Figure 6. Lateral protocerebrum: the hemiellipsoid body and the terminal medulla.
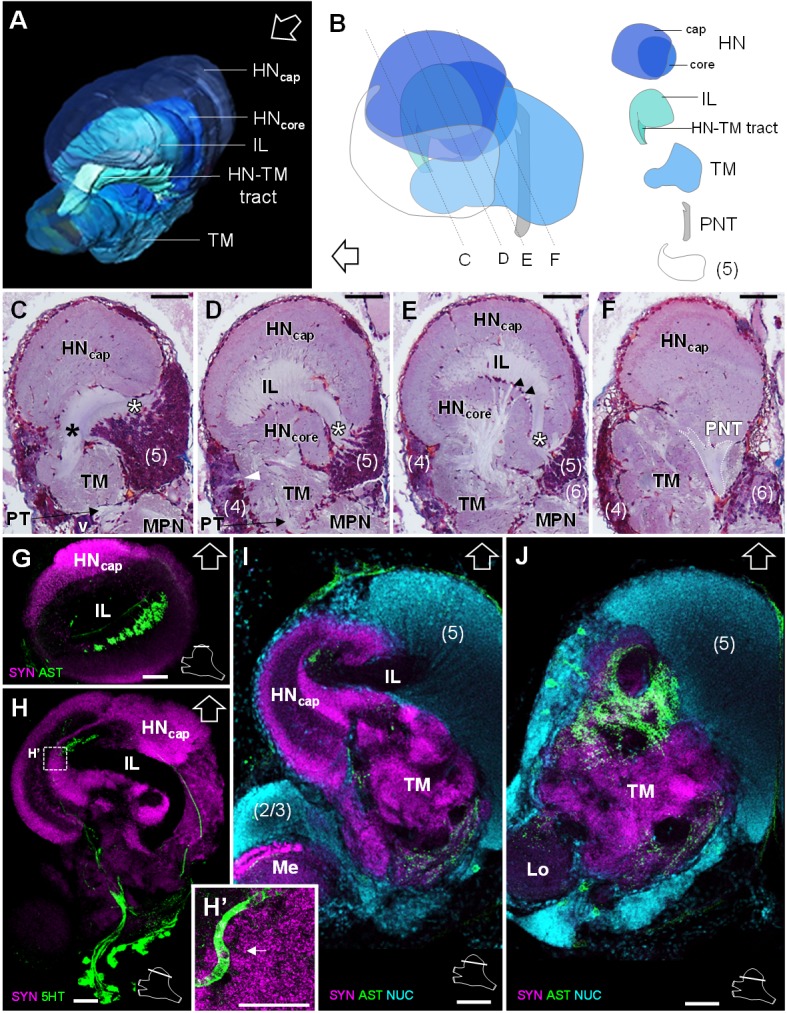
(A) 3D reconstruction of the lateral protocerebrum (right hemisphere), viewed from an anterior-left perspective, based on an image stack obtained by X-ray micro-CT scan. A conspicuous arcuate tract connects the anterior region of the terminal medulla to the cap region of the hemiellipsoid body (see also in C). (B) Schematic representation of the lateral protocerebrum (right hemisphere), viewed from the left. Dotted lines indicate the section’s position in C-F. (C-F) Frontal histological sections of the lateral protocerebrum, from anterior to posterior. The hemiellipsoid body and the terminal medulla receive axons from the cell somata in the cell cluster (5) (white asterisks, (C–E) and (4) (white arrowhead, (D). An arcuate tract connects the terminal medulla to the cap region of the hemiellipsoid body in the anterior region (black asterisk, (C). The terminal medulla also connects to the hemiellipsoid body in the middle region, via arborizing fibers (black arrowheads, (E). The projection neuron tract enters the hemiellipsoid body in the posterior region (F). (G–J’) Horizontal sections of the lateral protocerebrum, from dorsal to ventral, double or triple-labeled for synapsin immunoreactivity (SYN, magenta), allatostatin-like immunoreactivity (AST) or serotonin immunoreactivity (5HT) (both showed in green), and a nuclear marker (NUC, cyan). The inset (H’) shows an enlargement of the hemiellipsoid body neuropil cap region, with microglomeruli (white arrow). Each section’s position is sketched in the bottom right corners. Black and white open arrows point towards anterior of the body axis. Scale bars = 100 µm (except in H’, scale bar = 50 µm). Abbreviations: see text and appendix 1.
