Abstract
Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) is a point-of-care viscoelastic method and enables to assess viscoelastic profiles of whole blood in various clinical settings. ROTEM-guided bleeding management has become an essential part of patient blood management (PBM) which is an important concept in improving patient safety. Here, ROTEM testing and hemostatic interventions should be linked by evidence-based, setting-specific algorithms adapted to the specific patient population of the hospitals and the local availability of hemostatic interventions. Accordingly, ROTEM-guided algorithms implement the concept of personalized or precision medicine in perioperative bleeding management (‘theranostic’ approach). ROTEM-guided PBM has been shown to be effective in reducing bleeding, transfusion requirements, complication rates, and health care costs. Accordingly, several randomized-controlled trials, meta-analyses, and health technology assessments provided evidence that using ROTEM-guided algorithms in bleeding patients resulted in improved patient’s safety and outcomes including perioperative morbidity and mortality. However, the implementation of ROTEM in the PBM concept requires adequate technical and interpretation training, education and logistics, as well as interdisciplinary communication and collaboration.
Keywords: Algorithms, Bleeding management, Health care costs, Impedance aggregometry, Patient blood management, Thromboelastometry
Introduction
Rotational thromboelastometry-guided (ROTEM-guided) bleeding management is an essential part of patient blood management (PBM) which is an important concept in improving patient safety [1].
The treatment of bleeding is to stop the bleeding and to avoid the need for massive transfusion that is associated with high morbidity and mortality [2–5]. Prophylactic and/or inappropriate plasma and platelet transfusion does not prevent bleeding and transfusion and is associated with worse outcomes including mortality [6–11]. Two-thirds of transfusion-related mortality is based on transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), and transfusion-related immunomodulation (TRIM) with hospital-acquired infections [12].
Ratio-based transfusion concepts do not correct coagulopathy and do not reduce mortality in patients with severe hemorrhage [13–17]. Ratio-based concepts do not stop bleeding. It just gains time to identify the reason for bleeding (coagulopathic and/or surgical) and to perform adequate hemostatic interventions to stop bleeding. Accordingly, some centers are using a hybrid approach starting with a ratio-based transfusion concept until coagulation data are available and enable a more effective targeted hemostatic therapy [18].
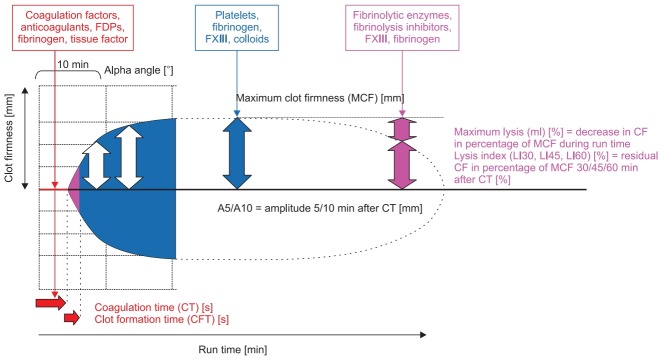
Time is life in severe bleeding! Here, the turnaround time of standard laboratory coagulation tests (SLCT) is too long (30–90 min) to guide clinical decisions [19–21]. In contrast, point-ofcare (POC) ROTEM provides test results within 10–15 min, as shown in Fig. 1. Here, early amplitudes of clot firmness at 5 and 10 min after the time to initiate clotting (coagulation time, CT), e.g., amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after CT (A5; actually not yet available in the US) and amplitude of clot firmness 10 min after CT (A10; early clot firmness parameter also available in the US), correlate very well with maximum clot firmness (MCF), plasma fibrinogen concentration, and platelet count and are essential for a short turnaround time of ROTEM analysis (Table 1 and Fig. 2) [21–26]. POC ROTEM testing does not only enable a shorter turnaround time compared to SLCTs, but these assays (such as FIBTEM) are also superior to SLCTs (such as plasma fibrinogen concentration) to predict bleeding and transfusion in several clinical settings [27–31].
Fig. 1.
ROTEM trace (‘temogram’) displaying the clinically most important parameters and their informative value. FDPs: fibrin (ogen) split products. Courtesy of Klaus Görlinger, Germany.
Table 1.
ROTEM delta (sigma) and ROTEM platelet Assays
| Assay | Activators and additives | Clinical comments |
|---|---|---|
| ROTEM delta (and sigma) assays | ||
| EXTEM | CaCl2 + recombinant tissue factor + polybrene | Deficiency of factors of the extrinsic pathway; VKAs and DOACs; indication for PCC administration; clot firmness based on platelet and fibrin contribution |
| FIBTEM | CaCl2 + recombinant tissue factor + polybrene + cytochalasin D | Fibrin polymerization; dose calculation for fibrinogen concentrate or cryoprecipitate; hyperfibrinolysis; FXIII deficiency |
| APTEM | CaCl2 + recombinant tissue factor + polybrene + aprotinin/tranexamic acid | Verifying the effect of antifibrinolytic drugs; differential diagnosis to clot retraction and FXIII deficiency (in combination with EXTEM) |
| INTEM | CaCl2 + ellagic acid | Deficiency of factors of the intrinsic pathway; unfractionated heparin (UFH) and protamine effects (in combination with HEPTEM) |
| HEPTEM | CaCl2 + ellagic acid + heparinase | Testing in patients with very high heparin plasma concentrations; UFH and protamine effects (in combination with INTEM) |
| NATEM | CaCl2 | Tissue factor-expression on circulating cells (e.g., monocytes or malignant cells); other anticoagulants (e.g., LMWH) |
| NA-HEPTEM | CaCl2 + heparinase | Tissue factor-expression on circulating cells (e.g., monocytes or malignant cells) in blood samples with heparin or HLE; other anticoagulants (e.g., LMWH) (in combination with NATEM) |
| ECATEM | CaCl2 + ecarin | Direct thrombin inhibitors (e.g., hirudin, argatroban, bivalirudin, dabigatran); not sensitive to heparin; new preparation under development |
| ROTEM platelet assays | ||
| ARATEM | Arachidonic acid (AA) | COX-1 (e.g., aspirin) and GPIIbIIIa receptor inhibitor effects; effects of CPB, trauma and sepsis |
| ADPTEM | Adenosine di-phosphate (ADP) | ADP (P2Y12) (e.g., clopidogrel and prasugrel) and GPIIbIIIa receptor inhibitor effects; effects of CPB, trauma and sepsis |
| TRAPTEM | Thrombin receptor-activating peptide-6 (TRAP-6) | Thrombin (PAR-1) (e.g. vorapaxar) and GPIIbIIIa receptor inhibitor effects; effects of CPB, trauma and sepsis |
VKAs: vitamin K antagonists, DOACs: direct oral anticoagulants, PCC: protamine complex concentrate, UFH: unfractionated heparin, LMWH: low molecular weight heparin, HLE: Heparin-like effect, COX-1: cyclooxygenase-1, CPB: cardiopulmonary bypass, ADP: adenosine diphosphate, PAR-1: protease-activated receptor-1.
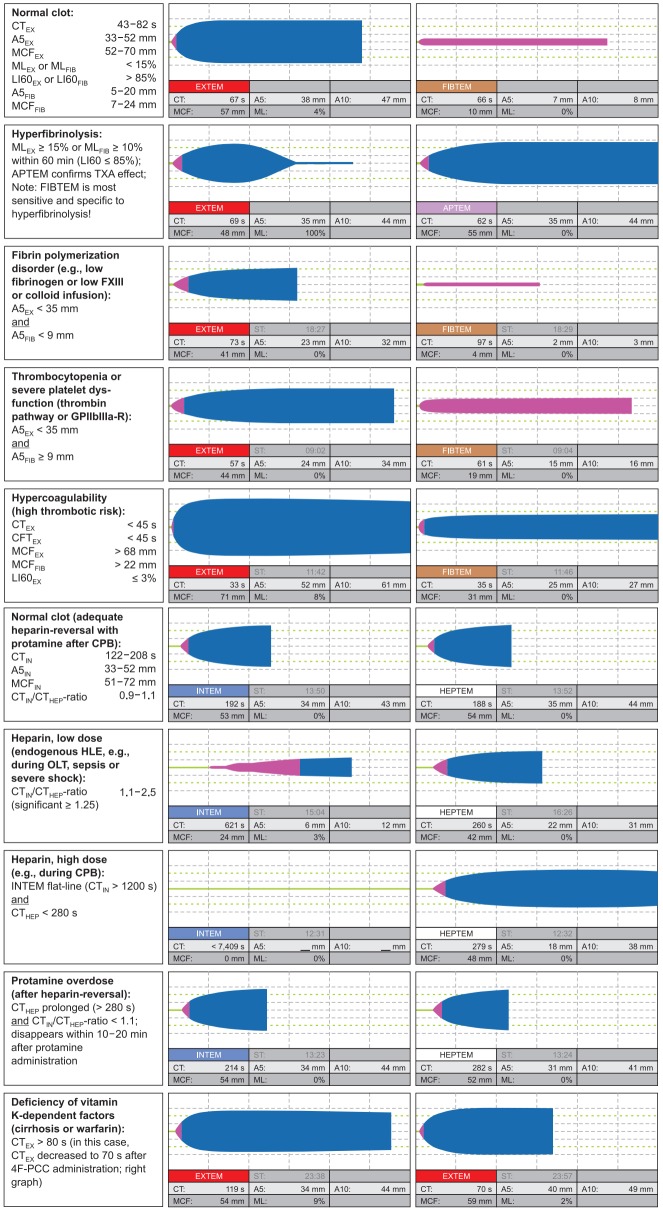
Fig. 2.
Characteristic ROTEM traces. The diagnostic performance is increased by test combinations, e.g., EXTEM and FIBTEM, EXTEM and APTEM, or INTEM and HEPTEM. CT: coagulation time, A5: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after CT, A10: amplitude of clot firmness 10 min after CT, MCF: maximum clot firmness, ML: maximum lysis during runtime, LI60: lysis index 60 min after CT, TXA: tranexamic acid (or other antifibrinolytic drug), FXIII: coagulation factor XIII, GPIIbIIIa-R: GPIIbIIIa-receptor, CFT: clot formation time, CPB: cardiopulmonary bypass, HLE: heparin-like effect, OLT: orthotopic liver transplantation, 4F-PCC: four factor prothrombin complex concentrate, EX: EXTEM, FIB: FIBTEM, HEP: HEPTEM, IN: INTEM. Courtesy of Klaus Görlinger, Germany.
ROTEM-guided bleeding management algorithms have been shown to be effective in reducing transfusion requirements, health care costs, and complication rates. Several randomized clinical trials (RCTs), meta-analyses, and health technology assessments provided evidence that using ROTEM-guided algorithms in bleeding patients resulted in improved patient’s safety and outcomes including perioperative morbidity and mortality [32–36].
Accordingly, ROTEM-guided algorithms implement the concept of personalized or precision medicine in perioperative bleeding management (‘theranostic’ approach). However, the implementation of ROTEM in the PBM concept requires adequate technical and interpretation training, education and logistics, as well as interdisciplinary communication and collaboration.
Basic Concepts of POC ROTEM-guided Bleeding Management Algorithms
All presented ROTEM-guided algorithms are based on a similar structure. The aims of algorithms include administering the right hemostatic intervention(s), in the right dose (fibrinogen and platelet dose calculation, Table 2), at the right time (‘Treat first what kills first!’), and in the right sequence, as shown in Figs. 3 and 4.
Table 2.
FIBTEM-guided Fibrinogen Substitution
| Targeted increase in FIBTEM A5 (A10) (mm) | Fibrinogen dose (mg/kg bw) | Fibrinogen concentrate (ml/kg bw) | Cryoprecipitate (ml/kg bw) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 12.5 | 0.6 (1 g per 80 kg) | 1 (5 U per 80 kg) |
| 4 | 25 | 1.2 (2 g per 80 kg) | 2 (10 U per 80 kg) |
| 6 | 37.5 | 1.9 (3 g per 80 kg) | 3 (15 U per 80 kg) |
| 8 | 50 | 2.5 (4 g per 80 kg) | 4 (20 U per 80 kg) |
| 10 | 62.5 | 3.1 (5 g per 80 kg) | 5 (25 U per 80 kg) |
| 12 | 75 | 3.8 (6 g per 80 kg) | 6 (30 U per 80 kg) |
Here, fibrinogen dose calculation is based on the targeted increase in FIBTEM A5 (A10) in mm. In case of severe bleeding, high plasma volume (e.g., in pregnancy, significant hemodilution, or TACO) and/or factor XIII deficiency, the achieved increase in FIBTEM A5 (A10) may be lower than the calculated increase. A5: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after CT, A10: amplitude of clot firmness 10 min after CT, bw: body weight, TACO: transfusion-associated circulatory overload.
Fig. 3.
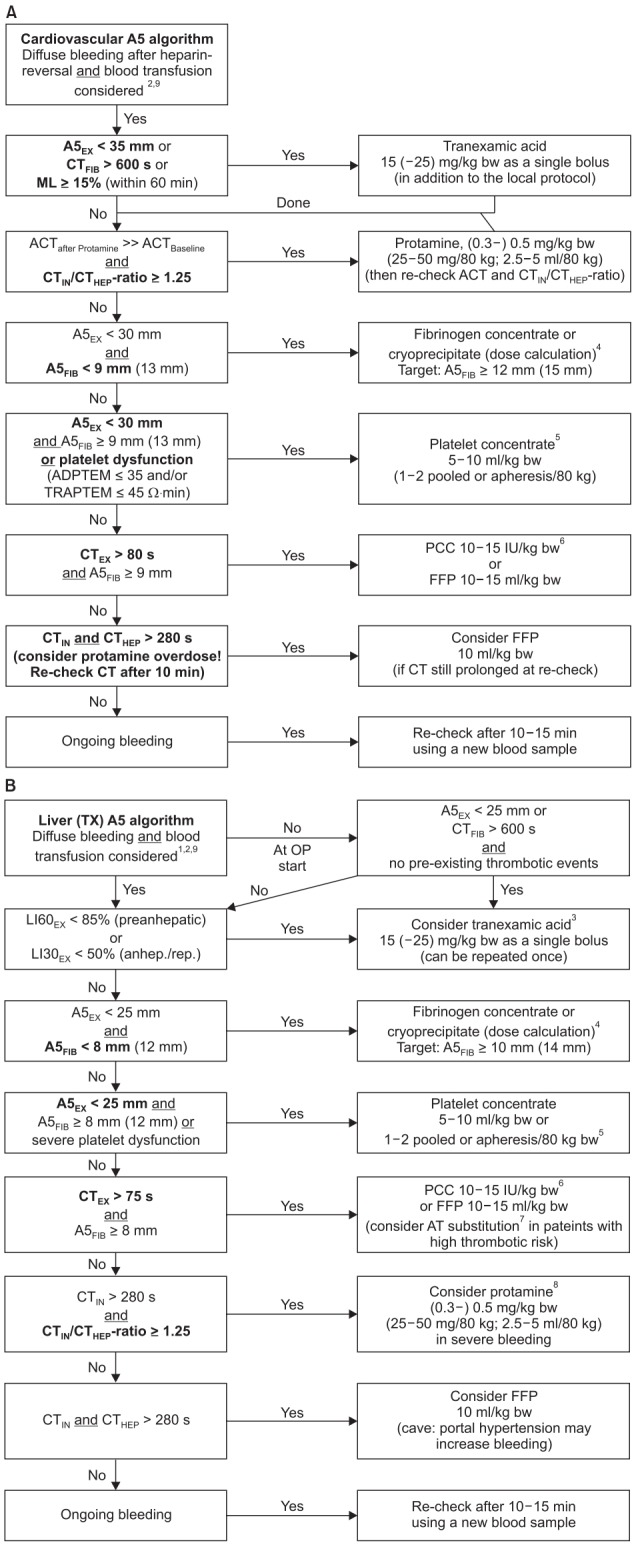
Evidence-based algorithms for ROTEM (A5)-guided bleeding management in (A) cardiovascular surgery and (B) liver transplantation. Algorithm footnotes: 1Timing of ROTEM-analysis during orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT): Baseline; re-check after 60 min or in case of bleeding during pre-anhepatic phase; 5–10 min after cava clamping (early anhepatic phase); 30–45 mm after cava clamping (late anhepatic phase); 5–10 min after reperfusion; 30–45 min after reperfusion; skin closure; and always in case of diffuse bleeding as well as 10–15 min after a specific hemostatic intervention. 2Check basic conditions: Temp. > 35℃; pH > 7.3; Cai2+ > 1 mmol/L; Hb ≥ 7 g/dl. 3Antifibrinolytic therapy [105,107]: EACA can be used instead of TXA (based on local practice). CTFIB > 600 s represents a flat-line in FIBTEM. Only pre-anhepatic hyperfibrinolysis is associated with increased mortality in OLT [103]; hyperfibrinolysis at/after reperfusion without diffuse bleeding may be self-limiting; re-check ROTEM analysis after ML reached 15% and consider avoidance of TXA treatment. 4Fibrinogen dose calculation (stepwise approach; see Table 2): Fibrinogen dose (g) = targeted increase in A5FIB (mm) × body weight (kg) / 160. Correction factor (140–160 mm kg/g) depends on the actual plasma volume. 10 U Cryoprecipitate ≈ 2 g Fibrinogen concentrate. 5Platelet concentrate transfusion: Cave: Platelet transfusion is associated with increased mortality in liver transplantation [123]! Consider compensation by increased A5FIB ≥ 12 mm. Cardiovascular surgery: Check platelet function with ROTEM platelet (ADPTEM and TRAPTEM) or Multiplate after weaning from CPB and heparin reversal with protamine: A5EX 23–30 mm or ADPTEM ≤ 35 Ohm∙min: 1 pooled or apheresis platelet concentrate. A5EX 15–22 mm or (ADPTEM ≤ 35 Ohm∙min and TRAPTEM ≤ 45 Ohm∙min): 2 platelet concentrates. A5EX < 15 mm: 2 platelet concentrates + fibrinogen substitution. 6If 4-factor prothrombin-complex-concentrate (4F-PCC) is not available: 10–15 ml FFP /kg bw or 45 (−90) µg rFVIIa /kg bw (if patient is normothermic and pH > 7.3, Cai2+ > 1 mmol/L, A5EX ≥ 30 mm, and A5FIB ≥ 9 mm but FFP is not effective to decrease CTEX ≤ 80 s and CTHEP ≤ 280 s). 7Anti-thrombin (AT) substitution: Consider AT substitution in patients with an increased risk of thrombosis (e.g., primary biliary cirrhosis, Budd-Chiari-Syndrome, portal vein thrombosis, malignancies) and/ or known pre-existing severe AT deficiency. 8Protamine: Endogenous heparin effect after liver graft reperfusion usually is self-limiting and does not require reversal by protamine. However, consider protamine administration in severe bleeding. 9Simultaneous interventions: Maximal three interventions at the same time (in first analysis and severe bleeding). Maximal two interventions at the same time (in second analysis and moderate to severe bleeding). Only one intervention at the same time (in second or later analysis and mild to moderate bleeding). A5EX: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after coagulation time in EXTEM, CTFIB: coagulation time in FIBTEM (CTFIB > 600 s reflects a flat-line in FIBTEM), ML: maximum lysis (within 1 h run time), ACT: activated clotting time, CTIN: coagulation time in INTEM, CTHEP: coagulation time in HEPTEM, bw: body weight, A5FIB: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after CT in FIBTEM, CTEX: coagulation time in EXTEM, PCC: prothrombin complex concentrate, FFP: fresh frozen plasma, LI60: Lysis Index (residual clot firmness in % of MCF) 60 min after CT, LI30: Lysis Index (residual clot firmness in % of MCF) 30 min after CT, IU: international units, AT: anti-thrombin, Cai2+: ionized Calcium concentration, EACA: epsilon-aminocaproic acid, TXA: tranexamic acid, CPB: cardiopulmonary bypass, rFVIIa: activated recombinant factor VII. Courtesy of Klaus Görlinger, Germany.
Fig. 4.
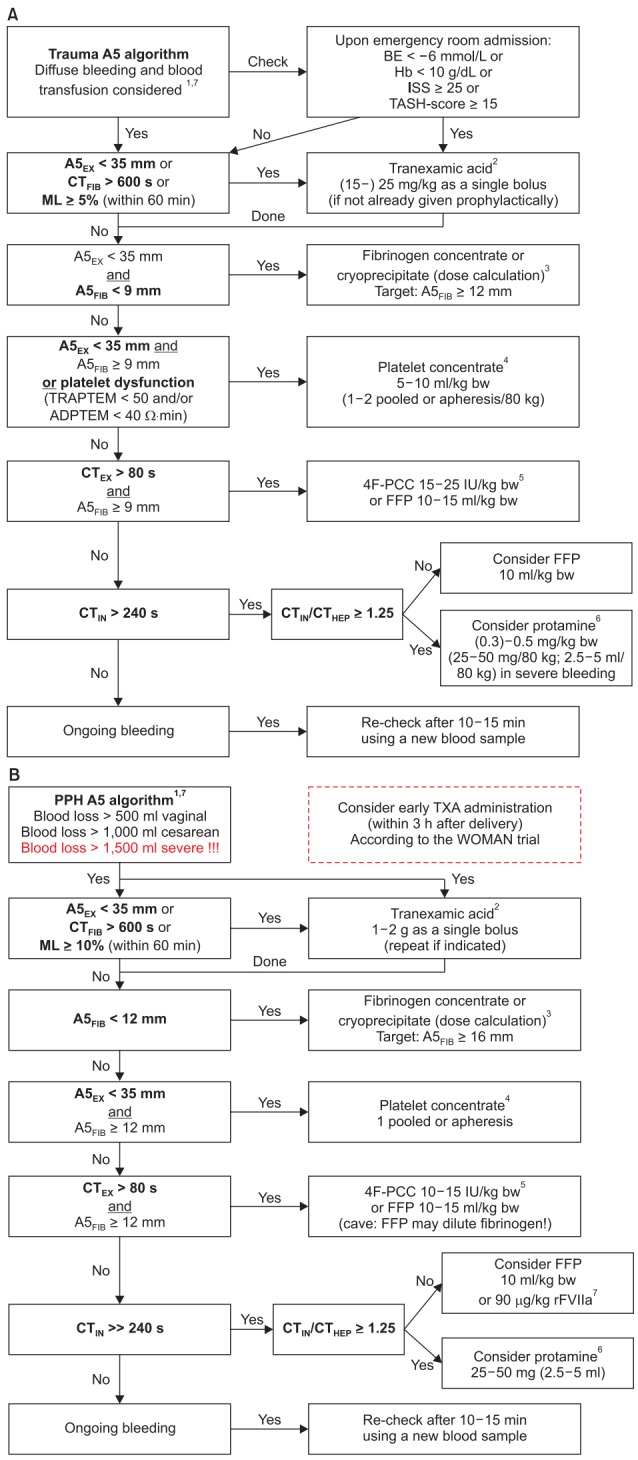
Evidence-based algorithms for ROTEM (A5)-guided bleeding management in (A) trauma/orthopedic surgery and (B) obstetrics/postpartum hemorrhage. Algorithm footnotes: 1Check basic conditions: Temp. > 35℃; pH > 7.3; Cai2+ > 1 mmol/L; Hb ≥ 7 g/dl. 2Antifibrinolytic therapy [105,142-146,153,157,195]: Prophylactic administration of TXA can be given within 3 h after trauma or delivery [142-144,195]. Continuous infusion of TXA can be performed in trauma [142-144]. CTFIB > 600 s represents a flat-line in FIBTEM. EACA can be used instead of TXA (based on local practice). 3Fibrinogen dose calculation (stepwise approach; see Table 2): Fibrinogen dose (g) = targeted increase in A5FIB (mm) × body weight (kg)/ 160. Correction factor (140–160 mm kg/g) depends on the actual plasma volume. 10 U Cryoprecipitate ≈ 2 g Fibrinogen concentrate. 4Platelet concentrate transfusion: Check platelet function with ROTEM platelet (ADPTEM and TRAPTEM) or Multiplate, if available [168-169]. Cave: Platelet transfusion might not improve platelet function in TIC [170]. Consider compensation by increased A5FIB ≥ 12 mm. Consider TXA (25 mg/kg) and/or desmopressin (DDAVP; 0.3 µg/kg) in patients with dual antiplatelet therapy and/or ADPTEM < 30 Ω∙min. Expected increase per pooled/apheresis PC per 80 kg: 8–10 mm in A5EX. A5EX 28–35 mm or ADPTEM < 40 Ω∙min: 1 pooled or apheresis platelet concentrate. A5EX 20–28 mm or (ADPTEM < 40 Ω∙min and TRAPTEM < 50 Ω∙min): 2 pooled or apheresis platelet concentrates. A5EX < 20 mm: 2 platelet concentrates + fibrinogen substitution (≥ 4 g). 5If 4-factor prothrombin-complex-concentrate (4F-PCC) is not available: 10–15 ml FFP /kg bw or 45–90 µg rFVIIa /kg bw (if patient is normothermic and pH > 7.3, and Cai2+ > 1 mmol/L, and A5EX ≥ 35 mm, and A5FIB ≥ 9 mm but FFP is not effective to decrease CTEX ≤ 80 s and CTHEP ≤ 240 s). Consider acquired hemophilia A in early severe bleeding, EXTEM and FIBTEM are normal but CTIN and CTHEP are significantly prolonged (see Fig. 6). Therapy: rFVIIa. 6Protamine: Endogenous HLE might occur in severe trauma and shock. Hemodynamic stabilization is the most important therapy. However, protamine administration might be considered in severe bleeding. 7Simultaneous interventions: Maximal three interventions at the same time (in first analysis and severe bleeding). Maximal two interventions at the same time (in second analysis and moderate to severe bleeding). Only one intervention at the same time (in second or later analysis and mild to moderate bleeding). ISS: injury severity score, TASH: trauma associated sever hemorrhage, A5EX: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after coagulation time (CT) in EXTEM, CTFIB: CT in FIBTEM (CTFIB > 600 s reflects a flatline in FIBTEM), ML: maximum lysis (within 1 h run time), A5FIB: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after CT in FIBTEM, bw: body weight, CTEX: CT in EXTEM, 4F-PCC: four factor prothrombin complex concentrate, IU: international units, FFP: fresh frozen plasma, CTIN: CT in INTEM, CTHEP: CT in HEPTEM, PPH: postpartum hemorrhage, TXA: tranexamic acid, rFVIIa: activated recombinant factor VII, Cai2+: ionized Calcium concentration, EACA: epsilon-aminocaproic acid, TIC: trauma-induced coagulopathy, HLE: heparin-like effect. Courtesy of Klaus Görlinger, Germany.
The first step is always the presence or absence of clinically relevant bleeding and the potential need for blood transfusion. The second (and maybe third) step deals with important setting-specific issues such as fibrinolysis management and anticoagulation reversal (cardiovascular surgery). The next two steps take care for clot firmness management (fibrinogen and platelet transfusion).
A fibrinogen deficiency is most often associated with a prolonged CT in EXTEM assay (CTEX). Therefore, only if the FIBTEM clot amplitude in the early 5 and 10 min tracing (A5FIB or A10FIB, respectively) is adequate, CTEX values can be interpreted adequately. In other words, ROTEM results should be interpreted in a reasonable sequence (A5FIB prior to CTEX) as given by the algorithms, not according to their availability (CTEX prior to A5FIB). This avoids potential misinterpretation of ROTEM results. The other reason is that fibrinogen concentration drops down first in severe bleeding before thrombin generation is affected (except in bleeding due to anticoagulants or hemophilia). Furthermore, an increase in thrombin generation seems to be associated with a higher risk of thromboembolic complications compared to a substitution of substrates—in particular, fibrinogen. Therefore, clot firmness management, e.g., a reduced A5FIB and A5 in EXTEM assay (A5EX), should precede thrombin generation management, e.g., a prolonged CTEX and CT in INTEM assay (CTIN).
ROTEM reference ranges have been established for several populations of healthy individuals (geographically, US and non-US), neonates, infants, children, adolescents, and adults, as well as for pregnant women (1st–3rd trimester and peri-partum) [37–42]. However, the reference ranges describing the 95% prediction interval for a specific population of healthy individuals can be used for orientation only and are not designed to predict bleeding or transfusion requirements.
Cut-off or trigger values (e.g., used in ROTEM algorithms) to guide clinical decision-making are determined in setting-specific observational studies by receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis or multivariate regression analysis [27–31,43–45].
Target values for ROTEM-guided algorithms have been validated by setting-specific interventional trials to assess whether a therapeutic intervention results in the achievement of hemostasis, reduction in transfusion requirements, and/or improvement in patient outcomes [32,45,46].
The following rules have to be considered when using ROTEM-guided bleeding management algorithms.
• Avoid any inappropriate blood transfusion or hemostatic intervention.
• ROTEM is not designed to answer the question ‘Will this patient bleed?’ but ‘Why does this patient bleed?’
• The first decision in every ROTEM-guided bleeding management algorithm presented in Figs. 3 and 4 is the clinical question whether diffuse (coagulopathic/microvascular) bleeding is present and blood transfusion has to be considered. If the answer to this clinical question is ‘No,’ the ROTEM algorithm ends at this point.
• Accordingly, don’t treat pathologic laboratory results (‘numbers’) in the absence of bleeding (low positive predictive value of SLCTs [14%–24%], viscoelastic [15%–24%], and platelet function testing [27%–50%]) in order to avoid any overtreatment that might result in thromboembolic events and increased health care costs [31,47,48].
• Use the high negative predictive value of viscoelastic (90%–97%) and platelet function testing (80%–95%) in ROTEM algorithms (that excludes reasons for bleeding). Accordingly, ‘Not-to-do (restrictive) POC ROTEM algorithms’ consider only hemostatic interventions with a high potential to stop the bleeding but avoid thromboembolic events (‘therapeutic window’ concept) [31,47,48].
• If both, POC viscoelastic (ROTEM delta or ROTEM sigma) and platelet function testing (ROTEM platelet) are normal, surgical bleeding has to be considered and treated adequately.
• However, the limitations of every diagnostic device and assay have to be considered (e.g., effect of antiplatelet drugs and von Willebrand disease for viscoelastic testing) [49].
Thromboelastometry and Whole Blood Impedance Aggregometry Devices and Reagents
The ROTEM system includes the semi-automated ROTEM delta system that works with a computer-driven automated pipette and provides four independent channels for viscoelastic testing and, in combination with the ROTEM platelet module, two additional channels for whole blood impedance aggregometry for POC platelet function analysis. Accordingly, the ROTEM platelet module covers the blind spot of thromboelastometry. The ROTEM sigma device is a cartridge-based fully-automated thromboelastometry system, and its cartridge includes four assays (actually EXTEM C, FIBTEM C, INTEM C, and APTEM C [type 1 or complete cartridge] or EXTEM C, FIBTEM C, INTEM C, and HEPTEM C [type 2 or complete + hep cartridge]). Here, no pipetting is needed and the closed blood sampling vial can be connected to the cartridge. In particular, the ROTEM sigma can easily be handled at the point-of-care by the medical staff without pipetting skills.
Three different types of reagents are used in the ROTEM system. First, there are the so-called liquid reagents (LR) for the ROTEM delta system (Table 1) that require several pipetting steps by combining 1–2 different liquid reagents for each assay. Here, the extrinsically activated assays EXTEM, FIBTEM, and APTEM contain the heparin inhibitor polybrene that inactivates up to 5 IU/ml unfractionated heparin. This enables the use and interpretation of these assays even under high heparin concentrations, such as on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) [50–52]. The ‘beads’ reagents used in the ROTEM sigma cartridges perform in the same way and the results are stored in the database under the terms EXTEM C, FIBTEM C, and APTEM C. Furthermore, the so-called single use reagents (SUR) are available for ROTEM delta and ROTEM platelet (Table 1). However, the ROTEM delta SURs have an important limitation:
Notably, the SURs for the assays EXTEM S, FIBTEM S, and APTEM S do not contain a heparin inhibitor. Therefore, SURs must not be used in patients treated with unfractionated heparin (UFH) (e.g., in cardiovascular surgery or in patients with therapeutic anticoagulation with UFH) as well as in patients in whom a significant endogenous liberation of heparinoids can be expected (e.g., after graft reperfusion in liver transplantation or in patients with severe shock). UFH can result in prolonged CT and clot formation time (CFT) as well as in reduced clot firmness (A-values and MCF) by using SURs in these settings. A heparin effect can be verified by the test combination INTEM (S) and HEPTEM (S).
All HEPTEM assays (LR, SUR, and C [cartridge-based assay for ROTEM sigma]) contain heparinase that eliminates up to 7 IU/ml heparin and can therefore be used in blood samples with high heparin concentrations [50,51].
The most important ROTEM parameters used in bleeding management algorithms are explained in Fig. 1, and characteristic ROTEM traces are displayed in Fig. 2.
ROTEM-guided Algorithms in Different Clinical Settings
In cardiovascular surgery
Most patients undergoing cardiac surgery already might get antifibrinolytic drugs prophylactically according to a local protocol. In this case, ROTEM-guided management of fibrinolysis is of minor importance.
In complex cardiac surgery, heparin-neutralization in liquid reagents (ROTEM delta) and cartridges (ROTEM sigma) allows for ROTEM analysis in blood samples with high heparin concentrations at the end of CPB, e.g., at aortic declamping [32,46,52–55]. This enables the timely ordering of blood products such as cryoprecipitate and platelet concentrates—in particular, if factor concentrates such as fibrinogen concentrate are not available. During cardiac surgery, the time window to perform hemostatic interventions is limited to 30–45 min between heparin-reversal by protamine and chest closure/transport of the patient to the intensive care unit (ICU). Therefore, a short turnaround time of POC testing and a short ‘time-to-treat’ are most important in this setting.
Detection of a residual heparin effect or a protamine overdose is essential in cardiovascular surgery before other hemostatic interventions are considered (step 3 of the algorithm in Fig. 3A). Notably, a prolonged activated clotting time (ACT) is not specific for a residual heparin effect. In centers using a 1 : 1 ratio between the primary heparin dose and the protamine dose administered for heparin reversal, a protamine overdose might even be more often the reason for an elusive ACT prolongation. Ichikawa et al. [56] reported a very weak correlation between ACT (r = 0.12) as well as activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) (r = 0.36) and the heparin concentration determined by the anti-Xa activity. In contrast, the CTIN/CTHEP-ratio correlated well (r = 0.72) with the anti-Xa activity. Furthermore, Ichikawa et al. demonstrated that an anti-Xa activity below 0.2 U/ml corresponding to a CTIN/CTHEP-ratio below 1.25 was not associated with increased postoperative mediastinal blood loss. In contrast, protamine overdose is not only associated with an elusively prolonged ACT (inhibition of factor V activation), CTIN/CTHEP-ratio ≤ 1, but also with a significant and long-acting inhibition of platelet function including the adenosine diphosphate (ADP)- and thrombin receptor-activating peptide (TRAP)-pathway [57–60]. RCTs confirmed that a protamine overdose is associated with a significant increase in blood loss, transfusion requirements, and need for re-surgery after cardiac surgery [61,62]. Therefore, a 1 : 1 ratio between primary heparin dose and protamine dose cannot be recommended. Here, a heparin to protamine ratio of 1 : 0.6–0.8 seems to be more effective [56,61,62]. Additional protamine administration is definitively not beneficial in patients with a prolonged ACT due to a protamine overdose.
Furthermore, a low FIBTEM amplitude has to be considered as a reason for a prolonged ACT, CTIN, CTHEP, and CTEX— in particular, in children undergoing cardiac surgery, since fibrinogen levels are diluted quickly in this patient population, as described ahead [63]. Fibrinogen is a key factor for bleeding after cardiovascular surgery since it is diluted and consumed quickly during and after CPB. Karkouti et al. [64] demonstrated that a post-CPB fibrinogen level below 2 g/L—that corresponds to an A5FIB < 9 mm (A10FIB < 10 mm) [21]—is associated with a significantly increased probability of transfusion of ≥ 5 U red blood cells (RBCs). This is in line with the results reported by other authors [52,65] and the reason to set the cut-off value for fibrinogen/cryoprecipitate substitution to A5FIB < 9 mm in the cardiovascular algorithm. Ranucci et al. [66–69] demonstrated that fibrinogen substitution in cardiac surgery is very effective to stop bleeding in patients with hypofibrinogenemia but that a substitution higher than an A5FIB of 16 mm (corresponding to a plasma fibrinogen concentration of about 3 g/L) does not show any further improvement. Therefore, the first target in our cardiovascular algorithm is an A5FIB ≥ 12 mm (fibrinogen concentration ≥ 2.5 g/L) and the second target (if bleeding continues in complex cardiovascular surgery) is an A5FIB ≥ 15 mm (fibrinogen concentration ≥ 3 g/L). An A5FIB ≥ 12 mm (fibrinogen concentration ≥ 2.5 g/L) may compensate for thrombocytopenia (< 100/nl) or platelet dysfunction after CPB [53,70]. The dose calculation for fibrinogen concentrate or cryoprecipitate are based on the targeted increase in FIBTEM amplitude and presented in Table 2 [46,53,66,71,72].
Notably, neither fibrinogen nor prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) or recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) are magic bullets in bleeding management and should only be given if indicated by the clinical situation and ROTEM results and in an adequate dose as a part of a bleeding management algorithm.
Thrombocytopenia as well as platelet dysfunction are frequent after cardiac surgery with CPB and have to be considered as a reason for intra- and post-operative bleeding. The expected increase in A5FIB (A10FIB, MCF) after platelet transfusion (one pooled or apheresis platelet concentrates in an adult patient) is about 8–10 mm (only about 5 mm in cirrhotic patients) (Fig. 3B) [73–75]. This can be used for dosing in our algorithm.
Since viscoelastic testing is not sensitive to the effects of antiplatelet drugs, CPB, and protamine on platelet function, POC whole blood impedance aggregometry (ROTEM platelet) is an ideal complement to thromboelastometry in cardiovascular surgery [32,46,53,76,77]. Pre-operative platelet function testing can be used to detect a residual platelet function defect in patients treated with antiplatelet drugs or other drugs that might impair platelet function in order to reduce the waiting time until surgery after cessation of ADP-receptor antagonists [78–82]. However, the intra- and post-operative changes in platelet function seem to be more significant and important for peri-operative bleeding management in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with CPB [47,60,82–85]. Accordingly, platelet function testing results achieved after protamine administration demonstrated the best correlation with postoperative chest tube drainage and postoperative transfusion requirements that were dependent on the degree of platelet inhibition and the number of pathways inhibited [47]. The corresponding cut-off values for ROTEM platelet ADPTEM and TRAPTEM after protamine administration have been implemented in our cardiovascular algorithm (Fig. 3A). Notably, several studies and one meta-analysis demonstrated that the incorporation of POC platelet function testing into transfusion management algorithms is associated with a reduction in blood loss and transfusion requirements in cardiac surgery patients [32,46,54,55,86].
The last part of the algorithm deals with impaired thrombin generation. Here, a deficiency of coagulation factors of the extrinsic pathway is detected by a CTEX > 80 s in the cardiovascular algorithm if A5FIB is normal (≥ 9 mm). Blasi et al. [87] reported that a CTEX ≥ 84 s predicted the International Normalized ratio (INR) > 1.5 in 93% of the cases, whereas a CTEX below this value predicted a safe INR value of < 1.5 in 100% of cases in patients taking acenocoumarol after elective heart valve replacement (ROC AUC = 0.998). These results have been confirmed by Schmidt et al. [88] in patients treated with warfarin. In contrast, the false-negative rate for detecting warfarin coagulopathy with kaolin- and rapid-TEG was clinically unacceptable (45.5% and 40.9%, respectively) [89]. The aim is to increase the activity of the vitamin K-dependent factors to about 40–60% that is enough to generate sufficient thrombin but avoids any overtreatment with the risk of thrombosis [48,52,71,90]. Several studies demonstrated that the approach of ROTEM-guided therapy with factor concentrates (fibrinogen and four-factor PCC)—in particular, in the cardiovascular setting—was associated with a significant risk reduction for thromboembolic events (OR [95% CI]: 0.44 [0.28–0.70]; P = 0.0006) [32–34,46,91,92]. In contrast to PCC, plasma transfusion is associated with a high incidence of TACO and right ventricular failure [7,11,93–95].
An A10 (US) version of the cardiovascular algorithm has been published in the Critical Care Handbook of the Massachusetts General Hospital [96].
In liver transplantation and visceral surgery
The liver transplantation and visceral surgery ROTEM algorithm (Fig. 3B) has a similar structure compared to the cardiovascular algorithm (Fig. 3A). Both start with the clinical detection of diffuse bleeding and the consideration of blood transfusion, followed by management of fibrinolysis, clot firmness, and thrombin generation. However, fibrinolysis management and the detection of endogenous heparin-like effects are more important in this setting [97]. SCLT in cirrhotic patients are most often characterized by thrombocytopenia and an increased INR. However, these pathologic SCLT results are not associated with increased bleeding because in this patient population a re-balance of hemostasis has to be considered. Since this re-balance take place on a low level, it can be disturbed easily and can result in bleeding as well as in thrombosis [97]. Notably, liberal transfusion of blood products—in particular, plasma— is associated with nosocomial infections, citrate intoxication, TRALI, TACO, and portal hypertension that again promotes bleeding and is associated with increased hospital mortality [98,99]. Accordingly, a restrictive transfusion strategy is associated with decreased mortality in patients with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding [100]. It should be avoided to treat numbers of the SCLT results. Unnecessary plasma and platelet transfusion can lead to citrate intoxication, portal hypertension, and organ failure through TACO and TRALI.
Sixty to 80% of patients undergoing liver transplantation reveal fibrinolysis—most often after reperfusion of the liver graft. However, most of them are self-limiting within 30–180 min without any need for additional treatment [101–103]. Fibrinolysis during the resection phase (pre-anhepatic phase) is associated with increased 30-day (26% vs. 0%; P = 0.000) and 6-month mortality (32% vs. 4%; P = 0.003), and fibrinolysis after reperfusion is associated with thrombosis in the portal vein and hepatic arteria (42% vs. 8%; P = 0.002) [103]. Accordingly, administration of antifibrinolytic drugs should be considered carefully—in particular, if fibrinolysis occurs after reperfusion—and no increase in blood transfusions during liver transplantation has been reported after the withdrawal of aprotinin [101–104]. Low clot firmness in EXTEM (A5EX < 25 mm) and a flat-line in FIBTEM (CTFIB > 600 s) are good predictors for fibrinolysis and can be used for risk analysis at the beginning of surgery [105,106]. Notably, FIBTEM is the most sensitive assay for fibrinolysis because in this assay diagnosis of fibrinolysis is not affected by the occurrence of platelet-mediated clot retraction [107,108].
Several observational studies reported cut-off values for EXTEM and FIBTEM clot firmness amplitudes (A5, A10, MCF) to predict bleeding and to guide fibrinogen substitution and platelet transfusion during and after liver transplantation [31,43,44,109]. With a cut-off value of 25 mm for A5EX (35 mm for A10EX and 45 mm for MCFEX) and a cut-off value of 8 mm for A5FIB (9 mm for A10FIB and 10 mm for MCFFIB), lower levels of clot firmness seem to be adequate in liver transplantation compared to the cardiovascular, trauma, and obstetric setting. Notably, FIBTEM is superior to predict bleeding in liver transplantation compared to plasma fibrinogen concentration since it does not only assess the quantity of fibrinogen but also fibrin polymerization that is affected by dysfibrinogens, factor XIII activity, and colloids [110–113]. Implementation of FIBTEM-guided fibrinogen substitution in bleeding management algorithms during liver transplantation significantly reduced transfusion requirements for red blood cells, plasma, and platelets [31,92,97,101,114–118]. In contrast, preemptive administration of fibrinogen concentrate did not influence transfusion requirements in an RCT in liver transplantation [119].
ROTEM-guided platelet transfusion during liver transplantation or in patients with cirrhosis who had to undergo invasive procedures could reduce platelet transfusion by 64 to 75% compared to transfusion trigger of platelet count < 50 × 109/L without any additional bleeding events [92,97,120–122]. This is of particular importance since platelet transfusion during liver transplantation is associated with reduced 1-year survival (74 vs. 92%; P < 0.001) [123].
INR can be used to characterize the severity of liver disease (e.g., in MELD score) but not to assess thrombin generation and bleeding risk in patients with cirrhosis [97,124–127]. Here, CTEX with a cut-off of 75 s is superior to predict bleeding in this patient population and CTEX-guidance can reduce fresh frozen plasma (FFP) transfusion and PCC administration significantly [31,97,124–129]. This helps to avoid overtreatment and thromboembolic events [92,97,125–130]. FFP is not effective in increasing thrombin generation in patients with cirrhosis but is associated with a high risk of TACO and portal hypertension [92,97,116,126,130]. In contrast to modern four-factor PCCs that contains significant amounts of protein C and S, rFVIIa does not contain any anticoagulants and has been shown to be associated with an increased incidence of thromboembolic events—in particular, arterial thrombosis—in liver transplantation and other clinical settings and should therefore be avoided [131,132].
Endogenous heparinization or a heparin-like effect (HLE) is well described in patients during liver transplantation [97,101,105,133,134]. A mild (CTIN/CTHEP-ratio ≥ 1.25) to severe (CTIN/CTHEP-ratio ≥ 2.0) HLE can be detected in about 50% after liver graft reperfusion (CTIN, 270–3312 s). The CTIN/CTHEP-ratio is more sensitive to identify HLE than APTT. Severe HLE was associated with increased transfusion requirements, and HLE during the anhepatic phase was associated with increased 3-month mortality [135]. HLE after reperfusion is most often self-limiting after hemodynamic stabilization [97,101]. If not, HLE can be reversed by small amounts of protamine [97,101,136].
Since the SURs for the assays EXTEM S, FIBTEM S, and APTEM S do not contain a heparin inhibitor, SURs must not be used in patients undergoing liver transplantation. A HLE can result in misinterpretation of ROTEM results due to prolonged CT and CFT as well as in reduced clot firmness amplitudes (A-values and MCF) by using SURs in this setting [97].
ROTEM results can also be used to assess the risk for thrombosis, and the ‘therapeutic window’ concept of ROTEM-guided bleeding management can be used to avoid thromboembolic complications [31,49,97,116,118,126,137]. Hincker et al. [137] reported that pre-operative APTT, INR, and platelet count were not able to predict post-operative thromboembolic events after major non-cardiac surgery. In contrast, INTEM and EXTEM A10 (A10EX cut-off, 61.5 mm; ROC AUC, 0.751) were the best predictors of thromboembolic complications. FIBTEM was not predictive for thromboembolic events in this study. In contrast, several studies in patients with cirrhosis and/or undergoing liver transplantation demonstrated a predictive value of increased MCFFIB (cut-off between 18 and 25 mm; risk ratio [RR] up to 4.8) for portal vein and hepatic artery thrombosis. In particular, this applies to patients with hereditary or acquired thrombophilia (e.g., anti-thrombin, protein C or protein S deficiency, factor V Leiden mutation, lupus anticoagulant, antiphospholipid antibodies) and patients with hepatocellular or cholangiocellular carcinoma [138–141]. Again, this emphasizes the need for a correct dose-adjustment and that overtreatment—also with fibrinogen—should strictly be avoided.
An A10 (US) version of the liver algorithm has been published recently in an US textbook about bleeding management [97].
In trauma and orthopedic surgery
The trauma and orthopedic surgery ROTEM A5 algorithm is presented in Fig. 4A.
In trauma, a previous RCT (CRASH-2 trial) postulated that tranexamic acid (TXA) should be given to all trauma patients with significant hemorrhage within 3 h after injury, since TXA administration was associated with a RR for death of 0.91 (99% CI, 0.85–0.97) (14.5% vs. 16.0% all-cause mortality) in this study [142]. However, this study demonstrated an increase in mortality if TXA administration was started later than 3 h after injury (RR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.12–1.84; 4.4% vs. 3.1% mortality due to bleeding) [143,144]. Accordingly, TXA should only be started later than 3 h after injury if signs of trauma-induced coagulopathy (A5EX < 35 mm or FIBTEM flat-line [CTFIB > 600 s]) or hyperfibrinolysis (EXTEM or FIBTEM maximum lysis [ML] ≥ 5% within 60 min) are present [105,145–147]. However, it is still under debate whether prophylactic or therapeutic administration of TXA should be performed in hospitals with access to viscoelastic testing [145–155]. Physiologic fibrinolysis and fibrinolysis shutdown are defined in ROTEM as an EXTEM LI60 82–97.9% and ≥ 98%, respectively [156].
Notably, FIBTEM is the most sensitive assay for fibrinolysis [107,157].
Davenport et al. demonstrated that acute traumatic coagulopathy (ATC) is functionally characterized by a reduction in ROTEM clot firmness amplitude [20,36,158–160]. With a cutoff value of A5EX ≤ 35 mm, ROTEM can identify ATC at 5 min after CT and predict the need for massive transfusion (detection rate for A5EX ≤ 35 mm, 71% vs. 43% for INR > 1.2; P < 0.001). In patients with A5EX > 35 mm transfusion requirements were below 2 U RBC/12 h and 1 U FFP/12 h. For A5EX < 35 mm transfusion requirements for RBCs and FFP increase significantly. This allows for initiation and termination of massive transfusion protocols in hemorrhaging trauma patients [161,162].
In the same way Schöchl et al. [27] showed that FIBTEM (A5FIB and A10FIB) provided early prediction of massive transfusion (≥ 10 U RBCs within 24 h of admission). Here, an A10FIB < 8 mm (plasma fibrinogen level < 150 mg/dl) was associated with an increased incidence of massive transfusion. An A10FIB ≤ 4 mm (plasma fibrinogen level < 100 mg/dl) provided a ROC AUC of 0.83 for the prediction of massive transfusion. Furthermore, the crucial factor of fibrinogen for the hemostatic competence in trauma has been confirmed by Hagemo et al. [163], who detected a dramatic increase in 28-day mortality in trauma patients if admission fibrinogen concentration was below a critical value of 2.29 g/L (corresponding to an A10FIB of 12.5 mm and an A5FIB of 11.5 mm). These results have been confirmed by an international prospective validation study including 808 trauma patients [28]. An A5EX cut-off value of ≤ 37 mm had a detection rate of 66.3% for ATC. An A5EX threshold value of ≤ 40 mm predicted massive transfusion in 72.7%. An A5FIB cut-off value of ≤ 8 mm detected ATC in 67.5%, and an A5FIB cut-off value ≤ 9 mm predicted massive transfusion in 77.5%. Accordingly, an A5EX and A5FIB cut-off value of 35 mm and 9 mm have been selected for fibrinogen substitution and platelet transfusion in our trauma algorithm. The same cut-off values have been recommended by the consensus group on viscoelastic test-based transfusion guidelines for early trauma resuscitation and the German AWMF guidelines on the management of multiple traumas [164–166]. Similar cut-off values are used in the European multicenter RCT iTACTIC (implementing Treatment Algorithms for the Correction of Trauma-Induced Coagulopathy; ClinicalTrials.gov, ID: NCT02593877): A5FIB < 10 mm for fibrinogen substitution and (A5EX–A5FIB) < 30 mm for platelet transfusion [167]. This is also in line with the FIBTEM cut-off values published by Na et al. [29] to predict massive bleeding in total hip replacement arthroplasty.
Furthermore, ATC is characterized by an early platelet dysfunction mainly affecting the ADP and TRAP pathway in whole blood impedance aggregometry [168]. Chapman et al. [169] reported a cut-off value of 53 Ω∙min (ROC AUC, 0.97) for ROTEM platelet TRAPTEM and a cut-off value of 65 Ω∙min (ROC AUC, 0.88) for ROTEM platelet ADPTEM to predict massive transfusion (≥ 10 U RBCs) or death from hemorrhage within 6 h of injury. However, interventional studies are needed to assess whether early platelet dysfunction in trauma can only be used as a biomarker for severe trauma or to guide platelet transfusion in this setting [170].
Impaired thrombin generation with the need for plasma transfusion or four-factor PCC administration is considered in our trauma algorithm if CTEX > 80 s and A5FIB ≥ 9 mm according to the consensus group on viscoelastic test-based transfusion guidelines for early trauma resuscitation and the German AWMF guidelines on the management of multiple trauma [164–166]. This is also in line with the iTACTIC protocol [167]. In severe traumatic hemorrhage, fixed-ratio RBC and plasma transfusion is not effective to treat ATC and to reduce mortality [12–17,171]. Innerhofer et al. compared in their RCT the efficacy of ROTEM-guided administration of coagulation factor concentrates (fibrinogen, factor XIII, and four-factor PCC) versus plasma transfusion to treat ACT and to stop bleeding [172,173]. After two therapeutic loops, FFP failed in 52% to treat ATC and to stop bleeding and a rescue cross-over to ROTEM-guided administration of coagulation factor concentrates was needed. In contrast, ROTEM-guided administration of coagulation factor concentrates failed only in 4% and rescue cross-over to FFP transfusion was needed. Furthermore, massive transfusion rate (12% vs. 30%; P = 0.042), number of days on hemofiltration (11.0 vs. 27.0; P = 0.038), multiple organ failure rate (50% vs. 66%; P = 0.15), and venous thrombosis rate (8% vs. 18%; P = 0.22) were lower in the ROTEM-guided group. Accordingly, the European Trauma Guidelines suggest in their recommendation 33 that PCC or plasma be administered in the bleeding patient based on evidence of delayed coagulation initiation using viscoelastic monitoring provided that fibrinogen levels are normal [174].
Endogenous heparinization with a HLE detected by viscoelastic testing (CTIN/CTHEP -ratio) has been reported in 5% of patients with severe trauma and seems to be linked to endothelial glycocalyx degradation [175].
Finally, thrombosis is a big issue in trauma, orthopedics, and neurosurgery, and overtreatment should definitively be avoided by implementing the ‘therapeutic window’ concept of ROTEM-guided bleeding management. This also includes the timely start of thromboprophylaxis in the post-operative period [137,172,176–178].
An A10 (US) version of the trauma algorithm has been published recently in an US textbook about trauma induced coagulopathy [145].
In obstetrics surgery and postpartum hemorrhage
The obstetrics and postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) algorithm (Fig. 4B) is very similar to the trauma algorithm (Fig. 4A) but takes into account the shift in fibrinogen and FIBTEM reference ranges during pregnancy and the different A5FIB cut-off and target values determined for this setting in observational and interventional trials [41,42].
As mentioned earlier, the most often reason for PPH is uterine atony and placental complications (TONE and TISSUE from the 4Ts: TONE, TISSUE, TRAUMA, THROMBIN) and hemostatic interventions (plasma transfusion, platelet transfusion, coagulation factor concentrates) should only be done in case of coagulopathy [179]. Accordingly, the ISTH Scientific Subcommittees (SSC) on Women’s Health Issues in Thrombosis and Haemostasis and on disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) recommend that (1) ‘if POC or laboratory test of hemostasis are normal, then no FFP is required’ and (2) they ‘recommend against the use of fibrinogen concentrate in an unmonitored or pre-emptive manner’ [180]. However, every severe bleeding can result in coagulopathy, finally. Accordingly, the management of PPH is still challenging [181–183].
Notably, prepartum A5FIB and plasma fibrinogen values cannot predict PPH but FIBTEM at the beginning of PPH can predict progress of hemorrhage and transfusion requirements and can be used to guide hemostatic therapy in PPH [33,184–189]. Of course, prepartum SCLTs and ROTEM results can be helpful in patients with hereditary coagulation factor deficiencies [190]. However, hereditary issues should be known in most cases from medical history.
Hyperfibrinolysis most often occur in PPH with severe shock or in patients with amniotic fluid embolism—in the later it can be accompanied by DIC [191–194]. Nevertheless, it is recommended to give TXA early (within 3 h after labor) in patients with PPH based on the WOMAN trial (World Maternal Antifibrinolytic Trial) [144,195]. In the WOMAN trial, death from bleeding could be reduced by TXA (1.5% vs. 1.9%; P = 0.045; RR [95% CI], 0.81 [0.65–1.00]). However, all-cause mortality did not change significantly (2.3% vs. 2.6%, P = 0.16; RR [95% CI], 0.88 [0.74–1.05]) since an increase in sepsis (0.2% vs. 0.1%; P = 0.15; RR [95% CI], 1.87 [0.79–4.40]) and organ failure (0.3% vs. 0.2%; P = 0.29; RR [95% CI], 1.87 [0.75–2.53]) outweighed the reduction in mortality due to bleeding. As already reported in the CRASH-2 trial, the benefits of TXA were most prominent if administered within 3 h after delivery [144,195]. Therefore, TXA should be given as soon as possible after onset of PPH [144,195]. A continuous infusion of TXA was not anymore used in the WOMAN trial [195]. The incidence of hyperfibrinolysis in the Nigerian subpopulation and the pathomechanisms responsible for the beneficial effects of TXA in the WOMAN trial have been assessed using ROTEM and whole blood impedance aggregometry [196,197].
Quick changes in plasma fibrinogen concentration and fibrin polymerization (FIBTEM) are key issues in the development and progression of severe PPH [26,30,189,198]. Here, Collins et al. [30] showed that A5FIB (adjusted OR [95% CI], 0.85 [0.77–0.95]; P = 0.02) is superior to Clauss fibrinogen (adjusted OR [95% CI], 0.93 [0.49–1.19]; P = 0.813) to predict progression of PPH to a total blood loss of more than 2500 ml. Women progressing to 8 U blood products (RBCs + FFP + platelets) had a median (IQR) fibrinogen and A5FIB of 2.1 (1.8–3.4) g/L and 12 (7–17) mm, respectively, compared with 3.9 (3.2–4.5) g/L and 19 (17– 23) mm for those not progressing. Accordingly, the A5FIB cut-off value for our PPH algorithm was set to < 12 mm and the target to ≥ 16 mm (discriminating point in the study 17 mm). This is in line with the Liverpool algorithm published by Mallaiah et al. [185] and the recommendations from the ISTH SSC [180]. Mallaiah et al. [185,199] and Smith et al. [200,201] reported in their follow up a significant reduction in blood transfusion (P < 0.0001), large volume blood transfusion (> 5 U RBCs; 11.2% vs. 28.6%; P = 0.006), hysterectomy rate (5.6% vs. 14%; P = 0.089), TACO (0% vs. 9%; P < 0.001), and ICU admission (1.9% vs. 9%; P = 0.027). Very similar results have recently been published by Snegovskikh et al. [186]. Here again, the estimated blood loss, RBC, and FFP transfusion was significantly reduced (P < 0.001), as well as the hysterectomy rate (25.0% vs. 53.5%; P = 0.013), the ICU admission rate (3.6% vs. 43.1%; P < 0.001), and the length of hospitalization after delivery (4 vs. 5 days; P < 0.001). In contrast, preemptive treatment of PPH (estimated blood loss ≥ 1500 ml) with fibrinogen concentrate was not effective in an RCT since the mean fibrinogen concentration at randomization was 4.5 ± 1.2 g/L [202]. This is in agreement with the results of the OBS2 RCT that did not show any benefit in the subgroup administering fibrinogen concentrate if A5FIB was 13–15 mm. Only patients with an A5FIB ≤ 12 mm showed a reduction in blood loss after study drug (300 ml vs. 700 ml) and transfusion of allogeneic blood products (1.0 vs. 3.0 units) [203,204]. This again, confirmed the A5FIB cut-off and target values used in our PPH algorithm.
Impaired thrombin generation is rarely an issue in PPH but can occur due to ongoing bleeding and dilution (Fig. 5) or in case of acquired hemophilia (Fig. 6). The first issue can be treated with 4F-PCC or FFP and the second issue with rFVIIa or activated PCC administration.
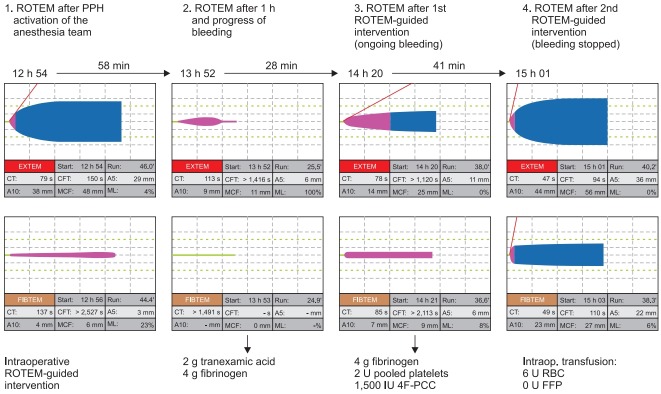
Fig. 5.
A case of ROTEM-guided bleeding management in postpartum hemorrhage. The first ROTEM was performed after PPH activation of the anesthesia team. The first ROTEM showed already a decreased FIBTAM A5 (4 mm) and a late hyperfibrinolysis in FIBTEM (ML 23%). Unfortunately, this has not been treated at this time and coagulopathy and bleeding progressed within the next hour. Due to the delay in treatment, the second ROTEM showed a fulminant hyperfibrinolysis and a flat-line in FIBTEM. Accordingly, 2 g tranexamic acid and 4 g fibrinogen concentrate have been administered (calculated increase in A5FIB, 8 mm) within 20 min after the second ROTEM analysis and the effect has been checked with the third ROTEM analysis 8 min later. Here, the measured increase in A5FIB was 2 mm below the calculated increase due to the ongoing bleeding. The prolonged EXTEM CT in the second ROTEM (due to the lack of fibrinogen) normalized in the third ROTEM (borderline results with CTEX 78 s and CTFIB 85 s). EXTEM and FIBTEM clot firmness (A5) improved but were still too low and associated with ongoing bleeding. Therefore, further 4 g fibrinogen concentrate, 2 pooled platelet concentrates, and 1500 IU 4F-PCC have been administered in the second ROTEM-guided intervention. This intervention stopped the bleeding and the fourth ROTEM analysis showed a normal temogram for a pregnant woman. The time between the second and fourth ROTEM analysis—including the two ROTEM-guided interventions—was 69 min and overall 6 U RBC and no FFP have been transfused to the patient. No TRALI, TACO, or other complications occurred, and the patient could be extubated after surgery and discharged from the ICU the next morning. PPH: postpartum hemorrhage, A5: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after CT, A10: amplitude of clot firmness 10 min after CT, ML: maximum lysis during runtime, CT: coagulation time, CFT: clot formation time, MCF: maximum clot firmness, 4F-PCC: four factor prothrombin complex concentrate, RBC: red blood cells, FFP: fresh frozen plasma, TRALI: transfusion-related acute lung injury, TACO: transfusion-associated circulatory overload. Courtesy of Klaus Görlinger, Germany
Fig. 6.
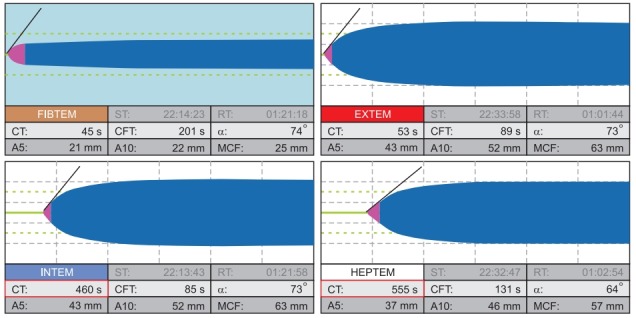
ROTEM pattern of acquired hemophilia A with inhibitors to FVIII. Characteristic for acquired hemophilia, this ROTEM shows a significantly prolonged INTEM and HEPTEM CT (460 s and 555 s, respectively) but short CTs in EXTEM and FIBTEM (53 s and 45 s, respectively) since the extrinsic and common pathway are not affected by this coagulopathy. The appropriate treatment is rFVIIa (recombinant activated factor VII) or activated PCC (FEIBA, Factor Eight Inhibitor Bypassing Activity). ST: start time, RT: run time, CT: coagulation time, CFT: clot formation time, α: alpha angle in °, A5: amplitude of clot firmness 5 min after CT, A10: amplitude of clot firmness 10 min after CT, MCF: maximum clot firmness, ML: maximum lysis during runtime. Courtesy of Klaus Görlinger, Germany.
Since precision individualized medicine is more and more accepted as best practice in traumatic hemorrhage and PPH, ROTEM-guided management of coagulopathy in trauma and PPH is recommended in several national and international guidelines, and some authors even postulated that coagulation POC testing should be mandatory in the trauma emergency room and on the labor ward [164–166,174,188,205–213].
Impact on Transfusion Requirements, Patient Outcomes, and Health Care Costs
Implementation of ROTEM-guided bleeding management algorithms as an essential part of PBM resulted in significant reduction in bleeding, transfusion requirements, complication rates, and hospital costs. Here, the highest evidence is available for cardiovascular surgery [32–35,45,46,54,55,66,69,214–218] but data supporting the efficacy and safety of ROTEM-guided bleeding management in other clinical settings are increasing [12,35–36,92,101,114–118,172,185,186,189,219–228]. Accordingly, Deppe et al. [34] reported in their meta-analysis including nine RCTs, eight cohort studies and 8332 patients an odds ratio (OR) of 0.63 (95% CI, 0.56–0.71; P < 0.0001) for patients receiving allogeneic blood products, 0.63 (95% CI, 0.50–0.78; P < 0.0001) for RBC transfusion, 0.31 (95% CI, 0.13–0.74; P < 0.0001) for plasma transfusion, 0.62 (95% CI, 0.42–0.92, P = 0.0292) for platelet transfusion, 0.56 (95% CI, 0.45–0.71; P < 0.00001) for re-exploration due to postoperative bleeding, 0.64 (95% CI, 0.31–1.30; P = 0.1345) for cerebrovascular events, 0.77 (95% CI, 0.61–0.98; P = 0.0278) for postoperative acute kidney injury (AKI), and 0.44 (95% CI, 0.28–0.70; P = 0.0005) for thromboembolic events. Furthermore, the Cochrane analysis published in 2016 [35] demonstrated a RR for mortality in trials using ROTEM of 0.44 (95% CI, 0.21–0.93; P = 0.03) and in studies using TEG of 0.72 (95% CI, 0.25–2.07; P = 0.54). Analyzing ROTEM- and TEG-guided studies together showed a RR for mortality of 0.52 (95% CI, 0.28–0.95; P = 0.03). The Cochrane analysis also confirmed the significant reduction in transfusion requirements and in AKI with the need for dialysis (RR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.28–0.76; P = 0.003).
Two large multi-center cohort studies analyzing transfusion requirements and patient outcomes before and after implementing PBM—including ROTEM-guided bleeding management—recruited 129,719 and 605,046, respectively [229,230]. Here, Meybohm et al. [229] reported as their main outcome a relative reduction in mean RBC transfusion by 17% (1.05 ± 0.05 vs. 1.21 ± 0.05 units; P < 0.001) and in acute renal failure by 30% (1.67% vs. 2.39%; P < 0.001). Leahy et al. [230,231] demonstrated a reduction of RBCs, plasma, and platelets transfused per admission by 41% (P<0.001), representing cost-savings of AU$ 18,507,092 (US$ 18,078,258), corresponding to an estimated activity-based cost-savings of AU$ 80–100 million (US$ 78–97 million). Furthermore, they reported risk-adjusted reductions in hospital-acquired infections (OR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.73–0.86; P<0.001), acute myocardial infarction/stroke (OR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.58–0.82; P < 0.001), hospital mortality (OR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.67–0.77; P<0.001), and length of hospital stay (incidence rate ratio, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.84–0.87; P<0.001). In summary, these large cohort studies including more than 700,000 patients confirmed that the implementation of a PBM program including ROTEM-guided bleeding management resulted in reduced blood product utilization, blood product-related cost savings, and improved patient outcomes.
In a meta-analysis assessing the efficacy of implementing a multimodal PBM program addressing each of the three PBM pillars including 17 studies comprising 235,779 surgical patients, transfusion rate was reduced by 39% (RR, 0.61; 95% CI, 055–0.68; P < 0.00001), hospital length of stay was reduced in mean by 0.45 days (95% CI, 0.25–0.65 days; P < 0.00001), total number of complications was reduced by 20% (RR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.74–0.88; P < 0.00001), and mortality rate was reduced by 11% (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80–0.98; P = 0.02) [232].
Accordingly, European, American, and Australian perioperative bleeding management, trauma, and PBM guidelines recommend implementing PBM including POC-guided bleeding management algorithms [164,166,174,180,205–210,233]. The implementation of PBM is also supported by the Australian Government and the European Commission [234–237].
Cost-savings can be divided into transfusion-associated costs and cost-savings by reducing potentially preventable complications [33,238,239]. In a health-economic analysis including eight studies (five cohort studies, two RCTs, and one meta-analysis published between 2012 and 2017) and 755,733 patients, the mean calculated blood product acquisition cost-savings were US$ 977,703 per 1000 patients and mean calculated PPC-related cost-savings 1,786,729 per 1000 patients [240]. Here, the reported cost-savings have been highest in studies focusing on patients with a high bleeding risk [32,218] and lowest in cohort studies looking at the whole patient population of hospitals implementing PBM [229,230].
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest
Klaus Görlinger is working as the Medical Director of Tem Innovations since July 2012. Daniel Dirkmann, Fuat Saner and Marc Maegele are members of the scientific advisory committee of Instrumentation Laboratory and received travel expense refunds and speakers fees from Tem Innovations, Instrumentation Laboratory/Werfen, and CSL Behring. Antonio Pérez-Ferrer, Angelo Augusto Pérez Calatayud and Tae-Yop Kim reported no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article.
Author Contributions
Klaus Görlinger (Conceptualization; Visualization; Writing –original draft)
Antonio Pérez-Ferrer (Conceptualization; Writing – review & editing)
Daniel Dirkmann (Conceptualization; Writing – review & editing)
Fuat Saner (Conceptualization)
Marc Maegele (Writing – review & editing)
Angel Augusto Perez Calatayud (Writing – review & editing)
Tae-Yop Kim (Writing – review & editing)
References
- 1.Zacharowski K, Spahn DR. Patient blood management equals patient safety. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2016;30:159–69. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2016.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bochicchio GV, Napolitano L, Joshi M, Bochicchio K, Meyer W, Scalea TM. Outcome analysis of blood product transfusion in trauma patients: a prospective, risk-adjusted study. World J Surg. 2008;32:2185–9. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9655-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E, Castelvecchio S, Pelissero G. Major bleeding, transfusions, and anemia: the deadly triad of cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96:478–85. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Turan A, Yang D, Bonilla A, Shiba A, Sessler DI, Saager L, et al. Morbidity and mortality after massive transfusion in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery. Can J Anaesth. 2013;60:761–70. doi: 10.1007/s12630-013-9937-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ruseckaite R, McQuilten ZK, Oldroyd JC, Richter TH, Cameron PA, Isbister JP, et al. Descriptive characteristics and in-hospital mortality of critically bleeding patients requiring massive transfusion: results from the Australian and New Zealand Massive Transfusion Registry. Vox Sang. 2017;112:240–8. doi: 10.1111/vox.12487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Inaba K, Branco BC, Rhee P, Blackbourne LH, Holcomb JB, Teixeira PG, et al. Impact of plasma transfusion in trauma patients who do not require massive transfusion. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210:957–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Desborough M, Sandu R, Brunskill SJ, Doree C, Trivella M, Montedori A, et al. Fresh frozen plasma for cardiovascular surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(7):CD007614. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007614.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baharoglu MI, Cordonnier C, Salman RA, de Gans K, Koopman MM, Brand A, et al. Platelet transfusion versus standard care after acute stroke due to spontaneous cerebral haemorrhage associated with antiplatelet therapy (PATCH): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;387:2605–13. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30392-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Warner MA, Chandran A, Jenkins G, Kor DJ. Prophylactic plasma transfusion is not associated with decreased red blood cell requirements in critically Ill patients. Anesth Analg. 2017;124:1636–43. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Warner MA, Jia Q, Clifford L, Wilson G, Brown MJ, Hanson AC, et al. Preoperative platelet transfusions and perioperative red blood cell requirements in patients with thrombocytopenia undergoing noncardiac surgery. Transfusion. 2016;56:682–90. doi: 10.1111/trf.13414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bolton-Maggs PH, Cohen H. Serious Hazards of Transfusion (SHOT) haemovigilance and progress is improving transfusion safety. Br J Haematol. 2013;163:303–14. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Khan S, Brohi K, Chana M, Raza I, Stanworth S, Gaarder C, et al. Hemostatic resuscitation is neither hemostatic nor resuscitative in trauma hemorrhage. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;76:561–7. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Khan S, Davenport R, Raza I, Glasgow S, De’Ath HD, Johansson PI, et al. Damage control resuscitation using blood component therapy in standard doses has a limited effect on coagulopathy during trauma hemorrhage. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41:239–47. doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3584-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Balvers K, van Dieren S, Baksaas-Aasen K, Gaarder C, Brohi K, Eaglestone S, et al. Combined effect of therapeutic strategies for bleeding injury on early survival, transfusion needs and correction of coagulopathy. Br J Surg. 2017;104:222–9. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Holcomb JB, Tilley BC, Baraniuk S, Fox EE, Wade CE, Podbielski JM, et al. Transfusion of plasma, platelets, and red blood cells in a 1:1:1 vs a 1:1:2 ratio and mortality in patients with severe trauma: the PROPPR randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;313:471–82. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cannon JW, Johnson MA, Caskey RC, Borgman MA, Neff LP. High ratio plasma resuscitation does not improve survival in pediatric trauma patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017;83:211–7. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.McQuilten ZK, Crighton G, Brunskill S, Morison JK, Richter TH, Waters N, et al. Optimal dose, timing and ratio of blood products in massive transfusion: results from a systematic review. Transfus Med Rev. 2018;32:6–15. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2017.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Winearls J, Reade M, Miles H, Bulmer A, Campbell D, Görlinger K, et al. Targeted coagulation management in severe trauma: the controversiesand the evidence. Anesth Analg. 2016;123:910–24. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Toulon P, Ozier Y, Ankri A, Fléron MH, Leroux G, Samama CM. Point-of-care versus central laboratory coagulation testing during haemorrhagic surgery. A multicenter study. Thromb Haemost. 2009;101:394–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Davenport R, Manson J, De’Ath H, Platton S, Coates A, Allard S, et al. Functional definition and characterization of acute traumatic coagulopathy. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:2652–8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182281af5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Olde Engberink RH, Kuiper GJ, Wetzels RJ, Nelemans PJ, Lance MD, Beckers EA, et al. Rapid and correct prediction of thrombocytopenia and hypofibrinogenemia with rotational thromboelastometry in cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2014;28:210–6. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2013.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Görlinger K, Dirkmann D, Solomon C, Hanke AA. Fast interpretation of thromboelastometry in non-cardiac surgery: reliability in patients with hypo-, normo-, and hypercoagulability. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:222–30. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dirkmann D, Görlinger K, Dusse F, Kottenberg E, Peters J. Early thromboelastometric variables reliably predict maximum clot firmness in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a step towards earlier decision making. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2013;57:594–603. doi: 10.1111/aas.12040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Perez-Ferrer A, Vicente-Sanchez J, Carceles-Baron MD, Van der Linden P3, Faraoni D. Early thromboelastometry variables predict maximum clot firmness in children undergoing cardiac and non-cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115:896–902. doi: 10.1093/bja/aev369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Song JG, Jeong SM, Jun IG, Lee HM, Hwang GS. Five-minute parameter of thromboelastometry is sufficient to detect thrombocytopenia and hypofibrinogenaemia in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Br J Anaesth. 2014;112:290–7. doi: 10.1093/bja/aet325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Toffaletti JG, Buckner KA. Use of earlier-reported rotational thromboelastometry parameters to evaluate clotting status, fibrinogen, and platelet activities in postpartum hemorrhage compared to surgery and intensive care patients. Anesth Analg. 2019;128:414–23. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schöchl H, Cotton B, Inaba K, Nienaber U, Fischer H, Voelckel W, et al. FIBTEM provides early prediction of massive transfusion in trauma. Crit Care. 2011;15:R265. doi: 10.1186/cc10539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hagemo JS, Christiaans SC, Stanworth SJ, Brohi K, Johansson PI, Goslings JC, et al. Detection of acute traumatic coagulopathy and massive transfusion requirements by means of rotational thromboelastometry: an international prospective validation study. Crit Care. 2015;19:97. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0823-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Na HS, Shin HJ, Do SH. FIBTEM provides prediction of massive bleeding in total hip replacement arthroplasty. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2016;27:340–6. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Collins PW, Lilley G, Bruynseels D, Laurent DB, Cannings-John R, Precious E, et al. Fibrin-based clot formation as an early and rapid biomarker for progression of postpartum hemorrhage: a prospective study. Blood. 2014;124:1727–36. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-567891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dötsch TM, Dirkmann D, Bezinover D, Hartmann M, Treckmann JW, Paul A, et al. Assessment of standard laboratory tests and rotational thromboelastometry for the prediction of postoperative bleeding in liver transplantation. Br J Anaesth. 2017;119:402–10. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Weber CF, Görlinger K, Meininger D, Herrmann E, Bingold T, Moritz A, et al. Point-of-care testing: a prospective, randomized clinical trial of efficacy in coagulopathic cardiac surgery patients. Anesthesiology. 2012;117:531–47. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318264c644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Whiting P, Al M, Westwood M, Ramos IC, Ryder S, Armstrong N, et al. Viscoelastic point-of-care testing to assist with the diagnosis, management and monitoring of haemostasis: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1–228. doi: 10.3310/hta19580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Deppe AC, Weber C, Zimmermann J, Kuhn EW, Slottosch I, Liakopoulos OJ, et al. Point-of-care thromboelastography/thromboelastometrybased coagulation management in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis of 8332 patients. J Surg Res. 2016;203:424–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wikkelsø A, Wetterslev J, Møller AM, Afshari A. Thromboelastography (TEG) or thromboelastometry (ROTEM) to monitor haemostatic treatment versus usual care in adults or children with bleeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(8):CD007871. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007871.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brohi K, Eaglestone S. Traumatic coagulopathy and massive transfusion: improving outcomes and saving blood. Programme Grants Appl Res. 2017;5:1–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lang T, Bauters A, Braun SL, Pötzsch B, von Pape KW, Kolde HJ, et al. Multi-centre investigation on reference ranges for ROTEM thromboelastometry. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2005;16:301–10. doi: 10.1097/01.mbc.0000169225.31173.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schenk B, Görlinger K, Treml B, Tauber H, Fries D, Niederwanger C, et al. A comparison of the new ROTEMⓇ sigma with its predecessor, the ROTEMdelta. Anaesthesia. 2019;74:348–56. doi: 10.1111/anae.14542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Oswald E, Stalzer B, Heitz E, Weiss M, Schmugge M, Strasak A, et al. Thromboelastometry (ROTEM) in children: age-related reference ranges and correlations with standard coagulation tests. Br J Anaesth. 2010;105:827–35. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeq258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sokou R, Foudoulaki-Paparizos L, Lytras T, Konstantinidi A, Theodoraki M, Lambadaridis I, et al. Reference ranges of thromboelastometry in healthy full-term and pre-term neonates. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017;55:1592–7. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.de Lange NM, van Rheenen-Flach LE, Lancé MD, Mooyman L, Woiski M, van Pampus EC, et al. Peri-partum reference ranges for ROTEM(R) thromboelastometry. Br J Anaesth. 2014;112:852–9. doi: 10.1093/bja/aet480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Oudghiri M, Keita H, Kouamou E, Boutonnet M, Orsini M, Desconclois C, et al. Reference values for rotation thromboelastometry (ROTEMⓇ) parameters following non-haemorrhagic deliveries. Correlations with standard haemostasis parameters. Thromb Haemost. 2011;106:176–8. doi: 10.1160/TH11-02-0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Blasi A, Beltran J, Pereira A, Martinez-Palli G, Torrents A, Balust J, et al. An assessment of thromboelastometry to monitor blood coagulation and guide transfusion support in liver transplantation. Transfusion. 2012;52:1989–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fayed N, Mourad W, Yassen K, Görlinger K. Preoperative thromboelastometry as a predictor of transfusion requirements during adult living donor liver transplantation. Transfus Med Hemother. 2015;42:99–108. doi: 10.1159/000381733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nakayama Y, Nakajima Y, Tanaka KA, Sessler DI, Maeda S, Iida J, et al. Thromboelastometry-guided intraoperative haemostatic management reduces bleeding and red cell transfusion after paediatric cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114:91–102. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Görlinger K, Dirkmann D, Hanke AA, Kamler M, Kottenberg E, Thielmann M, et al. First-line therapy with coagulation factor concentrates combined with point-of-care coagulation testing is associated with decreased allogeneic blood transfusion in cardiovascular surgery: a retrospective, single-center cohort study. Anesthesiology. 2011;115:1179–91. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31823497dd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Petricevic M, Konosic S, Biocina B, Dirkmann D, White A, Mihaljevic MZ, et al. Bleeding risk assessment in patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery using ROTEM(Ⓡ) platelet and Multiplate(Ⓡ) impedance aggregometry. Anaesthesia. 2016;71:636–47. doi: 10.1111/anae.13303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Faraoni D, Emani S, Halpin E, Bernier R, Emani SM, DiNardo JA, et al. Relationship between transfusion of blood products and the incidence of thrombotic complications in neonates and infants undergoing cardiacsurgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017;31:1943–8. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2017.04.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Görlinger K, Iqbal J, Dirkmann D, Tanaka KA. In: Whole blood assay: thromboelastometry. In: Management of Bleeding Patients. Teruya J, editor. Basel: Springer Nature Switzerland AG; 2016. pp. 37–64. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gronchi F, Perret A, Ferrari E, Marcucci CM, Flèche J, Crosset M, et al. Validation of rotational thromboelastometry during cardiopulmonary bypass: A prospective, observational in-vivo study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2014;31:68–75. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328363171a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ortmann E, Rubino A, Altemimi B, Collier T, Besser MW, Klein AA. Validation of viscoelastic coagulation tests during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13:1207–16. doi: 10.1111/jth.12988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mace H, Lightfoot N, McCluskey S, Selby R, Roy D, Timoumi T, et al. Validity of thromboelastometry for rapid assessment of fibrinogen levels in heparinized samples during cardiac surgery: a retrospective, single-center, observational study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30:90–5. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2015.04.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Görlinger K, Shore-Lesserson L, Dirkmann D, Hanke AA, Rahe-Meyer N, Tanaka KA. Management of hemorrhage in cardiothoracic surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2013;27(Suppl 4):S20–34. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2013.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Karkouti K, McCluskey SA, Callum J, Freedman J, Selby R, Timoumi T, et al. Evaluation of a novel transfusion algorithm employing pointof-care coagulation assays in cardiac surgery: a retrospective cohort study with interrupted time-series analysis. Anesthesiology. 2015;122:560–70. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Karkouti K, Callum J, Wijeysundera DN, Rao V, Crowther M, Grocott HP, et al. Point-of-care hemostatic testing in cardiac surgery: a stepped-wedgeclustered randomized controlled trial. Circulation. 2016;134:1152–62. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ichikawa J, Kodaka M, Nishiyama K, Hirasaki Y, Ozaki M, Komori M. Reappearance of circulating heparin in whole blood heparin concentration-based management does not correlate with postoperative bleeding after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2014;28:1003–7. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2013.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ni Ainle F, Preston RJ, Jenkins PV, Nel HJ, Johnson JA, Smith OP, et al. Protamine sulfate down-regulates thrombin generation by inhibiting factor V activation. Blood. 2009;114:1658–65. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-222109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mittermayr M, Velik-Salchner C, Stalzer B, Margreiter J, Klingler A, Streif W, et al. Detection of protamine and heparin after termination of cardiopulmonary bypass by thrombelastometry (ROTEM): results of a pilot study. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:743–50. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31818657a3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gertler R, Wiesner G, Tassani-Prell P, Braun SL, Martin K. Are the point-of-care diagnostics MULTIPLATE and ROTEM valid in the setting of high concentrations of heparin and its reversal with protamine? J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011;25:981–6. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2010.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ortmann E, Klein AA, Sharples LD, Walsh R, Jenkins DP, Luddington RJ, et al. Point-of-care assessment of hypothermia and protamine-induced platelet dysfunction with multiple electrode aggregometry (MultiplateⓇ) in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth Analg. 2013;116:533–40. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31827cee88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Koster A, Börgermann J, Gummert J, Rudloff M, Zittermann A, Schirmer U. Protamine overdose and its impact on coagulation, bleeding, and transfusions after cardiopulmonary bypass: results of a randomized double-blind controlled pilot study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2014;20:290–5. doi: 10.1177/1076029613484085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Meesters MI, Veerhoek D, de Lange F, de Vries JW, de Jong JR, Romijn JW, et al. Effect of high or low protamine dosing on postoperative bleeding following heparin anticoagulation in cardiac surgery. A randomised clinical trial. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116:251–61. doi: 10.1160/TH16-02-0117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Yamamoto T, Wolf HG, Sinzobahamvya N, Asfour B, Hraska V, Schindler E. Prolonged activated clotting time after protamine administration does not indicate residual heparinization after cardiopulmonary bypass in pediatric open heart surgery. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;63:397–403. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1554998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Karkouti K, Callum J, Crowther MA, McCluskey SA, Pendergrast J, Tait G, et al. The relationship between fibrinogen levels after cardiopulmonary bypass and large volume red cell transfusion in cardiac surgery: an observational study. Anesth Analg. 2013;117:14–22. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318292efa4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Reinhöfer M, Brauer M, Franke U, Barz D, Marx G, Lösche W. The value of rotation thromboelastometry to monitor disturbed perioperative haemostasis and bleeding risk in patients with cardiopulmonary bypass. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008;19:212–9. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e3282f3f9d4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E, Crapelli GB, Rahe-Meyer N, Menicanti L, Frigiola A, et al. Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of fibrinogen concentrate supplementation after complex cardiac surgery. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4:e002066. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E. Fibrinogen supplementation after cardiac surgery: insights from the Zero-Plasma trial (ZEPLAST) Br J Anaesth. 2016;116:618–23. doi: 10.1093/bja/aev539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ranucci M, Pistuddi V, Baryshnikova E, Colella D, Bianchi P. Fibrinogen levels after cardiac surgical procedures: association with postoperative bleeding, trigger values, and target values. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102:78–85. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E, Pistuddi V, Menicanti L, Frigiola A. The effectiveness of 10 years of interventions to control postoperative bleeding in adult cardiac surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017;24:196–202. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivw339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E, Ranucci M, Silvetti S. Fibrinogen levels compensation of thrombocytopenia-induced bleeding following cardiac surgery. Int J Cardiol. 2017;249:96–100. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.09.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Tanaka KA, Bader SO, Görlinger K. Novel approaches in management of perioperative coagulopathy. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2014;27:72–80. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Collins PW, Solomon C, Sutor K, Crispin D, Hochleitner G, Rizoli S, et al. Theoretical modelling of fibrinogen supplementation with therapeutic plasma, cryoprecipitate, or fibrinogen concentrate. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113:585–95. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Flisberg P1, Rundgren M, Engström M. The effects of platelet transfusions evaluated using rotational thromboelastometry. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:1430–2. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31819bccb7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Tripodi A, Primignani M, Chantarangkul V, Lemma L, Jovani M, Rebulla P, et al. Global hemostasis tests in patients with cirrhosis before and after prophylactic platelet transfusion. Liver Int. 2013;33:362–7. doi: 10.1111/liv.12038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kander T, Tanaka KA, Norström E, Persson J, Schött U. The effect and duration of prophylactic platelet transfusions before insertion of a central venous catheter in patients with bone marrow failure evaluated with point-of-care methods and flow cytometry. Anesth Analg. 2014;119:882–90. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Görlinger K, Jambor C, Hanke AA, Dirkmann D, Adamzik M, Hartmann M, et al. Perioperative coagulation management and control of platelet transfusion by point-of-care platelet function analysis. Transfus Med Hemother. 2007;34:396–411. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Karon BS, Tolan NV, Koch CD, Wockenfus AM, Miller RS, Lingineni RK, et al. Precision and reliability of 5 platelet function tests in healthy volunteers and donors on daily antiplatelet agent therapy. Clin Chem. 2014;60:1524–31. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.226332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Scharf RE. Drugs that affect platelet function. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2012;38:865–83. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1328881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E, Soro G, Ballotta A, De Benedetti D, Conti D. Multiple electrode whole-blood aggregometry and bleeding in cardiac surgery patients receiving thienopyridines. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91:123–9. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ranucci M, Colella D, Baryshnikova E, Di Dedda U. Effect of preoperative P2Y12 and thrombin platelet receptor inhibition on bleeding after cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113:970–6. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Polzin A, Helten C, Dannenberg L, Mourikis P, Naguib D, Achilles A, et al. Platelet reactivity in patients on aspirin and clopidogrel therapy measured by a new bedside whole-blood assay. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2019;73:40–7. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Mahla E, Suarez TA, Bliden KP, Rehak P, Metzler H, Sequeira AJ, et al. Platelet function measurement-based strategy to reduce bleeding and waiting time in clopidogrel-treated patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery: the timing based on platelet function strategy to reduce clopidogrel-associated bleeding related to CABG (TARGET-CABG) study. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;5:261–9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.111.967208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Romlin BS, Söderlund F, Wåhlander H, Nilsson B, Baghaei F, Jeppsson A. Platelet count and function in paediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective observational study. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113:847–54. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Romlin BS, Söderlund F, Wåhlander H, Hallhagen S, Wessman C, Baghaei F, et al. Perioperative monitoring of platelet function in paediatric cardiac surgery by thromboelastometry, or platelet aggregometry? Br J Anaesth. 2016;116:822–8. doi: 10.1093/bja/aew053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Petricevic M, Milicic D, White A, Boban M, Mihaljevic MZ, Piljic D, et al. Development of a concept for a personalized approach in the perioperative antiplatelet therapy administration/discontinuation management based on multiple electrode aggregometry in patients undergoing coronary artery surgery. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015;40:383–91. doi: 10.1007/s11239-015-1246-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Corredor C, Wasowicz M, Karkouti K, Sharma V. The role of point-of-care platelet function testing in predicting postoperative bleeding following cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesthesia. 2015;70:715–31. doi: 10.1111/anae.13083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Blasi A, Muñoz G, de Soto I, Mellado R, Taura P, Rios J, et al. Reliability of thromboelastometry for detecting the safe coagulation threshold in patients taking acenocoumarol after elective heart valve replacement. Thromb Res. 2015;136:669–72. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2015.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Schmidt DE, Holmström M, Majeed A, Näslin D, Wallén H, Ågren A. Detection of elevated INR by thromboelastometry and thromboelastography in warfarin treated patients and healthy controls. Thromb Res. 2015;135:1007–11. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2015.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Dunham CM, Rabel C, Hileman BM, Schiraldi J, Chance EA, Shima MT, et al. TEGⓇ and RapidTEGⓇ are unreliable for detecting warfarincoagulopathy: a prospective cohort study. Thromb J. 2014;12:4. doi: 10.1186/1477-9560-12-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Hanke AA, Joch C, Görlinger K. Long-term safety and efficacy of a pasteurized nanofiltrated prothrombin complex concentrate (Beriplex P/N): a pharmacovigilance study. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:764–72. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Grottke O, Levy JH. Prothrombin complex concentrates in trauma and perioperative bleeding. Anesthesiology. 2015;122:923–31. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Görlinger K, Fries D, Dirkmann D, Weber CF, Hanke AA, Schöchl H. Reduction of fresh frozen plasma requirements by perioperative point-of-care coagulation management with early calculated goal-directed therapy. Transfus Med Hemother. 2012;39:104–13. doi: 10.1159/000337186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Refaai MA, Goldstein JN, Lee ML, Durn BL, Milling TJ, Jr, Sarode R. Increased risk of volume overload with plasma compared with fourfactor prothrombin complex concentrate for urgent vitamin K antagonist reversal. Transfusion. 2015;55:2722–9. doi: 10.1111/trf.13191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Sarode R, Milling TJ, Jr, Refaai MA, Mangione A, Schneider A, Durn BL, et al. Efficacy and safety of a 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate in patients on vitamin K antagonists presenting with major bleeding: a randomized, plasma-controlled, phase IIIb study. Circulation. 2013;128:1234–43. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Clifford L, Jia Q, Subramanian A, Yadav H, Schroeder DR, Kor DJ. Risk factors and clinical outcomes associated with perioperativetransfusion-associated circulatory overload. Anesthesiology. 2017;126:409–18. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ahn Y, Goerlinger K. In: Coagulopathy and hypercoagulability. In: Critical Care Handbook of the General Massachusetts Hospital. 6th ed. Wiener-Kronish JP, Bachi A, Chamin JE, Cobb JP, Eikermann M, Quraishi SA, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2016. pp. 322–50. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Görlinger K, Sakai T, Dirkmann D, Planinsic RM, Saner FH. In: Bleeding related to liver transplant. In: Management of Bleeding Patients. Teruya J, editor. Basel: Springer Nature Switzerland AG; 2016. pp. 263–80. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Smith NK, Kim S, Hill B, Goldberg A, DeMaria S, Zerillo J. Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) and transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO) in liver transplantation: a case report and focused review. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018;22:180–90. doi: 10.1177/1089253217736298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Pandey CK, Singh A, Kajal K, Dhankhar M, Tandon M, Pandey VK, et al. Intraoperative blood loss in orthotopic liver transplantation: The predictive factors. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2015;7:86–93. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v7.i6.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Wang J, Bao YX, Bai M, Zhang YG, Xu WD, Qi XS. Restrictive vs liberal transfusion for upper gastrointestinal bleeding: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:6919–27. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Görlinger K. Coagulation management during liver transplantation. Hamostaseologie. 2006;26(3 Suppl 1):S64–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Poon KS, Chen CC, Thorat A, Chiang YY, Jeng LB, Yang HR, et al. Fibrinolysis after reperfusion of liver graft. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2015;53:41–3. doi: 10.1016/j.aat.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Shimauchi T, Yamaura K, Higashi M, Abe K, Yoshizumi T, Hoka S. Fibrinolysis in living donor liver transplantation recipients evaluated using thromboelastometry: impact on mortality. Transplant Proc. 2017;49:2117–21. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2017.09.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Schofield N, Sugavanam A, Thompson K, Mallett SV. No increase in blood transfusions during liver transplantation since the withdrawal of aprotinin. Liver Transpl. 2014;20:584–90. doi: 10.1002/lt.23839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Dirkmann D, Görlinger K, Peters J. Assessment of early thromboelastometric variables from extrinsically activated assays with and without aprotinin for rapid detection of fibrinolysis. Anesth Analg. 2014;119:533–42. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Kim EH, Song SH, Kim GS, Ko JS, Gwak MS, Lee SK. Evaluation of “flat-line” thromboelastography after reperfusion during liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2015;47:457–9. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2014.11.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Abuelkasem E, Lu S, Tanaka K, Planinsic R, Sakai T. Comparison between thrombelastography and thromboelastometry in hyperfibrinolysis detection during adult liver transplantation. Br J Anaesth. 2016;116:507–12. doi: 10.1093/bja/aew023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Katori N, Tanaka KA, Szlam F, Levy JH. The effects of platelet count on clot retraction and tissue plasminogen activator-induced fibrinolysis on thrombelastography. Anesth Analg. 2005;100:1781–5. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000149902.73689.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Sabate A, Blasi A, Costa M, Reyes R, Beltran J, Torres F. Assessment of rotational thromboelastometry for the prediction of red blood cell requirements in orthotopic liver transplantation. Minerva Anestesiol. 2018;84:447–54. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.17.12023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Caldwell SH, Sanyal AJ. Coagulation disorders and bleeding in liver disease: future directions. Clin Liver Dis. 2009;13:155–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2008.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Bedreli S, Sowa JP, Malek S, Blomeyer S, Katsounas A, Gerken G, et al. Rotational thromboelastometry can detect factor XIII deficiency and bleeding diathesis in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2017;37:562–8. doi: 10.1111/liv.13254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Raspé C, Besch M, Charitos EI, Flöther L, Bucher M, Rückert F, et al. Rotational thromboelastometry for assessing bleeding complications and factor XIII deficiency in cardiac surgery patients. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018 doi: 10.1177/1076029618797472. Advance Access published on Sep 9, 2018, doi:10.1177/1076029618797472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Fenger-Eriksen C, Moore GW, Rangarajan S, Ingerslev J, Sørensen B. Fibrinogen estimates are influenced by methods of measurement and hemodilution with colloid plasma expanders. Transfusion. 2010;50:2571–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2010.02752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Noval-Padillo JA, León-Justel A, Mellado-Miras P, Porras-Lopez F, Villegas-Duque D, Gomez-Bravo MA, et al. Introduction of fibrinogen in the treatment of hemostatic disorders during orthotopic liver transplantation: implications in the use of allogenic blood. Transplant Proc. 2010;42:2973–4. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Alamo JM, León A, Mellado P, Bernal C, Marín LM, Cepeda C, et al. Is “intra-operating room” thromboelastometry useful in liver transplantation? A case-control study in 303 patients. Transplant Proc. 2013;45:3637–9. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Kirchner C, Dirkmann D, Treckmann JW, Paul A, Hartmann M, Saner FH, et al. Coagulation management with factor concentrates in liver transplantation: a single-center experience. Transfusion. 2014;54:2760–8. doi: 10.1111/trf.12707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Leon-Justel A, Noval-Padillo JA, Alvarez-Rios AI, Mellado P, Gomez-Bravo MA, Álamo JM, et al. Point-of-care haemostasis monitoring during liver transplantation reduces transfusion requirements and improves patient outcome. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;446:277–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Zamper RP, Amorim TC, Queiroz VN, Lira JD, Costa LG, Takaoka F, et al. Association between viscoelastic tests-guided therapy with synthetic factor concentrates and allogenic blood transfusion in liver transplantation: a before-after study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018;18:198. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0664-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Sabate A, Gutierrez R, Beltran J, Mellado P, Blasi A, Acosta F, et al. Impact of preemptive fibrinogen concentrate on transfusion requirements in liver transplantation: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Transplant. 2016;16:2421–9. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Fayed NA, Abdallah AR, Khalil MK, Marwan IK. Therapeutic rather than prophylactic platelet transfusion policy for severe thrombocytopenia during liver transplantation. Platelets. 2014;25:576–86. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2013.849335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Debernardi Venon W, Ponzo P, Sacco M, Mengozzi G, Raso S, Valpreda A, et al. Usefulness of thromboelastometry in predicting the risk of bleeding in cirrhotics who undergo invasive procedures. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;27:1313–9. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Basili S, Raparelli V, Napoleone L, Talerico G, Corazza GR, Perticone F, et al. Platelet count does not predict bleeding in cirrhotic patients: results from the pro-liver study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:368–75. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2017.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Pereboom IT, de Boer MT, Haagsma EB, Hendriks HG, Lisman T, Porte RJ. Platelet transfusion during liver transplantation is associated with increased postoperative mortality due to acute lung injury. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:1083–91. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e3181948a59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Tripodi A, Primignani M, Chantarangkul V, Viscardi Y, Dell’Era A, Fabris FM, et al. The coagulopathy of cirrhosis assessed by thromboelastometry and its correlation with conventional coagulation parameters. Thromb Res. 2009;124:132–6. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2008.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Mallett SV, Sugavanam A, Krzanicki DA, Patel S, Broomhead RH, Davidson BR, et al. Alterations in coagulation following major liver resection. Anaesthesia. 2016;71:657–68. doi: 10.1111/anae.13459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Saner FH, Kirchner C. Monitoring and treatment of coagulation disorders in end-stage liver disease. Visc Med. 2016;32:241–8. doi: 10.1159/000446304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Tripodi A, Primignani M, Mannucci PM, Caldwell SH. Changing concepts of cirrhotic coagulopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:274–81. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Abuelkasem E, Mazzeffi MA, Lu SY, Planinsic RM, Sakai T, Tanaka KA. Ex vivo evaluation of 4 different viscoelastic assays for detecting moderate to severe coagulopathy during liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2016;22:468–75. doi: 10.1002/lt.24379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Bedreli S, Sowa JP, Gerken G, Saner FH, Canbay A. Management of acute-on-chronic liver failure: rotational thromboelastometry may reduce substitution of coagulation factors in liver cirrhosis. Gut. 2016;65:357–8. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Abuelkasem E, Hasan S, Mazzeffi MA, Planinsic RM, Sakai T, Tanaka KA. Reduced requirement for prothrombin complex concentrate for the restoration of thrombin generation in plasma from liver transplantrecipients. Anesth Analg. 2017;125:609–15. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Lodge JP, Jonas S, Jones RM, Olausson M, Mir-Pallardo J, Soefelt S, et al. Efficacy and safety of repeated perioperative doses of recombinant factor VIIa in liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:973–9. doi: 10.1002/lt.20470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Simpson E, Lin Y, Stanworth S, Birchall J, Doree C, Hyde C. Recombinant factor VIIa for the prevention and treatment of bleeding in patients without haemophilia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;(3):CD005011. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005011.pub4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Kettner SC, Gonano C, Seebach F, Sitzwohl C, Acimovic S, Stark J, et al. Endogenous heparin-like substances significantly impair coagulation in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Anesth Analg. 1998;86:691–5. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199804000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Senzolo M, Agarwal S, Zappoli P, Vibhakorn S, Mallett S, Burroughs AK. Heparin-like effect contributes to the coagulopathy in patients with acute liver failure undergoing liver transplantation. Liver Int. 2009;29:754–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.01977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Yassen K, Refaat E, Helal S, Metwally A, Youssef S, Görlinger K. Perioperative heparinase rotational thromboelastometry monitoring during and after adult living related liver transplantation. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018;35(e-Suppl 56):286. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Gouvêa G, Toledo R, Diaz R, Auler L, Enne M, Martinho JM. Protamine sulphate for treatment of severe post-reperfusion coagulopathy in pediatric liver transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2009;13:1053–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2008.01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Hincker A, Feit J, Sladen RN, Wagener G. Rotational thromboelastometry predicts thromboembolic complications after major non-cardiac surgery. Crit Care. 2014;18:549. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0549-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Rossetto V, Spiezia L, Senzolo M, Rodriguez-Castro KI, Maggiolo S, Simioni P. Whole blood rotation thromboelastometry (ROTEMⓇ) profiles in subjects with non-neoplastic portal vein thrombosis. Thromb Res. 2013;132:e131–4. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Zanetto A, Senzolo M, Vitale A, Cillo U, Radu C, Sartorello F, et al. Thromboelastometry hypercoagulable profiles and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49:440–5. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2016.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Blasi A, Molina V, Sanchez-Cabús S, Balust J, Garcia-Valdecasas JC, Taura P. Prediction of thromboembolic complications after liver resection for cholangiocarcinoma: is there a place for thromboelastometry? Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2018;29:61–6. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Kamel Y, Hassanin A, Ahmed AR, Gad E, Afifi M, Khalil M, et al. Perioperative thromboelastometry for adult living donor liver transplant recipients with a tendency to hypercoagulability: a prospective observational cohort study. Transfus Med Hemother. 2018;45:404–12. doi: 10.1159/000489605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.CRASH-2 trial collaborators. Shakur H, Roberts I, Bautista R, Caballero J, Coats T, et al. Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage (CRASH-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:23–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60835-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.CRASH-2 collaborators, Roberts I, Shakur H, Afolabi A, Brohi K, Coats T, et al. The importance of early treatment with tranexamic acid in bleeding trauma patients: an exploratory analysis of the CRASH-2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;377:1096–101. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60278-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Gayet-Ageron A, Prieto-Merino D, Ker K, Shakur H, Ageron FX, Roberts I. Effect of treatment delay on the effectiveness and safety of antifibrinolytics in acute severe haemorrhage: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data from 40 138 bleeding patients. Lancet. 2018;391:125–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32455-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Görlinger K, Dirkmann D, Hanke AA. In: Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM). In: Trauma Induced Coagulopathy. Gonzalez E, Moore HB, Moore EE, editors. Basel: Springer Nature Switzerland AG; 2016. pp. 267–98. [Google Scholar]
- 146.Chapman MP, Moore EE, Ramos CR, Ghasabyan A, Harr JN, Chin TL, et al. Fibrinolysis greater than 3% is the critical value for initiation of antifibrinolytic therapy. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;75:961–7. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3182aa9c9f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Moore EE, Moore HB, Gonzalez E, Sauaia A, Banerjee A, Silliman CC. Rationale for the selective administration of tranexamic acid to inhibit fibrinolysis in the severely injured patient. Transfusion. 2016;56 Suppl 2:S110–4. doi: 10.1111/trf.13486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Roberts I. Fibrinolytic shutdown: fascinating theory but randomized controlled trial data are needed. Transfusion. 2016;56 Suppl 2:S115–8. doi: 10.1111/trf.13490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Maegele M. Uncritical use of tranexamic acid in trauma patients : Do no further harm! Unfallchirurg. 2016;119:967–72. doi: 10.1007/s00113-016-0236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Valle EJ, Allen CJ, Van Haren RM, Jouria JM, Li H, Livingstone AS, et al. Do all trauma patients benefit from tranexamic acid? J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;76:1373–8. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Harvin JA, Peirce CA, Mims MM, Hudson JA, Podbielski JM, Wade CE, et al. The impact of tranexamic acid on mortality in injured patients with hyperfibrinolysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:905–9. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Meizoso JP, Karcutskie CA, Ray JJ, Namias N, Schulman CI, Proctor KG. Persistent fibrinolysis shutdown is associated with increased mortality in severely injured trauma patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;224:575–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.12.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Moore HB, Moore EE, Huebner BR, Stettler GR, Nunns GR, Einersen PM, et al. Tranexamic acid is associated with increased mortality in patients with physiological fibrinolysis. J Surg Res. 2017;220:438–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.04.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Meizoso JP, Dudaryk R, Mulder MB, Ray JJ, Karcutskie CA, Eidelson SA, et al. Increased risk of fibrinolysis shutdown among severely injured trauma patients receiving tranexamic acid. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018;84:426–32. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Johnston LR, Rodriguez CJ, Elster EA, Bradley MJ. Evaluation of military use of tranexamic acid and associated thromboembolicevents. JAMA Surg. 2018;153:169–75. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Stettler GR, Moore EE, Moore HB, Nunns GR, Silliman CC, Banerjee A, et al. Redefining postinjury fibrinolysis phenotypes using two viscoelastic assays. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019;86:679–85. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Harr JN, Moore EE, Chin TL, Chapman MP, Ghasabyan A, Stringham JR, et al. Viscoelastic hemostatic fibrinogen assays detect fibrinolysis early. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015;41:49–56. doi: 10.1007/s00068-014-0400-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Frith D, Davenport R, Brohi K. Acute traumatic coagulopathy. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2012;25:229–34. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e3283509675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Veigas PV, Callum J, Rizoli S, Nascimento B, da Luz LT. A systematic review on the rotational thrombelastometry (ROTEMⓇ) values for the diagnosis of coagulopathy, prediction and guidance of blood transfusion and prediction of mortality in trauma patients. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2016;24:114. doi: 10.1186/s13049-016-0308-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Davenport RA, Brohi K. Cause of trauma-induced coagulopathy. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016;29:212–9. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Wanderer JP, Nathan N. Massive transfusion protocols: when to turn on, and off, the fire hose. Anesth Analg. 2017;125:1827. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Foster JC, Sappenfield JW, Smith RS, Kiley SP. Initiation and termination of massive transfusion protocols: current strategies and future prospects. Anesth Analg. 2017;125:2045–55. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Hagemo JS, Stanworth S, Juffermans NP, Brohi K, Cohen M, Johansson PI, et al. Prevalence, predictors and outcome of hypofibrinogenaemia in trauma: a multicentre observational study. Crit Care. 2014;18:R52. doi: 10.1186/cc13798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Inaba K, Rizoli S, Veigas PV, Callum J, Davenport R, Hess J, et al. 2014 Consensus conference on viscoelastic test-based transfusion guidelines for early trauma resuscitation: report of the panel. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78:1220–9. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Maegele M, Schöchl H, Menovsky T, Maréchal H, Marklund N, Buki A, et al. Coagulopathy and haemorrhagic progression in traumatic brain injury: advances in mechanisms, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:630–47. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Bouillon B für die Deutsche Gesellschaft für Unfallchirurgie (Hrsg.) AWMF Register-Nr. 012/019. Stand: 2016 July. Available from http://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/012-019l_S3_Polytrauma_ Schwerverletzten-Behandlung_2017-08.pdf.
- 167.Baksaas-Aasen K, Van Dieren S, Balvers K, Juffermans NP, Næss PA, Rourke C, et al. Data-driven development of ROTEM and TEG algorithms for the management of trauma emorrhage: a prospective observational multicenter study. Ann Surg. 2018 doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002825. Advance Access published on May 23, 2018, doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000002825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Solomon C, Traintinger S, Ziegler B, Hanke A, Rahe-Meyer N, Voelckel W, et al. Platelet function following trauma. A multiple electrode aggregometry study. Thromb Haemost. 2011;106:322–30. doi: 10.1160/TH11-03-0175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Chapman MP, Moore EE, Moore HB, Gonzalez E, Morton AP, Silliman CC, et al. Early TRAP pathway platelet inhibition predicts coagulopathic hemorrhage in trauma. Shock. 2015;43(Suppl 1):33. [Google Scholar]
- 170.Vulliamy P, Gillespie S, Gall LS, Green L, Brohi K, Davenport RA. Platelet transfusions reduce fibrinolysis but do not restore platelet function during trauma hemorrhage. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017;83:388–97. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Gonzalez EA, Moore FA, Holcomb JB, Miller CC, Kozar RA, Todd SR, et al. Fresh frozen plasma should be given earlier to patients requiring massive transfusion. J Trauma. 2007;62:112–9. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000250497.08101.8b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Innerhofer P, Fries D, Mittermayr M, Innerhofer N, von Langen D, Hell T, et al. Reversal of trauma-induced coagulopathy using firstline coagulation factor concentrates or fresh frozen plasma (RETIC): a single-centre, parallel-group, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4:e258–71. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Grottke O, Rossaint R. Coagulation factor concentrates and point-of-care coagulation monitoring: both might be essential for optimal treatment of trauma-induced coagulopathy. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4:e246–7. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Rossaint R, Bouillon B, Cerny V, Coats TJ, Duranteau J, Fernández-Mondéjar E, et al. The European guideline on management of major bleeding and coagulopathy following trauma: fourth edition. Crit Care. 2016;20:100. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1265-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Ostrowski SR, Johansson PI. Endothelial glycocalyx degradation induces endogenous heparinization in patients with severe injury and early traumatic coagulopathy. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73:60–6. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31825b5c10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Holley AD, Reade MC. The ‘procoagulopathy’ of trauma: too much, too late? Curr Opin Crit Care. 2013;19:578–86. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Moore HB, Moore EE, Liras IN, Wade C, Huebner BR, Burlew CC, et al. Targeting resuscitation to normalization of coagulating status: Hyper and hypocoagulability after severe injury are both associated with increased mortality. Am J Surg. 2017;214:1041–5. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2017.08.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Dhillon NK, Smith EJ, Ko A, Harada MY, Yang AR, Patel KA, et al. The risk factors of venous thromboembolism in massively transfused patients. J Surg Res. 2018;222:115–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.09.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Solomon C, Collis RE, Collins PW. Haemostatic monitoring during postpartum haemorrhage and implications for management. Br J Anaesth. 2012;109:851–63. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Collins P, Abdul-Kadir R, Thachil J. Management of coagulopathy associated with postpartum hemorrhage: guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:205–10. doi: 10.1111/jth.13174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.McNamara H, Mallaiah S, Barclay P, Chevannes C, Bhalla A. Coagulopathy and placental abruption: changing management with ROTEMguided fibrinogen concentrate therapy. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2015;24:174–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2014.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.James AH, McLintock C, Lockhart E. Postpartum hemorrhage: when uterotonics and sutures fail. Am J Hematol. 2012;87 Suppl 1:S16–22. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Lockhart E. Postpartum hemorrhage: a continuing challenge. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015;2015:132–7. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2015.1.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Kaufner L, Henkelmann A, von Heymann C, Feldheiser A, Mickley L, Niepraschk-von Dollen K, et al. Can prepartum thromboelastometryderived parameters and fibrinogen levels really predict postpartum hemorrhage? J Perinat Med. 2017;45:427–35. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2016-0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Mallaiah S, Barclay P, Harrod I, Chevannes C, Bhalla A. Introduction of an algorithm for ROTEM-guided fibrinogen concentrate administration in major obstetric haemorrhage. Anaesthesia. 2015;70:166–75. doi: 10.1111/anae.12859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Snegovskikh D, Souza D, Walton Z, Dai F, Rachler R, Garay A, et al. Point-of-care viscoelastic testing improves the outcome of pregnancies complicated by severe postpartum hemorrhage. J Clin Anesth. 2018;44:50–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2017.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Girard T, Mörtl M, Schlembach D. New approaches to obstetric hemorrhage: the postpartum hemorrhage consensus algorithm. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2014;27:267–74. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Butwick AJ, Goodnough LT. Transfusion and coagulation management in major obstetric hemorrhage. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2015;28:275–84. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Collins PW, Bell SF, de Lloyd L, Collis RE. Management of postpartum haemorrhage: from research into practice, a narrative review of the literature and the Cardiff experience. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2019;37:106–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2018.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Hanke AA, Elsner O, Görlinger K. Spinal anaesthesia and caesarean section in a patient with hypofibrinogenaemia and factor XIII deficiency. Anaesthesia. 2010;65:641–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2010.06324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Truong HT, Browning RM. Anaphylaxis-induced hyperfibrinolysis in pregnancy. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2015;24:180–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2014.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Annecke T, Geisenberger T, Kürzl R, Penning R, Heindl B. Algorithm-based coagulation management of catastrophic amniotic fluid embolism. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2010;21:95–100. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e328332cfe2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Collins NF, Bloor M, McDonnell NJ. Hyperfibrinolysis diagnosed by rotational thromboelastometry in a case of suspected amniotic fluid embolism. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2013;22:71–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2012.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Chen CH, Lee KC, Hsieh YJ. Amniotic fluid embolism complicated with pulmonary embolism during cesarean section: management with TEE and ROTEMⓇ. Asian J Anesthesiol. 2017;55:93–4. doi: 10.1016/j.aja.2017.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.WOMAN Trial Collaborators Effect of early tranexamic acid administration on mortality, hysterectomy, and other morbidities in women with post-partum haemorrhage (WOMAN): an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2105–16. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30638-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Roberts I, Shakur H, Fawole B, Kuti M, Olayemi O, Bello A, et al. Haematological and fibrinolytic status of Nigerian women with postpartum haemorrhage. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018;18:143. doi: 10.1186/s12884-018-1794-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Dallaku K, Shakur H, Edwards P, Beaumont D, Roberts I, Huque S, et al. Statistical analysis plan for the WOMAN-ETAPlaT study: effect of tranexamic acid on platelet function and thrombin generation. Wellcome Open Res. 2016;1:30. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.10105.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Charbit B, Mandelbrot L, Samain E, Baron G, Haddaoui B, Keita H, et al. The decrease of fibrinogen is an early predictor of the severity of postpartum hemorrhage. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:266–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Mallaiah S, Chevannes C, McNamara H, Barclay P. A reply. Anaesthesia. 2015;70:760–1. doi: 10.1111/anae.13128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Smith RA, Mallaiah S, Chevannes C, McNamara H. Lessons from four years’ experience in the use of ROTEM-guided fibrinogen concentrate in major obstetric haemorrhage. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2017;31(Suppl 1):S7. [Google Scholar]
- 201.Smith RA, Mallaiah S, Barclay P, Chevannes C, McNamara H. Improved outcomes with ROTEM-guided fibrinogen concentrate in major obstetric haemorrhage. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2017;31(Suppl 1):S14. [Google Scholar]
- 202.Wikkelsø AJ, Edwards HM, Afshari A, Stensballe J, Langhoff-Roos J, Albrechtsen C, et al. Pre-emptive treatment with fibrinogen concentrate for postpartum haemorrhage: randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114:623–33. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Collins PW, Cannings-John R, Bruynseels D, Mallaiah S, Dick J, Elton C, et al. Viscoelastometric-guided early fibrinogen concentrate replacement during postpartum haemorrhage: OBS2, a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 2017;119:411–21. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Collins PW, Cannings-John R, Bruynseels D, Mallaiah S, Dick J, Elton C, et al. Viscoelastometry guided fresh frozen plasma infusion for postpartum haemorrhage: OBS2, an observational study. Br J Anaesth. 2017;119:422–34. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Blood Management Practice guidelines for perioperative blood management: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Blood Management*. Anesthesiology. 2015;122:241–75. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Klein AA, Arnold P, Bingham RM, Brohi K, Clark R, Collis R, et al. AAGBI guidelines: the use of blood components and their alternatives 2016. Anaesthesia. 2016;71:829–42. doi: 10.1111/anae.13489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Kozek-Langenecker SA, Ahmed AB, Afshari A, Albaladejo P, Aldecoa C, Barauskas G, et al. Management of severe perioperative bleeding: guidelines from the European Society of Anaesthesiology: first update 2016. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2017;34:332–95. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Curry NS, Davenport R, Pavord S, Mallett SV, Kitchen D, Klein AA, et al. The use of viscoelastic haemostatic assays in the management of major bleeding: a British Society for Haematology Guidelin. Br J Haematol. 2018;182:789–806. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Schlembach D, Helmer H, Henrich W, von Heymann C, Kainer F, Korte W, et al. Peripartum Haemorrhage, Diagnosis and Therapy. Guideline of the DGGG, OEGGG and SGGG (S2k Level, AWMF Registry No.015/063, March 2016) Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2018;78:382–99. doi: 10.1055/a-0582-0122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Roullet S, de Maistre E, Ickx B, Blais N, Susen S, Faraoni D, et al. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2018. Position of the French working group on perioperative haemostasis (GIHP) on viscoelastic tests: what role for which indication in bleeding situations? Advance Access published on Feb 3, 2018, doi:10.1016/j.accpm.2017.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Collis R. Coagulation point-of-care testing on the labour ward should be mandatory. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2016;27:66–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2016.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Abir G, Mhyre J. Maternal mortality and the role of the obstetric anesthesiologist. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2017;31:91–105. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2017.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.McDonnell NJ, Browning R. How to replace fibrinogen in postpartum haemorrhage situations? (Hint: Don’t use FFP!) Int J Obstet Anesth. 2018;33:4–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2017.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Pearse BL, Smith I, Faulke D, Wall D, Fraser JF, Ryan EG, et al. Protocol guided bleeding management improves cardiac surgery patient outcomes. Vox Sang. 2015;109:267–79. doi: 10.1111/vox.12279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Trevisan D1, Zavatti L, Gabbieri D, Pedulli M, Giordano G, Meli M. Point-of-care-based protocol with first-line therapy with coagulation factor concentrates is associated with decrease allogenic blood transfusion and costs in cardiovascular surgery: an Italian single-center experience. Minerva Anestesiol. 2016;82:1077–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Vasques F, Spiezia L, Manfrini A, Tarzia V, Fichera D, Simioni P, et al. Thromboelastometry guided fibrinogen replacement therapy in cardiac surgery: a retrospective observational study. J Anesth. 2017;31:286–90. doi: 10.1007/s00540-016-2271-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Mehaffey JH, Schubert SA, Gelvin MG, Charles EJ, Hawkins RB, Johnston LE, et al. A new intraoperative protocol for reducing perioperative transfusionsin cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;104:176–81. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.10.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Smith I, Pearse BL, Faulke DJ, Naidoo R, Nicotra L, Hopkins P, et al. Targeted bleeding management reduces the requirements for bloodcomponent therapy in lung transplant recipients. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017;31:426–33. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2016.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Buscher H, Zhang D, Nair P. A pilot, randomised controlled trial of a rotational thromboelastometry-based algorithm to treat bleeding episodes in extracorporeal life support: the TEM Protocol in ECLS Study (TEMPEST) Crit Care Resusc. 2017;19(Suppl 1):29–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Smart L, Mumtaz K, Scharpf D, Gray NO, Traetow D, Black S, et al. Rotational thromboelastometry or conventional coagulation tests in liver transplantation: comparing blood loss, transfusions, and cost. Ann Hepatol. 2017;16:916–23. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.5283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Schaden E, Kimberger O, Kraincuk P, Baron DM, Metnitz PG, Kozek-Langenecker S. Perioperative treatment algorithm for bleeding burn patients reduces allogeneic blood product requirements. Br J Anaesth. 2012;109:376–81. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Nardi G, Agostini V, Rondinelli B, Russo E, Bastianini B, Bini G, et al. Trauma-induced coagulopathy: impact of the early coagulation support protocol on blood product consumption, mortality and costs. Crit Care. 2015;19:83. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0817-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Haas T, Spielmann N, Restin T, Seifert B, Henze G, Obwegeser J, et al. Higher fibrinogen concentrations for reduction of transfusion requirements during major paediatric surgery: A prospective randomised controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115:234–43. doi: 10.1093/bja/aev136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Guan J, Cole CD, Schmidt MH, Dailey AT. Utility of intraoperative rotational thromboelastometry in thoracolumbar deformity surgery. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;27:528–33. doi: 10.3171/2017.5.SPINE1788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Naik BI, Pajewski TN, Bogdonoff DI, Zuo Z, Clark P, Terkawi AS, et al. Rotational thromboelastometry-guided blood product management in major spine surgery. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23:239–49. doi: 10.3171/2014.12.SPINE14620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Prat NJ, Meyer AD, Ingalls NK, Trichereau J, DuBose JJ, Cap AP. Rotational thromboelastometry significantly optimizes transfusion practices for damage control resuscitation in combat casualties. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017;83:373–80. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Fries D, Innerhofer P, Spahn DR. Transfusion approaches and mortality in trauma patients: a narrativereview. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2017;43:759–71. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1605570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Stein P, Kaserer A, Sprengel K, Wanner GA, Seifert B, Theusinger OM, et al. Change of transfusion and treatment paradigm in major trauma patients. Anaesthesia. 2017;72:1317–26. doi: 10.1111/anae.13920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Meybohm P, Herrmann E, Steinbicker AU, Wittmann M, Gruenewald M, Fischer D, et al. Patient blood management is associated with a substantial reduction of red blood cell utilization and safe for patient’s outcome: a prospective, multicenter cohort study with a noninferiority design. Ann Surg. 2016;264:203–11. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Leahy MF, Hofmann A, Towler S, Trentino KM, Burrows SA, Swain SG, et al. Improved outcomes and reduced costs associated with a health-system-wide patient blood management program: a retrospective observational study in four major adult tertiary-care hospitals. Transfusion. 2017;57:1347–58. doi: 10.1111/trf.14006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Leahy MF, Roberts H, Mukhtar SA, Farmer S, Tovey J, Jewlachow V, et al. A pragmatic approach to embedding patient blood management in a tertiary hospital. Transfusion. 2014;54:1133–45. doi: 10.1111/trf.12362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Althoff FC, Neb H, Herrmann E, Trentino KM, Vernich L, Füllenbach C, et al. Multimodal patient blood management program based on a three-pillarstrategy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2019;269:794–804. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Pagano D, Milojevic M, Meesters MI, Benedetto U, Bolliger D, von Heymann C, et al. 2017 EACTS/EACTA Guidelines on patient blood management for adult cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53:79–111. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezx325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.National Blood Authority Australia PBM guidelines: module 1-6. 2011-2018. Available from https://www.blood.gov.au/pbm-guidelines.
- 235.National Blood Authority Australia National blood management implementation strategy 2017-2021. Better management of patients’ blood … better patient outcomes. 2017 Available from https://www.blood.gov.au/implementing-pbm.
- 236.European Commission. Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety . A guide for health authorities. Publications office of the European Union; Luxembourg: Mar, 2017. Building national programmes of patient blood management (PBM). A guide for health authorities. Available from https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/blood_tissues_organs/docs/2017_eupbm_authorities_en.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 237.European Commission. Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety . Publications office of the European Union; Luxembourg: Mar, 2017. Supporting patient blood management (PBM) in the EU. A practical implementation guide for hospitals. Available from https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/blood_tissues_organs/docs/2017_eupbm_hospitals_en.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 238.Görlinger K, Kozek-Langenecker SA. In: Economic aspects and organization. In: Perioperative Hemostasis. Coagulation for Anesthesiologists. Marcucci CE, Schoettker P, editors. Basel: Springer Publishing; 2015. pp. 421–45. [Google Scholar]
- 239.Fuller RL, McCullough EC, Bao MZ, Averill RF. Estimating the costs of potentially preventable hospital acquired complications. Health Care Financ Rev. 2009;30:17–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Görlinger K, Dirkmann D, Tanaka AK, Shander A, Spahn DR, Hofmann A. Implementation of thromboelastometry-guided patient blood management results in cost-savings for blood product acquisition and potentially preventable hospital acquired complications. 10th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Health Economics (DGGÖ); 2018. pp. 228–9. [Google Scholar]