Abstract
Whole-genome sequencing analysis of Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium isolates from the Frankfurt metropolitan region revealed that 78/94 isolates were MLST type ST117, cgMLST complex type CT71 with a common vanB chromosomal insertion site. This indicates circulation of a single VRE clone in a catchment area of 5,000-km2 with 3 million inhabitants.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13756-019-0573-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: VRE, ST117, cgMLST, WGS
Background
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VREfm) are an important cause of nosocomial infections worldwide [1]. The WHO ranks VREfm on its high priority list of multidrug-resistant microorganisms because of increasing prevalence and transmission rates in community and healthcare settings [2]. Since 2014 there has been a dramatic increase of VREfm prevalence among clinical samples in Germany. Marked regional differences have been noted, with high VREfm prevalence within an east-west axis in central Germany (“VRE-belt”), that includes the German federal state of Hesse [3, 4].
The presence and impact of epidemic VREfm on individual patients entering the healthcare system particularly within the “VRE-belt” is poorly understood. Here we report on the genome-based analysis and comparison of VREfm isolated from patients with or without a prior history of hospitalization during admission to intensive care units or other wards with patients at risk for VREfm colonization/infection i.e. hemato-oncological and transplantation units.
Sampling area, patient characteristics
Sampling was performed between November 2017 and June 2018 in 17 hospitals within the Frankfurt am Main metropolitan region, all of whom are members of the Network on multidrug-resistant organisms in the Rhine-Main area (MDRO Network Rhine-Main). The size of hospitals varied between 100 and 1488 beds. Among these, 11/17 were tertiary care hospitals, while the remaining six hospitals were either standard care (n = 3), general hospitals (n = 2) or a specialized clinic (n = 1) (Additional file 1: Table S1). Participating hospitals were requested to provide VREfm isolates from samples obtained from patients at admission (within 72 h) to intensive care units or other wards where patients with a high risk for VREfm colonization/infection were treated, i.e. hemato-oncological and transplant units (n = 85, anal/rectal swabs, stool specimens). An active admission screening of all patients or of defined risk patients was not performed in this study. Hence, determining the prevalence of VRE carriage at admission was not the purpose of this study. The number of isolates per hospital (Additional file 1: Table S1) was dependent on the size of the catchment area of the respective hospital. For hospitals that did not have the requested amount of VREfm-positive screening samples within the study period, VREfm from clinical samples were included (n = 10). These comprised of isolates from blood cultures, urine, wound smears, intra-abdominal surgery smears and a central venous catheter isolate. Identification and antibiotic resistance determination of VREfm was performed using standard laboratory methods and technologies (e.g. chromID VRE plates, MALDI MS, VITEK II, BioMérieux, Nürtingen, Germany) in the labs providing regular microbiological service for the participating hospitals.
In total, VREfm isolates from 95 patients were included. Patient meta-data was collected using a questionnaire (Table 1).
Table 1.
Depiction of the patient meta-data
| Parameter | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 54 | 56.8 |
| Female | 41 | 43.2 | |
| Age | <60 | 15 | 15.8 |
| 60- < 70 | 21 | 22.1 | |
| 70- < 80 | 29 | 30.5 | |
| > 80 | 29 | 30.5 | |
| Not reported | 1 | 1.1 | |
| Underlying disease | Hemato/oncology | 19 | 20.0 |
| Cardiology | 19 | 20.0 | |
| Other | 36 | 37.9 | |
| Not reported | 21 | 22.1 | |
| Travel abroad during the last 12 months | None | 45 | 47.4 |
| Yes | 8 | 8.4 | |
| Indeterminate | 42 | 44.2 | |
| Previous hospital stays within the last 12 month | No | 13 | 13.6 |
| Yes | 76 | 80.0 | |
| Not ascertainable | 6 | 6.3 | |
| Previous antimicrobial therapy* | Vancomycin | 9 | 9.5 |
| Teicoplanin | 6 | 6.3 | |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 25 | 26.3 | |
| Carbapenem | 19 | 20.0 | |
| Cephalosporin | 20 | 21.1 | |
| Penicillin | 12 | 12.6 | |
| Metronidazole | 12 | 12.6 | |
| Quinolone | 17 | 17.9 | |
| Treated with antibiotics | 72 | 75.8 | |
| No antibiotic treatment | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Not reported | 21 | 22.1 |
*multiple answers were possible
The mean age of the patients was 71.2 ± 14.6 years, and ranged from a new-born to 95 years old. Fifty-four patients were male and 41 female. Information regarding a previous hospital stay during the last 12 months was reported in 93.6% (89/95) of the patients. Of these, 85% (76/89) reported a hospital stay. An underlying disease was reported in 77.9%. For 72/95 patients, an antimicrobial therapy during the past 12 months was recorded. Prior treatment with vancomycin was reported in 9.5%. VREfm was a first-time detection in 81 patients. Pre-existing VREfm carriage was known in 14 cases prior to the study.
Characteristics of the VREfm isolates
VREfm were isolated and tested for susceptibility by the participating MDRO Network Rhine-Main centres using standard procedures for clinical diagnostic laboratories. VREfm isolates were generally were ampicillin-, fluoroquinolone- and carbapenem-resistant and linezolid-susceptible.
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) was performed as reported earlier [5, 6]. Resistance gene prediction, and Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) was performed using goseqit tools (https://www.goseqit.com/, Additional file 2: Table S2). Ninety-three VREfm harbored vanB, and a single isolate harbored vanA. One isolate did not harbor any van gene and was excluded from further analysis.
Analysis of the virulence genes was performed using goseqit tools. The presence of the enterococcal surface protein Esp required for promoting biofilm formation (Additional file 2: Table S2), and the PTSclin phosphotransferase system associated with colonization potential of clinical isolates [7] as well as the uptake and utilization of amino sugars such as β-N-acetylglucosamine commonly found in mucin on the surfaces of epithelial cells and in biofilms were detected using blastn [8]. All van-encoding isolates harbored the efaAfm gene, suggested to be involved in cell wall adherence, which is concordant with the results from earlier studies [9]. Ninety-two isolates harbored the hylEfm, acm and PTSclin, while 90/94 isolates carried the esp gene.
Almost all isolates (90/94), regardless of source, were ST117 with the remaining four isolates each representing ST80, ST192, ST262 and ST1428. The ST262 isolate harbored a vanA gene.
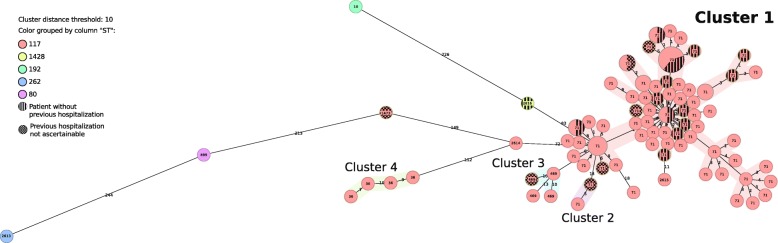
The use of MLST-based data to classify VREfm is controversial because of its high recombination rates that masks relatedness of otherwise highly related strains. Therefore, further differentiation of the ST117 isolates using a core-genome MLST (cgMLST) was performed (Ridom SeqSphere+ 5.1.0., Ridom GmbH, Münster, Germany; Enterococcus faecium scheme [10]). This analysis revealed that 78/90 (87%) of the ST117 isolates, i.e. from both non-clinical as well as clinical samples, were all members of a single cgMLST complex type (CT71, Fig. 1). Minor CTs detected in ST117 isolates were CT469 (n = 4), CT36 (n = 4), CT2614 (n = 1), CT2615 (n = 1) and CT1473 (n = 1).
Fig. 1.
Minimum spanning tree of the sequenced VREfm isolates based on the cgMLST data. The figure was created according to reference [10]. Cluster distance threshold was set to 10 cgMLST alleles. Size of circles is according to number of isolates. Numbers in the circles indicate the complex type of the respective isolates. Colors of circles indicate multilocus sequence types
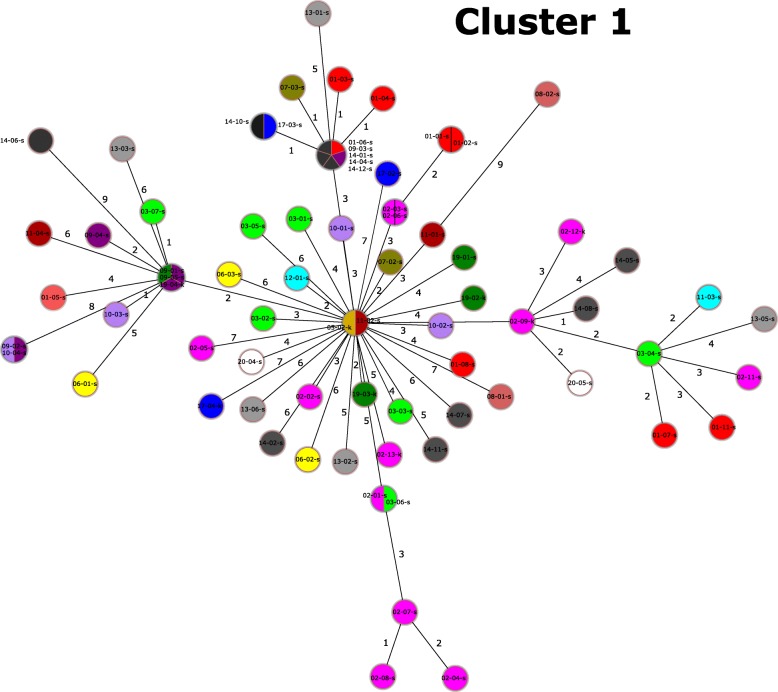
Of the CT71 isolates, 74/78 clustered into one cgMLST cluster type (Fig. 2, Cluster 1), that exhibited up to 10 cgMLST allele differences. All isolates of Cluster 1 harbored an identical insertion of a vanB-encoding Tn1549-like transposon into a gene of unknown function (HMPREF0351_10592), previously reported for the vanB-encoding VREfm of the sequence type ST192 [11]. Thus, these isolates constitute a clone, which we designate as the ST117/CT71/vanB clone.
Fig. 2.
Minimum spanning tree of Cluster 1 based on cgMLST information. Different colours depict different clinics. Cluster distance threshold was set to 10 cgMLST alleles. Size of circles is representative and reflects the number of isolates
Statistical analyses using the Mann-Whitney U test [12] did not support an association of the CT71 clone with any of the patient data characteristics detailed in the Table 1 (Additional file 3: Table S3).
Discussion
Surveillance, hygiene/infection control programs and antibiotic stewardship interventions for VREfm have been implemented in healthcare settings throughout Europe [13, 14]. However, the impact of these measures on the VRE influx by individual patients (colonization) entering the healthcare system is poorly understood. Here we characterized VREfm isolated from rectal swabs of patients during admission with and without prior history of hospitalization within the so-called “VRE-belt” in central Germany. Core genome-based phylogenetic analysis classifies all of the VREfm from this study as members of the hospital-associated clade A1 (data not shown) and shows that a single ST117 clonal lineage, with cgMLST complex type CT71 is predominant in the Rhine-Main metropolitan area within a patient population with a high-risk profile for VREfm acquisition. Previous epidemiological data indicated that the emergence of ST117 with its three major CTs, CT36, CT71 and CT469 is recent, and presently accounts for over one-third of all VREfm isolated from bloodstream infections in Germany and the Netherlands [15].
The repeated isolation of a single predominant ST117/CT71/vanB clone at geographically separated institutions (Additional file 5: Figure S1) throughout the reporting period suggests that it has highly adaptive properties for effective transmission and a capacity for persistence in the hospital environment. Indeed, ST117/CT71/vanB VREfm isolates harbored elements associated with persistence, such as the collagen-binding acm and the enterococcal surface protein Esp, required for promoting biofilm formation (Additional file 2: Table S2). In addition, the PTSclin phosphotransferase system associated with colonization potential of clinical isolates [7] was present in all ST117/CT71/vanB isolates. Further studies are warranted to understand the impact of these genes in the distribution of the ST117/CT71/vanB clone.
A limitation of the study is the relatively short collection period and the number of isolates analyzed. Nevertheless, the discovery of a single predominant clone in geographically separated individual institutions within such a large catchment area is unprecedented. There are several possible explanations for this phenomenon: Firstly, our data indicate ongoing inter-hospital spread or even a multihospital outbreak, as near-identical isolates (≤10 cgMLST alleles) of the ST117/CT71/vanB clone were detected in different hospitals (Fig. 2, Additional file 6: Figure S2). The latter phenomenon would require the movement of patients among the different hospitals sampled. This is true even for the smallest group of patients included in this study, i.e. those who have been reported to have previous stays in other participating hospitals (Additional file 6: Figure S2, Additional file 4: Table S4). Secondly, 14.9% (11/74) of the patients harboring this clone did not report any previous hospital stay within the last 12 months (Table 1). This indicates either acquisition of the VREfm in a hospital before more than 12 months ago, a nosocomial acquisition during the current hospital stay, or an acquisition through the dissemination of this clone in communal spaces outside of healthcare institutions. Further studies are required to answer the questions raised here, with particular focus on the presence of this clone in the community, healthcare-independent populations and other reservoirs (livestock, food, water).
Conclusion
We report the detection of a near-ubiquitous VREfm clone (ST117/CT71/vanB) circulating within the metropolitan region in and around Frankfurt am Main/Germany. The presence both of a single clone in such a large catchment area and the detection of a possible multi-hospital VRE transmission in this study has only been revealed as a result of WGS-based analysis. As vancomycin resistance is associated with enhanced mortality among patients in hospital settings, in particular bloodstream infections [16, 17], the prevention of VREfm infections is a major objective. The presence of a VREfm clone within different institutions questions whether infection control and antimicrobial stewardship interventions can be effective without an understanding of the VREfm carriage state and transmission dynamics in human populations within the catchment area studied. The results of our study call for the establishment of a multihospital infection control approach, including rapid detection tools to identify predominant clones and for a genome-based long-term surveillance to be able to detect newly emerging clones. In addition, the use of clone-based strategies for eradication i.e. based on vaccines or bacteriophages, would be interesting avenues for further pursuit.
Additional files
Table S1. Characteristics of the sequenced isolates. Depicts the characteristics of each VREfm isolate presented in this study. (DOCX 14 kb)
Table S2. Characteristics of the participating hospitals. Depicts selected characteristics of the hospitals participating in the study. (DOCX 30 kb)
Table S3. Statistical analysis of parameters associated with ST117/CT71/vanB clone carriage. Depicts the statistical analysis of parameters associated with the carriage of the ST117/CT71/vanB clone. (DOCX 12 kb)
Table S4. Information on previous hospital stays of the patients. Depicts previous hospital stays of the patients, including information in which hospitals they previously resided. (DOCX 17 kb)
Figure S1. Regional distribution of the Cluster 1 VREfm ST117/CT71/vanB isolates. Depicts the regional distribution of Cluster 1 VREfm ST117/CT71/vanB isolates. Districts may include more than one hospital. The original map was extracted from Googlemaps (https://www.google.de/maps/@50.2354853,8.7072805,11z). (PDF 2079 kb)
Figure S2. Interaction map between the different participating hospitals. Indicates the patients’ previous hospital history, whereever known. Connections between hospitals mark previous hospital stays in another hospital, while circles indicate a previous stay in the same hospital. (PDF 15 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank all clinics for participating in the study, for collection of the isolates. We thank Christina Gerstmann (Institute of Medical Microbiology, Giessen, Germany) for excellent technical assistance. We are indebted to Paul Higgins (Institute of Medical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany) for help with the cgMLST typing.
The members of the Rhine-Main VREfm study group are the following (alphabetical order): Sabine Albert-Braun1, Klaus-Peter Hunfeld2, Volkhard Kempf3, Andreas Kneifel4, Adnan Kukic5, Bernhard Jahn-Mühl6, Katharina Madlener7, Klaus Oberdorfer8, Jörn-Peter Oeltze9, Jörg Schulze10, Navid Sotoudeh11, Rolf Tessmann12.
Author affiliations of study group members:
1 Klinikum Frankfurt Höchst, Frankfurt/Main, Germany.
2 Institute for Laboratory Medicine, Microbiology & Infection Control, North West Medical Centre, Frankfurt/Main, Germany.
3 University Hospital, Goethe University, Frankfurt/Main, Germany.
4 Klinikum Hanau, Hanau, Germany.
5 Hochtaunuskliniken, Bad Homburg, Germany.
6 AGAPLESION HYGIENE, Frankfurter Diakonie Kliniken, Frankfurt/Main, Germany.
7 Kerckhoff Klinik, Bad Nauheim, Germany.
8 MVZ Labor Dr. Limbach & Kollegen GbR, Heidelberg, Germany.
9 DKD HELIOS Klinik, Wiesbaden, Germany.
10 Sana Klinikum, Offenbach, Germany.
11 Krankenhaus Bad Soden, Bad Soden, Germany.
12 Berufsgenossenschaftliche Unfallklinik, Frankfurt/Main, Germany.
Email addresses of study group members
• Sabine.Albert-Braun@KlinikumFrankfurt.de
• hunfeld.klaus-peter@khnw.de
• volkhard.kempf@kgu.de
• andreas_kneifel@klinikum-hanau.de
• adnan.kukic@hochtaunus-kliniken.de
• Bernhard.Jahn@agaplesion.de
• k.madlener@kerckhoff-klinik.de
• klaus.oberdorfer@labor-limbach.de
• joern-peter.oeltze@helios-kliniken.de
• joerg.schulze@sana.de
• nsotoudeh@kliniken-mtk.de
• rolf.tessmann@bgu-frankfurt.de
Abbreviations
- cgMLST
Core genome multilocus sequence typing
- CT
Complex type
- MDRO
Multidrug-resistant organisms
- MLST
Multilocus sequence typing
- ST
Sequence type
- VRE
Vancomycin-resistant enterococci
- VREfm
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium
- WGS
Whole-genome sequencing
- WHO
World Health Organization
Authors’ contributions
UH and TC implemented the study. KS, MS and Rhine-Main VREfm study group provided isolates and gathered information. LF, MF, CI, UH, TC gathered and analyzed the data. TC, UH and LF wrote the manuscript, which all authors approved.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Bundesministerium fuer Bildung und Forschung (BMBF, Germany) within the German Center for Infection research (DZIF/grant number 8032808811 to TC). Support was also obtained from the Hessian Ministry of Social Affairs and Integration for the MDRO Network Rhine-Main and the Hessian Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Arts within the project HuKKH (Hessisches universitaeres Kompetenzzentrum Krankenhaushygiene).
Availability of data and materials
The raw sequencing data are available in ENA under the accession number PRJEB29744.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the medical faculty of the Justus-Liebig-University of Giessen (AZ: 179/16). All samples were taken as part of standard care procedures.
Consent for publication
Not applicable (no individual person’s data included).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ursel Heudorf and Trinad Chakraborty are senior authors that contributed equally to this article.
Contributor Information
Linda Falgenhauer, Email: linda.falgenhauer@mikrobio.med.uni-giessen.de.
Moritz Fritzenwanker, Email: moritz.fritzenwanker@mikrobio.med.uni-giessen.de.
Can Imirzalioglu, Email: Can.Imirzalioglu@mikrobio.med.uni-giessen.de.
Katrin Steul, Email: katrin.steul@stadt-frankfurt.de.
Marlene Scherer, Email: Marlene.Scherer@stadt-frankfurt.de.
Rhine-Main VREfm study group, Email: l.falgenhauer@gmail.com.
Ursel Heudorf, Email: ursel.heudorf@gmx.de.
Trinad Chakraborty, Email: Trinad.Chakraborty@mikrobio.med.uni-giessen.de.
Rhine-Main VREfm study group:
Sabine Albert-Braun, Klaus-Peter Hunfeld, Volkhard Kempf, Andreas Kneifel, Adnan Kukic, Bernhard Jahn-Mühl, Katharina Madlener, Klaus Oberdorfer, Jörn-Peter Oeltze, Jörg Schulze, Navid Sotoudeh, and Rolf Tessmann
References
- 1.Gilmore MS, Clewell DB, Ike Y, Shankar N. Enterococci: from commensals to leading causes of drug resistant infection [internet]. Gilmore MS, Clewell DB, Ike Y, Shankar N, editors. Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary; 2014. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK190426/ [PubMed]
- 2.Tacconelli E, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Harbarth S, Mendelson M, Monnet DL, et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis [Internet]. Elsevier; 2018 [cited 2018 Oct 1];18:318–27. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1473309917307533?via%3Dihub [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Gastmeier P, Schröder C, Behnke M, Meyer E, Geffers C. Dramatic increase in vancomycin-resistant enterococci in Germany. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:1660–1664. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Remschmidt C, Schröder C, Behnke M, Gastmeier P, Geffers C, Kramer TS. Continuous increase of vancomycin resistance in enterococci causing nosocomial infections in Germany −10 years of surveillance. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control; 2018;7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Fritzenwanker M., Imirzalioglu C., Gentil K., Falgenhauer L., Wagenlehner F.M., Chakraborty T. Incidental detection of a urinary Escherichia coli isolate harbouring mcr-1 of a patient with no history of colistin treatment. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2016;22(11):954–955. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.08.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Falgenhauer Linda, Imirzalioglu Can, Ghosh Hiren, Gwozdzinski Konrad, Schmiedel Judith, Gentil Katrin, Bauerfeind Rolf, Kämpfer Peter, Seifert Harald, Michael Geovana Brenner, Schwarz Stefan, Pfeifer Yvonne, Werner Guido, Pietsch Michael, Roesler Uwe, Guerra Beatriz, Fischer Jennie, Sharp Hannah, Käsbohrer Annemarie, Goesmann Alexander, Hille Katja, Kreienbrock Lothar, Chakraborty Trinad. Circulation of clonal populations of fluoroquinolone-resistant CTX-M-15-producing Escherichia coli ST410 in humans and animals in Germany. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 2016;47(6):457–465. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.03.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhang X, Top J, De Been M, Bierschenk D, Rogers M, Leendertse M, et al. Identification of a genetic determinant in clinical Enterococcus faecium strains that contributes to intestinal colonization during antibiotic treatment. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:1780–1786. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Altschul Stephen F., Gish Warren, Miller Webb, Myers Eugene W., Lipman David J. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1990;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Soheili Sara, Ghafourian Sobhan, Sekawi Zamberi, Neela Vasanthakumari, Sadeghifard Nourkhoda, Ramli Ramliza, Hamat Rukman Awang. Wide Distribution of Virulence Genes amongEnterococcus faeciumandEnterococcus faecalisClinical Isolates. The Scientific World Journal. 2014;2014:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2014/623174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.de Been Mark, Pinholt Mette, Top Janetta, Bletz Stefan, Mellmann Alexander, van Schaik Willem, Brouwer Ellen, Rogers Malbert, Kraat Yvette, Bonten Marc, Corander Jukka, Westh Henrik, Harmsen Dag, Willems Rob J. L. Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for High-Resolution Typing of Enterococcus faecium. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2015;53(12):3788–3797. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01946-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bender JK, Kalmbach A, Fleige C, Klare I, Fuchs S, Werner G. Population structure and acquisition of the vanB resistance determinant in German clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium ST192. Sci Rep [Internet] Nature Publishing Group; 2016;6:1–13. Available from: 10.1038/srep21847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Mann H, Whitney D. On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other. Ann Math Stat. 1947;18:50–60. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177730491. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Werner G, Coque TM, Hammerum AM, Hope R, Hryniewicz W, Johnson A, et al. Emergence and spread of vancomycin resistance among enterococci in Europe. Eurosurveillance. 2008;13. [PubMed]
- 14.Mutters NT, Mersch-Sundermann V, Mutters R, Brandt C, Schneider-brachert W, Frank U. Control of the spread of vancomycin- resistant enterococci in hospitals epidemiology and clinical relevance. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013;110:725–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Klare I, Bender JK, Koppe U, Abu Sin M, Eckmanns T. Eigenschaften, Häufigkeit und Verbreitung von Vancomycin- resistenten Enterokokken (VRE) in Deutschland – Update 2015/2016. Epidemiol Bull. 2017:519–27.
- 16.Weber S, Hogardt M, Reinheimer C, Wichelhaus TA, Kempf VAJ, Kessel J, et al. Bloodstream infections with vancomycin-resistant enterococci are associated with a decreased survival in patients with hematological diseases. Ann Hematol Annals of Hematology. 2019;98:763–773. doi: 10.1007/s00277-019-03607-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Prematunge Chatura, MacDougall Colin, Johnstone Jennie, Adomako Kwaku, Lam Freda, Robertson Jennifer, Garber Gary. VRE and VSE Bacteremia Outcomes in the Era of Effective VRE Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology. 2015;37(1):26–35. doi: 10.1017/ice.2015.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Characteristics of the sequenced isolates. Depicts the characteristics of each VREfm isolate presented in this study. (DOCX 14 kb)
Table S2. Characteristics of the participating hospitals. Depicts selected characteristics of the hospitals participating in the study. (DOCX 30 kb)
Table S3. Statistical analysis of parameters associated with ST117/CT71/vanB clone carriage. Depicts the statistical analysis of parameters associated with the carriage of the ST117/CT71/vanB clone. (DOCX 12 kb)
Table S4. Information on previous hospital stays of the patients. Depicts previous hospital stays of the patients, including information in which hospitals they previously resided. (DOCX 17 kb)
Figure S1. Regional distribution of the Cluster 1 VREfm ST117/CT71/vanB isolates. Depicts the regional distribution of Cluster 1 VREfm ST117/CT71/vanB isolates. Districts may include more than one hospital. The original map was extracted from Googlemaps (https://www.google.de/maps/@50.2354853,8.7072805,11z). (PDF 2079 kb)
Figure S2. Interaction map between the different participating hospitals. Indicates the patients’ previous hospital history, whereever known. Connections between hospitals mark previous hospital stays in another hospital, while circles indicate a previous stay in the same hospital. (PDF 15 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequencing data are available in ENA under the accession number PRJEB29744.