Abstract
Kv channels inhibit release indirectly by hyperpolarizing membrane potential, but the significance of Kv channel interaction with the secretory apparatus is not known. The Kv2.1 channel is commonly expressed in the soma and dendrites of neurons, where it could influence the release of neuropeptides and neurotrophins, and in neuroendocrine cells, where it could influence hormone release. Here we show that Kv2.1 channels increase dense-core vesicle (DCV)-mediated release after elevation of cytoplasmic Ca2+. This facilitation occurs even after disruption of pore function and cannot be explained by changes in membrane potential and cytoplasmic Ca2+. However, triggering release increases channel binding to syntaxin, a secretory apparatus protein. Disrupting this interaction with competing peptides or by deleting the syntaxin association domain of the channel at the C terminus blocks facilitation of release. Thus, direct association of Kv2.1 with syntaxin promotes exocytosis. The dual functioning of the Kv channel to influence release, through its pore to hyperpolarize the membrane potential and through its C-terminal association with syntaxin to directly facilitate release, reinforces the requirements for repetitive firing for exocytosis of DCVs in neuroendocrine cells and in dendrites.
Keywords: exocytosis, Kv2.1 channel, syntaxin 1A, dense-core vesicles (DCVs), PC12 cells, neuropeptides, SNAREs
Introduction
Regulated release of neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, and hormones by neurons and neuroendocrine cells relies on Ca2+-evoked exocytosis (Bennett et al., 1992a,b; Sollner et al., 1993; Bennett, 1995; Hanson et al., 1997; Hay and Scheller, 1997). Essential to this process are the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins that form the fusion complex that includes syntaxin 1A (syntaxin), SNAP25, and VAMP2 (Bennett et al., 1992a,b; Sollner et al., 1993; Bennett, 1995; Hanson et al., 1997; Hay and Scheller, 1997). Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, which mediate the influx of Ca2+ that triggers release (Bajjalieh and Scheller, 1995; Bennett, 1995; Sudhof, 1995; Hanson et al., 1997; Chapman, 2002), interact physically with protein components of the fusion complex (for review, see Catterall, 2000; Spafford et al., 2003), and accumulating evidence indicates that these interactions regulate the efficacy of neurotransmitter release (Mochida et al., 1996, 1998, 2003; Rettig et al., 1997; Wiser et al., 1999; Kang et al., 2002; Harkins et al., 2004). Another class of ion channels that influence exocytosis is the voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channels, the function of which is thought to be exerted solely and indirectly through their influence on membrane potential (Meir et al., 1999). However, the possibility that transmitter release is regulated by direct interaction between Kv channels and the exocytotic machinery has not been investigated.
Recently, we demonstrated interactions of SNAREs with the Kv channel Kv2.1. Specifically, Kv2.1 channels interact physically with syntaxin and SNAP25 in PC12 cells, oocytes, and in vitro (MacDonald et al., 2002; Leung et al., 2003; Michaelevski et al., 2003), and these interactions modulate Kv2.1 currents in HEK 293 cells, islet β-cells (MacDonald et al., 2002; Leung et al., 2003), and oocytes (Michaelevski et al., 2003; Tsuk et al., 2005). The Kv2.1 channel is commonly expressed in the soma and dendrites of neurons (Hwang et al., 1993; Trimmer, 1993; Rhodes et al., 1995; Du et al., 1998; Murakoshi and Trimmer, 1999), where it could influence the release of neuropeptides and neurotrophins, and in neuroendocrine cells (MacDonald et al., 2001; Yan et al., 2004; Wolf-Goldberg et al., 2006), where it is well positioned to regulate hormone release. Indeed, Kv2.1 and SNAREs are colocalized in pancreatic β-cell membranes in lipid rafts, where release occurs, and disruption of the rafts shunted the channels and SNAREs out of the rafts and affected insulin secretion (Xia et al., 2004). Thus, data suggest a possible role for Kv2.1 interaction with SNAREs in regulation of exocytosis.
Here the effect of the interaction of Kv2.1 with syntaxin on release is investigated in PC12 cells, amenable for optical and biochemical studies of dense-core vesicle (DCV)-mediated release and which natively express Kv2.1 channels, albeit at a low level compared with brain neurons (Sharma et al., 1993). We show that the channel regulates the capacity for release independent of pore function by interacting directly and dynamically with syntaxin. Thus, in addition to affecting excitability, Kv channels influence release by binding a component of the fusion machinery.
Materials and Methods
Constructs and antibodies.
The primary antibodies used were anti-Kv1.1–C terminus and anti-Kv2.1–C terminus (Alomone Labs, Jerusalem, Israel), monoclonal anti-HPC-1 (Sigma-Aldrich, Rehovot, Israel), and anti-synapsin (Calbiochem, La Jolla, CA). The DNAs of Kv1.1 and Kv2.1 fragments for production of glutathione S-transferase (GST)-fusion proteins were constructed as described previously (Jing et al., 1999; Michaelevski et al., 2003). The fusion proteins were synthesized as described previously (Jing et al., 1999). The Emerald green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged proANF construct was prepared as described previously (Han et al., 1999). pcDNA3-FLAG C1a was constructed by PCR amplification with Pfu polymerase (Promega, Madison, WI) using 100 ng of Kv2.1 plasmid as a template for 30 cycles of 1 min at 95°C, 1.5 min at 70°C, and 30 min at 72°C. The forward primer created an EcoRI site, followed by an initiation codon, a flag tag, and a NheI site; the reverse primer created a stop codon, followed by a NotI site. This fragment was cloned into EcoRI and NheI sites of pcDNA3. Two pore mutations (Malin and Nerbonne, 2002) were introduced into rat wild-type Kv2.1 in a pBluescript vector using the Quickchange Site-directed Mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA), followed by subcloning into EcoRI and NotI sites of pcDNA3 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) to produce pcDNA3-Kv2.1W365C/Y380T. Kv2.1ΔC1a, a deletion mutant of Kv2.1 lacking amino acids 421–523 was generated using overlapping PCR, as described previously (Wurch and Pauwels, 1998). Briefly, in the first reaction, the first 421 amino acids of Kv2.1 were amplified using the sense primer 5′-ATGCGGAATTCCGGTCGCTGGTCTGGC-3′ and the antisense primer 5′-TACTGTACATGTCTTCCAGGAAGGCGTCC-3′. A second fragment (amino acids 523–853) was amplified using the sense primer 5′-AAGGACGCCTTCCTGGAAGACATGTACAGT-3′ and the antisense primer 5′-GCTCTAGAGCGAGCTCAGATACTCTGATCC-3′. These two PCR products were used as templates for a third PCR amplification using the sense primer from the first reaction and the antisense primer from the second reaction. The PCR product was subcloned into EcoRI and XbaI sites of pGEMHJ. All constructs were sequenced in their entirely at the Tel-Aviv University Sequencing Facility. Restriction enzymes were purchased from New England Biolabs (Ipswich, MA), and T4 ligase was purchased from Lucigen Corporation (Middleton, WI).
Immunoprecipitation and pulldown in untreated PC12 cell proteins.
PC12 cells were grown in DMEM supplemented with 8% horse serum, 8% fetal calf serum, 2 mm l-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 0.1 mg/ml streptomycin and were maintained at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2. Cells were replated every 5 d. Immunoprecipitation from 1% 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS) lysate of 1–3 × 106 PC12 cells was performed with anti-Kv2.1 antibody in the absence (control) or presence of 15 μm recombinant Kv2.1 or Kv1.1 GST-fusion peptides, or the antigen peptide for the Kv2.1 antibody in the incubation buffer [20 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 100 mm NaCl, 5 mm EGTA, and 5 mm EDTA supplemented with a mixture of protease inhibitors (Boehringer Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany)]. After incubation at 4°C for 12 h, the immunoprecipitated proteins were pelletted, washed three times with washing buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, and 100 mm NaCl), separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted, and detected by anti-Kv2.1 and anti-syntaxin antibodies (immunoblot). Glutathione–Sepharose beads were added to the supernatant to pulldown syntaxin. Binding reactions were incubated at room temperature for 1 h with gentle rocking. After washing the beads with the incubation buffer, the bound GST-fusion proteins were eluted with 15 mm reduced glutathione in 30 ml of elution buffer (120 mm NaCl and 100 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8), subjected to SDS-PAGE (12% polyacrylamide), and immunoblotted with anti-syntaxin antibody or stained with Ponceau S.
Cross-linking and immunoprecipitation in permeable PC12 cells.
Cells were harvested by incubation and pipetting with ice-cold K-glutamate (KGlu) buffer (20 mm HEPES, pH 7.2, 120 mm KGlu, 20 mm potassium acetate, 2 mm EGTA, and 0.1% BSA) and were permeabilized by a single passage through a specific PC12 cell homogenizer designed according to specifications (Martin, 1989; Martin and Walent, 1989; Hay and Martin, 1992). Permeable cells (1–3 × 106) were incubated with 11 mm EGTA for 1 h to fully extract soluble components and rinsed three times and resuspended in KGlu buffer. Cells were then primed for 15 min at 30°C in the presence of 2 mm MgATP and 0.5 mg/ml rat brain cytosol [prepared as described previously (Hay and Martin, 1992)] (see Fig. 1b, primed), or were primed and triggered for 10 min at 30°C in the presence of 1.6 μm CaCl2 (1 μm free ionic [Ca2+]) (see Fig. 1b, triggered), or were not treated (as in Fig. 1a and supplemental Fig. 1, available at http//www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). The cells were then washed three times in KGlu buffer and treated with 5 mm dithiobis[succinnimidyl-propionate] (DTSSP; Pierce, Rockford, IL), a water-soluble, homo-bifunctional cross-linking reagent, for 1 h on ice. Cross-linking was quenched by the addition of 50 mm glycine for 15 min, followed by washing of the cells with KGlu buffer. A concentration of 1.6 μm CaCl2 was present throughout this process for the triggered samples. The cells were solubilized in RIPA buffer (50 mm Tris, pH 8, 150 mm NaCl, 1% NP-40, 0.5% deoxycholate, and 0.1% SDS) for 20 min at 4°C. Immunoprecipitates were collected by centrifugation for 15 min at 16,000 × g after incubation for 12 h with anti-Kv2.1 antibody at 4°C, followed by immobilization on protein A-Sepharose beads. Immunoprecipitates were eluted from the beads in boiling sample buffer containing 0.2 m dithiothreitol for analysis by SDS-PAGE (12% polyacrylamide) and immunoblotting with anti-Kv2.1 or anti-syntaxin antibodies.
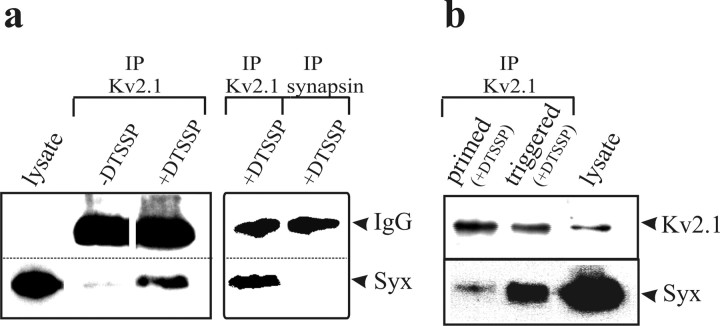
Figure 1.
In situ interaction of Kv2.1 with syntaxin is dynamic. a, Syntaxin coimmunoprecipitates with Kv2.1 from permeable PC12 cells only after cross-linking of the cells with DTSSP. Permeable PC12 cells, either cross-linked (+DTSSP) or not (−DTSSP), were solubilized under stringent conditions in RIPA buffer (see Materials and Methods), immunoprecipitated by Kv2.1 or synapsin antibodies as indicated above the lanes, and detected by Western blotting with anti-syntaxin antibody. The left and right panels are two separate experiments. The experiments shown are representative of three similar experiments. b, Interaction of Kv2.1 with syntaxin is enhanced after Ca2+ triggering of primed cells. Permeable PC12 cells (3 × 106 cells) underwent priming only (primed) or priming followed by triggering (triggered) and were cross-linked with 5 mm DTSSP. Proteins were detected by Western blotting with the corresponding antibodies, as indicated on the right. Lysate (no immunoprecipitation was performed) from 1 × 105 cells was loaded (lysate). IP, Immunoprecipitated; Syx, syntaxin antibody.
Immunoprecipitation of Xenopus oocyte proteins.
A total of 1% CHAPS or 1% Triton X-100 homogenates of [35S]Met/Cys-labeled oocytes were subjected to immunoprecipitation as described previously (Michaelevski et al., 2003; Tsuk et al., 2005). Oocytes were injected with 0.75 ng/oocyte syntaxin, 5 ng/oocyte Kv2.1, or 15 ng/oocyte Kv2.1ΔC1a mRNAs, as indicated in Figure 5c. Digitized scans were derived by PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics, Sunnyvale, CA), and relative intensities were quantitated by ImageQuant.
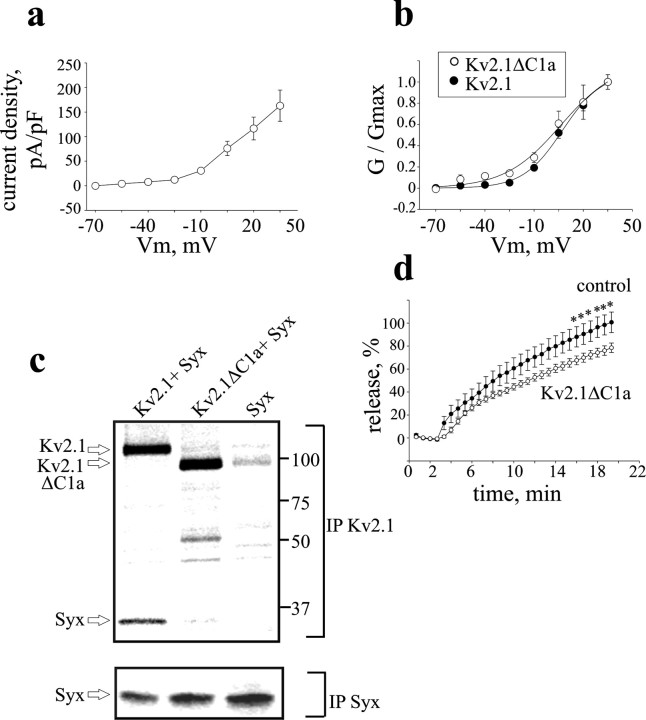
Figure 5.
A Kv2.1 mutant with impaired syntaxin-binding capacity does not enhance release. a, Averaged current densitiy–voltage relationships in PC12 cells transfected with the mutant channel (Kv2.1 ΔC1a; n = 6), derived as in Figure 2b. Note that the current densities of the mutant channel are similar to those of the wild-type channel (compare with Fig. 2b). b, Normalized conductance (G/Gmax)–voltage relationship of Kv2.1 ΔC1a superimposed on that of Kv2.1 (from Fig. 2c). c, Physical interaction of the Kv2.1ΔC1a channel with syntaxin in Xenopus oocytes is impaired. Digitized PhosphorImager scans of SDS-PAGE analysis of [35S]Met/Cys-labeled Kv2.1, Kv2.1ΔC1a, and syntaxin proteins coprecipitated by either anti-Kv2.1 antibody (IP Kv2.1) or anti-syntaxin antibody (IP Syx) from oocytes that were injected with Kv2.1 or Kv2.1ΔC1a together with syntaxin (+Syx), or injected with syntaxin alone (Syx) are shown. Arrows indicate the relevant proteins. The scans show that the amount of syntaxin coprecipitated with mutant channel (see IP Kv2.1) is significantly smaller than that coprecipitated with the same amount wild-type channel, although expression of syntaxin in oocytes expressing the mutant channel was not smaller than that of the wild type (see IP Syx). The results shown are from one of four independent experiments. d, Kv2.1ΔC1a overexpression does not enhance neuropeptide release induced by depolarization with high external KCl concentration. Cells were transfected with the mutant (Kv2.1ΔC1a) or with empty vector (control) (n = 12 and 10, respectively). *p < 0.05.
Time-lapse KCl-induced neuropeptide release.
PC12 cells were plated on polylysine-coated glass coverslips and transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) with Emerald GFP-tagged proANF (atrial natriuretic factor) (Han et al., 1999) in combination with Kv2.1 in pcDNA, pcDNA3-FLAG C1a, or both, or with pcDNA3-Kv2.1W365C/Y380T. Cotransfection of proANF with the empty vector (pcDNA3; control) served as a nonspecific control. Imaging experiments were conducted at 25°C 2 d after transfection using a Pentamax cooled, frame-transfer CCD camera (Photometrics, Tuscon, AZ) attached to a Nikon (Tokyo, Japan) Diaphot 300 inverted microscope equipped with a 40× oil-immersion objective. The 512 × 512 pixel images were subjected to 4 × 4 real-time binning and acquired on a Pentium III 833 MHz computer using WinTest Image Acquisition software (Photometrics). Incident light (∼480 nm) was provided by a Lamda DG-4 (Sutter Instruments, Novato, CA) light source containing a 150 W xenon bulb and a GFP-filter set (Omega Optical, Brattleboro, VT). Incident light exposure was synchronized with image acquisition to between 200 and 400 ms to minimize photobleaching. Images were acquired at 40 s intervals. Synchronization and timing of image acquisition with incident light exposure was controlled by an ITC-16 analog/digital converter (Instrutech, Port Washington, NY) connected to a Macintosh PPC 7600 computer running Igor Pro 5 (Wavemetrics, Lake Oswego, OR) with an ITC-16 XOP (Instrutech) installed. During the experiment, control solution containing (in mm) 140 NaCl, 2.8 KCl, 2 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, and 10 Na-HEPES, pH 7.4, was superfused through a 1 ml bath at a rate >2 ml/min. After five consecutive exposures, depolarization-evoked neuropeptide release was induced by superfusion with (in mm) 70 KCl, 70 NaCl, 10 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, and 10 Na-HEPES, pH 7.4. Average intensities for a region of interest (ROI) were calculated by summing the intensity of each pixel and dividing by the total number of pixels. Background fluorescence was quantified from an ROI in each image defined in an area containing no fluorescent cells. Background-subtracted average fluorescence intensities for each ROI at each exposure time point were then normalized to an average of the same measurement analyzed for time points before application of the depolarizing solution. Because these measurements quantify the amount of fluorescence remaining in the cell during depolarization, they were subtracted from 1 and multiplied by 100 to obtain the percentage of release at a particular time point. Only cells that exhibited stable basal fluorescence during the first five exposures were included in the analysis.
Electrophysiology.
Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings were conducted using a Multiclamp 700A patch-clamp amplifier (Molecular Devices, Foster City, CA) on PC12 cells. Ca2+ currents were eliminated by omitting Ca2+ from the extracellular solution and adding Cd2+. The extracellular solution contained the following (in mm): 120 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2 MgCl2, 10 HEPES, 10 d-glucose, and 0.5 CdCl2. pH was titrated to 7.4, and osmolarity was adjusted with sucrose to 325 mOsm. The intracellular solution contained the following(in mm): 100 potassium gluconate, 11 EGTA, 10 KCl, 1 MgCl2, and 2 MgATP2. pH was titrated to 7.2, and osmolarity was adjusted to 310–315 mOsm. Currents were acquired through an ITC-16 analog/digital converter using Synapse electrophysiological data acquisition software (Synergy Research, Ekero, Sweden) running on a Macintosh G3 computer. Currents were filtered at 2 kHz and digitized at 5 kHz. Currents were evoked with a series of 80 ms test pulses from a holding potential of −70 to +35 mV (15 mV increments). Cell capacitance was determined from cancellation of capacitance transients from 5 mV voltage steps using the Multiclamp Commander controlling software of the Multiclamp patch-clamp amplifier. Steady-state current amplitudes at the various potentials were measured relative to baseline and normalized to cell capacitance to yield current densities. Current densities were further normalized to the maximal density at +35 mV in a given cell. Conductance (G) values were derived from the corresponding current densities, assuming a reversal potential of −92.8 mV for K+ ions. For resting membrane potential measurements, PC12 cells were subjected to whole-cell current clamp with no holding current, and the membrane potential was measured immediately after patch membrane disruption in control and high-potassium solutions used in the neuropeptide release assays. Analyses were performed using Igor Pro 5 software (Wavemetrics) and custom-written macros.
Simultaneous measurements of [Ca2+]i and neuropeptide release.
PC12 cells were incubated with 4 μm fura-4 acetoxymethyl ester (AM) (Invitrogen, Eugene, OR) for 45 min in the 37°C incubator before being used for experiments (Groffen et al., 2006). To facilitate loading of the AM ester indicators, the mild detergent pluronic F-127 was added to fura-AM in a 1:1 ratio and vortexed thoroughly with 1 ml of DMEM (Invitrogen) immediately before incubation. PC12 cells loaded with the fura indicator were transferred to an inverted Olympus (Tokyo, Japan) IX-70 microscope for simultaneous measurement of calcium and GFP (TILL Photonics, Munich, Germany). Time-lapse imaging was performed with a CoolSNAP HQ camera (Photometrics) controlled by MetaFluor software (Molecular Devices, Downingtown, PA). A set of three images was acquired at 3.3 s intervals at incident light wavelengths of 488 nm to quantify the amount of GFP-tagged ANF protein and of 350 and 380 nm for fura-4 ratio imaging to determine intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. Exposure times were 500 ms for 488 nm wavelengths and 100 ms for 350 and 380 nm wavelengths. During the experiments, the cells were perfused continuously with external solution containing 140 mm NaCl, 3 mm KCl, 2 mm CaCl2, 10 mm HEPES, and 2 mg/ml glucose, pH 7.2–7.4, 300–320 mOsm. After recording for 35 s, the cells were stimulated by 70 mm KCl, which was applied locally through a four-barrel-like pipette for 15 s. After the application, the cells were washed with external solution. Between applications, the amount of calcium was allowed to decline to basal calcium levels. For calibration of the free intracellular calcium concentration, a series of BAPTA-buffered solutions containing defined concentrations of free calcium was calculated using Igor Pro with custom-written macros. Fura-4F (20 μm) was added to each of the calibration solutions (containing calcium concentrations of 0, 400, 800, or 10 mm), 10 μl of each solution was placed on a coverslip and imaged, and the ratios were determined for each solution. Ratiometric values could then be determined from the equation of Grynkiewicz et al. (1985) using Meta analyst software of the MethaMorph program (Molecular Devices) and were used to calculate the Ca+2 concentrations. Background fluorescence was measured at 350 and 380 nm and subtracted from the corresponding 350 and 380 nm images of the cells. Ratio images of the fluorescence intensities were obtained by dividing the subtracted 350 nm image by the subtracted 380 nm image. The intensity of the GFP fluorescence was quantitatively analyzed using Meta analyst software of the MethaMorph program (Molecular Devices). To measure the GFP, we analyzed the fluorescence intensity of ROIs.
Statistical analysis.
Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Student's t test was used to calculate the statistical significance of differences between two populations.
Results
In situ interaction of Kv2.1 with syntaxin is enhanced after triggering release
Previous immunoprecipitation studies indicate that Kv2.1 interacts with syntaxin 1A in PC12 lysates (Michaelevski et al., 2003). Here we set out to ensure that the channel–syntaxin interaction is authentic by excluding that binding between the proteins only occurs after detergent solubilization of concentrated extracts. Therefore, before solubilization and immunoprecipitation, permeable PC12 cells were treated with DTSSP, a membrane-impermeant, homo-bifunctional, reversible cross-linking reagent. Solubilization was performed under stringent conditions (RIPA buffer) and in very dilute conditions (up to 0.1 mg/ml total protein; see Materials and Methods) that minimize possible interactions in the lysate itself. Under these conditions, syntaxin immunoreactivity was coprecipitated by a Kv2.1 antibody and was detected in a monomeric form after reduction in the DTSSP thiol groups (Fig. 1a, IP Kv2.1 −DTSSP). As expected, in control experiments, in which the cross-linker was not present (−DTSSP) or in which DTSSP-treated cells were immunoprecipitated using an antibody directed at synapsin (that does not bind syntaxin: IP synapsin), little or no syntaxin was detected (Fig. 1a). Thus, cross-linking experiments verify that native Kv2.1 and syntaxin interact in situ.
Our next objective was to determine whether the interaction of the Kv channel with syntaxin is dynamic (i.e., whether it depends on the physiological state of the cells with regard to exocytosis). In permeable PC12 cells, DCV-mediated release is preceded by an ATP-dependent priming step, followed by a Ca2+-triggered fusion step (Hay and Martin, 1992; present study; and data not shown). Therefore, cells were subjected to cross-linking either just at the end of the priming phase or later, after the Ca2+-triggering phase. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis using the Kv2.1 antibody (Fig. 1b) revealed a fourfold increase (425 ± 68%; n = 5; p < 0.001) in the amount of syntaxin that associated with Kv2.1 in primed cells that underwent triggering by Ca2+, compared with cells that were only primed. However, the addition of Ca2+ ions to permeable cells that did not undergo priming did not increase the amount of coprecipitated syntaxin (n = 2) (supplemental Fig. 1, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material), excluding the possibility that the increased association is caused by the mere presence of Ca2+. Because membrane potential cannot change in permeable cells, the increase in syntaxin binding cannot reflect a difference in voltage-dependent gating. Therefore, these results are consistent with the hypothesis that Kv2.1 has highest affinity for syntaxin assembled into the SNARE complexes that mediate exocytosis. Yet, one cannot exclude other hypotheses. For instance, it is possible that the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) in the brain cytosols (present in the permeable cell preparation; see Materials and Methods) may have some ATPase activity that dissociates the SNARE complexes and generates monomeric syntaxin molecules that may interact strongly with Kv2.1. However, NSF/ATPase activity seems less probable to exist under the preparation conditions of the cytosols (Hay and Martin, 1992).
Pore-independent facilitation of release by Kv2.1
To gain insight into how the Kv2.1–syntaxin interaction may functionally affect exocytosis in living cells, depolarization-induced release of GFP-tagged prohormone was optically monitored (Han et al., 1999). Although Kv2.1 expression levels are very low in undifferentiated PC12 cells compared with native brain tissue (Sharma et al., 1993), we were able to detect Kv2.1 by immunoprecipitation from millions of cells (Fig. 1). However, the effects of Kv2.1–syntaxin interaction on release from single cells should be tested under conditions in which the density of Kv2.1 channels is similar to what is found in neurons. Overexpression of Kv2.1 in PC12 cells by transfection can result in current density and voltage dependence of activation (Fig. 2a–c) similar to those found in hippocampal neurons (Murakoshi and Trimmer, 1999; Du et al., 2000). Depolarization-induced release was quantified in cells transfected with a Kv2.1-containing vector and was compared with an empty vector control. Although Kv channels were thought to only inhibit exocytosis, release evoked by K+-induced depolarization was enhanced with additional expression of Kv2.1 (Fig. 2d).
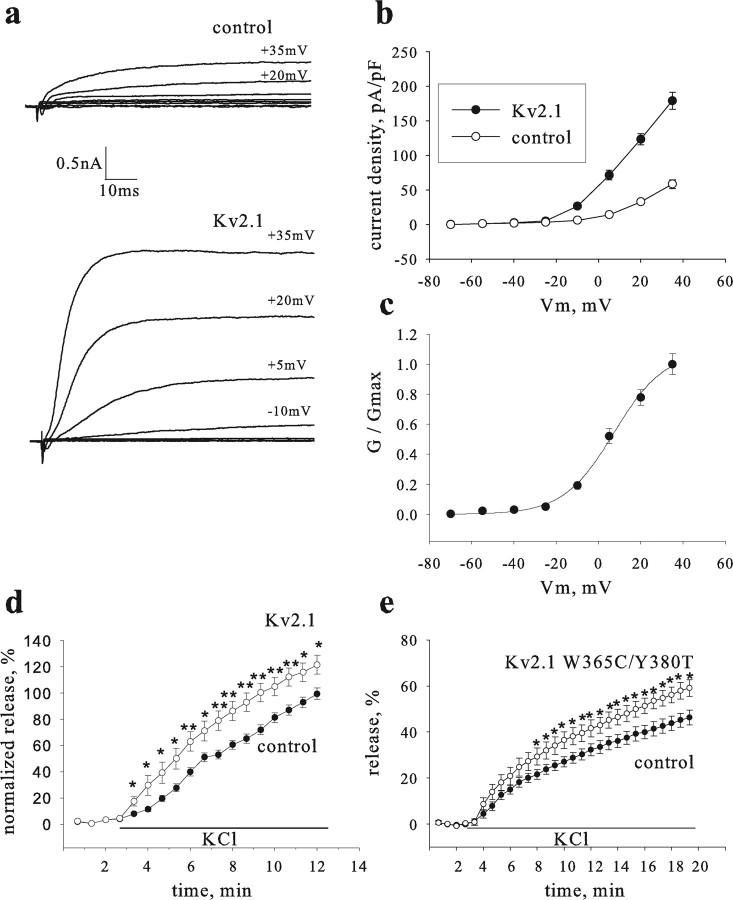
Figure 2.
Kv2.1 enhances release induced by depolarization with high external KCl concentration. The enhancement is independent on channel conductance. a, Examples of whole-cell voltage-clamped currents recorded from a control PC12 cell transfected with proANF-GFP cDNA (top) and a cell cotrasfected with proANF-GFP and Kv2.1 cDNAs (bottom). Currents were evoked by a series of steps to different potentials (noted adjacent to trace) from a holding potential of −70 mV. b, Averaged current density–voltage relationships for control and Kv2.1 cells (n = 5 and 7, respectively). c, Activation curve for Kv2.1 cells. Normalized conductance (G/Gmax)–potential relationships were fitted to a Boltzmann equation, G/Gmax = 1/(1 + exp ((Va1/2 − V)/a), and yielded a Va1/2 (half-activation voltage) of 5.8 ± 2.26 mV and an a (slope factor) of 11.8 ± 0.42. d, Time course of release induced by depolarization with high 70 mm extracellular KCl from PC12 cells cotransfected with proANF-GFP and either Kv2.1 (Kv2.1; open circles; n = 19) or empty vector (control; filled circles; n = 17). Results are the summary of eight independent experiments. e, A pore mutant channel enhances release induced by depolarization. Cells were transfected with the mutant (Kv2.1W365C/Y380T; open circles; n = 10) or with the empty vector (control; filled circles; n = 11). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001.
The above experimental conditions supposedly clamp the membrane potential near the reversal potential for K+ and thereby should minimize the impact of the Kv channel pore (i.e., minimize K+ currents). To determine directly whether Kv2.1 pore function is involved in the facilitation of depolarization-evoked release, a pore mutant (Kv2.1W365C/Y380T) that abolishes ion conduction (Malin and Nerbonne, 2002) was used. Control experiments conducted in Xenopus oocytes showed that this Kv2.1 mutant binds syntaxin to the same extent as wild-type channels and is expressed at the cell surface (supplemental Fig. 2, available at http//www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). After expression in PC12 cells, Kv2.1W365C/Y380T enhanced release to the same degree as the wild-type channel (Fig. 2e) (specifically, there was no statistical difference in the release measured after 12 min of depolarization). Thus, a functional pore was not required for the Kv2.1-mediated facilitation of depolarization-evoked release.
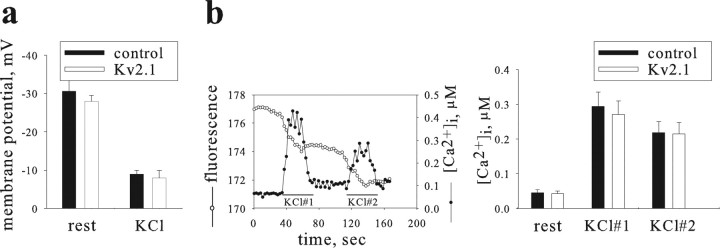
Follow-up experiments verified that Kv2.1 enhancement of release did not arise from effects on membrane potential or cytoplasmic Ca2+. First, membrane potential before stimulation was identical in cells overexpressing Kv2.1 and control cells expressing empty vector (Fig. 3a). Likewise, during KCl superfusion, depolarization was indistinguishable in both experimental groups (Fig. 3a). In addition, simultaneous monitoring of proANF-GFP and cytoplasmic Ca2+ transients indicated a correlated release of fluorescent ANF with a rise in intracellular free Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) (see a representative cell in Fig. 3b, left panel). Note that the basal level of [Ca2+]ι in cells transfected with Kv2.1 was similar to control cells (Fig. 3b, right panel). Moreover, superfusion of single cells with two consecutive 30 s pulses of 70 mm KCl solution elicited similar Ca2+ transients in both groups of cells (Fig. 3b). Together, these findings show that the observed facilitation of release by Kv2.1 was not attributable to differences in membrane potential or bulk intracellular Ca2+, in accordance with a pore-independent mechanism.
Figure 3.
Kv2.1 enhancement of release does not arise from differences in membrane potential or intracellular free Ca2+. a, Membrane potential, measured from GFP-expressing cells using the whole-cell current clamp. Increased depolarizations were observed when cells were bathed in 70 mm KCl solution (KCl) compared with control solution (rest); however, membrane potentials were similar for Kv2.1- and empty vector-transfected cells (control; 15 and 11 cells per group, respectively). b, Both resting and evoked Ca2+ levels are similar in Kv2.1-transfected and control cells. Left, In a single cell, intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i; filled circles) and depletion of proANF-GFP fluorescence (fluorescence; open circles) were measured during two extracellular applications of 70 mm KCl (bars). An increased rate of fluorescence depletion indicating proANF-GFP release coincides with the rise in intracellular Ca2+. Right, Bar graph showing that resting [Ca2+]i (left bars) and peak values during KCl application are similar for Kv2.1 and control cells (n = 13 and 14, respectively).
Kv2.1-derived syntaxin-binding peptides inhibit the facilitation of release by the channel
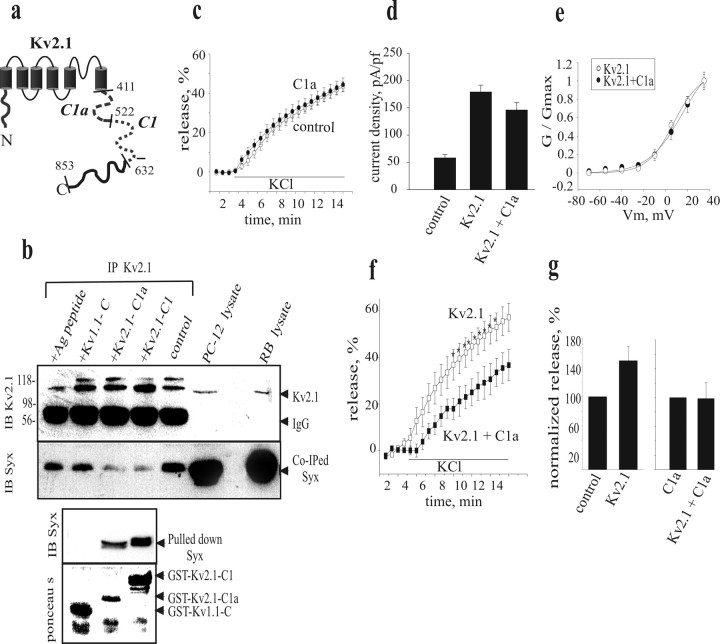
Previous in vitro binding of GST-fusion peptides corresponding to the major cytoplasmic parts of Kv channels with the recombinant cytoplasmic portion of syntaxin or the 35S-labeled full-length syntaxin synthesized in reticulocyte lysate showed that syntaxin binds the C1 and C1a domains of the cytoplasmic C terminus of Kv2.1 (Fig. 4a) but not to the C terminus of Kv1.1 (Fili et al., 2001; Michaelevski et al., 2003; Tsuk et al., 2005). Therefore, we examined whether the Kv2.1 syntaxin-binding peptides could be used to compete for the in vivo association of syntaxin with Kv2.1. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments in PC12 cells were performed in the presence or absence of GST-fused Kv2.1 peptides. These studies showed that the amount of syntaxin that was coimmunoprecipitated with Kv2.1 (Fig. 4b, Co-IPed Syx, control) was considerably reduced in the presence of Kv2.1-C1 and Kv2.1-C1a peptides. In contrast, the amount of coprecipitated syntaxin was considerably larger in the presence of the GST-fused Kv1.1-C-terminus peptide (Kv1.1-C), which does not bind syntaxin (Fig. 4b). Therefore, the Kv2.1-derived syntaxin-binding peptides specifically disrupt interaction of syntaxin with native Kv2.1 channels.
Figure 4.
The Kv2.1-C1a peptide competes with Kv2.1 for association with syntaxin to inhibit facilitation of release by Kv2.1. a, Schematic illustration of the Kv2.1 protein. Dashed segments are domains that bind syntaxin and were used in this study. b, Immunoprecipitation (IP) from PC12 cells was performed with anti-Kv2.1 antibody in the absence (control) or presence of recombinant Kv2.1 or Kv1.1 GST-fusion peptides, or the antigen (Ag) peptide for the Kv2.1 antibody, as indicated above the lanes. The immunoprecipitated Kv2.1 and the coimmunoprecipitated syntaxin (Kv2.1 and co-IPed Syx) proteins were detected by antibodies (IB), as indicated on the left side of the blots of the top panel. Molecular weights are also marked on the left. Glutathione-Sepharose beads were added to the supernatant to pulldown syntaxin (Pulled down Syx). Precipitated proteins were immunoblotted with anti-syntaxin antibody (IB Syx) or stained with ponceau S, as indicated on the left side of the bottom panel. c, f, g, Release induced by depolarization with 70 mm extracellular KCl concentration was assessed from PC12 cells (as in Fig. 2) that were transfected with empty vector (control; n = 9; c), with Kv2.1-C1a peptide (C1a; n = 15; c), with Kv2.1 alone (Kv2.1; n = 7; f) or with Kv2.1 together with Kv2.1-C1a (Kv2.1 + C1a; n = 6; f). *p < 0.05. Normalized release at 10 min after the onset of KCl application is shown in the bar diagram (g). In all cells the molar concentration of total transfected DNA was adjusted to be equal by the empty vector. d, Averaged current density at +35 mV in cells expressing Kv2.1 + C1a (n = 9) compared with those of control and Kv2.1 cells (the latter taken from Fig. 2b). e, The normalized conductance–voltage relationship from cells expressing Kv2.1 + C1a is superimposed on that of Kv2.1 (the latter taken from Fig. 2c).
This finding led us to examine the impact of the Kv2.1-C1a peptide on channel facilitation of depolarization-evoked release. Expression of C1a (which was verified by FLAG tag immunostaining) in the absence of exogenous Kv2.1 did not inhibit basal release (Fig. 4c). In addition, expression of Kv2.1-C1a peptide did not alter Kv current density or voltage dependence of activation (Fig. 4d,e). However, the Kv2.1-dependent enhancement of depolarization-evoked release was markedly inhibited in cells coexpressing the Kv2.1-C1a peptide (Fig. 4f,g), consistent with a role for the Kv2.1–syntaxin interaction in facilitation of release.
The syntaxin association domain is required for Kv2.1 facilitation of release.
The peptide competition experiment could reflect disruption of syntaxin binding to Kv2.1 or to another protein with homology to the C1a domain. To distinguish between these possibilities, the C1a domain was deleted from the wild-type channel. This deletion did not affect gross channel behavior because the current density and the voltage dependence of activation were similar to wild-type Kv2.1 (Fig. 5, compare a, b). However, coimmunoprecipitation analysis of proteins expressed in Xenopus oocytes (see a representative experiment in Fig. 5c) showed that the ratio of the immunostained intensities of syntaxin (coprecipitated by the Kv2.1 antibody) to the deletion mutant (Kv2.1ΔC1a) was reduced to 15.7 ± 1.3% (n = 4; p < 0.0005) of the wild-type controls. Hence, deleting the C1a domain crippled syntaxin binding without apparently altering channel gating, permeation, and expression.
Furthermore, the loss of the syntaxin association domain correlated with a loss of the Kv2.1-induced enhancement of depolarization-evoked release (Fig. 5d). Kv2.1ΔC1a produced a small statistically significant inhibition of release compared with empty vector control. Thus, eliminating the capacity of Kv2.1 to interact with syntaxin abolished the facilitation of release seen with the wild-type channel. Moreover, the small but statistically highly significant inhibition by Kv2.1ΔC1a may be ascribed, along two scenarios, to a dominant-negative function of this subunit with regard to the interaction of the Kv2.1 channel with syntaxin. First, during biosynthesis, the Kv2.1ΔC1a subunits may coassemble with the newly synthesized endogenous wild-type subunits to form heterotetramers with possibly reduced syntaxin binding capacity (the stoichiometric relationship between channel subunits and syntaxin molecules in a syntaxin-sensitive channel has not been determined yet). Alternatively, or in addition, homotetrameric mutant channels that do not bind syntaxin may scavange an endogenous channel-binding protein(s) other than syntaxin that forms, together with syntaxin and endogenous wild-type channels, an exocytosis-enhancing complex at the plasma membrane. These release results, along with the protein association experiments, support the conclusion that direct interaction between Kv2.1 and syntaxin is required for pore-independent enhancement of release.
Discussion
This study establishes that the Kv2.1 channel acts via its cytoplasmic syntaxin association domain to increase release after Ca2+ elevation. This effect is independent of the potassium ion flow through the channel pore, which tends to hyperpolarize the membrane potential to indirectly limit the opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. The actions of the Kv channel pore and syntaxin-binding domains might seem antagonistic, but in combination the two mechanisms reinforce the known activity dependence of DCV exocytosis. Single action potentials will not produce maximal exocytosis because membrane potential hyperpolarization from Kv channel pore activity will indirectly limit Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. However, release in response to repetitive firing that produces sustained Ca2+ elevation will be facilitated by the biochemical interaction of the channel with a key SNARE protein.
DCVs containing hormones, neuropeptides, or neurotrophins and Kv2.1 channels are colocalized in neuroendocrine cells and neuronal dendrites. Furthermore, Kv channels in nerve terminals also biochemically interact with syntaxin (Fili et al., 2001). Thus, the sculpting of release by direct interaction of Kv channels with secretory machinery may be widespread. In fact, the enhancement in release by the Kv2.1 syntaxin-binding domain is comparable to the effect of cAMP in PC12 cells (Ozaki et al., 2000) and the enhancement of transmitter release mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Li et al., 1998; Wardle and Poo, 2003), which is thought to play an important role in activity-induced long-term potentiation in the hippocampus (Tyler et al., 2002; Lu, 2003); for review see (Kovalchuk et al., 2004). Thus, the pore-independent enhancement of sustained release is an unexpected novel action of Kv channels that could be physiologically significant.
We suggest three possible mechanisms that could underlie the facilitation of exocytosis by the association of syntaxin with the Kv channel. First, DCVs undergo kiss-and-run exocytosis in neuroendocrine cells and dendrites (Scalettar, 2006). It has also been proposed that syntaxin lines the fusion pore (Jackson and Chapman, 2006). Therefore, it is possible that channel association with syntaxin promotes full-collapse fusion, which induces complete release, in place of the incomplete release associated with kiss-and-run exocytosis. Second, it is known that syntaxin function is affected by its structural conformation state. It has been shown in HEK293 cells that the functional interaction of the mutant open form of syntaxin (L165A, E166A) with Kv2.1 is stronger than that of wild-type syntaxin (Leung et al., 2005). Hence, the channel might influence the equilibrium between the closed and open conformations of this SNARE protein. Finally, many docked DCVs do not readily undergo release. Perhaps, the channel–syntaxin association influences whether a vesicle is in the reserve or releasable pool. Of course, more than one of these mechanisms may be relevant, and other possibilities abound. Regardless of the specifics, the physiological significance of Kv channels has been expanded: they act biochemically, as well as electrically, to control exocytosis.
Footnotes
This work was supported by Israel Science Foundation Grants 640/02 (I.L.) and 654/02 (M.B.), the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation (I.L.), and National Institutes of Health Grant R01 NS32385 (E.S.L.).
References
- Bajjalieh SM, Scheller RH. The biochemistry of neurotransmitter secretion. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:1971–1974. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.1971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett MK. SNAREs and the specificity of transport vesicle targeting. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7:581–586. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett MK, Calakos N, Kreiner T, Scheller RH. Synaptic vesicle membrane proteins interact to form a multimeric complex. J Cell Biol. 1992a;116:761–775. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett MK, Calakos N, Scheller RH. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992b;257:255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA. Structure and regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:521–555. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman ER. Synaptotagmin: a Ca(2+) sensor that triggers exocytosis? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:498–508. doi: 10.1038/nrm855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du J, Tao-Cheng JH, Zerfas P, McBain CJ. The K+ channel, Kv2.1, is apposed to astrocytic processes and is associated with inhibitory postsynaptic membranes in hippocampal and cortical principal neurons and inhibitory interneurons. Neuroscience. 1998;84:37–48. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du J, Haak LL, Phillips-Tansey E, Russell JT, McBain CJ. Frequency-dependent regulation of rat hippocampal somato-dendritic excitability by the K+ channel subunit Kv2.1. J Physiol (Lond) 2000;522:19–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-2-00019.xm. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fili O, Michaelevski I, Bledi Y, Chikvashvili D, Singer-Lahat D, Boshwitz H, Linial M, Lotan I. Direct interaction of a brain voltage-gated K+ channel with syntaxin 1A: functional impact on channel gating. J Neurosci. 2001;21:1964–1974. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-06-01964.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen AJ, Friedrich R, Brian EC, Ashery U, Verhage M. DOC2A and DOC2B are sensors for neuronal activity with unique calcium-dependent and kinetic properties. J Neurochem. 2006;97:818–833. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han W, Ng YK, Axelrod D, Levitan ES. Neuropeptide release by efficient recruitment of diffusing cytoplasmic secretory vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:14577–14582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson PI, Heuser JE, Jahn R. Neurotransmitter release—four years of SNARE complexes. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1997;7:310–315. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(97)80057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkins AB, Cahill AL, Powers JF, Tischler AS, Fox AP. Deletion of the synaptic protein interaction site of the N-type (CaV2.2) calcium channel inhibits secretion in mouse pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:15219–15224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401001101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay JC, Martin TF. Resolution of regulated secretion into sequential MgATP-dependent and calcium-dependent stages mediated by distinct cytosolic proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992;119:139–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay JC, Scheller RH. SNAREs and NSF in targeted membrane fusion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:505–512. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(97)80026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang PM, Fotuhi M, Bredt DS, Cunningham AM, Snyder SH. Contrasting immunohistochemical localizations in rat brain of two novel K+ channels of the Shab subfamily. J Neurosci. 1993;13:1569–1576. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01569.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson MB, Chapman ER. Fusion pores and fusion machines in Ca2+-triggered exocytosis. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2006;35:135–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.101958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing J, Chikvashvili D, Singer-Lahat D, Thornhill WB, Reuveny E, Lotan I. Fast inactivation of a brain K+ channel composed of Kv1.1 and Kvbeta1.1 subunits modulated by G protein beta gamma subunits. EMBO J. 1999;18:1245–1256. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.5.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y, Huang X, Pasyk EA, Ji J, Holz GG, Wheeler MB, Tsushima RG, Gaisano HY. Syntaxin-3 and syntaxin-1A inhibit L-type calcium channel activity, insulin biosynthesis and exocytosis in beta-cell lines. Diabetologia. 2002;45:231–241. doi: 10.1007/s00125-001-0718-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovalchuk Y, Holthoff K, Konnerth A. Neurotrophin action on a rapid timescale. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004;14:558–563. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2004.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung YM, Kang Y, Gao X, Xia F, Xie H, Sheu L, Tsuk S, Lotan I, Tsushima RG, Gaisano HY. Syntaxin 1A binds to the cytoplasmic C terminus of Kv2.1 to regulate channel gating and trafficking. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:17532–17538. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M213088200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung YM, Kang Y, Xia F, Sheu L, Gao X, Xie H, Tsushima RG, Gaisano HY. Open form of syntaxin-1A is a more potent inhibitor than wild-type syntaxin-1A of Kv2.1 channels. Biochem J. 2005;387:195–202. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li YX, Zhang Y, Lester HA, Schuman EM, Davidson N. Enhancement of neurotransmitter release induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1998;18:10231–10240. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-24-10231.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B. BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn Mem. 2003;10:86–98. doi: 10.1101/lm.54603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald PE, Ha XF, Wang J, Smukler SR, Sun AM, Gaisano HY, Salapatek AM, Backx PH, Wheeler MB. Members of the Kv1 and Kv2 voltage-dependent K(+) channel families regulate insulin secretion. Mol Endocrinol. 2001;15:1423–1435. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.8.0685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald PE, Wang G, Tsuk S, Dodo C, Kang Y, Tang L, Wheeler MB, Cattral MS, Lakey JR, Salapatek AM, Lotan I, Gaisano HY. Synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kilodaltons modulates Kv2.1 voltage-dependent K(+) channels in neuroendocrine islet beta-cells through an interaction with the channel N terminus. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:2452–2461. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malin SA, Nerbonne JM. Delayed rectifier K+ currents, IK, are encoded by Kv2 α-subunits and regulate tonic firing in mammalian sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 2002;22:10094–10105. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10094.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin TF. Cell cracking: permeabilizing cells to macromolecular probes. Methods Enzymol. 1989;168:225–233. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)68016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin TF, Walent JH. A new method for cell permeabilization reveals a cytosolic protein requirement for Ca2+-activated secretion in GH3 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:10299–10308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meir A, Ginsburg S, Butkevich A, Kachalsky SG, Kaiserman I, Ahdut R, Demirgoren S, Rahamimoff R. Ion channels in presynaptic nerve terminals and control of transmitter release. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:1019–1088. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1999.79.3.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelevski I, Chikvashvili D, Tsuk S, Singer-Lahat D, Kang Y, Linial M, Gaisano HY, Fili O, Lotan I. Direct interaction of t-SNAREs with the Kv2.1 channel: modal regulation of channel activation and inactivation gating. J Biol Chem. 2003;273:34320–34330. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304943200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochida S, Sheng ZH, Baker C, Kobayashi H, Catterall WA. Inhibition of neurotransmission by peptides containing the synaptic protein interaction site of N-type Ca2+ channels. Neuron. 1996;17:781–788. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochida S, Yokoyama CT, Kim DK, Itoh K, Catterall WA. Evidence for a voltage-dependent enhancement of neurotransmitter release mediated via the synaptic protein interaction site of N-type Ca2+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14523–14528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochida S, Westenbroek RE, Yokoyama CT, Zhong H, Myers SJ, Scheuer T, Itoh K, Catterall WA. Requirement for the synaptic protein interaction site for reconstitution of synaptic transmission by P/Q-type calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:2819–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.262787699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakoshi H, Trimmer JS. Identification of the Kv2.1 K+ channel as a major component of the delayed rectifier K+ current in rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1728–1735. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-05-01728.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki N, Shibasaki T, Kashima Y, Miki T, Takahashi K, Ueno H, Sunaga Y, Yano H, Matsuura Y, Iwanaga T, Takai Y, Seino S. cAMP-GEFII is a direct target of cAMP in regulated exocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:805–811. doi: 10.1038/35041046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig J, Heinemann C, Ashery U, Sheng ZH, Yokoyama CT, Catterall WA, Neher E. Alteration of Ca2+ dependence of neurotransmitter release by disruption of Ca2+ channel/syntaxin interaction. J Neurosci. 1997;17:6647–6656. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-17-06647.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes KJ, Keilbaugh SA, Barrezueta NX, Lopez KL, Trimmer JS. Association and colocalization of K+ channel α- and β-subunit polypeptides in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1995;15:5360–5371. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-07-05360.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalettar BA. How neurosecretory vesicles release their cargo. Neuroscientist. 2006;12:164–176. doi: 10.1177/1073858405284258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma N, D'Arcangelo G, Kleinlaus A, Halegoua S, Trimmer JS. Nerve growth factor regulates the abundance and distribution of K+ channels in PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1993;123:1835–1843. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner T, Bennett MK, Whiteheart SW, Scheller RH, Rothman JE. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993;75:409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spafford JD, Munno DW, Van Nierop P, Feng ZP, Jarvis SE, Gallin WJ, Smit AB, Zamponi GW, Syed NI. Calcium channel structural determinants of synaptic transmission between identified invertebrate neurons. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:4258–4267. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211076200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudhof TC. The synaptic vesicle cycle: a cascade of protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1995;375:645–653. doi: 10.1038/375645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer JS. Expression of Kv2.1 delayed rectifier K+ channel isoforms in the developing rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1993;324:205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81394-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuk S, Michaelevski I, Bentley GN, Joho RH, Chikvashvili D, Lotan I. Kv2.1 channel activation and inactivation is influenced by physical interactions of both syntaxin 1A and the syntaxin 1A/soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor-25 (t-SNARE) complex with the C terminus of the channel. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;67:480–488. doi: 10.1124/mol.104.005314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler WJ, Alonso M, Bramham CR, Pozzo-Miller LD. From acquisition to consolidation: on the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in hippocampal-dependent learning. Learn Mem. 2002;9:224–237. doi: 10.1101/lm.51202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle RA, Poo MM. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulation of GABAergic synapses by postsynaptic regulation of chloride transport. J Neurosci. 2003;23:8722–8732. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-25-08722.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiser O, Trus M, Hernandez A, Renstrom E, Barg S, Rorsman P, Atlas D. The voltage sensitive Lc-type Ca2+ channel is functionally coupled to the exocytotic machinery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:248–253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Goldberg T, Michaelevski I, Sheu L, Gaisano HY, Chikvashvili D, Lotan I. Target soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (t-SNAREs) differently regulate activation and inactivation gating of Kv2.2 and Kv2.1: Implications on pancreatic islet cell Kv channels. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70:818–828. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.021717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurch TL, Pauwels PJ. A modified overlap extension PCR method to create chimeric genes in the absence of restriction enzymes. Biotechnol Tech. 1998;12:653–657. [Google Scholar]
- Xia F, Gao X, Kwan E, Lam PP, Chan L, Sy K, Sheu L, Wheeler MB, Gaisano HY, Tsushima RG. Disruption of pancreatic beta-cell lipid rafts modifies Kv2.1 channel gating and insulin exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:24685–24691. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M314314200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan L, Figueroa DJ, Austin CP, Liu Y, Bugianesi RM, Slaughter RS, Kaczorowski GJ, Kohler MG. Expression of voltage-gated potassium channels in human and rhesus pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 2004;53:597–607. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.3.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]