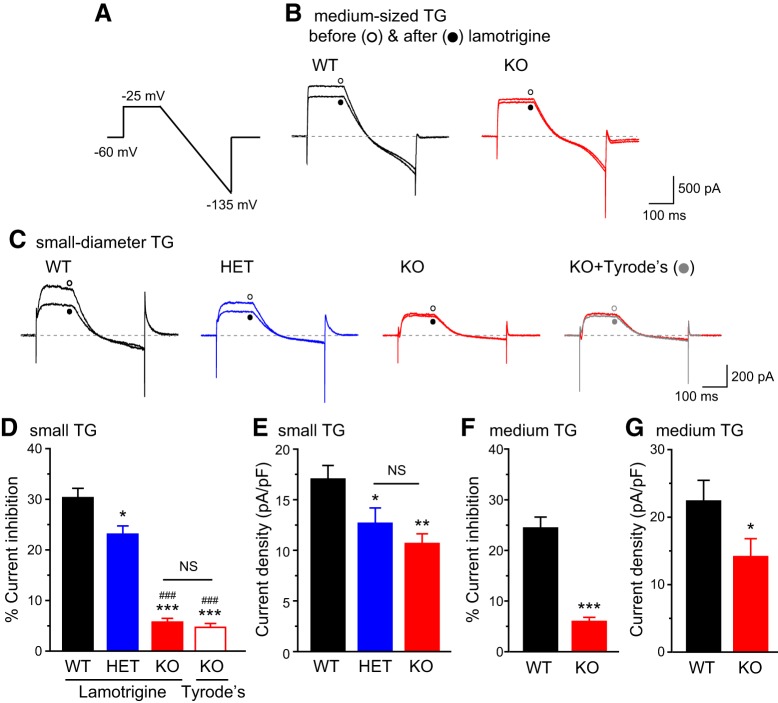
Figure 2.
Total persistent outward currents and lamotrigine-sensitive K+ currents in TG neurons from WT, HET, and TRESK KO mice. A, The voltage protocol used to record persistent outward currents and to minimize transient voltage-gated K+, Na+, and Ca2+ currents. B, Representative current traces from medium-sized (25–40 µm diameter) WT and KO TG neurons before and after the application of 30 µm lamotrigine. C, Representative current traces from small-diameter (<25 µm) WT, HET, and KO TG neurons before and after the application of 30 µm lamotrigine (or Tyrode’s solution), respectively. D, E, The percentage of lamotrigine-sensitive persistent K+ currents (D) and the total persistent outward current density (E) in small-diameter TG neurons (n = 14–20 neurons in each group, all measured at the end of the step to −25 mV). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test compared with the WT group; ###p < 0.001; compared with the HET group. NS, No statistically significant difference. F, G, The percentage of lamotrigine-sensitive persistent K+ currents (F) and the total persistent K+ current density (G) in medium-sized TG neurons from WT and KO mice (n = 15 and 21 neurons, respectively). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; two-tailed t test.