Abstract
This article reports experimental data related to the research article entitled “Mitochondrial aquaporin-8 is involved in SREBP-controlled hepatocyte cholesterol biosynthesis” [Danielli et al., 2019]. We present data about hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) release from mitochondria isolated from rat hepatocytes with or without silencing of aquaporin-8 (AQP8) protein expression. The rate of mitochondrial H2O2 release (pmoles/min/mg mitochondrial protein) was found to be decreased by about 50% in AQP8-knockdown mitochondria.
Specifications table
| Subject area | Biology |
| More specific subject area | Mitochondrial biology |
| Type of data | Figure |
| How data was acquired | The assay utilizes horseradish peroxidase to catalyze the H2O2-dependent oxidation of non-fluorescent Amplex™ Red to fluorescent resorufin red and detects only the release of hydrogen peroxide, since the size of HRP prevents it from entering the mitochondria. Fluorescence was followed at a 565 nm wavelength every 3 min for 33 min at 37 °C in an automatic microplate reader (Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector) equipped with a thermally controlled compartment. |
| Data format | Analyzed data |
| Experimental factors | Freshly isolated rat hepatocytes were cultured and subjected to silencing of AQP8 protein expression and the mitochondria were isolated. |
| Experimental features | H2O2 release in isolated AQP8-knockdown mitochondria |
| Data source location | Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina |
| Data accessibility | Data is available with this article |
| Related research article | M. Danielli, J. Marrone, A.M. Capiglioni, R.A. Marinelli. Mitochondrial aquaporin-8 is involved in SREBP-controlled hepatocyte cholesterol biosynthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018 (in press) [1] |
Value of the data
|
1. Data
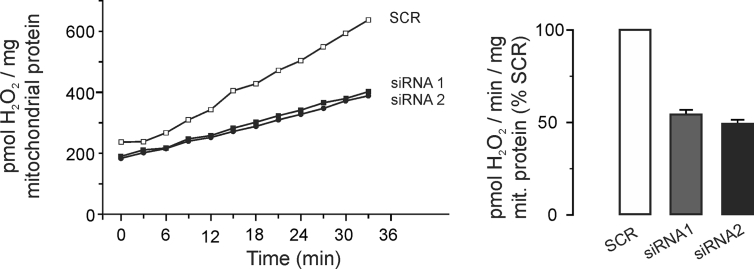
Here we show data of H2O2 release in mitochondria isolated from primary rat hepatocytes with or without knockdown of mitochondrial AQP8 (mtAQP8) protein expression (Fig. 1, left). The rate of mitochondrial H2O2 release (pmoles/min/mg mitochondrial protein) showed a reduction of about 50% in mitochondria from mtAQP8-knockdown hepatocytes (Fig. 1, right).
Fig. 1.
H2O2release from AQP8-knockdown rat hepatocyte mitochondria. Mitochondria were isolated from primary rat hepatocytes transfected for 24 or 48 h with siRNA specific for rat AQP8 or control scramble (SCR) (see Experimental design, materials and methods for details). The mtAQP8 protein expression was unaltered at 24 h but significantly decreased around 60% at 48 h [1]. Left: Time course of H2O2 release from mitochondria isolated from AQP8-knockdown hepatocytes (i.e., 48 h post-transfection). Data correspond to one of two independent experiments with similar results. Right: Rate of mitochondrial H2O2 release. Data are mean ± SEM of two independent experiments (siRNA1: 54% and siRNA2: 49%; expressed as percentage of scramble). At 24 h post-transfection with siRNAs or SCR, the rate of mitochondrial H2O2 release was unaltered (siRNA1: 105% and siRNA2: 99%; expressed as percentage of scramble; one of two independent experiments with similar results).
2. Experimental design, materials and methods
2.1. Materials and reagents
Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium, Pen-Strep antibiotic mixture, l-glutamine, and Lipofectamine 2000 Reagent were all from Invitrogen Corp., CA, USA Foetal Calf Serum were purchased from Internegocios S.A. laboratories, Bs As, Argentina. Silencer siRNA Construction kit was from Ambion, TX, USA, whilst collagenase type IV was from Sigma AldrichSigma, MO, USA as well as the protease inhibitor Phenyl-methylsulfonyl fluoride. Leupeptin was from Chemicon Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany). Amplex™ Red hydrogen peroxide/peroxidase assay kit was from Promega.
2.2. Isolation and culture of rat hepatocytes
Hepatocytes were isolated from normal livers of male Wistar rats by collagenase perfusion and mechanical disruption [2]. Cell viability (assessed by Trypan blue exclusion) was >85%. Hepatocytes were plated onto collagen-coated glass plates at 1.9 × 104 cells/cm2. Primary rat hepatocytes were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (4.5 g/l), supplemented with 2 mM l-glutamine, 10% heat-inactivated foetal calf serum and 100 I.U. penicillin/100 μg streptomycin at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Media was changed every other day.
2.3. Synthesis of short interfering RNA (siRNA) and AQP8 knockdown
As we previously reported [2], [3], the 21-nucleotide RNA duplexes were synthesized using the Silencer siRNA kit following the manufacturer's directions, with oligonucleotides synthesized by Invitrogen as templates. The siRNA1 and siRNA2 were targeted to two different regions of the rat AQP8 molecule. Corresponding control siRNA (SCR) was designed by randomly scrambling the nucleotides of siRNA1 [1], [2]. After 18 h of culture, hepatic cells were transfected with siRNAs by using Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent following the manufacturer instructions. After 24 and 48 h of transfection, cells were sonicated in 0.3 M sucrose containing 0.1 mM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride and 0.1 mM leupeptin and a 6000×g postnuclear mitochondrial fractions was prepared [2], [3]. Hepatocyte viability assessed by lactate dehydrogenase leakage was unaffected after at 24 or 48 h of transfection with siRNAs [1].
2.4. Mitochondrial H2O2 release in isolated mitochondria
H2O2 release from isolated mitochondria was measured by using the Amplex™ Red-horseradish peroxidase assay kit as previously described [3].
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants PIP2015-088 from CONICET and PICT 0439 from ANPCyT, Argentina (to R.A.M.).
Footnotes
Transparency document associated with this article can be found in the online version at https://10.1016/j.dib.2019.103722.
Transparency document
The following is the transparency document related to this article:
Multimedia Component 1
References
- 1.Danielli M., Marrone J., Capiglioni A.M., Marinelli R.A. Mitochondrial aquaporin-8 is involved in SREBP-controlled hepatocyte cholesterol biosynthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019;131:370–375. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Soria L.R., Marrone J., Calamita G., Marinelli R.A. Ammonia detoxification via ureagenesis in rat hepatocytes involves mitochondrial aquaporin-8 channels. Hepatology. 2013;57:2061–2071. doi: 10.1002/hep.26236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Marchissio M.J., Francés D.E.A., Carnovale C.E., Marinelli R.A. Mitochondrial aquaporin-8 knockdown in human hepatoma HepG2 cells causes ROS-induced mitochondrial depolarization and loss of viability. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012;264:246–254. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Multimedia Component 1