Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to establish the contribution of four founder alleles of NBN to prostate cancer risk and cancer survival.
Materials and Methods
Five thousand one hundred eighty-nine men with prostate cancer and 6,152 controls were genotyped for four recurrent variants of NBN (657del5, R215W, I171V, and E185Q).
Results
The NBN 657del5 mutation was detected in 74 of 5,189 unselected cases and in 35 of 6,152 controls (odds ratio [OR], 2.5; p < 0.001). In carriers of 657del5 deletion, the cancer risk was restricted to men with the GG genotype of the E185Q variant of the same gene. Among men with the GG genotype, the OR associated with 657del5 was 4.4 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.4 to 8.0). Among men with other E185Q genotypes, the OR associated with 657del5 was 1.4 (95% CI, 0.8 to 2.4) and the interaction was significant (homogeneity p=0.006). After a median follow-up of 109 months, mortality was worse for 657del5 mutation carriers than for non-carriers (hazard ratio [HR], 1.6; p=0.001). The adverse effect of 657del5 on survival was only seen on the background of the GG genotype of E185Q (HR, 1.9; p=0.0004).
Conclusion
The NBN 657del5 mutation predisposes to poor prognosis prostate cancer. The pathogenicity of this mutation, with regards to both prostate cancer risk and survival, is modified by a missense variant of the same gene (E185Q).
Keywords: NBN, NBS1, Mutation, Aggressive prostate cancer, Survival
Introduction
Mutations in several genes predispose to prostate cancer, including BRCA2, BRCA1, CHEK2, NBN, ATM and HOXB13 [1-9]. Homozygous mutations in the NBN gene (also called NBS1) are responsible for the Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS), which is characterized by spontaneous chromosomal instability, immunodeficiency and a predisposition to cancer [10]. The protein product of the NBN gene is part of the genome surveillance complex responsible for DNA damage repair [11]. A 5-bp deletion in exon 6 of the NBN gene (657-del5) is a founder mutation, which, in its homozygous state is present in the majority of NBS patients. Heterozygous carriers of the 657del5 truncating mutation exhibit increased susceptibility to prostate cancer [5]. It is not clear if other NBN variants (missense or truncating) predispose to cancer. It is important to define the range of pathogenic NBN mutations, because NBN is included in a number of cancer test panels and it is incumbent upon the physician to accurately predict the risk of a reported variant [12]. To establish the contribution of four founder alleles in NBN to prostate cancer in Poland, and to measure the impact of these variants on risk and survival, we genotyped 5,189 men with prostate cancer and 6,152 controls.
Materials and Methods
1. Patients
We studied men with unselected prostate cancer who were diagnosed between 1999 and 2015 in 14 centers situated throughout Poland. This study was initiated in Szczecin in 1999 and was extended to include Białystok, Olsztyn in 2002 and Opole in 2003. Other centers began recruiting between 2005 and 2008 (Koszalin, Gdansk, Lublin, Łodź, Warszawa, Wrocław, Poznan, Rzeszów, Bydgoszcz, and Zabrze). Only men with newly diagnosed prostate cancer were invited to participate in this study. All cases were unselected for age, clinical characteristics (stage, grade, prostate-specific antigen [PSA] level at time of diagnosis), family history and treatment received. Study subjects were asked to participate at the time of diagnosis or during an outpatient visit to an oncology clinic. Sixty-one hundred thirty men were invited and of these, 5,235 (85.4%) participated. All patients provided a blood sample within six mon-ths of diagnosis. The mean age of diagnosis was 67.8 years (range, 35 to 96 years). A family history was taken either by the construction of a family tree or the completion of a standardized questionnaire. All first- and second-degree relatives diagnosed with prostate cancer and the ages of diagnosis were recorded. Six hundred thirty-five men reported at least one first- or second-degree relative with prostate cancer (familial cases). In addition, information was recorded on PSA level at time of diagnosis, grade (Gleason score) and stage. The vital status and the date of death of all of the cases were requested from the Polish Ministry of the Interior and Administration in June 2016, and were obtained in July 2016. These data were available for 5,185 men with prostate cancer. Information on the specific treatment was not recorded. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Pome-ranian Medical University in Szczecin, Poland.
2. Genotyping
DNA was isolated from 5 to 10 mL of peripheral blood. NBN mutations were genotyped using TaqMan assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) using LightCycler Real-Time PCR 480 System (Roche Life Science, Indianapolis, IN). Laboratory technicians were blinded to case–control status. Four NBN variants were successfully analyzed in 5,189 of 5,235 cases (99.1%) and in 6,152 of 6,240 controls (98.6%).
3. Sanger sequencing
To investigate whether other NBN variants (i.e., those linked to the G allele of E185Q) may affect cancer risk among carriers of the 657del5 mutation, we sequenced the entire coding sequence of the NBN gene in 16 cancer patients with 657del5 (8 with the GG genotype of E185Q and 8 with the GC genotype). Sanger sequencing was performed in 16 amplicons. Sequencing reactions were performed using a BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Sequencing products were analyzed on the ABI prism 3500-XL Genetic Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
4. Controls
The control group included 6,240 cancer-free adults from (the genetically homogeneous population of) Poland. The control group consisted of 3,166 cancer-free men ages 23-90 years (mean age, 62.2 years) and 3,070 cancer-free women age 18 to 94 years (mean age, 54.0 years) [13,14]. The purpose of the control group was to estimate with accuracy the frequency of founder alleles of NBN in the underlying Polish population. The allele frequencies for all NBN variants in our control group were not dependent on age, sex, and the prevalence estimates of all mutations were similar in younger and in older controls. The frequency of NBN 657del5 truncating mutation in our controls and in 6,984 (non-overlapping) controls genotyped by Chrzanowska et al. [15] is 0.6%.
5. Statistical analysis
1) Odds ratios
The prevalences of all alleles in cases and controls were compared. Odds ratios (OR) were generated from two-by-two tables and statistical significance was assessed using the Fisher exact test or the chi-square test where appropriate. The ORs were used as estimates of relative risk. The Breslow-Day test was used for testing the homogeneity of ORs.
2) Survival analysis
For the survival analysis, the patients were followed from the date of biopsy until death or June 2016. The median follow-up was 109 months. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were constructed for carriers of mutations and for non-carriers. Comparison of survival curves was performed by log-rank test. Detailed clinical information was available for a subset of 2,219 patients (PSA level at diagnosis, tumor stage, and Gleason score). A multivariable Cox regression analysis was performed on these patients.
6. Ethical statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, Poland (IRB No. KB-0012/97/17) and performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients and controls provided written informed consent.
Results
The NBN 657del5 mutation was detected in 74 of 5,189 unselected cases (1.4%) compared to 35 of 6,152 controls (0.6%) (OR, 2.5; p < 0.001). It was present in 15 of 635 familial cases (2.4%) (OR, 4.2; p < 0.001).
None of the three missense variants was associated with prostate cancer risk (Table 1). However, we looked for possible interactions between NBN variants and we found a significant interaction between the 657del5 mutation and the E185Q variant (Table 2). Men with the GG genotype of the E185Q polymorphism and the 657del5 mutation were at four-fold elevated risk of prostate cancer (OR, 4.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.4 to 8.8). Among men with other E185Q genotypes (GC and GG), the 657del5 deletion was not associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer (OR, 1.4; 95% CI, 0.8 to 2.4). The statistical test to reject homogeneity of the OR was highly significant (p=0.006). A similar association was seen among men with familial prostate cancer. Among men with the NBN GG genotype of E185Q, the OR for familial prostate cancer associated with truncating 657del5 mutation was 7.2 (95% CI, 3.1 to 16.3). Among men with other E185Q genotypes of NBN (GC and CC), the 657del5 deletion was not associated with statistically significant increase in the risk of familial prostate cancer (OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 0.9 to 6.2; homogeneity p-value=0.080).
Table 1.
Effect of NBN variants on prostate cancer risk
| NBN variant | Unselected prostate cancer cases |
Familial prostate cancer cases |
Control No./Total (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No./Total (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | No./Total (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-value | ||
| 657del5 | 74/5,189 (1.4) | 2.5 (1.7-3.8) | < 0.001 | 15/635 (2.4) | 4.2 (2.3-7.8) | < 0.001 | 35/6,152 (0.6) |
| R215W | 13/5,189 (0.25) | 1.3 (0.5-3.4) | 0.762 | 2/635 (0.3) | 1.6 (0.3-8.2) | 0.889 | 6/3,122a) (0.2) |
| I171V | 140/5,189 (2.7) | 1.2 (0.9-1.5) | 0.351 | 8/635 (1.3) | 0.5 (0.3-1.1) | 0.120 | 73/3,122a) (2.3) |
| E185Q (GG genotype) | 2,207/5,189 (42.6) | 1.0 (0.9-1.1) | 0.994 | 270/634 (42.6) | 1.0 (0.8-1.2) | 0.982 | 2,617/6,152 (42.5) |
| E185Q (GC genotype) | 2,389/5,189 (46.0) | 1.0 (0.9-1.1) | 0.565 | 287/634 (45.3) | 1.0 (0.8-1.2) | 0.952 | 2,798/6,152 (45.5) |
| E185Q (CC genotype) | 593/5,189 (11.4) | 0.9 (0.8-1.1) | 0.379 | 77/518 (12.1) | 1.0 (0.8-1.3) | 0.954 | 737/6,152 (12.0) |
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
For R215W and R215W variants 3,122 controls were only genotyped.
Table 2.
Effect of NBN 657del5 on prostate risk among studied groups, by genotype of the E185Q missense variant
| Variants present | Unselected prostate cancer cases |
Familial prostate cancer cases |
Control No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | OR (95% Cl) | p-value | No. | OR (95% Cl) | p-value | ||
| Effect of NBN 657del5 on cancer risk among carriers of GG genotype of E185Q | |||||||
| NBN 657del5–negative and GG genotype | 2,157 | 4.4 (2.4-8.0) | < 0.001 | 260 | 7.2 (3.1-16.3) | < 0.001 | 2,603 |
| NBN 657del5–positive and GG genotype | 50 | 10 | 14 | 14 | |||
| Effect of NBN 657del5 on cancer risk among carriers of GC/CC genotype of E185Q | |||||||
| NBN 657del5–negative and GC/CC genotype | 2,958 | 1.4 (0.8-2.4) | 0.382 | 359 | 2.3 (0.9-6.2) | 0.161 | 3,514 |
| NBN 657del5–positive and GC/CC genotype | 24 | 5 | 21 | ||||
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
The characteristics of the prostate cancers in the 657del5 mutation carriers and non-carriers are presented in Table 3. Among carriers of the NBN 657del5 mutation, 39% were of advanced stage at diagnosis, compared to 25% of those cases with no NBN variant (men who tested negative for the 657del5 deletion and for the GG genotype of E185Q). However, the stage difference was restricted to 657del5 carriers who also had the GG genotype of E185Q. Among 657del5 carriers with the adverse GG allele, the proportion with advan-ced stage was 44% compared to 25% cases with no NBN variant (p=0.023). Among 657del5 carriers with other E185Q genotypes (GC and CC), advanced stage was present in only 29%, which is comparable to that of the non-carrier cases (25%, p=0.778).
Table 3.
Clinical characteristics of prostate cancers in carries of variant alleles in NBN
| 657del5 mutation (n=74) | p-value | 657del5 and E185Q GG genotype (n=50) | p-value | 657del5 and E185Q non-GG genotype (n=24) | p-value | Neither genotypea) (n=2,958) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of diagnosis (yr) | |||||||
| Mean | 67.0 | 0.505 | 67.0 | 0.586 | 67.0 | 0.697 | 67.8 |
| PSA level at diagnosis (ng/mL) | |||||||
| Median | 11.7 | 0.592 | 13.4 | 0.237 | 8.6 | 0.532 | 11.8 |
| ≤ 4.0 | 1/44 (2.3) | 0.724 | 1/27 (3.7) | 1.000 | 0/17 (0.0) | 1.000 | 86/1,652 (5.2) |
| 4.1-10 | 17/44 (38.6) | 1.000 | 6/27 (22.2) | 0.077 | 11/17 (64.7) | 0.044 | 647/1,652 (39.2) |
| 10.1-20.0 | 11/44 (25.0) | 1.000 | 9/27 (33.3) | 0.367 | 2/17 (11.8) | 0.271 | 407/1,652 (24.6) |
| > 20.0 | 15/44 (34.1) | 0.742 | 11/27 (40.7) | 0.297 | 4/17 (23.5) | 0.607 | 512/1,652 (30.1) |
| Gleason score | |||||||
| < 7 | 25/54 (47.2) | 0.522 | 17/36 (47.2) | 0.618 | 8/18 (44.4) | 0.638 | 1,011/1,957 (51.7) |
| 7 | 15/54 (28.3) | 0.892 | 8/36 (22.2) | 0.460 | 7/18 (38.9) | 0.438 | 579/1,957 (29.6) |
| > 7 | 14/54 (24.5) | 0.250 | 11/36 (30.6) | 0.085 | 3/18 (16.7) | 1.000 | 367/1,957 (18.7) |
| Stage | |||||||
| T1 | 14/49 (28.6) | 0.755 | 7/32 (21.9) | 0.256 | 7/17 (41.2) | 0.437 | 467/1,467 (31.8) |
| T2 | 16/49 (32.7) | 0.186 | 11/32 (34.4) | 0.370 | 5/17 (29.4) | 0.328 | 632/1,467 (43.1) |
| T3 | 8/49 (16.3) | 0.852 | 5/32 (15.6) | 0.820 | 3/17 (17.6) | 1.000 | 272/1,467 (18.5) |
| T4 | 11/49 (22.4) | 0.0004 | 9/32 (28.1) | 0.0002 | 2/17 (11.8) | 0.311 | 96/1,467 (6.5) |
| T3 or T4 | 19/49 (38.8) | 0.044 | 14/32 (43.7) | 0.023 | 5/17 (29.4) | 0.778 | 368/1,467 (25.1) |
Values are presented as number (%) unless otherwise indicated.
p-values are calculated with respect to carriers of neither genotype (657del5 negative and E185Q GG genotype negative cases) as reference group.
We obtained data about the presence of distant metastasis at diagnosis for 257 patients: of these, 37 patients had evidence of metastasis (M1) and 220 had no evidence of metastasis (M0). The frequency of NBN 657del5 mutation was particularly high among patients with metastatic disease (4/37, 10.8%) compared to those with no evidence of metastasis (1/220, 0.5%). All four men with metastatic disease and the 657del5 mutation carried the GG genotype of E185Q.
Data on survival was available for 5,185 men with prostate cancer (Table 4). After a median follow-up of 109 months there were 42 deaths (56.7%) among 74 carriers of NBN 657del5 mutation and 2,271 deaths (44.4%) among 5111 non-carriers. The median survival was 81 months for 657del5 carriers compared to 129 months for non-carriers (HR, 1.63; 95% CI, 1.1 to 2,4; p=0.001, log-rank test) (Fig. 1). The 10-year survival was 34% for 657del5 carriers compared to 53% for non-carriers. After adjusting for age of diagnosis, PSA, stage and grade, the HR for mortality associated with NBN 657del5 mutation was 1.52 (95% CI, 1.1 to 2.2; p=0.023) (S1 Table).
Table 4.
Survival of men with prostate cancer; by variant alleles of NBN
| Men with 657del5 mutation (n=74) | Men with 657del5 and E185Q GG genotype (n=50) | Men with 657del5 and E185Q non-GG genotype (n=24) | Men with neither genotypea) (n=2,956) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median follow-up (mo) | 90 | 90 | 87 | 106 |
| Proportion of deceased (%) | 56.8 | 62.0 | 45.8 | 43.8 |
| Median survival (mo) | 81 | 78 | 95 | 132 |
| 5-Year survival (%) | 56 | 51 | 66 | 69 |
| 10-Year survival (%) | 34 | 28 | 45 | 53 |
| HR | 1.6 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 1.0a) |
| 95% CI | 1.1-2.5 | 1.2-3.2 | 0.6-2.2 | - |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.659 | - |
Hazard ratio (HR), 95% confidence interval (CI), and p-values are calculated by log-rank test.
Reference group (men with prostate cancer without 657del5 and without GG genotype of E185Q.
Fig. 1.
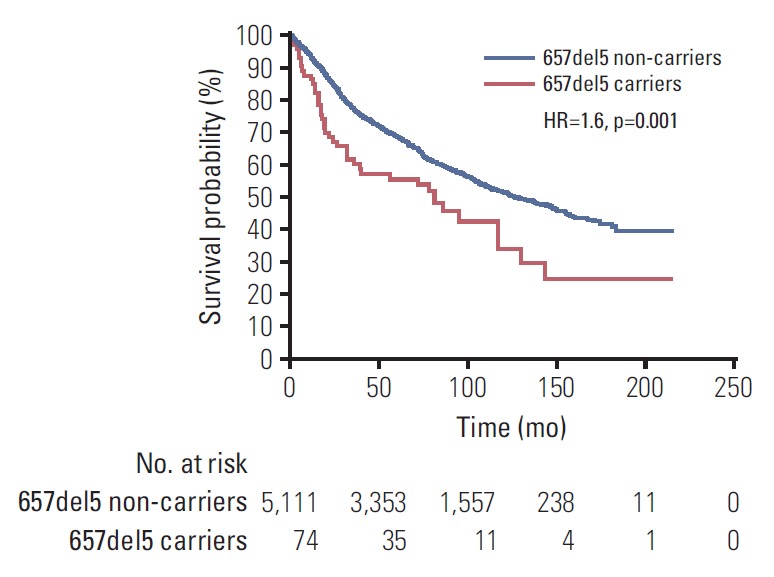
Kaplan-Meier curves of prostate cancer patients with 657del5 mutation in NBN, compared with prostate cancer patients without 657del5 variant (non-carriers). HR, hazard ratio.
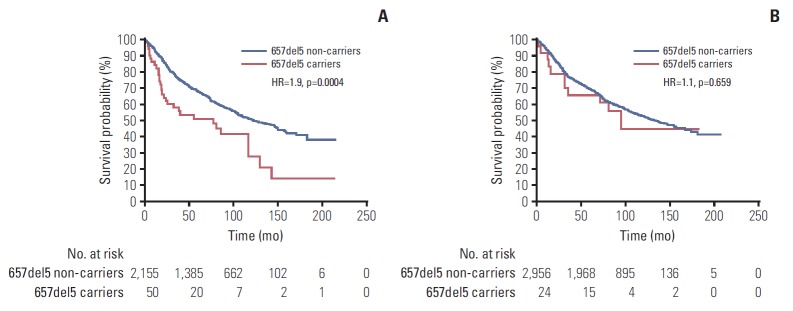
Survival was modified according to the background of E185Q missense variant. There were 31 deaths (62%) recorded in 50 carriers of NBN 657del5 mutation and the GG genotype, and 975 deaths (45.2%) in 2,155 men without 657del5 but with the GG genotype of E185Q. Among all men with the GG genotype of E185Q, survival experience was significantly worse for carriers of 657del5 NBN mutation, compared to non-carriers (HR, 1.9; p=0.0004, log-rank test; 10 year survival 28% vs. 53%, respectively) (Fig. 2). Among men with other alleles of E185Q (GC and CC), survival experience was similar for carriers of 657del5 NBN mutation and non-carriers (HR, 1.1; p=0.659; 10-year survival 45% vs. 53%, respectively).
Fig. 2.
Kaplan-Meier curves of prostate cancer patients with a 657del5 mutation in NBN and non-carriers: on the GG genotype background of E185Q (A); on the non-GG (GC and CC) genotype background of E185Q (B).
To investigate whether other NBN variants (i.e., those linked to the G allele of E185Q) may affect cancer risk among carriers of the 657del5 mutation, we sequenced the NBN gene in 16 prostate cancer patients (8 with the GG genotype of E185Q and 8 without) but we did not detect any other coding variants in sequence of the NBN gene.
Discussion
Here we extend our earlier work which established NBN 657del5 as a prostate cancer susceptibility allele [5,14]. In our previous study, we genotyped 3,750 prostate cancer cases and 3,956 controls for a single truncating mutation in NBN (657del5). We have enlarged our series to include 5,189 men with prostate cancer and 6,152 controls and we genotyped all subjects for four recurrent variants of NBN (657del5, R215W, I171V, and E185Q).
Recently Mijuskovic et al. [16] sequenced germline whole exomes from 139 aggressive (metastatic, age of diagnosis < 60) and 141 non-aggressive (low clinical grade, age of diagnosis ≥ 60) prostate cancer cases from the United Kingdom, and found that truncating variants of NBN were significantly enriched among patients with the aggressive phenotype. Two other studies explored the association between NBN and prostate cancer risk. In first study, the 657del5 allele was seen in seven of 3,037 men with prostate cancer (0.23%) and in none of 990 unaffected controls in the United States [17]. The clinical characteristics of the mutation positive cases are not descri-bed. In the second study, 94 familial prostate cancer cases from the USA were screened by whole exomesequencing. A novel truncating mutation of NBN, (2117 C>G mutation that results in a premature stop at codon 706 (S706X) was detec-ted in one family [18].
In the current study we also investigated the potential pathogenicity of three missense variants of NBN. These three variants (E185Q, R215W, I171V) were selected from over 84 known missense variants in NBN on the basis of suggestive prior evidence of pathogenicity and because they are founder alleles in the Polish population [19-25]. None of the three missense variants was associated with prostate cancer risk in the current study. However, in an examination of potential interactions between all four NBN variants an interesting pattern emerged. The excess cancer risk in carriers of 657del5 deletion was restricted to the subgroup of men who were homozygous for the GG genotype in codon 185 of the same gene. Among men with the GG genotype of E185Q, the OR associated with a truncating 657del5 mutation was 4.4 (95% CI, 2.4 to 8.0). Among men with other E185Q genotypes (GC and CC), the 657del5 deletion was not associated with prostate cancer (OR, 1.4; 95% CI, 0.8 to 2.4; homogeneity p=0.006). We saw a similar modifying effect of the E185Q GG allele on the pathogenicity of 657del5 when we studied clinical presentation and survival. The adverse effect of the 657del5 mutation on survival was present among carriers of the GG genotype of E185Q (HR, 1.9; p=0.0004), but was not present among 657del5 carriers with other E185Q genotypes (HR, 1.1; p=0.659). The two observations (the effect of E185Q on prostate cancer risk and prognosis among 657del5 mutation carriers) are independent, one validates the other. In addition, we saw similar interaction between these two NBN variants for risk of breast cancer (data not shown). Therefore, we propose that the pathogenicity of NBN 657del5 truncating mutation may be modified by the E185Q missense variant of the same gene.
To investigate whether other NBN variants (i.e., those linked to the G allele of E185Q) may affect cancer risk among carriers of the 657del5 mutation, we sequenced the entire NBN gene in 16 prostate cancer patients (8 with the GG genotype of E185Q and 8 without) but we did not detect any other coding variants in sequence of the NBN gene. This suggests that the E185Q polymorphism may be the functional variant with regard to risk modification.
The NBN 657del5 mutation is predicted to generate two truncated proteins of 219 (p26) and 754 (p70) amino acids in length. p26 lacks a critical domain necessary for MRE11 interaction [26,27]. The G allele of E185Q is in complete linkage disequilibrium with the 657del5 mutation. It was observed that 68% of unselected prostate cancer cases with the deletion have the G allele and 32% of the carriers have the C allele on the other (non-mutant) chromosome. Our data suggest that among deletion carriers it is necessary that the normal copy of the NBN protein carry a glutamic acid residue at position 185 to confer susceptibility to prostate cancer.
This observation has several clinical implications—we call into question the pathogenicity of the novel NBN mutations that have not been well studied—the risk of cancer is not the same for all 657del5 mutation carriers. It is important to establish the E185Q genotype status when counseling a carrier of a 657del5 deletion. Further, we question the practice of adding cancer susceptibility genes to testing panels before they have been well characterized for a range of truncating mutations in different ethnic populations.
Herein we describe a new model for inherited cancer susceptibility wherein the penetrance of a dominant cancer susceptibility gene is modified by other alleles of the same gene (in trans or in cis) which, on their own, do not increase risk. This phenomenon may explain to some degree why different risks of cancer have been reported for mutations in the same gene in different countries and further studies are needed in this regard. Based on these results, we consider it is premature to counsel men with truncating NBN mutations other than 657del5 that they are at increased risk of prostate cancer based on data derived from the single mutation, 657del5. It will be important to study this paradigm in other cancer genes as well. We describe a poor survival of men with the NBN 657del5/E185Q GG genotype.
There is no organized prostate screening program in Poland and the majority of the patients in this study presented because of symptoms or because of an abnormal digital rectal examination. We believe that prostate cancer screening is warranted in NBN carriers, because of the high risk of cancer (OR, 4.4), the high likelihood of presenting clinically with advanced disease and because of the poor survival experience of those who present with clinical signs or symptoms. It is also important to determine if therapy beyond the conventional therapy is valuable for men with prostate cancer and a NBN mutation.
In conclusion, our results provide compelling evidence that a founder 657del5 mutation in NBN predisposes to aggressive prostate cancers and that the pathogenicity of this truncating mutation is modified by another allele of the same gene (E185Q).
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by National Science Centre, Poland; project number: 2015/19/B/NZ2/02439.
We thank Daria Zanoza, for her support in this study.
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
* The Polish Hereditary Prostate Cancer Consortium
Other members of the Polish Hereditary Prostate Cancer Consortium: Adam Gołąb1, Bartłomiej Gliniewicz2, Andrzej Sikorski1, Marcin Słojewski1, Jerzy Świtała2, Tomasz Borkowski3, Andrzej Borkowski3, Andrzej Antczak4, Łukasz Wojnar4, Jacek Przybyła5, Marek Sosnowski5, Bartosz Małkiewicz6, Romuald Zdrojowy6, Paulina Sikorska-Radek7, Jozef Matych7, Jacek Wilkosz8, Waldemar Rożański8, Jacek Kiś9, Krzysztof Bar9, Piotr Bryniarski10, Andrzej Paradysz10, Konrad Jersak11, Jerzy Niemirowicz11, Piotr Słupski12, Piotr Jarzemski12, Michał Skrzypczyk13, Jakub Dobruch13, Paweł Domagała14, Bohdan Gorski15, Tomasz Byrski16, Michał Puszyński2, Michał Soczawa1, Sławomir Archimowicz2, Mirosław Kordowski2, Marcin Życzkowski10, Andrzej Borowka13, Joanna Bagińska17, Kazimierz Krajka17, Marek Szwiec18, Małgorzata Stawicka19, Olga Haus20, Hanna Janiszewska20, Agnieszka Stembalska21, Maria Małgorzata Sąsiadek21
1Clinic of Urology, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, 2Division of Urology, Maria Skłodowska-Curie Hospital, Szczecin, 3Department of Urology, Medical University, Warszawa, 4Chair of Urology, Medical University, Poznan, 5Department of Urology, Medical University of Lodz, Łodź, 6Department of Urology and Urological Oncology, University of Medicine, Wrocław, 7Division of Urology, Regional Hospital, Łódź, 8Second Department of Urology, Medical University of Lodz, Łodź, 9Department of Urology, University Hospital of Lublin, Lublin, 10Department of Urology, Medical University of Silesia, Zabrze, 11Department of Urology, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Administration Hospital, Łódź, 12Department of Urology, J. Biziel Hospital, Bydgoszcz, 13Department of Urology, Centre of Postgraduate Urology Education, Warsaw, 14Department of Pathology, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, 15Department of Genetics and Pathology, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, 16Department of Oncology, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, 17Clinic of Urology, Medical University, Gdansk, 18Department of Clinical Oncology, University Hospital in Zielona Gora, 19Department of Clinical Genetics and Pathology, University of Zielona Góra, Zielona Góra, 20Department of Clinical Genetics, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, 21Department of Genetics, Wroclaw Medical University, Wrocław, Poland
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary materials are available at Cancer Research and Treatment website (http://www.e-crt.org).
References
- 1.Struewing JP, Hartge P, Wacholder S, Baker SM, Berlin M, McAdams M, et al. The risk of cancer associated with specific mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 among Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1401–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199705153362001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dong X, Wang L, Taniguchi K, Wang X, Cunningham JM, McDonnell SK, et al. Mutations in CHEK2 associated with prostate cancer risk. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72:270–80. doi: 10.1086/346094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Edwards SM, Evans DG, Hope Q, Norman AR, Barbachano Y, Bullock S, et al. Prostate cancer in BRCA2 germline mutation carriers is associated with poorer prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:918–24. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Seppala EH, Ikonen T, Mononen N, Autio V, Rokman A, Matikainen MP, et al. CHEK2 variants associate with hereditary prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:1966–70. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cybulski C, Gorski B, Debniak T, Gliniewicz B, Mierzejewski M, Masojc B, et al. NBS1 is a prostate cancer susceptibility gene. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1215–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kirchhoff T, Kauff ND, Mitra N, Nafa K, Huang H, Palmer C, et al. BRCA mutations and risk of prostate cancer in Ashkenazi Jews. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:2918–21. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kote-Jarai Z, Leongamornlert D, Saunders E, Tymrakiewicz M, Castro E, Mahmud N, et al. BRCA2 is a moderate penetrance gene contributing to young-onset prostate cancer: implications for genetic testing in prostate cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:1230–4. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ewing CM, Ray AM, Lange EM, Zuhlke KA, Robbins CM, Tembe WD, et al. Germline mutations in HOXB13 and prostate-cancer risk. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:141–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Leongamornlert D, Mahmud N, Tymrakiewicz M, Saunders E, Dadaev T, Castro E, et al. Germline BRCA1 mutations increase prostate cancer risk. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:1697–701. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Varon R, Vissinga C, Platzer M, Cerosaletti KM, Chrzanowska KH, Saar K, et al. Nibrin, a novel DNA double-strand break repair protein, is mutated in Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Cell. 1998;93:467–76. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Carney JP, Maser RS, Olivares H, Davis EM, Le Beau M, Yates JR, 3rd, et al. The hMre11/hRad50 protein complex and Nijmegen breakage syndrome: linkage of double-strand break repair to the cellular DNA damage response. Cell. 1998;93:477–86. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Easton DF, Pharoah PD, Antoniou AC, Tischkowitz M, Tavtigian SV, Nathanson KL, et al. Gene-panel sequencing and the prediction of breast-cancer risk. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2243–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1501341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cybulski C, Wokolorczyk D, Jakubowska A, Huzarski T, Byrski T, Gronwald J, et al. Risk of breast cancer in women with a CHEK2 mutation with and without a family history of breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3747–52. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.34.0778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cybulski C, Wokolorczyk D, Kluzniak W, Jakubowska A, Gorski B, Gronwald J, et al. An inherited NBN mutation is associated with poor prognosis prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:461–8. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chrzanowska KH, Piekutowska-Abramczuk D, Popowska E, Gladkowska-Dura M, Maldyk J, Syczewska M, et al. Carrier frequency of mutation 657del5 in the NBS1 gene in a population of Polish pediatric patients with sporadic lymphoid malignancies. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:1269–74. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mijuskovic M, Saunders EJ, Leongamornlert DA, Wakerell S, Whitmore I, Dadaev T, et al. Rare germline variants in DNA repair genes and the angiogenesis pathway predispose prostate cancer patients to develop metastatic disease. Br J Cancer. 2018;119:96–104. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0141-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hebbring SJ, Fredriksson H, White KA, Maier C, Ewing C, McDonnell SK, et al. Role of the Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 gene in familial and sporadic prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:935–8. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zuhlke KA, Johnson AM, Okoth LA, Stoffel EM, Robbins CM, Tembe WA, et al. Identification of a novel NBN truncating mutation in a family with hereditary prostate cancer. Fam Cancer. 2012;11:595–600. doi: 10.1007/s10689-012-9555-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.di Masi A, Antoccia A. NBS1 heterozygosity and cancer risk. Curr Genomics. 2008;9:275–81. doi: 10.2174/138920208784533610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zheng J, Zhang C, Jiang L, You Y, Liu Y, Lu J, et al. Functional NBS1 polymorphism is associated with occurrence and advanced disease status of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50:689–96. doi: 10.1002/mc.20803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Roznowski K, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Mosor M, Pernak M, Litwiniuk M, Nowak J. I171V germline mutation in the NBS1 gene significantly increases risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;110:343–8. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9734-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mendez G, Cilli D, Berardinelli F, Viganotti M, Ascenzi P, Tanzarella C, et al. Cleavage of the BRCT tandem domains of nibrin by the 657del5 mutation affects the DNA damage response less than the Arg215Trp mutation. IUBMB Life. 2012;64:853–61. doi: 10.1002/iub.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gao P, Ma N, Li M, Tian QB, Liu DW. Functional variants in NBS1 and cancer risk: evidence from a meta-analysis of 60 publications with 111 individual studies. Mutagenesis. 2013;28:683–97. doi: 10.1093/mutage/get048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fang W, Qiu F, Zhang L, Deng J, Zhang H, Yang L, et al. The functional polymorphism of NBS1 p.Glu185Gln is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer in Chinese populations: case-control and a meta-analysis. Mutat Res. 2014;770:61–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2014.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ziolkowska-Suchanek I, Mosor M, Wierzbicka M, Fichna M, Rydzanicz M, Nowak J. Association of polymorphisms and haplotypes of the NBN gene with laryngeal cancer and multiple primary tumors of the head and neck. Head Neck. 2012;34:376–83. doi: 10.1002/hed.21741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Maser RS, Zinkel R, Petrini JH. An alternative mode of translation permits production of a variant NBS1 protein from the common Nijmegen breakage syndrome allele. Nat Genet. 2001;27:417–21. doi: 10.1038/86920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kobayashi J, Antoccia A, Tauchi H, Matsuura S, Komatsu K. NBS1 and its functional role in the DNA damage response. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:855–61. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.