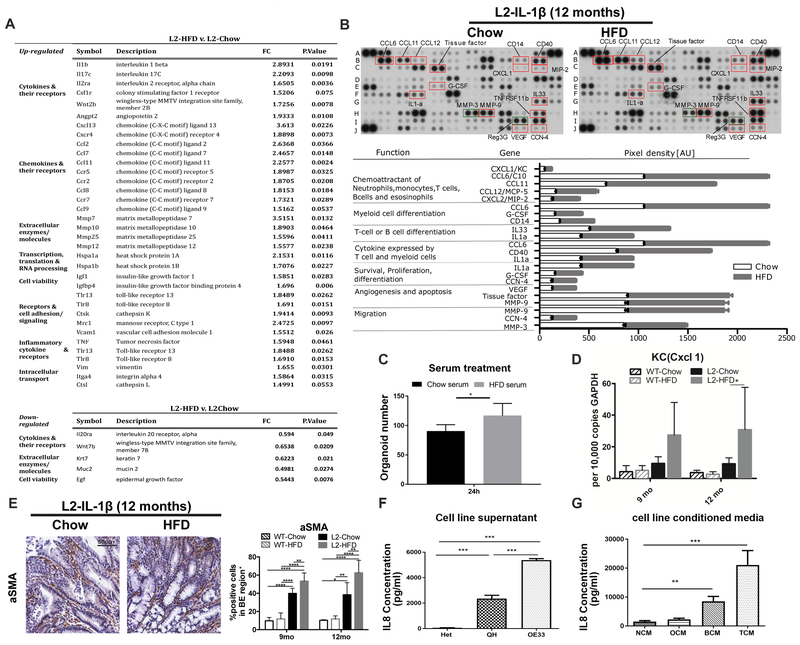
Figure 2. HFD induces a systemic immune response leading to a distinct local inflammatory microenvironment reaction.
(A) Gene expression analysis from SCJ tissue (n=3). (B) Cytokine array for chemoattractants of immune cells and cytokines/chemokines related to immune cell differentiation, cell survival, proliferation, angiogenesis and apoptosis in pooled esophageal tissue from12 month old L2-IL1B mice on Chow (n=4) or HFD (n=6). (C) Treatment with serum from L2-IL1B mice on HFD induces proliferation of 3D mouse BE organoids from L2-IL1B mice (Serum was collected and pooled from L2-IL1B mice maintained on Chow or HFD (n=3)). (D) qRT-PCR of CXCL1/KCin SCJ of L2-IL1B mice on HFD at 12 months (n=6). (E) a-SMA+ staining in L2-IL1B mice on HFD (n=6). (F) IL8 concentration in supernatant from esophageal squamous (Het), BE (QH) and EAC cell lines OE33 (n=3). (G) IL8 concentration in tissue conditioned medium from human normal esophagus, oesophagitis, BE and EAC. (n=10). NCM-normal conditioned medium, OCM-oesophagitis, BCM-BE, and TCM-EAC. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05) For (C,D) 2 way ANOVA with Sidak-Holm post-hoc was used, for (E,F) 1 way Anova with Tukey post-hoc was used. (G) used a Kruskal-Wallis test against NCM and Dunns post-ho. L2=L2-IL-1β, WT=wildtype, HFD=High fat diet