Martin, 2010; Gerik et al., 2005; Kraus et al., 2003). These findings establish a link between MAP kinases that regulate CWI and those that regulate osmotic stress responses.
Our previous study demonstrated that deletion of the phosphodiesterase MoPDEH gene had a progressive autolysis effect, which could also be recovered by 1 m sorbitol (Zhang et al., 2011a). In the present study, we followed this observation by providing a direct link between MoPdeH and the CWI regulatory pathway. We showed that MoPdeH specifically targets the CWI MAP kinase cascade by interacting with MoMck1 both in vivo and in vitro, but not the other two CWI MAP kinases (Fig. 1A–C), and that overexpression of MoMCK1 suppressed various defects of ΔMopdeH in growth, conidiation and pathogenicity, as well as intracellular cAMP levels. According to these results, we suppose that MoPdeH may be involved in CWI regulation in two ways: via the regulation of the expression of MoMck1 and by affecting the protein kinase activity of MoMck1 through a direct interaction. In S. cerevisiae, it has been shown that there is a genetic connection between Bck1 (MoMck1) and Pde2 (MoPdeH) (Costanzo et al., 2010; Costigan and Snyder, 1994; Sharifpoor et al., 2012). Our results further showed that MoPdeH regulates the expression of MoMck1 to influence several pathogenic‐related phenotypes. At the same time, we found that MoPdeH contains multiple putative phosphorylated sites, in particular four in the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase domain. Combination of these data with our result that MoPdeH interacts with MoMck1 in M. oryzae, we hypothesized that MoPdeH is phosphorylated by MoMck1 in vivo, and the phosphorylation of MoPdeH may be essential for its activation (four of the putative phosphorylated sites are in the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase domain). Moreover, MoPdeH may affect the protein kinase activity of MoMck1 through an allosteric effect (Tsai et al., 2008), which could explain why the expression of MKK1DD (constitutive activation of MoMps1) also partially suppressed the defect of ΔMopdeH. Our studies are significant in that they reveal a novel mechanism of CWI regulation by proteins that are involved in cAMP signalling in M. oryzae.
In C. neoformans, the mutant strains in BCK1, MKK2 and MPK1 homologues exhibited significantly decreased cAMP levels compared with the wild‐type strain, and exogenous cAMP could sufficiently rescue the sensitivity to SDS (Donlin et al., 2014). However, this was not the case in our study. The intracellular cAMP levels in the ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1 mutants were increased, possibly resulting from the down‐regulated expression of MoPDEH (Fig. S3A,B). This type of regulation suggests the presence of a feedback regulatory mechanism in M. oryzae. This indicates that there may exist distinct mechanisms of CWI regulation as a result of crosstalk between cAMP signalling and the MAP kinase cascade (Fig. 8).
Figure 8.
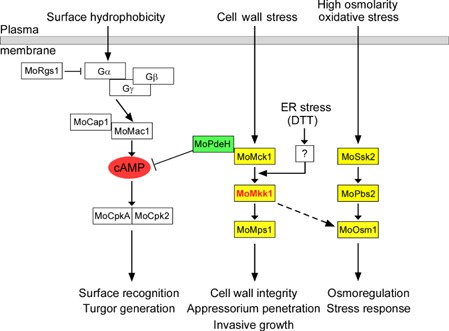
A proposed model for the crosstalk between the cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway and several other pathways in M agnaporthe oryzae. There might be novel crosstalk between the CWI pathway and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway through MoPdeH. The CWI pathway may also crosstalk with the dithiothreitol (DTT)‐induced unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway and the high osmolarity glycerol (HOG) pathway. The question mark represents an unknown sensor protein which can respond to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress (DTT) and subsequently activate the phosphorylation of the CWI pathway.
In plant‐pathogenic fungi, asexual spores (conidia) are the major source of primary inoculum and dissemination. We have shown previously that the ΔMopdeH mutant exhibits a higher cAMP level, but reduced conidial production, similar to the ΔMorgs1 mutant strain (MoRgs1 is one of the major regulators of G‐protein signalling that regulates cAMP levels in M. oryzae) (Zhang et al., 2011a, 2011b). In this way, as the cAMP levels in the ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1 mutants were increased, it is not surprising that all of these mutants showed a marked decrease in conidiation, or even a loss of conidiation, as seen in the ΔMomkk1 mutant. Incidentally, similar observations on conidiation defects of CWI cascade components have also been found in F. graminearum, Collectotrichum lagenarium and C. purpurea, but not in Mycosphaerella graminicola (Kojima et al., 2002; Mehrabi et al., 2006; Mey et al., 2002; Yun et al., 2014).
Unlike F. graminearum FgMKK1, whose deletion resulted in a significant defect in vegetative growth (Yun et al., 2014), the ΔMomkk1 mutant showed no difference in growth rates, but decreased pathogenicity. First, this may be a result of the fact that the ability of the ΔMomkk1 mutant to penetrate the host tissue is weakened and expansion in host plant cells is restricted. Similar to this observation, deletion of MoMCK1 and MoMPS1 resulted in a failed ability to penetrate plant tissues (Jeon et al., 2008; Xu et al., 1998). Moreover, deletion of MoMKK1 abrogated the phosphorylation ability of MoMps1, which may affect the function of the MoMps1 signalling pathway, resulting in a defect in pathogenicity. These data are consistent with the fact that MoMps1 signalling is required for appressorium penetration of plant cells (Xu et al., 1998). Second, the ΔMomkk1 mutant showed reduced chitin content and obviously uneven chitin distribution, together with down‐regulation of CHS expression levels. As the fungal cell wall primarily acts as a barrier against mechanical damage and is important for the maintenance of cell shape and integrity (Jendretzki et al., 2011), the decreased content and uneven distribution of chitin (the major component of the cell wall) may weaken the cell wall, further depressing the adaptability of the mutant to environmental challenges, which ultimately affects its pathogenicity. Indeed, previous studies have shown that, among seven CHS genes, three (CHS1, CHS6 and CHS7) are important for plant infection and pathogenicity (Kong et al., 2012). The decreased expression level of CHS genes in the ΔMomkk1 mutant may lead to reduced fitness and adaptability, leading to a defect in pathogenicity. Third, the ΔMomkk1 mutant showed increased sensitivity to several cell wall‐perturbing agents and osmotic stresses, and therefore was unable to cope with the stress on interaction with the host.
Moreover, a previous study has suggested that the fungal CWI regulatory pathway is not independent, but rather crosstalks with many other proteins or pathways to enhance its signalling capabilities (Fuchs and Mylonakis, 2009). In our study, we found that the ΔMomkk1 mutant showed increased sensitivity to several osmotic stresses, and the ΔMomck1 and ΔMomkk1 mutants showed down‐regulated MoOsm1 phosphorylation levels, indicating that MoMck1 and MoMkk1, as indispensable components of the CWI MAP kinase cascade, concurrently play a role in the regulation of the HOG pathway. Consistent with these findings, we found that CFW treatment increased the activation of MoOsm1 in the CWI mutants, but not in the wild‐type strain Guy11. This finding indicates that the two MAP kinase pathways (CWI and HOG pathways) may correspond to stresses in a coordinated fashion that, when one is blocked, the other will show increased activity against stress. The observation of crosstalk between the CWI signalling pathway and the HOG pathway is consistent with that reported in some filamentous fungi (Eliahu et al., 2007; Joubert et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2011; Ramamoorthy et al., 2007; Yun et al., 2014; Zheng et al., 2012). These results suggest that MoMkk1 plays a critical role in the crosstalk between the CWI and HOG regulatory pathways (Fig. 8).
Another crosstalk relationship observed was between the CWI and UPR regulatory pathways. As shown in Fig. 7C, both exogenous ER stress (DTT treatment) and endogenous ER stress (loss of MoHac1) can largely enhance the MoMps1 phosphorylation level. Indeed, the CWI and UPR pathways in S. cerevisiae are coordinately regulated by ER or cell wall stress inducers, and either stress (cell wall or ER stress) can activate the other pathway (Bonilla and Cunningham, 2003; Chen et al., 2005; Krysan, 2009; Scrimale et al., 2009). Simultaneously, a recent study has shown the importance of connections between these two pathways (CWI and UPR pathways) in filamentous fungi (Malavazi et al., 2014). Here, in M. oryzae, we also found that the phosphorylation of MoMps1 could be activated by ER stress in the ΔMomck1 mutant, but not in the ΔMomkk1 or ΔMomps1 strain, indicating that ER stress might activate the phosphorylation of MoMps1 by triggering a sensor protein (possibly an unknown protein kinase which can replace MoMck1 to phosphorylate MoMkk1 under DTT treatment) of DTT between MoMck1 and MoMkk1 (Fig. 8). As little is known about the specific mechanism of the activation process, we plan to investigate the interactive proteins of MoMkk1 following DTT treatment (especially protein kinases) with a protein affinity purification approach, aiming to find the specific protein(s) which can phosphorylate MoMkk1. However, loss of the CWI pathway component also has an effect on the regulation of UPR target genes. According to the information in the key signalling pathways involved in infection‐related morphogenesis (Li et al., 2012) and taken with our data above, we propose a model in which MoPdeH mediates crosstalk between the cAMP signalling pathway, HOG pathway and DTT‐induced UPR pathway (Fig. 8).
In summary, we have revealed a novel crosstalk mechanism between cAMP and CWI pathways through MoPdeH, characterized the main components of the MAP kinase cascade that regulates CWI, and explored additional crosstalk relationships between the CWI pathway and other pathways in M. oryzae. Given the importance of the role of the CWI regulatory pathway in the physiology and pathogenicity of M. oryzae and the urgent need for the development of novel fungicides for rice blast control, further studies on the CWI pathway and its crosstalk networks are warranted.
Experimental Procedures
Strains and culture conditions
The M. oryzae Guy11 strain was used as wild‐type for transformation in this study. All strains were cultured on CM agar plates for 3–15 days at 28 °C (Talbot et al., 1993). Mycelia were harvested from liquid CM and used for DNA and RNA extractions. For conidiation, culture blocks were inoculated on SDC (100 g straw, 40 g corn powder, 15 g agar in 1 L distilled water) agar medium (Zhang et al., 2011a) at 28 °C for 7 days in the dark, followed by 3 days of continuous illumination under fluorescent light. For medium containing cell wall‐perturbing agents, the final concentrations were 0.005%, 0.008% and 0.01% for SDS, 200, 400 and 600 μg/mL for CR, 200, 400 and 600 μg/mL for CFW, 30 mg/mL for caffeine and 15 mg/mL for lysing enzymes.
Targeted gene deletion and complementation
The MoMKK1 gene deletion mutant was generated using the standard one‐step gene replacement strategy. First, two fragments with 1.0 kb of sequences flanking the targeted gene were PCR amplified with primer pairs (Table S1, see Supporting Information). The resulting PCR products was digested with restriction endonucleases and ligated with the hygromycin resistance cassette (HPH) released from pCX62. Finally, the recombinant insert was sequenced. The 3.4‐kb fragment, which includes the flanking sequences and the HPH cassette, was amplified and transformed into Guy11 protoplasts. Putative mutants were first screened by PCR and later confirmed by Southern blotting analysis (Fig. S5). The complement fragment, which contains the entire MoMKK1 gene coding region and its native promoter region, was amplified by PCR with primers (Table S1) and inserted into pYF11 (bleomycin resistance) to complement the mutant strain. The MoMCK1 gene deletion mutant was obtained using a similar strategy.
qRT‐PCR analysis
For qRT‐PCR, total RNA was reverse transcribed into first‐strand cDNA using the oligo (dT) primer and M‐MLV Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA). qRT‐PCRs were performed following previously established procedures (Guo et al., 2010). qRT‐PCR was performed with three independent pools of tissues in three sets of experimental replicates.
Assays for vegetative growth, cuticle penetration and pathogenicity
Small squares of mycelia were picked from the edge of 4‐day‐old cultures and placed onto a variety of media (CM, MM, OM and SDC) (Zhang et al., 2010), supplemented with or without different compounds, and cultured in the dark at 28 °C. The colony diameter was measured after incubation for 7 days. All the experiments were repeated three times with three replicates each time.
Mycelia cultured in liquid CM for 2 days were harvested, used to inoculate barley leaf epidermis and incubated under humid conditions at 28 °C in the dark. After incubation for 30 h, appressorium formation and the development of invasive hyphae were examined under a microscope.
Pathogenicity assay was performed as described by Zhang et al. (2011c). In order to examine the pathogenicity of the mutants without conidia, mycelia cultured in liquid CM for 2 days were harvested and inoculated on unwounded or wounded rice or barley leaves. and kept in the same conditions as described above for 5 days (Dou et al., 2011).
Construction of MKK 1 T369D,T375D and MoMCK 1 overexpression constructs
To generate a MKK1 T369D,T375D construct, a 2.7‐kb upstream fragment, including the MoMKK1 native promoter and 1.1 kb from the start codon of the coding sequence [containing aspartic acid‐369 (Asp‐369)], and a 0.5‐kb downstream fragment, including the rest of the gene coding sequence (containing both Asp369 and Asp375), were co‐transformed with XhoI‐digested pYF11 into yeast strain XK1‐25 (Bruno et al., 2004). Plasmid pYF11::MoMKK T369D,T375D was rescued from the resulting tryptophan (Trp)‐positive yeast transformants.
For the generation of a MoMCK1 overexpression construct, the genomic DNA of Guy11 was amplified by PCR with the primers MCK1overF/MCK1overR (Table S1). The resulting PCR product contained the MoMCK1 gene sequence driven by the RP27 promoter. The fragment was co‐transformed with XhoI‐digested pYF11 into yeast strain XK1‐25 (Bruno et al., 2004). Plasmid pYF11::MoMCK1 was rescued from the resulting Trp‐positive yeast transformants.
Intracellular cAMP measurement, CFW staining and measurement of the chitin content
Mycelia cultured in liquid CM for 2 days were harvested, frozen in liquid nitrogen and lyophilized for 16 h. Intracellular cAMP extraction was performed as described previously (Liu et al., 2007). The cAMP levels were quantified according to the cAMP Biotrak Immunoassay System (BD Bioscience, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
Calcofluor staining, using Fluorescent Brightener 28 (10 μg/mL, Sigma‐Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for the microscopy of mycelial branches, was performed as described previously (Harris et al., 1994). Both of the mutants and Guy11 were cultured in liquid CM for 24 h. Mycelial tip plugs were removed and stained with 10 μg/mL CFW for 5 min in the dark, rinsed twice with phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS) and viewed under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX71, Tokyo, Japan).
Chitin (N‐acetylglucosamine, GlcNAc) content was analysed as described previously (Bulik et al., 2003; Song et al., 2010). First, mycelial samples were freeze–dried and then 5 mg of dried mycelia were resuspended in 1 mL of 6% KOH and heated at 80 °C for 90 min. Samples were centrifuged (16 000 g, 10 min) and pellets were washed with PBS in three cycles of centrifugation and suspension (16 000 g, 10 min) before final suspension in 0.5 mL of McIlvaine's buffer (pH 6). An aliquot of 100 mL (13 units) of Streptomyces plicatus chitinase (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added and incubated for 16 h at 37 °C with gentle mixing; 100‐mL samples were then combined with 100 mL of 0.27 m sodium borate (pH 9), heated for 10 min at 100 °C with final addition of 1 mL of freshly diluted (1 : 10) Ehrlich's reagent (10 g p‐dimethylaminobenzaldehyde in 1.25 mL of HCl and 8.75 mL of glacial acetic acid). After incubation at 37 °C for 20 min, 1 mL of the sample was transferred to a 2.5‐mL plastic cuvette (Greiner, Frickenhausen, Germany) and the absorbance at 585 nm was recorded. Standard curves were prepared with GlcNAc (Sigma). The experiment was repeated three times.
Y2H and GST pull‐down assays
The cDNAs of MoPDEH (including the whole long fragment and the four parts), MoMCK1 (the three parts), MoMKK1 and MoMPS1 were amplified with primer pairs BDPDEQCF/BDPDEQCR, ADMCK1F/ADMCK1R, ADMCK2F/ADMCK2R, ADMCK3F/ADMCK3R, BDMKKF/BDMKKR and ADMPSF/ADMPSR, respectively. The amplified products were cloned into the pGBKT7 and pGADT7 vectors (BD Biosciences Clontech, Oxford, UK), respectively. The cDNA of MoPDEH was amplified with primer pair BDPDEQCF/BDPDEQCR, the cDNAs of the three parts of MoMCK1 were amplified with primer pairs ADMCK1F/ADMCK1R, ADMCK2F/ADMCK2R, ADMCK3F/ADMCK3R, respectively. The cDNAs of MoMKK1 and MoMPS1 were amplified with primer pairs BDMKKF/BDMKKR and ADMPSF/ADMPSR, respectively. The amplified products of MoPDEH and MoMKK1 were cloned into the pGBKT7 vector and the amplified products of MoMPS1 and the three parts of MoMCK1 were cloned into pGADT7 vectors (BD Biosciences Clontech, Oxford, UK), respectively. After sequence verification, they were transformed into yeast AH109 strain following the manufacturer's recommended protocol (BD Biosciences Clontech). Transformants grown on synthetic dextrose medium lacking leucine and Trp (SD–Leu–Trp) were transferred to synthetic medium lacking Leu, Trp, adenine and histidine (SD–Leu–Trp–Ade–His). The interaction was further tested by investigation of the β‐galactosidase activity using 5‐bromo‐4‐chloro‐3‐indolyl‐β‐d‐galactopyranoside (X‐gal) (80 mg/L). Yeast strains for positive and negative controls were from the two‐hybrid assay kit.
GST, GST‐MoPdeH and His‐MoMck1B (342–842 amino acids) were expressed in Escherichia coli BL21‐CodonPlus (DE3) cells (Stratagene, Cedar Creek, Texas, USA). Cells were lysed in lysis buffer [50 mm Tris (pH 8.0), 50 mm NaCl, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride (PMSF) (Sigma‐Aldrich)] with a sonicator (Branson, Connecticut, USA). Samples were centrifuged (6268 g, 10 min) and the supernatants were transferred to a new 1.5‐mL tube and stored at −70 °C. The GST and GST‐MoPdeH supernatants were then mixed with 30 μL of glutathione Sepharose beads incubated at 4 °C for 4 h. Then, the recombinant GST‐MoPdeH or GST bound to glutathione Sepharose beads was incubated with E. coli cell lysate containing His‐MoMck1B (342–842 amino acids) at 4 °C for another 4 h. Finally, the beads were washed with buffer [50 mm Tris (pH 8.0), 50 mm NaCl, 1 mm PMSF (Sigma‐Aldrich), 1% Triton X‐100] five times and eluted from the beads. Eluted protein was analysed by immunoblot (IB) with monoclonal anti‐His and monoclonal anti‐GST antibodies.
Western blot analysis of protein phosphorylation
The mutants and wild‐type Guy11 strains were cultured in liquid CM for 2 days and then left untreated or treated with 10 mm DTT or 600 μg/mL CFW before the mycelia of each strain were harvested. Total proteins were isolated from vegetative hyphae as described by Bruno et al. (2004). The intensity of the signal corresponding to phosphorylated Mps1 was detected by binding of an antiphospho‐p44/42 MAP kinase antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, Massachusetts, USA), with the Mpk1 antibody (N‐terminal anti‐Mpk1) from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA) used as a control. Moreover, the phosphorylated MoOsm1 was examined using an antibody against dually phosphorylated p38 (Thr180/Tyr182) (Cell Signaling Technology), with an antiHog1 antibody (C‐terminal anti‐Hog1) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) used as a control. Each experiment was repeated three times.
BiFC assay
The MoMCK1‐CYFP and MoMPS1‐CYFP fusion constructs were generated by cloning the MoMCK1 and MoMPS1 fragments amplified with primer pairs phz68MCKF/phz68MCKR and phz68MPSF/phz68MPSR, respectively, into pHZ68 (Zhao et al., 2007). Similarly, the MoMKK1‐NYFP and MoMPDEH‐NYFP fusion constructs were generated by cloning the MoMKK1 and MoPDEH fragments amplified with primer pairs phz65MKKF/phz65MKKR and phz65PDEF/phz65PDER, respectively, into pHZ65. Construct pairs of MoMCK1‐CYFP and MoPDEH‐NYFP, MoMCK1‐CYFP and MoMKK1‐NYFP, and MoMPS1‐CYFP and MoMKK1‐NYFP were co‐transformed into protoplasts of Guy11. Transformants resistant to both hygromycin and zeocin were isolated and confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. YFP signals were examined with a Nikon 800 epifluoresence microscope (Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan).
Supporting information
Fig. S1 MoMCK1 gene expression level in the ΔMopdeH mutant. RNA was prepared from mycelia cultured in liquid complete medium (CM) at 28 °C for 2 days. ACTIN was used for normalization, and the values were calculated by the 2–ddCT method with quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR) data. Values represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from two independent experiments with three replicates each. The capital letters showed the significant changes compared to the wild type. The same letters in a column showed no significant difference.
Fig. S2 Overexpression of MoMCK1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔMopdeH mutant suppress defects in intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) level and conidiation. (A) Over‐expression of MoMCK1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔMopdeH mutant suppressed the increased intracellular cAMP level of the ΔMopdeH mutant. Bar chart showing the quantification of intracellular cAMP in the mycelia of the indicated strains following 2 days of culture in complete medium. Two biological repetitions with three replicates were assayed. The error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. (B) Statistical analysis of conidia production. The conidia produced by the wild‐type strain Guy11, over‐expression of MoMCK1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔMopdeH mutant strains grown on straw decoction and corn agar (SDC) medium for 10 days were collected, counted and analysed by Duncan analysis (P < 0.01). Three independent experiments yielded similar results. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). The capital letters showed the significant changes compared to the wild type. The same letters in a column showed no significant difference.
Fig. S3 The mitogen‐activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade regulates intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels. (A) Loss of cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway components leads to increased accumulation of total intracellular cAMP levels. Bar charts showing the quantification of intracellular cAMP in the mycelia of the indicated strains following 2 days of culture in complete medium. Two biological repetitions with three replicates were assayed. The error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. (B) Analysis of MoPDEH gene transcription in the three CWI mutants (ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1) in Magnaporthe oryzae using quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). Asterisks indicate significant differences between the mutant and wild‐type strains at p = 0.01, according to Duncan's range test.
Fig. S4 MoMkk1 interacts with MoMck1 and MoMps1. (A) Yeast two‐hybrid analysis of the interaction of MoMkk1 with MoMck1 and MoMps1. The three parts of MoMck1 and MoMps1 were inserted into vector pGADT7, whereas MoMkk1 was inserted into pGBKT7. Yeast cells were grown on synthetic dextrose (SD) medium lacking leucine (Leu), tryptophan (Trp), histidine (His) and adenine (Ade), and β‐galactosidase (LacZ) activities were investigated with positive and negative controls. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3 days before being photographed. (B) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for interactions of MoMkk1 with MoMck1 and MoMps1. Conidia of transformants expressing MoMKK1‐NYFP and MoMCK1‐CYFP constructs, MoMKK1‐NYFP and MoMPS1‐CYFP, were sequentially tested by both differential interference contrast (DIC) and epifluorescence microscopy. YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.
Fig. S5 Southern blot analysis of MoMKK1 and MoMCK1 deletion mutants. Southern blot analysis of gene knockout mutants with gene‐specific probes (probes 1 and 3) and hygromycin phosphotransferase (HPH) probe (probe 2). (A, B) Strategy of knocking out MoMKK1 and MoMCK1 genes in the Magnaporthe oryzae genome. Thick arrows indicate orientations of the genes and HPH genes. Thin lines below the arrows indicate the probe sequence of each gene. HI, HindIII.
Fig. S6 Pathogenicity test on barley. Detached barley leaves, unwounded and wounded by abrasion, were inoculated with mycelia of Guy11, the three mutants and complemented strains. Diseased leaves were photographed 5 days after inoculation. The two ΔMomck1 transformants with constitutively activated MoMps1 showed partially restored pathogenicity defects.
Fig. S7 MoMkk1 is important for aerial hyphal growth and asexual development. (A) The ΔMomkk1 mutant exhibited no difference in growth rates, but a lack of aerial hyphae, on complete medium (CM), minimal medium (MM), oatmeal medium (OM) and straw decoction and corn (SDC) medium after incubation at 28 °C for 7 days in darkness. (B) Conidia formation was observed under a light microscope at room temperature 24 h after induction of conidiation under cover slips.
Fig. S8 Statistical analysis of infectious hyphae. For each tested strain, 100 infecting hyphae (n = 100) were counted per replicate and the experiment was repeated three times.
Fig. S9 The ΔMomkk1 mutant exhibits altered tolerance to various osmotic stresses. (A) Sensitivity of each strain to osmotic stress. The three cell wall integrity (CWI) mutants (ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1) and the wild‐type strain Guy11 were incubated on complete medium (CM) supplemented with 0.7 m NaCl, 0.6 m KCl and 1 m sorbitol at 28 °C for 7 days before being photographed. The data comprise three independent experiments with triple replications each time that yielded similar results. (B) Colony diameters of the tested strains were measured and subjected to statistical analysis. The growth inhibition rate is relative to the growth rate of each untreated control [Inhibition rate = (diameter of untreated strain − diameter of treated strain)/(diameter of untreated strain × 100%)]. Three repeats were performed and similar results were obtained. Error bars represent the standard deviations and asterisks represent significant differences (P < 0.01).
Fig. S10 Cell wall integrity (CWI) is linked to the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway. Loss of the CWI pathway components affects the regulation of the UPR pathway. Expression analysis of three putative UPR target genes (MoSCJ1, MoKAR2 and MoSIL1) and MoHAC1 in three CWI pathway mutants (ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1) was tested by quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates and asterisks represent significant differences (P < 0.01). Experiments were performed three times with similar results.
Table S1 Primers used in this study.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr J. R. Xu for providing the ΔMomps1 mutant strain. This research was supported by the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Grant No. 31325022 to ZZ), Agriculture Innovation Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (CX15‐1054), Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 31271998, to ZZ) and the especially appointed professorship (Jiangsu, China).
References
- Adachi, K. and Hamer, J.E. (1998) Divergent cAMP signaling pathways regulate growth and pathogenesis in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea . Plant Cell, 10, 1361–1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla, M. and Cunningham, K.W. (2003) Mitogen‐activated protein kinase stimulation of Ca(2+) signaling is required for survival of endoplasmic reticulum stress in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell, 14, 4296–4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, K.S. , Tenjo, F. , Li, L. , Hamer, J.E. and Xu, J.R. (2004) Cellular localization and role of kinase activity of PMK1 in Magnaporthe grisea . Eukaryot. Cell, 3, 1525–1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulik, D.A. , Olczak, M. , Lucero, H.A. , Osmond, B.C. , Robbins, P.W. and Specht, C.A. (2003) Chitin synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in response to supplementation of growth medium with glucosamine and cell wall stress. Eukaryot. Cell, 2, 886–900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbo, N. and Perez‐Martin, J. (2010) Activation of the cell wall integrity pathway promotes escape from G2 in the fungus Ustilago maydis . PLoS Genet. 6, e1001009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. , Feldman, D.E. , Deng, C. , Brown, J.A. , De Giacomo, A.F. , Gaw, A.F. , Shi, G. , Le, Q.T. , Brown, J.M. and Koong, A.C. (2005) Identification of mitogen‐activated protein kinase signaling pathways that confer resistance to endoplasmic reticulum stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Mol. Cancer Res. 3, 669–677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W. and Dean, R.A. (1997) The adenylate cyclase gene MAC1 of Magnaporthe grisea controls appressorium formation and other aspects of growth and development. Plant Cell, 9, 1973–1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo, M. , Baryshnikova, A. , Bellay, J. , Kim, Y. , Spear, E.D. , Sevier, C.S. , Ding, H. , Koh, J.L. , Toufighi, K. , Mostafavi, S. , Prinz, J. , St Onge, R.P. , VanderSluis, B. , Makhnevych, T. , Vizeacoumar, F.J. , Alizadeh, S. , Bahr, S. , Brost, R.L. , Chen, Y. , Cokol, M. , Deshpande, R. , Li, Z. , Lin, Z.Y. , Liang, W. , Marback, M. , Paw, J. , San Luis, B.J. , Shuteriqi, E. , Tong, A.H. , van Dyk, N. , Wallace, I.M. , Whitney, J.A. , Weirauch, M.T. , Zhong, G. , Zhu, H. , Houry, W.A. , Brudno, M. , Ragibizadeh, S. , Papp, B. , Pál, C. , Roth, F.P. , Giaever, G. , Nislow, C. , Troyanskaya, O.G. , Bussey, H. , Bader, G.D. , Gingras, A.C. , Morris, Q.D. , Kim, P.M. , Kaiser, C.A. , Myers, C.L. , Andrews, B.J. and Boone, C. (2010) The genetic landscape of a cell. Science, 327, 425–431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costigan, C. and Snyder, M. (1994) SLK1, a yeast homolog of MAP kinase activators, has a RAS/cAMP‐independent role in nutrient sensing. Mol. Gen. Genet. 243, 286–296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, P.B. , Walker, W.H. and Habener, J.F. (1998) Cyclic AMP signaling and gene regulation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 18, 353–383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlin, M.J. , Upadhya, R. , Gerik, K.J. , Lam, W. , VanArendonk, L.G. , Specht, C.A. , Sharma, N.K. and Lodge, J.K. (2014) Cross talk between the cell wall integrity and cyclic AMP/protein kinase A pathways in Cryptococcus neoformans . MBio 5, e01573‐14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou, X. , Wang, Q. , Qi, Z. , Song, W. , Wang, W. , Guo, M. , Zhang, H. , Zhang, Z. , Wang, P. and Zheng, X. (2011) MoVam7, a conserved SNARE involved in vacuole assembly, is required for growth, endocytosis, ROS accumulation, and pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae . PLoS ONE, 6, e16439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliahu, N. , Igbaria, A. , Rose, M.S. , Horwitz, B.A. and Lev, S. (2007) Melanin biosynthesis in the maize pathogen Cochliobolus heterostrophus depends on two mitogen‐activated protein kinases, Chk1 and Mps1, and the transcription factor Cmr1. Eukaryot. Cell, 6, 421–429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, B.B. and Mylonakis, E. (2009) Our paths might cross: the role of the fungal cell wall integrity pathway in stress response and cross talk with other stress response pathways. Eukaryot. Cell, 8, 1616–1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa, T. , Kuga, Y. , Yano, S. , Yoshimi, A. , Tachiki, T. , Abe, K. , and Nishimura, M. (2009) Dynamics of cell wall components of Magnaporthe grisea during infectious structure development. Mol. Microbiol. 73, 553–570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka, T. , Mizutani, O. , Furukawa, K. , Sato, N. , Yoshimi, A. , Yamagata, Y. , Nakajima, T. and Abe, K. (2007) MpkA‐dependent and ‐independent cell wall integrity signaling in Aspergillus nidulans . Eukaryot. Cell, 6, 1497–1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerik, K.J. , Donlin, M.J. , Soto, C.E. , Banks, A.M. , Banks, I.R. , Maligie, M.A. , Selitrennikoff, C.P. and Lodge, J.K. (2005) Cell wall integrity is dependent on the PKC1 signal transduction pathway in Cryptococcus neoformans . Mol. Microbiol. 58, 393–408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M. , Guo, W. , Chen, Y. , Dong, S. , Zhang, X. , Zhang, H. , Song, W. , Wang, W. , Wang, Q. , Lv, R. , Zhang, Z. , Wang, Y. and Zheng, X. (2010) The basic leucine zipper transcription factor Moatf1 mediates oxidative stress responses and is necessary for full virulence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae . Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 23, 1053–1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris, S.D. , Morrell, J.L. and Hamer, J.E. (1994) Identification and characterization of Aspergillus nidulans mutants defective in cytokinesis. Genetics, 136, 517–532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z. , Xue, C. , Peng, Y. , Katan, T. , Kistler, H.C. and Xu, J.R. (2002) A mitogen‐activated protein kinase gene (MGV1) in Fusarium graminearum is required for female fertility, heterokaryon formation, and plant infection. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 15, 1119–1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie, K. , Takase, M. , Lee, K.S. , Levin, D.E. , Araki, H. , Matsumoto, K. and Oshima, Y. (1993) MKK1 and MKK2, which encode Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitogen‐activated protein kinase‐kinase homologs, function in the pathway mediated by protein kinase C. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3076–3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendretzki, A. , Wittland, J. , Wilk, S. , Straede, A. and Heinisch, J.J. (2011) How do I begin? Sensing extracellular stress to maintain yeast cell wall integrity. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 90, 740–744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J. , Goh, J. , Yoo, S. , Chi, M.H. , Choi, J. , Rho, H.S. , Park, J. , Han, S.S. , Kim, B.R. , Park, S.Y. , Kim, S. and Lee, Y.H. (2008) A putative MAP kinase kinase kinase, MCK1, is required for cell wall integrity and pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae . Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 21, 525–534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joubert, A. , Bataille‐Simoneau, N. , Campion, C. , Guillemette, T. , Hudhomme, P. , Iacomi‐Vasilescu, B. , Leroy, T. , Pochon, S. , Poupard, P. and Simoneau, P. (2011) Cell wall integrity and high osmolarity glycerol pathways are required for adaptation of Alternaria brassicicola to cell wall stress caused by brassicaceous indolic phytoalexins. Cell. Microbiol. 13, 62–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, K. , Kikuchi, T. , Takano, Y. , Oshiro, E. and Okuno, T. (2002) The mitogen‐activated protein kinase gene MAF1 is essential for the early differentiation phase of appressorium formation in Colletotrichum lagenarium . Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 15, 1268–1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.A. , Yang, J. , Li, G.T. , Qi, L.L. , Zhang, Y.J. , Wang, C.F. , Zhao, W.S. , Xu, J.R. and Peng, Y.L. (2012) Different chitin synthase genes are required for various developmental and plant infection processes in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae . PLoS Pathog. 8, e1002526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, P.R. , Fox, D.S. , Cox, G.M. and Heitman, J. (2003) The Cryptococcus neoformans MAP kinase Mpk1 regulates cell integrity in response to antifungal drugs and loss of calcineurin function. Mol. Microbiol. 48, 1377–1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan, D.J. (2009) The cell wall and endoplasmic reticulum stress responses are coordinately regulated in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Commun. Integr. Biol. 2, 233–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.S. and Levin, D.E. (1992) Dominant mutations in a gene encoding a putative protein kinase (BCK1) bypass the requirement for a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein kinase C homolog. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 172–182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.S. , Irie, K. , Gotoh, Y. , Watanabe, Y. , Araki, H. , Nishida, E. , Matsumoto, K. and Levin, D.E. (1993) A yeast mitogen‐activated protein kinase homolog (Mpk1p) mediates signalling by protein kinase C. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3067–3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H. and Dean, R.A. (1993) cAMP regulates infection structure formation in the plant pathogenic fungus Magnaporthe grisea . Plant Cell, 5, 693–700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler, K.B. , Wasserstrom, L. , Walther, A. and Wendland, J. (2013) Analysis of the cell wall integrity pathway of Ashbya gossypii . Microbiol. Res. 168, 607–614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesage, G. and Bussey, H. (2006) Cell wall assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 70, 317–343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin, D.E. (2005) Cell wall integrity signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 69, 262–291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin, D.E. (2011) Regulation of cell wall biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the cell wall integrity signaling pathway. Genetics, 189, 1145–1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin, D.E. , Fields, F.O. , Kunisawa, R. , Bishop, J.M. and Thorner, J. (1990) A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1, is required for the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell, 62, 213–224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. , Zhou, X. and Xu, J.‐R. (2012) Genetic control of infection‐related development in Magnaporthe oryzae . Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 15, 678–684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. , Suresh, A. , Willard, F.S. , Siderovski, D.P. , Lu, S. and Naqvi, N.I. (2007) Rgs1 regulates multiple Galpha subunits in Magnaporthe pathogenesis, asexual growth and thigmotropism. EMBO J. 26, 690–700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H. and Dean, R.A. (1997) G protein alpha subunit genes control growth, development, and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe grisea . Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 10, 1075–1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. , Soulie, M.C. , Perrino, C. and Fillinger, S. (2011) The osmosensing signal transduction pathway from Botrytis cinerea regulates cell wall integrity and MAP kinase pathways control melanin biosynthesis with influence of light. Fungal Genet. Biol. 48, 377–387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavazi, I. , Goldman, G.H. and Brown, N.A. (2014) The importance of connections between the cell wall integrity pathway and the unfolded protein response in filamentous fungi. Brief. Funct. Genomics, 13, 456–470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon, C.C. (2005) G proteins in development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 689–701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin, H. , Arroyo, J. , Sanchez, M. , Molina, M. and Nombela, C. (1993) Activity of the yeast MAP kinase homologue Slt2 is critically required for cell integrity at 37 °C. Mol. Gen. Genet. 241, 177–184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabi, R. , Van der Lee, T. , Waalwijk, C. and Gert, H.J. (2006) MgSlt2, a cellular integrity MAP kinase gene of the fungal wheat pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola, is dispensable for penetration but essential for invasive growth. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 19, 389–398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mey, G. , Held, K. , Scheffer, J. , Tenberge, K.B. and Tudzynski, P. (2002) CPMK2, an SLT2‐homologous mitogen‐activated protein (MAP) kinase, is essential for pathogenesis of Claviceps purpurea on rye: evidence for a second conserved pathogenesis‐related MAP kinase cascade in phytopathogenic fungi. Mol. Microbiol. 46, 305–318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, T.K. and Dean, R.A. (1995) The cAMP‐dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit is required for appressorium formation and pathogenesis by the rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe grisea . Plant Cell, 7, 1869–1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z. , Wang, Q. , Dou, X. , Wang, W. , Zhao, Q. , Lv, R. , Zhang, H. , Zheng, X. , Wang, P. and Zhang, Z. (2012) MoSwi6, an APSES family transcription factor, interacts with MoMps1 and is required for hyphal and conidial morphogenesis, appressorial function and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae . Mol. Plant Pathol. 13, 677–689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram, A.F. and Klis, F.M. (2006) Identification of fungal cell wall mutants using susceptibility assays based on Calcofluor white and Congo red. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2253–2256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy, V. , Zhao, X. , Snyder, A.K. , Xu, J.R. and Shah, D.M. (2007) Two mitogen‐activated protein kinase signalling cascades mediate basal resistance to antifungal plant defensins in Fusarium graminearum . Cell. Microbiol. 9, 1491–1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramanujam, R. and Naqvi, N.I. (2010) PdeH, a high‐affinity cAMP phosphodiesterase, is a key regulator of asexual and pathogenic differentiation in Magnaporthe oryzae . PLoS Pathog. 6, e1000897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrimale, T. , Didone, L. , de Mesy Bentley, K.L. and Krysan, D.J. (2009) The unfolded protein response is induced by the cell wall integrity mitogen‐activated protein kinase signaling cascade and is required for cell wall integrity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Mol. Biol. Cell, 20, 164–175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharifpoor, S. , van Dyk, D. , Costanzo, M. , Baryshnikova, A. , Friesen, H. , Douglas, A.C. , Youn, J.Y. , VanderSluis, B. , Myers, C.L. , Papp, B. , Boone, C. and Andrews, B.J. (2012) Functional wiring of the yeast kinome revealed by global analysis of genetic network motifs. Genome Res. 22, 791–801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song, W. , Dou, X. , Qi, Z. , Wang, Q. , Zhang, X. , Zhang, H. , Guo, M. , Dong, S. , Zhang, Z. , Wang, P. and Zheng, X. (2010) R‐SNARE homolog MoSec22 is required for conidiogenesis, cell wall integrity, and pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae . PLoS ONE, 5, e13193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear, E. and Ng, D.T. (2001) The unfolded protein response: no longer just a special teams player. Traffic, 2, 515–523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, N.J. , Ebbole, D.J. and Hamer, J.E. (1993) Identification and characterization of MPG1, a gene involved in pathogenicity from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea . Plant Cell, 5, 1575–1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W. , Ru, Y. , Hong, L. , Zhu, Q. , Zuo, R. , Guo, X. , Wang, J. , Zhang, H. , Zheng, X. , Wang, P. and Zhang, Z. (2015) System‐wide characterization of bZIP transcription factor proteins involved in infection‐related morphogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae . Environ. Microbiol. 17, 1377–1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.J. , del Sol, A. and Nussinov, R. (2008) Allostery: absence of a change in shape does not imply that allostery is not at play. J. Mol. Biol. 378, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valiante, V. , Heinekamp, T. , Jain, R. , Hartl, A. and Brakhage, A.A. (2008) The mitogen‐activated protein kinase MpkA of Aspergillus fumigatus regulates cell wall signaling and oxidative stress response. Fungal Genet. Biol. 45, 618–627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.R. , Staiger, C.J. and Hamer, J.E. (1998) Inactivation of the mitogen‐activated protein kinase Mps1 from the rice blast fungus prevents penetration of host cells but allows activation of plant defense responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 12 713–12 718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun, Y. , Liu, Z. , Zhang, J. , Shim, W.B. , Chen, Y. and Ma, Z. (2014) The MAPKK FgMkk1 of Fusarium graminearum regulates vegetative differentiation, multiple stress response, and virulence via the cell wall integrity and high‐osmolarity glycerol signaling pathways. Environ. Microbiol. 16, 2023–2037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. , Liu, K. , Zhang, X. , Song, W. , Zhao, Q. , Dong, Y. , Guo, M. , Zheng, X. and Zhan, Z. (2010) A two‐component histidine kinase, MoSLN1, is required for cell wall integrity and pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae . Curr. Genet. 56, 517–528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. , Liu, K. , Zhang, X. , Tang, W. , Wang, J. , Guo, M. , Zhao, Q. , Zheng, X. , Wang, P. and Zhang, Z. (2011a) Two phosphodiesterase genes, PDEL and PDEH, regulate development and pathogenicity by modulating intracellular cyclic AMP levels in Magnaporthe oryzae . PLoS ONE, 6, e17241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. , Tang, W. , Liu, K. , Huang, Q. , Zhang, X. , Yan, X. , Chen, Y. , Wang, J. , Qi, Z. , Wang, Z. , Zheng, X. , Wang, P. and Zhang, Z. (2011b) Eight RGS and RGS‐like proteins orchestrate growth, differentiation, and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae . PLoS Pathog. 7, e1002450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. , Xue, C. , Kong, L. , Li, G. and Xu, J.R. (2011c) A Pmk1‐interacting gene is involved in appressorium differentiation and plant infection in Magnaporthe oryzae . Eukaryot. Cell, 10, 1062–1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. , Mehrabi, R. and Xu, J.R. (2007) Mitogen‐activated protein kinase pathways and fungal pathogenesis. Eukaryot. Cell, 6, 1701–1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D. , Zhang, S. , Zhou, X. , Wang, C. , Xiang, P. , Zheng, Q. and Xu, J.‐R. (2012) The FgHOG1 pathway regulates hyphal growth, stress responses, and plant infection in Fusarium graminearum . PLoS ONE, 7, e49495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Fig. S1 MoMCK1 gene expression level in the ΔMopdeH mutant. RNA was prepared from mycelia cultured in liquid complete medium (CM) at 28 °C for 2 days. ACTIN was used for normalization, and the values were calculated by the 2–ddCT method with quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR) data. Values represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from two independent experiments with three replicates each. The capital letters showed the significant changes compared to the wild type. The same letters in a column showed no significant difference.
Fig. S2 Overexpression of MoMCK1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔMopdeH mutant suppress defects in intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) level and conidiation. (A) Over‐expression of MoMCK1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔMopdeH mutant suppressed the increased intracellular cAMP level of the ΔMopdeH mutant. Bar chart showing the quantification of intracellular cAMP in the mycelia of the indicated strains following 2 days of culture in complete medium. Two biological repetitions with three replicates were assayed. The error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. (B) Statistical analysis of conidia production. The conidia produced by the wild‐type strain Guy11, over‐expression of MoMCK1 and constitutive activation of MoMps1 in the ΔMopdeH mutant strains grown on straw decoction and corn agar (SDC) medium for 10 days were collected, counted and analysed by Duncan analysis (P < 0.01). Three independent experiments yielded similar results. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). The capital letters showed the significant changes compared to the wild type. The same letters in a column showed no significant difference.
Fig. S3 The mitogen‐activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade regulates intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels. (A) Loss of cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway components leads to increased accumulation of total intracellular cAMP levels. Bar charts showing the quantification of intracellular cAMP in the mycelia of the indicated strains following 2 days of culture in complete medium. Two biological repetitions with three replicates were assayed. The error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates. (B) Analysis of MoPDEH gene transcription in the three CWI mutants (ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1) in Magnaporthe oryzae using quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). Asterisks indicate significant differences between the mutant and wild‐type strains at p = 0.01, according to Duncan's range test.
Fig. S4 MoMkk1 interacts with MoMck1 and MoMps1. (A) Yeast two‐hybrid analysis of the interaction of MoMkk1 with MoMck1 and MoMps1. The three parts of MoMck1 and MoMps1 were inserted into vector pGADT7, whereas MoMkk1 was inserted into pGBKT7. Yeast cells were grown on synthetic dextrose (SD) medium lacking leucine (Leu), tryptophan (Trp), histidine (His) and adenine (Ade), and β‐galactosidase (LacZ) activities were investigated with positive and negative controls. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3 days before being photographed. (B) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for interactions of MoMkk1 with MoMck1 and MoMps1. Conidia of transformants expressing MoMKK1‐NYFP and MoMCK1‐CYFP constructs, MoMKK1‐NYFP and MoMPS1‐CYFP, were sequentially tested by both differential interference contrast (DIC) and epifluorescence microscopy. YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.
Fig. S5 Southern blot analysis of MoMKK1 and MoMCK1 deletion mutants. Southern blot analysis of gene knockout mutants with gene‐specific probes (probes 1 and 3) and hygromycin phosphotransferase (HPH) probe (probe 2). (A, B) Strategy of knocking out MoMKK1 and MoMCK1 genes in the Magnaporthe oryzae genome. Thick arrows indicate orientations of the genes and HPH genes. Thin lines below the arrows indicate the probe sequence of each gene. HI, HindIII.
Fig. S6 Pathogenicity test on barley. Detached barley leaves, unwounded and wounded by abrasion, were inoculated with mycelia of Guy11, the three mutants and complemented strains. Diseased leaves were photographed 5 days after inoculation. The two ΔMomck1 transformants with constitutively activated MoMps1 showed partially restored pathogenicity defects.
Fig. S7 MoMkk1 is important for aerial hyphal growth and asexual development. (A) The ΔMomkk1 mutant exhibited no difference in growth rates, but a lack of aerial hyphae, on complete medium (CM), minimal medium (MM), oatmeal medium (OM) and straw decoction and corn (SDC) medium after incubation at 28 °C for 7 days in darkness. (B) Conidia formation was observed under a light microscope at room temperature 24 h after induction of conidiation under cover slips.
Fig. S8 Statistical analysis of infectious hyphae. For each tested strain, 100 infecting hyphae (n = 100) were counted per replicate and the experiment was repeated three times.
Fig. S9 The ΔMomkk1 mutant exhibits altered tolerance to various osmotic stresses. (A) Sensitivity of each strain to osmotic stress. The three cell wall integrity (CWI) mutants (ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1) and the wild‐type strain Guy11 were incubated on complete medium (CM) supplemented with 0.7 m NaCl, 0.6 m KCl and 1 m sorbitol at 28 °C for 7 days before being photographed. The data comprise three independent experiments with triple replications each time that yielded similar results. (B) Colony diameters of the tested strains were measured and subjected to statistical analysis. The growth inhibition rate is relative to the growth rate of each untreated control [Inhibition rate = (diameter of untreated strain − diameter of treated strain)/(diameter of untreated strain × 100%)]. Three repeats were performed and similar results were obtained. Error bars represent the standard deviations and asterisks represent significant differences (P < 0.01).
Fig. S10 Cell wall integrity (CWI) is linked to the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway. Loss of the CWI pathway components affects the regulation of the UPR pathway. Expression analysis of three putative UPR target genes (MoSCJ1, MoKAR2 and MoSIL1) and MoHAC1 in three CWI pathway mutants (ΔMomck1, ΔMomkk1 and ΔMomps1) was tested by quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three replicates and asterisks represent significant differences (P < 0.01). Experiments were performed three times with similar results.
Table S1 Primers used in this study.


