Figure 5. Distal binding by PRDM16 regulates functionally distinct groups of genes.
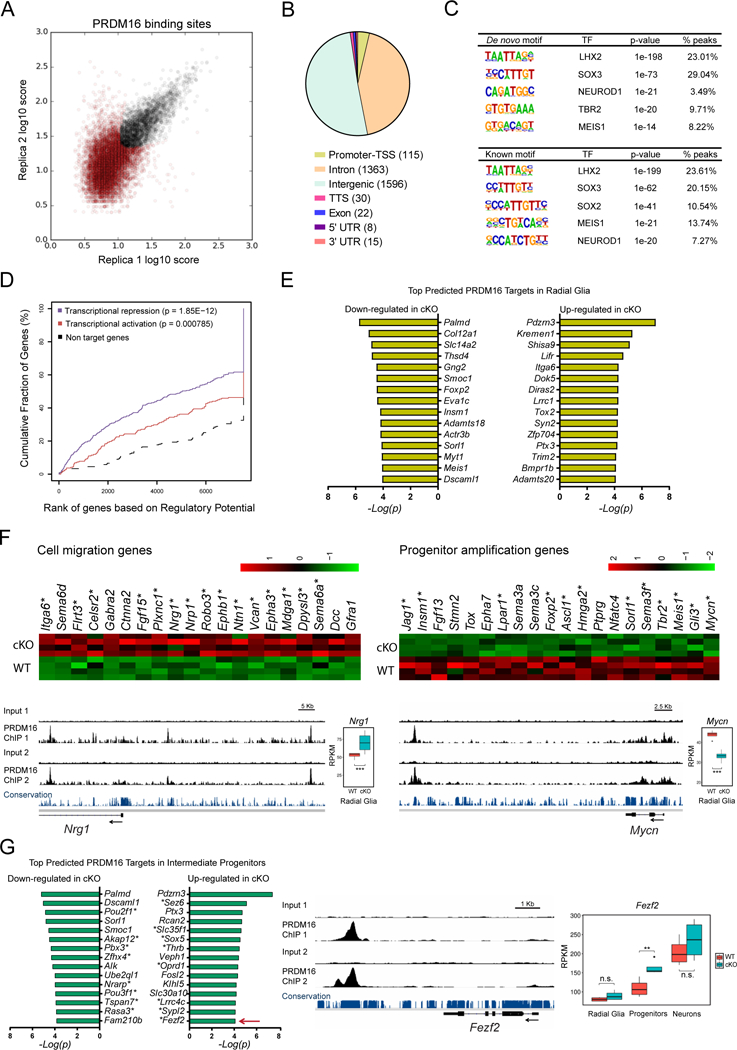
(A) Identification of genome-wide PRDM16 binding sites in the E15.5 cortex by ChIP-seq. The plot represents the irreproducible discovery rate (IDR) analysis of two independent biological replicates. A total of 3151 high-confidence PRDM16 binding sites were identified over an IDR < 0.05 (black circles).
(B) Distribution of PRDM16 binding sites across the genome. TSS, transcription start site; TTS, transcription termination site.
(C) De novo and known motif discovery within PRDM16 binding sites.
(D) Statistical integration of PRDM16 binding sites with differentially expressed genes in the cKO cortex predicts a dual function of PRDM16 as repressor (blue line) and activator (red line), using a set of non-differentially expressed genes as reference (black dashed line). The p-value for each function is indicated.
(E) Top predicted PRDM16 transcriptional targets in radial glia.
(F) Heat-maps and ChIP-seq tracks indicate examples of cell migration genes repressed by PRDM16 and progenitor amplification genes activated by PRDM16. Asterisks indicate predicted direct transcriptional targets of PRDM16. Nrg1 and Mycn are shown as examples for each group of genes.
(G) Top predicted PRDM16 transcriptional targets in intermediate progenitor cells. Asterisks indicate genes uniquely misregulated in intermediate progenitors, such as Fezf2 (arrow), which is shown as example of this group of genes.
Significant gene expression changes were identified using a FDR < 0.05 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; n.s., not significant).
