Abstract
Recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (follitropin alfa) and biosimilar preparations are available for clinical use. They have specific FSH activity and a unique glycosylation profile dependent on source cells. The aim of the study is to compare the originator (reference) follitropin alfa (Gonal-f®)- with biosimilar preparations (Bemfola® and Ovaleap®)-induced cellular responses in vitro. Gonadotropin N-glycosylation profiles were analyzed by ELISA lectin assay, revealing preparation specific-patterns of glycan species (Kruskal-Wallis test; p < 0.05, n = 6) and by glycotope mapping. Increasing concentrations of Gonal-f® or biosimilar (1 × 10−3-1 × 103 ng/ml) were used for treating human primary granulosa lutein cells (hGLC) and FSH receptor (FSHR)-transfected HEK293 cells in vitro. Intracellular cAMP production, Ca2+ increase and β-arrestin 2 recruitment were evaluated by BRET, CREB, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation by Western blotting. 12-h gene expression, and 8- and 24-h progesterone and estradiol synthesis were measured by real-time PCR and immunoassay, respectively. We found preparation-specific glycosylation patterns by lectin assay (Kruskal-Wallis test; p < 0.001; n = 6), and similar cAMP production and β-arrestin 2 recruitment in FSHR-transfected HEK293 cells (cAMP EC50 range = 12 ± 0.9–24 ± 1.7 ng/ml; β-arrestin 2 EC50 range = 140 ± 14.1–313 ± 18.7 ng/ml; Kruskal-Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 4). Kinetics analysis revealed that intracellular Ca2+ increased upon cell treatment by 4 μg/ml Gonal-f®, while equal concentrations of biosimilars failed to induced a response (Kruskal-Wallis test; p < 0.05; n = 3). All preparations induced both 8 and 24 h-progesterone and estradiol synthesis in hGLC, while no different EC50s were demonstrated (Kruskal-Wallis test; p > 0.05; n = 5). Apart from preparation-specific intracellular Ca2+ increases achieved at supra-physiological hormone doses, all compounds induced similar intracellular responses and steroidogenesis, reflecting similar bioactivity, and overall structural homogeneity.
Keywords: FSH, biosimilar, gonal-F, bemfola, ovaleap, glycosylation, assisted reproduction (ART)
Introduction
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a heterodimeric glycoprotein hormone produced by the pituitary and acting on the gonads (1). In fertile women, FSH controls reproduction supporting ovarian granulosa cell proliferation and follicular growth by binding to its G protein-coupled receptor (FSHR) (2).
FSH shares a 92-amino acid residue α subunit with other glycoprotein hormones and has a 111-amino acid residue, hormone-specific β subunit (3). Two N-linked heterogeneous oligosaccharide populations are bound to each protein backbone subunit and are involved in hormone folding and half-life, receptor binding, and activation (4, 5). After gonadotropin binding, FSHR conformation rearrangements occur, triggering intracellular signal transduction. Gαs protein signaling leads to adenylyl cyclase stimulation and cyclic-AMP (cAMP)/protein kinase A (PKA)-pathway activation (6, 7), resulting in cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) (8, 9) and extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) (10) phosphorylation. These phospho-proteins are key players modulating steroidogenesis, proliferation and survival/apoptosis (8, 11), all molecular events underlying reproductive functions (12). Upon ligand binding, FSHR recruits other heterotrimeric Gα proteins, including Gαq and Gαi (13–16), as well as other interactors (17), linking FSH action to multiple intracellular signaling pathways, such as the rapidly-activated, phospholipase C-dependent (18), cytosolic calcium cation (Ca2+) release (19). FSHR internalization and recycling is mediated by β-arrestin 1 and 2, which triggers G protein-independent ERK1/2 signaling (20, 21).
FSH exists in a number of isoforms differing in content and composition of oligosaccharides attached to the protein backbone (22). FSH glycoforms were proposed as biased receptor ligands (5, 23, 24) due to isoform-specific contact with FSHR (25) and intracellular signaling (26). Glycosylation is a post-translational process influencing the isoelectric point (pI) and half-life of the gonadotropin (27). In women, more glycosylated and acidic FSH isoforms, mainly due to sialylation, exhibit a prolonged in vivo half-life due to reduced kidney clearance and are secreted mostly during the early and mid-follicular phase, compared to FSH basic glycoforms, which are predominant before ovulation (28, 29). Highly acidic FSH isoforms are produced more after the menopause than during the fertile lifespan (30), suggesting that glycoform composition of circulating hormones is dynamic and might have a physiological role.
Several formulations of exogenous FSH may be used in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) to induce multiple follicle development. Both urinary and recombinant FSH and other gonadotropin preparations are commercially available, as well as follitropin alfa biosimilar drugs, which are recombinant compounds similar to the originator (31–33). Previous studies attempted to address effects of these preparations on ART outcomes, given their different glycosylation states featured as post-translational modifications by the cellular source and/or purification processes (31, 34, 35). In fact, previous analyses by mass spectrometry found preparation-specific pattern of glycans bound to the FSH β-subunits (36, 37).
In this study, the biochemical composition and hormone-induced cell response of the originator follitropin alfa and two biosimilar preparations were analyzed in vitro. Glycosylation pattern was assessed in regard to cAMP production, Ca2+ release, β-arrestin 2 recruitment, CREB, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation and steroid (i.e., progesterone and estradiol) synthesis, which were analyzed in human primary granulosa-lutein cells (hGLC) and HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the human FSHR cDNA.
Materials and Methods
Follitropin Alfa Reference Preparation (Gonal-f®) and Biosimilars
The reference follitropin alfa and two biosimilar preparations were analyzed: Gonal-f® provided by Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany), Ovaleap® purchased from Teva Pharmaceutical Industries (Tel Aviv, Israel) and Bemfola® from Finox Biotech (Kirchberg, Switzerland). Different batches of each preparation were tested by performing both biochemical and functional evaluations, as follows: two batches of Gonal-f® (AU016646, BA045956), two batches of Ovaleap® (S27266, R38915), and three batches of Bemfola® (PPS30400, PNS30388, PNS30230). Additional Gonal-f® (199F005, 199F049, 199F051) and Ovaleap® (S06622) batches were used for glycopeptide mapping. Comparison of hormone induced-signaling in vitro were performed by stimulating cells with gonadotropins concentrations expressed by mass rather than International Units (IU), since the latter depends of the in vivo activity in rats (38). Gonal-f® and biosimilar dosages were determined starting by the batch concentration declared by providers, consisting of 44 μg/ml for Gonal-f®, Ovaleap® and Bemfola®. Recombinant human choriogonadotropin (hCG; Ovitrelle®, Merck KGaA) was used as a negative control where indicated.
Silver Staining and Western Blotting Analysis
According to gonadotropin quantification provided by the producers, 300 ng of each compound were subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE. Gel electrophoresis was performed under denaturing-reducing or non-denaturing-non reducing conditions, followed by silver staining and Western blotting. Denaturing conditions consisted of boiling samples 5 min at 100°C, while reducing conditions were obtained by adding 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), disrupting disulfide bonds (39). Silver staining was performed after acrylamide gel electrophoresis, as previously described (40, 41). Briefly, fixation was performed by incubating gels 1 h in 50% ethanol buffer, in the presence of 12% acetic acid and 5 × 10–4% formalin (all from Sigma-Aldrich). After washes, gels were stained with 0.2% AgNO3 buffer 30 min-treatment and signals were developed by 3% Na2CO3 buffer, 0.0005% formalin and 4 × 10–4% Na2S2O3 before to be stopped. Originator follitropin alpha and biosimilars were evaluated by Western blotting using a rabbit anti-human polyclonal primary antibody against FSHβ/FSH (SAB1304978; Sigma-Aldrich), while the secondary antibody was anti-rabbit human horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated (#NA9340V; GE HealthCare, Little Chalfont, UK). Recombinant hCG (Ovitrelle; Merck KGaA) was used as a negative control. Signals were developed with ECL (GE HealthCare) and acquired using the VersaDoc Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
Lectin ELISA Assay and Glycopeptide Mapping
The technique was described previously (41, 42) and adapted to preparations used in this study. A 96-well-microtiter plate was coated overnight at 4°C with the anti-human gonadotropin α subunit monoclonal antibody HT13.3 (43), which recognizes all human glycoprotein hormone α subunits, in 0.1 M sodium carbonate/hydrogen carbonate buffer (pH = 9.6). Plates were washed with a saline buffer (TBS-T; 25 mM Tris, 140 mM NaCl, 3 mM KCl, 0.05%, Tween 20; pH = 7.4) and non-specific sites were saturated by 1 h-treatment at room temperature (RT) using TBS-T containing 2% polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 (Fluka, Sigma-Aldrich). Duplicate 5 ng samples of each hormone preparation were then incubated over-night, in 100 μl/well of the saturation buffer. After washing, biotinylated lectins (Vector laboratories Ltd, AbCys Biologie, Paris, France) were placed into wells and incubated for 2 h at RT. Lectins used were: Sambucus nigra agglutinin (SNA), Maackia amurensis agglutinin (MAA), Artocarpus Polyphemus lectin (jacalin), Ricinus communis agglutinin (RCA-1, ricin), Datura stramonium agglutinin (DSA), wheat germ agglutinin (WGA), Phaseolus vulgaris agglutinin (PHA-E) (Supplemental Table 1). They were diluted in saturation buffer containing 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM MnCl2. Plates were washed and peroxidase labeled NeutrAvidinTM (Pierce, Interchim, Montluçon, France) was added in each well (100 μl in TBS-T), for 1 h at RT. After incubation with TMB ELISA peroxidase substrate standard solution (UP664781; Interchim, Montluçon, France) 20 min at RT, reactions were stopped by adding 50 μl/well of 2 N H2SO4, and absorbance measured at 450 nm wavelength using a spectrophotometer. Blank values, consisting of samples maintained in the absence of hormones, were subtracted to obtain ELISA data.
Additional information about reagents, glycopeptide mapping, hydrophilic interaction chromatography, and mass spectrometry analysis is provided in the supplemental section (Supplemental Material and Methods).
Cell Culture and Transfection
HEK293 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS, 4.5 g/l glucose, 100 IU/ml penicillin, 0.1 mg/ml streptomycin, and 1 mM glutamine (all from Sigma-Aldrich). Transient transfections were performed in 96-well plates using Metafectene PRO (Biontex Laboratories GmbH, München, Germany), in order to obtain exogenous FSHR and cAMP CAMYEL-, β-arrestin 2- or aequorin Ca2+-BRET biosensor protein expression (15), as previously described (41). For cAMP evaluation, 50 ng/well of FSHR-expressing plasmid were mixed together with 0.5 μl/well of Metafectene PRO in serum-free medium and incubated 20 min. A 50 μl aliquot of cAMP CAMYEL biosensor-expressing plasmid-Metafectene PRO mix was added to each well-containing 1 × 105 cells, in a total volume of 200 μl/well, and incubated 2-days before stimulation with gonadotropins. One hundred ng/well of FSHR-Rluc8- and 100 ng/well of β-arrestin 2 biosensor-expressing plasmids were used for evaluating β-arrestin 2 recruitment. One hundred ng/well of FSHR- and 100 ng/well of aequorin biosensor-expressing plasmids were used to prepare cells for measure changes in intracellular Ca2+. All samples were prepared in duplicate and BRET measurements were performed using 2-day transfected cells, in 40 μl/well PBS and 1 mM Hepes.
Human primary granulosa lutein cells (hGLC) were isolated from ovarian follicles of about twenty donor women undergoing oocyte retrieval for ART, following written consent and with local Ethics Committee permission (Nr. 796 19th June 2014, Reggio Emilia, Italy). Patients had to match these criteria: absence of endocrine abnormalities and viral/bacterial infections, age between 25 and 45 years. Cells were recovered from the follicular washing fluid using a 50% Percoll density gradient (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK), following a protocol previously described (7, 44, 45). In order to restore expression of gonadotropin receptors (46), hGLC were cultured 6 days, then serum-starved over-night before use in experiments. Cells were cultured at 37°C and 5% CO2 in McCoy's 5A medium, supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 IU/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin and 250 ng/ml Fungizone (Sigma-Aldrich).
BRET Measurement of cAMP Production, and β-arrestin Recruitment and Intracellular Ca2+ Increase
Intracellular cAMP and Ca2+ increase, and β-arrestin 2 recruitment were evaluated following a previously described procedure (15, 41, 47). Cyclic-AMP production and Ca2+ increase were evaluated in transiently transfected HEK293 cells using the FSHR-expressing plasmid, together with the BRET-based cAMP biosensor CAMYEL (48), or the aequorin Ca2+-biosensor expression vector (49), respectively, while BRET experiments cannot be performed in hGLC due to sub-optimal transfection efficiency and the high mortality rate in this cell model. Recruitment of β-arrestin 2 was assessed after transient transfection of HEK293 cells with the C-terminal, Rluc-tagged FSHR cDNA plasmid (provided by Dr. Aylin C. Hanyaloglu, Imperial College, London, UK) and N-terminal, yPET-tagged β-arrestin 2 (provided by Dr. Mark G. Scott, Cochin Institute, Paris, France). Cells were incubated 30 min in 40 μl/well PBS and 1 mM Hepes, in the presence or in the absence of increasing concentrations of Gonal-f® or biosimilars (1 × 10−3-1 × 103 ng/ml range), and intracellular cAMP increase and β-arrestin 2 recruitment were measured upon addition of 10 μl/well of 5 μM Coelenterzine h (Interchim). A 4 × 103 ng/ml hormone concentration-induced intracellular Ca2+ increase was evaluated over 100 s in transfected cells. Recombinant follitropin alfa or biosimilar addition occurred at the 25 s time-point. Light emissions were detected at 475 ± 30 and 530 ± 30 nm wavelengths using the CLARIOstar plate reader equipped with a monocromator (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany).
Evaluation of ERK1/2 and CREB Phosphorylation
Hormone-induced ERK1/2 and CREB phosphorylation was analyzed by Western blotting following a protocol previously described (50). Human GLCs were seeded in 24-well plates (1 × 105 cells/well) and treated for 15 min with increasing concentrations of gonadotropin (1 × 101-1 × 103 ng/ml range). Cells were immediately lysed for protein extraction in ice-cold RIPA buffer along with PhosStop phosphatase inhibitor and a protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Cell lysates were subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE and Western blotting, while pERK1/2 and pCREB activation were evaluated using specific rabbit antibodies (#9101 and #9198, respectively; Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Danvers, MA, USA). Sample loads were normalized to total ERK1/2 (#4695; Cell Signaling Technology Inc.). Membranes were treated with secondary anti-rabbit HRP-conjugated antibody (#NA9340V; GE HealthCare) and signals developed with ECL (GE HealthCare). Signal detection employed the VersaDoc system using the QuantityOne analysis software (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.). Protein density volumes were semi-quantitatively evaluated by the ImageJ software (U. S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) (51).
Gene Expression Analysis
Hormone 50% effective concentrations (EC50s) were calculated from the cAMP dose-response curves and used for hGLC treatments before FSH-target gene expression analysis. Cells were seeded at 5 × 104 cells/well in 24-well plates and exposed to gonadotropins for 8 h, and RNA was then extracted using the automated workstation EZ1 Advanced XL (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Equal amounts of total RNA were retrotranscribed by iScript reverse transcriptase (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.), according to a previously validated protocol (52). The expression of STARD1 and CYP19A1 genes encoding steroid-acute regulatory protein (StAR) and aromatase enzymes, respectively, was evaluated by real time PCR (7, 44) using specific primer sequences and protocols previously validated (7). Target gene expression was normalized to ribosomal protein subunit 7 (RPS7) gene expression using the 2−ΔΔCt method (53). Experiments were recorded as the mean value of duplicates.
Steroid Hormone Stimulation Protocol and Measurement
Human GLCs were seeded in 24-well plates (4 × 104 cells/well) and treated 8 or 24 h with increasing hormone concentrations (1 × 10−3-1 × 103 ng/ml). Where appropriate, 1 μM 4-androstene-3,17-dione (androstenedione; #A9630; Sigma-Aldrich) was added, as a substrate to be converted to estrogen by the aromatase enzyme. Stimulations were terminated by freezing samples and total progesterone or estradiol was measured in the cell media by an immunoassay analyzer (ARCHITECT second Generation system; Abbot Diagnostics, Chicago, IL, USA).
Statistical Analysis
Data were graphically represented using box and whiskers plots, histograms, X-Y graphs and tables, and indicated as means ± standard error of means (SEM). Western blotting results were normalized to total ERK signals. Intracellular Ca2+ increase was represented as kinetics of acceptor emissions measured at 525 ± 30 nm, and area under the curve (AUC) values were extrapolated for comparisons between preparations. Dose-response curves for cAMP and β-arrestin 2 were obtained by data interpolation using non-linear regression. BRET data were represented as induced BRET changes by subtracting the ratio of donor/acceptor biosensor emissions of the untreated cells from the values of the stimulated cells. Data distributions were analyzed by D'Agostino and Pearson normality test, while differences were evaluated by Kruskal-Wallis or Friedman test with Dunn's multiple comparison post-test and considered significant when p < 0.05. Statistics were performed using the GraphPad Prism 6.01 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Results
Western Blotting and Silver Staining Analysis
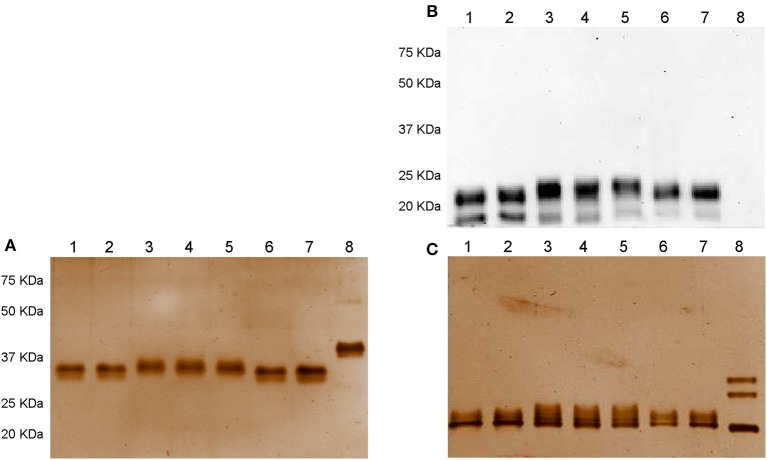
Samples comprising 300 ng/well of non-denatured and denatured Gonal-f® and biosimilar preparations were loaded onto a 12% acrylamide gel and separated by SDS gel electrophoresis under denaturing-reducing and non-denaturing-non reducing conditions. Denaturing conditions refer to 100°C-boiled samples, while reducing conditions were obtained by adding 2-mercaptoethanol. While no signals were detected under non denaturing-non reducing conditions by Western blotting (data not shown), two bands corresponding to the reference follitropin alfa and biosimilar preparations were revealed under denaturing-reducing conditions (Figure 1A). Ovaleap® and Gonal-f® preparations featured an ~20 KDa band, while a band corresponding to about 23 KDa molecular weight characterized Bemfola®. All preparations displayed a 15 KDa band of varying intensity. Recombinant hCG served as a negative control, providing no signal using the anti-FSH antibody.
Figure 1.
Western blotting (A) and silver staining analysis (B,C) of Gonal-f® and biosimilars under non-denaturing-non reducing and denaturing-reducing conditions. Samples comprising 300 ng of each preparation, according to the quantification provided by the manufacturer, were loaded. FSH presence was detected by rabbit anti-human polyclonal primary antibody against FSHβ/FSH. Recombinant hCG was used as negative control. Samples were loaded as follows: (1) Ovaleap® batch R38915, (2) Ovaleap® batch S27266, (3) Bemfola® batch PPS30400, (4) Bemfola® batch PNS30388, (5) Bemfola® batch PNS30230, (6) Gonal-f® batch AU016646, (7) Gonal-f® batch BA045956, (8) recombinant hCG. (A) Evaluation of FSH preparations under denaturing-reducing conditions, by Western blotting, using anti-FSHβ antibody. (B) Silver staining analysis of FSH preparations under non-denaturing-non reducing conditions. (C) Analysis of FSH preparations under denaturing-reducing conditions, by silver staining.
Analysis by silver staining under non denaturing-non reducing conditions revealed that all preparations shared an overall similar protein pattern characterized by a single band at about 37 KDa molecular weight (Figure 1B). hCG resulted in a 40 KDa band. All samples displayed signals at about 20 KDa molecular weight (Figure 1C). Interestingly, no 15-KDa signals were detected, oppositely to that demonstrated by Western blotting, likely to be attributed to the low amount of FSHβ bound by the antibody and undetectable using silver staining due to sub-optimal sensitivity of this method (54). Three 35–20 KDa bands corresponding to recombinant hCG Ovitrelle® were detected, as previously described (41).
Reference Follitropin Alfa and Biosimilar Reactivity to Lectins
The carbohydrate structure of follitropin alfa and biosimilars was investigated by ELISA, using a panel consisting of seven lectins characterized by specific recognition of different glycan features (Supplemental Table 1). Batches of each hormone were considered as experimental replicates and absorbance values measured at 450 nm were compared (Table 1).
Table 1.
ELISA lectin analysis of reference and biosimilar follitropin alfa preparations.
| Lectins | Gonal–f® | Ovaleap® | Bemfola® | pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance (nm; means ± SEM*103) | Absorbance (nm; means ± SEM*103) | Absorbance (nm; means ± SEM*103) | ||
| MAA | 74 ± 10 | 56 ± 1 | 60 ± 6 | 0.236 |
| SNA | −2 ± 1 | −35 ± 1 | −40 ± 1 | 0.236 |
| Jacalin | −1 ± 8 | −9 ± 4 | −17 ± 2 | 0.749 |
| Ricin | 120 ± 3 | 70 ± 2 | 180 ± 2 | <0.0001 |
| DSA | 250 ± 8 | 370 ± 13 | 460 ± 8 | 0.001 |
| PHA–E | 1300 ± 30 | 1350 ± 40 | 1300 ± 30 | 0.814 |
| WGA | 100 ± 7 | 50 ± 5 | 80 ± 3 | 0.809 |
Kruskal Wallis test and Dunn's post-test.
Bemfola® displayed structural peculiarities and variability, emerging by lectin analysis (Supplemental Table 2), due to significantly higher reactivity against ricin than other preparations (Kruskal-Wallis test; p < 0.05; n = 16; Table 1). Moreover, lectin assay revealed higher affinity of Bemfola® to DSA than Gonal-f® (Kruskal Wallis test; p < 0.05; n = 6). Ricin recognizes Galβ(1,4)GlcNAc monomers with higher affinity in the absence of sialylation in the terminal galactose, while DSA lectin binds Galβ(1,4) linked N-acetylglucosamine oligomers and a branched pentasaccharide sequence, including two N-acetyl lactosamine repeats linked to a mannose (55). No signal was detected with SNA lectin regardless of the hormone tested, indicating that sialic acid of the α(2,6) type is absent (56), likely due to the absence of galactoside α(2,6) sialyltransferase enzyme expression by CHO-K1 cells (57). Sialic acid of α(2,3) type is detected by MAA lectin in all samples (58), without any significant preparation-specific pattern. Jacalin failed to produce any signal, demonstrating the absence of O-glycans of the Galβ1-3GalNac or GalNac type (59). PHA-E lectin recognizes bi-antennary complex-type N-glycan with outer Gal and bisecting GlcNAc sequences (60), while WGA lectin reacts with GlcNAc sequences and sialic acid (61). Antennarity (Table 2), sialylation (Table 3), and sialic acid (Table 4) distribution were analyzed by glycopeptide mapping of Gonal-f® and Ovaleap® batches.
Table 2.
Antennarity of reference and biosimilar follitropin alfa preparations.
| Glycosylation site | Antennarity distribution |
Gonal-f® (means ± SEM) |
Ovaleap® (means ± SEM) |
pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asn52 | Di-antennary | 88.5 ± 0.5 | 90.6 ± 0.9 | >0.999 |
| Tri-antennary | 11.0 ± 0.6 | 9.1 ± 0.7 | ||
| Tetra-antennary | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | ||
| A-Index | 2.1 ± 0.0 | 2.1 ± 0.0 | ||
| Asn78 | Di-antennary | 91.5 ± 0.4 | 93.0 ± 0.5 | >0.999 |
| Tri-antennary | 8.3 ± 0.4 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | ||
| Tetra-antennary | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ||
| A-Index | 2.1 ± 0.0 | 2.1 ± 0.0 | ||
| Asn7 | Di-antennary | 10.7 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 0.6 | >0.999 |
| Tri-antennary | 66.5 ± 1.1 | 73.2 ± 1.7 | ||
| Tetra-antennary | 19.3 ± 0.9 | 17.3 ± 1.7 | ||
| One Repeat containing | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | ||
| A-Index | 3.2 ± 0.0 | 3.2 ± 0.0 | ||
| Asn24 | Mono-antennary | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | >0.999 |
| Di-antennary | 87.5 ± 0.7 | 83.0 ± 1.2 | ||
| Tri-antennary | 7.7 ± 0.4 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | ||
| Tetra-antennary | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 6.1 ± 1.2 | ||
| One Repeat containing | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | ||
| A-Index | 2.2 ± 0.0 | 2.2 ± 0.0 |
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
Table 3.
Sialylation distribution in reference and biosimilar follitropin alfa preparations.
| Glycosylation site | Sialylation indexes |
Gonal-f® (means ± SEM) |
Ovaleap® (means ± SEM) |
pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asn52 | S-extent (%) | 96.0 ± 0.1 | 97.5 ± 0.2 | >0.999 |
| S-index | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | ||
| Asn78 | S-extent (%) | 85.0 ± 0.3 | 90.1 ± 0.2 | 0.400 |
| S-index | 1.8 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.0 | ||
| Asn7 | S-extent (%) | 91.3 ± 0.2 | 95.4 ± 0.4 | 0.100 |
| S-index | 2.9 ± 0.0 | 3.0 ± 0.0 | ||
| Asn24 | S-extent (%) | 88.0 ± 0.2 | 92.3 ± 0.7 | 0.100 |
| S-index | 1.9 ± 0.0 | 2.0 ± 0.0 |
Mann-Whitney's U-test.
Table 4.
Sialic acid distribution in reference and biosimilar follitropin alfa preparations.
| Glycosylation site | Sialic acid |
Gonal-f® (means ± SEM) |
Ovaleap® (means ± SEM) |
pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asn52 | NANA | 97.3 ± 0.1 | 94.0 ± 0.1 | >0.999 |
| NGNA | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | ||
| O-Acetylated NANA | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | ||
| Asn78 | NANA | 95.0 ± 0.3 | 89.9 ± 0.2 | >0.999 |
| NGNA | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 4.4 ± 0.2 | ||
| O-Acetylated NANA | 5.0 ± 0.3 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | ||
| Asn7 | NANA | 97.5 ± 0.4 | 95.4 ± 0.5 | >0.999 |
| NGNA | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | ||
| O-Acetylated NANA | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | ||
| Asn24 | NANA | 92.8 ± 0.3 | 90.2 ± 0.5 | >0.999 |
| NGNA | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 3.6 ± 0.1 | ||
| O-Acetylated NANA | 7.0 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.4 |
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
These features were similarly represented among preparations (Kruskal-Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 6), as well as among batches (Supplemental Results), at least in Gonal-f® and Bemfola® (Chi-square test; p ≥ 0.05), which appeared to be homogeneous, overall (Supplemental Tables 3–5).
Evaluation of Intracellular cAMP Increase and β-Arrestin 2 Recruitment
Transfected, FSHR-expressing HEK293 cells were used to compare intracellular cAMP increases and β-arrestin 2 recruitment induced by 30-min treatment with increasing doses of reference follitropin alfa and biosimilars. Different batches of each preparation were tested and dose-response curves obtained by plotting cAMP and β-arrestin 2 levels in a semi-log X-Y graph (Supplemental Figure 1), in order to calculate and compare EC50 values obtained from the individual dose-response-curves (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
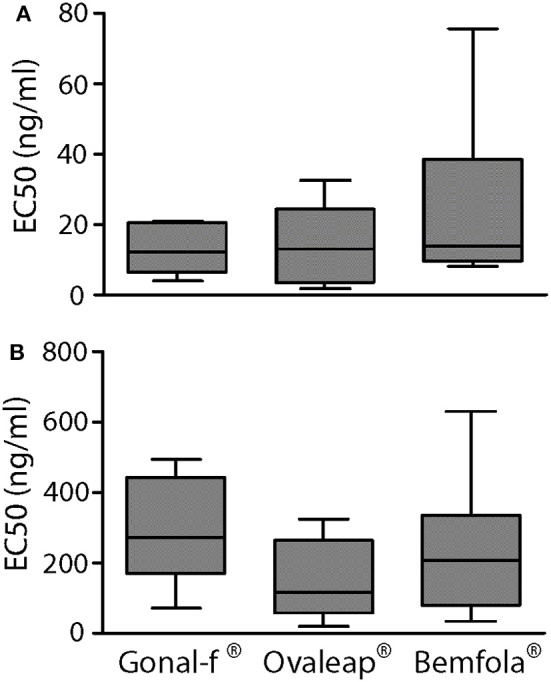
EC50 of cAMP response and β-arrestin 2 recruitment induced by Gonal-f® and biosimilars in transfected HEK293 cells. (A) Cells were transiently co-transfected with FSHR and CAMYEL sensor. cAMP was measured by BRET after 30 min stimulation with increasing doses of Gonal-f®, Ovaleap®, and Bemfola®. (B) Cells were transiently co-transfected with FSHR-Rluc8 and β-arrestin 2 –YPET sensors. β-arrestin 2 recruitment was measured by BRET after 30 min stimulation with increasing doses of hormones. EC50 values were extrapolated by non-linear regression. Data are represented as box and whiskers graphs (Kruskal Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4).
Although preparation-specific carbohydrate structures were detected (Table 1), no significant differences were found between Gonal-f® and biosimilars' EC50 required for activating cAMP (Table 5; 12.9 ± 2.5–24.2 ± 6.0 ng/ml range; Kruskal-Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4; Figure 2A) and β-arrestin 2 (Table 5; 140.7 ± 42.6–278.6 ± 56.9 ng/ml range; Kruskal-Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4; Figure 2B), consistent between batches (cAMP: 10 ± 0.0–28 ± 0.0 ng/ml range; β-arrestin 2: 64 ± 0.0–610 ± 0.2 ng/ml range; Kruskal-Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4; Supplemental Figure 1) and confirming similar potencies in vitro.
Table 5.
Efficiency (EC50) of 30 min-cAMP and β-arrestin 2 production induced by reference and biosimilar follitropin alfa preparations in transfected, FSHR-expressing HEK293 cells.
| Preparation |
EC50 cAMP (ng/ml; means ± SEM; n = 4) |
pa |
EC50 β-arrestin 2 (ng/ml; means ± SEM; n = 4) |
pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonal-f® | 12.9 ± 2.5 | 0.561 | 278.6 ± 56.9 | 0.223 |
| Ovaleap® | 14.7 ± 3.9 | 140.7 ± 42.6 | ||
| Bemfola® | 24.2 ± 6.0 | 234.9 ± 57.2 |
Kruskal-Wallis test.
Analysis of pERK1/2 and pCREB Activation
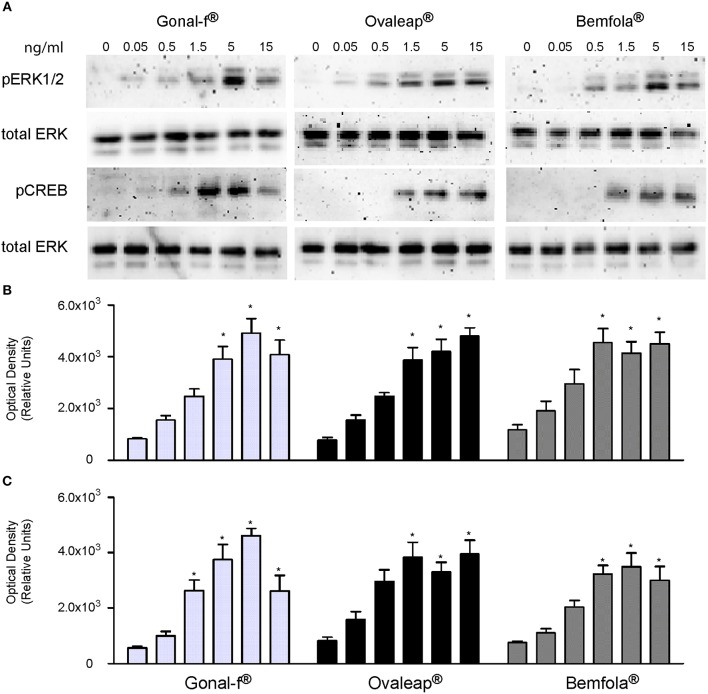
The phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and CREB was evaluated in hGLC, which naturally express endogenous FSHR. Cells were treated for 15 min with increasing hormone concentrations, and phospho-protein activation was evaluated by Western blotting and semi-quantitatively measured (Figure 3). Total ERK served as a normalizer.
Figure 3.
Evaluation of pERK1/2 and pCREB activation after Gonal-f® and biosimilars treatment of hGLC. Cells were stimulated by increasing doses of preparations. ERK1/2 and CREB phosphorylation were evaluated after 15 min by Western blotting (images representative of four independent experiments) (A). (B,C) Densitometric analysis of pERK1/2 (B) and pCREB (C) signals. The values were normalized to total ERK and represented as means ± SEM, then statistically evaluated (* = significant vs. control (0 dose); Kruskal Wallis test; p < 0.05; n = 4).
Similar ERK1/2 and CREB phosphorylation patterns were observed after stimulating cells with increasing doses of different batches of each preparation (Supplemental Figure 2). Mean results from batches of Gonal-f®, Ovaleap®, and Bemfola® were calculated and average hormone-specific pERK1/2 and pCREB activation results were reported (Figure 3). All preparations induced protein phosphorylation within the 1.5–15 ng/ml range (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.05; n = 4), consistently between different batches of each preparation (Friedman test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4). While no statistically significant differences between Gonal-f® and biosimilars' patterns of ERK1/2 phosphorylation were detected, pCREB activation occurred upon cell treatment by 0.5 ng/ml Gonal-f, differently to that obtained using both biosimilars (Friedman test, p < 0.05; n = 4). Interestingly, cell treatment by Gonal-f® and Bemfola® maximal concentrations (15 ng/ml) resulted in slightly decreased levels of CREB phosphorylation, not differing, however, significantly from the plateau levels of pCREB activation.
STARD1 and CYP19A1 Gene Expression Analysis
Expression of FSH target genes was analyzed by real time PCR in hGLC. For this purpose, cells were stimulated 12 h by Gonal-f®, Ovaleap® or Bemfola®. Hormones were administered at the EC50 calculated from cAMP data (12 ng/ml Gonal-f® and Ovaleap®, 24 ng/ml Bemfola®). Total RNA was reverse-transcribed to cDNA and used for STARD1 and CYP19A1 gene expression analysis by real-time PCR. Data were normalized over the RPS7 gene expression and represented as fold-increase over unstimulated cells in a bar-graph as means ± SEM (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
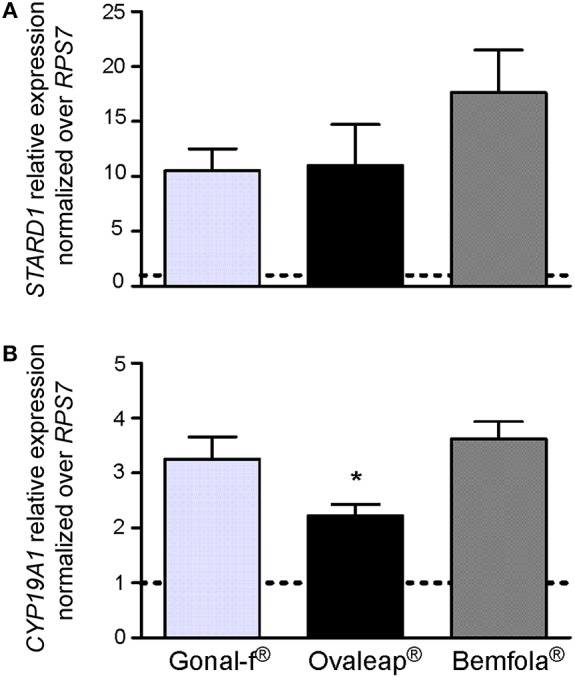
STARD1 and CYPA19A1 gene expression analysis. The expression of STARD1 (A) and CYPA19A1 (B) gene was evaluated in hGLC stimulated for 12 h with the EC50 of Gonal-f® or biosimilars (12 ng/ml Gonal-f® and Ovaleap®, 24 ng/ml Bemfola®) by real-time PCR. Each value was normalized over the RPS7 gene expression (means ± SEM; n = 4). Unstimulated cells served as control and are indicated as a dotted line. (*= significant vs. Bemfola®, Kruskal Wallis test; p < 0.05).
Gonal-f®, Ovaleap®, and Bemfola® resulted in about 15-fold STARD1 and 3-fold CYP19A1 increase compared to the basal level (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.05; n = 4). In particular, Ovaleap®-induced CYP19A1 expression level lower than what was obtained by Bemfola® treatment (Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.05; n = 4). Treatment using different batches did not to affect STARD1 and CYP19A1 expression levels, since no significant differences between lots of any preparation occurred (Kruskal-Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4; data not shown).
Steroid Synthesis Analysis
Progesterone production and androgen-to-estrogen conversion were evaluated in hGLC treated for 8 or 24 h with hormones. For this purpose, cells were maintained under continuous stimulation by increasing gonadotropin concentrations (1 × 10−3-1 × 103 ng/ml range) until reactions were stopped by freezing cell plates. To evaluate estradiol synthesis, androstenedione was added into wells as a substrate for the aromatase enzyme. Eight- and Twenty-four hours progesterone and estradiol dose-response curves were obtained and evaluated by non-linear regression, EC50 values calculated, and compared (Table 6).
Table 6.
FSH EC50 values (ng/ml) in inducing 8 h- and 24 h-progesterone and estradiol production induced by reference and biosimilar follitropin alfa preparations (means±SEM; n = 5) in human primary granulosa cells.
| Preparation | Progesterone | pa | Estradiol | pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 h | ||||
| Gonal-f® | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 10.3 ± 4.4 | ||
| Ovaleap® | 10.9 ± 3.7 | 0.285 | 5.6 ± 1.9 | 0.899 |
| Bemfola® | 4.4 ± 1.5 | 7.1 ± 2.6 | ||
| 24 h | ||||
| Gonal-f® | 15.4 ± 5.5 | 3.3 ± 1.0 | ||
| Ovaleap® | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 0.799 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 0.803 |
| Bemfola® | 7.3 ± 2.0 | 3.4 ± 1.0 | ||
Kruskal-Wallis test.
Reflecting cAMP accumulation, cell stimulation with Gonal-f®, Ovaleap®, and Bemfola® resulted in similar 8- and 24-h progesterone and estradiol production curves (Kruskal-Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 5), confirmed using different batches (Kruskal-Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 5; data not shown), as well as in similar progesterone and estradiol plateau levels (Kruskal-Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 5; Supplemental Table 6).
Intracellular Ca2+ Increase
Kinetics of intracellular Ca2+ increase was evaluated in a transiently transfected HEK293 cell line that co-expressed both FSHR- and Ca2+-biosensors, by BRET. Cells were monitored for over 100 s and 4 × 103 ng/ml hormone addition occurred at the 25 s time-point (Figure 5). A 10–20-fold supra-physiological FSH concentration was used, compared to FSH serum levels described in cycling women (62), due to the lack of an intracellular Ca2+ signal at lower hormone concentrations (data not shown). Thapsigargin and vehicle treatment were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Data were represented as means ± SEM. AUC values were calculated to compare preparation-specific intracellular Ca2+ increase.
Figure 5.
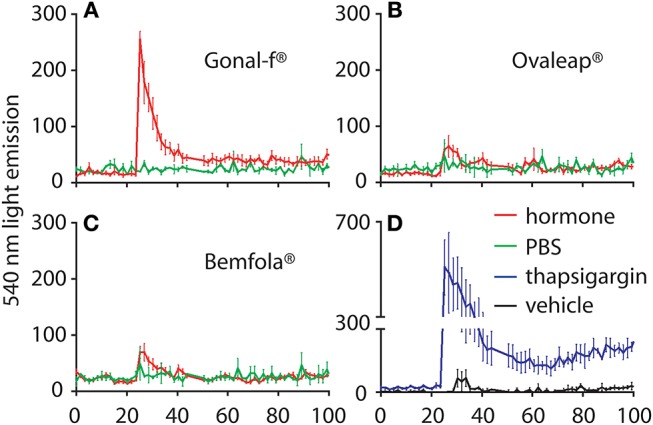
Calcium response kinetics in transfected HEK293 cells treated with Gonal-f® or biosimilars. Cells were transiently co-transfected with FSHR and aequorin sensors, then stimulated in duplicates with a fixed dose (4 × 103 ng/ml) of (A) Gonal-f®, (B) Ovaleap®, (C) Bemfola®. (D) Thapsigargin, PBS and hormone diluent were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. BRET signal was measured for 100 s. Data are represented as means ± SEM (n = 3). Area under the curve (AUC) values were calculated and differences were considered for p < 0.05 (Kruskal Wallis test).
Addition of vehicle failed to induce any intracellular Ca2+ increase, confirming the lack of activity exerted by the solvent used for hormone dilution on calcium response. After confirming the absence of batch-specific results (Kruskal-Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 3; data not shown), cell treatment by Gonal-f® induced rapid intracellular Ca2+ increase, which was about 230-fold higher than vehicle (Kruskal-Wallis test; p < 0.05; n = 3) and occurred within 1–2 s after hormone addition. Bemfola® and Ovaleap® induced only a minimal, not significant intracellular Ca2+ increase (Kruskal-Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 3). Maximal levels of intracellular Ca2+ were achieved under thapsigargin treatment, which served as a positive control and induced an about 600-fold greater increase compared to the basal level (Kruskal-Wallis test; p < 0.05; n = 3).
Discussion
We compared the biochemical profiles and hormone-induced cell responses of the reference follitropin alfa (Gonal-f®) and two biosimilars, Ovaleap® and Bemfola®, in vitro, revealing overall comparable hormone-induced intracellular signaling and steroidogenesis. Only the originator follitropin alfa induced hormone-specific pattern of CREB phosphorylation and, at supra-physiological concentrations (62), intracellular Ca2+ increase to transfected, FSHR-expressing cell lines.
Several gonadotropin formulations are commercially available, differing by source, purification process, and purity. Clinicians choose freely what preparation or combination of preparations will be administered to women undergoing ART (35). These preparations may differ in oligosaccharide content and number of branches attached to the protein backbone (63), depending on the glycosyltransferases equipment of the source cell. Gonal-f® is expressed by Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines (64), ensuring high bioactivity and batch-to-batch consistency (65, 66). Bemfola® is produced by a pre-adapted dihydrofolate reductase deficient CHO (CHO DHFR-) host cell line (67) and has demonstrated similar efficacy and safety in vivo as compared to the reference follitropin alfa, in a multi-center phase 3 study (68). Ovaleap® is also produced by a CHO-derived cell line after adaptation to serum free conditions (69) and has been demonstrated to be similar to follitropin alfa in vivo in a phase 3 clinical study (70).
Gonal-f® and Ovaleap® share two similar Western blotting patterns under denaturing and reducing conditions, likely due to specifically glycosylated FSH β-subunits (36, 37), while Bemfola® featured a ~23 instead of 20 KDa band according to its specific glycosylation pattern detected by mass spectrometry (36). Most of these signals were confirmed by silver staining, except for the absence of the 15 KDa band, likely due to sub-optimal sensitivity of the method (54). Analysis of native proteins contained in Gonal-f® and Ovaleap® batches, which were obtained by omitting treatment of samples by 100°C-heating and 2-mercaptoethanol reduction, revealed a single 37 KDa band consistent with the FSH heterodimer (71), while Bemfola® resulted in slightly higher apparent molecular weight. On the other hand, lectin assay revealed higher DSA signal in Bemfola® than Gonal-f®, likely due to different multiantennary complex structures on N-glycans demonstrated by glycopeptide mapping (36), and suggesting Bemfola®-specific glycosylation patterns. Lower ricin binding to Ovaleap® than to Bemfola® and Gonal-f® indicated a different content of Galβ1-4GlcNAc molecules (72).
Naturally occurring variations in carbohydrate structures were characterized during the follicular phase of the cycle (22) and might affect FSH bioactivity in vivo (73). Highly glycosylated FSH isoforms prevail at the early stages, while serum levels of less-acidic (sialylated) glycoforms increase at the mid-cycle until ovulation (29), suggesting a functional role of glycosylation and sialylated structures in modulating FSH bioactivity (26). However, crystallographic structures of FSH in complex with the receptor ectodomain suggested that carbohydrates are not located in the binding interface between the hormone and FSHR (74, 75), making unclear the physiological role of FSH sugar residues in hormone activity. In fact, analysis of signaling cascades revealed that cell treatment by Gonal-f® and biosimilars resulted in similar dose-response curves for both cAMP and β-arrestin 2, as well as ERK1/2 phosphorylation pattern. These results were replicated using different batches and are strengthened by similar ratios between EC50s observed for cAMP and β-arrestin 2 recruitment, confirming previously reported results obtained with follitropin alfa (15). On the other hand, the crystallographic structure of the human FSH bound to the extracellular binding domain of FSHR was obtained using partially deglycosylated hormone-receptor complexes (74). Therefore, it might be not fully descriptive of the role of sugar chains linked to the hormone in binding the receptor, providing a basis for explaining preparation-specific features, such as the higher potency of Gonal-f® in inducing CREB activation. These characteristics are likely linked to a relatively wide FSH EC50 range of progesterone response (Table 6; from 1.5 ± 0.3 to 10.9 ± 3.7 ng/ml), although not significantly different, presumably due to biased signaling (76, 77) of preparations.
Preparation-specific glycosylation patterns may be reflected by cellular response to supra-physiological doses of FSH in vitro. Biosimilar compounds induce barely detectable Ca2+ increases in FSHR-expressing HEK293 cells, which differed to that of Gonal-f® as previously reported using human pituitary FSH (78). FSHR is known to modulate intracellular Ca2+ increase via a molecular mechanism involving the phospholipase C (19). However, Gonal-f®-induced Ca2+ increase was obtained by hormone concentrations usually not achieved in vivo (62), while cAMP activation, and ERK1/2 CREB phosphorylation occurs at FSH doses achievable in serum, suggesting a supraphysiological shift from Gαs to Gαq protein-mediated activation of intracellular signaling cascades (8, 79). These data should be confirmed in other cell models, such as hGLC, since the pattern of intracellular signaling pathways is cell-specific and depends on the number and variety of GPCRs located at the cell surface (12, 79–81). Most importantly, preparation-specific activation of cAMP/β-arrestin 2 and intracellular Ca2+ increase indicated that these hormones might act as biased ligands under particular conditions, as well as the high sensitivity of the cAMP response detectable in vitro.
Confirming similar, FSH-induced STARD1 expression in hGLC, no differences in 8 and 24 h-progesterone and estradiol production between hormones was found, despite their structural peculiarities and lower Ovaleap®-induced CYP19A1 expression levels. Previous studies reported preparation-specific intracellular signaling resulting in similar long-term effects, measurable as 24-h steroid production (41, 45). These data are reminiscent of the earlier debate about recombinant and urinary FSH preparations, which provided similar pregnancy rate per fresh transfer (35, 68), as well as similar pharmacokinetic profiles (82). However, the matter is still debated. Different ART outcomes, depending on the use of Bemfola® vs. Gonal-f®, were postulated, possibly explained by different glycosylation, especially sialylation patterns between the two preparations and/or higher batch-to-batch variability (36) and estradiol production (82), observed with Bemfola®. Further in vivo investigations and extensive clinical experience are necessary to characterize the possible occurrence of biosimilar preparation-specific effects (31).
Conclusions
Different glycosylation profiles are characteristic of the follitropin alfa and subsequent biosimilar preparations, likely due to the specific enzymatic equipment of the source cell lines. These molecular peculiarities do not result in major preparation-specific signals mediated at the intracellular level and steroid synthesis, which were found to be overall similar when follitropin alfa and biosimilars are used at concentrations resembling those obtained under physiological conditions. In light of the specific molecular features of these commercial compounds and of the slight differences demonstrated by the present study, and considering the relevance of their use for clinical purposes, the comparison between the reference follitropin alfa and biosimilar preparations merits further investigations in a variety of experimental settings.
Data Availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.
Ethics Statement
Human primary granulosa lutein cells (hGLC) were isolated from ovarian follicles of donor women undergoing oocyte retrieval for ART, under written consent and local Ethics Committee permission (Nr. 796 19th june 2014, Reggio Emilia, Italy).
Author Contributions
LR wrote a manuscript draft, performed experiments, and data analysis. SS, CL, DK, FD, EP, SL, ST, EG, AP, and AS contributed to experiments and edited the manuscript. FP and TT provided scientific and methodological assistance and edited the manuscript. JD, AN, MV, and LA provided assistance to experimental procedures and manuscript editing. ER and MS provided scientific support, data interpretation, and manuscript drafting. LC provided experiment management, data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript editing.
Conflict of Interest Statement
EG, AP, and AS are Merck KGaA employees. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Funding. This study was supported by the Departments of Excellence Programme of the Italian Ministry of University and Research to the Department of Biomedical, Metabolic and Neural Sciences, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy) and by the French National Research Agency (ANR) under the program Investissements d'Avenir Grant Agreement (LabEx MabImprove: ANR-10-LABX-53), and ARD 2020 Biomédicaments grant from Région Center Val de Loire. MS is a LE STUDIUM RESEARCH FELLOW, Loire Valley Institute for Advanced Studies, Orléans & Tours, France,—INRA—Center Val de Loire, 37380 Nouzilly, France, receiving funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 665790.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2019.00503/full#supplementary-material
Cyclic-AMP response and β-arrestin 2 recruitment induced by different batches of Gonal-f® and biosimilars in trasfected HEK293 cells. (A–C) Cells were transiently co-transfected with FSHR and the CAMYEL sensor. Cyclic-AMP was measured by BRET after 30 min stimulation with increasing doses of (A) Gonal-f®, (B) Ovaleap®, and (C) Bemfola® batches. (D–F) Recruitment of β-arrestin 2 was measured in FSHR-Rluc8 and β-arrestin 2-YPET biosensor-expressing cells by BRET, after 30-min treatment of with increasing doses of (D) Gonal-f®, (E) Ovaleap®, and (F) Bemfola®. Data were represented as means ± SEM. No significant differences between EC50 values were found (Kruskal Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4).
Densitometric analysis of pERK1/2 and pCREB activation induced by different batches of Gonal-f® and biosimilars in hGLC. Cells were stimulated with increasing doses of FSH preparations and 15 min- ERK1/2 (A) and CREB (B) phosphorylation evaluated by semi-quantitative Western blotting. Values were normalized to total ERK and represented as means ± SEM. Differences between batches of each preparation was statistically evaluated (Kruskal Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 4).
Lectin specific binding sites.
ELISA lectin analysis of different batches of originator and biosimilar follitropin alfa. Lectins were used as follows: MAA (n = 20), SNA (n = 14), Jacalin (n = 6), ricin (n = 16), DSA (n = 6), PHA-E (n = 8), WGA (n = 8). Hormone reactivity to lectins was represented as absorbance measured at 450 nm (means ± SEM)*103, after subtracting values obtained in the absence of gonadotropin. Data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test, taking p < 0.05 as significant.
Antennarity distribution of Gonal-f® and Ovaleap® batches.
Sialylation distribution of follitropin alfa and Ovaleap® batches. Asn7, Asn24, Asn52, and Asn78 were analyzed in terms of percentage.
Sialic acids distribution of follitropin alfa originator and Ovaleap® batches.
Eight h- and twenty four hours-progesterone and estradiol plateau levels induced by Gonal-f® and biosimilar stimulation of human primary granulosa cells. Data are represented as means ± SEM (Kruskal-Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 5).
Glycopeptide mapping.
Supplemental Results.
References
- 1.Themmen APN, Huhtaniemi IT. Mutations of gonadotropins and gonadotropin receptors: elucidating the physiology and pathophysiology of pituitary-gonadal function. Endocr Rev. (2000) 21:551–83. 10.1210/edrv.21.5.0409 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simoni M, Gromoll J, Nieschlag E. The follicle-stimulating hormone receptor: biochemistry, molecular biology, physiology, and pathophysiology. Endocr Rev. (1997) 18:739–73. 10.1210/er.18.6.739 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lamminen T, Jokinen P, Jiang M, Pakarinen P, Simonsen H, Huhtaniemi I. Human FSHβ subunit gene is highly conserved. Mol Hum Reprod. (2005) 11:601–5. 10.1093/molehr/gah198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bishop LA, Robertson DM, Cahir N, Schofield PR. Specific roles for the asparagine-linked carbohydrate residues of recombinant human follicle stimulating hormone in receptor binding and signal transduction. Mol Endocrinol. (1994) 8:722–31. 10.1210/me.8.6.722 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ulloa-Aguirre A, Timossi C, Damián-Matsumura P, Dias JA. Role of glycosylation in function of follicle-stimulating hormone. Endocrine. (1999) 11:205–16. 10.1385/ENDO:11:3:205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gloaguen P, Crépieux P, Heitzler D, Poupon A, Reiter E. Mapping the follicle-stimulating hormone-induced signaling networks. Front Endocrinol. (2011) 2:45. 10.3389/fendo.2011.00045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Casarini L, Moriondo V, Marino M, Adversi F, Capodanno F, Grisolia C, et al. FSHR polymorphism p.N680S mediates different responses to FSH in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2014) 393:83–91. 10.1016/j.mce.2014.06.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Conti M. Specificity of the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate signal in granulosa cell function. Biol Reprod. (2002) 67:1653–61. 10.1095/biolreprod.102.004952 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hunzicker-Dunn M, Maizels ET. FSH signaling pathways in immature granulosa cells that regulate target gene expression: branching out from protein kinase A. Cell Signal. (2006) 18:1351–9. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.02.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Seger R, Hanoch T, Rosenberg R, Dantes A, Merz WE, Strauss JF, et al. The ERK signaling cascade inhibits gonadotropin-stimulated steroidogenesis. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:8847. 10.1074/jbc.A117.006852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ulloa-Aguirre A, Reiter E, Crépieux P. FSH receptor signaling: complexity of interactions and signal diversity. Endocrinology. (2018) 159:3020–35. 10.1210/en.2018-00452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Casarini L, Santi D, Simoni M, Potì F. “Spare” luteinizing hormone receptors: facts and fiction. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 29:208–17. 10.1016/j.tem.2018.01.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Quintana J, Hipkin RW, Sánchez-Yagüe J, Ascoli M. Follitropin (FSH) and a phorbol ester stimulate the phosphorylation of the FSH receptor in intact cells. J Biol Chem. (1994) 269:8772–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Saltarelli D. Heterotrimetric Gi/o proteins control cyclic AMP oscillations and cytoskeletal structure assembly in primary human granulosa-lutein cells. Cell Signal. (1999) 11:415–33. 10.1016/S0898-6568(99)00012-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ayoub MA, Landomiel F, Gallay N, Jégot G, Poupon A, Crépieux P, et al. Assessing gonadotropin receptor function by resonance energy transfer-based assays. Front Endocrinol. (2015) 6:130. 10.3389/fendo.2015.00130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Escamilla-Hernandez R, Little-Ihrig L, Zeleznik AJ. Inhibition of rat granulosa cell differentiation by overexpression of Gαq. Endocrine. (2008) 33:21–31. 10.1007/s12020-008-9064-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nechamen CA, Thomas RM, Dias JA. APPL1, APPL2, Akt2 and FOXO1a interact with FSHR in a potential signaling complex. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2007) 260–2:93–9. 10.1016/j.mce.2006.08.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lin YF, Tseng MJ, Hsu HL, Wu YW, Lee YH, Tsai YH. A novel follicle-stimulating hormone-induced G alpha h/phospholipase C-delta1 signaling pathway mediating rat sertoli cell Ca2+-influx. Mol Endocrinol. (2006) 20:2514–27. 10.1210/me.2005-0347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Minegishi T, Tano M, Shinozaki H, Nakamura K, Abe Y, Ibuki Y, et al. Dual coupling and down regulation of human FSH receptor in CHO cells. Life Sci. (1997) 60:2043–50. 10.1016/S0024-3205(97)00191-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kara E, Crépieux P, Gauthier C, Martinat N, Piketty V, Guillou F, et al. A phosphorylation cluster of five serine and threonine residues in the C-terminus of the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor is important for desensitization but not for beta-arrestin-mediated ERK activation. Mol Endocrinol. (2006) 20:3014–26. 10.1210/me.2006-0098 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Reiter E, Ahn S, Shukla AK, Lefkowitz RJ. Molecular mechanism of β-arrestin-biased agonism at seven-transmembrane receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2012) 52:179–97. 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.010909.105800 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wide L, Eriksson K. Dynamic changes in glycosylation and glycan composition of serum FSH and LH during natural ovarian stimulation. Ups J Med Sci. (2013) 118:153–64. 10.3109/03009734.2013.782081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Davis JS, Kumar TR, May JV, Bousfield GR. Naturally occurring follicle-stimulating hormone glycosylation variants. J Glycomics Lipidom. (2014) 04:e117 10.4172/2153-0637.1000e117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ulloa-Aguirre A, Zarinan T. The follitropin receptor: matching structure and function. Mol Pharmacol. (2016) 90:596–608. 10.1124/mol.116.104398 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Meher BR, Dixit A, Bousfield GR, Lushington GH. Glycosylation effects on FSH-FSHR interaction dynamics: a case study of different FSH glycoforms by molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0137897. 10.1371/journal.pone.0137897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jiang C, Hou X, Wang C, May JV, Butnev VY, Bousfield GR, et al. Hypoglycosylated hFSH has greater bioactivity than fully glycosylated recombinant hFSH in human granulosa cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2015) 100:E852–60. 10.1210/jc.2015-1317 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Helenius A, Aebi M. Intracellular functions of N-linked glycans. Science. (2001) 291:2364–9. 10.1126/science.291.5512.2364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ulloa-Aguirre A, Timossi C, Barrios-de-Tomasi J, Maldonado A, Nayudu P. Impact of carbohydrate heterogeneity in function of follicle-stimulating hormone: studies derived from in vitro and in vivo models. Biol Reprod. (2003) 69:379–89. 10.1095/biolreprod.103.016915 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Anobile CJ, Talbot JA, McCann SJ, Padmanabhan V, Robertson WR. Glycoform composition of serum gonadotrophins through the normal menstrual cycle and in the post-menopausal state. Mol Hum Reprod. (1998) 4:631–9. 10.1093/molehr/4.7.631 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wide L, Hobson BM. Qualitative difference in follicle-stimulating hormone activity in the pituitaries of young women compared to that of men and elderly women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1983) 56:371–5. 10.1210/jcem-56-2-371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Orvieto R, Seifer DB. Biosimilar FSH preparations- are they identical twins or just siblings? Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2016) 14:32 10.1186/s12958-016-0167-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Roger SD, Mikhail A. Biosimilars: opportunity or cause for concern? J Pharm Pharm Sci. (2007) 10:405–10. Available online at: https://sites.ualberta.ca/~csps/JPPS10_3/ReviewArticle_1308/R_1380.html [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Santi D, Simoni M. Biosimilar recombinant follicle stimulating hormones in infertility treatment. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2014) 14:1399–409. 10.1517/14712598.2014.925872 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brinsden P, Akagbosu F, Gibbons LM, Lancaster S, Gourdon D, Engrand P, et al. A comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of two recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone preparations in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer. Fertil Steril. (2000) 73:114–6. 10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00450-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Casarini L, Brigante G, Simoni M, Santi D. Clinical applications of gonadotropins in the female: assisted reproduction and beyond. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. (2016) 143:85–119. 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mastrangeli R, Satwekar A, Cutillo F, Ciampolillo C, Palinsky W, Longobardi S. In-vivo biological activity and glycosylation analysis of a biosimilar recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone product (Bemfola) compared with its reference medicinal product (GONAL-f). PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0184139. 10.1371/journal.pone.0184139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Walton WJ, Nguyen VT, Butnev VY, Singh V, Moore WT, Bousfield GR. Characterization of human FSH isoforms reveals a nonglycosylated β-subunit in addition to the conventional glycosylated β-subunit. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2001) 86:3675–85. 10.1210/jc.86.8.3675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Steelman SL, Pohley FM. Assay of the follicle stimulating hormone based on the augmentation with human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinology. (1953) 53:604–16. 10.1210/endo-53-6-604 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Smithies O. Disulfide-bond cleavage and formation in proteins. Science. (1965) 150:1595–8. 10.1126/science.150.3703.1595 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chevallet M, Luche S, Rabilloud T. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Nat Protoc. (2006) 1:1852–8. 10.1038/nprot.2006.288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Riccetti L, Klett D, Ayoub MA, Boulo T, Pignatti E, Tagliavini S, et al. Heterogeneous hCG and hMG commercial preparations result in different intracellular signalling but induce a similar long-term progesterone response in vitro. Mol Hum Reprod. (2017) 23:685–97. 10.1093/molehr/gax047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Legardinier S, Klett D, Poirier JC, Combarnous Y, Cahoreau C. Mammalian-like nonsialyl complex-type N-glycosylation of equine gonadotropins in MimicTM insect cells. Glycobiology. (2005) 15:776–90. 10.1093/glycob/cwi060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bidart JM, Troalen F, Bousfield GR, Birken S, Bellet DH. Antigenic determinants on human choriogonadotropin alpha-subunit. I. Characterization of topographic sites recognized by monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. (1988) 263:10364–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Casarini L, Lispi M, Longobardi S, Milosa F, La Marca A, Tagliasacchi D, et al. LH and hCG action on the same receptor results in quantitatively and qualitatively different intracellular signalling. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e46682. 10.1371/journal.pone.0046682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Casarini L, Riccetti L, De Pascali F, Nicoli A, Tagliavini S, Trenti T, et al. Follicle-stimulating hormone potentiates the steroidogenic activity of chorionic gonadotropin and the anti-apoptotic activity of luteinizing hormone in human granulosa-lutein cells in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2016) 422:103–14. 10.1016/j.mce.2015.12.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nordhoff V, Sonntag B, von Tils D, Götte M, Schüring AN, Gromoll J, et al. Effects of the FSH receptor gene polymorphism p.N680S on cAMP and steroid production in cultured primary human granulosa cells. Reprod Biomed Online. (2011) 23:196–203. 10.1016/j.rbmo.2011.04.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Riccetti L, Yvinec R, Klett D, Gallay N, Combarnous Y, Reiter E, et al. Human luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin display biased agonism at the LH and LH/CG receptors. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:940. 10.1038/s41598-017-01078-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jiang LI, Collins J, Davis R, Lin KM, DeCamp D, Roach T, et al. Use of a cAMP BRET sensor to characterize a novel regulation of cAMP by the sphingosine 1-phosphate/G13 pathway. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:10576–84. 10.1074/jbc.M609695200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tricoire L, Tsuzuki K, Courjean O, Gibelin N, Bourout G, Rossier J, et al. Calcium dependence of aequorin bioluminescence dissected by random mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2006) 103:9500–5. 10.1073/pnas.0603176103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Casarini L, Riccetti L, De Pascali F, Gilioli L, Marino M, Vecchi E, et al. Estrogen modulates specific life and death signals induced by LH and hCG in human primary granulosa cells in vitro. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:926. 10.3390/ijms18050926 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. (2012) 9:671–5. 10.1038/nmeth.2089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Riccetti L, De Pascali F, Gilioli L, Potì F, Giva LB, Marino M, et al. Human LH and hCG stimulate differently the early signalling pathways but result in equal testosterone synthesis in mouse Leydig cells in vitro. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2017) 15:2. 10.1186/s12958-016-0224-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–ΔΔCT method. Methods. (2001) 25:402–8. 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kavran JM, Leahy DJ. Silver staining of SDS-polyacrylamide Gel. Methods Enzymol. 541:169–76. 10.1016/B978-0-12-420119-4.00014-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yamashita K, Totani K, Ohkura T, Takasaki S, Goldstein IJ, Kobata A. Carbohydrate binding properties of complex-type oligosaccharides on immobilized Datura stramonium lectin. J Biol Chem. (1987) 262:1602–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Shibuya N, Goldstein IJ, Broekaert WF, Nsimba-Lubaki M, Peeters B, Peumans WJ. The elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) bark lectin recognizes the Neu5Ac(alpha 2-6)Gal/GalNAc sequence. J Biol Chem. (1987) 262:1596–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Xu X, Nagarajan H, Lewis NE, Pan S, Cai Z, Liu X, et al. The genomic sequence of the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-K1 cell line. Nat Biotechnol. (2011) 29:735–41. 10.1038/nbt.1932 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wang WC, Cummings RD. The immobilized leukoagglutinin from the seeds of Maackia amurensis binds with high affinity to complex-type Asn-linked oligosaccharides containing terminal sialic acid-linked alpha-2,3 to penultimate galactose residues. J Biol Chem. (1988) 263:4576–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kabir S. Jacalin: a jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) seed-derived lectin of versatile applications in immunobiological research. J Immunol Methods. (1998) 212:193–211. 10.1016/S0022-1759(98)00021-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Narasimhan S, Freed JC, Schachter H. The effect of a “bisecting” N-acetylglucosaminyl group on the binding of biantennary, complex oligosaccharides to concanavalin A, Phaseolus vulgaris erythroagglutinin (E-PHA), and Ricinus communis agglutinin (RCA-120) immobilized on agarose. Carbohydr Res. (1986) 149:65–83. 10.1016/S0008-6215(00)90370-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Monsigny M, Roche AC, Sene C, Maget-Dana R, Delmotte F. Sugar-lectin interactions: how does wheat-germ agglutinin bind sialoglycoconjugates? Eur J Biochem. (1980) 104:147–53. 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04410.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sherman BM, Korenman SG. Hormonal characteristics of the human menstrual cycle throughout reproductive life. J Clin Invest. (1975) 55:699–706. 10.1172/JCI107979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Grass J, Pabst M, Chang M, Wozny M, Altmann F. Analysis of recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) by mass spectrometric approaches. Anal Bioanal Chem. (2011) 400:2427–38. 10.1007/s00216-011-4923-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Howles CM. Genetic engineering of human FSH (Gonal-F). Hum Reprod Update. (1996) 2:172–91. 10.1093/humupd/2.2.172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bassett RM, Driebergen R. Continued improvements in the quality and consistency of follitropin alfa, recombinant human FSH. Reprod Biomed Online. (2005) 10:169–77. 10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60937-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wolfenson C, Groisman J, Couto AS, Hedenfalk M, Cortvrindt RG, Smitz JE, et al. Batch-to-batch consistency of human-derived gonadotrophin preparations compared with recombinant preparations. Reprod Biomed Online. (2005) 10:442–54. 10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60819-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.EMA/65507/2013 rev.1 Assessment Report. Bemfola International non-Proprietary Name: Follitropin Alfa (2014). p. 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rettenbacher M, Andersen AN, Garcia-Velasco JA, Sator M, Barri P, Lindenberg S, et al. A multi-centre phase 3 study comparing efficacy and safety of Bemfola(®) versus Gonal-f(®) in women undergoing ovarian stimulation for IVF. Reprod Biomed Online. (2015) 30:504–13. 10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.EMA/CHMP/41467/2013 Ovaleap International Non-Proprietary Name: Follitropin Alfa. (2013). p. 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Strowitzki T, Kuczynski W, Mueller A, Bias P. Randomized, active-controlled, comparative phase 3 efficacy and safety equivalence trial of Ovaleap® (recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone) in infertile women using assisted reproduction technology (ART). Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2016) 14:1. 10.1186/s12958-015-0135-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Fox KM, Dias JA, Van Roey P. Three-dimensional structure of human follicle-stimulating hormone. Mol Endocrinol. (2001) 15:378–89. 10.1210/mend.15.3.0603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Green ED, Brodbeck RM, Baenziger JU. Lectin affinity high-performance liquid chromatography. Interactions of N-glycanase-released oligosaccharides with Ricinus communis agglutinin I and Ricinus communis agglutinin II. J Biol Chem. (1987) 262:12030–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Campo S, Andreone L, Ambao V, Urrutia M, Calandra RS, Rulli SB. Hormonal regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone glycosylation in males. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:17. 10.3389/fendo.2019.00017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Fan QR, Hendrickson WA. Structure of human follicle-stimulating hormone in complex with its receptor. Nature. (2005) 433:269–277. 10.1038/nature03206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Jiang X, Liu H, Chen X, Chen PH, Fischer D, Sriraman V, et al. Structure of follicle-stimulating hormone in complex with the entire ectodomain of its receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2012) 109:12491–6. 10.1073/pnas.1206643109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ayoub MA, Yvinec R, Jégot G, Dias JA, Poli S-M, Poupon A, et al. Profiling of FSHR negative allosteric modulators on LH/CGR reveals biased antagonism with implications in steroidogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2016) 436:10–22. 10.1016/j.mce.2016.07.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Klein Herenbrink C, Sykes DA, Donthamsetti P, Canals M, Coudrat T, Shonberg J, et al. The role of kinetic context in apparent biased agonism at GPCRs. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10842. 10.1038/ncomms10842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Younglai EV, Kwan TK, Kwan CY, Lobb DK, Foster WG. Dichlorodiphenylchloroethylene elevates cytosolic calcium concentrations and oscillations in primary cultures of human granulosa-lutein cells. Biol Reprod. (2004) 70:1693–700. 10.1095/biolreprod.103.026187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Jonas KC, Chen S, Virta M, Mora J, Franks S, Huhtaniemi I, et al. Temporal reprogramming of calcium signalling via crosstalk of gonadotrophin receptors that associate as functionally asymmetric heteromers. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:2239. 10.1038/s41598-018-20722-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tranchant T, Durand G, Gauthier C, Crépieux P, Ulloa-Aguirre A, Royère D, et al. Preferential β-arrestin signalling at low receptor density revealed by functional characterization of the human FSH receptor A189 V mutation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2011) 331:109–18. 10.1016/j.mce.2010.08.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zhu X, Gilbert S, Birnbaumer M, Birnbaumer L. Dual signaling potential is common among Gs-coupled receptors and dependent on receptor density. Mol Pharmacol. (1994) 46:460–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wolzt M, Gouya G, Sator M, Hemetsberger T, Irps C, Rettenbacher M, et al. Comparison of pharmacokinetic and safety profiles between Bemfola(®) and Gonal-f(®) after subcutaneous application. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. (2016) 41:259–65. 10.1007/s13318-015-0257-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Cyclic-AMP response and β-arrestin 2 recruitment induced by different batches of Gonal-f® and biosimilars in trasfected HEK293 cells. (A–C) Cells were transiently co-transfected with FSHR and the CAMYEL sensor. Cyclic-AMP was measured by BRET after 30 min stimulation with increasing doses of (A) Gonal-f®, (B) Ovaleap®, and (C) Bemfola® batches. (D–F) Recruitment of β-arrestin 2 was measured in FSHR-Rluc8 and β-arrestin 2-YPET biosensor-expressing cells by BRET, after 30-min treatment of with increasing doses of (D) Gonal-f®, (E) Ovaleap®, and (F) Bemfola®. Data were represented as means ± SEM. No significant differences between EC50 values were found (Kruskal Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 4).
Densitometric analysis of pERK1/2 and pCREB activation induced by different batches of Gonal-f® and biosimilars in hGLC. Cells were stimulated with increasing doses of FSH preparations and 15 min- ERK1/2 (A) and CREB (B) phosphorylation evaluated by semi-quantitative Western blotting. Values were normalized to total ERK and represented as means ± SEM. Differences between batches of each preparation was statistically evaluated (Kruskal Wallis test; p ≥ 0.05; n = 4).
Lectin specific binding sites.
ELISA lectin analysis of different batches of originator and biosimilar follitropin alfa. Lectins were used as follows: MAA (n = 20), SNA (n = 14), Jacalin (n = 6), ricin (n = 16), DSA (n = 6), PHA-E (n = 8), WGA (n = 8). Hormone reactivity to lectins was represented as absorbance measured at 450 nm (means ± SEM)*103, after subtracting values obtained in the absence of gonadotropin. Data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test, taking p < 0.05 as significant.
Antennarity distribution of Gonal-f® and Ovaleap® batches.
Sialylation distribution of follitropin alfa and Ovaleap® batches. Asn7, Asn24, Asn52, and Asn78 were analyzed in terms of percentage.
Sialic acids distribution of follitropin alfa originator and Ovaleap® batches.
Eight h- and twenty four hours-progesterone and estradiol plateau levels induced by Gonal-f® and biosimilar stimulation of human primary granulosa cells. Data are represented as means ± SEM (Kruskal-Wallis test, p ≥ 0.05; n = 5).
Glycopeptide mapping.
Supplemental Results.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.