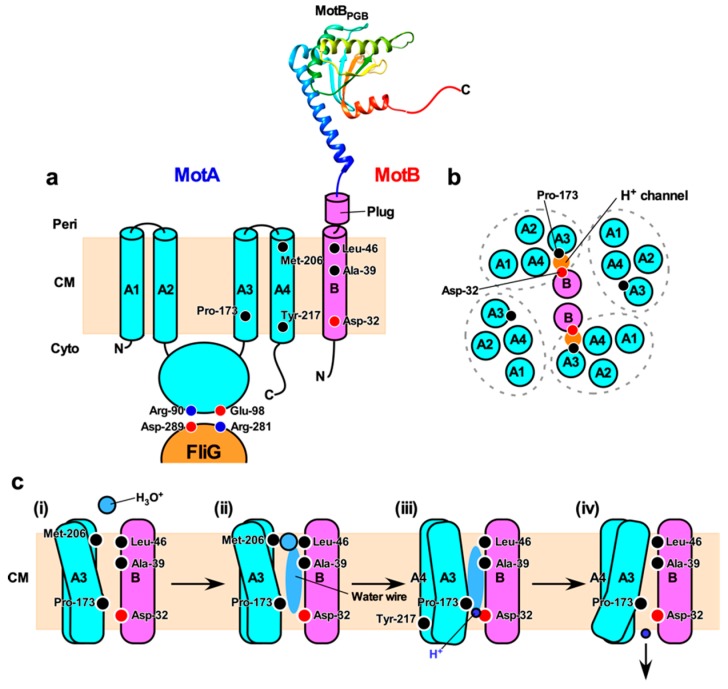
Figure 2.
H+ translocation mechanism of the flagellar motor. (a) Topology of the E. coli MotA and MotB and a crystal structure of the peptidoglycan-binding domain of MotB (MotBPGB, PDB code: 2ZVY). Highly conserved Arg-90 and Glu-98 residues in the cytoplasmic loop between transmembrane helices 2 (A2) and 3 (A3) interact with conserved Asp-289 and Arg-281 residues of FliG, respectively, to drive motor rotation. Asp-32 of MotB provides a binding site for H+. Pro-173, Met-206 and Tyr-217 of MotA and Ala-39 and Leu-46 of MotB are involved in the H+ relay mechanism. Cyto, cytoplasm; CM, cytoplasmic membrane; Peri, periplasm. (b) Arrangement of transmembrane segments of MotA and MotB. The MotAB complex has two proton channels. Four MotA subunits are positioned with their TM3 (A3) and TM4 (A4) segments adjacent to the MotB dimer, and their TM1 (A1) and TM2 (A2) segments on the outside. (c) A plausible model for H+ translocation through MotAB stator complex (see text for details).