Abstract
The cold- and menthol-sensitive transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channel is important for both physiological temperature detection and cold allodynia. Activation of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) by proinflammatory mediators inhibits these channels. It was proposed that this inhibition proceeds via direct binding of Gαq to the channel. TRPM8 requires the plasma membrane phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2 or PIP2] for activity. However, it was claimed that a decrease in cellular levels of this lipid upon receptor activation does not contribute to channel inhibition. Here, we show that supplementing the whole-cell patch pipette with PI(4,5)P2 reduced inhibition of TRPM8 by activation of Gαq-coupled receptors in mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons isolated from both sexes. Stimulating the same receptors activated phospholipase C (PLC) and decreased plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2 levels in these neurons. PI(4,5)P2 also reduced inhibition of TRPM8 by activation of heterologously expressed muscarinic M1 receptors. Coexpression of a constitutively active Gαq protein that does not couple to PLC inhibited TRPM8 activity, and in cells expressing this protein, decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels using a voltage-sensitive 5′-phosphatase induced a stronger inhibition of TRPM8 activity than in control cells. Our data indicate that, upon GPCR activation, Gαq binding reduces the apparent affinity of TRPM8 for PI(4,5)P2 and thus sensitizes the channel to inhibition induced by decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Increased sensitivity to heat in inflammation is partially mediated by inhibition of the cold- and menthol-sensitive transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) ion channels. Most inflammatory mediators act via G-protein-coupled receptors that activate the phospholipase C pathway, leading to the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2]. How receptor activation by inflammatory mediators leads to TRPM8 inhibition is not well understood. Here, we propose that direct binding of Gαq both reduces TRPM8 activity and sensitizes the channel to inhibition by decreased levels of its cofactor, PI(4,5)P2. Our data demonstrate the convergence of two downstream effectors of receptor activation, Gαq and PI(4,5)P2 hydrolysis, in the regulation of TRPM8.
Keywords: DRG neuron, G-protein, GPCR, PIP2, TRPM8
Introduction
Transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) is a nonselective Ca2+-permeable cation channel activated by cold temperatures, as well as chemical agonists such as menthol, icilin, and WS12 (Almaraz et al., 2014). It is expressed in the primary sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and trigeminal ganglia (TG), and mice lacking these channels display deficiencies in sensing moderately cold (Bautista et al., 2007; Colburn et al., 2007; Dhaka et al., 2007) as well as noxious cold temperatures (Knowlton et al., 2010). TRPM8 may also play a role in cold allodynia induced by nerve injury (Xing et al., 2007).
DRG neurons express receptors for various inflammatory mediators, such as bradykinin, ATP, and prostaglandins. Most of those receptors couple to heterotrimeric G-proteins in the Gαq family and lead to activation of phospholipase C (PLC) (Rohacs, 2016). Activation of these Gαq-protein-coupled receptors induces thermal hyperalgesia (Caterina et al., 2000) via mechanisms including sensitizing the heat- and capsaicin-activated transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV1) channels (Cesare and McNaughton, 1996; Tominaga et al., 2001) and inhibiting the cold-activated TRPM8 (Premkumar et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2012).
The mechanism of the inhibition of TRPM8 by Gαq-coupled receptors is not fully understood. Protein kinase C (PKC) has been demonstrated to be involved in sensitization of TRPV1 (Numazaki et al., 2002; Bhave et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2008), but its involvement in TRPM8 inhibition is controversial (Premkumar et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2012). It was proposed that binding of Gαq to TRPM8 mediates inhibition of the channel (Zhang et al., 2012; Li and Zhang, 2013). Similar to most TRP channels (Rohacs, 2014), TRPM8 requires the membrane phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2 or PIP2] for activity (Liu and Qin, 2005; Rohács et al., 2005; Daniels et al., 2009; Zakharian et al., 2010). Ca2+ influx through the channel was shown to activate a Ca2+-sensitive PLC isoform, and the resulting decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels limits channel activity, leading to desensitization (Rohács et al., 2005; Daniels et al., 2009; Yudin et al., 2011, 2016). Stimulation of Gαq-coupled receptors leads to the activation of PLCβ isoforms, which hydrolyze PI(4,5)P2, but it was questioned whether this leads to a decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels in DRG neurons (Liu et al., 2010) and it was argued that a decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels does not play a role in TRPM8 channel inhibition (Zhang et al., 2012).
Here, we revisited this question and demonstrate that the decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels plays an important role in inhibition of TRPM8 by Gαq-coupled receptor activation in DRG neurons. First, we show that application of a mixture of inflammatory mediators that activate Gαq-coupled receptors (inflammatory cocktail) decreased PI(4,5)P2 levels and inhibited TRPM8 activity in DRG neurons. Supplementing the whole-cell patch pipette with PI(4,5)P2 alleviated the inhibition of TRPM8 by these receptor agonists. Excess PI(4,5)P2 also decreased the inhibition of heterologously expressed TRPM8 by activation of muscarinic M1 receptors. Coexpression of a constitutively active Gαq that is deficient in PLC activation inhibited TRPM8 activity, which is consistent with earlier results (Zhang et al., 2012). Coexpression of the PLC-deficient Gαq also increased the sensitivity of TRPM8 to inhibition by decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels using a specific voltage-sensitive phosphoinositide 5-phosphatase, providing a mechanistic framework of how Gαq inhibits TRPM8. Overall, our data indicate that a decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels and direct binding of Gαq converge on inhibiting TRPM8 activity upon cell surface receptor activation.
Materials and Methods
DRG neuron isolation and preparation.
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School. DRG neurons were isolated from 2- to 6-month-old WT C57BL6 (RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664) or TRPM8-GFP mice (Takashima et al., 2007) (RRID:IMSR_JAX:020650), as described previously (Yudin et al., 2016) with some modifications. We have extensively characterized electrophysiological properties of GFP+ DRG neurons in this reporter mouse in our earlier work (Yudin et al., 2016). DRG neurons were isolated from mice of either sex, anesthetized, and perfused via the left ventricle with ice-cold Hank's buffered salt solution (HBSS; Invitrogen). DRGs were harvested from all spinal segments after laminectomy and removal of the spinal column and maintained in ice-cold HBSS for the duration of the isolation. Isolated ganglia were cleaned from excess dorsal root nerve tissue and incubated in an HBSS-based enzyme solution containing 3 mg/ml type I collagenase (Worthington) and 5 mg/ml dispase (Sigma-Aldrich) at 37°C for 35 min, followed by mechanical trituration by repetitive pipetting through an uncut 1000 μl pipette tip. Digestive enzymes were then removed after centrifugation of the cells at 80 × g for 10 min. Cells were then either directly resuspended in growth medium and seeded onto glass coverslips coated with a mixture of poly-d-lysine (Invitrogen) and laminin (Sigma-Aldrich) or were first transfected using the Amaxa nucleoporator according to the manufacturer's instructions (Lonza). Briefly, 60,000–100,000 cells obtained from each animal were resuspended in 100 μl of nucleofector solution after complete removal of digestive enzymes. The cDNA used for transfecting neurons was prepared using the Endo-free Plasmid Maxi Kit from QIAGEN.
Vectors and reagent for transduction with the green PI(4,5)P2 Sensor (CAG-Promoter) #D0405G and red PI(4,5)P2 sensor (#D0405R) were obtained from Montana Molecular. Before seeding onto glass coverslips, ∼60,000–100,000 cells were resuspended in 500 μl of transduction mixture after complete removal of digestive enzymes. Neurons were maintained in culture for at least 24 h before measurements in DMEM-F12 supplemented with 10% FBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 100 IU/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin.
Human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cell culture and preparation.
HEK293 cells were obtained from the ATCC (catalog #CRL-1573, RRID:CVCL_0045) and cultured in minimal essential medium (Invitrogen) containing supplements of 10% (v/v) Hyclone-characterized FBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 100 IU/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin. Transient transfection was performed at ∼70% cell confluence with the Effectene reagent (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Cells were incubated with the lipid–DNA complexes overnight (16–20 h). The cDNA used for transfecting HEK 293 cells was prepared using the Endo-free Plasmid Maxi Kit from QIAGEN. The cDNA for the PLC deficient Gαq construct 3Gqiq was obtained from Dr. Xuming Zhang's laboratory (Zhang et al., 2012). The Q209L mutant of 3Gqiq was generated using the QuikChange Mutagenesis Kit (Agilent Technologies). Transduction was performed at ∼70% cell confluence with BacMam green PI(4,5)P2 sensor with CAG promoter and BacMam M1 receptor (Montana Molecular) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Cells were incubated with the transduction mixture overnight (16–24 h). Cells were then trypsinized and replated onto poly-d-lysine-coated glass coverslips and incubated for at least an additional 2 h (in the absence of the transfection reagent) before measurements. All mammalian cells were kept in a humidity-controlled tissue culture incubator maintaining 5% CO2 at 37°C.
Electrophysiology.
For whole-cell patch-clamp recordings, the room where the experiments were performed was heated to 27–30°C, as described previously (Yudin et al., 2016). This slightly higher than conventional room temperature was used because TRPM8 may show some basal activity at 22–24°C. Patch pipettes were pulled from borosilicate glass capillaries (1.75 mm outer diameter, Sutter Instruments) on a P-97 pipette puller (Sutter Instrument) to a resistance of 4–6 MΩ. After formation of seals, the whole-cell configuration was established and currents were measured at a holding potential of −60 mV (DRG neurons) or with a voltage ramp protocol from −100 mV to +100 mV (HEK293 cells) using an Axopatch 200B amplifier (Molecular Devices). Currents were filtered at 2 kHz using the low-pass Bessel filter of the amplifier and digitized using a Digidata 1440 unit (Molecular Devices). In some experiments, membrane potential pulses of indicated lengths to 100 mV were applied to activate the voltage-sensitive phosphatase (Ci-VSP), as described previously (Velisetty et al., 2016). Measurements were conducted in solutions based on either Ca2+-free (NCF) medium containing the following (in mm): 137 NaCl, 4 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 5 HEPES, 5 MES, 10 glucose, and 5 EGTA, pH adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH, or Ca2+ containing (NCF) medium containing the following (in mm): 137 NaCl, 5 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 10 HEPES, 10 glucose, and 2 CaCl2, pH adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH (Lukacs et al., 2013a). Intracellular solutions for DRG measurements (NIC-DRG) containined the following (in mm): 130 K-gluconate, 10 KCl, 2 MgCl2, 2 Na2ATP, 0.2 Na2GTP, 1.5 CaCl2, 2.5 EGTA, and 10 HEPES, pH adjusted to 7.25 with KOH. Intracellular solutions for HEK293 whole-cell measurements (NIC-HEK) consisted of the following (in mm): 130 KCl, 10 KOH, 3 MgCl2, 2 Na2ATP, 0.2 Na2GTP, 0.2 CaCl2, 2.5 EGTA, and 10 HEPES, pH adjusted to 7.25 with KOH (Lukacs et al., 2013b). DiC8 PI(4,5)P2 (Cayman Chemical) was dissolved in NIC. Carbachol and all chemicals in the inflammatory cocktail were from Sigma-Aldrich, BIM IV was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, and WS12 was from Alomone Labs.
Ca2+ imaging.
Ca2+-imaging measurements were performed with an Olympus IX-51 inverted microscope equipped with a DeltaRAM excitation light source (Photon Technology International). DRG neurons or HEK 293 cells were loaded with 1 μm fura-2 AM (Invitrogen) for 50 min in extracellular solution supplemented with 0.1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin before measurement at room temperature (27–30°C). Images at 340 and 380 nm excitation wavelengths were recorded with a Roper Cool-Snap digital CCD camera; emission wavelength was 510 nm. Measurements were conducted in NCF solution supplemented with 2 mm CaCl2. Image analysis was performed using Image Master software (PTI).
Confocal fluorescence imaging.
Confocal measurements for Figures 3, 4, and 7 were conducted with an Olympus FluoView-1000 confocal microscope in the frame scan mode (Olympus) using a 60× water-immersion objective at room temperature (∼25°C). GFP and YFP fluorescence were measured using an excitation wavelength of 473 nm; emission was detected through a 515/50 nm band-pass filter. WT DRG neurons or HEK 293 cells were transfected with YFP-Tubby R332H or YFP-Tubby WT cDNA at least 24 h before confocal measurements. Before each experiment, neurons or HEK 293 cells were serum deprived in Ca2+-free or 2 mm Ca2+-containing NCF solution for at least 20 min. For transduction experiments, WT DRG neurons or HEK 293 cells were transduced at least 24 h before confocal measurements by BacMam green PI(4,5)P2 sensor with CAG promoter and BacMam M1 receptor. Before each experiment, neurons or HEK 293 cells were serum-deprived in DPBS (Sigma-Aldrich) for 30 min in the dark. Image analysis was performed using Olympus FluoView-1000 and ImageJ. Confocal measurements in TRPM8-GFP reporter mouse DRG neurons with the red PI(4,5)P2 sensor (see Fig. 5) were conducted with a Nikon A1R-A1 confocal laser scanning microscope system using a 20× objective at room temperature (∼25°C). GFP fluorescence was measured at excitation wavelength 488 nm; emission was detected through a 525/50 nm bandpass filter. Red fluorescence was measured at excitation wavelength 561 nm; emission was detected through a 595/50 band-pass filter. Confocal images were collected using the NIS-Elements imaging software. Image analysis was performed using NIS-Elements, MetaMorph, and ImageJ software.
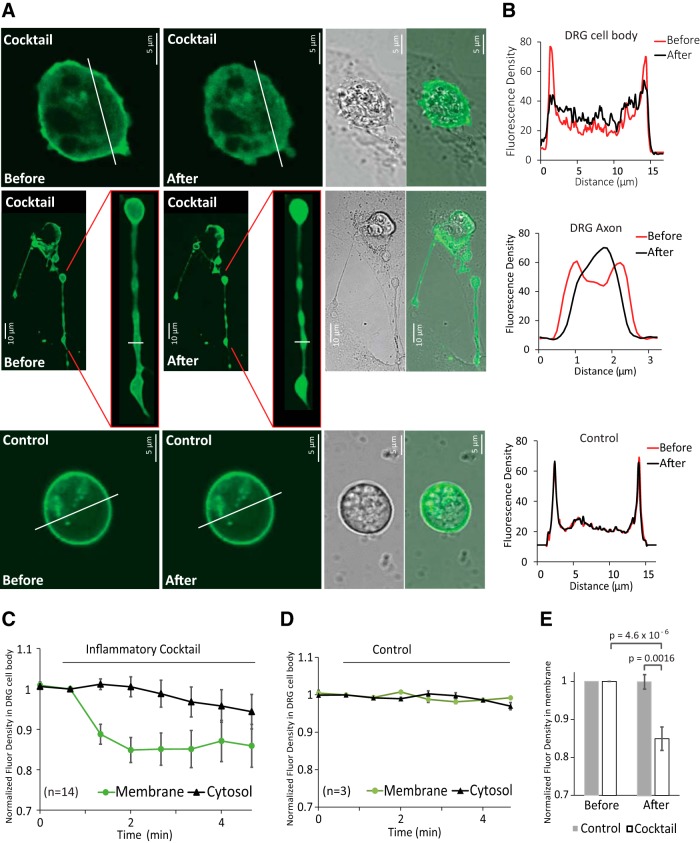
Figure 3.
Receptor-induced decrease of PI(4,5)P2 in the plasma membrane of DRG neurons. A, Confocal images of WT mouse DRG neurons transfected with YFP-tagged R322H Tubby domain as a reporter of plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2. Images are representatives of reporter distribution before and after application of either inflammatory cocktail (same as in Figs. 1 and 2) or control solution (2 mm Ca2+ NCF). Measurements were conducted in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution. Neurons were serum deprived in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution for 20 min. B, Graphs correspond to fluorescence intensities plotted along the lines indicated in each image in A before (red) and after (black) application of inflammatory cocktail or control. C, D, Time courses of fluorescence density changes for YFP-tagged R322H Tubby in response to control solution (C) or inflammatory cocktail (D) in plasma membrane and cytosol of neuron cell body. E, Statistical analysis of fluorescence density right before and 1 min after application of inflammatory cocktail (n = 14 neurons from 2 independent DRG preparations from 4 mice) and control solution (n = 3) displayed. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with two-way ANOVA (F(3,30) = 12.37, p = 1.9 × 10−5). Fluorescence density values were normalized to the time point of right before application of inflammatory cocktail or control solution for each group.
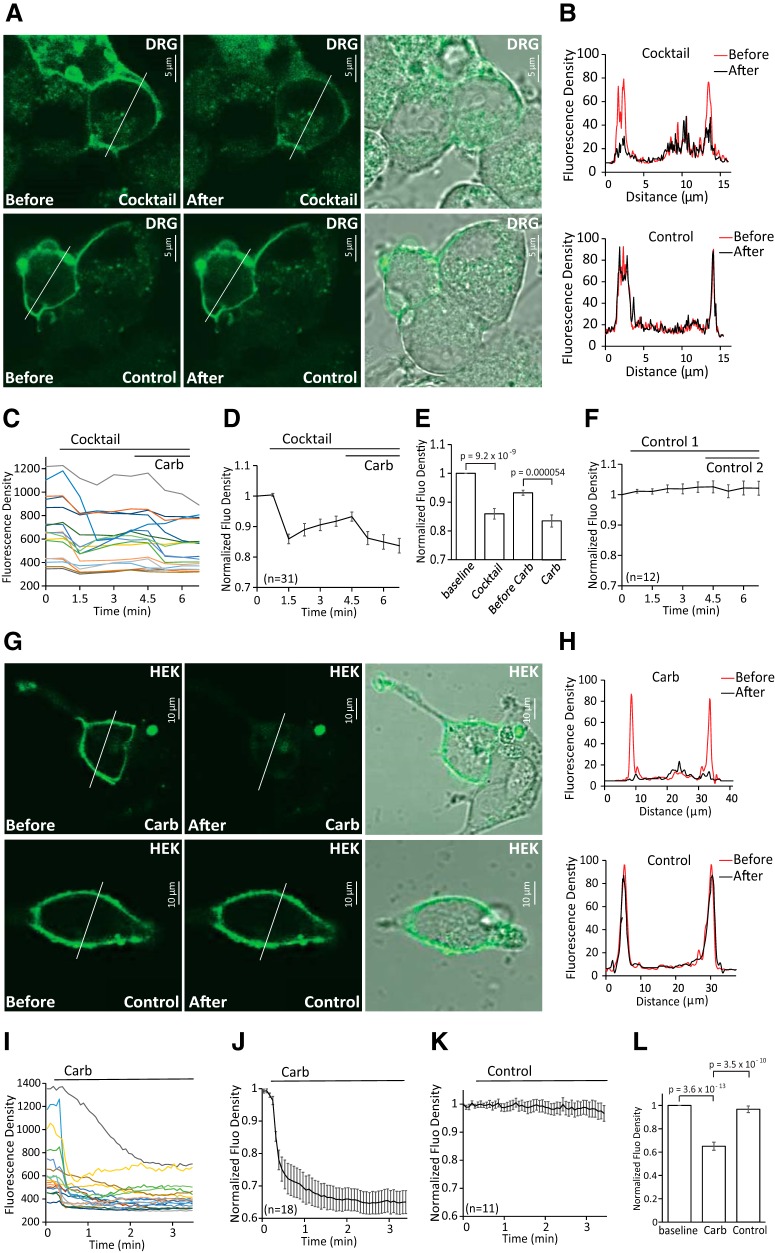
Figure 4.
Receptor-induced decrease of PI(4,5)P2 in DRG neurons and HEK 293 cells. A, Confocal images of WT mouse DRG neurons transduced with green PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam and human muscarinic cholinergic receptor 1 (M1). Images are representatives of reporter distribution before and after application of either the inflammatory cocktail (same as in Fig. 1) or control solution (2 mm Ca2+ NCF). Measurements were conducted in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution. B, Graphs correspond to fluorescence intensities plotted along the lines indicated in each image in A before (red) and after (black) application of inflammatory cocktail or control. C, Representative traces of time course changes for green PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam in response to cocktail followed by 100 μm carbachol in DRG neurons. D, Averaged time course of fluorescence density changes for green PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam in response to cocktail followed by 100 μm carbachol in DRG neurons. Four GFP+ neurons showed no changes in red fluorescence in response to cocktail application and only one of those four responded to carbachol; these cells were excluded from the summary. E, Statistical analysis of fluorescence density at baseline, 40 s after application of cocktail just before application of carbachol and 40 s after application of carbachol in neurons (n = 31) from two different DRG neuron preparations from two mice. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with one-way ANOVA (F(3,124) = 21.07, p = 4.5 × 10−11). Fluorescence density values were normalized to baseline. F, Time course of fluorescence density changes for green PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam in response to two applications of control solution (2 mm Ca2+ NCF) in DRG neurons (n = 12). G, Confocal images of HEK 293 cells transduced with green PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam as reporters of PI(4,5)P2 and human muscarinic receptor 1 (M1) receptor. Images are representatives of reporter distribution before and after application of either 100 μm carbachol or control solution (2 mm Ca2+ NCF). Measurements were conducted in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution. H, Graphs correspond to fluorescence intensities plotted along the lines indicated in each image in G before (red) and after (black) application of 100 μm carbachol or control. I, Representative traces of time course changes for green PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam in response to carbachol. J, K, Average time course of fluorescence density changes for green PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam in response to carbachol or control (2 mm Ca2+ NCF) in HEK 293 cells. L, Statistical analysis of fluorescence density at baseline and after application of carbachol (n = 18) or control (n = 11). Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with one-way ANOVA (F(2,44) = 60.03, p = 2.7 × 10 −13). Fluorescence density values were normalized to baseline.
Figure 7.
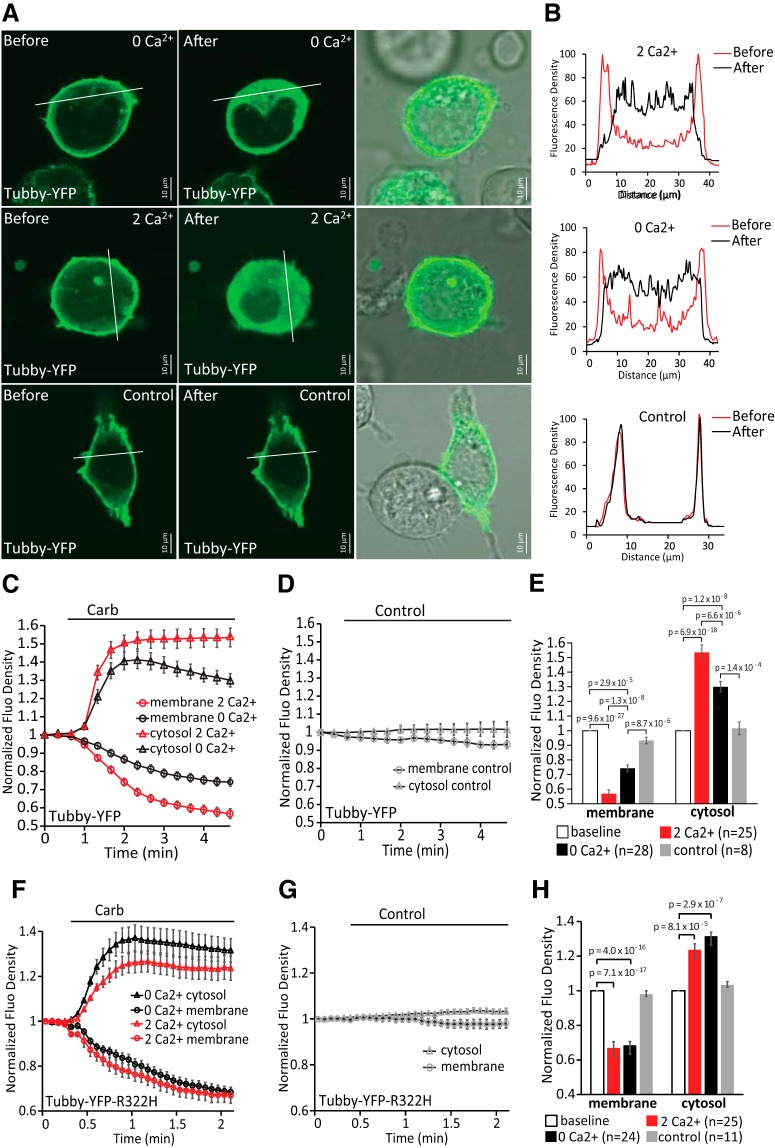
Receptor-induced depletion of PI(4,5)P2 in the plasma membrane of HEK 293 cells in the presence or absence of calcium. A, Confocal images of HEK 293 cells transfected with YFP-tagged WT Tubby domain as reporters of plasma membrane phosphoinositides and M1 receptor in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF or Ca2+-free NCF solution. Images are representatives of reporter distribution before and after application of either 100 μm carbachol or control solution (2 mm Ca2+ NCF). B, Graphs correspond to fluorescence intensities plotted along the lines indicated in each image in A before (red) and after (black) application of carbachol or control. C, D, Time courses of fluorescence density changes for YFP-tagged WT Tubby in response to carbachol (C) or control (D) in plasma membrane and cytosol of HEK 293 cells. E, Statistical analysis of fluorescence density at baseline and at the end after application of carbachol (n = 25 for 2 mm Ca2+ NCF, n = 28 for Ca2+-free NCF) and control (n = 8) is shown. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with one-way ANOVA (membrane: F(3,85) = 89.12, p = 0; cytosol: F(3,85) = 45.20, p = 0). Fluorescence density values were normalized to the baseline for each group. F, G, Similar experiments to those shown in C and D in HEK293 cell transfected with YFP-tagged R322H Tubby domain and M1 receptors. H, Statistical analysis of fluorescence density at baseline and at the end after application of carbachol (n = 25 for 2 mm Ca2+ NCF, n = 24 for Ca2+-free NCF) and control (n = 11) is shown. Bars represent mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA (membrane: F(3,80) = 57.41, p = 0; cytosol: F(3,80) = 12.97, p = 5.5 × 10−7). Fluorescence density values were normalized to the baseline for each group.
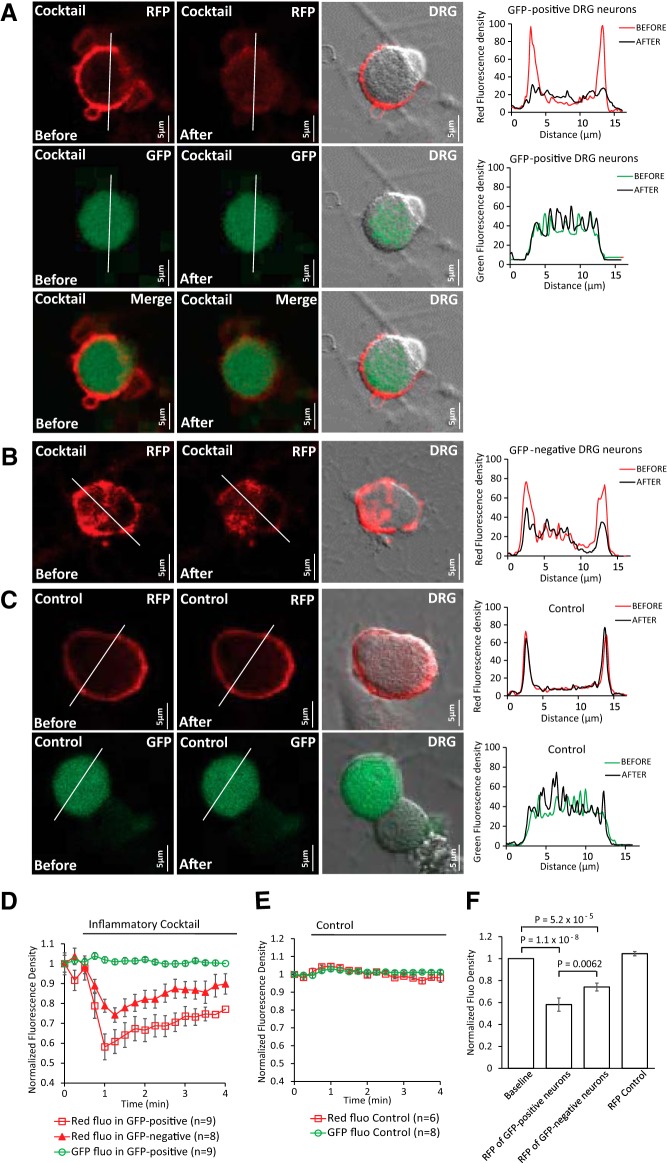
Figure 5.
Receptor-induced decrease of PI(4,5)P2 in TRPM8+ and TRPM8− DRG neurons. A–C, Confocal images of TRPM8-GFP mouse DRG neurons transduced with red PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam. Images are representatives of fluorescence density before and after application of either the inflammatory cocktail (same as in Fig. 1) or control solution (2 mm Ca2+ NCF). Graphs correspond to fluorescence intensities plotted along the lines indicated in each image before (red) and after (black) application of cocktail or control. (A, GFP+ DRG neurons with red PI(4,5)P2 sensor; B, GFP− DRG neurons with red PI(4,5)P2 sensor; C, bleaching controls of red fluorescence and GFP fluorescence in neurons). Measurements were conducted in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution. D, Averaged time course of fluorescence density changes for red PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam and GFP fluorescence in response to cocktail in DRG neurons. Four GFP− neurons with red fluorescence were excluded due to no changes of red fluorescence density after application of cocktail. E, Averaged time course of fluorescence density changes for red PI(4,5)P2 sensor BacMam and GFP fluorescence in response to control solution in DRG neurons. F, Statistical analysis of red fluorescence density at baseline and at the peak response after application of cocktail or control. Data are shown from three different neuron preparations from three mice. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with one-way ANOVA (F(3,28) = 31.02, p = 4.8 × 10−9). Fluorescence density values were normalized to baseline.
Total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) imaging.
TIRF measurements were performed on an Olympus IX-81 inverted microscope equipped with an ORCA-FLASH 4.0 camera (Hamamatsu) and a single-line TIRF illumination module. Excitation light was provided by a 488 nm argon laser through a 60× numerical aperture 1.49 TIRF objective. For the experiments shown in Figure 8, HEK293 cells were transfected with the human M1 receptor and either TRPM8 tagged with GFP on its N terminus (GFP-TRPM8) or with YFP-tubby. The GFP-TRPM8 clone was generated by subcloning the TRPM8 coding region into the pEGFP-C1 vector between the Xho1 and EcoR1 sites using standard molecular biological techniques. Cells were plated on 25 mm round glass coverslips and solutions were manually applied to the chamber with gentle mixing. For the experiments shown in Figure 9, E and F, HEK293 cells were transfected with GFP-TRPM8 or GFP-TRPM8 plus 3GqiqQ209L. Data were analyzed using MetaMorph and ImageJ software.
Figure 8.
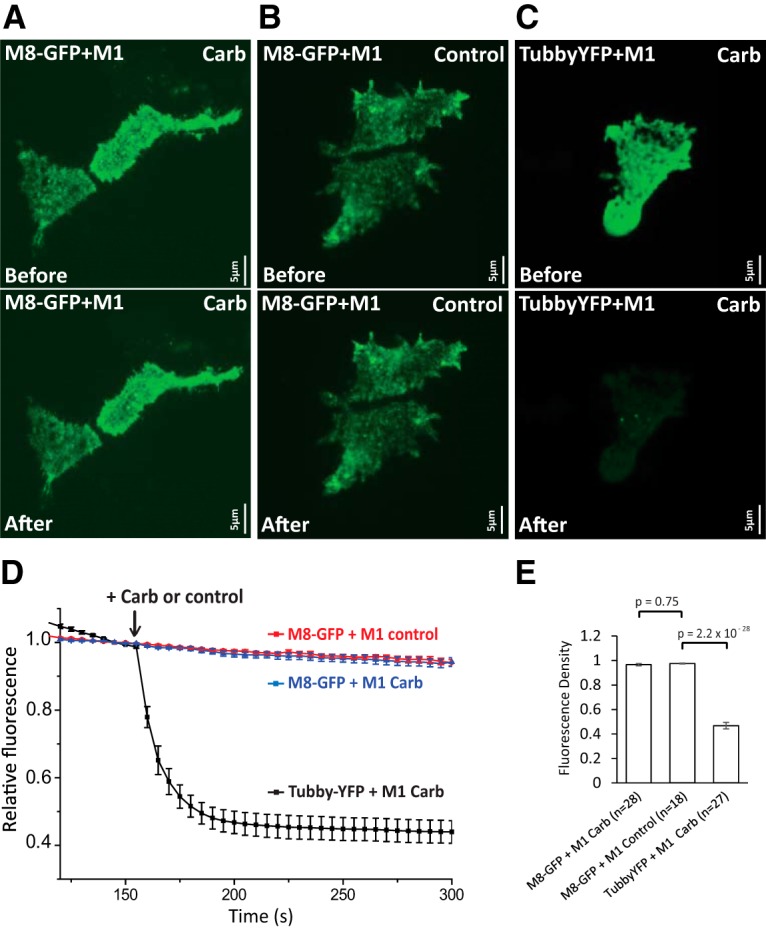
Muscarinic receptor activation does not reduce cell surface TRPM8 levels. TIRF measurements were performed as described in the Materials and Methods section in HEK293 cells transfected either with M1 muscarinic receptors and GFP-TRPM8 (M8-GFP) or M1 muscarinic receptors and the tubby YFP PI(4,5)P2 sensor. A–C are representative TIRF images before (top) and after (bottom) the application of carbachol (A, C) or no application of carbachol (B). D time course of TIRF fluorescence in the three groups, the application of 100 μm carbachol is indicated by the arrow; mean ± SEM is plotted. Fluorescence was normalized to the point before the application of carbachol. E, Summary of the three groups 50 s after the application of carbachol. Fluorescence was normalized to the point before the application of carbachol (one-way ANOVA, F(2,70) = 258.2, p = 0).
Figure 9.
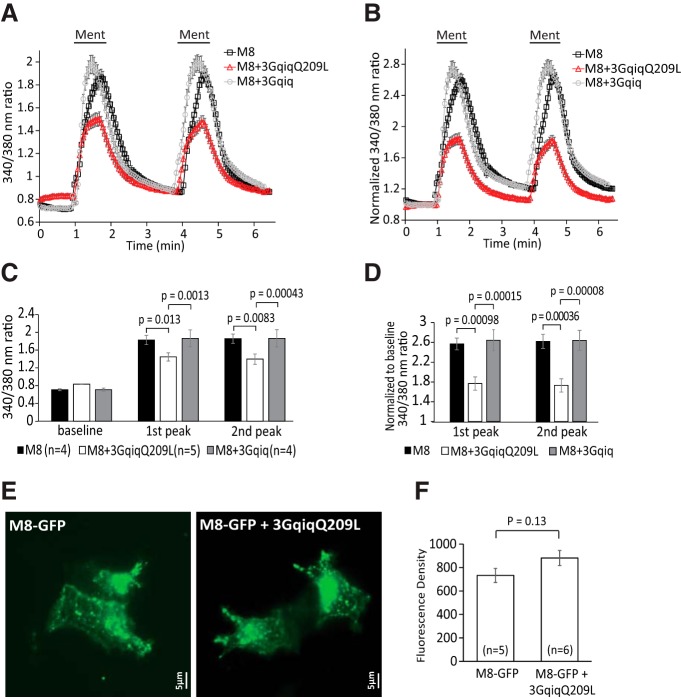
A PLC-deficient Gαq chimera inhibits TRPM8 activity, but does not decrease cell surface expression A, Ca2+-imaging measurements (mean ± SEM) of HEK 293 cells transfected with TRPM8 plus 3GqiqQ209L or 3Gqiq in response to two applications of 200 μm menthol. B, Pooled data of A normalized to baseline. C, D, Statistical summary of A and B, respectively. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with two-way ANOVA (F(8,30) = 25.55, p = 2.2 × 10−11 for C and F(5,20) = 11.10, p = 3.2 × 10−5 for D). Fluorescence values of 340/380 ratio were normalized to the baseline for each group. Two peaks of menthol responses were analyzed; for the TRPM8 group n = 4 slides (103 cells), for the TRPM8 + 3GqiqQ209L group n = 5 slides (84 cells), and for the TRPM8 + 3Gqiq group n = 4 slides (103 cells). E, Representative TIRF images from HEK293 cells cotransfected with GFP-TRPM8, or GFP-TRPM8 plus 3GqiqQ209L. TIRF images were obtained 24–36 h after transfection, as described in the Materials and Methods section. F, Summary for data obtained from five and six coverslips from three different transfections. The experimenter blinded to the transfection collected similar number of random images from each cover slide. The average fluorescence intensity of cells from one cover slide was taken as one individual data point. The total number of cells analyzed was 139 for TRPM8 and 148 for TRPM8 plus 3GqiqQ209L. Statistical comparison was performed with two-sample t test.
Experimental design and statistical analysis.
Data analysis was performed in Excel and in Microcal Origin. Data collection was randomized. Data were analyzed with t test or ANOVA with Fisher's post hoc test; p-values are reported in the figures and results of the ANOVA are reported in the figure legends. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM for most experiments.
Results
PI(4,5)P2 alleviates inhibition of TRPM8 by activation of Gαq-coupled receptors in DRG neurons
Mouse DRG neurons express a number of different GPCRs (Thakur et al., 2014). To identify Gαq-coupled receptors coexpressed with TRPM8, first we performed Ca2+-imaging experiments in DRG and TG neurons isolated from TRPM8-GFP reporter mice. We consecutively applied 500 μm menthol, 2 μm bradykinin, 1 μm prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and 500 nm endothelin (ET) (Fig. 1A,B). Most DRG neurons (62%) and TG neurons (84%) that were activated by menthol responded to bradykinin, PGE2, or ET, but no individual agonist stimulated all TRPM8+ neurons.
Figure 1.
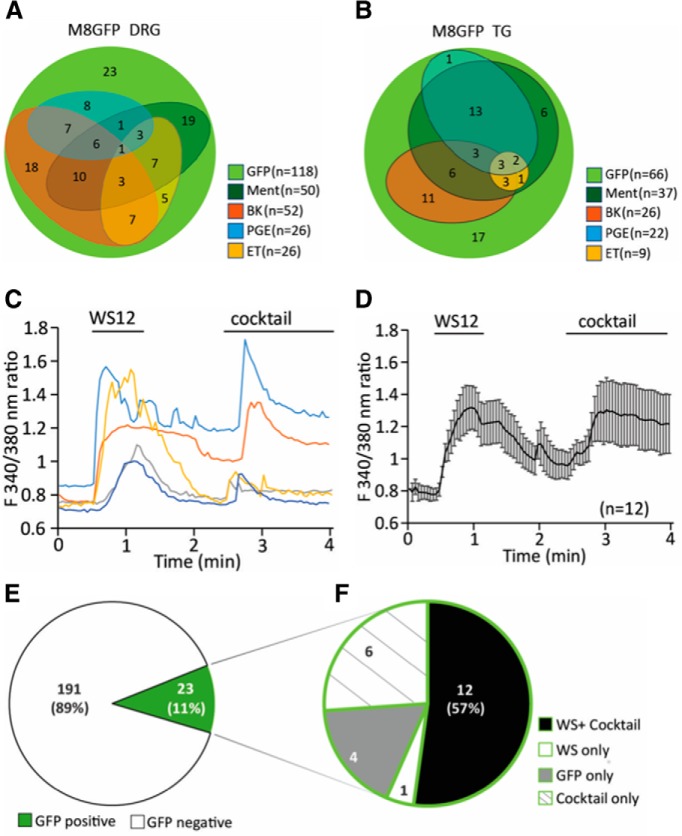
Ca2+ responses of DRG neurons to agonists of Gαq-coupled receptors and TRPM8 channels. A, Venn diagram showing the number of DRG neurons responding to 500 μm menthol, 2 μm bradykinin (BK), 1 μm PGE2, and 500 nm ET. Experiments were performed on neurons from three independent preparations from three mice both for DRG and trigeminal (TG) neurons. B, Venn diagram showing the number of TG neurons responding to the same stimuli. C, Representative traces of Ca2+-imaging measurements in TRPM8-GFP mouse DRG neurons. TRPM8 channels were activated by 10 μm WS12. A mixture containing 100 μm ADP, 100 μm UTP, 500 nm bradykinin, 100 μm histamine, 100 μm serotonin, 10 μm PGE2, and 10 μm PGI2 (cocktail) was applied to activate various Gαq-coupled receptors. Measurements were conducted in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution. D, Summary data of Ca2+-imaging measurements on n = 12 neurons that responded to both the cocktail and WS12 displayed as mean ± SEM. E, GFP+ neurons constitute 11% (23 neurons) of all DRG neurons (214 neurons, 2 independent preparations from 2 mice). F, Within these GFP+ neurons, 12 neurons (57%) respond to both WS12 and the inflammatory cocktail four neurons (12%) respond to neither WS12 nor cocktail six neurons (26%) only respond to cocktail and one neuron only responds to WS12.
Next, we measured Ca2+ signals in DRG neurons in response to the more specific TRPM8 agonist WS12 and, to activate various Gαq-coupled receptors, we applied a mixture (inflammatory cocktail) containing 100 μm ADP, 100 μm UTP, 500 nm bradykinin, 100 μm histamine, 100 μm serotonin, 10 μm PGE2, and 10 μm prostaglandin I2 (PGI2) (Fig. 1C,D), similar to that used by (Zhang et al., 2012). We found that 11% of all DRG neurons were GFP+ and 57% of GFP+ neurons responded to WS12 (Fig. 1E,F). This response rate is comparable to earlier results, indicating the incomplete overlap of endogenous TRPM8 expression and GFP expression from the TRPM8 promoter-GFP BAC clone (Takashima et al., 2007; Yudin et al., 2016). Within these GFP+ neurons, almost all neurons activated by WS12 responded to the inflammatory cocktail. Only one neuron (of 23 GFP+ neurons) was stimulated by WS12 but not by the inflammatory cocktail (Fig. 1F).
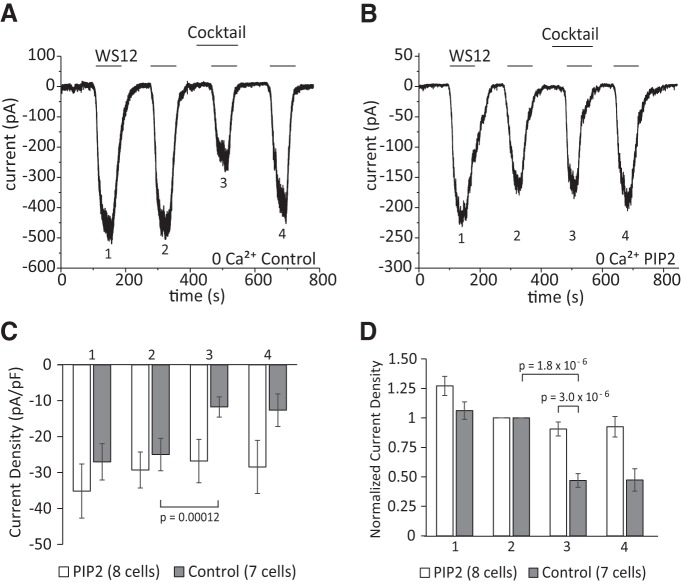
Next, we performed whole-cell patch-clamp experiments on DRG neurons isolated from TRPM8-GFP reporter mice and tested the effect of supplementing the patch pipette solution with the water-soluble diC8 PI(4,5)P2. We used a protocol of consecutive 1 min applications of 10 μm WS12 in Ca2+-free NCF solution to avoid desensitization. We used WS12 instead of menthol, as it is more specific for TRPM8 and the latter may also activate other channels such as TRPA1 (Yudin et al., 2016). The inflammatory cocktail was applied 1 min before the third application of WS12 (Fig. 2A,B). Without diC8 PI(4,5)P2, the inflammatory cocktail reduced WS12-induced current amplitudes by 53% (Fig. 2A,C,D). When we included diC8 PI(4,5)P2 in the patch pipette solution, WS12-induced currents decreased only by 9% on average after the application of the inflammatory cocktail (Fig. 2B–D). Baseline current amplitudes induced by WS12 before the application of the inflammatory cocktail were not different between control and PI(4,5)P2 dialyzed neurons (Fig. 2C). These findings show that TRPM8 channel activity is inhibited by Gαq-coupled receptors in DRG neurons and this inhibition is alleviated by excess PI(4,5)P2.
Figure 2.
Intracellular dialysis of PI(4,5)P2 alleviates inhibition of TRPM8 activity by Gαq-coupled receptors in DRG neurons. A, B, Representative whole-cell voltage-clamp traces of inward currents recorded at −60 mV from DRG neurons isolated from TRPM-GFP mice. Measurements were conducted in Ca2+-free NCF solution [control-no lipid supplement (A), 100 μm diC8 PI(4,5)P2 supplement (B)]. WS12 (10 μm) was applied to activate TRPM8 channels four times, as indicated by the horizontal lines. The inflammatory cocktail containing 100 μm ADP, 100 μm UTP, 500 nm bradykinin, 100 μm histamine, 100 μm serotonin, 10 μm PGE2, and 10 μm PGI2 was applied between the second and third application of WS12, as indicated by the horizontal line. C, D, Statistical analysis of n = 7 neurons from 5 different DRG neuron preparations from 5 mice (control group) and n = 8 neurons (diC8 PI(4,5)P2 group) displayed from 5 different DRG neuron preparations from 5 mice. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with two-way ANOVA for D (F(7,52) = 16.82, p = 2.3 × 10−11) and with t test for C. Four peaks of current responses in each group were analyzed. Raw current densities are shown in C; current values normalized to the peak of the second current response in each group are shown in D.
Receptor-induced decrease of PI(4,5)P2 in the plasma membrane
There are conflicting results on whether plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2 levels decrease in DRG neurons in response to stimulating endogenous Gαq-coupled bradykinin receptors (Liu et al., 2010; Lukacs et al., 2013b), and there is no information on the effects of other Gαq-coupled receptors (Rohacs, 2016). Therefore we investigated whether there is a decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels in response to the inflammatory cocktail that we used in our electrophysiology experiments. We transfected DRG neurons with the YFP-tagged R322H Tubby PI(4,5)P2 sensor using the Amaxa nucleoporator system. This YFP-tagged phosphoinositide binding domain of the Tubby protein contains the R322H mutation that decreases its affinity for PI(4,5)P2, thus increasing its sensitivity to small, physiological decreases in PI(4,5)P2 levels (Quinn et al., 2008; Lukacs et al., 2013b). The Tubby-based fluorescent sensor binds to PI(4,5)P2 specifically; it is located in the plasma membrane in resting conditions and, when PI(4,5)P2 levels decrease, this indicator is translocated to the cytoplasm, where we monitored it using confocal microscopy. Application of the inflammatory cocktail induced rapid decrease of fluorescence in the plasma membrane and a less pronounced, variable increase in the cytoplasm in the neuron cell bodies (Fig. 3A,B, middle) as well as in the neuronal processes (Fig. 3A,B, bottom), indicating decreased PI(4,5)P2 levels. Figure 3, C–E, summarizes these results.
We also monitored PI(4,5)P2 levels using a different fluorescence based sensor the BacMam PI(4,5)P2 sensor kit from Montana Molecular. This green PI(4,5)P2 sensor is based on a dimerization-dependent fluorescent PI(4,5)P2 binding protein (Tewson et al., 2013). The kit also contains cDNA for the M1 muscarinic receptor, a Gαq-coupled receptor, to serve as a positive control. Isolated neurons transduced with the green BacMam PI(4,5)P2 sensor showed prominent plasma membrane labeling. Administration of inflammatory cocktail induced robust decrease of fluorescence in the plasma membrane, indicating decreased PI(4,5)P2 levels. Carbachol was applied at the end of the experiment to activate M1 receptors, which induced a further decrease of fluorescence in most DRG neurons (Fig. 4A–F).
We also tested receptor-induced depletion of PI(4,5)P2 in HEK293 cells transduced with the green BacMam PI(4,5)P2 sensor and the BacMam M1 receptor. After 24 h of culture, HEK 293 cells showed prominent plasma membrane labeling. Administration of carbachol in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution induced robust decrease of fluorescence levels in the plasma membrane; no changes were detected in “bleaching” control experiments (Fig. 4G–L).
To determine whether PI(4,5)P2 levels decreased in TRPM8+ cells, we transduced DRG neurons isolated from TRPM8-GFP mice with a red BacMam PI(4,5)P2 sensor (Fig. 5). We found that application of the inflammatory cocktail decreased PI(4,5)P2 levels in both GFP+ (Fig. 5A) and GFP− neurons (Fig. 5B). Although all nine GFP+ neurons that we tested responded to the cocktail only eight of 12 GFP− neurons showed a clear response. The decrease in PI(4,5)P2 was significantly larger in GFP+ neurons compared with responding GFP− neurons (Fig. 5D,F). Overall, we conclude that activation of Gαq-coupled receptors decreases PI(4,5)P2 levels in the plasma membrane of TRPM8+ DRG neurons.
PI(4,5)P2 alleviates inhibition of TRPM8 activity by heterologously expressed Gαq-coupled receptors
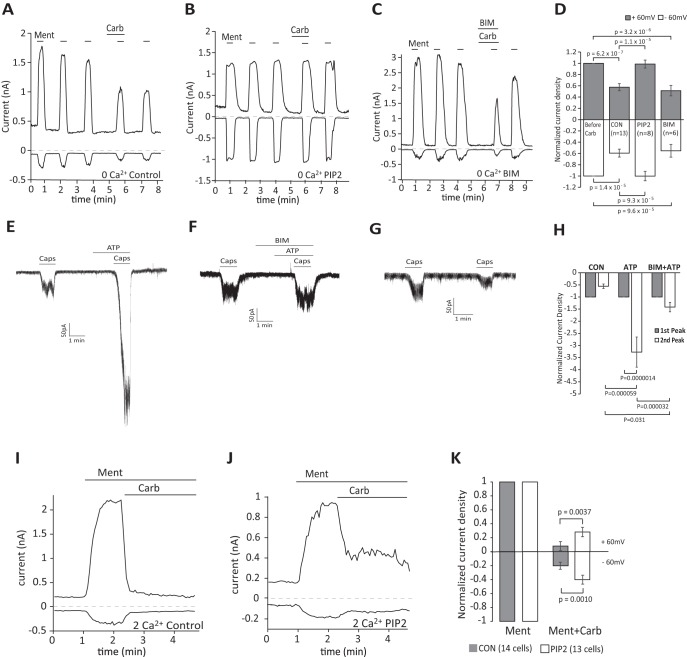
We showed that PI(4,5)P2 alleviated inhibition of TRPM8 activity by Gαq-coupled receptors in DRG neurons. Next we investigated whether this was reproducible in HEK293 cells coexpressing TRPM8 and M1 receptors, which were reported to inhibit TRPM8 (Li and Zhang, 2013). We performed whole-cell patch-clamp experiments with or without supplementing the patch pipette solution with the water-soluble diC8 PI(4,5)P2 (Fig. 6A,B,D). First, we used a protocol of consecutive 20 s applications of 200 μm menthol in Ca2+-free NCF solution. Carbachol was applied 80 s before the fourth application of menthol. Current amplitudes induced by menthol were partially reduced by carbachol to 58% (at +60 mV) and 60% (at −60 mV) of currents induced by menthol only. When the patch pipette contained diC8 PI(4,5)P2, there was no decrease in current amplitudes after carbachol application (Fig. 6B,D). We also investigated whether PKC played a role in this inhibition (Fig. 6C,D). Previous studies reported contradictory results on the effects of PKC inhibitors on TRPM8 inhibition induced by Gαq-coupled receptors (Premkumar et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2012). We coapplied the PKC inhibitor BIM IV (1 μm) with 100 μm carbachol for 80 s before the fourth application of menthol. We found no significant effect of BIM IV on carbachol-induced inhibition of TRPM8 (Fig. 6C,D), similar to the findings of Zhang et al. (2012). As a positive control for BIM, we show that it inhibited sensitization of capsaicin-induced TRPV1 currents in HEK293 cells by stimulating endogenous purinergic receptors with 100 μm ATP (Fig. 6E–H).
Figure 6.
Intracellular dialysis of PI(4,5)P2 alleviates inhibition of TRPM8 activity by Gαq-coupled receptors in HEK 293 cells. A–C, Representative whole-cell voltage-clamp traces of inward currents recorded at −60 mV and + 60 mV in Ca2+-free NCF solution for HEK 293 cells transfected with TRPM8 channels and M1 receptors [control-no lipid supplement (A), whole-cell patch pipette supplemented with 100 μm diC8PI(4,5)P2 (B), cells treated with the PKC inhibitor BIM IV (1 μm) (C)]. Menthol (200 μm) was applied to activate TRPM8 channels five times, carbachol (100 μm) was applied to activate the M1 receptor. D, Statistical analysis at −60 mV and + 60 mV corresponding to A–C. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with one-way ANOVA(+60 mV: F(3,36) = 20.08, p = 8.1 × 10−8; −60 mV: F(3,36) = 13.80, p = 3.8 × 10−6). Current values were normalized to the third current response to menthol. E–G, Representative whole-cell voltage-clamp traces of inward currents recorded at − 60 mV in Ca2+-free NCF solution for HEK 293 cells transfected with TRPV1 channels; applications of 20 nm capsaicin, 100 μm ATP, and 1 μm BIM are indicated by the horizontal lines. H, Statistical analysis of control (n = 6 cells), ATP (n = 6 cells), and BIM+ATP (n = 6 cells) both at −60 mV (corresponding to E–G). Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with two-way ANOVA (F(5,30) = 13.03, p = 8.8 × 10−7). Current values of the second peak were normalized to the first peak induced by capsaicin. I, J, Representative whole-cell voltage-clamp traces of inward currents recorded at − 60 mV and + 60 mV in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution for HEK 293 cells transfected with TRPM8 channels and M1 receptors; applications of 200 μm menthol and 100 μm carbachol are indicated by the horizontal lines; 100 μm diC8 PI(4,5)P2 was added to the whole-cell patch pipette solution in J, no lipid was added in I. K, Statistical analysis of n = 14 cells (control) and n = 13 cells (diC8 PI(4,5)P2) both at −60 mV and +60 mV (corresponding to I and J). Bars represent mean ± SEM, two-way ANOVA (+60 mV: F(3,50) = 106.8, p = 0 and −60 mV F(3,50) = 104.0, p = 0). Current values at the time point of 1.5 min after application of carbachol were analyzed. Current values were normalized to the peak current value under menthol application before carbachol.
Next, we performed similar experiments in NCF solution containing 2 mm Ca2+ (Fig. 6I–K). Upon application of carbachol, TRPM8 currents induced by menthol were inhibited by 82% at +60 mV and 71% at −60 mV. The effect was partially alleviated by including diC8 PI(4,5)P2 in the patch pipette solution; current inhibition decreased to 63% (at +60 mV) and 54% (at −60 mV) under these conditions (Fig. 6K).
Next, we investigated whether the stronger inhibition in the presence of extracellular Ca2+ was due to different levels of PI(4,5)P2 depletion. We transfected HEK293 cells with the YFP-tagged WT Tubby and M1 receptor and monitored translocation with confocal microscopy. The YFP-tagged WT Tubby has higher affinity for PI(4,5)P2 than the YFP-tagged R322H Tubby (Quinn et al., 2008), so it may be more sensitive to changes at high levels of PI(4,5)P2 depletion. HEK293 cells transfected with YFP-tagged WT tubby showed prominent plasma membrane labeling and application of 100 μm carbachol both in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution and in Ca2+-free NCF solution induced translocation of fluorescent sensors from the plasma membrane to the cytoplasm (Fig. 7A–E). Fluorescence levels in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution decreased more in the plasma membrane and increased more in the cytosol than in Ca2+-free NCF solution (Fig. 7C) and this difference was statistically significant (Fig. 7E). This indicates that M1 receptor activation induced a larger decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels in the presence of extracellular Ca2+ compared with that in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. This correlates well with the stronger inhibition of TRPM8 in the presence of extracellular Ca2+. We also used the lower-affinity YFP-tagged R322H Tubby in 2 mm Ca2+ NCF solution and in Ca2+-free NCF solution and found that there was no significant difference between the carbachol-induced fluorescence changes (Fig. 7F–H). This is likely due to the large decrease of PI(4,5)P2 levels in both conditions, differentiating between which is outside of the dynamic range of this probe.
Activation of Gαq-coupled receptors does not decrease cell surface expression of TRPM8
To determine whether activation of Gαq-coupled receptors decreases the surface expression of TRPM8 channels, we transfected HEK293 cells with GFP-tagged TRPM8 and M1 muscarinic receptors and performed TIRF-imaging experiments. TIRF selectively illuminates a narrow region above the glass cover slide, which consists mainly of the plasma membrane at the bottom of the cells attached to the glass. This technique has been used to study channel trafficking as well as to study phosphoinositide dynamics (Yao and Qin, 2009; Stratiievska et al., 2018). Application of 100 μm carbachol did not induce any detectable decrease of the TIRF signal in HEK 293 cells transfected with GFP-tagged TRPM8 and M1 muscarinic receptors (Fig. 8A,B,D,E). Fluorescence showed a slow decrease due to photobleaching, which was indistinguishable from that in negative control cells without the application of carbachol (Fig. 8D). As a positive control to show that carbachol diffuses to the narrow space between the plasma membrane and the cover glass to an extent that is sufficient to activate M1 receptors, we also transfected cells with the tubby-YFP PI(4,5)P2 sensor and M1 receptors. Application of carbachol in these cells induced a rapid and robust decrease of TIRF signal (Fig. 8C–E), indicating translocation of the PI(4,5)P2 probe from the plasma membrane to the cytoplasm, which signifies receptor activation and depletion of PI(4,5)P2.
Gαq sensitizes TRPM8 to inhibition by PI(4,5)P2 depletion
Our data so far showed that PI(4,5)P2 depletion plays an important role in TRPM8 inhibition. To test the relationship between PI(4,5)P2 and Gαq regulation of TRPM8, we used a chimera between Gαq and Gαi that does not couple to PLC, but inhibits TRPM8 activity (Zhang et al., 2012). The 3Gqiq chimera and its constitutively active variant 3GqiqQ209L were shown not to decrease PI(4,5)P2 levels when expressed in HEK 293 cells using the same tubby-YFP sensor we used for our experiments (Zhang et al., 2012). First we performed Ca2+-imaging experiments and compared responses to menthol application in HEK293 cells cotransfected with TRPM8 and either 3Gqiq or 3GqiqQ209L (Fig. 9A,B). Menthol-induced Ca2+ signals were significantly smaller in cells expressing 3GqiqQ209L than in cells expressing WT 3Gqiq or TRPM8 only (Fig. 9A–D). This is consistent with the whole-cell patch-clamp results of Zhang et al. (2012), who found that 3GqiqQ209L inhibited TRPM8 activity and 3Gqiq did not.
Next, we investigated whether the decreased menthol-induced Ca2+ signals in cells expressing the 3GqiqQ209L construct was due to decreased surface expression of TRPM8. We coexpressed 3GqiqQ209L with the GFP-tagged TRPM8 in HEK293 cells, measured plasma membrane fluorescence using TIRF microscopy, and compared it with cells expressing GFP-TRPM8 alone. Figure 9, E and F, shows that in cells coexpressing the 3GqiqQ209L, the TIRF signal of GFP-TRPM8 did not decrease, but rather showed a slight, statistically nonsignificant increase. These data indicate that the decrease in menthol-induced Ca2+ signal in cells expressing 3GqiqQ209L was not caused by decreased surface expression of TRPM8.
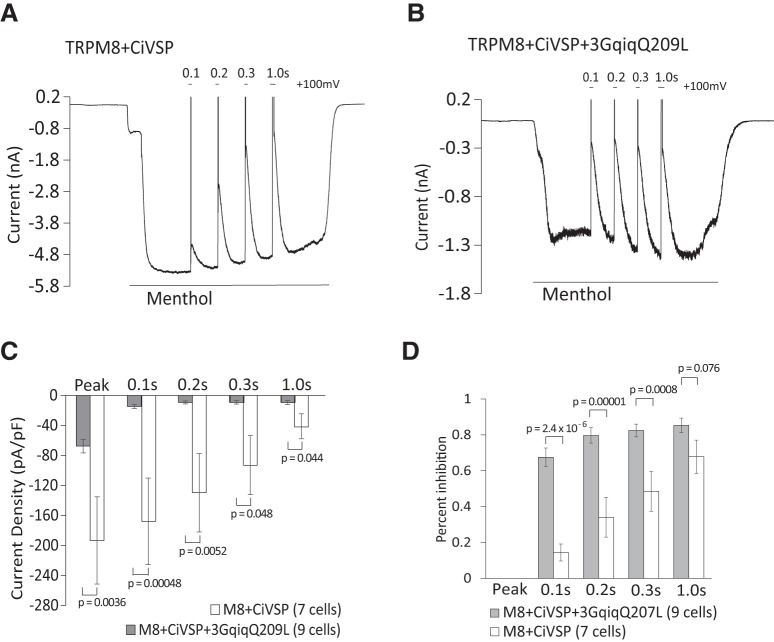
Next, we investigated whether the presence of Gαq has any effect on the level of inhibition evoked by decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels. To bypass the PLC pathway, we used a voltage-sensitive 5′ phosphatase (Ci-VSP) to decrease PI(4,5)P2 levels by converting this lipid to PI(4)P (Iwasaki et al., 2008). Whole-cell patch-clamp experiments were performed in HEK293 cells cotransfected with TRPM8 and Ci-VSP with or without 3GqiqQ209L in Ca2+-free NCF solution (Fig. 10A–D). Consistent with the Ca2+-imaging experiments, menthol-induced currents before the activation of ciVSP were smaller in cells expressing the 3GqiqQ209L (Fig. 10C). Ci-VSP was activated by depolarizing pulses to 100 mV for 0.1 s, 0.2 s, 0.3 s, and 1 s; menthol-induced currents were gradually reduced by 15%, 34%, 49%, and 68%, respectively, in cells without 3GqiqQ209L. In cells expressing 3GqiqQ209L, the same depolarizing pulses induced higher levels of inhibition of menthol-evoked currents, 68%, 80%, 72%, and 85%, respectively (Fig. 10D). These results indicate that TRPM8 is inhibited more by PI(4,5)P2 depletion in the presence of Gαq.
Figure 10.
TRPM8 is inhibited more efficiently by PI(4,5)P2 depletion in the presence of Gαq. A, B, Representative whole-cell voltage-clamp traces of inward currents recorded at −60 mV from HEK 293 cells transfected with TRPM8 and the voltage-sensitive phosphatase CiVSP (A) or with ciVSP, TRPM8, and 3GqiqQ209L (B). Measurements were conducted in Ca2+-free NCF solution. TRPM8 channels were activated by 500 μm menthol. CiVSP was activated by +100 mV steps for 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 1 s. C, Summary of raw current densities before the application of voltage steps (peak) and after voltage steps to +100 mV for 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 1 s for each group; n = 7 for TRPM8 + CiVSP and n = 9 for TRPM8 + CiVSP + 3GqiqQ209L (two-way ANOVA, F(9,70) = 5.40, p = 1.3 × 10−5). D. Summary of the same data expressed as current inhibition induced by voltage steps. Bars represent mean ± SEM; statistical significance was calculated with two-way ANOVA (F(7,56) = 13.66, p = 3.7 × 10−10).
We conclude that PI(4,5)P2 alleviates inhibition of TRPM8 activity by Gαq-coupled receptors in DRG neurons. Gαq not only directly inhibits TRPM8, as proposed by Zhang et al. (2012), but also sensitizes the channel to inhibition by decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels; therefore, the two pathways converge to inhibit TRPM8 activity upon GPCR activation.
Discussion
Converging evidence demonstrates that TRPM8 channels require the plasma membrane phospholipid PI(4,5)P2 for activity. TRPM8 currents show a characteristic decrease (rundown) in excised inside-out patches, which can be restored by applying PI(4,5)P2 to the cytoplasmic surface of the membrane patch (Liu and Qin, 2005; Rohács et al., 2005). Increasing endogenous PI(4,5)P2 levels with MgATP also restored TRPM8 activity in excised patches after current rundown (Yudin et al., 2011). PI(4,5)P2 is also required for the cold- or menthol-induced activity of the purified TRPM8 protein in planar lipid bilayers, indicating a direct effect on the channel (Zakharian et al., 2009, 2010). PI(4,5)P2 was also shown to modulate the cold threshold of the channel (Fujita et al., 2013). Consistent with dependence of the activity of TRPM8 on PI(4,5)P2, it was shown that selectively decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels in intact cells is sufficient to inhibit channel activity either by using specific chemically inducible phosphoinositide phosphatases (Varnai et al., 2006; Daniels et al., 2009) or voltage-sensitive phosphatases such as ciVSP (Yudin et al., 2011).
Stimulating cell surface receptors that couple to Gαq and activate PLC inhibits TRPM8 activity, but the mechanism is not fully elucidated (Liu and Qin, 2005; Premkumar et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2012; Li and Zhang, 2013; Than et al., 2013). Based on the following arguments, it was proposed that this inhibition proceeds via direct binding of Gαq to the channel (Zhang et al., 2012). Application of Gαq and GTPγS inhibited TRPM8 activity in excised inside-out patches in the presence of PI(4,5)P2. Direct binding of Gαq to TRPM8 was demonstrated by immunoprecipitation. Coexpression of a constitutively active mutant (Q209L) chimera between Gαi and Gαq (3Gqiq) that does not activate PLC inhibited TRPM8 activity (Zhang et al., 2012).
It was also proposed that decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels does not contribute to TRPM8 inhibition by Gαq-coupled receptors (Zhang et al., 2012) based on the following data. Histamine inhibited TRPM8 in the presence of the PLC inhibitor U73122. However, the inhibition was less than that without the drug, indicating potential involvement of PLC activation. Two mutants in the putative TRP domain were also tested, and the authors argued that since these “PI(4,5)P2-insensitive” TRPM8 mutants were inhibited by Gαq-coupled receptor activation, PI(4,5)P2 depletion is not involved. However, these mutants are more sensitive to PI(4,5)P2 depletion due to their decreased apparent affinity for the lipid (Rohács et al., 2005) and, indeed, the K995Q mutant was somewhat more inhibited by histamine than WT TRPM8 and the extent of inhibition for the R1008Q is difficult to evaluate due to the very small current amplitudes (Zhang et al., 2012). Finally, the constitutively active Q209L mutant of the 3Gqiq chimera that does not activate PLC and does not decrease PI(4,5)P2 levels inhibited TRPM8 activity when coexpressed in HEK 293 cells. However, the inhibition was substantially smaller than that induced by the constitutively active Gα, indicating that PLC-dependent mechanisms may also be involved (Zhang et al., 2012). In conclusion, most of the data discussed here are compatible with PI(4,5)P2 depletion contributing to TRPM8 inhibition.
To test the involvement of PI(4,5)P2 depletion, we supplemented the whole-cell patch pipette with this lipid and observed reduced inhibition of TRPM8 activity by Gαq-coupled receptor activation both in DRG neurons and in an expression system. In DRG neurons, we used an inflammatory cocktail, similar to that described by Zhang et al. (2012) for two reasons. First, DRG neurons are highly heterogenous and we could not find a single agonist that reliably induced a Ca2+ signal (indicating PLC activation) in all TRPM8+ neurons. Second, inflammation is mediated, not by a single proinflammatory agonist, but rather a combination of them, which is sometime referred to as an “inflammatory soup.”
Whereas activation of PLC induces PI(4,5)P2 hydrolysis, it is debated to what extent PI(4,5)P2 is decreased in native tissues upon activation of endogenous receptors (Nasuhoglu et al., 2002) and it is clearly cell type and agonist specific (van der Wal et al., 2001). Liu et al. (2010), using a fluorescent PI(4,5)P2 sensor, the YFP-tagged PI(4,5)P2 binding domain of the tubby protein (Quinn et al., 2008), showed that bradykinin activated PLC in rat DRG neurons, but it did not decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels. Our earlier data using the same sensor show that bradykinin induced a small decrease in PI(4,5)P2 levels in mouse DRG neurons (Lukacs et al., 2013b). Here, we demonstrate, using the tubby-based PI(4,5)P2 sensor that application of the same inflammatory Gαq-activating cocktail we used in our patch-clamp measurements decreased PI(4,5)P2 levels in most DRG neurons. Using a different, red PI(4,5)P2 sensor we also show that the PI(4,5)P2 decrease was larger in TRPM8+ neurons than in cells not expressing TRPM8 (Fig. 5D,F).
We found that coexpressing the PLC-deficient, constitutively active 3GqiqQ209L inhibited menthol-induced Ca2+ signals in HEK 293 cells expressing TRPM8, confirming the results of Zhang et al. (2012). This decrease cannot be accounted for by a decreased number of channels because surface expression of TRPM8 did not decrease when 3GqiqQ209L was coexpressed. This is consistent with the findings of Zhang et al. (2012), who showed that coexpressing 3GqiqQ209L did not change the expression level of TRPM8 detected by Western blot. We also found that the presence of 3GqiqQ209L markedly increased the sensitivity of inhibition of TRPM8 by decreasing PI(4,5)P2 levels with the voltage-sensitive phosphoinositide 5-phosphatase ciVSP. Thus, Gαq binding allows even small decreases in PI(4,5)P2 concentrations, such as those occurring during physiological receptor activation, to inhibit channel activity.
The increased sensitivity to PI(4,5)P2 depletion indicates that Gαq binding to the channel decreases the apparent affinity of the channel for PI(4,5)P2 (Rohacs, 2007). It is estimated that basal plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2 levels correspond to the effect of 40 μm diC8 PI(4,5)P2 applied to excised patches (Collins and Gordon, 2013). This concentration of PI(4,5)P2 induced ∼80% of the maximal current in excised patches at 17°C in the presence of 500 μm menthol at physiological negative membrane potentials (Rohács et al., 2005). This indicates that resting plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2 concentrations do not fully saturate TRPM8, so the decreased apparent affinity to PI(4,5)P2 upon Gαq binding is expected to reduce TRPM8 current levels even without any decrease in PI(4,5)P2 concentrations. This is consistent with reduced menthol induced Ca2+ signals and current amplitudes when GqiqQ209L was coexpressed. We show that TRPM8 surface expression did not decrease upon receptor activation and when the GqiqQ209L was coexpressed, so the decreased apparent affinity for PI(4,5)P2 is likely to be responsible also for the reduced current amplitudes upon direct Gαq binding.
Overall, we conclude that upon receptor activation, binding of Gαq not only directly inhibits TRPM8, but also sensitizes it to PI(4,5)P2 depletion, and thus the two pathways converge and synergize in reducing channel activity.
Footnotes
The authors thank Joshua Berlin for insightful comments; David Julius (UCSF) for providing the rat TRPM8 clone; David McKemy (University of Southern California) for providing the TRPM8 GFP reporter mouse line; Yasushi Okamura (Osaka University, Japan) for providing the ci-VSP and dr-VSP clones; Nikita Gamper (University of Leeds) and Andrew Tinker (University College London) for providing the tubby-R332H-YFP clone; Xuming Zhang (Aston University, Birmingham, UK) for providing the 3Gqiq clone; Linda Zabelka for maintaining the mouse colony; and Luke Fritzky for help using the Nikon A1R-A1 confocal system. T.R. was supported by the National Institutes of Health (Grants NS055159 and GM093290).
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Almaraz L, Manenschijn JA, de la Peña E, Viana F (2014) TRPM8. Handb Exp Pharmacol 222:547–579. 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautista DM, Siemens J, Glazer JM, Tsuruda PR, Basbaum AI, Stucky CL, Jordt SE, Julius D (2007) The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature 448:204–208. 10.1038/nature05910 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhave G, Hu HJ, Glauner KS, Zhu W, Wang H, Brasier DJ, Oxford GS, Gereau RW 4th (2003) Protein kinase C phosphorylation sensitizes but does not activate the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:12480–12485. 10.1073/pnas.2032100100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterina MJ, Leffler A, Malmberg AB, Martin WJ, Trafton J, Petersen-Zeitz KR, Koltzenburg M, Basbaum AI, Julius D (2000) Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science 288:306–313. 10.1126/science.288.5464.306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesare P, McNaughton P (1996) A novel heat-activated current in nociceptive neurons and its sensitization by bradykinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:15435–15439. 10.1073/pnas.93.26.15435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colburn RW, Lubin ML, Stone DJ Jr, Wang Y, Lawrence D, D'Andrea MR, Brandt MR, Liu Y, Flores CM, Qin N (2007) Attenuated cold sensitivity in TRPM8 null mice. Neuron 54:379–386. 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.04.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins MD, Gordon SE (2013) Short-chain phosphoinositide partitioning into plasma membrane models. Biophys J 105:2485–2494. 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.09.035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels RL, Takashima Y, McKemy DD (2009) Activity of the neuronal cold sensor TRPM8 is regulated by phospholipase C via the phospholipid phosphoinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem 284:1570–1582. 10.1074/jbc.M807270200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaka A, Murray AN, Mathur J, Earley TJ, Petrus MJ, Patapoutian A (2007) TRPM8 is required for cold sensation in mice. Neuron 54:371–378. 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.02.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita F, Uchida K, Takaishi M, Sokabe T, Tominaga M (2013) Ambient temperature affects the temperature threshold for TRPM8 activation through interaction of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. J Neurosci 33:6154–6159. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5672-12.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki H, Murata Y, Kim Y, Hossain MI, Worby CA, Dixon JE, McCormack T, Sasaki T, Okamura Y (2008) A voltage-sensing phosphatase, ci-VSP, which shares sequence identity with PTEN, dephosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:7970–7975. 10.1073/pnas.0803936105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton WM, Bifolck-Fisher A, Bautista DM, McKemy DD (2010) TRPM8, but not TRPA1, is required for neural and behavioral responses to acute noxious cold temperatures and cold-mimetics in vivo. Pain 150:340–350. 10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L, Zhang X (2013) Differential inhibition of the TRPM8 ion channel by galphaq and galpha 11. Channels (Austin) 7:115–118. 10.4161/chan.23466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B, Qin F (2005) Functional control of cold- and menthol-sensitive TRPM8 ion channels by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. J Neurosci 25:1674–1681. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3632-04.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B, Linley JE, Du X, Zhang X, Ooi L, Zhang H, Gamper N (2010) The acute nociceptive signals induced by bradykinin in rat sensory neurons are mediated by inhibition of M-type K+ channels and activation of Ca2+-activated Cl- channels. J Clin Invest 120:1240–1252. 10.1172/JCI41084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacs V, Rives JM, Sun X, Zakharian E, Rohacs T (2013a) Promiscuous activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channels by negatively charged intracellular lipids, the key role of endogenous phosphoinositides in maintaining channel activity. J Biol Chem 288:35003–35013. 10.1074/jbc.M113.520288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacs V, Yudin Y, Hammond GR, Sharma E, Fukami K, Rohacs T (2013b) Distinctive changes in plasma membrane phosphoinositides underlie differential regulation of TRPV1 in nociceptive neurons. J Neurosci 33:11451–11463. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5637-12.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasuhoglu C, Feng S, Mao Y, Shammat I, Yamamato M, Earnest S, Lemmon M, Hilgemann DW (2002) Modulation of cardiac PIP2 by cardioactive hormones and other physiologically relevant interventions. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C223–C234. 10.1152/ajpcell.00486.2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numazaki M, Tominaga T, Toyooka H, Tominaga M (2002) Direct phosphorylation of capsaicin receptor VR1 by protein kinase cepsilon and identification of two target serine residues. J Biol Chem 277:13375–13378. 10.1074/jbc.C200104200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar LS, Raisinghani M, Pingle SC, Long C, Pimentel F (2005) Downregulation of transient receptor potential melastatin 8 by protein kinase C-mediated dephosphorylation. J Neurosci 25:11322–11329. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3006-05.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn KV, Behe P, Tinker A (2008) Monitoring changes in membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in living cells using a domain from the transcription factor tubby. J Physiol 586:2855–2871. 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.153791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohacs T. (2007) Regulation of TRP channels by PIP2. Pflugers Arch 453:753–762. 10.1007/s00424-006-0153-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohacs T. (2014) Phosphoinositide regulation of TRP channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol 233:1143–1176. 10.1007/978-3-319-05161-1_18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohacs T. (2016) Phosphoinositide signaling in somatosensory neurons. Adv Biol Regul 61:2–16. 10.1016/j.jbior.2015.11.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohács T, Lopes CM, Michailidis I, Logothetis DE (2005) PI(4,5)P2 regulates the activation and desensitization of TRPM8 channels through the TRP domain. Nat Neurosci 8:626–634. 10.1038/nn1451 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratiievska A, Nelson S, Senning EN, Lautz JD, Smith SE, Gordon SE (2018) Reciprocal regulation among TRPV1 channels and phosphoinositide 3-kinase in response to nerve growth factor. Elife 7:e38869. 10.7554/eLife.38869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima Y, Daniels RL, Knowlton W, Teng J, Liman ER, McKemy DD (2007) Diversity in the neural circuitry of cold sensing revealed by genetic axonal labeling of transient receptor potential melastatin 8 neurons. J Neurosci 27:14147–14157. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4578-07.2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewson PH, Quinn AM, Hughes TE (2013) A multiplexed fluorescent assay for independent second-messenger systems: decoding GPCR activation in living cells. J Biomol Screen 18:797–806. 10.1177/1087057113485427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakur M, Crow M, Richards N, Davey GI, Levine E, Kelleher JH, Agley CC, Denk F, Harridge SD, McMahon SB (2014) Defining the nociceptor transcriptome. Front Mol Neurosci 7:87. 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Than JY, Li L, Hasan R, Zhang X (2013) Excitation and modulation of TRPA1, TRPV1, and TRPM8 channel-expressing sensory neurons by the pruritogen chloroquine. J Biol Chem 288:12818–12827. 10.1074/jbc.M113.450072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga M, Wada M, Masu M (2001) Potentiation of capsaicin receptor activity by metabotropic ATP receptors as a possible mechanism for ATP-evoked pain and hyperalgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:6951–6956. 10.1073/pnas.111025298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wal J, Habets R, Várnai P, Balla T, Jalink K (2001) Monitoring agonist-induced phospholipase C activation in live cells by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem 276:15337–15344. 10.1074/jbc.M007194200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnai P, Thyagarajan B, Rohacs T, Balla T (2006) Rapidly inducible changes in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate levels influence multiple regulatory functions of the lipid in intact living cells. J Cell Biol 175:377–382. 10.1083/jcb.200607116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velisetty P, Borbiro I, Kasimova MA, Liu L, Badheka D, Carnevale V, Rohacs T (2016) A molecular determinant of phosphoinositide affinity in mammalian TRPV channels. Sci Rep 6:27652. 10.1038/srep27652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing H, Chen M, Ling J, Tan W, Gu JG (2007) TRPM8 mechanism of cold allodynia after chronic nerve injury. J Neurosci 27:13680–13690. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2203-07.2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao J, Qin F (2009) Interaction with phosphoinositides confers adaptation onto the TRPV1 pain receptor. PLoS Biol 7:e46. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudin Y, Lukacs V, Cao C, Rohacs T (2011) Decrease in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate levels mediates desensitization of the cold sensor TRPM8 channels. J Physiol 589:6007–6027. 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.220228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudin Y, Lutz B, Tao YX, Rohacs T (2016) Phospholipase C δ4 regulates cold sensitivity in mice. J Physiol 594:3609–3628. 10.1113/JP272321 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakharian E, Thyagarajan B, French RJ, Pavlov E, Rohacs T (2009) Inorganic polyphosphate modulates TRPM8 channels. PLoS One 4:e5404. 10.1371/journal.pone.0005404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakharian E, Cao C, Rohacs T (2010) Gating of transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channels activated by cold and chemical agonists in planar lipid bilayers. J Neurosci 30:12526–12534. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3189-10.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Li L, McNaughton PA (2008) Proinflammatory mediators modulate the heat-activated ion channel TRPV1 via the scaffolding protein AKAP79/150. Neuron 59:450–461. 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.05.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Mak S, Li L, Parra A, Denlinger B, Belmonte C, McNaughton PA (2012) Direct inhibition of the cold-activated TRPM8 ion channel by Gαq. Nat Cell Biol 14:851–858. 10.1038/ncb2529 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]