Abstract
Background
Mentally ill patients die on average 10 years earlier than the general population, largely due to general medical disorders. This study is the first to explore in a large German sample the prevalence, mortality, and medical comorbidity in patients with severe mental illness (SMI). The patients were affected by borderline personality disorder (BPD), psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder, or severe unipolar depression.
Methods
Our database consists of billing data from all adults with statutory health insurance in Germany. Twelve-month administrative SMI prevalence and medical comorbidity were estimated using cross-sectional data from 2016 (age = 18; N = 59 561 310). Two-year mortality was established longitudinally in a randomly selected subset of the billing data (most recent mortality information available for 2012 to 2014; 2012: n = 15 590 107).
Results
Severe unipolar depression had the highest prevalence (2.01%), followed by psychotic disorders (1.25%), BPD (0.34%), and bipolar disorder (0.29%). While the prevalence of malignant neoplasms showed moderate deviations from reference values [severe unipolar depression: OR = 1.30 (95% CI = 1.29; 1.31), BPD: OR = 1.11 (1.09; 1.14), psychotic disorders: OR = 0.90 (0.89; 0.90), bipolar disorder: OR = 1.07 (1.06; 1.09)], other disease groups (infectious, endocrine/nutritional/metabolic, circulatory, respiratory) were substantially elevated in all categories of SMI. Mortality rates for psychotic disorders, BPD, bipolar disorder, and severe unipolar depression were increased (OR = 2.38 [95% CI=2.32; 2.44], 2.30 [2.08; 2.54], 1.52 [1.42; 1.62], and 1.40 [1.37; 1.44], respectively), with a loss of 2.6 to 12.3 years, depending on age, sex, and SMI.
Conclusion
Mortality is substantially elevated in all SMI patients. The results underline the need to remove barriers to adequate general medical care, both on the patient and the provider side, to reduce excess mortality.
Extensive research has shown increased mortality among patients with mental disorders, especially in those affected by severe mental illness (SMI) (1, 2), which typically includes schizophrenia and uni-/bipolar depression (2– 4, e1).
In a recent meta-analysis, Walker and colleagues (5) revealed that mortality in mentally ill patients is more than twice as high as in the general population, with two third of the deaths being due to natural causes. In total, an estimated 8 million deaths worldwide (14.3%) are due to mental disorders every year and the reduction in life span is estimated at 10 years (median) (5). Some authors have described even greater shortening of life, between 13 and 30 years (6, 7). In Germany, the number of seriously mentally ill adults is estimated at 1–2% of the population, i.e., up to 1 million affected individuals (8). The global burden of mental disorders is a serious public health problem (9, 10). Alongside unnatural causes of death such as accidents and suicide, the increased number of premature deaths is largely attributable to physical illness such as cardiovascular disease and endocrine and metabolic disorders (3, e1). Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the general German population (11).
Research on mortality and medical morbidity in SMI usually focuses on schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe depression. Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is also a clinically severe mental illness but has rarely been studied with regard to mortality and medical morbidity.
To extend the research findings to BPD, we conducted the first population-based registry study using adult data from all statutory health insurance funds in Germany, representing a very large collective (age ≥ 18; N = 59 561 310). Previously, no such study could be conducted in Germany, a country with some of the strictest data protection regulations in the world (12), and until recently no national claims data composed of persons insured by all statutory health insurance funds were available for such analyses. Since BPD has not been included in this context before, in Germany or elsewhere, the present study makes a unique contribution to the understanding of comorbidity and mortality in SMI.
We set out to quantify:
Medical comorbidity and risk factors in SMIs, including BPD.
(Increased) mortality in SMI patients and estimated reduction in life span.
Additionally, 12-month SMI prevalences in Germany were determined.
Methods
Datasets and study types
The database consists of billing data (§ 295 German Social Code V) from all adults with statutory health insurance who had contact with general or specialist physicians or psychotherapists accredited to invoice the German regional associations of statutory health insurance physicians (ASHIP) (13).
Twelve-month prevalence and medical comorbidity of SMI patients were examined cross-sectionally using the latest available billing data (2016: age ≥ 18 years; N = 59 561 310). Patients who had no contact with the health system in 2016 were not included in the analyses.
The dataset from 2016 lacks information on mortality. Using the most recent data available, 2-year mortality was calculated longitudinally for the years 2013 and 2014 for patients with and without a SMI diagnosis in 2012 (2012: n = 15 590 107).
Diagnostic assessment
Psychiatric diagnoses were operationalized using routine diagnoses (coded according to ICD-10) assigned by medical service providers to the (same) patient. Based on previous research (14) and relevance for psychiatric health care (e2), we included BPD (F60.3x), psychotic disorders (schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders, F2x), bipolar affective disorder (F31.x, including manic episode, F30.x), and severe unipolar depression (F32.2/33.2, F32.3/F33.3; eMethods).
Based on clinical and theoretical considerations, a selected range of general medical conditions were specified according to ICD-10 code and relevant risk factors of mortality and included in comorbidity analyses (etable 1).
eTable 1. Medical morbidity and risk factors in patients with and without borderline personality disorder, psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder, or severe unipolar depression (complete data; administrative data of all statutory health insured adults in Germany, age ≥ 18 years*1, 2016).
| Borderline personality disorder | Psychotic disorders | Bipolar disorder | Severe unipolar depression | ||||||
| Medical morbidity / risk factor (base rate, i.e., prevalence in whole population) | ICD-10 code | OR*2 | (95% CI) | OR*2 | (95% CI) | OR*2 | (95% CI) | OR | 95-%-KI |
| Hepatitis, human immunodeficiency virus (0.675%) | B15–B24 | 4.28 | [4.15; 4.40] | 2.39 | [2.35; 2.44] | 1.91 | [1.84; 1.99] | 2.08 | [2.05; 2.12] |
| Malignant neoplasms (MN) (8.062%) | C00–C97 | 1.11 | [1.09; 1.14] | 0.90 | [0.89; 0.90] | 1.07 | [1.06; 1.09] | 1.30 | [1.29; 1.31] |
| MN of lip, oral cavity, and pharynx (0.153%) | C00–C14 | 1.33 | [1.15; 1.53] | 0.98 | [0.92; 1.03] | 0.97 | [0.89; 1.12] | 1.36 | [1.31; 1.42] |
| MN of digestive organs (1.051%) | C15–C26 | 1.25 | [1.17; 1.33] | 0.92 | [0.90; 0.94] | 1.01 | [0.97; 1.05] | 1.25 | [1.23; 1.27] |
| MN of respiratory and other intrathoracic organs (0.376%) | C30–C39 | 1.29 | [1.17; 1.43] | 1.05 | [1.01; 1.09] | 1.00 | [0.93; 1.08] | 1.45 | [1.42; 1.48] |
| MN of bronchus and lung (0.288%) | C34 | 1.32 | [1.18; 1.48] | 1.07 | [1.03; 1.11] | 0.99 | [0.91; 1.07] | 1.46 | [1.42; 1.50] |
| MN of bone and articular cartilage (0.040%) | C40–C41 | 1.32 | [1.07; 1.64] | 1.06 | [0.95; 1.18] | 1.36 | [1.12; 1.65] | 1.56 | [1.45; 1.67] |
| Melanoma and other MN of skin (2.455%) | C43–C44 | 0.91 | [0.87; 0.96] | 0.76 | [0.75; 0.77] | 0.99 | [0.97; 1.02] | 1.08 | [1.07; 1.09] |
| MN of mesothelial and soft tissue (0.107%) | C45–C49 | 1.28 | [1.09; 1.50] | 0.96 | [0.90; 1.03] | 1.15 | [1.01; 1.30] | 1.53 | [1.47; 1.60] |
| MN of breast (1.493%) | C50 | 0.10 | [0.93; 1.02] | 1.00 | [0.99; 1.02] | 1.15 | [1.12; 1.19] | 1.36 | [1.35; 1.38] |
| MN of female genital organs (0.482%) | C51–C58 | 1.70 | [1.61; 1.80] | 1.08 | [1.05; 1.11] | 1.13 | [1.06; 1.19] | 1.34 | [1.32; 1.37] |
| MN of male genital organs (1.190%) | C60–C63 | 0.98 | [0.90; 1.05] | 0.77 | [0.75; 0.79] | 1.09 | [1.04; 1.14] | 1.37 | [1.35; 1.39] |
| MN of prostate (1.080%) | C61 | 0.93 | [0.85; 1.02] | 0.74 | [0.72; 0.76] | 1.06 | [1.01; 1.11] | 1.36 | [1.33; 1.38] |
| MN of urinary tract (0.682%) | C64–C68 | 1.16 | [1.07; 1.27] | 0.90 | [0.88; 0.93] | 1.01 | [0.96; 1.07] | 1.33 | [1.30; 1.35] |
| MN of eye. brain, other CNS sites (0.114%) | C69–C72 | 1.42 | [1.25; 1.61] | 1.28 | [1.21; 1.36] | 1.27 | [1.13; 1.43] | 1.79 | [1.72; 1.86] |
| MN of thyroid and other endocrine glands (0.175%) | C73–C75 | 1.12 | [1.00; 1.25] | 0.95 | [0.90; 1.00] | 1.35 | [1.24; 1.48] | 1.47 | [1.43; 1.52] |
| MN of ill-defined, secondary, and unspecific sites (1.075%) | C76–C80 | 1.22 | [1.16; 1.30] | 0.96 | [0.94; 0.98] | 1.07 | [1.02; 1.11] | 1.42 | [1.40; 1.44) |
| MN (primary) of lymphoid, hematopoietic, and related tissues (0.657%) | C81–C96 | 1.17 | [1.09; 1.25] | 0.92 | [0.89; 0.94] | 1.04 | [0.99; 1.10] | 1.33 | [1.31; 1.36] |
| Hodgkin lymphoma (0.078%) | C81 | 1.08 | [0.92; 1.27] | 1.04 | [0.96; 1.12] | 1.10 | [0.94; 1.29] | 1.51 | [1.43; 1.59] |
| MN as primary tumors at several sites (0.012%) | C97 | 1.35 | [0.78; 2.33] | 0.94 | [0.77; 1.15] | 1.31 | [0.92; 1.88] | 1.65 | [1.46; 1.87] |
| Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic ‧diseases (48.590%) | E00–E90 | 1.70 | [1.69; 1.72] | 1.42 | [1.42; 1.43] | 1.61 | [1.59; 1.63] | 1.75 | [1.74; 1.76] |
| Diabetes mellitus (12.801%) | E10–E14 | 1.85 | [1.82; 1.88] | 1.61 | [1.60; 1.62] | 1.27 | [1.25; 1.28] | 1.41 | [1.40; 1.41] |
| Obesity (12.442%) | E66 | 2.08 | [2.06; 2.10] | 1.60 | [1.59; 1.61] | 1.45 | [1.43; 1.47] | 1.53 | [1.53; 1.54] |
| Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism and other lipidemias (22.891%) | E78 | 1.34 | [1.32; 1.36] | 0.99 | [0.99; 1.00] | 1.13 | [1.11; 1.14] | 1.37 | [1.37; 1.38] |
| Organic mental disorders and dementias (4.063%) | F0, G30–G31 | 4.60 | [4.50; 4.71] | 8.43 | [8.37; 8.49] | 3.85 | [3.79; 3.92] | 3.09 | [3.07; 3.11] |
| Mental and behavioral disorders due to alcohol (2.239%) | F10 | 12.23 | [12.06; 12.40] | 4.25 | [4.22; 4.29] | 4.10 | [4.03; 4.17] | 3.18 | [3.15; 3.20] |
| Mental and behavioral disorders due to psychotropic substances (except alcohol) (6.937%) | F11–F19 | 5.28 | [5.22; 5.33] | 3.02 | [3.00; 3.03] | 2.27 | [2.24; 2.30] | 2.18 | [2.17; 2.20] |
| Diseases of the circulatory system (47.391%) | I00–I99 | 1.50 | [1.49; 1.52] | 1.15 | [1.14; 1.16] | 1.26 | [1.25; 1.28] | 1.63 | [1.62; 1.63] |
| Hypertension (35.640%) | I10–I15 | 1.40 | [1.39; 1.42] | 1.01 | [1.00; 1.02] | 1.12 | [1.11; 1.14] | 1.42 | [1.42; 1.43] |
| Ischemic heart disease (8.841%) | I20–I25 | 1.60 | [1.56; 1.64] | 1.02 | [1.02; 1.03] | 1.13 | [1.11; 1.15] | 1.53 | [1.52; 1.54] |
| Cardiac arrhythmia (9.722%) | I44–I49 | 1.46 | [1.43; 1.49] | 0.97 | [0.96; 0.97] | 1.11 | [1.09; 1.13] | 1.33 | [1.32; 1.33] |
| Atrial fibrillation (4.246%) | I48 | 1.18 | [1.13; 1.22] | 0.93 | [0.92; 0.94] | 0.98 | [0.96; 1.00] | 1.15 | [1.14; 1.16] |
| Heart failure (4.783%) | I50 | 1.82 | [1.77; 1.88] | 1.48 | [1.47; 1.49] | 1.32 | [1.29; 1.34] | 1.53 | [1.52; 1.55] |
| Cerebrovascular disease (6.365%) | I60–I69 | 1.79 | [1.74; 1.83] | 1.39 | [1.38; 1.40] | 1.47 | [1.44; 1.49] | 1.76 | [1.75; 1.77] |
| Diseases of the arteries, arterioles, capillaries (7.230%) | I70–I79 | 1.66 | [1.63; 1.70] | 1.01 | [1.00; 1.02] | 1.15 | [1.14; 1.17] | 1.41 | [1.40; 1.42] |
| Respiratory system diseases (46.156%) | J00–J99 | 1.41 | [1.40; 1.42] | 0.96 | [0.96; 0.97] | 1.16 | [1.15; 1.17] | 1.43 | [1.42; 1.43] |
| Pneumonia (1.008%) | J12–J18 | 1.74 | [1.67; 1.81] | 1.71 | [1.68; 1.74] | 1.55 | [1.49; 1.61] | 1.67 | [1.64; 1.67] |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (6.060%) | J43–J44 | 2.60 | [2.55; 2.64] | 1.58 | [1.57; 1.59] | 1.43 | [1.41; 1.46] | 1.79 | [1.78; 1.80] |
| Asthma (7.549%) | J45–J46 | 2.12 | [2.09; 2.14] | 1.07 | [1.06; 1.08] | 1.31 | [1.29; 1.33] | 1.60 | [1.59; 1.61] |
| Injuries, poisonings, other consequences of external causes (28.229%) | S00–T98 | 1.96 | [1.94; 1.97] | 1.19 | [1.18; 1.19] | 1.38 | [1.37; 1.40] | 1.49 | [1.48; 1.49] |
| External causes of morbidity and mortality (0.297%) | V01–Y98 | 4.29 | [4.12; 4.46] | 1.81 | [1.76; 1.87] | 1.85 | [1.73; 1.97] | 1.88 | [1.84; 1.93] |
| Accidents (0.161%) | V01–X59 | 2.20 | [2.05; 2.36] | 1.26 | [1.20; 1.33] | 1.49 | [1.35; 1.64] | 1.41 | [1.35; 1.46] |
| Intentional self-harm (0.011%) | X60–X84 | 56.22 | [52.76; 59.90] | 18.81 | [17.57; 20.15] | 11.10 | [9.53; 12.93] | 15.73 | [14.73; 16.68] |
All odds ratios (OR) are shown, irrespective of significance or effect size; in the case of a lower/upper CI limits of <1 or >1 respectively, the result is statistically significant (p <0.05; in most cases
p < 0.01); effects that are both significant and rated as substantial (OR >1.436 or OR <0.696) are in bold type.
Results are adjusted for age and sex.
*1 Data from statutory health insurance funds; 2016: N = 59 561 310 (not included: adults in Germany with private [10.5%] and no [ca. 2%] health insurance); mean age = 51.25 years, % female 55.40; ICD-10 diagnoses included: F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/F31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F33.2/F33.3
*2 OR with 95% CI; adjusted for age and sex; reference groups: respective diagnosis not present
Ethical standards
The local ethics committee of the Faculty of Medicine, RWTH Aachen University, raised no ethical or professional objections to the research project.
Statistical analyses
We present 12-month administrative prevalences for the year 2016. Odds ratios (OR) of the medical conditions and risk factors (adjusted for age group [18–24, 25–34, 35–44, 45–54, 55–59, 60–64, 65–69, 70–74, 75–79, 80–84, 85–89, 90–94, 95+] and sex, inclusive interaction) were calculated by means of multiple logistic regression and separated for six subgroups (three age groups [18–39, 40–64, 65+] × sex).
In order to evaluate whether significant ORs were also substantial in terms of effect size, we selected the established cut-offs originally proposed by Chinn (15): OR >1.436 and OR <0.696. Base rates of all medical diagnoses are provided to enhance interpretation of ORs (etable 1).
Mortality rates for 2013 to 2014 were calculated as a raw percentage for patients with and without a diagnosis of SMI in 2012. OR were calculated according to the Mantel–Haenszel (OR-MH) method to account for variation in OR across age and sex groups (16). The OR indicate increased mortality of patients with a specific SMI compared with patients without that SMI. Due to the low prevalence of mortality rates, the OR resemble relative risks (RR).
Loss of life years was estimated using statistical life tables for the general German population in 2014 (eMethods) (17). The difference in life expectancy between the total population and a particular SMI population was taken as proxy for lost life years.
Results
Twelve-month prevalence
Severe unipolar depression had the highest 12-month prevalence (2.009%; n = 1 196 710), followed by psychotic disorders (1.245%; n = 741 528), BPD (0.341%; n = 203 378), and bipolar disorder (0.288%; n = 171 494; Table 1). BPD prevalence dropped with age, while other SMIs showed a rise after the age of 40 years and then remained relatively stable. Prevalence was higher in women than in men.
Table 1. Administrative prevalences (2016) of borderline personality disorder, psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder, and severe unipolar depression by age and sex*1.
|
Borderline personality disorder*2 |
Psychotic disorders |
Bipolar disorder |
Severe unipolar depression |
|
| 12-month prevalence (total) % | 0.341 | 1.245 | 0.288 | 2.009 |
| (n) | (203 378) | (741 528) | (171 494) | (1 196 710) |
| Women % | 0.448 | 1.270 | 0.319 | 2.383 |
| Men % | 0.210 | 1.215 | 0.249 | 1.550 |
| 18–39 years | 0.626 | 0.791 | 0.174 | 1.070 |
| 40–59 years | 0.331 | 1.439 | 0.349 | 2.522 |
| 60–79 years | 0.094 | 1.392 | 0.349 | 2.376 |
| 80+ years | 0.077 | 1.723 | 0.284 | 2.366 |
| Mean age (SD) | 38.93 (15.05) | 56.08 (17.98) | 55.43 (16.92) | 56.27 (16.85) |
*1 Data from statutory health insurance funds; N = 59 561 310; mean age = 51.25 years (SD = 19.38); % female = 55.40; ICD-10 diagnoses included: F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F32.3/F33.3; no confidence intervals shown because sample represents whole population.
*2 The decrease in borderline personality disorder (BPD) prevalence with increasing age corresponds to the finding that affective (e.g., anxiety, depression, anger) and interpersonal characteristics (indicating abandonment and dependence) of BPD are most common and most stable. Impulsive symptoms (e.g., suicide attempts, self-injury), i.e., acute conditions requiring immediate intervention, are the least consistent and stable (e6). This could lead to low rates of recognition by the medical system in elderly patients.
Medical comorbidity
The greatest effects (etable 1) were found for relevant risk factors, external causes of morbidity/mortality (e.g., intentional self-harm, substance use disorders), and neurodegenerative diseases. While malignant neoplasms were particularly prevalent in severe unipolar depression, other disease groups (infectious/parasitic, endocrine/nutritional/metabolic, circulatory, and respiratory diseases) were substantially elevated in all SMIs, especially in BPD.
There were no substantial decreases in comorbidities or risk factors (OR <0.696), but a significant effect was found for psychotic disorders with regard to malignant neoplasms (OR = 0.90; eTable1).
Mortality and life years lost
In total, 288 503 patients from the 2012 sample died in 2013 or 2014. Across age and sex, BPD was associated with a 2.30-fold (95% CI [2.08; 2.54]) increase in mortality rate within this two-year period compared with patients without BPD. Two-year mortality rates for psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder, and severe unipolar depression were increased by factors of 2.38 (2.32; 2.44), 1.52 (1.42; 1.62), and 1.40 (1.37; 1.44), respectively (Table 2, eTable 2).
Table 2. Increased 2-year mortality rates in men and women with and without borderline personality disorder, psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder, and severe unipolar depression*1.
|
Borderline personality disorder |
Psychotic disorders |
Bipolar disorder |
Severe unipolar depression |
|||||
| OR*2 | (95% CI)*2 | OR | (95% CI)*2 | OR | (95% CI)*2 | OR | (95% CI)*2 | |
| Increased 2-year mortality rate (total) | 2.30*3 | (2.08; 2.54) | 2.38*3 | (2.32; 2.44) | 1.52*3 | (1.42; 1.62) | 1.40*3 | (1.37; 1.44) |
| Men | 2.40 | (1.93; 2.54) | 2.66 | (2.56; 2.76) | 1.59 | (1.44; 1.76) | 1.48 | (1.42; 1.54) |
| Women | 2.21 | (2.08; 2.77) | 2.24 | (2.17; 2.31) | 1.47 | (1.34; 1.60) | 1.33 | (1.33; 1.41) |
*1 Data from statutory health insurance funds; subsample (N = 15 590 107) with information on mortality (deaths in this subsample, 2013 to 2014: n = 288 503); ICD-10 diagnoses included: F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/F31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F32.3/F33.3
*2 Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals according to the Mantel–Haenszel method; adjusted for age group and gender; reference groups: respective diagnosis not present
*3 The stratum-specific OR varied significantly (Breslow–Day test; for details see eTable 2): 1.29 to 7.08 (borderline personality disorder), 0.98 to 11.22 (psychotic disorders), 0.68 to 6.13 (bipolar disorder), 1.04 to 4.48 (severe unipolar depression)
eTable 2. Increased 2-year mortality rates in men and women with and without borderline personality disorder, psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder and severe unipolar depression (administrative data of all statutory health insured adults in Germany, age ≥ 18 years*1, 2013 to 2014). Analysis stratified for sex and age.
|
Borderline personality disorder |
Psychotic disorders |
Bipolar disorder |
Severe unipolar depression |
||||||
| Age | OR*2 | 95% CI | OR*2 | 95% CI | OR*2 | 95% CI | OR*2 | 95% CI | |
| Increased 2-year mortality rate (total) | 2.30 | [2.08–2.54] | 2.38 | [2.32; 2.44] | 1.52 | [2.32; 2.44] | 1.40 | [1.37; 1.44] | |
| 18–24 years | 2.58 | [1.28; 5.18] | 11.29 | [7.77; 16.39] | 3.40 | [0.85; 13.65] | 3.84 | [2.17; 6.81] | |
| 25–34 years | 3.69 | [2.52; 5.40] | 8.08 | [6.57; 9.94] | 3.16 | [1.50; 6.64] | 3.08 | [2.23; 4.25] | |
| 35–44 years | 3.75 | [2.78; 5.05] | 4.21 | [3.59; 4.95] | 3.56 | [2.42; 5.25] | 2.26 | [1.86; 2.75] | |
| 45–54 years | 2.02 | [1.57; 2.59] | 3.30 | [3.02; 3.59] | 1.77 | [1.38; 2.26] | 1.70 | [1.54; 1.88] | |
| 55–59 years | 1.28 | [0.83; 1.96] | 2.84 | [2.58; 3.12] | 1.30 | [0.97; 1.73] | 1.12 | [1.00; 1.25] | |
| 60–64 years | 1.70 | [1.12; 2.57] | 2.42 | [2.21; 2.65] | 1.48 | [1.17; 1.89] | 1.12 | [1.01; 1.24] | |
| 65–69 years | 2.42 | [1.63; 3.58] | 2.67 | [2.45; 2.91] | 1.33 | [1.04; 1.69] | 1.30 | [1.18; 1.44] | |
| 70–74 years | 2.06 | [1.46; 2.89] | 2.59 | [2.43; 2.76] | 1.52 | [1.28; 1.80] | 1.41 | [1.32; 1.52] | |
| 75–79 years | 2.16 | [1.59; 2.94] | 2.54 | [2.40; 2.69] | 1.49 | [1.27; 1.74] | 1.36 | [1.28; 1.45] | |
| 80–84 years | 2.68 | [2.05; 3.50] | 2.13 | [2.01; 2.25] | 1.46 | [1.25; 1.72] | 1.30 | [1.23; 1.38] | |
| 85–89 years | 2.09 | [1.57; 2.77] | 1.89 | [1.79; 2.00] | 1.31 | [1.09; 1.56] | 1.26 | [1.19; 1.34] | |
| 90–94 years | 1.89 | [1.28; 2.77] | 1.64 | [1.53; 1.76] | 1.16 | [0.90; 1.49] | 1.19 | [1.09; 1.29] | |
| 95+ years | 0.97 | [0.38; 2.48] | 1.19 | [1.03; 1.38] | 0.92 | [0.53; 1.60] | 1.12 | [0.93; 1.33] | |
| Men | All | 2.40 | [1.93; 2.54] | 2.66 | [2.56; 2.76] | 1.59 | [1.44; 1.76] | 1.48 | [1.42; 1.54] |
| 18–24 years | 3.40 | [1.09; 10.60] | 11.22 | [7.23; 17.42] | 6.13 | [1.53; 24.66] | 4.48 | [2.12; 9.46] | |
| 25–34 years | 3.86 | [2.00; 7.45] | 7.58 | [5.94; 9.68] | 3.41 | [1.28; 9.11] | 2.60 | [1.58; 4.25] | |
| 35–44 years | 4.66 | [3.03; 7.17] | 4.17 | [3.42; 5.09] | 3.78 | [2.23; 6.41] | 2.47 | [1.87; 3.25] | |
| 45–54 years | 2.37 | [1.66; 3.37] | 3.19 | [2.85; 3.57] | 1.74 | [1.23; 2.47] | 1.92 | [1.67; 2.20] | |
| 55–59 years | 1.29 | [0.71; 2.34] | 2.68 | [2.35; 3.05] | 1.35 | [0.91; 1.99] | 1.26 | [1.08; 1.46] | |
| 60–64 years | 2.32 | [1.43; 3.77] | 2.35 | [2.07; 2.67] | 1.38 | [0.99; 1.94] | 1.15 | [1.00; 1.33] | |
| 65–69 years | 2.45 | [1.45; 4.13] | 2.53 | [2.23; 2.88] | 1.36 | [0.97; 1.92] | 1.26 | [1.08; 1.48] | |
| 70–74 years | 2.56 | [1.69; 3.87] | 2.84 | [2.58; 3.11] | 1.67 | [1.31; 2.12] | 1.60 | [1.43; 1.79] | |
| 75–79 years | 2.47 | [1.63; 3.74] | 2.86 | [2.61; 3.14] | 1.77 | [1.40; 2.23] | 1.58 | [1.42; 1.75] | |
| 80–84 years | 2.36 | [1.58; 3.53] | 2.38 | [2.15; 2.64] | 1.56 | [1.19; 2.04] | 1.54 | [1.39; 1.71] | |
| 85–89 years | 1.93 | [1.17; 3.19] | 2.07 | [1.81; 2.37] | 1.48 | [1.03; 2.12] | 1.31 | [1.15; 1.50] | |
| 90–94 years | 1.93 | [0.81; 4.58] | 2.07 | [1.66; 2.59] | 0.89 | [0.43; 1.82] | 1.44 | [1.16; 1.79] | |
| 95+ years | – | – | 0.98 | [0.57; 1.69] | 0.68 | [0.06; 7.55] | 1.04 | [0.54; 2.01] | |
| Women | All | 2.21 | [2.08; 2.77] | 2.24 | [2.17; 2.31] | 1.47 | [1.34; 1.60] | 1.33 | [1.33; 1.41] |
| 18–24 years | 3.14 | [1.29; 7.63] | 10.45 | [5.15; 21.20] | 1.00 | [1.00; 1.00] | 3.92 | [1.61; 9.52] | |
| 25–34 years | 5.08 | [3.17; 8.13] | 7.97 | [5.37; 11.84] | 3.45 | [1.11; 10.76] | 4.44 | [2.89; 6.81] | |
| 35–44 years | 3.86 | [2.55; 5.83] | 4.10 | [3.12; 5.38] | 3.74 | [2.11; 6.60] | 2.45 | [1.86; 3.23] | |
| 45–54 years | 2.15 | [1.52; 3.05] | 3.58 | [3.13; 4.10] | 2.07 | [1.47; 2.91] | 1.81 | [1.57; 2.09] | |
| 55–59 years | 1.46 | [0.78; 2.71] | 3.35 | [2.91; 3.86] | 1.41 | [0.92; 2.17] | 1.20 | [1.02; 1.41] | |
| 60–64 years | 1.09 | [0.49; 2.43] | 2.84 | [2.48; 3.24] | 1.80 | [1.28; 2.53] | 1.29 | [1.12; 1.50] | |
| 65–69 years | 2.51 | [1.37; 4.58] | 3.25 | [2.89; 3.64] | 1.46 | [1.04; 2.07] | 1.61 | [1.41; 1.83] | |
| 70–74 years | 1.42 | [0.75; 2.66] | 2.79 | [2.55; 3.05] | 1.58 | [1.25; 2.01] | 1.57 | [1.42; 1.73] | |
| 75–79 years | 1.89 | [1.19; 3.02] | 2.64 | [2.45; 2.84] | 1.41 | [1.13; 1.76] | 1.43 | [1.32; 1.55] | |
| 80–84 years | 2.90 | [2.00; 4.21] | 2.19 | [2.04; 2.35] | 1.49 | [1.22; 1.83] | 1.32 | [1.23; 1.42] | |
| 85–89 years | 2.14 | [1.49; 3.09] | 1.94 | [1.81; 2.06] | 1.29 | [1.05; 1.60] | 1.29 | [1.21; 1.39] | |
| 90–94 years | 1.87 | [1.16; 3.02] | 1.63 | [1.50; 1.77] | 1.23 | [0.93; 1.63] | 1.17 | [1.06; 1.28] | |
| 95+ years | 1.00 | [0.36 ; 2.76] | 1.23 | [1.05; 1.46] | 0.95 | [0.52; 1.76] | 1.14 | [0.93; 1.40] | |
| Breslow–Day test | Chi2(df 24) = 50.42; p = 0.001 | Chi2(df 25) = 642.52; p < 0.001 | Chi2(df 25)= 50.55; p = 0.002 | Chi2(df 25) = 185.52; p <0.001 | |||||
*1 Data from statutory health insurance funds; subsample (n = 15 590 107) with information on mortality (deaths in this subsample, 2013 to 2014: n = 288 503); ICD-10 diagnoses included: F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/F31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F32.3/F33.3
*2 Odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) according to the Mantel–Haenszel method; adjusted for age-group and sex; reference groups: respective diagnosis not present
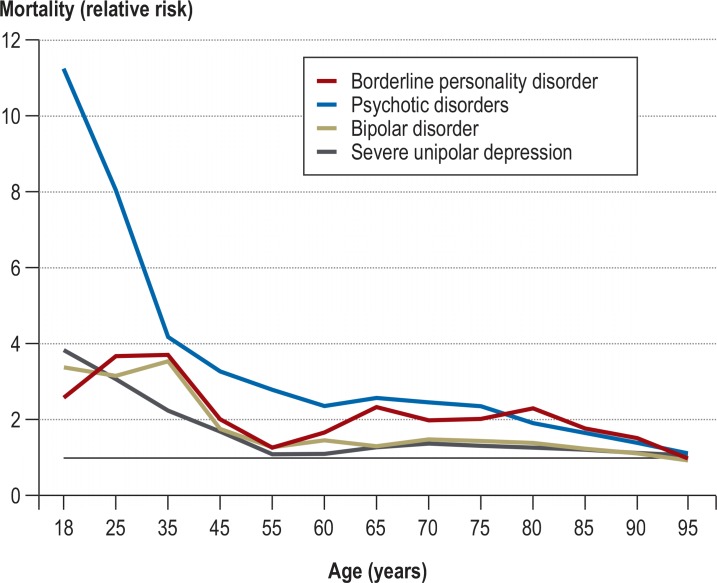
Figure 1 shows the relative risk of death over the whole life span between SMI patients and patients without the given SMI (ratio). The elevation in mortality among SMI patients was greatest at young age (particularly in psychotic disorders: 11-fold), where the annual risk of death is low (<0.1% in the general population). In old age (e.g., 85 years), where the general annual risk is high (around 16%), BPD, psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder, and severe unipolar depression still showed statistically significantly elevated mortality rates (RR = 1.78 (95% CI = 1.34; 2.36), 1.66 (1.57; 1.75), 1.25 (1.04; 1.49), 1.21 (1.14; 1.29); eFigure 1) (18).
Figure 1.
Mortality rates in patients with severe mental illness (SMI) compared with patients without the respective SMI (relative risk) over the whole adult life span. The elevated risk of death of SMI patients is particularly high at young age.
Data from statutory health insurance funds; subsample (n = 15 590 107) with information on mortality (deaths in this subsample, 2013 to 2014: n = 288 503); results based on a simple descriptive analysis relating age- and sex-specific mortality rates of patients without a specific SMI to those of patients with the respective SMI; ICD-10 diagnoses included: F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/F31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F32.3/F33.3
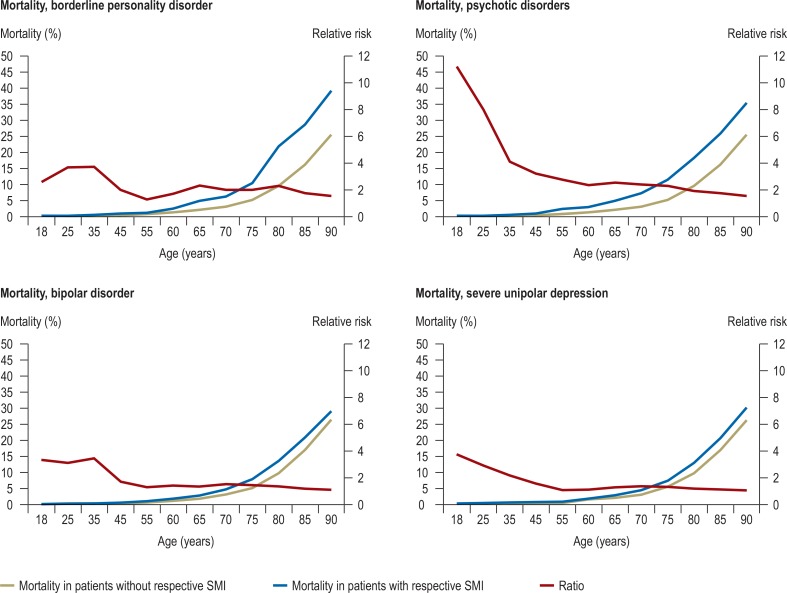
eFigure.
Age-dependent mortality in patients with SMI and in patients without the specific SMI, together with the relative risk (SMI vs. no SMI) over the whole adult life span. Data from statutory health insurance funds; subsample (n = 15 590 107) with information on mortality (deaths in this subsample, 2013 to 2014: n = 288 503). The results are based on a descriptive analysis: age- and gender-specific mortality rates of patients with SMI (ICD-10 diagnoses: F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/F31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F32.3/F33.3) to patients without the respective SMI
SMI = severe mental illness
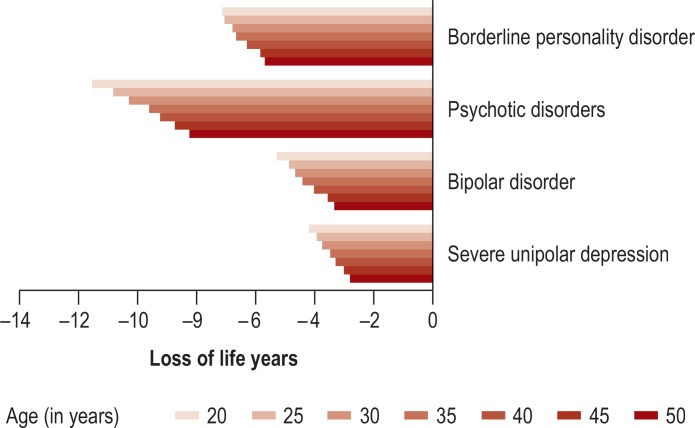
The estimated loss of life years for SMI patients was greatest in psychotic disorders (ranging from 8.2 years [age 50] to 11.5 years [age 20]), followed by BPD (5.7 years [age 50] to 7.1 years [age 20]); higher in younger than in older patients; and more pronounced in men than in women (Figure 2, eTable 3).
Figure 2.
Estimated loss of life years by age for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) compared with total population.
Data from statutory health insurance funds; subsample (n = 15 590 107) with information on mortality (deaths in this subsample, 2013 to 2014: n = 288 503); ICD-10 diagnoses included: F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/F31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F32.3/F33.3
eTable 3. Estimated loss of life years by age in SMI patients compared with the total population (administrative data of all statutory health insured adults in Germany, age ≥ 18 years*1, 2013 to 2014).
|
Borderline personality disorder |
Psychotic disorders |
Bipolar disorder |
Severe unipolar depression |
|||||||||
| Age | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | Total |
| 20 years | −9.3 | −6.6 | −7.1 | −12.3 | −10.6 | −11.5 | −6.1 | −4.7 | −5.3 | −4.8 | −3.8 | −4.2 |
| 25 years | −9.1 | −6.5 | −7.1 | −11.3 | −10.1 | −10.8 | −5.5 | −4.4 | −4.9 | −4.4 | −3.7 | −3.9 |
| 30 years | −8.7 | −6.2 | −6.8 | −10.7 | −9.8 | −10.3 | −5.2 | −4.3 | −4.7 | −4.2 | −3.5 | −3.7 |
| 35 years | −8.4 | −5.9 | −6.7 | −9.9 | −9.3 | −9.6 | −4.9 | −4.1 | −4.4 | −4.0 | −3.2 | −3.5 |
| 40 years | −7.9 | −5.6 | −6.3 | −9.4 | −9.0 | −9.2 | −4.4 | −3.8 | −4.0 | −3.7 | −3.0 | −3.3 |
| 45 years | −7.1 | −5.2 | −5.8 | −8.9 | −8.6 | −8.7 | −3.8 | −3.4 | −3.5 | −3.4 | −2.8 | −3.0 |
| 50 years | −6.8 | −5.0 | −5.7 | −8.3 | −8.2 | −8.2 | −3.6 | −3.2 | −3.3 | −3.1 | −2.6 | −2.8 |
*1 Data from statutory health insurance funds; subsample (n = 15 590 107) with information on mortality (deaths in this subsample, 2013 to 2014: n = 288 503); ICD-10 diagnoses included:
F60.3x, F2x, F30.x/F31.x, F32.2/F33.2/F32.3/F33.3; SMI = severe mental illness
Discussion
The present study focused on excess mortality and medical comorbidity in people with severe mental illness (SMI), a highly relevant topic with regard to sociopolitical equity and health care participation (19). Analyses of SMI comorbidity revealed many clinically significant associations contributing to excess mortality due to natural causes.
Besides HIV and hepatitis, elevated medical comorbidities included obesity, diabetes, cardiac and cerebrovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pneumonia, and some cancers. Furthermore, the risk of death was markedly elevated in SMI—including BPD—and associated with a substantial loss of life years.
Although the risk of suicide is highly elevated in SMI patients, the excess mortality can mainly be attributed to somatic causes. According to official statistics for the period 2013 to 2014, in Germany around 1.2% of all deaths are documented as suicides (18).
Based on the assumption from previous findings that up to 90% of completed suicides are associated with mental disorders in general (5, 20, 21), we estimated that the SMIs included in our study (which are more severe but less prevalent) accounted for 70% ofcompleted suicides. Thus, our data suggest that 24% of SMI excess mortality per year can be attributed to suicide and 76% to somatic causes (i.e., medical morbidity) or other, unnatural causes (eMethods). In part our findings replicate long-standing data on poor medical health in people with SMI (1– 5), and our results suggest good external validity of the data.
Nonetheless, compared with recent reviews, excess mortality seems relatively low, although within the range of most studies. One reason might be that the German social and healthcare systems offer relatively good free general access to mental and medical care. Furthermore, our prevalence estimates are conservative, since SMI patients with zero contact to the health care system are not represented.
The statutory health insurance database is unique in covering the majority of SMI patients in Germany. The proportion of SMI can be assumed to be lower in the privately insured population than in those with statutory insurance (22). Moreover, routine data are not affected by selection bias with regard to recruitment or participants’ willingness to participate in a study.
Nevertheless, routine records and thus administrative prevalences are usually less valid than datasets based on standardized diagnostic procedures (23, e3). The inclusion of only severely ill patients in the current study contributes to higher validity of the diagnoses. As a consequence, however, the findings may not be generalizable to less severe disease courses. Furthermore, we must assume that the true SMI prevalence is higher than reported here due to patient- and healthcare system-related factors such as underutilization, nonrecognition, undertreatment, stigmatization, and inadequate mental health services in certain regions (24).
Our prevalence rates of bipolar disorder are lower than reported in previous clinical or epidemiological field studies (e.g., 0.8% for any bipolar disorder [23]). This may reflect flawed sensitivity (unrecognized cases) and specificity (e.g., diagnosis of unipolar depression or schizoaffective disorder diagnosis instead of bipolar disorder) in routine care, as well as the episodic nature of (hypo-)manic symptoms (i.e., many lifelong illnesses are not coded in every 12-month period). However, we do not believe that the low prevalence rates affect the reported associations between bipolar disorders and medical comorbidities or mortality.
Potential flaws in SMI diagnostics may impair the validity of associations of SMI with medical comorbidity and mortality: Underdiagnosis, for example, leads to underestimation of association effects in patients who make use of healthcare services. However, in patients who do not use these services, underdiagnosis contributes to neither overestimation nor underestimation of associations. Counterintuitive findings such as lower medical comorbidity (e.g., disorders of lipoprotein metabolism, cardiac arrhythmia) in psychotic disorders than in other SMIs, despite the fact that this group has the highest mortality rates, may be due to underrecognition and undertreatment (25, e3). Assuming that this bias applies to SMI patients in general, medical comorbidity—but not mortality—may be under-estimated.
It is conventional to define SMI on the basis of specific coded diagnoses (26) but one should not neglect the fact that other mental disorders can also be associated with severe distress, role impairment, and disability.
Considering the lack of direct measures of severity (e.g., a score ≤ 50 on the Global Assessment of Functioning scale [27]), we believe that our diagnosis-based approach (including the addition of BPD to conventional SMIs) is the most feasible way to address medical comorbidity and mortality in patients with SMI.
The dataset does not include information on:
Privately insured or self-funding patients
(Pre-/semi-) inpatient care
Psychiatric hospital/university outpatient services
Medical/occupational rehabilitation
Remedies and appliances
Socioeconomic variables and family background.
Since SMIs are very probably less prevalent in privately insured patients (no statistics available), the findings of the present study are representative only for patients with statutory health insurance (22).
Patients who (within a given year) visit only psychiatric hospital outpatient services before or after hospitalization and patients with exclusively long hospitalizations are not coded in the present billing data. However, it can be assumed that these patients also have at least one contact per year with other psychiatric/general healthcare facilities and thus were not lost in our dataset.
Outlook and implications for care
Medical comorbidity and mortality in the mentally ill are increased by an accumulation of health risks caused, for instance, by socioeconomic problems (e.g., unemployment, poverty, social isolation, imprisonment, homelessness) and associated lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, alcohol/drug use, poor nutrition, obesity, physical inactivity, unprotected sex, psychological trauma). At the same time, people with chronic mental disorders are on the margins of normal medical care: they use health services only to a limited extent, and there are indications of poor compliance by this group of patients (3, 40).
Focusing on mental health problems often prevents care providers from dealing constructively with the medical illness. Furthermore, for various reasons the principles of inclusion and equity are not guaranteed for this patient group in the medical sector (28).
Other factors related to the communication between doctor and patient may also be relevant. Physicians frequently attribute a patient’s symptoms to his or her mental disorder when they are actually related to a general medical condition. Alternatively, physicians may ignore physical health in the presence of prominent psychiatric symptoms (‘diagnostic overshadowing’) (29, e4). Here, models of collaborative care show promising effects (30– 32). Many risk factors for “natural causes of death” (e.g., obesity) can be influenced (6, 33– 35, e5), which emphasizes the need for further investigation of interventions to reduce mortality in SMI. In this context, effective treatment strategies for patients with comorbid substance use disorders might be crucial, as increased mortality is likely to be caused to a considerable extent by related physical illness (4).
Furthermore, although psychotropic drugs significantly reduce mortality overall, they can have adverse effects that promote the occurrence of medical comorbidities (36, 37). Examples are (38, e2):
Diabetes and subsequent metabolic syndrome
Increased cardiovascular mortality caused by pronounced weight gain as an adverse effect of many atypical antipsychotics
Increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality caused by many psychotropic drugs with anticholinergic effects, such as antidepressants and antipsychotics
Severe arrhythmias caused by pharmacologically induced QT prolongation
Thus, the pharmacological management of medical illness has to be specifically tailored to SMI patients.
In conclusion, the need for health-promoting interventions is beyond question and should be reflected in all treatment guidelines regarding SMI (39).
Supplementary Material
eMethods
Methods
Datasets and study types
The database consists of billing data (§ 295 German Social Code V) from all adults with statutory health insurance who had contact with general or specialist physician or psychotherapist services accredited to invoice the German regional associations of statutory health insurance physicians (ASHIP) (e7).
In the German healthcare system the ASHIP are responsible for the organization of the out-of-hospital (ambulatory) health services as well as for the settlement and billing of the ambulatory physicians and therapists treating patients who have statutory health insurance. Hence each ASHIP constitutes a formal organization of the ambulatory physicians and psychotherapists in the region concerned. Patients with no contact to the health system are not included in the analyses.
Medical records of the same patient’s contacts with different physicians were linked based on the patient’s surname, forename, and date of birth. Data include patient-related information (age, gender, place of residence, diagnoses, insurance status, services used) as well as information on the care provider (physician, practice, specialist field, main services).
The 12-month prevalence and medical comorbidity data for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) were examined in cross-section using the most recent available billing data (2016; age ≥ 18 years; N = 59 561 310). In 2016, approximately 89% of the German population (all ages) had statutory health insurance, while the rest were predominantly covered by private health insurance (10.5%). Among the statutorily insured, approximately 90% had at least one visit to an ambulatory physician within 12 months. The ambulatory claims data cover approximately 97% of all medical treatments of statutorily insured adults (e8).
For reasons of data protection, the aforementioned dataset of the total population does not contain all information coded in the course of routine clinical care. The sample is made up of representative subsets with comprehensive information (patients born on two particular days of the week) enhanced with data of insured patients born on the same days who had no physician contact (data from statutory health insurance funds). This dataset is used by the Institut des Bewertungsausschusses (the body which defines the conditions for reimbursement of ASHIP physicians) for the administrative purpose of estimating changes in the annual average health utilization and mortality (e9). Using the most recent available data from these subsets, 2-year mortality was calculated longitudinally for the years 2013 to 2014 for patients with and without a specific SMI diagnosis in 2012 (2012: n = 15 590 107).
Diagnostic assessment
Psychiatric diagnoses were operationalized via routine diagnoses (coded according to ICD-10) assigned by medical service providers to the (same) patient. Based on previous research (e10) and relevance for healthcare (e2), we included borderline personality disorder (BPD; F60.3x), psychotic disorders (schizophrenia, schizotypal, and delusional disorders, F2x), bipolar affective disorder (F31.x, including manic episodes, F30.x), and severe unipolar depression (F32.2/33.2, F32.3/F33.3).
For the sake of clear argumentation and to avoid overlap between identified SMI diagnoses, the following hierarchy rules were applied:
Based on clinical and theoretical considerations, a selected range of ICD-10 general medical conditions were specified and included in comorbidity analyses (see eTable 1):
Ethical standards
The local ethics committee of the Faculty of Medicine, RWTH Aachen University, raised no ethical or professional objections to the research project.
Statistical analyses
We present the 12-month administrative prevalences of selected SMIs for the year 2016 (for patients with at least one visit to a physician). Odds ratios (OR) for medical conditions and risk factors (adjusted for age group [18–24, 25–34, 35–44, 45–54, 55–59, 60–64, 65–69, 70–74, 75–79, 80–84, 85–89, 90–94, 95+] and sex, inclusive interaction) were calculated with multiple logistic regression and separated for six subgroups (three age groups [18–39, 40–64, 65+] × sex).
In order to evaluate whether significant OR were also substantial with regard to effect size, we chose the established cut-offs first described by Chinn (15) with OR > 1.436 or OR < 0.696. These cut-offs describe significant OR of at least small effect size. Base rates of all medical diagnoses are additionally provided to facilitate interpretation of the OR.
Mortality rates for 2013 to 2014 were calculated as raw percentages for patients with and without a specific diagnosis of SMI in 2012. OR were calculated according to the Mantel–Haenszel method (OR-MH) to account for varying OR across age and sex groups (e11).
The strata for the OR-MH were defined by age groups 18–24 years, 25–34, 35–44, 45–54, 55–59, 60–64, 65–69, 70–74, 75–79, 80–84, 85–89, 90–94, 95+ and sex. They indicate increased mortality of patients with a specific SMI compared to patients without the SMI. Due to the low prevalence of mortality rates, OR resemble relative risks (RR).
The age-related risk of death in SMI compared with the total population was calculated as the raw percentage of deaths in the respective population. Since the follow-up time series for the mortality data were relatively short (2013 to 2014), we did not examine any medical comorbidities as mediators of mortality or survival time.
Loss of life years was estimated using statistical life tables for the general German population in 2014 (see below, “Estimation of loss of life years”) (e9). Age- and sex-specific death rates in the life tables were adjusted to represent the particularly high rates of the four SMIs from the aforementioned calculation of the risks of death. Age- and sex-specific life expectancies were then calculated from the adjusted sum of further life years divided by the number of survivors for every age cohort. The differences in life expectancies between the total population and a particular SMI population were taken as proxy for lost life years.
Estimation of loss of life years
If
q(x) = probability of dying between ages x and x+1
l(x) = number surviving to age x
d(x) = number dying between ages x to x+1
L(x) = person-years lived between ages x to x+1
T(x) = total number of person-years lived above age x
e(x) = expected life years at age x
delta(x) = difference between d(x) and [l(x) – L(x)]
then
(1) l(x+1) = l(x)–d(x)
(2) d(x) = q(x) * 100
(3) L(x) = [l(x) + l(x+1)]/2
(4) 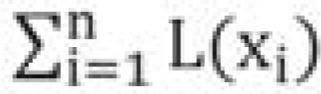
(5) e(x) = T(x)/l(x)
For equations (1) and (2), q(x) was adjusted by multiplying by q(x) in the given age and sex group with SMI divided by q(x) in the same age and sex group of the general population. Equations (3) to (5) were then recalculated. The difference between e(x) of the general population and e(x) for the respective SMI was taken as the estimator of life years lost. Thus for a particular age and sex the expectation of life years was estimated for the general population and for the SMI of interest. The difference was taken as life years lost due to the SMI of interest.
Suicide rate estimation
In the observation period, there were approximately 1.75 million deaths and approximately 21 000 suicides in Germany (Federal Health Monitoring [e15, e16]). The suicide rate among all deaths in the general population is therefore approximately 1.2%.
Based on the assumption from previous findings (5, 20, 21), that up to 90% of completed suicides are associated with some form of mental illness, we estimate that the proportion of SMI (more severe, but less widespread) among all suicides is 70% (e12– e14). Therefore, an estimated 14,700 of the suicides in Germany were SMI cases.
The SMI prevalence in Germany amounts to 3.9%. In the observation period, the mortality rate was 1.9 times higher. We estimate that 130 000 deaths were SMI cases, 61 500 of them due to excess mortality.
A total of 14 700 suicides among 61 500 deaths due to excess mortality corresponds to 24%. In other words, 76% of excess mortality cannot be explained by suicide. The estimate refers only to the absolute number of deaths, not to the years of life lost (which are higher for deaths at younger ages). Furthermore, other unnatural causes of death such as accidents are not considered.
If an F2x diagnosis was present, it was defined as the main diagnosis.
If both F30/F31 and F32/F33 had been coded (possibly by different treating physicians) in one patient, bipolar affective disorder was selected as the diagnosis.
If both F60.3 and F32/F33 had been diagnosed, BPD was defined as the diagnosis under study.
If both F60.3 and F30/F31 had been diagnosed: (1) If only one of the two diagnoses had been assigned by a specialist, this diagnosis was used in the analysis. 2) If no differentiation was possible in step 1, cases were assigned to both BPD and bipolar affective disorder and thus contributed to both cohorts (total 5700 cases).
Severe unipolar depression (F32.2/33.2, F32.3/F33.3) was taken as the diagnosis if no additional other SMI had been coded.
Viral hepatitis/HIV (B15–B24)
Malignant neoplasms (C00–C97)
Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases (E00–E90)
Diseases of the circulatory system (I00–I90)
Diseases of the respiratory system (J00–J99)
Relevant risk factors of mortality (mental and behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance use [F1x])
Organic mental disorders/Alzheimer disease/other degenerative diseases of the nervous system (F0/G30–G31)
Injury, poisoning, and other consequences of external factors (S00–T98)
External causes of morbidity and mortality (V01–Y98)
The Clinical Perspective.
In Germany, people with severe mental illness (SMI), compared with the general population, suffer more frequently from numerous medical comorbidities and show a greatly increased risk of death. Approximately 75% of the excess mortality is due to natural causes resulting from physical diseases. The following medical comorbidities must receive special attention in psychiatric healthcare: cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, metabolic-endocrine disease (particularly diabetes mellitus type 2), infections, and selected oncological diseases.
According to scientific research (40), the risk factors for medical diseases in SMI patients are essentially lifestyle-related (e.g., smoking, overweight, lack of exercise). Comorbid substance-related disorders must also be taken into account. Studies from industrialized countries suggest that healthcare system-related factors contribute significantly to excess mortality in SMI patients.
On average, people with SMI receive less qualified medical care than the general population. In order to improve medical health in SMI patients, close integration of psychiatric/psychotherapeutic and general healthcare must be pursued. In the individual treatment setting, behavioral characteristics of psychiatric disease (e.g., anhedonia, emotional instability) have to be considered, as they can have a considerable impact on the diagnostic and therapeutic management of medical disorders.
To avoid excess mortality, close attention should be paid to the known, readily detectable cardiovascular diseases, e.g., overweight, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. The adverse effect profiles of psychopharmaceuticals (including interactions with other medications) may influence the indications and thus require special consideration, if necessary in consultation with an experienced psychiatrist. For patients who do not take sufficient advantage of the healthcare services available to them, attempts should be made to mobilize appropriate support (intensified medical guidance).
Key Messages.
In Germany, the 12-month administrative prevalence is highest for severe unipolar depression (2.01%), followed by psychotic disorders (1.25%), borderline personality disorder (0.34%), and bipolar disorder (0.29%).
Two-year mortality rates are markedly increased in all groups of patients with SMI, particularly among the young.
The loss of life years ranges from 2.6 years (female patients with severe unipolar depression at age 50) to 12.3 years (male patients with psychotic disorders at age 20) and is higher in men than in women.
Besides human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis, medical comorbidities found more frequently in patients with SMI include obesity, diabetes, cardiac and cerebrovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pneumonia, and some cancers.
Although the risk of suicide is highly elevated in SMI patients, we estimate that around three fourths of excess mortality is attributable to natural causes of death.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments
We thank Jessica Junger, PhD and Mandy Schulz, PhD for assistance and Dominik Graf von Stillfried, PhD and Frank Bergmann, MD for support. Furthermore, we are very grateful to Michael Deuschle, MD, Hans Grabe, MD, Ralf-Dieter Hilgers, PhD, and Steffi Riedel-Heller, MD for their comments on earlier drafts.
Funding
The work of Frank Jacobi on the present study was supported by the German Association for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics (DGPPN).
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
References
- 1.Wahlbeck K, Westman J, Nordentoft M, Gissler M, Laursen TM. Outcomes of nordic mental health systems: life expectancy of patients with mental disorders. Br J Psychiatry. 2011;199:453–458. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.110.085100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ösby U, Westman J, Hällgren J, Gissler M. Mortality trends in cardiovascular causes in schizophrenia, bipolar and unipolar mood disorder in Sweden 1987 - 2010. Eur J Public Health. 2016;26:867–871. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckv245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.De Hert M, Correll CU, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. I. Prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry. 2011;10:52–77. doi: 10.1002/j.2051-5545.2011.tb00014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hjorthøj C, Østergaard MLD, Benros ME, et al. Association between alcohol and substance use disorders and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and unipolar depression: A nationwide, prospective, register-based study. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2015;2:801–808. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Walker ER, McGee RE, Druss BG. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA psychiatry. 2015;72:334–341. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.2502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Parks J, Svendsen D, Singer P, Foti ME, Mauer B. Morbidity and mortality in people with serious mental illness Alexandria, VA (USA); 2006. www.namiut.org/images/stories/october_2006_morbidity_and_mortality_pub.pdf (last accessed on 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lutterman T, Ganju V, Schacht L, Shaw R, Monihan K, Huddle M. Sixteen state study on mental health performance measures DHHS Publication No. (SMA) 03-3835. Rockville, MD. Center for Mental Health Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2003 [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gühne U, Becker T, Salize HJ, Riedel-Heller SG. How many people in Germany are seriously mentally ill? Psychiatr Prax. 2015;42:415–423. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1552715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.World Health Organization. Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization 2017. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/254610/1/WHO-MSD-MER-2017.2-eng.pdf (last accessed on 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wittchen HU, Jacobi F, Rehm J, et al. The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011;21:655–679. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Statistisches Bundesamt (Destatis) Todesursachen [death causes] https://www.destatis.de/DE/ZahlenFakten/GesellschaftStaat/Gesundheit/Todesursachen/Todesursachen.html (last accessed on 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taylor Wessing. Global intellectual property index: 5th report. 2016. https://united-kingdom.taylorwessing.com/documents/get/576/gipi5-report.pdf/show_on_screen (last accessed on 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- 13.Erhart M. Swart E, Ihle P, Gothe H, Matusiewicz D, editors. KV-Daten-Stichprobe des Zentralinstituts für die kassenärztliche Versorgung Handbuch Routinedaten. Bern: Huber; 2014:279–282. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Canadian Mental Health Association. The relationship between mental health, mental illness and chronic physical conditions. 2008. https://ontario.cmha.ca/documents/the-relationship-between-mental-health-mental-illness-and-chronic-physical-conditions/ (last accessed 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chinn S. A simple method for converting an odds ratio to effect size for use in meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2000;19:3127–3131. doi: 10.1002/1097-0258(20001130)19:22<3127::aid-sim784>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 19592;2(47):19–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Statistisches Bundesamt. Sterbetafel (Periodensterbetafel): Deutschland, 2014 [Mortality table (periodical mortality table): 2014] https://www-genesis.destatis.de/genesis/online/logon?sequenz=tabelleErgebnis&selectionname=12621-0001&sachmerkmal=GES&sachschluessel=GESM/-GESW (last accessed 12 December 2017) [Google Scholar]
- 18.Das Informationssystem der Gesundheitsberichterstattung des Bundes. [The information system of the federal health monitoring] http://www.gbe-bund.de (last accessed 23 November 2018) doi: 10.1007/s00103-004-0832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rosenbaum L. Closing the mortality gap - mental illness and medical care. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1585–1589. doi: 10.1056/NEJMms1610125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Arsenault-Lapierre G, Kim C, Turecki G. Psychiatric diagnoses in 3275 suicides. A meta-analysis BMC Psychiatry. 2004;4:1–11. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-4-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jayatilleke N, Hayes RD, Dutta R, et al. Contributions of specific causes of death to lost life expectancy in severe mental illness. Eur Psychiatry. 2017;43:109–115. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.02.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rattay P, Butschalowsky H, Rommel A, et al. Utilisation of outpatient and inpatient health services in Germany: results of the German health interview and examination survey for adults (DEGS1) Bundesgesundheitsblatt - Gesundheitsforsch - Gesundheitsschutz. 2013;56:832–844. doi: 10.1007/s00103-013-1665-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jacobi F, Höfler M, Siegert J, et al. Twelve-month prevalence, comorbidity and correlates of mental disorders in Germany: the mental health module of the German health interview and examination survey for adults (DEGS1-MH) Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2014;23:304–319. doi: 10.1002/mpr.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Melchior H, Schulz H, Härter M. Faktencheck Gesundheit-Regionale Unterschiede in der Diagnostik und Behandlung von Depressionen [Facts check health-regional differences in the diagnosis and treatment of depression] Gütersloh: Bertelsmann Stiftung. 2014 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Laursen TM, Munk-Olsen T, Agerbo E, Gasse C, Mortensen PB. Somatic hospital contacts, invasive cardiac procedures, and mortality from heart disease in patients with severe mental disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(7):713–720. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kessler RC, Aguilar-gaxiola S, Alonso J, et al. The global burden of mental disorders: an update from the WHO World Mental Health (WMH) Surveys. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2009;18:23–33. doi: 10.1017/s1121189x00001421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ruggeri M, Leese M, Thornicroft G, Bisoffi G, Tansella M. Definition and prevalence of severe and persistent mental illness. Br J Psychiatry. 20001;77(21):49–55. doi: 10.1192/bjp.177.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.De Hert M, Cohen D, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. II. Barriers to care, monitoring and treatment guidelines, plus recommendations at the system and individual level. World Psychiatry. 2011;10:138–151. doi: 10.1002/j.2051-5545.2011.tb00036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jones S, Howard L, Thornicroft G. ‚Diagnostic overshadowing‘: worse physical health care for people with mental illness. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2008;118:169–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2008.01211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chwastiak L, Vanderlip E, Katon W. Treating complexity: collaborative care for multiple chronic conditions. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2014;26:638–647. doi: 10.3109/09540261.2014.969689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Druss BG, Zhap L, Von Esenwein SA, et al. The health and recovery peer (HARP) program: a peer-led intervention to improve medical self-management for persons with serious mental illness. Schizophr Res. 2011;118:264–270. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.01.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Reilly S, Planner C, Gask L, et al. Collaborative care approaches for people with severe mental illness. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;11 doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009531.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Caneo C. Managing cardiovascular disease risk in patients with severe mental illness. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5:97–98. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gierisch JM, Nieuwsma JA, Bradford DW, et al. Pharmacologic and behavioral interventions to improve cardiovascular risk factors in adults with serious mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75:e424–e440. doi: 10.4088/JCP.13r08558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McGinty EE, Baller J, Azrin ST, Juliano-Bult D, Daumit GL. Interventions to address medical conditions and health-risk behaviors among persons with serious mental illness: A comprehensive review. Schizophr Bull. 20164;2(19):6–124. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbv101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tiihonen J, Lönnqvist J, Wahlbeck K, et al. 11-year follow-up of mortality in patients with schizophrenia: a population-based cohort study (FIN11 study) Lancet. 2009;374:620–627. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60742-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Torniainen M, Mittendorfer-Rutz E, Tanskanen A, et al. Antipsychotic treatment and mortality in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2015;41:656–663. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbu164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Correll CU, Detraux J, De Lepeleire J, De Hert M. Effects of antipsychotics, antidepressants and mood stabilizers on risk for physical diseases in people with schizophrenia, depression and bipolar disorder. World Psych. 2015;14:119–136. doi: 10.1002/wps.20204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Deutsche Gesellschaft für Psychiatrie, Psychotherapie und Nervenheilkunde (2013) S3-Leitlinie Psychosoziale Therapien bei schweren psychischen Erkrankungen [S3 guideline psychosocial therapies for severe mental illnesses]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. https://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/038-020l_S3_Psychosoziale_Therapien_10-2012.pdf (last accessed 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- 40.World Health Organization. Guidelines for the management of physical health conditions in adults with severe mental disorders. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/275718/9789241550383-eng.pdf?ua=1 and https://www.who.int/mental_health/evidence/evidence_profiles_severe_mental_disorders.pdf?ua=1 (last accessed on 4 January 2019) [Google Scholar]
- E1.Lederbogen F, Schwarz P, Häfner S, Schweiger U, Bohus M, Deuschle M. Cardiac and metabolic risk factors in severe mental illness: task of a prevention manager. Nervenarzt. 2015;86:866–871. doi: 10.1007/s00115-014-4232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E2.Hewer W, Schneider F. Somatic morbidity in psychiatric patients. Nervenarzt. 2016;87:787–801. doi: 10.1007/s00115-016-0146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E3.Crump C, Winkleby MA, Sundquist K, Sundquist J. Comorbidities and mortality in persons with schizophrenia: a Swedish national cohort study. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170:324–333. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12050599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E4.Shefer G, Henderson C, Howard LM, Murray J, Thornicroft G. Diagnostic overshadowing and other challenges involved in the diagnostic process of patients with mental illness who present in emergency departments with physical symptoms - a qualitative study. PLoS One. 2014;9 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111682. e111682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E5.Daumit GL, Dickerson FB, Wang NY, et al. A behavioral weight-loss intervention in persons with serious mental illness. Int J Obes. 2013;368:1594–1602. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E6.Zanarini MC, Frankenbur FR. The essential nature of Borderline psychopathology. J Pers Disord. 2007;21:518–535. doi: 10.1521/pedi.2007.21.5.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E7.Erhart M. Swart E, Ihle P, Gothe H, Matusiewicz D, editors. KV-Daten-Stichprobe des Zentralinstituts für die kassenärztliche Versorgung Handbuch Routinedaten (2nd edition) Bern: Huber. 2014:279–282. [Google Scholar]
- E8.Von Stillfried D, Czihal T, Erhart M. Rolle der Krankenhäuser in der Notfallversorgung in Deutschland: Daten belegen massiven Reformbedarf [Role of hospitals in emergency care in Germany: data show massive need for reform]. Zi-Paper 2017. https://www.zi.de/fileadmin/images/content/Publikationen/Zi-Paper_11-2017_Notfallversorgung.pdf. (last accessed 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- E9.Statistisches Bundesamt. Sterbetafel (Periodensterbetafel): Deutschland, 2014 [Mortality table (periodical mortality table): 2014] https://www-genesis.destatis.de/genesis/online/logon?sequenz=tabelleErgebnis&selectionname=12621-0001&sachmerkmal=GES&sachschluessel=GESM/-GESW (last accessed 12 December 2017) [Google Scholar]
- E10.Canadian Mental Health Association. The relationship between mental health, mental illness and chronic physical conditions. 2008. https://ontario.cmha.ca/documents/the-relationship-between-mental-health-mental-illness-and-chronic-physical-conditions/ (last accessed 23 November 2018) [Google Scholar]
- E11.Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959;22:719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E12.Arsenault-Lapierre G, Kim C, Turecki G. Psychiatric diagnoses in 3275 suicides: a meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2004;4:1–11. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-4-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E13.Walker ER, McGee RE, Druss BG. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72:334–341. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.2502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E14.Jayatilleke N, Hayes RD, Dutta R, et al. Contributions of specific causes of death to lost life expectancy in severe mental illness. Eur Psychiatry. 2017;43:109–115. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.02.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E15.Gesundheitsberichterstattung des Bundes. Gesundheit in Deutschland, 2015; Suizid. www.gbe-bund.de/gbe10/abrechnung.prc_abr_test_logon?p_aid=40796124&p_uid=gast&p_sprache=D&p_knoten=FID&p_suchstring=25403#fid24248 (last accessed on 13 May 2019) [Google Scholar]
- E16.Gesundheitsberichterstattung des Bundes. Sterbefälle, Sterbeziffern je 100000 Einwohner (altersstandardisiert) (ab 1980); www.gbe-bund.de/oowa921-install/servlet/oowa/aw92/dboowasys921.xwdevkit/xwd_init?gbe.isgbetol/xs_start_neu/&p_aid=i&p_aid=73506397&nummer=8&p_sprache=D&p_indsp=-&p_aid=47774495 (last accessed on 13 May 2019) [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eMethods
Methods
Datasets and study types
The database consists of billing data (§ 295 German Social Code V) from all adults with statutory health insurance who had contact with general or specialist physician or psychotherapist services accredited to invoice the German regional associations of statutory health insurance physicians (ASHIP) (e7).
In the German healthcare system the ASHIP are responsible for the organization of the out-of-hospital (ambulatory) health services as well as for the settlement and billing of the ambulatory physicians and therapists treating patients who have statutory health insurance. Hence each ASHIP constitutes a formal organization of the ambulatory physicians and psychotherapists in the region concerned. Patients with no contact to the health system are not included in the analyses.
Medical records of the same patient’s contacts with different physicians were linked based on the patient’s surname, forename, and date of birth. Data include patient-related information (age, gender, place of residence, diagnoses, insurance status, services used) as well as information on the care provider (physician, practice, specialist field, main services).
The 12-month prevalence and medical comorbidity data for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) were examined in cross-section using the most recent available billing data (2016; age ≥ 18 years; N = 59 561 310). In 2016, approximately 89% of the German population (all ages) had statutory health insurance, while the rest were predominantly covered by private health insurance (10.5%). Among the statutorily insured, approximately 90% had at least one visit to an ambulatory physician within 12 months. The ambulatory claims data cover approximately 97% of all medical treatments of statutorily insured adults (e8).
For reasons of data protection, the aforementioned dataset of the total population does not contain all information coded in the course of routine clinical care. The sample is made up of representative subsets with comprehensive information (patients born on two particular days of the week) enhanced with data of insured patients born on the same days who had no physician contact (data from statutory health insurance funds). This dataset is used by the Institut des Bewertungsausschusses (the body which defines the conditions for reimbursement of ASHIP physicians) for the administrative purpose of estimating changes in the annual average health utilization and mortality (e9). Using the most recent available data from these subsets, 2-year mortality was calculated longitudinally for the years 2013 to 2014 for patients with and without a specific SMI diagnosis in 2012 (2012: n = 15 590 107).
Diagnostic assessment
Psychiatric diagnoses were operationalized via routine diagnoses (coded according to ICD-10) assigned by medical service providers to the (same) patient. Based on previous research (e10) and relevance for healthcare (e2), we included borderline personality disorder (BPD; F60.3x), psychotic disorders (schizophrenia, schizotypal, and delusional disorders, F2x), bipolar affective disorder (F31.x, including manic episodes, F30.x), and severe unipolar depression (F32.2/33.2, F32.3/F33.3).
For the sake of clear argumentation and to avoid overlap between identified SMI diagnoses, the following hierarchy rules were applied:
Based on clinical and theoretical considerations, a selected range of ICD-10 general medical conditions were specified and included in comorbidity analyses (see eTable 1):
Ethical standards
The local ethics committee of the Faculty of Medicine, RWTH Aachen University, raised no ethical or professional objections to the research project.
Statistical analyses
We present the 12-month administrative prevalences of selected SMIs for the year 2016 (for patients with at least one visit to a physician). Odds ratios (OR) for medical conditions and risk factors (adjusted for age group [18–24, 25–34, 35–44, 45–54, 55–59, 60–64, 65–69, 70–74, 75–79, 80–84, 85–89, 90–94, 95+] and sex, inclusive interaction) were calculated with multiple logistic regression and separated for six subgroups (three age groups [18–39, 40–64, 65+] × sex).
In order to evaluate whether significant OR were also substantial with regard to effect size, we chose the established cut-offs first described by Chinn (15) with OR > 1.436 or OR < 0.696. These cut-offs describe significant OR of at least small effect size. Base rates of all medical diagnoses are additionally provided to facilitate interpretation of the OR.
Mortality rates for 2013 to 2014 were calculated as raw percentages for patients with and without a specific diagnosis of SMI in 2012. OR were calculated according to the Mantel–Haenszel method (OR-MH) to account for varying OR across age and sex groups (e11).
The strata for the OR-MH were defined by age groups 18–24 years, 25–34, 35–44, 45–54, 55–59, 60–64, 65–69, 70–74, 75–79, 80–84, 85–89, 90–94, 95+ and sex. They indicate increased mortality of patients with a specific SMI compared to patients without the SMI. Due to the low prevalence of mortality rates, OR resemble relative risks (RR).
The age-related risk of death in SMI compared with the total population was calculated as the raw percentage of deaths in the respective population. Since the follow-up time series for the mortality data were relatively short (2013 to 2014), we did not examine any medical comorbidities as mediators of mortality or survival time.
Loss of life years was estimated using statistical life tables for the general German population in 2014 (see below, “Estimation of loss of life years”) (e9). Age- and sex-specific death rates in the life tables were adjusted to represent the particularly high rates of the four SMIs from the aforementioned calculation of the risks of death. Age- and sex-specific life expectancies were then calculated from the adjusted sum of further life years divided by the number of survivors for every age cohort. The differences in life expectancies between the total population and a particular SMI population were taken as proxy for lost life years.
Estimation of loss of life years
If
q(x) = probability of dying between ages x and x+1
l(x) = number surviving to age x
d(x) = number dying between ages x to x+1
L(x) = person-years lived between ages x to x+1
T(x) = total number of person-years lived above age x
e(x) = expected life years at age x
delta(x) = difference between d(x) and [l(x) – L(x)]
then
(1) l(x+1) = l(x)–d(x)
(2) d(x) = q(x) * 100
(3) L(x) = [l(x) + l(x+1)]/2
(4) 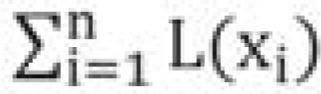
(5) e(x) = T(x)/l(x)
For equations (1) and (2), q(x) was adjusted by multiplying by q(x) in the given age and sex group with SMI divided by q(x) in the same age and sex group of the general population. Equations (3) to (5) were then recalculated. The difference between e(x) of the general population and e(x) for the respective SMI was taken as the estimator of life years lost. Thus for a particular age and sex the expectation of life years was estimated for the general population and for the SMI of interest. The difference was taken as life years lost due to the SMI of interest.
Suicide rate estimation
In the observation period, there were approximately 1.75 million deaths and approximately 21 000 suicides in Germany (Federal Health Monitoring [e15, e16]). The suicide rate among all deaths in the general population is therefore approximately 1.2%.
Based on the assumption from previous findings (5, 20, 21), that up to 90% of completed suicides are associated with some form of mental illness, we estimate that the proportion of SMI (more severe, but less widespread) among all suicides is 70% (e12– e14). Therefore, an estimated 14,700 of the suicides in Germany were SMI cases.
The SMI prevalence in Germany amounts to 3.9%. In the observation period, the mortality rate was 1.9 times higher. We estimate that 130 000 deaths were SMI cases, 61 500 of them due to excess mortality.
A total of 14 700 suicides among 61 500 deaths due to excess mortality corresponds to 24%. In other words, 76% of excess mortality cannot be explained by suicide. The estimate refers only to the absolute number of deaths, not to the years of life lost (which are higher for deaths at younger ages). Furthermore, other unnatural causes of death such as accidents are not considered.
If an F2x diagnosis was present, it was defined as the main diagnosis.
If both F30/F31 and F32/F33 had been coded (possibly by different treating physicians) in one patient, bipolar affective disorder was selected as the diagnosis.
If both F60.3 and F32/F33 had been diagnosed, BPD was defined as the diagnosis under study.
If both F60.3 and F30/F31 had been diagnosed: (1) If only one of the two diagnoses had been assigned by a specialist, this diagnosis was used in the analysis. 2) If no differentiation was possible in step 1, cases were assigned to both BPD and bipolar affective disorder and thus contributed to both cohorts (total 5700 cases).
Severe unipolar depression (F32.2/33.2, F32.3/F33.3) was taken as the diagnosis if no additional other SMI had been coded.
Viral hepatitis/HIV (B15–B24)
Malignant neoplasms (C00–C97)
Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases (E00–E90)
Diseases of the circulatory system (I00–I90)
Diseases of the respiratory system (J00–J99)
Relevant risk factors of mortality (mental and behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance use [F1x])
Organic mental disorders/Alzheimer disease/other degenerative diseases of the nervous system (F0/G30–G31)
Injury, poisoning, and other consequences of external factors (S00–T98)
External causes of morbidity and mortality (V01–Y98)