Abstract
Pawhuskin A is an isoprenylated stilbene that was isolated from Dalea purpurea and reported to have affinity for the opioid receptor in vitro. It has been synthesized through a convergent sequence that joins a prenylated aldehyde with a geranylated phosphonate in a stereoselective Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons condensation to afford the target E olefin isomer. This synthesis confirms the structure assigned to the natural product, and establishes a route that may be used to explore its biological activity and to prepare more active analogs.
Graphical Abstract
Early in 2004, Belofsky and coworkers reported the isolation of several compounds from Dalea purpurea, including three new isoprenylated stilbenes that they named pawhuskins A–C (Figure 1, 1–3).1 These three compounds were shown to have affinity for the opioid receptor in bioassays that quantified displacement of 3H-naloxone from a preparation of rat striatal tissue that included the α, κ, and μ receptors2. Our earlier work on synthesis of the schweinfurthins3, also doubly prenylated stilbenes, allowed a rapid synthesis of pawhuskin C.4 Because it bears an acyclic isoprenoid substituent on just one of the arene rings, pawhuskin C can be viewed as the simplest member of its family. However, pawhuskin A is the most active with respect to opioid receptor binding, and its substitution pattern differs from that of pawhuskin C or the natural5,6 (e.g. 4 or 5) or synthetic3,7 schweinfurthins.
Figure 1.
The natural pawhuskins and two related schweinfurthins.
Within the past few years, it has been recognized that non-nitrogenous compounds can bind at the opioid receptors and demonstrate activity or block the binding of active agents.8 The diterpenoid salvinorin A9 was found to be a κ selective agonist, and then more recently the pawhuskins have been reported to bind at opioid receptors although their specificity hasn’t been established. Whether the pawhuskins bind at hitherto unrecognized sites or bind at known sites in these receptors is not yet clear, and whether they can serve as agonists or antagonists has not yet been determined. However, there are compelling needs for new analgesics for treatment of pain, as well as for compounds that block opiate binding for use in pharmacological interventions in cases of stimulant abuse.10
The combination of interesting biological activity and the need for different protocols for introduction of the isoprenoid substituents led to an interest in the preparation of this compound. In this paper, we report an efficient synthesis of pawhuskin A that confirms the structure assigned to the natural product and paves the way for exploration of structure-activity relationships.
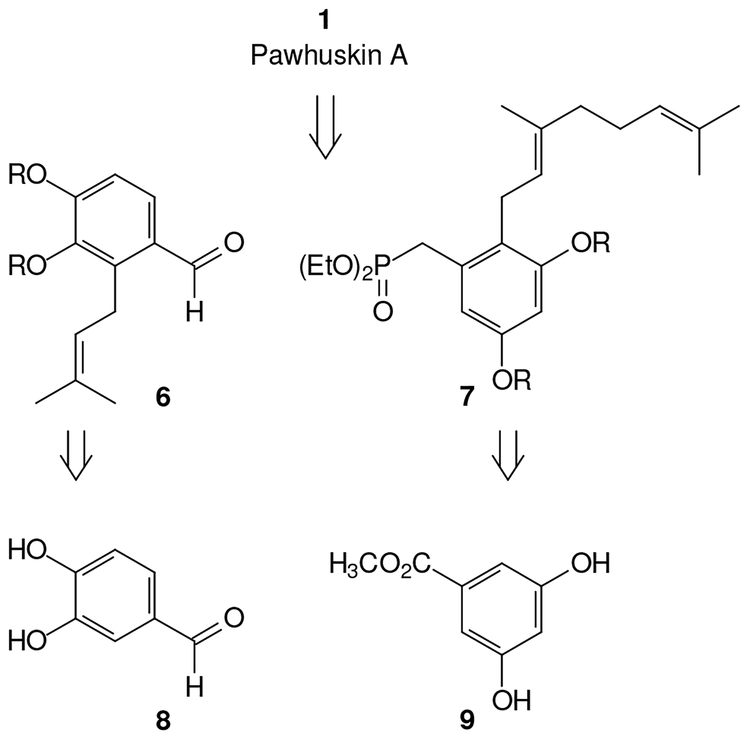
Retrosynthesis of pawhuskin A (Figure 2) through disconnection of the central stilbene olefin to intermediates appropriate for Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons condensation leads to either the aryl aldehyde 6 as the left half and a benzylic phosphonate 7 as the right half, which we chose to pursue, or to the opposite pairing. The aldehyde 6 could then be recognized in commercial 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (8) while the phosphonate 7 might be derived from commercial methyl 3,5-dihydroxybenzoate (9).
Figure 2.
Retrosynthesis of pawhuskin A.
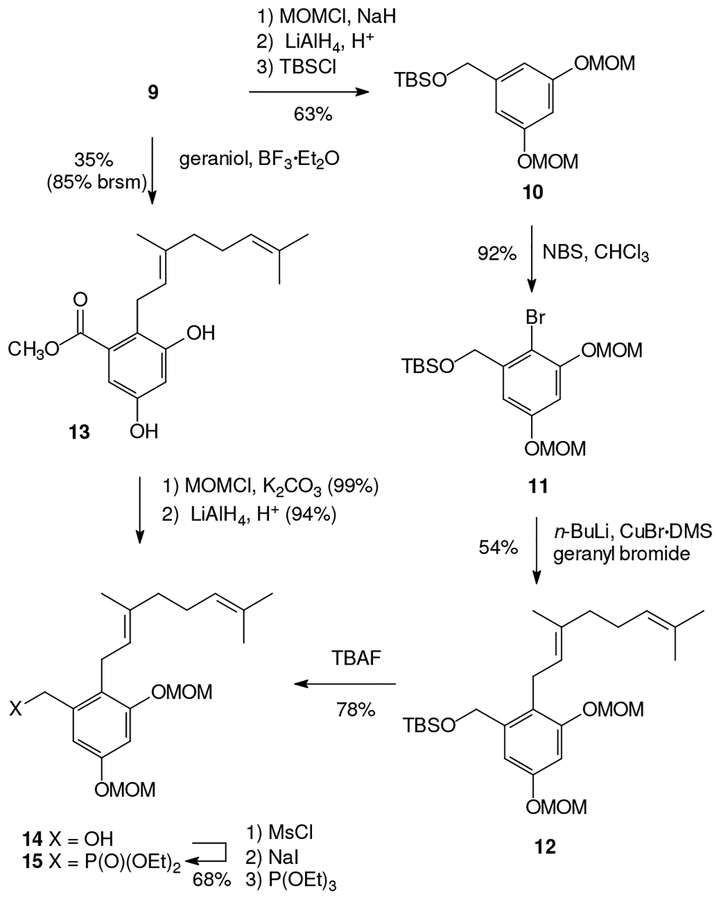
In a synthetic sense, preparation of the phosphonate appeared to require the longer sequence. Initially, conversion of ester 9 to the protected benzylic alcohol 10 was accomplished by variations on literature methods (Scheme 1).11 After formation of the TBS ether 10, bromination with NBS provided the aryl bromide 11 in good yield.12 Halogen-metal exchange and reaction with geranyl bromide in the presence of CuBrDMS gave the target carbon skeleton 12 in moderate yield, and treatment of this silyl ether with TBAF afforded the benzylic alcohol 14. An alternate route to compound 14 through the resorcinol derivative 13 was explored and proved significantly more efficient. For this sequence the ester 9 was treated with geraniol and BF3OEt2 to obtain the target carbon skeleton directly.13 While the yield for this reaction was modest (35%), a substantial amount of the starting material was recovered and the yield based on recovered starting material was very attractive (85%). Subsequent introduction of the MOM groups and reduction with LiAlH4 proceeded smoothly to afford the benzylic alcohol 14 in a very direct fashion. Conversion of alcohol 14 to the corresponding phosphonate 15 also proceeded smoothly through formation of the mesylate, displacement with NaI, and a final reaction with P(OEt)3.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of phosphonate 15.
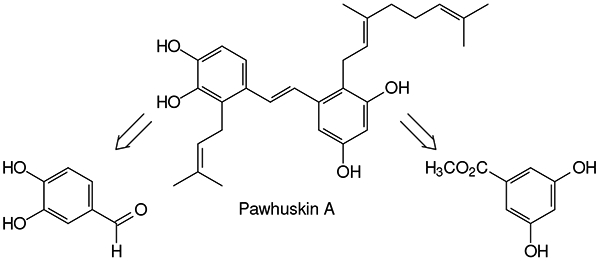
Synthesis of the complementary aldehyde began with preparation of the substituted benzaldehyde required for the anticipated Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons (HWE) condensation (Scheme 2). Commercial 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (8) was readily converted to the MOM-protected benzyl alcohol 16.14 After treatment of this alcohol with excess n-BuLi to induce directed ortho metallation and CuBr-DMS, reaction with prenyl bromide afforded the substituted arene 17. Oxidation of the benzylic alcohol 17 to the corresponding aldehyde 18 occurred readily upon treatment with MnO2. The HWE condensation of aldehyde 18 and phosphonate 15 was straightforward, providing the trans-stilbene 19 with no trace of the isomeric cis product. Hydrolysis of the four MOM groups was accomplished with CSA in MeOH to afford pawhuskin A (1). While the yield for this last step is somewhat disappointing, it does reflect cleavage of four separate protecting groups and is consistent with yields observed in other such highly protected systems.15 The final product gave 1H and 13C NMR data identical to those of the natural product.
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of pawhuskin A.
In conclusion, the natural product pawhuskin A has been prepared by a convergent sequence ending in formation of the central stilbene and deprotection of the MOM groups. The required phosphonate intermediate 15 can be prepared in a straightforward fashion from the corresponding alcohol 14. This key alcohol 14 was prepared through two different sequences, a more traditional approach that required six steps from commercial methyl 3,5-dihydroxybenzoate and gave the desired product in ~25% overall yield, and a new strategy that required only three steps and provided this key intermediate in ~33% overall yield (and almost 80% overall yield based on recovered starting material). By means of this new sequence, the synthesis reported here should provide sufficient material to explore the biological properties of pawhuskin A in more detail, and allow synthesis of analogs for more extensive structure activity relationship studies.
Experimental Section.
General Experimental Procedures.
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) and Et2O were distilled from Na and benzophenone and used immediately, while CH2Q2 was distilled from CaH2. Anhydrous DMF was used directly without further purification. All non-aqueous reactions were done under an Ar atmosphere, in oven or flame-dried glassware, and with magnetic stirring. Flash chromatography was done on silica gel with an average of 40–63 μm particle size. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded at 300 MHz with CDQ3 as solvent and (CH3)4Si as internal standard unless otherwise noted. High resolution and electrospray (ES) mass spectra were obtained at the University of Iowa Mass Spectrometry Facility. The elemental analyses were conducted by Atlantic Microlab, Inc. (Norcross, GA).
Synthesis of aryl bromide 11.
To a stirred solution of silyl ether 1015 (5.38 g, 15.7 mmol) in CHCl3 was added NBS (2.82 g, 15.8 mmol) at room temperature, the reaction was heated to reflux for 2 hours, and then allowed to cool to room temperature. The reaction mixture was quenched by addition of H2O and extracted into CHQ3. The combined organic layers were washed twice with H2O, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated in vacuo to afford a yellow oil. Final purification by flash chromatography (17% EtOAc in hexanes) gave aryl bromide 11 as a clear oil (6.06 g, 92%) having spectral properties identical to the known compound.12
tert-Butyl[{2-(2E-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl)-3,5-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzyl}oxy] dimethylsilane (12).
To a solution of aryl bromide 11 (0.52 g, 1.31 mmol) in THF (10 mL) at −78 °C was added n-BuLi (0.60 mL, 1.44 mmol, 2.4 M hexanes), and the resulting solution was stirred for 1 hour. After CuBrDMS (0.30 g, 1.45 mmol) was added and the reaction was stirred for 30 minutes, geranyl bromide (0.29 mL, 1.45 mmol) was added and the reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 10 hours. The reaction was quenched by addition of saturated NH4CI, extracted with EtOAc, and the combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated to afford a yellow oil. Final purification by column chromatography (8% to 18% EtOAc in hexanes) afforded the geranylated arene 12 (340 mg, 54%) as a clear oil: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 6.91 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 5.16 (s, 2H), 5.15 (s, 2H), 5.08 – 5.02 (m, 2H), 4.69 (s, 2H), 3.47 (s, 3H), 3.46 (s, 3H), 3.28 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 2 δ 156.1, 155.3, 141.5, 134.6, 131.3, 124.2, 122.8, 120.8, 107.4, 102.0, 94.6, 94.6, 62.6, 56.0, 55.9, 39.7, 26.7, 25.9 (3C), 25.7, 23.9, 18.4, 17.6, 16.1, −5.3(2C). Anal. C 67.95%, H 9.71%, calcd for C27H46O5Si C 67.74%, H 9.68%.
2-[(2E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl]-3,5-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzyl Alcohol (13).
The silyl ether 12 (107 mg, 0.23 mmol) was dissolved in THF (10 mL) and the solution was cooled to 0 °C. To this solution was added TBAF (0.26 mL, 1.00 M in THF), the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature, and after 1.5 hours it was quenched by addition of saturated NH4CL After extraction with EtOAc, the combined organic extract was washed with water and brine, dried over MgSO4, and concentrated in vacuo to give a yellow oil. Final purification by flash chromatography (30% EtOAc in hexanes) gave the benzylic alcohol 13 (65 mg, 78%): 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 6.79 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.17 (s, 2H), 5.15 (s, 2H), 5.11 − 5.02 (m, 2H), 4.64 (s, 2H), 3.47 (s, 3H), 3.47 (s, 3H), 3.38 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 2.08 −1.94 (m, 4H), 1.77 (s, 3H), 1.65 (s, 3H), 1.57 (s, 3H); 13C NMR δ 156.2, 155.9, 140.9, 135.1, 131.4, 124.1, 123.4, 122.4, 108.8, 103.0, 94.6, 94.6, 63.3, 56.0, 56.0, 39.7, 26.6, 25.6, 24.1, 17.6, 16.1; HRMS(FAB) calcd for C21H33O5 (M+H)+: 365.2328. Found: 365.2319.
Methyl 2-(3,7-Dimethyl-octa-2,6-dienyl)-3,5-dihydroxybenzoate (13).
To a solution of benzoate 9 (4.00 g, 23.8 mmol) in dioxane (100 mL) was added BF3OEt2 (1.2 mL, 9.5 mmol). The reaction was heated to 50 °C and geraniol (2.08 mL, 11.9 mmol) in dioxane (20 mL) was added dropwise over 50 minutes. After the reaction was allowed to stir for an additional 2 hours, it was poured into H2O and extracted with Et2O (300 mL). The combined organic fractions were washed with brine, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated in vacuo. Final purification by flash column chromatography (25–35% EtOAc in hexanes) gave the geranylated compound 13 (1.27 g, 35%) as a light yellow oil as well as recovered benzoate 9 (2.35 g, 59%): 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 6.86 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 5.20 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 5.07–5.00 (m, 1H), 4.83 (s, 2H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.59 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 2.12–1.99 (m, 4H), 1.78 (s, 3H), 1.66 (s, 3H), 1.58 (s, 3H); 13C NMR δ 169.1, 156.9, 154.9, 138.6, 132.34, 132.31, 124.1, 122.5, 120.5, 109.8, 107.5, 52.6, 40.0, 26.7, 26.1, 26.0, 18.0, 16.5; HRMS m/z 304.1675 (calcd for C18H24O4, 304.1673).
Methyl 2-(3,7-Dimethyl-octa-2,6-dienyl)-3,5-bis-methoxymethoxybenzoate.
To a solution of compound 13 (272 mg, 0.89 mmol) in acetone (50 mL) was added anhydrous K2CO3 (1.23 g, 8.94 mmol). After the reaction was allowed to stir for 15 minutes, MOMCl (0.34 mL, 4.47 mmol) was added and the solution was heated to 60 °C for 6 hours. The reaction was allowed to cool to room temperature, the acetone was removed in vacuo, and EtOAc (100 mL) was added. The solution then was washed with saturated NH4Cl, H2O, and brine, dried (MgSO4), and finally concentrated in vacuo to give the protected ester (348 mg, 99%), as a yellow oil: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 7.09 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 5.17 (s, 2H), 5.15 (s, 2H), 5.12 (m, 1H), 5.05 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.59 (d, J = 6.9, 2H), 3.46 (s, 3H), 3.45 (s, 3H), 2.08–1.90 (m, 4H), 1.74 (s, 3H), 1.63 (s, 3H), 1.56 (s, 3H); 13C NMR δ 168.6, 156.6, 155.9, 135.0, 132.4, 131.5, 126.0, 124.6, 123.5, 110.2, 107.1, 94.8 (2C), 56.4, 56.3, 52.4, 40.1, 27.0, 25.9, 25.6, 17.9, 16.5; HRMS m/z 392.2204 (calcd for C22H32O6, 392.2199).
[2-(3,7-Dimethyl-octa-2,6-dienyl)-3,5-bis-methoxymethoxyphenyl]methanol (14).
To a suspension of LiAlH4 (29 mg, 0.75 mmol) in THF (5 mL) at 0 °C was added the intermediate ester (151 mg, 0.38 mmol) in THF (2 mL) dropwise. The reaction was allowed to stir for 1 hour and then quenched by addition of H2O. The reaction mixture was acidified with 1 M HCl (5 mL) and then diluted with EtOAc, washed with brine, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated in vacuo. Final purification by flash column chromatography (25% EtOAc in hexanes) gave alcohol 14 (130 mg, 94%). Both 1H and 13C NMR data matched those reported above.
Diethyl [2-{(2E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl}−3,5-bis(methoxymethoxy)benzyl] phosphonate (15).
Methanesulfonyl chloride (0.26 mL, 3.4 mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of alcohol 14 (302 mg, 0.83 mmol) and Et3N (0.20 mL 1.4 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (8 mL) at 0 °C and, the reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature over 1.5 hours, quenched by addition of H2O, and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with saturated NH4Cl and brine, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated in vacuo. The resulting residue and NaI (135 mg, 0.90 mmol) were stirred in acetone (9 mL) for 16 hours. This reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo to afford a red solid, which was dissolved in EtOAc. After the resulting yellow solution was washed once with NaHCO3 and then with Na2S2O3 (10% aq.) until the color faded, it was washed with brine, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated in vacuo. The resulting yellow oil was added to triethyl phosphite (1 mL) and the mixture was heated at 100 °C for 10 hours. After the solution was allowed to cool to room temperature, the excess phosphite was removed under high vacuum. The initial yellow oil was purified by flash chromatography (50% EtOAc in hexanes) to afford phosphonate 15 (274 mg, 68%) as a clear oil: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) q 6.70 – 6.68 (m, 2H), 5.15 (s, 2H), 5.13 (s, 2H), 5.07 – 5.00 (m, 2H), 4.07 – 3.98 (m, 4H), 3.46 – 3.45 (m, 2H), 3.46 (s, 3H), 3.45 (s, 3H), 3.13 (d, JHP = 22 Hz, 2H), 2.09 – 1.95 (m, 4H), 1.78 (s, 3H), 1.65 (s, 3H), 1.57 (s, 3H), 1.26 (t, JHP = 7.0 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (CDCl3) q 155.9, 155.7 (d, JCP = 3.8 Hz), 134.8, 132.0 (d, JCP = 9.1 Hz), 131.2, 124.0,124.2, 122.9, 111.4, 102.4 (d, JCP = 3.7 Hz), 94.6, 94.6, 62.0 (d, JCP = 6.17, 2C), 56.0, 55.9, 39.6, 30.4 (d, JCP = 137 Hz), 26.6, 25.6, 24.6, 17.6, 16.3, 16.3, 16.1; 31P NMR q 27.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C25H41O7P: 484.2590; Found: 484.2595.
Synthesis of [3,4-Bis(methoxymethoxy)-2-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)phenyl]methanol (17).
To a stirred solution of alcohol 164, 14 (203 mg, 0.92 mmol) in THF (4 L) was added n-BuLi (0.78 mL of a 2.48 M solution in hexanes) at 0 °C and the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes at 0 °C. To this mixture was added CuBr as its dimethyl sulfide complex (201 mg, 0.98 mmol), and the reaction was allowed to stir for 30 minutes at 0 °C. After prenyl bromide (0.11 mL, 0.98 mmol) was added dropwise at 0 °C, the mixture was stirred for 2 hours at 0 °C, then quenched by addition of H2O and extracted with Et2O. The combined organic layers were dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated in vacuo to afford a dark yellow oil. The oil was purified by flash chromatography (15–20% EtOAc in hexanes) to give the prenylated arene 17 as a light yellow oil (92 mg, 35%): 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 7.10 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H), 7.00 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H), 5.19 (s, 2 H), 5.15 (t, J = 1.5, 1 H), 5.11 (s, 2 H), 4.60 (s, 2 H), 3.59 (s, 3 H), 3.54 (s, 1 H), 3.52 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 2 H), 3.50 (s, 3 H) 1.80 (s, 3 H), 1.69 (s, 3 H); 13C NMR δ 149.9, 145.3, 135.0, 134.1, 132.4, 125.1, 123.8, 114.3, 99.6, 96.4, 63.6, 57.9, 56.6, 26.0, 25.7, 18.3. Anal. C 65.13%, H 8.44%, calcd for C16H24O5, C 64.84%, H 8.16%.
3,4-Bis(methoxymethoxy)-2-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)benzaldehyde (18).
To a stirred solution of benzyl alcohol 17 (116 mg, 0.39 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (10 mL) was added MnO2 (0.80 g, 7.80 mmol) at 0 °C and the resulting mixture was stirred for 22 hours while it was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite and the pad was rinsed with EtOAc, Et2O, hexanes, and MeOH. After the combined filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to afford a yellow oil, final purification by flash chromatography (30% EtOAc in hexanes) gave the aldehyde 18 as a pale yellow oil (91 mg, 79%). The 1H and 13C NMR data were identical to reported data.16
Tetra(methoxymethyl)pawhuskin A (19).
NaH (as a 60% dispersion in mineral oil, 46 mg, 1.15 mmol) and 15-crown-5 (0.03 mL, 0.12 mmol) were dissolved in THF (5 mL) and the solution was cooled to 0 °C. Aldehyde 18 (32 mg, 0.11 mmol) and phosphonate 15 (106 mg, 0.22 mmol) were dissolved in THF (3 mL) and transferred via syringe to the NaH suspension. The mixture was stirred for 22 hours while it was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction mixture was quenched by addition of H2O (10 mL) and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated in vacuo to afford a yellow oil. The yellow oil was purified by flash chromatography (25% EtOAc in hexanes) to afford stilbene 19 as a yellow oil (44 mg, 63%): 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 7.29 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 7.10 (s, 2 H), 7.02 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H), 6.93 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1 H), 6.74 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1 H), 5.21 (s, 2 H), 5.18 (s, 2 H), 5.17 (s, 2 H), 5.15 (t, J = 1.5 Hz, 1 H), 5.13 (t, J = 0.9 Hz, 1 H), 5.11 (s, 2 H), 5.05 (tt, J = 6.6, 1.2 Hz, 1 H), 3.60 (s, 3 H), 3.56 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.51 (s, 3 H), 3.49 (s, 3H), 3.48 (s, 3 H), 3.45 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2 H), 2.05–1.97 (m, 4 H), 1.80 (s, 3 H), 1.79 (s, 3 H), 1.69 (s, 3 H), 1.62 (s, 3 H), 1.55 (s, 3 H); 13C NMR δ 156.3, 156.0, 149.5, 144.8, 138.8, 134.9, 134.7, 132.3, 131.9, 131.6, 128.7, 127.5, 124.6, 123.7, 123.4, 123.2, 122.3, 114.5, 106.9, 103.1, 99.6, 95.4, 95.0, 95.0, 57.9, 56.6, 56.3, 56.3, 40.1, 27.1, 26.2, 25.9, 25.9, 25.0, 18.5, 18.0, 16.7; HRMS calcd for C37 H52 O8 (M+) 624.3662, found 624.3657.
Pawhuskin A (1).
To a stirred solution of stilbene 19 (42 mg, 0.06 mmol) was added camphorsulphonic acid (4 mg, 0.02 mmol) and the mixture was stirred at 55 °C for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was quenched by addition of saturated NH4Cl and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated in vacuo to afford a yellow oil. Final purification by flash chromatography (30% EtOAc in hexanes) gave pawhuskin A (1) as a yellow oil (11 mg, 36%). Both 1H and13C NMR spectra were identical to published data.1
Acknowledgements.
Financial support from the Roy J. Carver Charitable Trust and from the National Institutes of Health, through a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (P01 ES012020) and the Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS) and an Oncology Research Training Award (2 T32 CA79445) through the Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center, is gratefully acknowledged.
References and Notes.
- (1).Belofsky G; French AN; Wallace DR; Dodson SL J. Nat. Prod 2004, 67, 26–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (2).Pasternak GW; Wilson HA; Snyder SH Mol. Pharm 1975, 11, 340–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (3).Neighbors JD; Beutler JA; Wiemer DF J. Org. Chem 2005, 70, 925–931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (4).Neighbors JD; Salnikova MS; Wiemer DF Tetrahedron Lett 2005, 46, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar]
- (5).a) Beutler JA; Shoemaker RH; Johnson T; Boyd MR J. Nat. Prod 1998, 61, 1509–1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b) Beutler JA; Jato J; Cragg GM; Boyd MR Nat. Prod. Lett 2000, 14, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- (6).Yoder BJ; Cao S; Norris A; Miller JS; Ratovoson F; Razafitsalama J; Andriantsiferana R; Rasamison VE; Kingston DGI J. Nat. Prod 2007, 70, 342–346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (7).a) Mente NR; Wiemer AJ; Neighbors JD; Beutler JA; Hohl RJ; Wiemer DF Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett, 2007, 17, 911–915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b) Mente NR; Neighbors JD; Wiemer DF J. Org. Chem 2008, ASAP, web release date September 17, 2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (8).McCurdy CR; Scully SS Life Sci 2005, 78, 476–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (9).a) Roth BL; Baner K; Westkaemper R; Siebert D; Rice KC; Steinberg S; Ernsberger P; Rothman RB Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 2002, 99, 11934–11939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b) Prisinzano TE; Rothman RB Chem. Rev 2008, 108, 1732–1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (10).Prisinzano TE; Tidgewell K; Harding WW The AAPS Journal, 2005, 7, E592–E599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (11).Townsend CA; Davis SG; Christensen SB; Link JC; Lewis CP J. Am. Chem. Soc 1981, 103, 6885–6888. [Google Scholar]
- (12).Kaiser F; Schmalz H-G Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 7345–7355. [Google Scholar]
- (13).The conditions employed were essentially those described in:; Yamada K; Tahara Y; Toyada M; Irino O; Misaki N; US Patent # 4,906,669, 1990.
- (14).Wang Y; Mathis CA; Haung G; Holt DP; Debnath ML; Klunk WE J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm 2002, 45, 647–664. [Google Scholar]
- (15).Treadwell EM; Cermak SC; Wiemer DF J. Org. Chem 1999, 64, 8718–8723. [Google Scholar]
- (16).Zhao LY; Li YL Chin. Chem. Lett 1994, 5, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar]