Abstract
Purpose
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common cancer worldwide. Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1), a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), has been reported to be aberrantly expressed in hypoxic cancer cells. MALAT1 plays a significant role in many malignancies, including HCC. The aim of this study was to explore the role of MALAT1 in hypoxic HCC cells and its underlying regulatory mechanism.
Materials and Methods
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) assay was performed to detect the mRNA levels of MALAT1 and microRNA-200a (miR-200a) in HCC cells. Cell invasion and migration ability were evaluated by Transwell assay. Starbase v2.0 and luciferase reporter assay were employed to identify the association between MALAT1 and miR-200a. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were measured by MTT assay and flow cytometry, respectively.
Results
MALAT1 levels were significantly upregulated in HCC cells under hypoxia. Hypoxia promoted proliferation, migration, and invasion, and blocked apoptosis in Hep3B cells, which were weakened by knockdown of MALAT1. Starbase v2.0 showed that MALAT1 and miR-200a have a complementarity region, and luciferase reporter assay verified that MALAT1 interacted with miR-200a in Hep3B cells. Moreover, MALAT1 negatively regulated the expression of miR-200a. miR-200a levels were dramatically downregulated in HCC cells under hypoxia. Upregulation of miR-200a inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induced apoptosis in Hep3B cells under hypoxia. Interestingly, downregulation of miR-200a partially reversed the tumor-suppressive effect of knockdown of MALAT1 on Hep3B cells in hypoxic condition.
Conclusion
LncRNA MALAT1 was involved in proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis by interacting with miR-200a in hypoxic Hep3B cells, revealing a new mechanism of MALAT1 involved in hypoxic HCC progression.
Keywords: MALAT1, miR-200a, HCC, proliferation, hypoxic
INTRODUCTION
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common malignancy worldwide, especially in several regions of Africa and Asia,1 and the burden of this devastating cancer is expected to further increase in coming years. The incidence of HCC is complex and multifactorial,2,3 and its molecule mechanism has not been fully elucidated. Better understanding of the mechanisms underlying HCC progression is crucial for improving the diagnosis and successful treatment of HCC.
Evidence from experimental and clinical studies increasingly pointed that hypoxia plays a fundamental role in solid tumor development,4 and that it appears to be strongly associated with tumor propagation, malignant progression, or resistance to therapy.4,5 Although hypoxia plays an important role in the metastasis of HCC, its underlying mechanism still remains largely unclear.
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is a class of non-coding RNA with a length greater than 200 nucleotides (nt). LncRNAs have been implicated in a large range of biological procession, such as epigenetic regulation, transcriptional regulation, and posttranscriptional regulation.6 LncRNAs were involved in hypoxia-promoted tumor progression. For instance, lncRNA BC005927 could be induced by hypoxia in gastric cancer (GC) cells and mediates hypoxia-induced GC cell metastasis, and increased BC005927 expression was correlated with a higher tumor-node-metastasis stage.7 Also, lncRNA-BX111 promoted metastasis and progression of pancreatic cancer through regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox transcription factor 1 (ZEB1) under hypoxia, and overexpression of lncRNA-BX111 dramatically enhanced proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells.8 LncRNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) has been reported to be abnormally expressed in various types of cancers. Previous studies have shown that MALAT1 plays a pivotal role in the differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of many tumor cells.9,10,11,12 Also, the role of MALAT1 in HCC has been reported as well. Hou, et al.13 found that MALAT1 promoted the migration and invasion of HCC by upregulating silent information regulator 1 via microRNA (miR)-204 sponging. However, whether MALAT1 would influence HCC cells under hypoxic conditions remains unknown.
In this study, we first revealed that MALAT1 was involved in HCC cell proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion through miR-200a sponge activity cells under hypoxia, revealing a new mechanism of MALAT1 involved in hypoxic HCC progression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture and oxygen conditions
HCC cell lines Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B were obtained from Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). All cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% of fetal bovine serum (FBS, Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) and 1% of penicillin/streptomycin stock solution (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Hypoxic conditions were maintained in a humidified variable aerobic workstation at 37℃ (N-control). To induce hypoxia, oxygen concentrations were reduced from 20% to 1% (H-control), while carbon dioxide (CO2) remained at 5%.
Reagents and transfection
MALAT1 expression plasmid (MALAT1), pcDNA3.1 vector (vector), small interfering RNA (si-RNA) against MALAT1 (si-MALAT1), si-RNA negative control (si-NC), miR-200a mimic (miR-200a), mimic negative control (miR-NC), miR-200a inhibitor (anti-miR-200a), and inhibitor negative control (anti-miR-NC) were synthesized by GENEWIZ Co. Ltd. (Suzhou, China). Hep3B cells (70% confluence in 6-well plates) were transfected with above-mentioned plasmids or oligos using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
Total RNA was extracted from cells using Trizol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) were isolated using miRNeasy mini kits (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) reversely transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) using TaqMan® MicroRNA Reverse Transcription kit (Biosystems, Forster City, CA, USA). To quantify mRNAs, reverse transcription was performed using Prime Script™ RT reagent kit (Takara, Shiga, Japan). Quantitative PCR was performed using TaqMan® Universal PCR Master Mix II (Biosystems), qPCR primers were as follows: U6-R, 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCAGCACA-3′; U6-F, 5′-AACGCTTCACGAATTT-GCGT-3′; MALAT1-F, 5′-ATGCGA GTTGTTCTCCGTCT-3′; MALAT1-R, 5′-TATCTGCGGTTTCCTCAAGC-3′; miR-200a-F, 5′-CACCGCCTCCCATTGTC-3′; miR-200a-R, 5′-CACAGGAAGTCAGTTCAGACC-3′. Relative expression levels of miRNA or lncRNA (normalized to U6 small nuclear RNA) were analyzed by 2−ΔΔCt method.
MTT assay
Hep3B cells were seeded into 96-well plates (2×103 cells/well), and were transfected with miR-200a, miR-NC, anti-miR-200a, si-MALAT1, si-NC, or si-MALAT1+anti-miR-200a. At 24 h after transfection, cells were challenged with hypoxia for 24 hours, after which 20 µL of MTT (5 mg/mL, Sigma) was added into each well and incubated for another 4 h at 37℃. The mixed medium was then discarded, and 150 µL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Sigma) was added to dissolve the precipitates. Cell proliferation was evaluated by measuring the absorbance at 570 nm using a microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA).
Transwell invasion and migration assay
We seeded 1×105 of Hep3B cells, which were suspended in 500 µL serum-deprived culture medium, into the upper compartment of Transwell apparatus (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA). For cell invasion assay, the membranes of upper compartments were matrigel pre-coated, and un-coated ones were used for cell migration assay. Cells were cultured for 24 h, and cells migrated to the underside of upper compartment membrane in response to culture medium supplemented with 5% FBS in lower compartment were fixed with methanol and stained with crystal violet. The number of migrated cells were counted in five randomly picked view under microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany).
Cell apoptosis assay
Cell apoptosis was analyzed using FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Hep3B cells were collected and digested with trypsin, washed with pre-cooled PBS, and resuspended in 200 µL binding buffer. Cells were then labeled with 10 µL Annexin V-FITC and 5 µL propidium iodide (PI) in dark for 15 min at room temperature. Cell apoptotic rate was detected with FACS Calibur flow cytometer and Cell Quest software (BD Biosciences).
Luciferase reporter assay
A wild-type (WT) fragment of MALAT1 containing putative miR-200a binding site and its mutated (MUT) seed sequence were purchased from Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China), and were inserted downstream of a luciferase reporter gene on pmirGLO dual-luciferase miRNA target expression vectors (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), named as MALAT1-WT and MALAT1-MUT, respectively. Hep3B cells were cotransfected with MALAT1-WT or MALAT1-MUT and miR-200a or miR-NC using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cell were harvested at 48 h after transfection. Dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega) was used to detect luciferase activity according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Statistical analysis
All data were expressed as mean±SD from three separate experiments. All statistical analyses were performed by SPSS 20.0 statistical software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Student's t-test or ANOVA was performed for significance test. A p value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
MALAT1 was upregulated in HCC cells by hypoxia
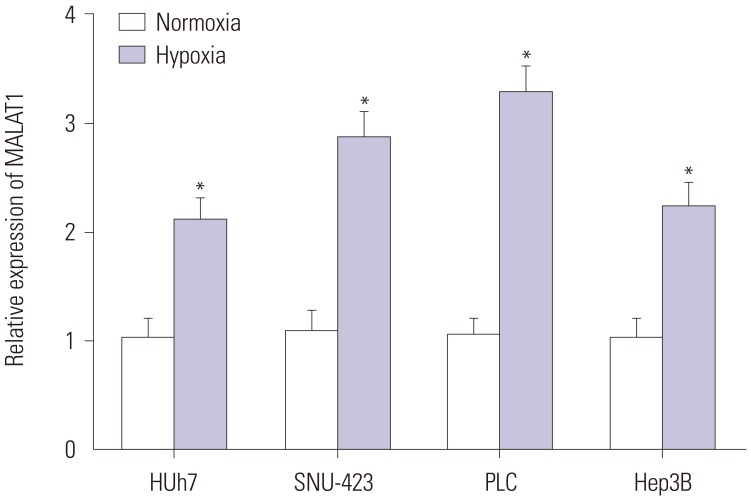
To investigate MALAT1 expression levels in HCC cells in response to hypoxia, Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B cells were incubated under hypoxic (1% O2) or normoxic (20% O2) condition. MALAT1 expression levels in these cells were detected by qRT-PCR. We found that MALAT1 expression was increased in all HCC cells after being exposed to hypoxic condition (Fig. 1). Hep3B cell line was used for further analysis.
Fig. 1. MALAT1 was upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by hypoxia. qRT-PCR assay was performed to measure the expression of MALAT1 in Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B cells cultured under normoxic or hypoxic condition. *p<0.05. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
Knockdown of MALAT1 suppressed growth and induced apoptosis of Hep3B cells after hypoxia challenge
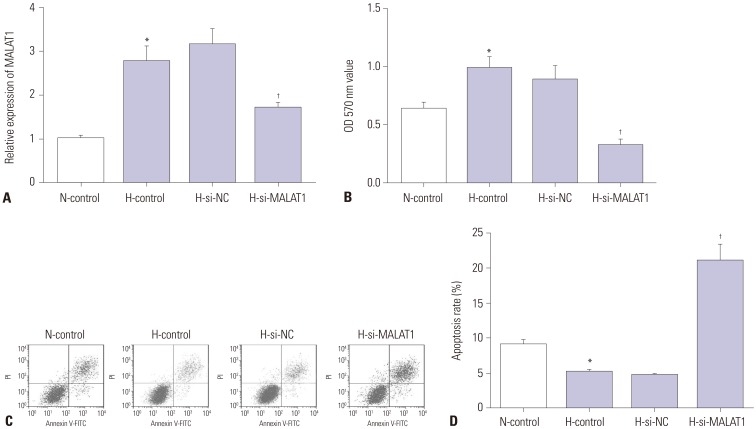
Based on the results mentioned above, the effects of MALAT1 knockdown on proliferation and apoptosis of Hep3B cells under hypoxic condition were further explored. First, Hep3B cells were transfected with MALAT1 siRNA or negative control siRNA. Hep3B cells after transfection were then cultured under hypoxic condition for 24 hours, followed by re-oxygenation for 48 hours. qRT-PCR assay showed that the relative expression of MALAT1 was significantly decreased in si-MALAT1-transfected Hep3B cells compared with negative control siRNA transfected ones (Fig. 2A). MTT assay showed that the proliferation of Hep3B cells was significantly increased by hypoxia challenge, which was significantly attenuated by MALAT1 knockdown (Fig. 2B). Cell apoptosis assay revealed that hypoxia challenge reduced Hep3B cell apoptosis in vitro, which was significantly attenuated by MALAT1depletion (Fig. 2C and D).
Fig. 2. Knockdown of MALAT1 suppressed growth and induced apoptosis of Hep3B cells after hypoxia challenge. Hep3B cells were transfected with si-NC or si-MALAT1. For N-control group, cells were cultured under normoxia condition for 72 hours; for H-control group, cells were first challenged with hypoxia (1% oxygen) for 24 hours, followed by culturing under normoxia condition for 48 hours. (A) MALAT1 expression level in each treatment group was measured by qRT-PCR. (B) Hep3B cell proliferation in each treatment group was evaluated by MTT assay. (C and D) Hep3B cell apoptotic rate in each treatment group was detected by flow cytometry. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-si-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
Knockdown of MALAT1 suppressed migration and invasion of Hep3B cells promoted by hypoxia
To investigate the role of MALAT1 in HCC cell migration and invasion under hypoxia, Transwell assay was performed to analyze the migration and invasion of Hep3B cells with MALAT1 depletion under hypoxia. We found that hypoxia improved the migration and invasion abilities of Hep3B cells, which were significantly inhibited by MALAT1 silencing (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Knockdown of MALAT1 suppressed migration and invasion of Hep3B cells promoted by hypoxia. Hep3B cells were transfected with si-NC or si-MALAT1, and normoxia and hypoxia treatment were performed as described in Fig. 2A. Cell migration (A) and invasion (B) were evaluated by Transwell assay. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-si-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
MALAT1 interacted with miR-200a in hypoxic Hep3B cells
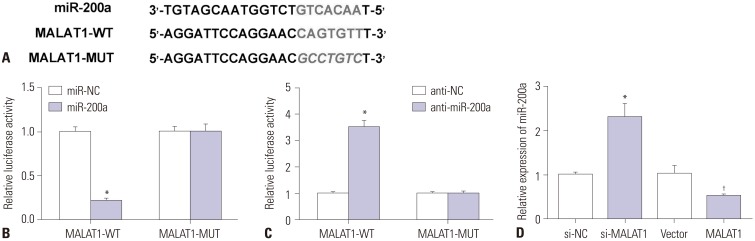
Starbase v2.0 (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/starbase2/) suggested that miR-200a has binding sites with MALAT1. Luciferase reporter plasmids containing WT or MUT MALAT1 binding sites of miR-200a were established (Fig. 4A). Luciferase reporter assay indicated that miR-200a mimic significantly decreased the luciferase activity of MALAT1-WT group, and miR-200a inhibitor significantly enhanced the luciferase activity of MALAT1-WT group. However, miR-200a mimic or inhibitor showed no significant impact on the luciferase activity in MALAT1-MUT group, respectively (Fig. 4B and C). To further investigate the effect of MALAT1 on miR-200a expression, Hep3B cells were transfected with si-MALAT1, si-NC, pcDNA MALAT1, or pcDNA3.1 vector. We found that miR-200a was significantly upregulated in si-MALAT1-transfected Hep3B cells, while downregulated in pcDNA MALAT1-transfected cells (Fig. 4D).
Fig. 4. MALAT1 interacted with miR-200a in hypoxic Hep3B cells. (A) The predicted binding sites between miR-200a and MALAT1 mRNA through Starbase v2.0. Luciferase reporter plasmids containing wild-type (WT) or mutated (MUT) MALAT1 binding sites of miR-200a were established. (B and C) Hep3B cells were co-transfected with MALAT1-WT or MALAT1-MUT luciferase reporter and miR-200a, miR-NC, anti-NC, or anti-miR-200a, followed by the determination of luciferase activity at 48 h after transfection. (D) Hep3B cells were transfected with si-NC, si-MALAT1, pcDNA3.1 empty vector, and pcDNA-MALAT1 overexpression plasmid, and miR-200a expression level was measured by qRT-PCR. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-miR-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
Upregulation of miR-200a inhibited the proliferation, invasion, migration, and induced apoptosis in Hep3B cells under hypoxia
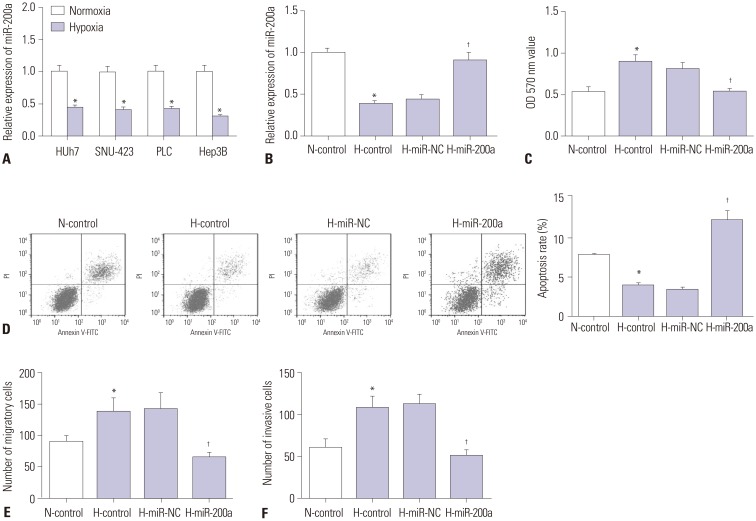
To explore miR-200a expression in response to hypoxia, Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B cells were incubated 48 h in hypoxic or normoxic conditions. Then, qRT-PCR was performed to detect the expression of miR-200a. We found that miR-200a expression levels were significantly decreased in these HCC cell lines after hypoxia challenge (Fig. 5A). To further investigate the possible roles of miR-200a in Hep3B cells proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion under hypoxia, miR-200a mimic or mimic control was transfected into Hep3B cells. Expression of miR-200a in Hep3B cells was significantly reduced after hypoxia challenge, which was significantly improved by miR-200a mimic transfection (Fig. 5B). MTT and flow cytometry results demonstrated that miR-200a mimic transfection significantly attenuated the effect on Hep3B cell proliferation and anti-apoptosis by hypoxia challenge (Fig. 5C and D). Transwell assay results further showed that miR-200a mimic transfection significantly inhibited cell migration and invasion ability of Hep3B cells promoted by hypoxia (Fig. 5E and F).
Fig. 5. Upregulation of miR-200a inhibited the proliferation, invasion, migration, and induced apoptosis in Hep3B cells under hypoxia. Hep3B cells in (B–F) were treated as described in Fig. 2. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of miR-200a in Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B cells with or without hypoxia challenge. (B) miR-200a expression level in Hep3B cells was measured by qRT-PCR assay. (C) Cell proliferation was evaluated by MTT assay. (D) Cell apoptotic rate was detected by flow cytometry. (E and F) Cell migration and invasion were evaluated by Transwell assay. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-miR-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
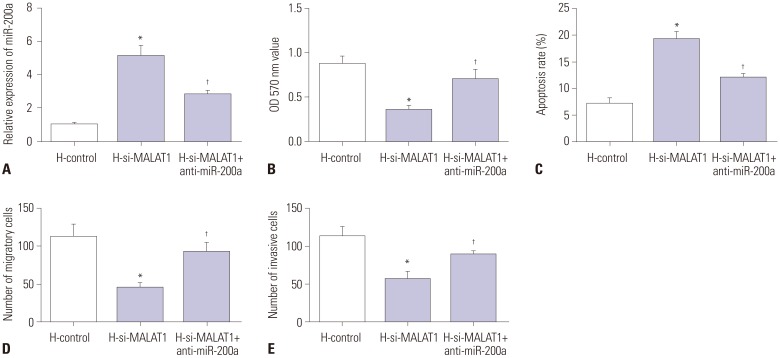
Downregulation of miR-200a partially reversed the effect of MALAT1 knockdown on hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells
To further confirm whether MALAT1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells by sponging miR-200a, Hep3B cells were co-transfected with si-MALAT1 and miR-200a inhibitor. Knockdown of MALAT1 significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion, while inducing apoptosis of hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells. All of these effects were significantly attenuated by miR-200a inhibitor transfection (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6. Downregulation of miR-200a partially reversed the effect of MALAT1 knockdown on hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells. Hep3B cells were transfected with si-MALAT1 or si-MALAT1+anti-miR-200a and were challenged with normoxia or hypoxia as described in Fig. 2. (A) miR-200a expression in each group was evaluated by qRT-PCR. (B) Cell proliferation was detected by MTT assay. (C) Cell apoptotic rate was detected by flow cytometry. (D and E) Cell migration and invasion were measured by Transwell assay. *p<0.05: when compared with H-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-si-MALAT1 group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
DISCUSSION
Liver cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide,14 and HCC accounts for approximately 90% of all cases of primary liver cancer.15 Increasing evidence suggested noncoding RNAs, including lncRNAs and miRNAs, as important regulator in the development of HCC with potential diagnostic and therapeutic values.16 MALAT1 has been reported to exert oncogenic roles in multiple cancers, including HCC.17,18 This study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of MALAT1 in HCC cells under hypoxia. We performed qRT-PCR to monitor the expression levels of MALAT1 and miR-200a in HCC cell lines (Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B) under hypoxia or normoxia. Our data suggested that MALAT1 was upregulated, while miR-200a was downregulated in HCC cell lines (Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B) by hypoxia challenge. MALAT1 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induced apoptosis in hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells, while miR-200a mimic transfection had the same effects. Silencing of miR-200a significantly attenuated the effect of MALAT1 knockdown on hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells. Notably, we confirmed that miR-200a interacted with MALAT1 in HCC cells. Our results suggest that MALAT1 may contribute to the development of HCC promoted by hypoxia by regulating miR-200a.
MALAT1 is a well-known lncRNA associated with cancer.19 Researchers have revealed that MALAT1 can be an oncogenic factor in HCC.18 For instance, Malakar, et al.20 showed that lncRNA MALAT1 was upregulated in HCC, but also in liver tumors from a mouse model of hepatic carcinogenesis. In addition, MALAT1 could act as a proto-oncogene through Wnt pathway activation and induction of oncogenic splicing factor serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1. Chen, et al.21 demonstrated that MALAT1 was upregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines, and that MALAT1 might serve as a prognostic indicator for HCC patients. Furthermore, MALAT1 regulated ZEB1 expression by sponging miR-143-3p and promoted HCC progression. These data suggested that MALAT1 may exhibit vital roles in the development and progression of HCC. Hypoxia is a common feature of many solid tumors, including HCC, which can participate in tumor progression. However, the effects of MALAT1 on hypoxia-treated HCC cells have not been examined. In this study, we first found that MALAT1 was increased by hypoxia challenge in HCC cells in vitro, especially in Hep3B cell line. Furthermore, the promotion of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as inhibition of apoptosis of Hep3B cells induced by hypoxia were attenuated by MALAT1 knockdown. These results implicated that MALAT1 may be involved in hypoxia-promoted HCC cell malignancy and tumor progression.
LncRNAs can regulate gene expression by “sponging” miRNAs.22,23 MiRNAs are short noncoding RNA molecules of 17–22 nt in length, and are involved in the oncogenesis and progression of multiple cancers.24 Previous studies have manifested that miRNAs were abnormally expressed in HCC and participated in fundamental biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.25,26
Many researchers have reported that miR-200a inhibited HCC cell proliferation,27,28,29,30 and that it plays an important role in protecting cardiomyocyte survival under hypoxic conditions. Li, et al.31 pointed that miR-200a level was decreased in H/R-cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMECs), and thymosin beta 4 attenuated hypoxia-reoxygenation induced CMECs injury by miR-200a-Nrf2 signaling. Sun, et al.32 manifested that miR-200a was significantly downregulated in ischemic myocardial tissues and hypoxic cardiomyocytes, and suppression of Keap1 by miR-200a exerted cardioprotective effect against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis. The role of miR-200a in hypoxic HCC cells remains unknown. In the present study, we found that miR-200a was markedly downregulated in HCC cells by hypoxia, suggesting that miR-200a might be involved in the cancer progression of hypoxic HCC. Starbase v2.0 suggested that MALAT1 and miR-200a has binding sites, which was further authenticated by luciferase reporter assay. We disclosed that miR-200a interacted with MALAT1 and MALAT1 negatively regulated miR-200a expression in Hep3B cells. In addition, upregulation of miR-200a inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induced apoptosis in hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells, indicating that miR-200a may participate in hypoxia-challenged HCC progression. Moreover, MALAT1 knockdown had the same effect on Hep3B cells compared with miR-200a mimic transfection. In addition, miR-200a depletion attenuated the effect of MALAT1 knockdown on Hep3B cell proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis. These results disclosed that MALAT1 was involved in HCC cell malignancy promoted by hypoxia by sponging miR-200a.
Taken together, we first demonstrated that MALAT1 participated in hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion in vitro by sponging miR-200a, providing novel insight into the vital role of lncRNA-miRNA functional network in cancer development. MALAT1 might serve as a possible therapeutic target for HCC management. The potential molecular mechanism which was involved in the regulation of MALAT1 and miR-200a, as well as the role of MALAT1 in other cell lines (Huh7 and SNU-423), need to be further investigated.
Footnotes
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
- Conceptualization: Zheng-Bin Zhao, Fei Chen.
- Data curation: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
- Formal analysis: Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
- Funding acquisition: Zheng-Bin Zhao, Xiao-Fang Bai.
- Investigation: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
- Methodology: Zheng-Bin Zhao, Xiao-Fang Bai.
- Project administration: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
- Resources: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
- Software: Xiao-Fang Bai, Fei Chen.
- Supervision: Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
- Validation: Fei Chen, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
- Visualization: Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
- Writing—original draft: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
- Writing—review & editing: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
References
- 1.Ferenci P, Fried M, Labrecque D, Bruix J, Sherman M, Omata M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): a global perspective. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44:239–245. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181d46ef2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J, de Guevara LL. The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 2010;15(Suppl 4):5–13. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-S4-05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stuart KE, Anand AJ, Jenkins RL. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Prognostic features, treatment outcome, and survival. Cancer. 1996;77:2217–2222. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960601)77:11<2217::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Höckel M, Vaupel P. Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:266–276. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.4.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tatum JL, Kelloff GJ, Gillies RJ, Arbeit JM, Brown JM, Chao KS, et al. Hypoxia: importance in tumor biology, noninvasive measurement by imaging, and value of its measurement in the management of cancer therapy. Int J Radiat Biol. 2006;82:699–757. doi: 10.1080/09553000601002324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lipovich L, Johnson R, Lin CY. MacroRNA underdogs in a microRNA world: evolutionary, regulatory, and biomedical significance of mammalian long non-protein-coding RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1799:597–615. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu X, Wang Y, Sun L, Min J, Liu J, Chen D, et al. Long noncoding RNA BC005927 upregulates EPHB4 and promotes gastric cancer metastasis under hypoxia. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:988–1000. doi: 10.1111/cas.13519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Deng SJ, Chen HY, Ye Z, Deng SC, Zhu S, Zeng Z, et al. Hypoxia-induced LncRNA-BX111 promotes metastasis and progression of pancreatic cancer through regulating ZEB1 transcription. Oncogene. 2018;37:5811–5828. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tian X, Xu G. Clinical value of lncRNA MALAT1 as a prognostic marker in human cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e008653. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tian W, Du Y, Ma Y, Gu L, Zhou J, Deng D. MALAT1-miR663a negative feedback loop in colon cancer cell functions through direct miRNA-lncRNA binding. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:857. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0925-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang X, Li M, Wang Z, Han S, Tang X, Ge Y, et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 by miR-101 and miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:3925–3935. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.596866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yang MH, Hu ZY, Xu C, Xie LY, Wang XY, Chen SY, et al. MALAT1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation/migration/invasion via PRKA kinase anchor protein 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852:166–174. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.11.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hou Z, Xu X, Zhou L, Fu X, Tao S, Zhou J, et al. The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-204 and releasing SIRT1. Tumour Biol. 2017;39:1010428317718135. doi: 10.1177/1010428317718135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mehta A, Herrera H, Block T. Glycosylation and liver cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2015;126:257–279. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2014.11.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16018. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shi B, Zhang X, Chao L, Zheng Y, Tan Y, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive analysis of key genes, microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Open Bio. 2018;8:1424–1436. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wu Y, Huang C, Meng X, Li J. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1: insights into its biogenesis and implications in human disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21:5017–5028. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150724115625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Toraih EA, Ellawindy A, Fala SY, Al Ageeli E, Gouda NS, Fawzy MS, et al. Oncogenic long noncoding RNA MALAT1 and HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:653–669. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhao M, Wang S, Li Q, Ji Q, Guo P, Liu X. MALAT1: a long non-coding RNA highly associated with human cancers. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:19–26. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Malakar P, Shilo A, Mogilevsky A, Stein I, Pikarsky E, Nevo Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development by SRSF1 upregulation and mTOR activation. Cancer Res. 2017;77:1155–1167. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen L, Yao H, Wang K, Liu X. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates ZEB1 expression by sponging miR-143-3p and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118:4836–4843. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guil S, Esteller M. RNA-RNA interactions in gene regulation: the coding and noncoding players. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015;40:248–256. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J, Thum T. Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: background, mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 2016;96:1297–1325. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00041.2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122:6–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chu R, Mo G, Duan Z, Huang M, Chang J, Li X, et al. miRNAs affect the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via dysregulation of their biogenesis and expression. Cell Commun Signal. 2014;12:45. doi: 10.1186/s12964-014-0045-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Song Y, Wang F, Huang Q, Cao Y, Zhao Y, Yang C. MicroRNAs contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2015;15:459–466. doi: 10.2174/1389557515666150324125353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gong Y, Mao J, Wu D, Wang X, Li L, Zhu L, et al. Circ-ZEB1.33 promotes the proliferation of human HCC by sponging miR-200a-3p and upregulating CDK6. Cancer Cell Int. 2018;18:116. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0602-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tak H, Kang H, Ji E, Hong Y, Kim W, Lee EK. Potential use of TIA-1, MFF, microRNA-200a-3p, and microRNA-27 as a novel marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497:1117–1122. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen SY, Ma DN, Chen QD, Zhang JJ, Tian YR, Wang ZC, et al. MicroRNA-200a inhibits cell growth and metastasis by targeting Foxa2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 2017;8:617–625. doi: 10.7150/jca.17394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang X, Wang J, Qu S, Zhang H, Ruan B, Gao Y, et al. MicroRNA-200a suppresses metastatic potential of side population cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma by decreasing ZEB2. Oncotarget. 2015;6:7918–7929. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li Y, Zhu X, Liu X, Du A, Yu B. MiR-200a mediates protection of thymosin beta 4 in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells as a novel mechanism under hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. . J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jul 02; doi: 10.1002/jcb.29237. [Epub] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sun X, Zuo H, Liu C, Yang Y. Overexpression of miR-200a protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis by modulating the kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling axis. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38:1303–1311. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]