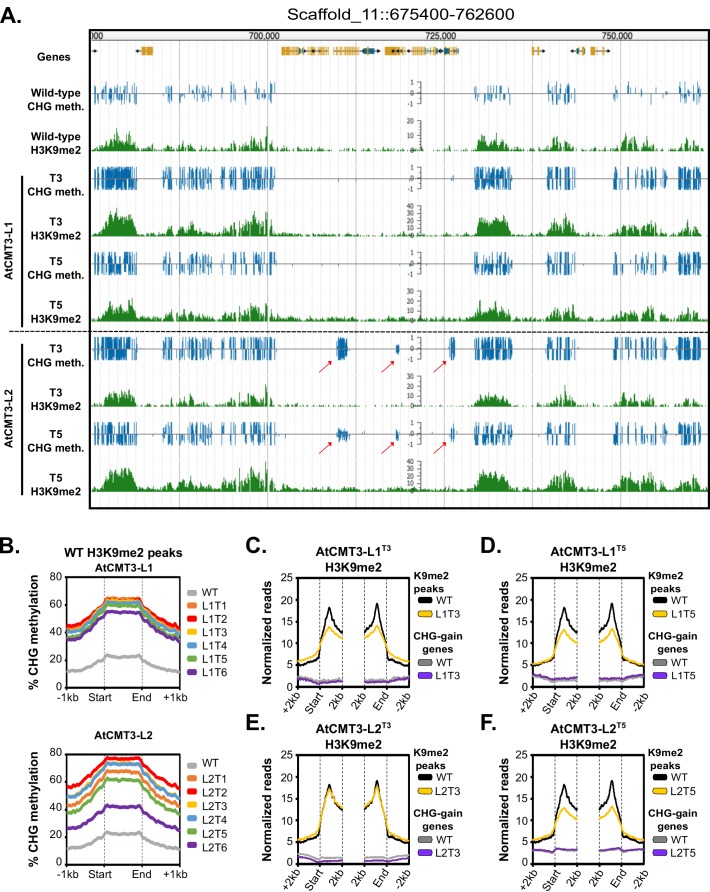
Figure 3. Gains in CHG methylation do not alter H3K9me2 levels or distribution.
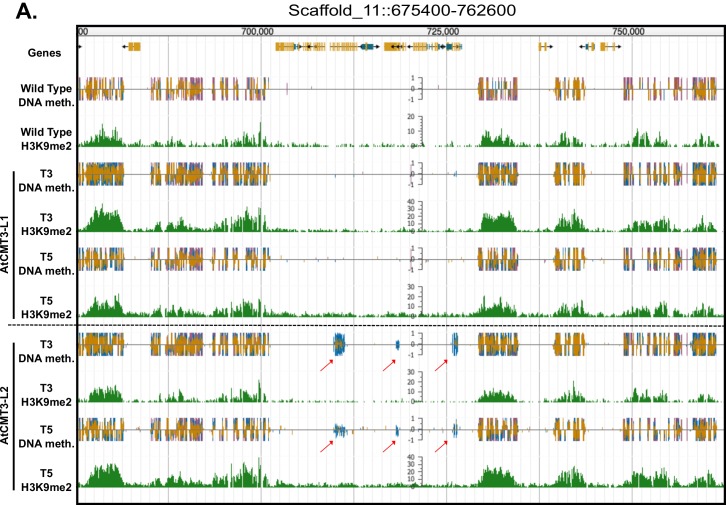
(A) Genome browser view of CHG methylation levels and H3K9me2 ChIP sequencing levels in the T3 and T5 generations of the AtCMT3-L1 and L2 lineages. Arrows indicate gains of CHG methylation over gene bodies in the AtCMT3-L2 generations that do not show H3K9me2 enrichment. Scales on methylation tracks designate the weighted percent methylation, with 1 = 100% on the top strand and −1 = 100% on the bottom strand. Scales on the H3K9me2 tracks indicate the number of mapped reads and are not adjusted for library size (See C-F for comparison of normalized reads). DNA methylation is only shown in the CHG context. For DNA methylation in all contexts see Figure 3—figure supplement 1. (B) Metaplot of % CHG methylation over H3K9me2 ChIP peaks identified in wild type plants. (C–F) Metaplot of H3K9me2 ChIP-sequencing enrichment over H3K9me2 ChIP peaks defined in wild type plants and over CHG-gain genes in AtCMT3-L1T3 (C), AtCMT3-L1T5 (D), AtCMT3-L2T3 (E), and AtCMT3-L2T5 (F). Reads were normalized to library size. See Supplementary file 5 for lists of CHG-gain genes in each lineage.