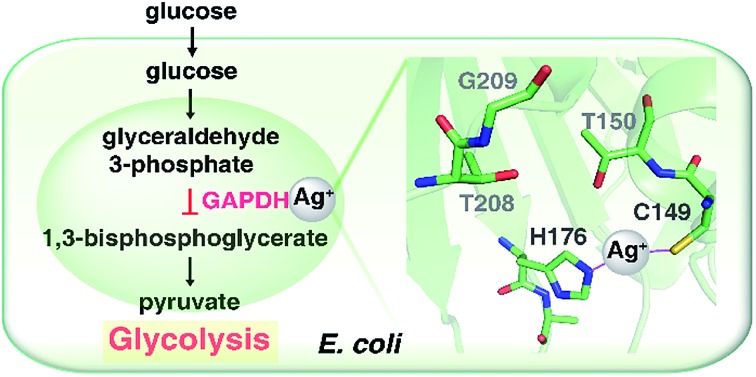
 We report for the first time that antimicrobial Ag+ targets the glycolytic pathway through inhibiting the key enzyme of GAPDH.
We report for the first time that antimicrobial Ag+ targets the glycolytic pathway through inhibiting the key enzyme of GAPDH.
Abstract
Silver has long been used as an antibacterial agent, yet its molecular targets remain largely unknown. Using a custom-designed coupling of gel electrophoresis with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (GE-ICP-MS), we identified six silver-binding proteins in E. coli. The majority of the identified proteins are associated with the central carbon metabolism of E. coli. Among them, we unveil that GAPDH, an essential enzyme in glycolysis, serves as a vital target of Ag+ in E. coli for the first time. We demonstrate that silver inhibits the enzymatic function of GAPDH through targeting Cys149 in its catalytic site. The X-ray structure reveals that Ag+ coordinates to Cys149 and His176 with a quasi-linear geometry (S–Ag–N angle of 157°). And unexpectedly, two Ag+ ions coordinate to Cys288 in the non-catalytic site with weak argentophilic interaction (Ag···Ag distance of 2.9 Å). This is the first report on antimicrobial Ag+ targeting a key enzyme in the glycolytic pathway of E. coli. The findings expand our knowledge on the mode of action and bio-coordination chemistry of silver, particularly silver-targeting residues in proteins at the atomic level.
Introduction
The rapid emergence of drug-resistant pathogens and the dwindling pipeline of new antibiotics pose a serious threat to human health globally. Alternative strategies to tackle this problem are urgently needed. Metal ions have been used as antimicrobial agents and disinfectants historically. In particular, certain metals, e.g., Ag+ and Bi3+, exhibit great potential in killing multidrug-resistant bacteria and in improving the cure rates of infections from resistant strains.1–15 There has been a tremendous increase in the applications of silver and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in the healthcare and food industry due to their outstanding antibacterial properties.5,7,8,16–18
In spite of the enormous efforts being made to explore the mode of action of silver, its molecular targets remain obscure.10,16,19–23 Proteins are deemed to be important targets of silver due to its antibacterial activities.5,19,24–29 However, silver-binding proteins at cellular levels remain largely unidentified owing to the lack of appropriate analytical techniques.30–32 Currently, most studies are based on putative targets without evidence showing the direct binding of silver to the proteins in cellulo.5,8,15,16 Hence, the authentic silver-binding protein targets remain largely unidentified, which hinders further exploration on the mode of action of silver. The limited knowledge about silver-binding proteins impedes, in turn, the investigation of silver-targeting sites in proteins, especially at the atomic level.
We have previously developed a robust approach by hyphenating continuous-flow gel electrophoresis with ICP-MS (GE-ICP-MS), allowing the simultaneous separation and detection of bismuth and its binding proteins in Helicobacter pylori.32–35 Herein, using the custom-made GE-ICP-MS system, we identified six silver-binding proteins with the majority of them being associated with the central metabolism. Among these proteins, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was unveiled for the first time as a target of Ag+in vivo to account for its antibacterial activity against E. coli. We further evaluate the interactions of Ag+ with GAPDH biochemically and structurally, demonstrating a diversified coordination of Ag+ to GAPDH by X-ray crystallography. Importantly, Ag+ inhibits the enzymatic activity of GAPDH through targeting to Cys149 and His176 at its active site.
Results and discussion
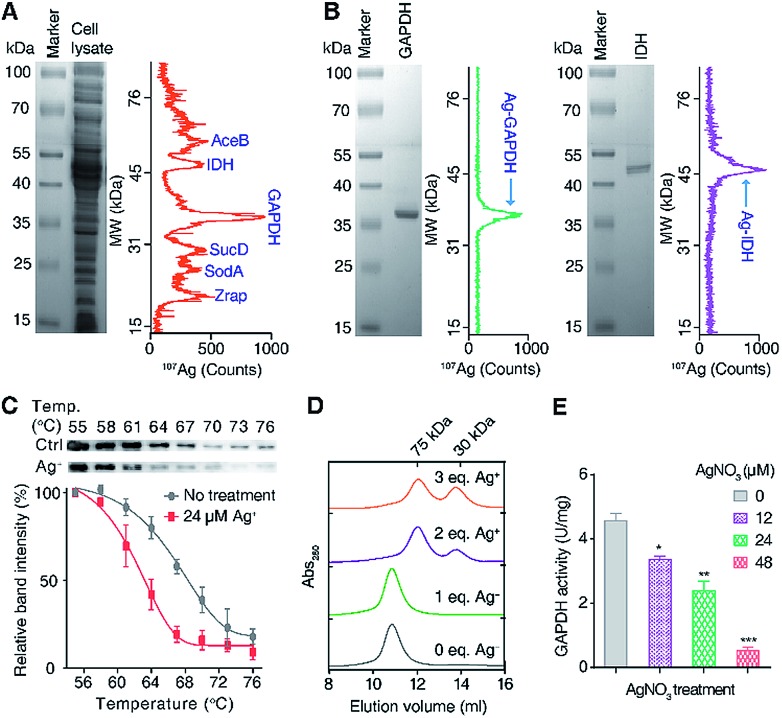
To exploit the direct Ag+-binding proteins in E. coli, we extracted the proteins in E. coli after treatment with 24 μM (IC50 value) AgNO3 for 2 h in Luria–Bertani medium and analyzed by GE-ICP-MS. Iodine (127I) labelled proteins were used as internal calibration standards for the molecular weight (MW) determination (Table S1†).33 Seven 107Ag peaks were observed in the electropherogram in the MW window from 10 to 80 kDa (Fig. 1A). The protein fractions corresponding to each of the peaks were collected and submitted for identification via peptide mass fingerprinting. In total, six proteins corresponding to six 107Ag peaks were identified, including zinc resistance-associated protein (Zrap), superoxide dismutase [Mn] (SodA), succinyl-CoA synthetase alpha subunit (SucD), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH), and malate synthase A (AceB) (Table S2†). To validate whether the approach can accurately track Ag+-binding proteins, we overexpressed and purified two proteins (GAPDH and IDH) with the purity being confirmed by size-exclusion chromatography (Fig. S1†) and SDS-PAGE (Fig. 1B), incubated them with Ag+, and examined their silver-binding capability by GE-ICP-MS. As shown in Fig. 1B, two peaks at the MW of ca. 36 and 47 kDa were observed, corresponding to the monomers of Ag-bound GAPDH and IDH, respectively, demonstrating that GE-ICP-MS enables the tracking of the authentic silver-binding proteins.
Fig. 1. Identification and validation of silver-binding proteins in E. coli. (A) Separation and identification of silver-binding proteins in E. coli by GE-ICP-MS. (B) GE-ICP-MS electropherograms of purified proteins with pre-incubation of Ag+. (C) Cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA) of wild-type E. coli after incubation with or without 24 μM Ag+. The soluble fractions of the intracellular GAPDH protein were quantified by western blotting. The band intensities at different temperatures are normalized to 55 °C. (D) Analysis of the oligomeric states of GAPDH after incubation with different amounts of Ag+ by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). (E) In vivo activity of GAPDH in E. coli after treatment with different concentrations of AgNO3. All experiments were performed in triplicate. One representative of three replicates is shown (A, B and D). The results are shown as mean ± SEM (C and E). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.
Among the identified Ag+-binding proteins, the highest peak corresponded to the Ag–GAPDH complex. GAPDH is a housekeeping enzyme in the glycolytic pathway and has attracted enormous interest due to its significance in glucose metabolism and non-metabolic functions.36,37 Extracellular GAPDH has been reported to interact with various host components and acts as a virulence factor in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.37–39 GAPDH therefore serves as a vital target for the design of antibacterial agents.36,40 In view of the essential role particularly in the glycolytic pathway of E. coli, we hypothesize that GAPDH may serve as an important target of Ag+ against E. coli.
To verify whether Ag+ binds to GAPDH in cellulo, a cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA) was employed.41,42 Ag+ at a concentration of 24 μM was added into the E. coli cells in the early exponential phase and treated for 1 h. The cells were then harvested and subjected to the CETSA study according to the standard protocols.41,42 As shown in Fig. 1C, the treatment of Ag+ resulted in a shift in the apparent aggregation temperature (Tagg) of intracellular wild-type (WT) GAPDH from 68.2 °C to 63.1 °C, confirming that Ag+ destabilizes the thermal stability of GAPDH in vivo.
To further evaluate how silver destabilizes GAPDH, we examined the oligomeric states of GAPDH after incubation with different amounts of Ag+ by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). Apo-form GAPDH was eluted at 10.8 ml, corresponding to a protein with the MW of around 150 kDa, consistent with a tetrameric form of the apo-GAPDH. Addition of increasing amounts of Ag+ led to two new peaks appearing at 12.1 and 13.8 ml, corresponding to MWs of ca. 72 and 36 kDa, respectively, indicative of the formation of dimeric and monomeric forms of GAPDH induced by Ag+ (Fig. 1D). Therefore, destabilization of GAPDH by Ag+ might be attributable to its alteration of the quaternary structure of GAPDH from a tetramer to a dimer or a monomer.
To examine whether the binding of Ag+ to GAPDH affects the activity of GAPDH in vivo, we measured the activity of GAPDH in the lysate of E. coli cells after treatment with different concentrations of AgNO3. As shown in Fig. 1E, the activity of GAPDH decreased from 4.6 U mg–1 (without treatment) to 3.4, 2.4 and 0.5 U mg–1 in the cell lysates of E. coli after treatment with 12, 24 and 48 μM AgNO3, respectively (Fig. 1E), validating that the binding of Ag+ to GAPDH is able to inhibit its activity in vivo.
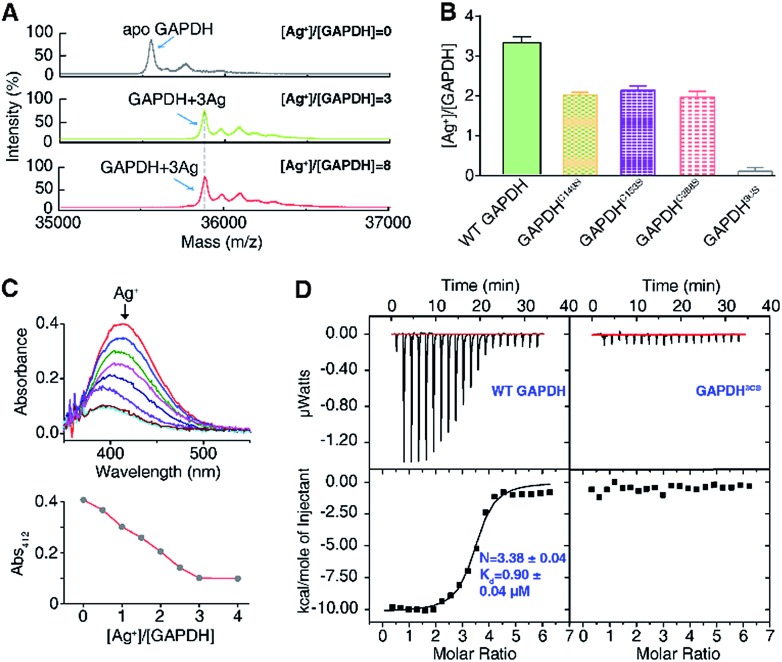
To explore the silver-targeting site in GAPDH, we first examined the binding stoichiometry of Ag+/GAPDH by MALDI-TOF MS. For GAPDH in the absence of Ag+, a peak at m/z of 35 554.6 corresponding to the GAPDH monomer was observed. Upon addition of Ag+ at concentrations from 0 to 3 eq., an intense peak at m/z of 35 875.8 appeared, corresponding to GAPDH with three Ag+ ions bound (calcd m/z of 35 875.2). Further increasing the Ag+ concentration to 8 eq. led to no peaks at higher values of m/z, verifying that the binding stoichiometry of Ag+/GAPDH is 3 : 1 (Fig. 2A). The binding ratios of Ag+ to the wild-type (WT) GAPDH was further confirmed to be 3.3 ± 0.2 by quantifying the amounts of the protein and the metal by the BCA assay and ICP-MS, respectively (Fig. 2B).
Fig. 2. Silver ions bind to cysteines of GAPDH. (A) MALDI-TOF mass spectrum of apo-GAPDH and GAPDH after incubation with 3 and 8 eq. of Ag+. (B) Ag+-binding capability of WT GAPDH and its variants measured by ICP-MS (n = 3). (C) Free thiol contents in GAPDH measured by Ellman's assay (n = 3). (D) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) results of Ag+ binding to WT GAPDH and GAPDH3CS (n = 3). The data were fitted to a one-set-of-site binding model using Origin software. One representative of three replicates is shown (C). The results are shown as mean ± SEM (B).
Given that silver ions are highly thiophilic, we then examined whether the three cysteine residues (Cys149, Cys153, and Cys288) are involved in Ag+ binding. We measured the content of free thiols of GAPDH pre-incubated with different molar ratios of Ag+ by Ellman's assay. As shown in Fig. 2C, about 3 eq. of Ag+ could completely deplete the free thiols of GAPDH, indicating that cysteines are involved in Ag+ binding. We subsequently mutated the three cysteine residues to serine individually. The Ellman's assay showed that 2 eq. of Ag+ could completely deplete the free thiols in the three single mutants GAPDHC149S, GAPDHC153S, and GAPDHC288S (Fig. S2†). Consistent with the Ellman's assay, the ICP-MS results showed that the GAPDHC149S, GAPDHC153S, and GAPDHC288S mutants bind two Ag+ ions per monomer whereas the triple Cys mutant had no detectable Ag+ binding (Fig. 2B), which is further confirmed by the MALDI-TOF MS data (Fig. S3†).
We next measured the binding affinity of Ag+ towards GAPDH by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). By fitting the data to the one-site binding model (Fig. 2D), we show that the WT GAPDH binds 3.38 ± 0.04 molar equivalents of Ag+ with an apparent dissociation constant (Kd) of 0.90 ± 0.04 μM (Fig. 2D and Table S5†). Subsequently, we examined the binding affinity of Ag+ to GAPDH variants (C149S, C153S, and C288S) similarly. All these three single Cys mutants bound to approximately two molar equivalents of Ag+ with affinities similar to those of the WT GAPDH, i.e., GAPDHC149S, GAPDHC153S and GAPDHC288S bind 2.07 ± 0.12, 2.29 ± 0.12 and 2.46 ± 0.04 molar equivalents of Ag+ ions with similar binding affinity (Fig. S4 and Table S5†). All of the single Cys mutants lost one Ag+ binding site, confirming that each Cys residue in GAPDH binds one Ag+ ion. For the triple Cys mutant GAPDH3CS, no evident Ag+ binding was observed by ITC (Fig. 2D), confirming that the deletion of three Cys residues caused a complete loss of its Ag+-binding capability. Collectively, these data demonstrate that Ag+ binds to GAPDH mainly via Cys residues, with three Cys sites showing similar binding affinity and each cysteine site binds one Ag+ ion.
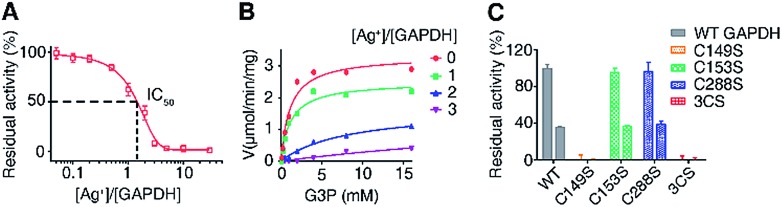
To examine the effects of Ag+-binding on the function of GAPDH, the activity of purified GAPDH after incubation with different amounts of Ag+ was measured by using a Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Activity Assay Kit. The steady-state kinetics using G3P as a substrate showed a Ag+ dose-dependent inhibition of the enzymatic activity of purified GAPDH with 1.5 eq. and 3 eq. of Ag+ inhibiting the activity of GAPDH by 50% and 90%, respectively (Fig. 3A).
Fig. 3. Silver inhibits the activity of GAPDH through binding to Cys149. (A) Dose dependent inhibition of GAPDH by Ag+ (n = 3). (B) GAPDH activity in the presence of different amounts of Ag+. GAPDH activity is defined as μmol min–1 mg–1 (n = 3). (C) Normalized residual activity of WT GAPDH and GAPDH mutants in the absence (left) and presence (right) of 2 eq. of Ag+ (n = 3). One representative of three replicates is shown (B). The results are shown as mean ± SEM (A and C).
Previous studies on the catalytic mechanism of GAPDH and the crystal structure of E. coli GAPDH (EcGAPDH) showed that the substrate G3P binds to Cys149 covalently and a hemiacetal intermediate between G3P and Cys149 is formed in the first step of the catalytic reaction.43,44 Since we demonstrated that all three cysteine residues are involved in Ag+ binding, we speculate that the binding of Ag+ to the vital Cys149 site could affect the binding of the substrate G3P to this site, thereby inhibiting the enzyme activity. To validate this hypothesis, we examined the effects of Ag+ on the enzyme kinetics of GAPDH. The apparent Vmax decreased from 3.3 μmol min–1 mg–1 to 0.50 μmol min–1 mg–1 when the molar ratios of Ag+/GAPDH increased from 0 to 3; however the KM values of Ag+-inactivated GAPDH for G3P increased from 1.2 mM (native enzyme) to 9.2 mM (Fig. 3B and Table S6†). The increased KM values but decreased Vmax values suggest that Ag+ interferes with the substrate binding, hampering the formation of the enzyme–substrate complex. Therefore, Ag+ exerts an inhibitory effect on GAPDH via either a mixed-type inhibition or an irreversible inhibition mechanism.45 We further calculated the apparent Ki values by using a mixed-type inhibition model with the equations shown in ESI Method.† Our results show that Ag+ inhibits GAPDH with the apparent Ki values of 0.17 ± 0.012 and 0.37 ± 0.026 μM for binding to the free GAPDH and to the GAPDH-G3P complex, respectively.
We next compared the enzymatic activity of GAPDHC149S, GAPDHC153S and GAPDHC288S with or without treatment of Ag+. As Cys149 acts as a nucleophile in the active site of GAPDH, a site-directed mutation of Cys149 to Ser diminished the enzymatic activity completely under identical conditions (Fig. 3C), confirming the importance of this residue for the catalytic activity of GAPDH. It is thus consistent with the observation that the binding of Ag+ to this residue inhibits the enzymatic activity of GAPDH. In contrast, the activities of GAPDHC153S and GAPDHC288S remained as 96% and 97%, respectively, of that of WT GAPDH. Similar to the WT GAPDH, 2 eq. of Ag+ inhibited nearly 60% of the activity of GAPDHC153S and GAPDHC288S (Fig. 3C). For the triple Cys mutant GAPDH3CS, no activities for both apo- and Ag+-treated GAPDH3CS were observed. Clearly, the inhibitory effect of Ag+ on GAPDH is mainly attributed to its binding to Cys149 among the three Cys residues.
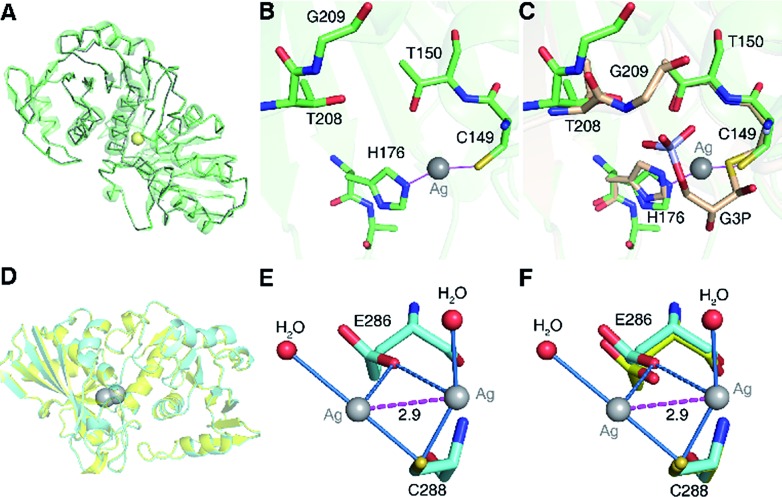
To understand the inhibitory mechanism of Ag+ on GAPDH at the atomic level,46 we first crystalized and resolved the apo-form GAPDH at a resolution of 2.3 Å (Fig. S5A and Table S7†). To obtain the Ag+-bound crystals, GAPDH incubated with 4 eq. of Ag+ was used for crystallization. Octahedral crystals of Ag-bound GAPDH were obtained after one week (Fig. S5B†). The structure of Ag+-bound GAPDH (Ag–GAPDH-1) was resolved at 3.1 Å resolution by molecular replacement using a previously reported GAPDH structure (PDB: ; 1DC4) as the template (Fig. 4A, S5C and Table S7†). Each asymmetric unit of Ag–GAPDH-1 contains sixteen unique chains. The overall conformation of Ag–GAPDH-1 is similar to apo-GAPDH with a root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) of 0.47 Å when Chain A of the two structures was superimposed (Fig. 4A). However, subtle conformational changes were observed at the silver-binding sites (Fig. 4C). The positive electron density on the mFo-DFc map between Cys149 and His176 is sufficiently high for a fully occupied silver ion.
Fig. 4. Crystallographic analysis reveals the inhibitory mechanism of Ag+ against GAPDH at the atomic level. (A) Superimposition of Ag-bound GAPDH (Ag–GAPDH-1) (green) with native GAPDH (grey) (RMSD, 0.47 Å). (B) The coordination geometry of silver in the active site of Ag-bound GAPDH with Ag+ is shown as a grey sphere. (C) An overlay image comparing the relative position of Ag+ (grey sphere) with the substrate G3P (PDB: ; 1DC4). (D) Overall structure of Ag-bound GAPDH at the Cys288 site and the superimposition of Ag–GAPDH-2 (Cyan) with native GAPDH (Grey) (RMSD, 0.32 Å). (E) The coordination geometry of silver at the Cys288 site with Ag+ ions is shown as grey spheres, water as red spheres, the argentophilic interactions of adjacent Ag+ as the purple dashed line and weak interactions between the O atom from Glu286 and Ag+ ions as blue dashed lines. (F) An overlay image comparing the relative position of Ag–GAPDH-2 and apo-GAPDH. (A and D) Structural alignment was done for Cα residues using DaliLite.
In contrast to in vitro studies, only one Ag+ ion was identified to bind GAPDH at the active site in the co-crystallized structure. We could not observe the other two silver ions, probably due to the dissociation during the crystallization process. In the Ag–GAPDH-1 structure, the silver ion is buried inside a solvent-inaccessible site in a loop and is coordinated by the side-chains of two residues, i.e., the Sγ and Nε2 of the conserved residues Cys149 and His176, respectively (Fig. 4B). Similar coordination of Ag to Cys and His was observed in a silver-bound urease structure.47 There is a flexible loop and a β-sheet located between Cys149 and His176. The bond lengths of Ag+ to Cys149-Sγ and His176-Nε2 are comparable (2.2 Å) with a quasi-linear S–Ag–N angle of 157° (Tables 1 and 2). The coordination of silver induced minor conformational changes of Cys149 and His176 (Fig. 4C). In comparison with G3P-bound GAPDH (PDB: ; 1DC4), the side chain of His176 in Ag–GAPDH-1 moves towards Cys149 by ∼0.7 Å for silver-binding (Fig. 4C).43 In G3P-bound GAPDH (PDB: ; 1DC4), residues of 208–211 move (ca. 2 Å for Gly209) towards the catalytic cavity to interact with the substrate via hydrogen bonds, whereas these residues stay away from the silver ion in the Ag-bound GAPDH structure. The crystallographic data are coherent with the biochemical data that Ag+ binds to the thiol group of Cys149, which could inhibit the capability of the nucleophilic attack of the sulfur to the carbonyl group of G3P, resulting in the inhibition of the enzymatic activity of GAPDH.
Table 1. Metal–ligand distances in Ag–GAPDH-1 and Ag–GAPDH-2.
| Metal | Ligand | Distance (Å) | |
| Ag–GAPDH-1 | Ag1 | Cys149-Sγ | 2.2 |
| Ag1 | His176-Nε2 | 2.2 | |
| Ag–GAPDH-2 | Ag1 | Cys288-Sγ | 2.6 |
| Ag2 | Cys288-Sγ | 2.3 | |
| Ag1 | HOH1 | 2.8 | |
| Ag2 | HOH2 | 2.4 | |
| Ag1 | Ag2 | 2.9 | |
| Ag1 | Glu286-Oε2 | 3.2 a | |
| Ag2 | Glu286-Oε2 | 3.3 a |
aOnly weak interactions exist.
Table 2. Ligand-Ag-ligand angles in Ag–GAPDH-1 and Ag–GAPDH-2 a .
| Atom 1 | Atom 2 | Atom 3 | Angle (°) | |
| Ag–GAPDH-1 | His176-Nε2 | Ag1 | Cys149-Sγ | 157.0 |
| Ag–GAPDH-2 | HOH1 | Ag1 | Cys288-Sγ | 160.5 |
| HOH2 | Ag2 | Cys288-Sγ | 147.9 |
aAll Ag atoms and water molecules are assigned their universal chain IDs. The measurements are based on the atomic coordination for the polymeric Chain A and Ag atoms or water molecules.
Apart from Cys149, which forms a hemithioacetal intermediate with the substrate G3P,43,44 His176 at the active site is involved in the binding of the phosphate group of G3P and the activation of the nucleophilicity of Cys149, and acts as a hydrogen donor to facilitate the formation of tetrahedral intermediates in catalysis.43,48 Given the pivotal role of His176 in the catalytic process, we then mutated His176 to Ser (H176S) and measured the activity of GAPDHH176S. The site-directed mutagenesis of His176 to Ser could diminish the enzymatic activity of GAPDH by over 95% (Fig. S6A†), validating the importance of His176 in the catalytic process of GAPDH. Thus, the binding of Ag+ to His176 as demonstrated by the crystal structure also disrupts the function of His176 and thereby further inhibits the activity of GAPDH.
Moreover, we measured the binding ratio of Ag+ to GAPDHH176S by MALDI-TOF MS and ICP-MS. Our results showed that three Ag+ ions are bound to each monomer of GAPDHH176S, indicating that the mutation of His176 has no obvious effect on the binding of Ag+ to the Cys149-His176 catalytic site (Fig. S6B and C†). However, the mutation of Cys149 in GAPDH reduced the stoichiometry of Ag : GAPDH from 3 to 2 (vide supra). This indicates that Ag+ has much higher affinity towards Cys149 than His176, consistent with the soft feature of silver ions.
We further prepared the double mutant of GAPDHC153S/C288S and examined the effect of site-directed mutation of Cys153 and Cys288 to Ser on the binding properties and enzyme activity of GAPDH. MALDI-TOF MS analysis of apo GAPDHC153S/C288S (m/z 35 522.2) and GAPDHC153S/C288S after treatment with 2 eq. or 4 eq. of Ag+ showed that GAPDHC153S/C288S binds to 1 eq. of Ag+ (calcd m/z of 35 629.1, found m/z of 35 629.2) (Fig. S7A†), which is further confirmed by ICP-MS measurements (1.1 ± 0.07) (Fig. S7B†). We next compared the enzymatic activity of GAPDHC153S/C288S with or without the treatment of Ag+. GAPDHC153S/C288S retained 92% activity compared with that of the WT GAPDH. Two eq. of Ag+ could completely inhibit the enzymatic activity of GAPDHC153S/C288S but only inhibited nearly 60% of the activity of WT GAPDH (Fig. S7C†). Collectively, the crystal structure of silver-bound GAPDH together with our biochemical data demonstrate that silver inhibits the activity of GAPDH by binding to Cys149 and His176 in the catalytic site, thereby interfering with the substrate binding and enzyme–substrate complex formation.
GAPDH is an essential enzyme in the glycolytic pathway of E. coli and gapdh gene knockout was found to prevent bacterial growth in LB culture medium.49 Since our biochemical and X-ray crystallographic data clearly demonstrate that Ag+ could inhibit the physiological function (enzymatic activity) of GAPDH in vitro and in vivo by binding to the residues of Cys149 and His176 in the active site, we therefore further examined the susceptibility of Ag+ against WT E. coli and GAPDHC149S/H176S producer by measuring MIC50. As shown in Fig. S8A,† both the WT E. coli and the mutant E. coli displayed nearly identical growth curves in the absence of Ag+ with a typical S-shaped growth curve, indicating that the site mutation does not affect the growth of E. coli. In contrast, the MIC50 values of Ag+ for WT and mutant E. coli were calculated to be 24.4 ± 0.5 and 34.5 ± 0.7 μM, respectively (Fig. S8B†), again suggesting that the E. coli GAPDHC149S/H176S mutant is less sensitive towards Ag+ than the WT one. Taken together, we demonstrate that Ag+ binds to GAPDH and inhibits its activity in vivo, thereby contributing to attenuating bacterial growth.
To further evaluate the binding properties of Ag+ to the other two Cys residues, we resolved another X-ray crystal structure of the silver-bound GAPDH (Ag–GAPDH-2) at a resolution of 2.6 Å with silver located at a non-catalytic site (Fig. S5D†). The Ag–GAPDH-2 crystal was obtained by soaking apo-GAPDH crystals into a cryo-protectant solution supplemented with 2 mM AgNO3. Similar to Ag–GAPDH-1, the structure showed no significant overall conformational change between the Ag-bound and apo-form GAPDH, with a RMSD of 0.32 Å when superimposing Ag–GAPDH-2 to apo-GAPDH via Chain A (Fig. 4D and Table S7†). Identification of silver was achieved through the significantly positive peaks (>20σ) in the mFo-DFc (difference Fourier) map. The crystal structure shows that two silver ions are bound to one Cys288-Sγ, a solvent-accessible site, with each silver ion coordinates to Cys288-Sγ and an additional water molecule (Fig. 4E). The observation of two silver ions bound to Cys288 in the crystal structure is likely due to the use of a high concentration of AgNO3 (2 mM) for crystal soaking albeit only one silver ion binds to Cys288 in solution (vide supra). Surprisingly, weak argentophilic interactions with a Ag···Ag distance of 2.9 Å between the two silver ions that bind to Cys288 were noted (Fig. 4E). Similar argentophilic interactions between silver ions in di-nuclear,47,50 tetra-nuclear51 and even hepta-nuclear52 forms were observed in ferredoxin and metallothionein.
The mutation of Cys288 to Ser inhibited the silver-binding capability in this site (Fig. 2B), confirming that the surrounding environment does not allow other types of strong interactions with the metal ion. The binding of silver ions to Cys288 does not induce any significant conformational changes at the local site compared with that of apo-GAPDH (Fig. 4F). The nearest potential metal-binding residue is Glu286 with an Ag–O distance of 3.2 to 3.3 Å, which is too long for primary or secondary covalent-bonding interactions (Fig. 4F and Table 1). Thus, only weak interactions exist, which may be important in maintaining the conformation of the metal-binding loop and in stabilizing the backbone conformation on the protein surface. Interestingly, no more silver ions were bound to GAPDH when further increasing the soaking time of apo-GAPDH crystals to 30 min, indicating that the Cys149 and Cys153 sites are non-solvent exposed and silver ions are unable to access these two sites in the packed crystal structure of GAPDH. Thus, how silver ions coordinate to the Cys153 site warrants further investigation.
Conclusions
In summary, our study features the identification of silver-binding proteins with GAPDH as one of the vital molecular targets of antibacterial Ag+ against E. coli. We show that Ag+ binds to the three cysteine sites of EcGAPDH by various biochemical characterization processes. The crystal structures of the Ag+–GAPDH complex reveal that Ag+ binds at both catalytic and non-catalytic sites. We unveil that Ag+ inhibits the enzymatic activity of GAPDH by binding to Cys149 and His176 in the active site via a mixed-type or an irreversible inhibition, thereby preventing the substrate binding and substrate-enzyme complex formation. This study provides the first direct evidence that silver ions can disrupt the glycolytic pathway via inhibiting the vital enzyme, opening a new perspective for the design of novel inhibitors for GAPDH with antibacterial activities. Pharmacologically, GAPDH obeys the cardinal rules of “druggability” due to its disease relevance and the presence of an inhibitory site (e.g., catalytic domain of the enzyme).53,54 Small molecule inhibitors targeting GAPDH have been reported as efficient antibacterial agents, indicating that targeting this enzyme might be a promising anti-bacterial strategy.5 However, the catalytic sites of GAPDH are conserved among humans and bacteria. And GAPDH from S. aureus is recently identified as a Cu+-binding protein with its activity being inhibited by Cu+ (a mimic of Ag+) in vitro and in vivo.55 Thus, improving the selectivity and reducing the side effects of silver or other small molecule inhibitors targeting GAPDH remains a big challenge. Designing of novel silver nanomaterials with low toxicity to humans but high antibacterial activity might be a promising strategy. Besides, the interactions between silver and the remaining five identified silver-binding proteins, with the number of Cys residues ranging from one to six, warrant further exploration.
Additional information
The coordinates and structural factors of apo-GAPDH, Ag–GAPDH-1, and Ag–GAPDH-2 were deposited at the Protein Data Bank with accession codes 6IOJ, ; 6IO4, and ; 6IO6, respectively. Correspondence and request for materials should be addressed to H. S. (; Email: hsun@hku.hk).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (1733616P, 17307017P and R7070-18), the National Science Foundation of China (21671203) and The University of Hong Kong for an e-SRT on Integrative Biology and a Hong Kong PhD Fellowship (HKPF) for Haibo Wang. We thank the Center for Genomic Sciences, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine for the mass spectrometry facilities. The crystal diffraction data were collected at the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF), Chinese Academy of Sciences. We thank the staff at the BL17U1 beamline of SSRF for their generous help. Norman and Cecilia Yip Foundation is acknowledged for support.
Footnotes
†Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c9sc02032b
References
- Lemire J. A., Harrison J. J., Turner R. J. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013;11:371–384. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017;10:1062–1065. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J. Antibiotics. 2018;7:112. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7040112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm K. M. Nat. Chem. 2011;3:178. doi: 10.1038/nchem.970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt S., Brunetto P. S., Gagnon J., Priebe M., Giese B., Fromm K. M. Chem. Rev. 2013;113:4708–4754. doi: 10.1021/cr300288v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morones-Ramirez J. R., Winkler J. A., Spina C. S., Collins J. J. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013;5:190ra181. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maillard J.-Y., Hartemann P. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013;39:373–383. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2012.713323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernousova S., Epple M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013;52:1636–1653. doi: 10.1002/anie.201205923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Lai T.-P., Gao P., Zhang H., Ho P.-L., Woo P. C.-Y., Ma G., Kao R. Y.-T., Li H., Sun H. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:439. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02828-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos K. D., Orvig C. Chem. Rev. 2014;114:4540–4563. doi: 10.1021/cr400460s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldevila-Barreda J. J., Metzler-Nolte N. Chem. Rev. 2019;119:829–869. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler-Nolte N., Guo Z. Dalton Trans. 2016;45:12965. doi: 10.1039/c6dt90135b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patra M., Gasser G., Metzler-Nolte N. Dalton Trans. 2012;41:6350–6358. doi: 10.1039/c2dt12460b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser G., Metzler-Nolte N. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012;16:84–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Wang R., Sun H. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019;52:216–227. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng K., Setyawati M. I., Leong D. T., Xie J. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018;357:1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. W. Surgical Infections. 2009;10:289–292. doi: 10.1089/sur.2008.9941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajipour M. J., Fromm K. M., Ashkarran A. A., Aberasturi D. J. d., Larramendi I. R. d., Rojo T., Serpooshan V., Parak W. J., Mahmoudi M. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30:499–511. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok C.-N., Ho C.-M., Chen R., He Q.-Y., Yu W.-Y., Sun H., Tam P. K.-H., Chiu J.-F., Che C.-M. J. Proteome Res. 2006;5:916–924. doi: 10.1021/pr0504079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugala N., Lemire J., Chatfield-Reed K., Yan Y., Chua G., Turner R. J. Genes. 2018;9:344. doi: 10.3390/genes9070344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung W. K., Koo H. C., Kim K. W., Shin S., Kim S. H., Park Y. H. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008;74:2171–2178. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02001-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W.-R., Xie X.-B., Shi Q.-S., Zeng H.-Y., Ou-Yang Y.-S., Chen Y.-B. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010;85:1115–1122. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Q. L., Wu J., Chen G. Q., Cui F. Z., Kim T. N., Kim J. O. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000;52:662–668. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(20001215)52:4<662::aid-jbm10>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verano-Braga T., Miethling-Graff R., Wojdyla K., Rogowska-Wrzesinska A., Brewer J. R., Erdmann H., Kjeldsen F. ACS Nano. 2014;8:2161–2175. doi: 10.1021/nn4050744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai S., Behra R., Nestler H., Suter M. J.-F., Sigg L., Schirmer K. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014;111:3490–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319388111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X., Yang F., Wang R., He X., Li H., Kao R. Y. T., Xia W., Sun H. Chem. Sci. 2017;8:8061–8066. doi: 10.1039/c7sc02251d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X., Yang F., Li H., So P.-K., Yao Z., Xia W., Sun H. Inorg. Chem. 2017;56:15041–15048. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b02380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon O., Slenters T. V., Brunetto P. S., Villaruz A. E., Sturdevant D. E., Otto M., Landmann R., Fromm K. M. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010;54:4208–4218. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01830-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm K. M. Chimia. 2013;67:851–854. doi: 10.2533/chimia.2013.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Tsang C.-N., Sun H. Metallomics. 2009;1:25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetkovic A., Menon A. L., Thorgersen M. P., Scott J. W., Poole II F. L., Jenney Jr F. E., Lancaster W. A., Praissman J. L., Shanmukh S., Vaccaro B. J., Trauger S. A., Kalisiak E., Apon J. V., Siuzdak G., Yannone S. M., Tainer J. A., Adams M. W. W. Nature. 2010;466:779–782. doi: 10.1038/nature09265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Wang H., Li H., Sun H. Dalton Trans. 2015;44:437–447. doi: 10.1039/c4dt02814g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Cheng T., He B., Li L., Wang Y., Lai Y.-T., Jiang G., Sun H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013;52:4916–4920. doi: 10.1002/anie.201300794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Hu L., Yang X., Chang Y.-Y., Hu X., Li H., Sun H. Metallomics. 2015;7:1399–1406. doi: 10.1039/c5mt00054h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Hu L., Xu F., Quan Q., Lai Y.-T., Xia W., Yang Y., Chang Y. Y., Yang X., Chai Z., Wang J., Chu I. K., Li H., Sun H. Chem. Sci. 2017;8:4626–4633. doi: 10.1039/c7sc00766c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy-Kanniappan S., Kunjithapatham R., Geschwind J.-F. Oncotarget. 2012;3:940–953. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querol-García J., Fernández F. J., Marin A. V., Gómez S., Fullà D., Melchor-Tafur C., Franco-Hidalgo V., Albertí S., Juanhuix J., Córdoba S. R. d., Regueiro J. R., Vega M. C. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:541. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egea L., Aguilera L., Giménez R., Sorolla M. A., Aguilar J., Badía J., Baldoma L. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007;39:1190–1203. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau S. K. P., Tse H., Chan J. S. Y., Zhou A. C., Curreem S. O. T., Lau C. C. Y., Yuen K.-Y., Woo P. C. Y. FEBS J. 2013;280:6613–6626. doi: 10.1111/febs.12566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cane D. E., Sohng J.-K. Biochemistry. 1994;33:6524–6530. doi: 10.1021/bi00187a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina D. M., Jafari R., Ignatushchenko M., Seki T., Larsson E. A., Dan C., Sreekumar L., Cao Y., Nordlund P. Science. 2013;341:84–87. doi: 10.1126/science.1233606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jafari R., Almqvist H., Axelsson H., Ignatushchenko M., Lundbäck T., Nordlund P., Molina D. M. Nat. Protoc. 2014;9:2100. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun M., Park C.-G., Kim J.-Y., Park H.-W. Biochemistry. 2000;39:10702–10710. doi: 10.1021/bi9927080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougin A., Corbier C., Soukri A., Wonacott A., Branlant C., Branlant G. Protein Eng. 1988;2:45–48. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Si Y.-X., Ji S., Fang N.-Y., Wang W., Yang J.-M., Qian G.-Y., Park Y.-D., Lee J., Yin S.-J. Process Biochem. 2013;48:1706–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q.-S., Zhang K.-H., Cui Y., Wang Z.-J., Pan Q.-Y., Liu K., Sun B., Zhou H., Li M.-J., Xu Q., Xu C.-Y., Yu F., He J.-H. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2018;29:68. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei L., Cianci M., Vara A. G., Ciurli S. Dalton Trans. 2018;47:8240–8247. doi: 10.1039/c8dt01190g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soukri A., Mougin A., Corbier C., Wonacott A., Branlant C., Branlant G. Biochemistry. 1989;28:2586–2592. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T., Ara T., Hasegawa M., Takai Y., Okumura Y., Baba M., Datsenko K. A., Tomita M., Wanner B. L., Mori H. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006;2:2006. doi: 10.1038/msb4100050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baiocco P., Ilari A., Ceci P., Orsini S., Gramiccia M., Muccio T. D., Colotti G. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011;2:230–233. doi: 10.1021/ml1002629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martic M., Jakab-Simon I. N., Haahr L. T., Hagen W. R., Christensen H. E. J. Biol. Inorg Chem. 2013;18:261–276. doi: 10.1007/s00775-012-0971-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. W., Narula S. S., Armitage I. M. FEBS Lett. 1996;379:85–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg M. D., Bhargava P., Kim P. M., Putluri V., Snowman A. M., Putluri N., Calabresi P. A., Snyder S. H. Science. 2018;360:449–453. doi: 10.1126/science.aan4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L., Kepp O., Heiden M. G. V., Kroemer G. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2013;12:829–846. doi: 10.1038/nrd4145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarrant E., Riboldi G. P., McIlvin M. R., Stevenson J., Barwinska-Sendra A., Stewart L. J., Saito M. A., Waldron K. J. Metallomics. 2019;11:183–200. doi: 10.1039/c8mt00239h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.