Figure 8.
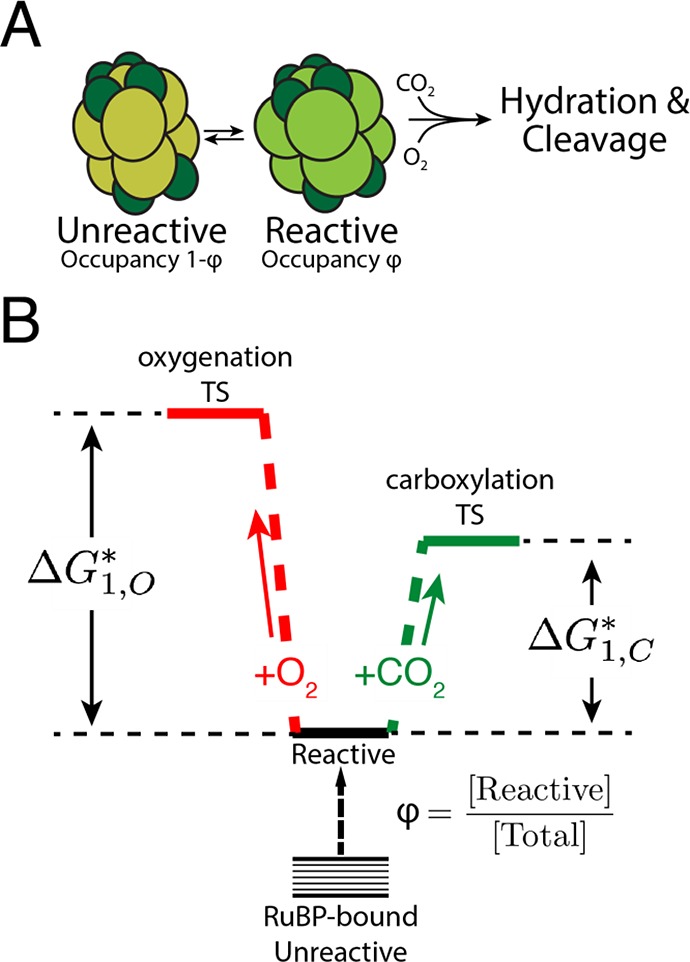
A power-law relationship between kcat,C/KC and kcat,O/KO can be explained by an active site that fluctuates between “reactive” and “unreactive” states. (A) In this model, CO2 and O2 react with bound RuBP only when the enzyme is in the reactive state, which has an occupancy φ. (B) φ can vary between related enzymes. In the reactive state, CO2 and O2 react with the bound RuBP with intrinsic reactivities ΔG*1,C and ΔG*1,O that do not vary between related Rubiscos. If the difference in intrinsic reactivities (ΔG*1,O – ΔG*1,C) is constant, we derive a power-law relationship between kcat,C/KC and kcat,O/KO with an exponent of 1.0. This relationship requires a constant SC/O (Supporting Information).
